Antimicrobial Therapy
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
bactericidal
lethal to pathogen
bacteriostatic
prevents growth, host has to evenly muster own defenses to kill pathogen
Narrow spectrum
antibacterial treatment, treat limited # of organisms, less likely to disrupt flora, used when pathogen is identified by lab test (culture and sensitivity)
Broad spectrum
antribacterial treatment, “broad side of the barn” treats multiple organisms; more likely to disrupt flora; often used when pathogen is unknown
antiobiotics 2 lethal types of hypersensitivities
anaphylaxis, stevens-johnson syndrome
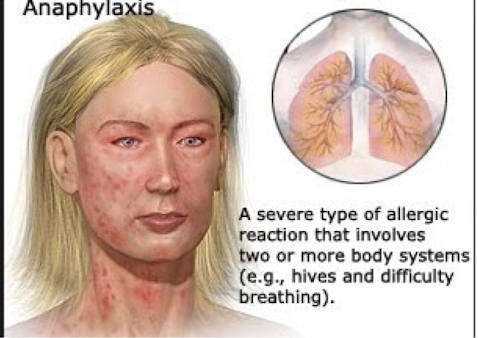
anaphylaxis signs
bronchospasm and harm to at least one other organ system, shock
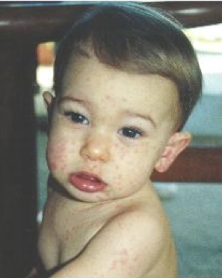
stevens-johnson syndrome signs
facial swelling, tongue swelling, hives, skin pain and peeling, red/puple rash, blisters skin and mucous membranes; often lethal, life-altering
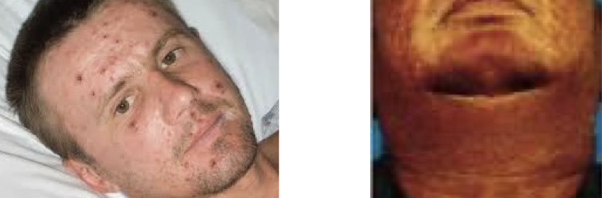
antiobiotics less lethal types of hypersensitivities
generalized rash, red neck (or “red man” syndrome)
aminoglycosides (gentamicin) can be toxic to which specific organ(s)
renal & ototoxicity
gentamicin is used for which spectrum
narrow spectrum
vancomycin can be toxic to which specific organ(s)
renal & ototoxicity
chloramphenicol can be toxic to which specific organ(s)
bone marrow
Most all antibiotics can be toxic to
GI which can cause N/V/D and dehydration, often prescribed with probiotics, lactobacillus, and yogurt can help
Which lab test is often done on more dangerous antibiotics
peak and trough, trough done just before drug administration and peak done usually 1-2 hours after drug administration
What ADE is most likely to occur when broad spectrum antibiotics are used
superinfection, normal flora is disrupted and emergence of a new infection (black furry tongue, candidiasis (thrush), vaginitis
Common drug drug interactions with antibiotics
hormonal contraceptives (with some), protein binding competition, liver enzyme competition, liver enzyme competition, antagonism effects, potentiation effects
How can we prevent resistence to antimicrobial drugs?
use a narrow spectrum, use less often, use older antibiotics, complete drug course
How to prevent resistance in hospitals?
Prevent infection (Vaccinations, d/c catheters ASAP), diagnose and treat effectively (target thew pathogen: C&S; access the experts), use antimicrobials correctly (use of software to make choices, avoid contamination of lab specimens, treat infection not colonization, “no to Vanco” drug of last resort), prevent transmission (isolation protocols, handwashing)
What may be done while waiting for C&S?
can send for “gram stain” to help narrow the choice of antimicrobial
antibiotics should not be used as prophylactic for
colds
antibiotics can be used for sore throat if
strep is cultured
antibiotics can be used for bronchitis only if
chronic lung (asthma/COPD)
Antibiotics can be used as prophylaxis for
history of valvular heart disorders prior to dentistry/surgery/obstetrical procedures, group beta strep (genitalia) and pregnancy, immunosuppressed clients, prior to major surgery
When are multiple antibiotics given
organism(s) unknown, infection is severe, immunosuppressed host, prevention of resistence (ex: TB), may decrease toxicity because doses of individual drugs can be lower
Multiple antibiotics downside
increased risk of allergic reactions and superinfections, possible antagonism of effects, increased costs
What do penicillins do?
interfere with cell wall synthesis and bacteria cell division (bactericidal)
penicillin common uses
gram + cocci, rods, anaerobes; pharyngitis, endocarditis, pneumonia, meningitis, syphillis, gonorrhea, URI, UTI, otitis, sinusitis
penicillin V administration
oral, should be taken with food
penicillins ADEs
rash to anaphylaxis, GI (N/V/D), decreased RBCs, superinfection
penicillins teaching
report rash immediately, complete entire amount, if long term CBC to see if it changes, Pen V taken with food
penicillins used in which spectrum
narrow spectrum
ampicillins used in which spectrum
broad spectrum
MRSA infections are commonly acquired
by hospitalized clients - “nosocomial" infection
What is MRSA treated with
IV vancomycin (bazooka antibiotic)
vancomycin actions are similar to
penicillin
vancomycin is used in which spectrum
narrow spectrum
Common uses of vancomycin
MRSA, colitis from antibiotics with + culture for C diff
Vancomycin ADEs
ototoxicity and renal toxicity, red neck syndrome, hypotension/chills/fever, N/V/D, stomatits
Vancomycin nursing implications
High alert double check!, infuse slowly > 60 min on pump, vesicant, peak/trough, asses renal (BUN/creatinine), report tinnitus/diahrrea
cephalosprons are the most
widely used antibiotics
Huge danger in cephalosporin use
name similarities
cefazolin (Ancef) is often used for
clients who are allergic to penicillin, actions are similar to penicillin, but cross sensitivity is 1-15% in those with mild allergy to PCN and should not be given to those with STRONG allergy to penicillin
cefazolin (Ancef) is effective against
E. coli, pre-op/post-op prophylaxis
cefaclor (Ceclor) route
po
cefotetan (Cefotan) route
IV
cefaclor (Ceclor) ADE
bleeding (interference with Vit K), Disulfram/Antabuse reaction with alcohol
tetracyclines spectrum
broad-spectrum
tetracyclines route
PO, IM, IV
tetracyclines ADE
Category D (not for use in pregnancy) interferes with calcification (not for children under 8), photosensitivity, GI: N/V/D, liver
tetracycline uses
broad spectrum, STIs, pharyngitis, UTIs
gentamicin action
inhibits protein synthesis, bacteriostatic in low doses; -cidal in high doses
gentamicin uses
gram -, TB, alternative for MRSA, narrow spectrum
gentamicin ADEs
NOT usually drug of first choice, ototoxicity, renal toxicity, neurotoxicity (weakness/paralysis; dizziness, ataxia)
aminoglycosides nursing implications
C&S to identify pathogen and correct drug strongly reccomended; report hearing loss/ringing in ear/problems with balance/headache; renal function: high fluid intake, I&O, check BUN & creatinine; peak/trough trough needs to be low preferably zero; inactivated by long-acting penicillins (separate doses if both are given)
penicillins and aminoglycosides
not compatable in same IV
erythromycin route and dose
usually po, often dosing is short
erythromycin uses
broad spectrum: staph aureus; pneumonia; good alternative for persons allergic to penicillin
erythromycin ADEs
GI side effects very common, superinfections
erythromycin nursing implications
taken on empty stomach, report severe diarrhea especially in children (>10% weight loss), daily weights to make sure no dehydration
trimethoprin plus sulfamethoxazole use
broad spectrum, UTI, otitis, prostate inflammation
sulfonamides ADEs
Renal: calculi, nephrotoxicity; hematologic: decrease in RBC and WBC; hypersensitivity 3%, photosensitivity; GI: N/V/D may be significant; hyperkalemia
Sulfonamides contraindications
< 2 months, pregnancy - cat D, breastfeeding, clients with renal impairment, cross-sensitivity with: loop diuretics, sulfonylureas (glyburide), NSAIDs
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome mortality
25%
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome sx
fever, general ill feeling, pruritis, joint aches, skin lesions, peeling (palms), not immediate days later
Sulfa drugs should not be given if
there is hypersensitivity to related drugs
Sulfonamides Nursing implications
push fluids, I&O, BUN, creatinine, CBC; empty stomach unless N/V (if with food may need to up dose; Report: sore throat, fever, pallor; photosensitivity
ciprofloxacin (Cipro) route
po usually
ciprofloxacin (Cipro) mechanism and use
Interrupts DNA synthesis; broad-spectrum: E. coli, UTIs, STIs, resp infections, ANTHRAX (prevents disease if anthrax spores are inhaled, taken for 60 days)
ciprofloxacin (Cipro) ADEs
photosensitivity; GI: N/V/D; CNS toxicity: dizziness, confusion, visual disturbances IN ELDERLY; TENDON RUPTURE (ACHILLES) this effect is most likely if elderly and on prednisone
ciprofloxacin nursig implications
photosensitivity: wear clothing that protects against sun & use sunscreen; urine may be brown or orange, stains; push fluids I & O, discontinue if tendon pain/swelling; empty stomach (food will decrease absorption; milk and antacids should be avoided)
Chloramphenicol use
serious, broad spectrum; H. flu influenza resistant to penicillins; fatal blood disorders (sepsis)
Chloramphenicol side effects
fatal aplastic anemia, bone marrow suppression (lowered production of all cells, dose related, reversible), Gray baby syndrome (primature newborns, toxic reaction causing ashen-gray cyanosis, vascular collapse, discontinued immediately), sold OTC in Mexico and other countries, told “its good for baby ear pain”
chloramphenicol nursing implications
CBC is routine, monitor drug levels, not used in infants anymore, most common now: purchased out of country and taken OTC
Pros of multiple antimicrobials
sever infection (meningitis), infection with several pathogens, prevent resistance (TB), decrease toxicity
Cons of multiple antimicrobials
Increase risk of allergy, superinfection, increasd cost, development of incredibly drug resistant microbes