Unit 7 Vocabulary AP Human Geography
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 7 industries and economic processes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Industry
any economic activity that uses machinery on a large scale to process raw materials into finished goods
Industrialization
the process by which the interaction of social and economic factors leads to the development of industries
Industrial Revolution
a revolution that began in Europe and North America that marked the shift from small-scale, hand-crafted production to power-driven mass production
Cottage Industries
members of families spread out in rural areas working in their homes to make goods
Economic Sectors
the structure of a country’s economy by distinct economic activities that can be categorized into sectors. These sectors consist of the primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary.
Primary Sector
economic activity that involves harvesting raw materials from the earth
Secondary Sector
economic activity that involves turning raw materials into finished products
Tertiary Sector
economic activity that focuses on providing goods and services
Quaternary Sector
subsection of the tertiary that involves specialized services and frontier research
Quinary Sector
a subset of the quaternary sector that involves leadership in frontier industries like government and science
Postindustrial Economy
an economic pattern marked by extremely low primary sector employment, relatively low secondary sector employment, and predominant tertiary sector employment
Gross Domestic Product
the total value of all goods and services produced by a country’s citizens and companies within the country in a year
Dual Economy
two distinct divisions of economic activity across the economic sectors within a country or region
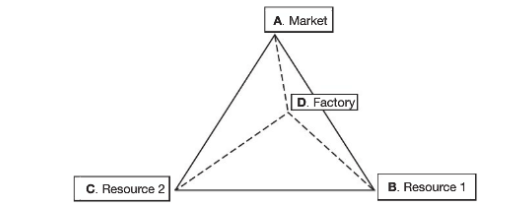
Least-Cost Theory
a model that geographers use to analyze spatial patterns in the secondary economic sector. The theory considers the factors that influence where enterprises locate manufacturing production
Agglomeration
the advantage for companies in the same or similar industries in locating near each other in order to take advantage of specialized labor, materials, and services
Break-of-Bulk Points
locations where it is economically advantageous to break raw materials into smaller units before shipping them farther. These sites are often located at places where the mode of transportation changes
Industrial Parks
areas where a cluster of industrial sites are located
Bulk-Reducing Industries
industries where raw materials cost more to transport than finished goods
Bulk-Gaining Industries
industries where finished goods cost more to transport than raw materials
Human Development
the processes involved in the improvement of people’s freedoms, rights, capabilities, choices, and material conditions
Gross National Income
the total value of goods and services globally produced by a country in a year divided by the country’s population
Human Development Index
a measure that includes three key measures of human development; life expectancy at birth, access to education, and standard of living; to determine overall levels of development of countries
Gender Development Index
a measure that uses health, knowledge, and standard of living and compares them by gender to determine gender disparity
Gender Inequality Index
a measure that calculates gender inequality in three categories; reproductive health, empowerment, and labor-market participation
Gross National Product
the total vale of the goods and services produced by a country’s citizens and companies both domestically and internationally in year
Formal Sector
businesses, enterprises, and other economic activities that have government supervision, monitoring, and protection, and are taxed
Informal Sector
any part of a country’s economy that is outside of government regulation and is not taxed
Microloans
very small short-term loans with low interest intended to help people in need
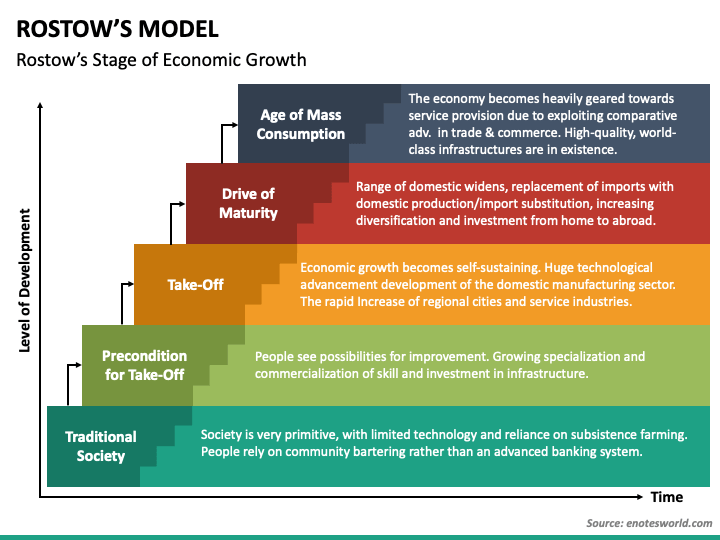
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth
an economic development model that measures a country’s economic development in 5 stages; traditional society, the most primitive form of organization, preconditions for takeoff, where people begin to seek inventions and technology to innovate the production process, takeoff, where industrial processes begin to take hold, drive to maturity, where a country’s economic successes begin to become the norm, and high mass consumption, when a country enters the post-industrial stage
Dependency Theory
the description of the development challenges and limitations faced by poorer countries and the political and economic relationships poorer countries have with richer countries
Comparative Advantage
the relative cost advantages of producing certain goods and services for trade rather than in-country consumption
Complementary Advantage
the mutually beneficial trade relationship between two countries that results when they have different comparative advantages
Neoliberalism
the belief that open markets and free trade across the globe will lead to economic development everywhere
Deindustrialization
the change that occurs with the decline in the percent of workers employed in the secondary sector and a reduction of a region’s industrial capacity or activity
Growth Poles
places of economic activity clustered around one or more high-growth industries that stimulate economic growth by capitalizing on some special asset
Just-in-time Delivery
the process of using computer logistics to ensure that materials are delivered when they are needed for short-term production so that companies can avoid paying to store extra inventory at their facilities
Fordism
the faster and more efficient production strategy of automation, standardization, economies of scale, and a division of labor in which each worker has just one task
Post-Fordism
the system of production that relies on automation through the use of robots and computer systems and is centered on low-volume manufacturing and flexible systems that allow for quick responses to changes in the market
Offshore Outsourcing
the process of companies increasingly moving production to places outside the country in which they are headquartered
International Division of Labor
a division of labor based on the world systems theory in which periphery countries participate in a different sector of labor than the core
Special Economic Zones
an area within a country that is subject to different and more beneficial economic regulations than other areas
Export Processing Zones
sites where manufacturing of exports is done without tariffs
Free Trade Zones
economic zones that provide customs-related advantages and exemptions from tariffs and taxes
Ecotourism
a type of tourism that can gain revenue with minimal environmental impact