Lecture 2.3 - Cell Division
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to cell division processes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including definitions of important terms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Chromatin
Combination of DNA and proteins that make up chromosomes
Chromosome
A tightly coiled form of the DNA-protein complex; in molecular biology, refers to a single DNA molecule and associated proteins.
Chromatid
Identical copies of the same chromosome, often referred to as sister chromatids.
Centromere
The location at which sister chromatids are most closely attached.
Binary fission
The method of cell division in prokaryotes, where a single parent cell divides into two daughter cells.
Mitosis
A process of cell division in eukaryotes that results in two genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
Meiosis
A process of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes, producing four haploid gametes, allowing for sexual reproduction.
Diploid
Cells that contain two sets of homologous chromosomes; for humans, this is typically 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
Haploid
Organisms that have only 1 set of chromosomes (1n)
Cell cycle
The series of phases that a cell goes through, including interphase and mitotic phases.
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm, resulting in two separate daughter cells after mitosis.
Cleavage furrow
The narrow groove formed by actin microfilaments during cytokinesis in animal cells.
Gametes
Sex cells produced by meiosis that have half the number of chromosomes as the parental cell.
Alleles
Different versions of a gene that exist on homologous chromosomes.
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis that increases genetic diversity.
Independent assortment
The distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells in meiosis that leads to genetic variation.
Endosymbiotic theory
The theory that explains the origins of mitochondria and chloroplasts within eukaryotic cells.
S phase
The part of interphase where DNA is replicated.
Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and DNA is synthesized before mitosis.
Cell division
How cells reproduce (1 parent cell divides into 2 daughter cells)
In unicellular organisms cell division…
Reproduction
In multicellular organisms…
Simple cell division enables growth
Daughter cells
Genetically identical to parent cell and each other
Prokaryotes divide by…
Binary fission
Eukaryotes divide by…
Mitosis or meiosis
Three steps of binary fission
Copy genome
Increase cell size
Split in two daughter cells
Copy genome - Binary fission
From one origin of replication, replicate DNA in both directions to produce 2 large circular chromosomes
Tightly pack chromosomes with special proteins + supercoiling
Two different cell division processes
Mitosis and meiosis
Why does mitosis occur?
Typical cell division, growth and repair
Why does meiosis occur?
Necessary for sexual reproduction
Additional steps to avoid excess DNA and increase genetic variability of offspring
What occurs in interphase of the cell cycle?
G1, S, G2
Two sections in the cell cycle
Interphase and mitotic phase
What occurs in the mitotic phase of the cell cycle
Mitosis, cytokinesis
What happens during S phase of the cell cycle
Copy all DNA starting from many points of origin
How long does the cell cycle take
24 hours
How long does a cell stay in interphase for
~23 hours
How long does a cell stay in mitosis for?
<1 hour
In early stages of mitosis
Condense into tightly packed chromatin fibres wrapped around special proteins called histones
What happens in G1 of the cell cycle?
Cell growth, normal gene expression
What happens in G2 of the cell cycle?
Cell growth, duplicate organelles
What happens in mitosis?
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
What happens in cytokinesis?
2 new cells divide
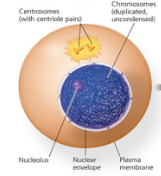
Name the phase
Interphase
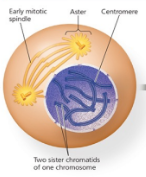
Name the phase
Prophase
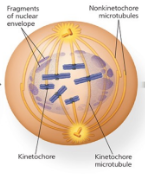
Name the phase
Prometaphase
Name the phase
Interphase
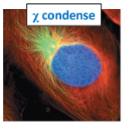
Name the phase
Prophase
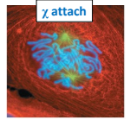
Name the phase
Prometaphase
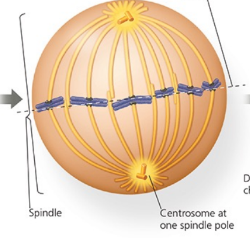
Name the phase
Metaphase
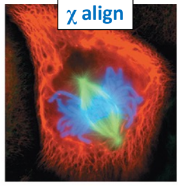
Name the phase
Metaphase
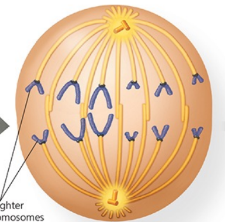
Name the phase
Anaphase
Name the phase
Anaphase
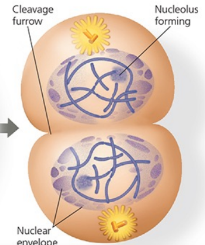
Name the phase
Telophase and cytokinesis
Name the phase
Telophase and cytokinesis
Actin microfilaments form…
A ring on inside of cell membrane, in middle of dividing cells → forms a narrow groove
Filaments are…
Drawn together, pinching the cell membrane together → separates cytoplasm into two identical daughter cells
What must be recreated between daughter cells
Plants cell walls
Which of the following correctly matches a phase of the cell cycle with its description
G1, follows cell division
Errors in the cell cycle…
Can lead to uncontrolled cell growth - can lead to cancer
Is cancer a disease of mitosis of meiosis?
Mitosis
How many chromosomes does humans have?
Humans have 46 chromosomes, organized into 23 pairs, including one pair of sex chromosomes. (n = 23, 2n = 46)
Alleles
Both chromosomes in a homologous pair have the same genes, just different versions of the genes

Haploid or diploid
Haploid

Haploid or diploid
Diploid
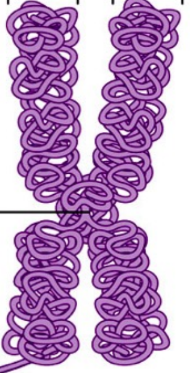
Name the molecule
Chromosome
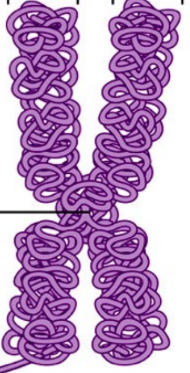
Name the middle
Centromere
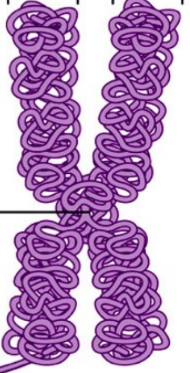
Name the arms
Chromatid
Sexual reproduction
fusion of two cells from different individuals
What would happen if you fused two diploid cells?
You would produce a tetraploid cell, which contains four sets of chromosomes.
Gametes
For sexual reproduction to be possible, organisms need to produce cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parental cell
Cell division - mitosis
Produces 2 genetically identical diploid cells (each has 2n chromosomes)
Cell division - meiosis
Produces 4 haploid cells with half the number of chromosomes as parent cell (each has 1n chromosome)
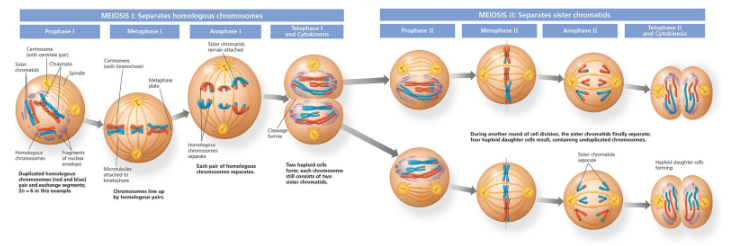
Process of diploid and haploid cells
1 diploid cell (2n chromosomes (each with 2 chromatids)) (Meiosis 1) → 2 haploid cells (1n chromosome (each with 2 chromatids)) (start of meiosis 2) → 4 haploid cells (1n chromosome (each with 1 chromatid)) (after meiosis 2)
Stages of meiosis
Prophase 1, metaphase 1,anaphase 1, telophase 1, cytokinesis, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2, cytokinesis.
Meiosis produces…
Much greater genetic diversity than mitosis
Independent assortment
New combinations
Crossing over
Mixing chromosomes
Advantage of genetic diversity
Provides greater flexibility to adapt to changes in the environment
Asexual reproduction creates…
Exact clones
Advantage of asexual reproduction
Good if species is well adapted to its environment but if environment changes it takes time to adapt
Sexual reproduction creates…
Different versions
Advantage of sexual reproduction
Some may be better adapted to various environments, so if environment changes, there are already well-suited versions
Asexual reproduction
Produces 2 identical daughter cells (clones_
Allows reproduction from a single cell
Is Asexual reproduction mitosis or meiosis
Mitosis, as it results in identical daughter cells.
Sexual reproduction
Produces 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes), genetically different from parent and from each other
Requires 2 organisms, each providing 1 haploid (male provides sperm, female provides egg)
Is sexual reproduction mitosis and meiosis
Meiosis
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is
A sperm
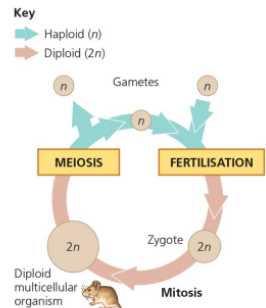
Name the type of sexual life cycle
Animal
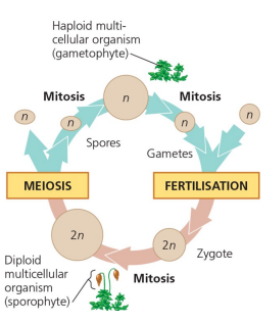
Name the type of sexual life cycle
Plant
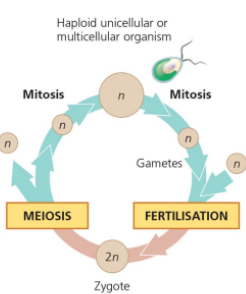
Name the type of sexual life cycle
Most fungi and some protists
Which of the cells are haploid?
1. Sex cell (gamete)
2. Skin cell
3. Muscle cell
Sex cell
Does mitochondria have its on DNA?
Yes
How does mitochondria divide?
Binary fission
Mitochondria in sexual reproduction
Inherited exclusively from the mother (mitochondria in sperm are destroyed by egg after fertilisation)
Analysis of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)…
Can help establishing maternal ancestry (and evolutionary history)