business management pt 2: business departments and organisational structures
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what are the 12 departments?
Finance and Accounting
General Management
HR
Customer Service
Facility Management
Operations
Marketing and Communications
Sales
IT
Legal
Purchase
R&D
what is general management?
C-suite so CEO etc
develops and executes overall business strategies, responsible for entire organization
responsible for: determining strategies, planning, monitoring execution of plans, guiding the workforce, maintaining punctuality and disciplinary issues
they are leaders, mentors, managers, deciders and builders
what is marketing and communication?
they identify customer needs and create products and services to satisfy them
responsible for: branding, market research, understanding market segments, product decisions and distribution, promotion and price decisions, content creation, events, international communication and business support
what is marketing?
process of promoting and selling products through market research, advertising and sales strategies
increases revenue and market share by understanding consumer behavior and developing targeted campaigns
creating value for customers and driving sales throguh promotion, price and distribution strategies
identifying customer needs and creating offers that satisfy them, build brand loyalty through campaigns
activities: market research, product development, advertising, public relations, pricing and sales promotion
using: market research tools, digital marketing platforms, campaigns, SEO and social media
for who: target customers and potential buyers
→ finding out what the customer wants, making offers for that, driving sales for said offers through campaigns and advertising
what is communications?
act of conveying messages and information between business and its audience, internally and externally
managing the flow of information between an organization and its stakeholders, employees, customers and the public
build and maintain relationships, build trust, manage reputation, enhance company image, ensure clarity in messaging internally and externally
activities: corporate communication, internal communication, crisis management, media relations and PR
using: press releases, internal newsletters, corporate blogs, public speaking, media events
for who: employees, media, customers, partners, shareholders and public
→ managing brand image communication within and outside company, trust, reputation, image, messaging clarity and consistency, press and media relations
marketing vs communications
marketing is sales, communication is information
marketing is for customers and potential customers, communication is within company + press & media + partners + customers + general public
marketing is increasing revenue, communication is about brand image and trust
marketing is analysing the market and customer, communication is information flow and relationships
operations
- ensures that the production process is completed from start to finish
- these production processes need to line up with the goals and functions of other departments within a company
- responsibilities: improving production, streamlining, employee communication, ensuring compliance with government agencies on regulations
finance and accounting
the finance department is responsible for acquiring and utilizing money for financing the activities of the company
assesses short-term and long-term capital requirements
long-term capital requirements are maintenance of office building vehicles, office infrastructure, business equipment and investments
short-term capital requirements involve labor and staff payments, providing communication facility, payment of electricity and other resources
responsibilities: budgeting, financial, planning, financial growth (mostly finance)
a healthy cash flow is needed to fund the day-to-day running of the business, cover any unexpected costs and help support the company's growth
responsibilites: financial records, payroll, taxation, balance sheet management (mostly accounting)
what is accounting?
process of recording, classifying and summarizing financial transactions to provide accurate financial statements
to ensure accuracy of financial statements and compliancy with laws
looks at past performance and financial records
tracking and reporting financial transactions for internal and external stakeholders as well as regulation compliance
activities: bookkeeping, preparing financial statements, auditing and tax reporting
using: balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements and tax returns
→ looking at past performance and financial records to provide accurate financial statements to report to stakeholders (internal and external) and comply with laws and tax
what is finance?
management of assets, liabilities and capital to maximize wealth and achieve financial goals
future financial planning, investment strategies and resource allocation
to make strategic decisions regarding investments, capital structure and funding to enhance finacial performance
using financial resources optimally to grow wealth
activities: managing investments, budgeting, raising capital, risk management and financial forecasting
using: financial models, investment portfolios, capital budgeting and valuation reports
→ strategic financial plannign and investing (resource allocation) to maximize wealth and minimize risk
finance vs accounting
finance is future, accounting is past
finance is growing wealth, accounting is tracking and reporting financial activities
finance is strategy, accounting is recording and reporting
what is sales?
- responsible for selling the relevant products and services to consumers, first link between the business itself and consumers
- staff must have deep knowledge of the product and strong communication skills to convince consumers
- sales staff identifies and cultivates new customers
- sales staff recommends best suited products to the customer by assessing their needs
- they sell a product successfully by approaching, presenting key features, resolving customer queries, and closing the sell
- the sales staff maintains cordial relationship with the customers
- the sales department has a crucial role: it's the generator of income for the business
→ by making sales and retaining customers, the sales department helps the business grow
- responsibilities: lead generation, account (big customers) management, pitching, referrals, affiliated selling
→ link between customer and business, advising and marketing to customers, generators of income
what are the differences between customers, consumers and clients?
consumers are end users but might not have bought it (e.g. gifts or kids)
customers are the ones who purchase but might not be end users
customers become consumers if the make the purchase and use the product or service
clients are customers who purchase professional services
the term client is used for B2B and luxury (big accounts, high end)
customers buy products, clients buy advice and solutions
what is human resources?
- recruiting skilled, and experienced manpower according to vacant positions of different departments
- conducting orientation programs and trainings for new staff, recognizing the best facets of staff and motivating them to achieve organization objectives
- responsibilities: recruitment, training, pay compensation, employee benefits and relations, legal compliance
→ recruit new employees & manage current employees through paying, training and handling issues, & also responsible for legal compliance
what is the legal department?
- responsible for all legal and legal related external matters such as litigation, investigations, compliance, mergers and acquisitions
- this is a diverse, complex, and often unpredictable portfolio of challenges
- responsibilities: transaction, support, contracting, compliance, legislative & regulatory knowledge, litigation, risk assessment, intellectual property
→ business operations like mergers, acquisitions and risk assessment / “problem solving” like litigation / legal compliance / intellectual property care
what is procurement/purchase?
- purchasing department procures the goods and services to be consumed by other departments in the business organization
- by following a standard procedure of procurement, this department ensures the enterprise has appropriate and timely supply of all the required goods and services
- responsibilities: supplier selection, order, placement, supplier audit (checking a company and if they respect terms of contract)
→ mediatory between suppliers and company, make sure company has all materials/products/services it needs, also checks suppliers (audits)
what is the facility department?
- facilities managers are usually in charge of organising the security, maintenance, and repairs of your building
- protects employees and their property, prevents unauthorised access, and ensures your building meets legal requirements
- facility management is responsible for the efficient and effective delivery of logistics and other support services related to real property
- responsibilities: environment (functionality, comfort and safety), process & technology
→ security of facilities and employees, maintenance and repairs of building, logistics deliveries to facilities
what is research and development?
R&D: the generation of new knowledge
- develops new products, processes or services, or improves those that already exist
- checks technological feasibility
- dives into experimentation and innovation
- the R&D cycle: ideation, theorising, research, exploration, design, prototype, development
→ tests and develops new products, services or processes for a company
what is customer service?
their representatives are the ones who provide support and assistance and make sure your customers receive the quality service they deserve from a brand
- customers brought in due to marketing and sales are valuable assets and need to be taken care of
- responsibilities:
answer questions about a company's products or services
process orders and transactions
resolve issues and troubleshooting technical problems
provide proactive customer outreach
handle customer complaints
collect and analyze customer feedback
respond to customer reviews
track customer service KPIs and metrics
→ customers are expensive, marketing budget has been paid to aquire them so retention is important
→ customer service answers questions, resolves issues, collects and analyses feedback as well as tracking KPIs and metrics
what is IT?
- information technology
- department that keeps network stable, programs running, and systems strong
- without an information technology department, you would likely experience data breaches and an overall decrease in productivity
- responsibilities: employee IT training, maintenance and updates (IS), IT security, policy, crisis management
→ safety and efficiency of technological systems, training employees in IT, complying with policies, crisis management (e.g. data leaks)
→ maintenance and updates is more IS (information systems)
how do you build a good team?
know yourself and your team members through personality tests like MBTI or the VALS framework
you need a mixture of personalities, interests and skills
diversity is important
what is an organizational structure?
organigrams
a system that outlines how certain activities are directed to achieve goals of an organization
they define who does activites like task allocation, coordination and supervision
they depend on a company’s size, industry and goals
most often used organizational chart formats are hierarchical and flat
there is no one best organizational structure, they depend on the company and it’s industry
what are the benefits of organizational structures?
they add organization to a company as they determine:
how information flows between levels
the company’s hierarchy
the pay structure (salary grades and ranges)
having the right strcuture helps teams stay organized and collaborate productively, improves communication and leads to more efficient and effective operations
what are the 9 structures?
hierarchical
flat/horizontal
functional
divisional
matrix
team or project based
network
circular
line-and-staff
what is an organizational chart?
they are charts that show how a company is organized/it’s structure
they include the role and name of an employee as well as their position in the structure
what is a centralized organizational structure?
clear responsibilities for each role, subordinate roles are under guidance of their superiors
decisions flow in a top-down direction
employees have to work hard to buy favor or court those with decision making power to go after their goals
micro management can easily occur
processes are defined easily and often thoroughly followed
what is a decentralized organizational structure?
adopted by many startups
allows companies to be fast, agile and adaptable
employees have high level of personal agency
usually still include built-in hierarchies like chief operating officer having a higher level than entry level associates
teams are empowered to make their own decisions without needing approval from top executives
→ decision making power is distributed among various levels
employees have to take on initiative and bring creative problem solving skills
what is the hierarchical structure?
- a traditional structure in which employees are grouped and report upwards to a single chain of command
- usually in a pyramid shape
- this structure is based on several levels of management, with a clear distinction between top, middle, and lower management
- key aspects: clear chain of command, top-down decision-making, defined roles and responsibilities
→ clear positions, top makes decisions, you have clear bosses and people underneath you
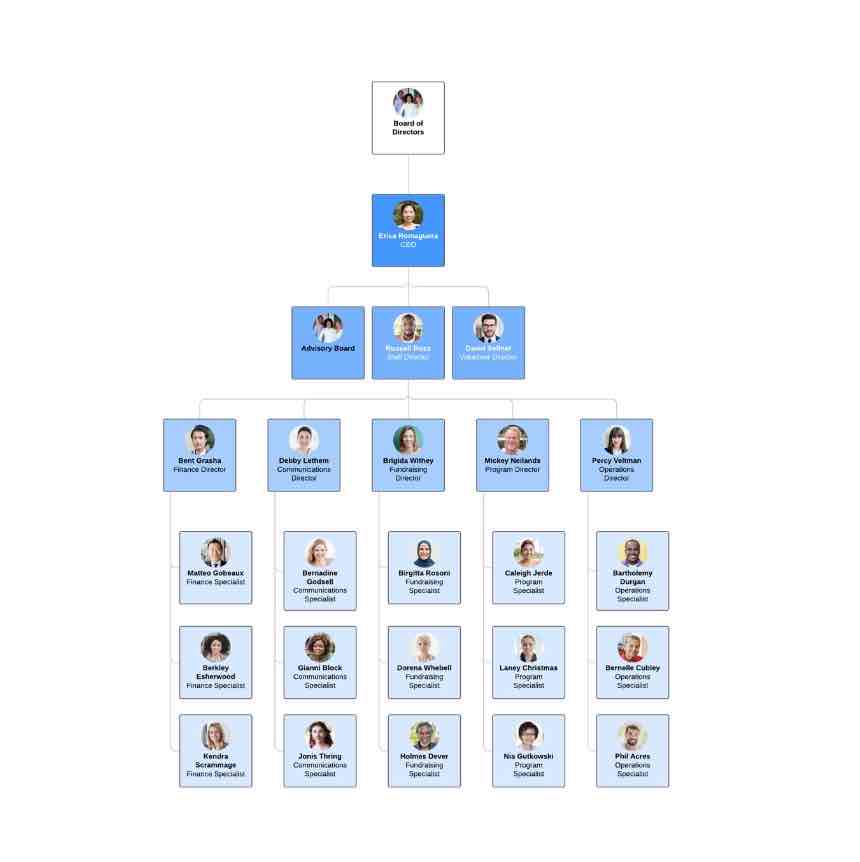
what is the horizontal/flat structure?
a structure with few or no levels of middle management between staff and executives
employees often have more autonomy, and decision-making is decentralized
key aspects: fewer management layers, more employee involvement in decision-making, encourages flexibility and communication
→ employees are more involved in decisions, flexibility and communication between all, less layers
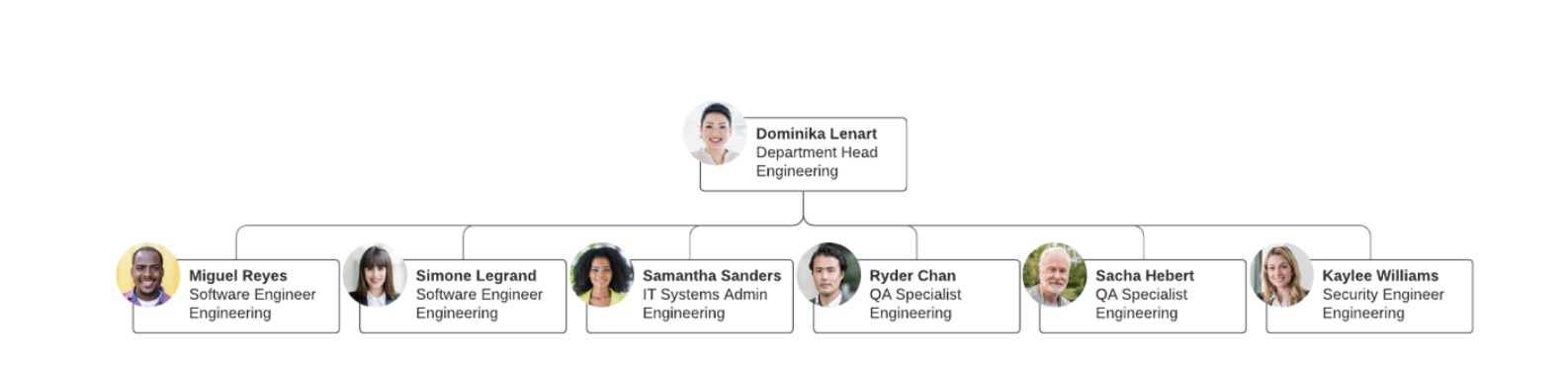
what is the functional structure?
- organizes employees based on specific functions or departments within the organization, such as marketing, finance, human resources, etc
- each function operates independently, and employees specialize in their role
- key aspects: departmentalization by function, operational efficiency, specialization
- hard for external stakeholders to know who to talk to
→ divides based on functions that then all operate individually, employees specialise in their role, all about efficiency
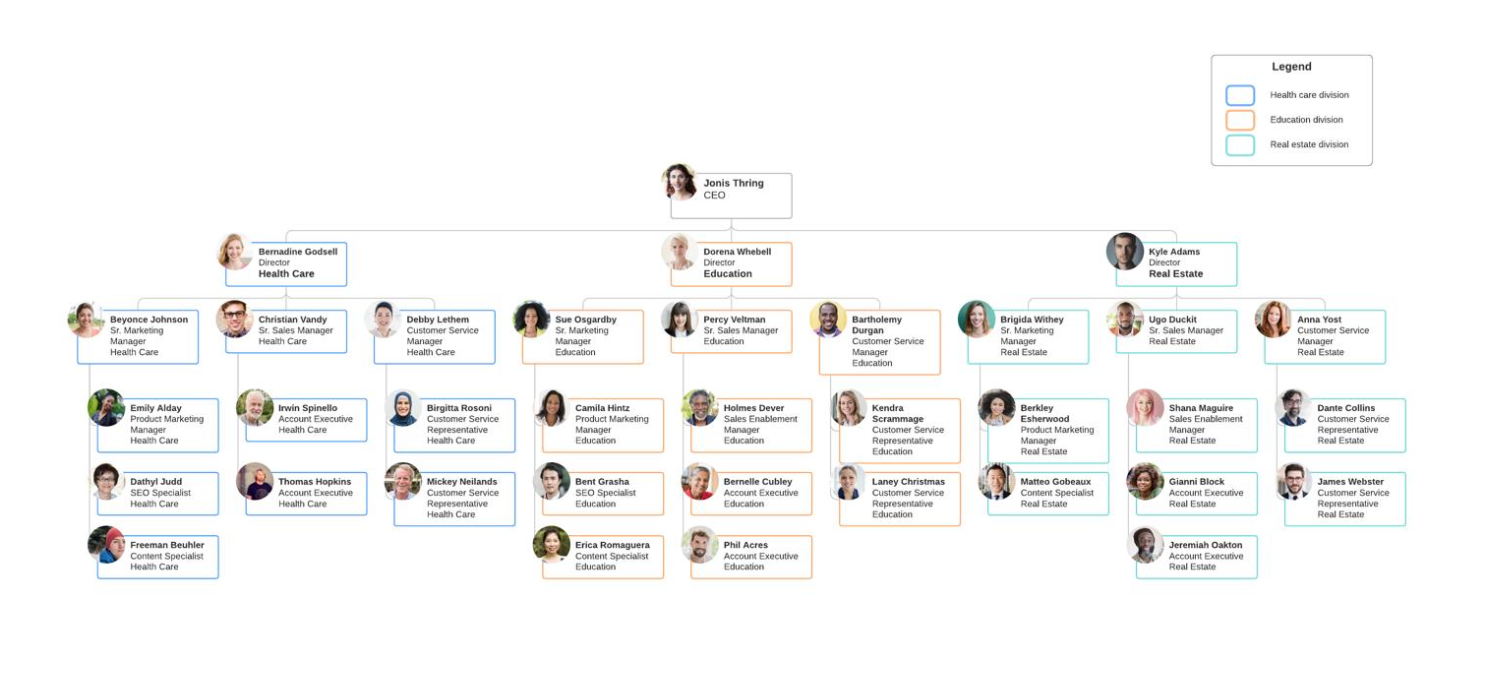
what is divisional structure?
subdivides the company based on some specific criteria:
employees are grouped together by product lines, geographic region, market, or some other natural division
each division operates semi-autonomously, with its own functional teams like marketing, finance, and operations
key aspects: divisions operate independently, organized by product line or geography, flexibility to manage different products or markets
usually good for big companies, can create competition between divisions
market-based (luxury, mass market)
product-based (car, fuel, etc)
process-based (esp engineering companies/dividing processes like R&D and customer acquisition)
geographic (by region)
→ divides based on either market, product line, process or geography
→ for bigger companies, divisions operate independently, can create competition between them
what is market based division?
dividing based on markets like luxury and mass market or if a company is in multiple markets like real estate, healthcare and education
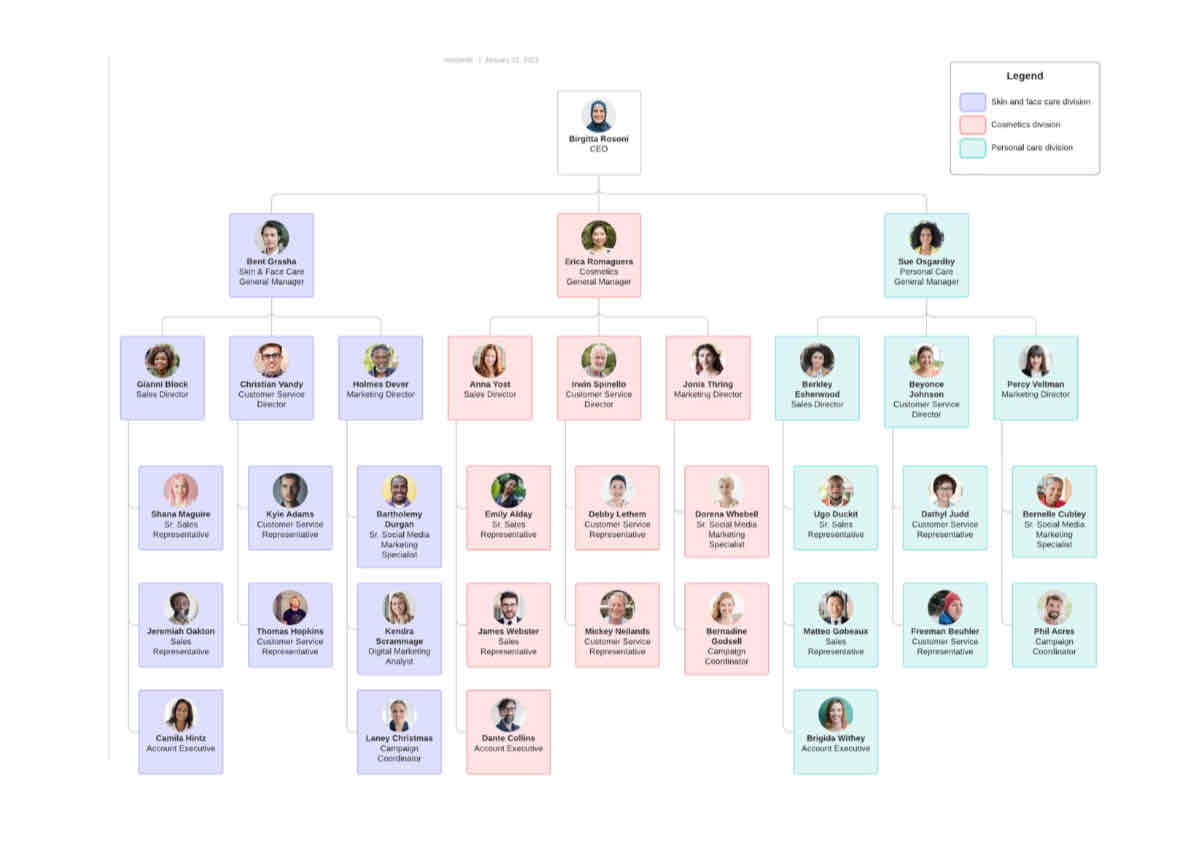
what is product based division
division based on different product lines or categories
eg a personal care brand does:
skincare, cosmetics and personal care
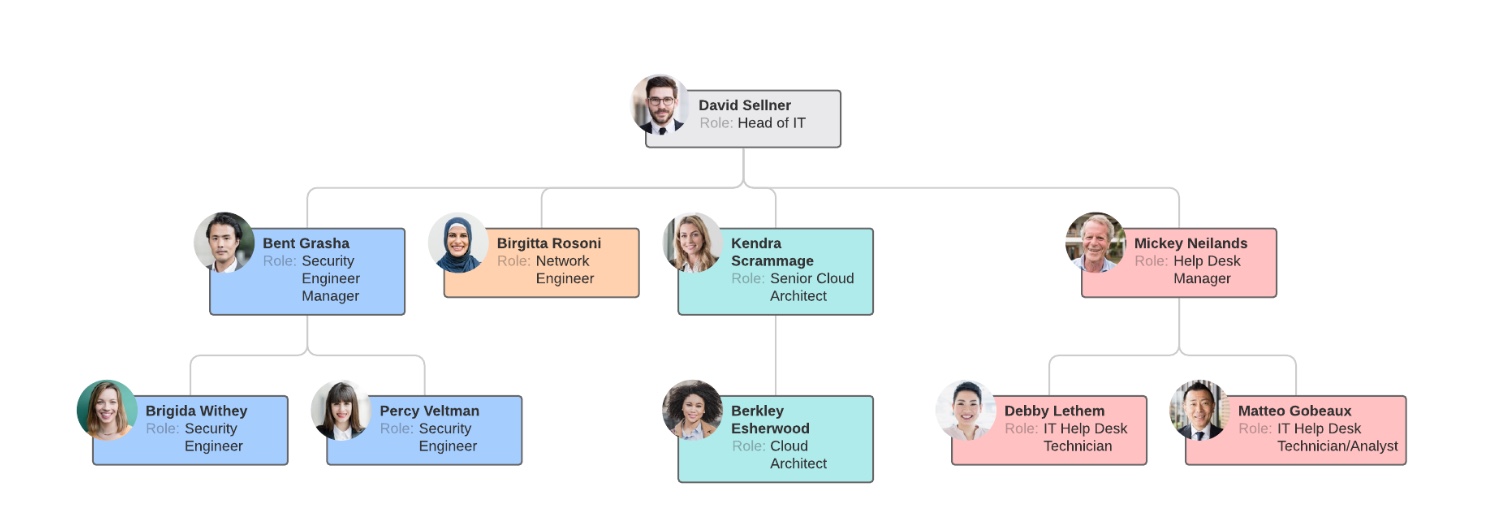
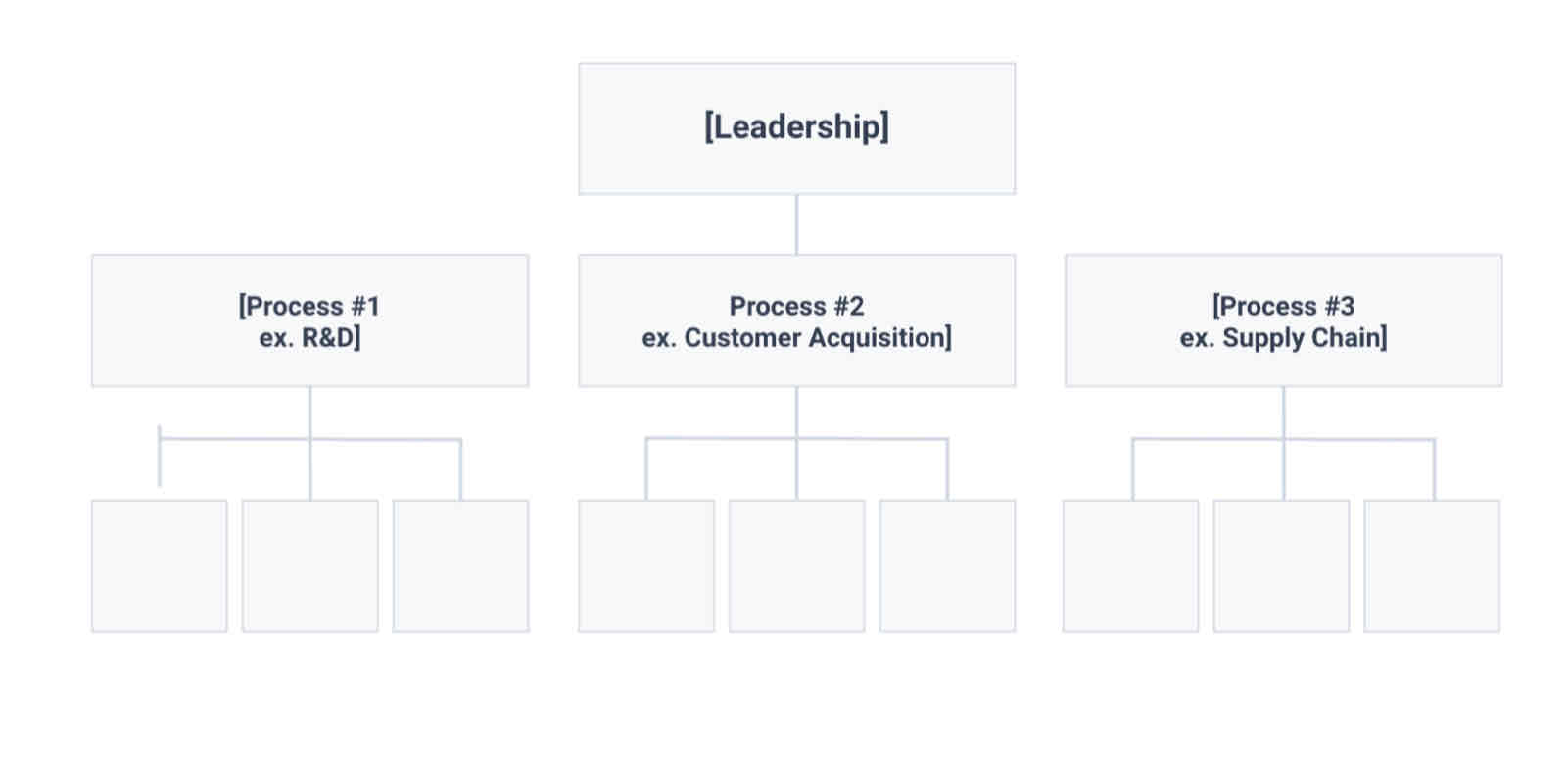
what is process based
division based on different processes the company is involved in
especially used in engineering
eg R&D, Supply Chain and Customer Acquisition
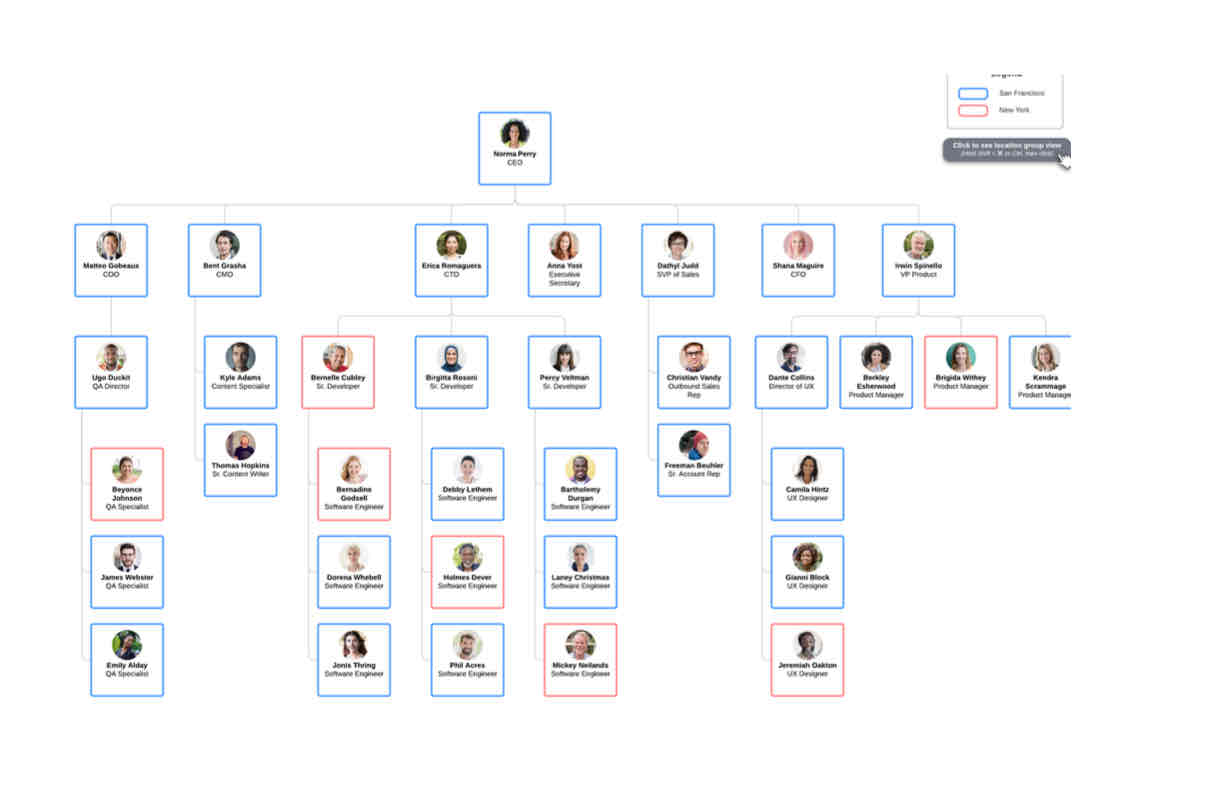
what is geographic based division
dividing teams based on their location
eg in a developing team there’s a senior developer for san francisco and one for new york
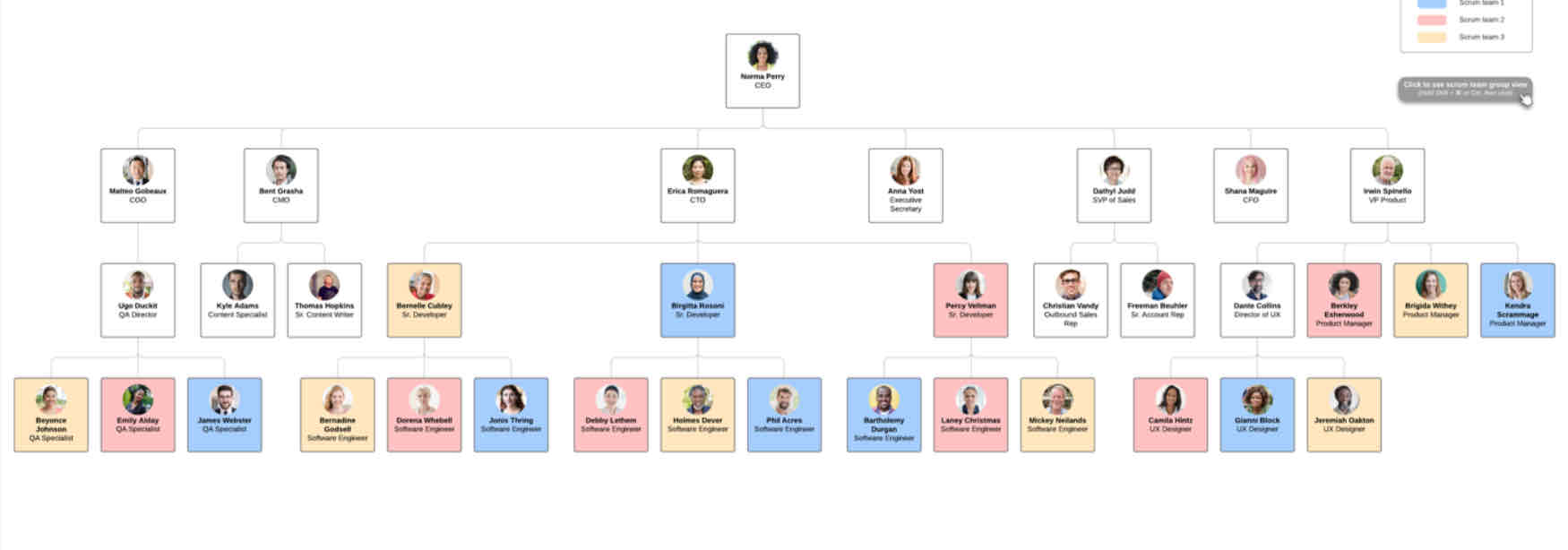
what is team based division
structure that organizes the company into teams that work on specific projects or tasks
teams are given the authority to make decisions and manage their own work, often with a focus on collaboration and innovation.
key aspects: Collaborative decision-making, emphasis on teamwork, less hierarchical.
dividing employees into teams for specific tasks or projects, collaboration, teams make decisions together
ex: there will be three senior developers managing their teams and all reporting to CTO
what is a project based structure?
organises a company around projects not functions or products
after projects are completed, teams are dissolved and members reassigned
key aspects: flexible teams formed around projects, adaptable, project managers have central role
eg: engineering or construction firms with larger projects
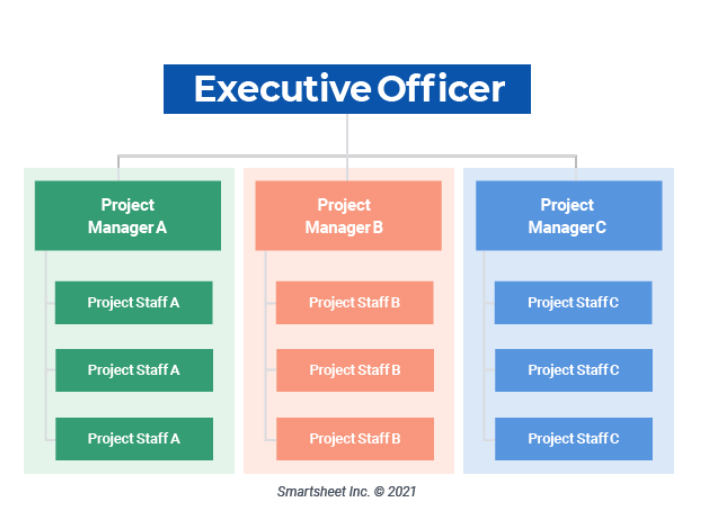
what is the matrix structure?
a hybrid structure of functional and divisional
employees report to more than one manager (usually functional manager and also product/project manager) → multiple lines of authority
ex: software developer reports to CTO but also search function project manager
key aspects: dual reporting, cross functional teams, better coordination across projects
→ mix of functional and divisional, there are managers for projects and managers for functions
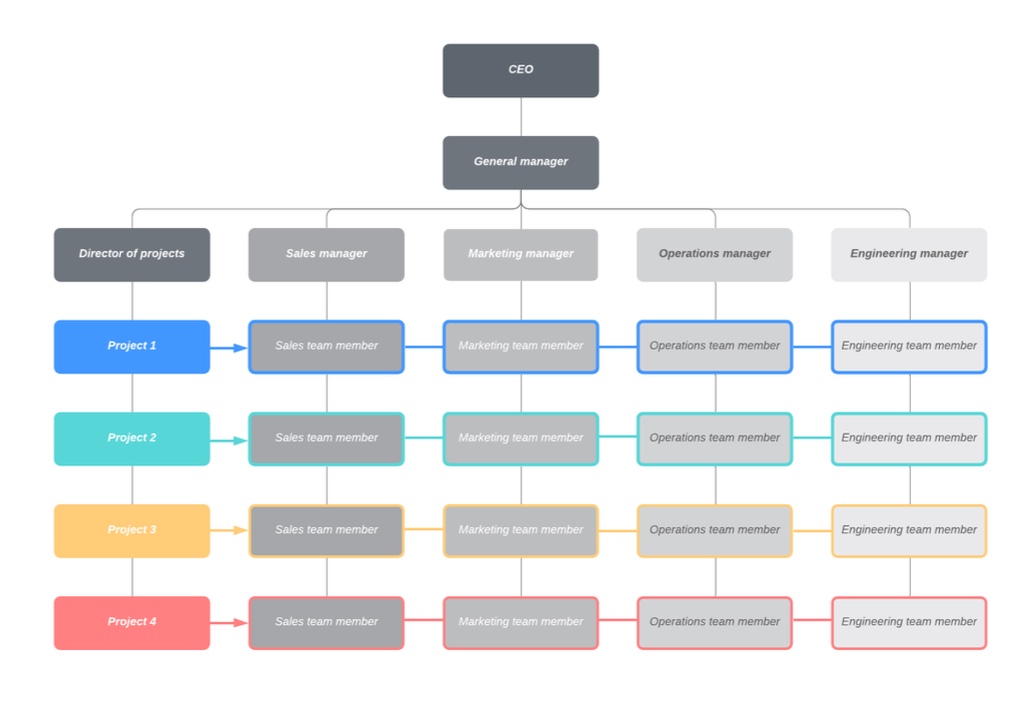
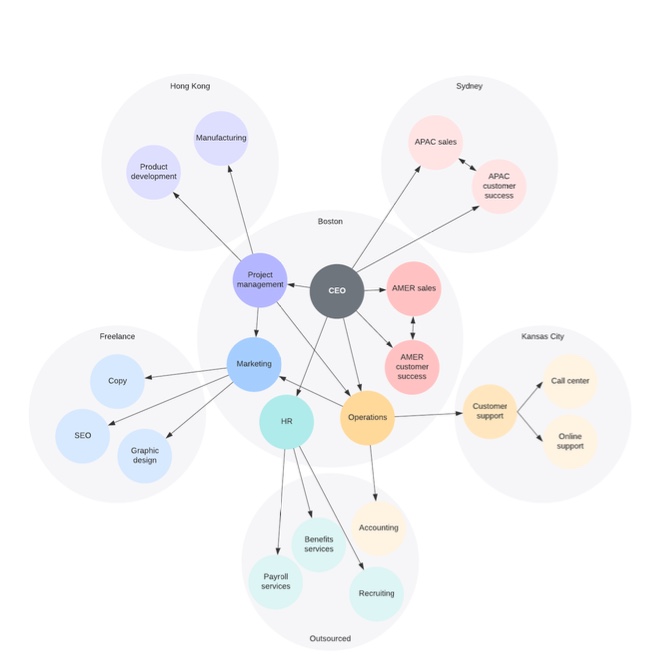
what is the network structure?
flexible, fluid structure
relies on network of relationships inside and outside organization
useful if company outsources some functions or collaborates with external organisations but wants to maintain core internal teams
key aspects: outsourcing and partnerships, flexible and decentralised, adapts easily to changes
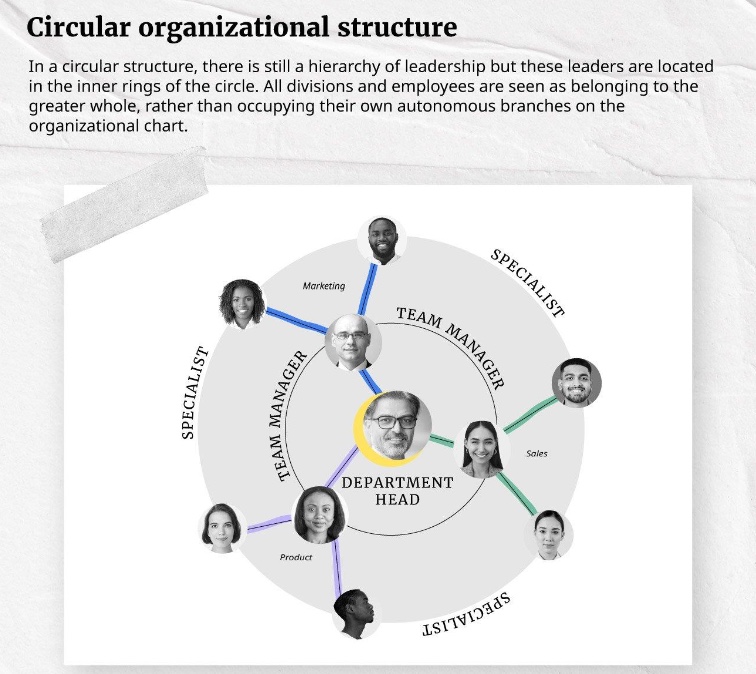
what is the circular structure?
leadership at centre rather than top
communication from central management flows outward in a circular manner
key aspects: central leadership with decentralised decision making, focus on communication and collaboration
example: companies that emphasise leadership through influence rather than command
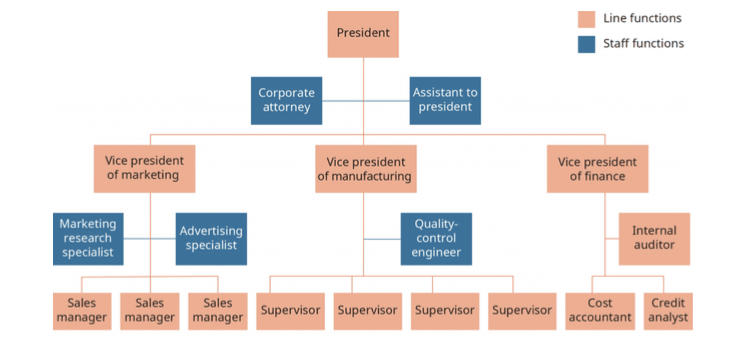
what is the line and staff structure?
clear change of command
but with additional staff functions that support line positions
line positions directly contribute to company goals (production etc)
staff positions give specialised advice and support (HR, IT etc)
key aspects: clear hierarchy with specialized support roles, balance between operational and advisory functions
ex: manufacturing firm that have very distinct operational and support departments
what are important aspects of organisational structures?
they outline how certain activities are directed to achieve the goals of a company
if done successfully, they define each employee’s job and their position in the bigger system
centralised structure: defined chain of command
decentralised structure: almost every employee has high level of personal agency
senior leaders need to consider a variety of factors before deciding organisational type
eg. business goals, industry and company culture