BIO 50 LEC - INORGANIC AND ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Atom
smallest unit of an element
Proton - + charged
Neutron - - no charge
Electron - — charged
Sub-atomic particles of an atom
Elements
Fundamental units of matter
matter
anything that occupies space and has mass (weight)
Carbon
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
96% of the body is made from 4 elements
Electron Configuration
- chemical behavior of an atom is determined by its electron configuration
– distribution of electrons in the atom’s electron shell
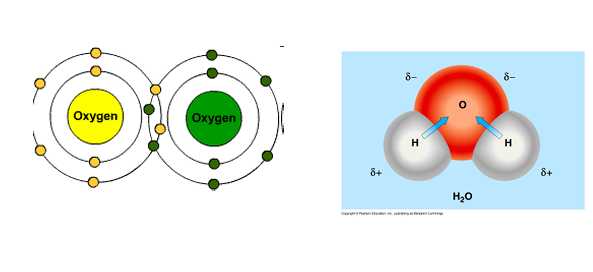
Covalent bond
Sharing of valence electrons
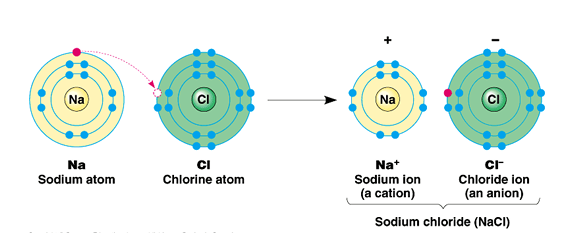
Ionic bond
• Unequal sharing of electrons
• Salts
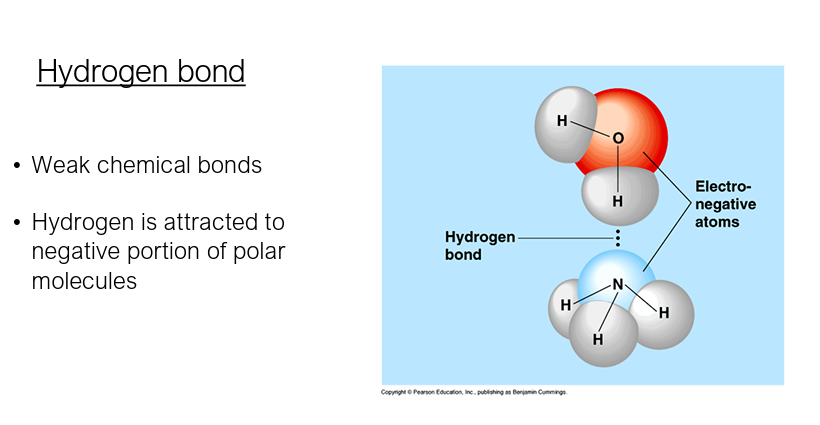
Hydrogen bond
• Weak chemical bonds
• Hydrogen is attracted to negative portion of polar molecules
Organic Compounds
• Contain carbon
• Most are covalently bond
Inorganic Compounds
• Lack carbon
• Tend to be simpler compounds
Intracellular
fluid located within cells
Extracellular
fluid outside body cells
High specific heat
amount of heat that must be lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1ºC
High surface tension
how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
High heat of vaporization
quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1g of it to be converted from liquid to the gaseous state
100ºC
Expansion upon freezing
achieves maximum density at 4ºC
at 0ºC, water becomes locked into a crystallline lattice
Versatile solvent
allows aqueous solutions of life
contains a diversity of dissolved substances
Dehydration
It removes a water molecule, forming a new bond.
Hydrolysis
adds a water molecule, breaking a bond
SALTS (Ions)
charged particles; electrolytes
important for nerve impulse conduction; muscle contraction
Acids
a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
Bases
a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
pH
measures the relative concentration of hydrogen ions
neutral
pH 7
acidic
pH below 7
basic
pH above 7
Buffers
substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH – in a solution
• carbohydrates
• lipids/ fats
• proteins
• Nucleotides and nucleic acids
Organic compounds
Polymers
large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits strung together
Carbohydrates
composed of C : H : O in a 1 : 2 : 1 ratio
Importance:
- energy source
- transportable forms of energy
- structural material
• Monosaccharides
• Disaccharides
• Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates are classified according to size. Classification:
monosaccharide
simple sugar
disaccharide
double sugar
polysaccharide
starch
triglycerides (neutral fats)
steroids
Common lipids in the human body
Neutral fats (triglycerides)
• Found in fat deposits
• Source of stored energy
• Composed of three fatty acids and one glycerol molecule
Saturated fatty acids
fatty acids that contain only single covalent bonds
Unsaturated fatty acids
fatty acids that contain one or more double covalent bonds
Steroids
• Include cholesterol, bile salts, vitamin D, and some hormones
Cholesterol
the basis for all steroids made in the body
Proteins
-50% dry weight of cell
- polymers of amino acid
- peptide bond
Amino Acid
- possess both carboxyl and amino groups
- R-side chain
phenylalanine
leucine
isoleucine
methionine
tryptophan
proline
threonine
alanine
cysteine
glycine
valine
serine
arginine
20 Amino Acids
glycine
simplest amino acid
aspartic acid
an acidic amino acid
lysine
basic amino acid
cysteine
sulfur-containing amino acid
hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail
phospholipid has ____ head and ______ tail
structural proteins
the function of this type of protein is support
example: insects and spiders use silk fibers to make their cocoons and webs, respectively. Collagen and elastin provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. Keratin is the portion of hair, horns, feathers, and other skin appendages.
storage proteins
the function of this type of protein is to store amino acids
Example: Ovalbumin is the protein of egg white, used as an amino acid source for the developing embryo. Casein, the protein of milk, is the major source of amino acids for baby mammals. Plant have storage proteins in their seeds.
transport proteins
the function of this type of protein is transport other substances
Example: Hemoglobin, the iron-containing protein of vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lung to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules aross cell membranes.
hormonal proteins
the function of this type of protein: coordination of an organism’s activities
Example: Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, help regulate the concentration of sugar in the blood of vertebrates.
Receptor Proteins
the function of this type of protein: response of cll to chemical stimuli
Example: Receptor built into the membrane of a nerve cll detect chemical signals rlased by other nerve cells.
Contractile Proteins
the function of this type of protein: movement
Example: Actin and myosin are responsible for the movement of muscles. Other proteins are responsible for the undulations of the organelles called cilia and flagella.
defensive proteins
the function of this type of protein: protection against disease
Example: Antibodies combat bacteria and viruses.
Enzymatic proteins
the function of this type of protein: selective acceleration of chemical reactions
Example: digestive enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of the polymers in food
Primary Structure (1º)
Secondary Structure (2º)
Tertiary Structure (3º)
Quarternary Structure (4º
Levels of Protein Structure
Primary Structure (1º)
unique sequence of amino acids
Secondary Structure (2º)
repeated coiling or folding of the primary structure
Tertiary Structure (3º)
irregular contortions of the 2º formed by the bonds of the side chains (R groups) of the amino acid
Quarternary Structure (4º)
overall protein structure that results from the aggregation of several polypeptide subunits.
Globular Proteins
Also known as functional proteins
Function as antibodies or enzymes
Can be denatured
Enzymes
Acts as biological catalysts
Increase the rate of chemical reactions
nitrogenous base; 5-C sugar; phosphate group
Nucleotides
(basic structure)
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Chemical energy used by all cells
Replenished by oxidation of food fuels
DNA and RNA
storage, transmission of genetic information
purines (e.g. adenine and guanine)
this has double rings made of carbon and nitrogen
pyrimidines (e.g. cytosine, thymine, uracil)
only has one ring made up of (4) carbons and (2) nitrogen atoms
phosphate, sugar, adenine
adenine nucleotide structure