L2: Protein Isolation & Protein Assay & SDS-PAGE
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are enzymes?
biological catalysts (proteins) that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed in the process.
When a cell is lysed to extract protein out, what is in the supernatant layer and what is in the pellet form?
Supernatant:
protein
DNA/RNA
Salts
Sugars
Pellets:
lipids
Bulky complex carbs
What should you AVOID to protect proteins from being damaged?
Heat
Strong Acids
Strong Bases
What are good techniques to use to create a lysate?
Mechanical
Chemical detergents
Grinding: mortar & pestle
Sonicators
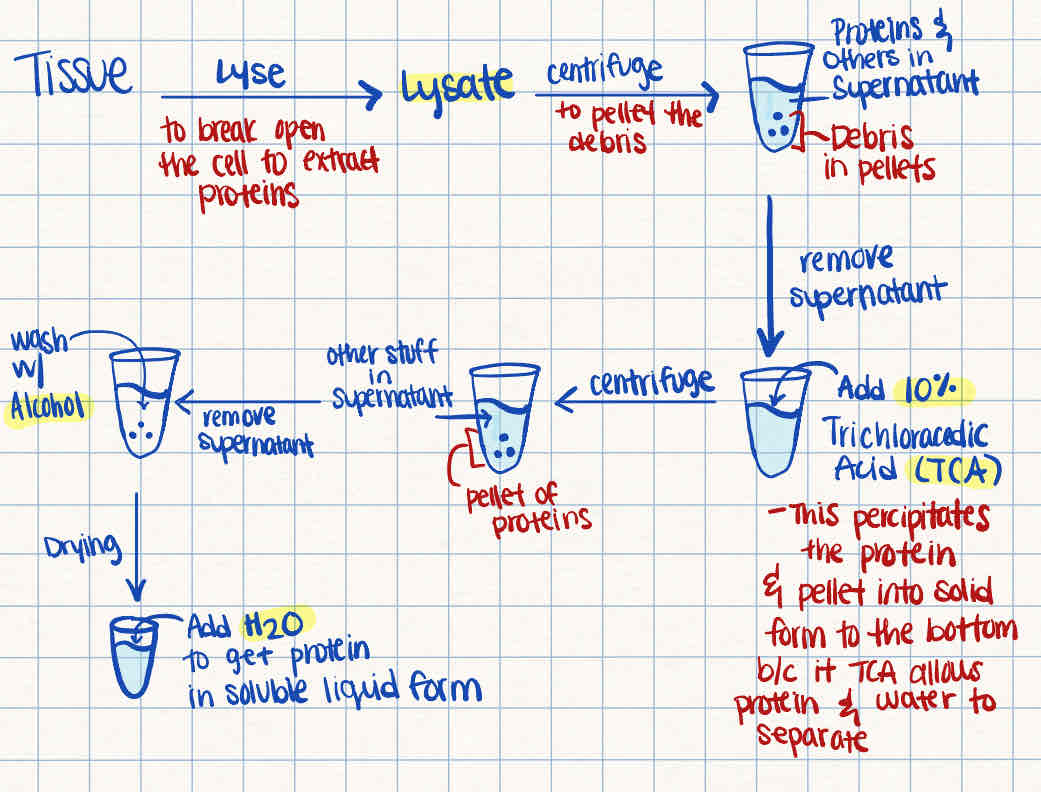
What is the procedure of extracting proteins from the tissue?
Tissue is lysed: to break open the cell to extract the proteins out
Centrifuge: to pellet the debris
Remove supernatant: proteins and others are in the supernatant while the debris is in the pellet form
Add 10% TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid): to precipitate the protein and pellet into solid form allowing protein and water to separate
Centrifuge: to pellet the proteins
Remove supernatant
Wash with alcohol & allow to dry
Add water: to get protein in soluble liquid form
What are the cons of performing a lysate on tissues to extract protein?
It can ruin the SHAPE of proteins
can prevent you from using the Native Protein Isolation Strategy
What are 2 isolation strategies of protein?
Native proteins: folded naturally
Denatured proteins: protein unfolding down to primary structure
What technique is used to quantify protein?
Protein Assay
What is protein assay technique?
Method used to measure the concentration of protein in a sample
What are the 3 types of protein assay techniques?
Bradford assay
Lowery assay
BCA assay
What is a Bradford Assay
uses Coomassie Blue Dye, which binds to protein
When the dye reacts with protein it changes color from brown to blue
Quick and easy
What is a Lowry Assay
interacts with Copper Ions to make a blue color when it reacts with protein
What is BCA Assay?
Reacts with Copper and changes color to purple when it reacts with protein
What happens when there is too much protein in an SDS-PAGE?
Data will be too difficult to analyze
What happens if there is not enough protein in an SDS-PAGE gel?
The bands will be too faint to analyze in the data
What technique is used to analyze the concentration of protein?
Spectrophotometer
measures the absorbance of LIGHT at specific wavelengths
What is an SDS-PAGE?
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a detergent
it is a Protein Gel that separated proteins based on Molecular Weight
Why are proteins separated based on molecular weight?
Some proteins can be the same size but with different weight due to amino acids differing by their R-groups
What is the PAGE mean in SDS-PAGE?
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
sticks together by cross-linking fibers via chemical reactions
What type of technique is PAGE?
Used to separate proteins or nucleic acids based on their SIZE and CHARGE.
The molecules are loaded into a Polyacrylamide gel and moves through it when an electric current is applied
What are the 4 forces that help hold protein in their tertiary shape?
Hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
Disulfide bonds
What are hydrogen bonds?
breaks down by using HEAT
Forms between polar side chains or backbone groups
What are ionic bonds?
reducing agent: SDS
Occurs between oppositely charged side chains
What are hydrophobic interactions?
reducing agent: SDS
Nonpolar side chains cluster away from water in protein
What are disulfide bonds?
Reducing agent: DDT or Beta-ME
Covalent bonds that give a strong structural support
Disulfide bridges can be broken down by using what reducing agents?
DDT or Beta-ME
In an SDS-PAGE gel, what type of liquid is used to place the gel in?
Electrolyte buffer
What are the units for the size standard in an SDS-PAGE gel?
KiloDaltons (KDa)
What is in a protein sample load for an SDS-PAGE
DDT
SDS
HEAT
Loading Dye
In an SDS-PAGE, what are the 2 types of dyes used to stain the gel after running to visualize proteins?
Coomassie Blue
Silver Nitrate
Proteins can be a mixed charge of positive charges or negative charges, what can be used to neutralize the charge?
SDS can be used as a detergent