periodicity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
periodicity definition
trends in the chemical properties of elements across a period
elements in the same group have similar properties
Shielding definition
when inner electrons block the attraction between the nucleus and outer electrons
atomic radius along a period
decreases
no. of protons increases, so nuclear charge increases
attraction between nucleus and electrons increases
same shielding
atomic radius down a group
increases
nuclear charge decreases
greater distance between nucleus and electrons
ionisation energy along a period
increases
atomic radius decreases
nuclear charge increases
attraction between electrons and nucleus increases
same shielding
ionisation energy definition
the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms in the gaseous state, to form one mole of gaseous ions
ionisation energy down a group
decreases
atomic radius increases
as you go down the group there is more shielding
ionisation energy along a period
increases
nuclear charge increases
atomic radius decreases
same shielding
explain why the second ionisation energy of magnesium is greater than the first ionisation energy of magnesium
because the electron is being removed a positive ion
therefore it more energy is needed
first ionisation energy graph for period 3 elements
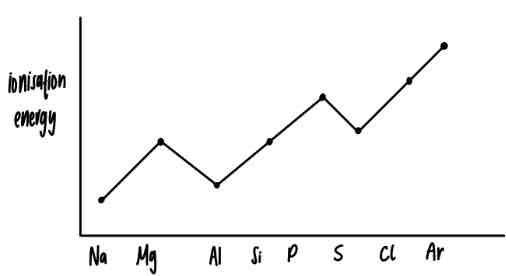
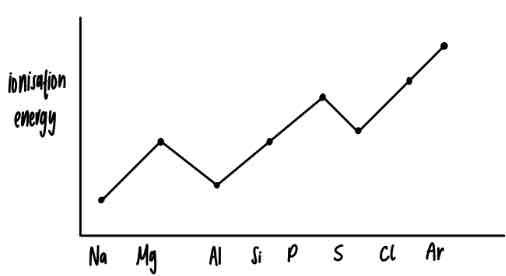
reason for the dip in ionisation energy at aluminium
electronic configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p¹
outer electron in 3p orbital
3p orbital is higher in energy than 3s
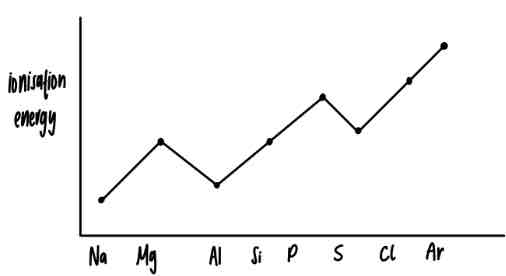
reason for the dip at sulfur
electronic configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁴
paired electron in (3)p-orbital
- (remember the bus stop method for electron pairing in orbitals)the electron pair repels
suggest why the first ionisation energy of krypton is lower than the first ionisation energy of argon
krypton has more shielding than argon
explain why the second ionisation energy of sodium is greater than the second ionisation energy of magnesium
electronic configuration of sodium: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹
electronic configuration of magnesium: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²
for the second I.E, sodium loses an electron from a 2p orbital whereas magnesium loses energy from a 3s orbital
less shielding in sodium
therefore more attraction between electrons and nucleus
metallic bonding
contains lattice of positive metal ions and delocalised electrons
strong attraction between them
explain how metals conduct electricity
delocalised electrons flow in a given direction
explain why sodium has a lower boiling point than magnesium
Mg has more protons than Na
Mg is a smaller atom than Na
therefore greater attraction between nucleus and delocalised electrons
(delocalised bc were talking abt metals)
so therefore stronger metallic bonding
explain why metals are malleable
have layers of atoms/ions that can slide over one another
state the structure shown by a crystal of silicon and explain why the melting point of silicon is very high
giant covalent structure
has strong covalent bonds, which require lots of energy to break
state the structure shown by crystals of sulfur and phosphorous. explain why the melting point of sulfur is higher than the melting point of phosphorus
simple molecular structure
sulfur molecule (S₈) is a larger molecule than phosphorus molecule (P₄)
therefore stronger vdw’s forces between sulfur molecules
requires more energy to overcome these forces
explain, in terms of crystal structure and bonding, why silicon(IV) dioxide has a higher melting point than phosphorus(V) oxide
silicon dioxide is a giant covalent molecule whereas phosphorus dioxide is a simple covalent compound
silicon dioxide has strong covalent bonds which needs lots of energy to be broken
whereas phosphorus dioxide only has vdw’s forces between its molecules
in terms of atomic structure, explain why van der Waals’ forces in liquid argon are very weak
argon are single atoms/monoatomic, with the electrons closer to the nucleus
therefore they cannot be easily polarised
which ion has the largest radius:
F⁻
Mg²⁺
Na⁺
O²⁻
O²⁻
which of these elements has the highest second ionisation energy and why:
Na
Mg
Ne
Ar
Na
bc removing electron will make noble gas configuration, which will make it very difficult to remove 2nd electron