Exchange surfaces - ventillation + heart
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Inspiration
External intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract
Causes diaphragm to flatten moving rib cage upward and outward
Volume of the thorax now increases
This decreases lung pressure - below atmospheric pressure
Causing air to flow into the lungs
Why does inspiration considered active
Requires energy
Muscle contraction
Expiration
External intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax
Causes rib cage to move downward and inward causing diaphragm to curve
Volume of the thorax decreases - increases lung pressure above atmospheric pressure
Forcing out air from lungs
Vital capacity
Maximum volume of air an individual can inhale and exhale in one deep breath
Tidal volume
The air inhaled and exhaled while at rest
Residual volume
Volume of air that stays in lungs so they do not collapse
Breathing rate
Number of breaths taken per minute
Stroke Volume
Volume of blood cm3 pumped by the heart in 1 minute
Hear Rate
Number of heart beats per minute
Cardiac Output Stroke
Stroke volume x heart rate
Why is expiration considered passive
No muscle contraction
No recoil of tissue
What is the septum?
The septum is the wall between the left and right sides of the heart
Septum prevents the mix of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from different sides of the heart
How do valves work?
Open when the pressure of blood behind them is greater than the pressure in front of them
Close when the pressure of blood in front of them is greater than the pressure behind them
Why are valves important?
Prevent backflow of blood into the wrong chamber
Maintains correct pressure of blood in chambers
How are the right atrium and right ventricle separated
By the tricuspid valve
How are the left atrium and left ventricle seperated
By the bicuspid valve
How is the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery separated
Semi lunar valve
How is the left ventricle and aorta seperated
Semi lunar valve
Why is left ventricle wall thicker?
Enables stronger contractions
Generating a higher blood pressure
To push blood over a longer distance to the whole body rather than just the lungs in the right ventricle
Deoxygenated blood
Vena cava carries deoxygenated blood -—> right atrium -—> tricuspid valve —-> right ventricle -—>semi lunar valve ——> pulmonary artery (heart to lungs)
Oxygenated blood
Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood ——> left atrium ——> bicuspid valve ——> left ventricle —->semi lunar valve —-> aorta
Aorta adpatation
Very elastic to recoil and withstand a high blood pressure from heart
Sends oxygenated blood to rest of the body
How does Blood flow
High pressure —→ low pressure
How does contraction change pressure
Increases pressure
How does relaxation change pressure
Decreases pressure
Why is the heart described as myogenic
Cardiac muscle can initiate its own contractions
Where are AV and SV node found
In right atrium
What is the role of the AV node
AV node delays impulse
Allows atria to fully contract so all blood enters ventricles
Prevents ventricles contracting at the same time as atria - which would result in not all blood entering ventricles before pumped out
Blood will go from ventricles to aorta/ pulmonary artery
Not all blood would be pumped out
Role of bundle of his
Transports impulse
Why is there not ventricular systole in bundle of His
Has an insulating layer
Ventricular walls are not affected by impulse
Do not contract
Why does heart contract from apex
Ensures that all blood is squeezed out of the hurt
Artery lumen
Artery lumen is smaller
This is because artery wall is much thicker than a vein
Vein lumen
Veins lumen is bigger and irregular shape
Thinner wall
Muscular layer artery
Much thicker in arteries compared to veins - so can constrict and dilate to control volume of blood pumped out of heart
Muscular layer vein
Thin - cannot control blood flow
Elastic layer artery
Much thicker - maintain blood pressure
Stretch and Recoil in response to heart beat
Elastic layer - veins
Veins carry blood at a much more low pressure
Thin elastic layer
Wall artery
Much thicker in the artery - prevent vessels bursting at high pressures
Valves - artery
No valves
Veins artery
Have valves
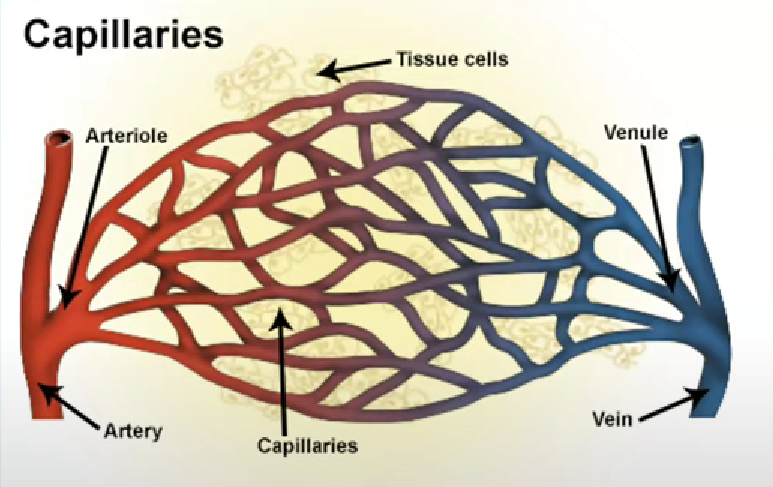
Capillary
One cell thick
Only red blood cells can just fit through diameter of lumen
Blood flow is slower in capillaries
More time for diffusion
Arterioles - muscular wall
Connect arteries to capillaries
Much thicker muscular layer than arteries
Restrict blood flow before capillaries
Decreases pressure of blood going into capillaries
As this could damage capillaries
Arterioles - Elastic layer
Thinner as does not need to recoil and stretch to withstand high pressures
Low pressures
Arterioles - Wall thickness
Thinner as pressure is lower
Arterioles - valves
No valves
Capillaries - elastic layer
No elastic layer
Capillaries - muscle layer
No muscle layer
Capillary wall thickness
One cell thick - short diffusion distance
Slows blood so more diffusion can occur