Rhythm review unit 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Where do healthy rhythms originate?
Sinus node
What 5 components do you need to analyze a rhythm
regularity, rate, p-wave morphology, PRI, QRS
When we look at whether the QRS intervals equal or not we are measuring what?
Regularity
Rate
ventricular rate or atrial rate
Ventricular Rate
R-wave to R-wave
Atrial Rate
P-wave to p-wave
What are the ways to calculate rate
6 second, 10 second, 300, 1500
What factors do you consider for p-wave morphology
Is p-wave 1:1 with QRS? are the shapes the same? are they coming from the same area? is it followed by a qrs
What factors do you consider for QRS?
Duration: is the complex wide narrow?
Normal duration is <0.12 seconds
morphology: does each qrs look the same, is it wide/narrow.
what does a wide QRS mean?
its taking longer to depolarize the ventricles than normal
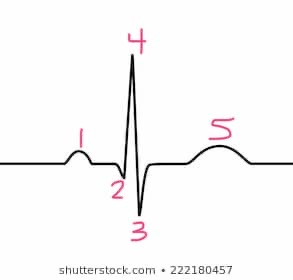
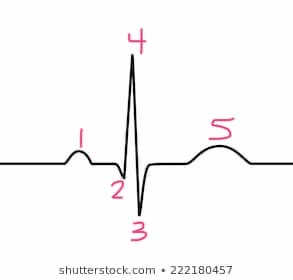
1
p -wave
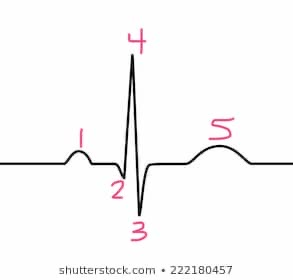
5
t-wave
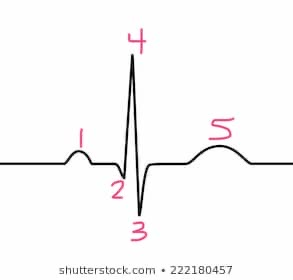
s-wave
3
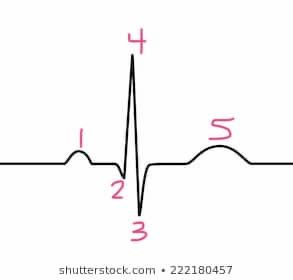
4
r-wave
5
t-wave
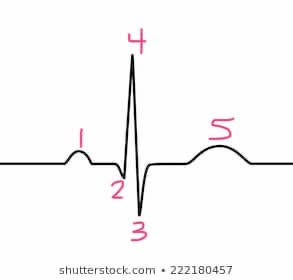
2
q-wave
ventricular rate is determined by
QRS complex frequency
atrial rate is determined by
p-waves
Layers of the heart inner to outer
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium. Encased in pericardium.
Top two heart chambers
Left atrium, right atrium
bottom two chambers of the heart
Left ventricle right ventricle
Arteries move blood..
away from the heart
veins move blood
towards the heart
Ventricular systole
heart contracts to pump blood out
Ventricular diastole
heart relaxing and filling with blood
Atrial systole
Atrial kick
Atrial diastole
Occurs during ventricular systole
pulmonary circulation
blood to and from the lungs
systemic circulation
blood flow to the body
coronary circulation
blood flow to the heart