BDSC Science year 9 Final Exam
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is the process of respiration in living organisms?
Respiration is the process of converting glucose into energy, which comes in two states: aerobic and anaerobic.
Write the equation for respiration
Glucose + oxygen → energy + carbon dioxide + water.

Why does heart rate increase during exercise?
During exercise, the body needs more energy, so the heart must pump faster to transport glucose, oxygen, CO2, and water more frequently to and from the cells.

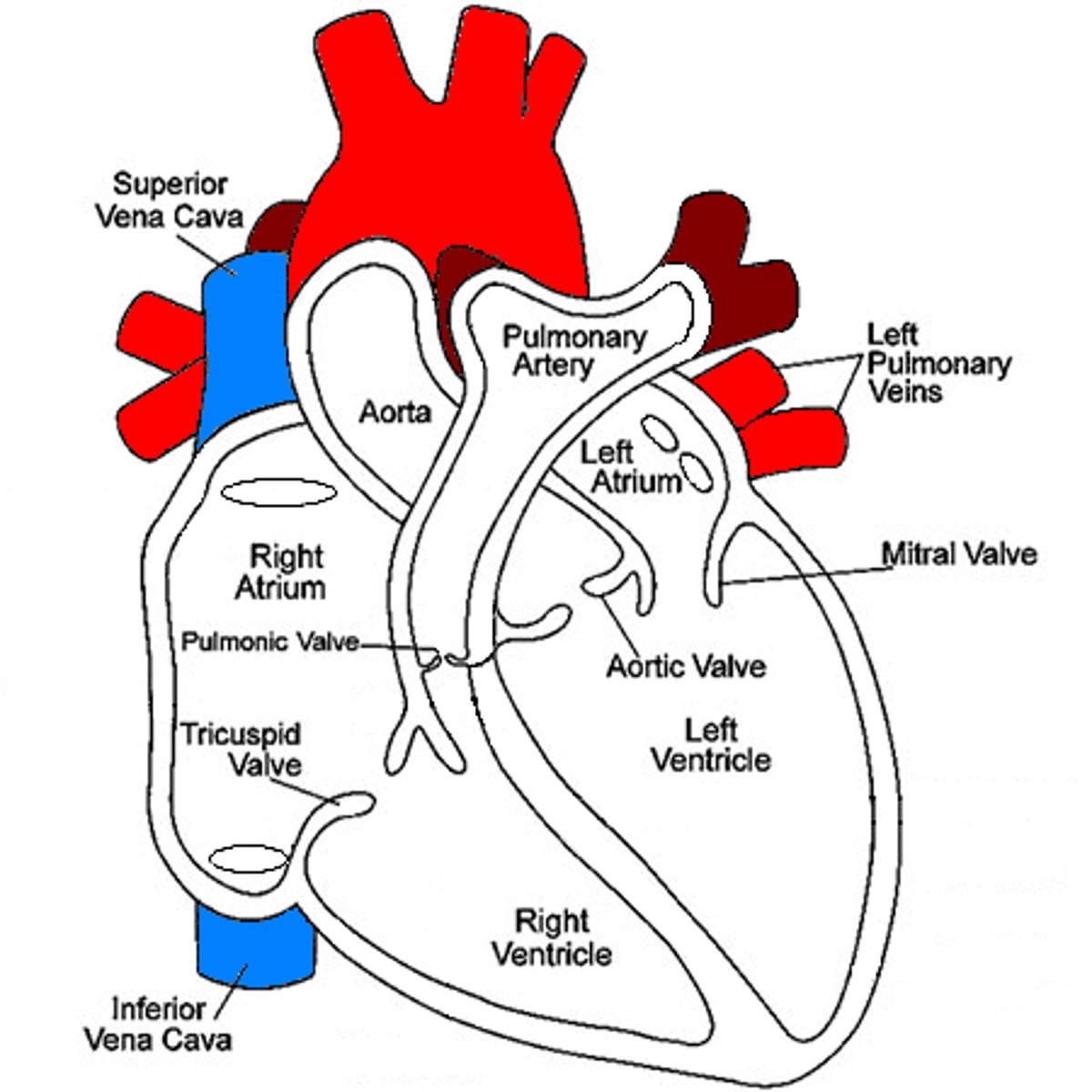
What is the function of the vena cava
The vena cava is a large vein that carries blood to the heart from other areas of the body.
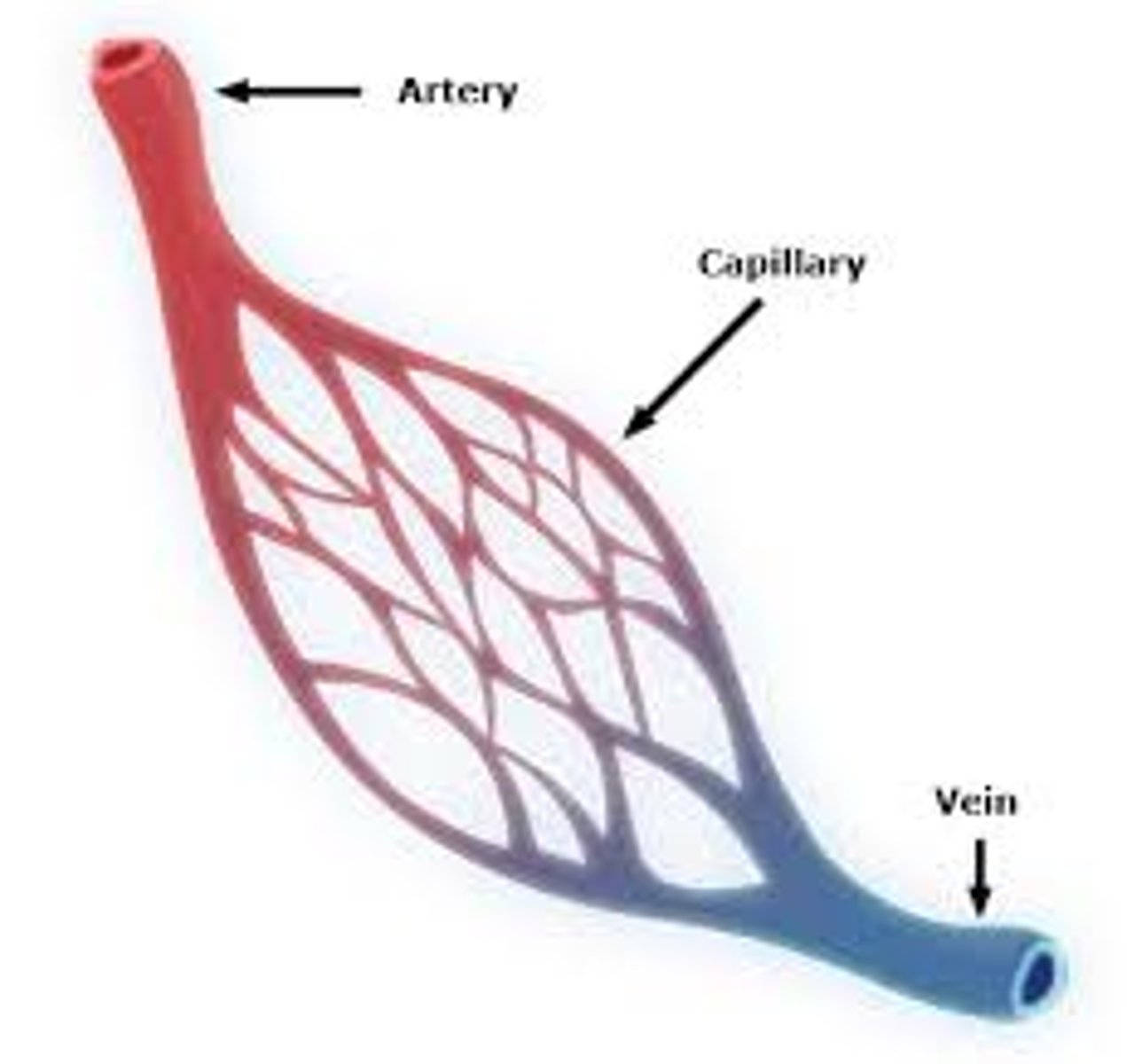
What do arteries and veins do?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood to the heart.
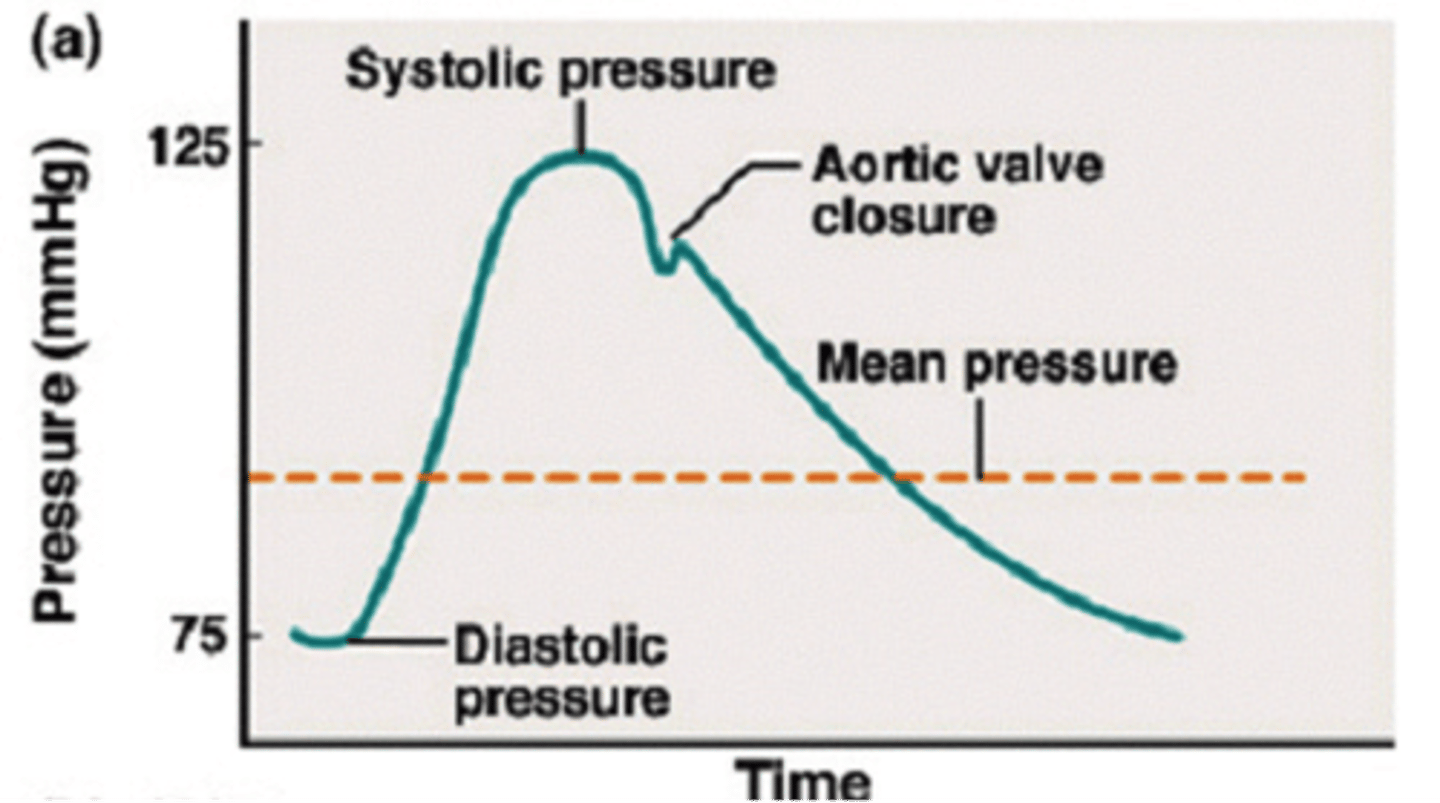
Define systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Systolic blood pressure is when the heart contracts and creates larger pressure on artery walls (normal range 90-120). Diastolic blood pressure is when the heart relaxes and there is less pressure on the artery walls (normal range 60-80).
Describe the role of the alveoli in the lungs.
The alveoli are thin saclike structures where gas exchange happens; CO2 is removed from the blood into the alveoli and O2 moves into the blood.
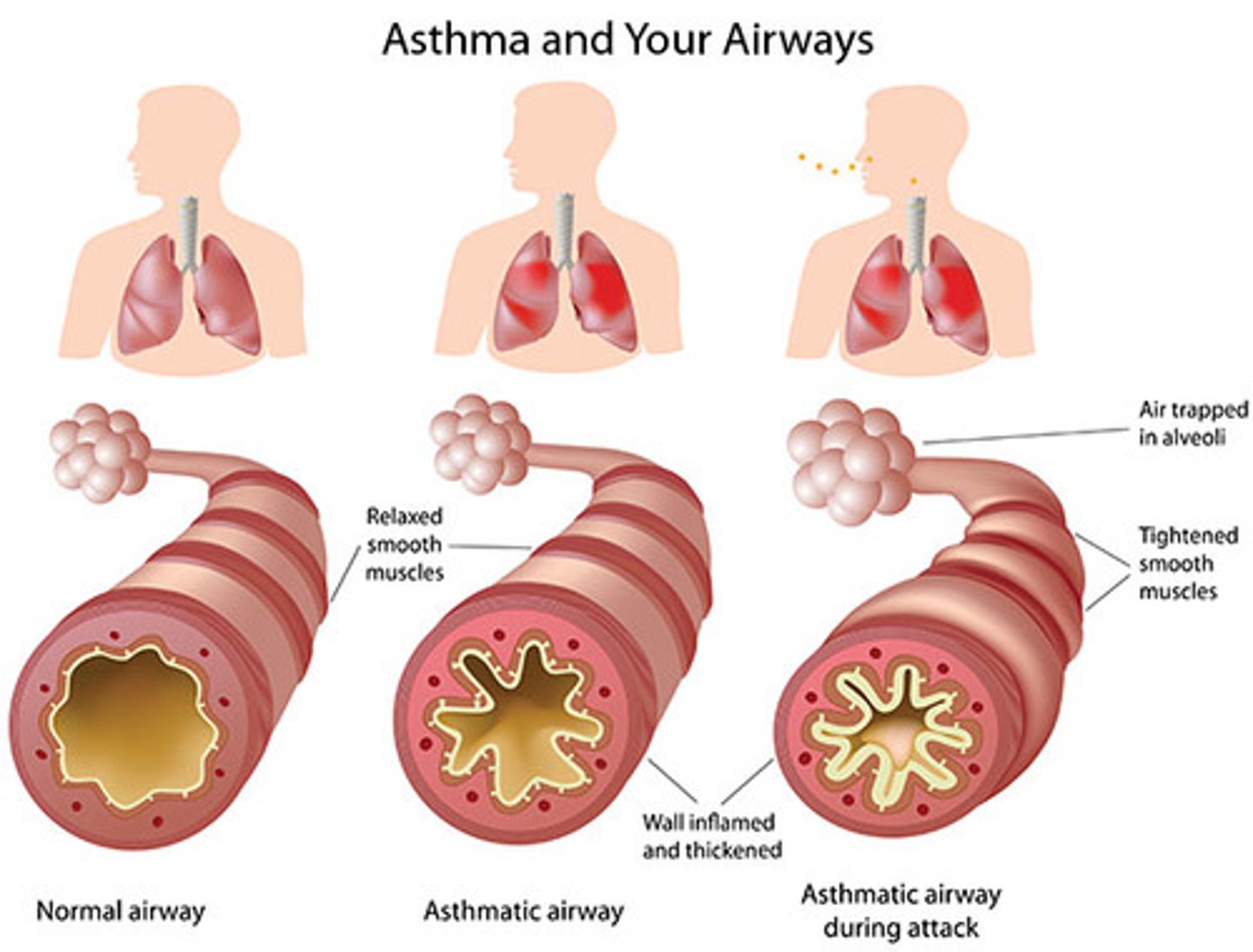
What happens during an asthma attack?
During an asthma attack, the muscle wall contracts, and the lining of the airways becomes swollen and inflamed, causing narrowing of the airways and increased mucous secretions.
What are the main functions of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas in digestion?
The liver creates bile, the gallbladder stores bile and releases it, and the pancreas creates enzymes and insulin.
List the food groups and their main functions.
Carbohydrates: Release energy
Proteins: Help you grow and cell repair
Fats: Provide energy, help absorb vitamins, and maintain warmth
Minerals: Build bones, influence muscle and nerve function, regulate water balance
Vitamins: Help the body concentrate and function
Water: Maintain hydration
Fibre: Regulate blood sugar levels and bowel function
What is a pathogen and give three examples
A pathogen is an organism or biological agent that can cause a disease. Examples include Virus Bacteria Fungi
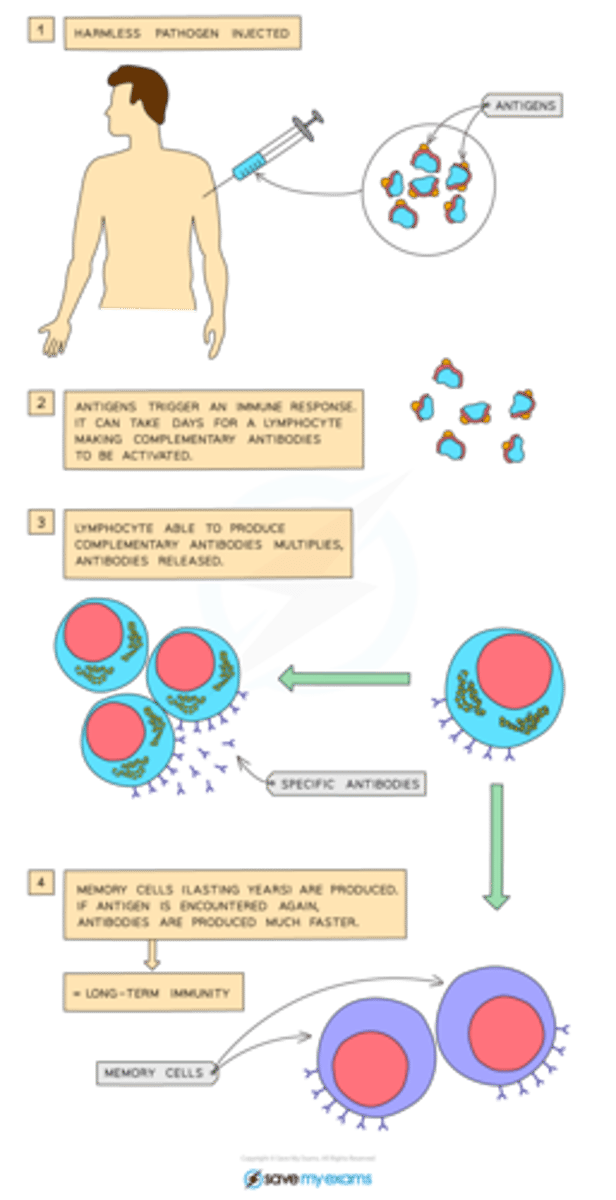
Describe the process of immunisation
Immunization involves introducing a weakened version of a pathogen to the body through vaccination. The body prepares antibodies to counter the pathogen, and leftover antibodies will destroy any future pathogens.
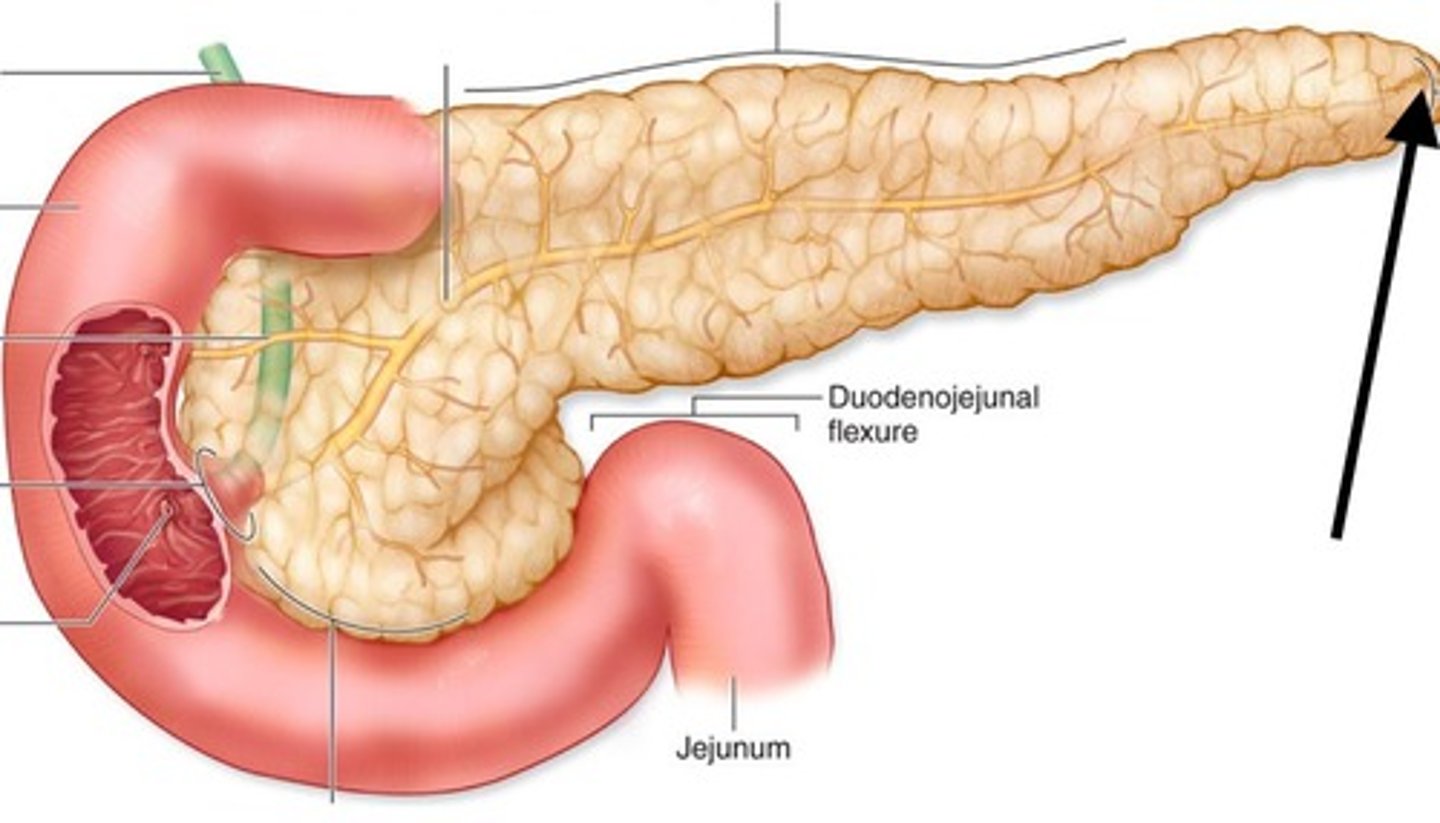
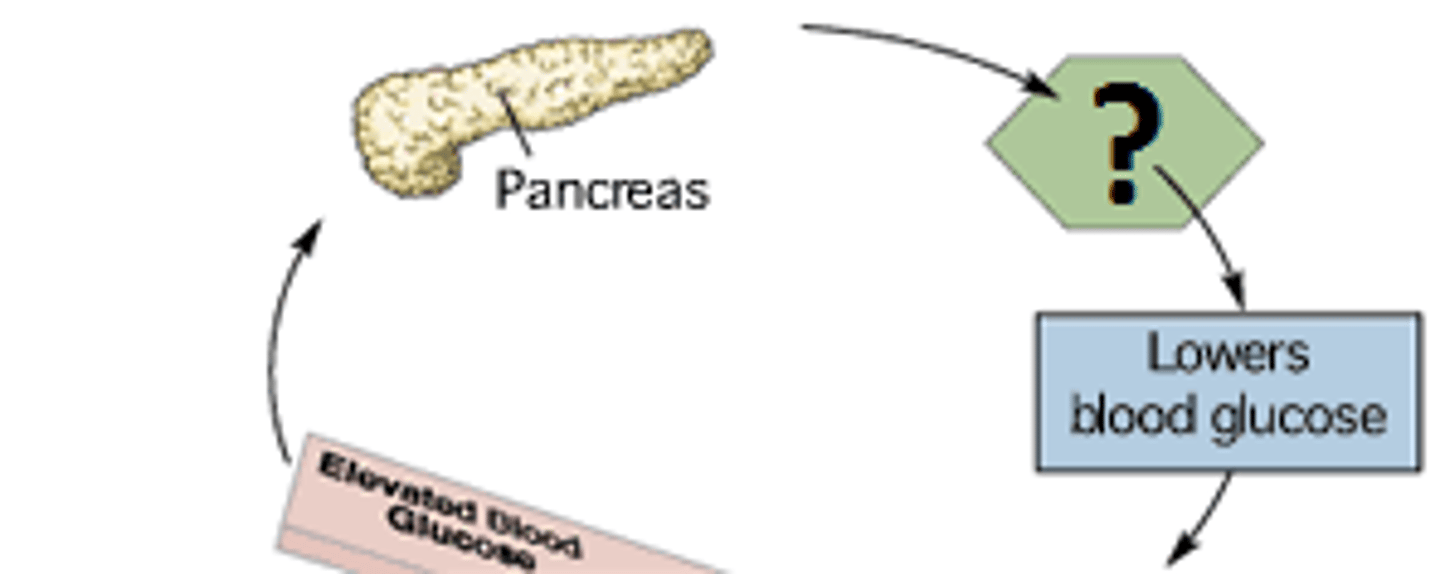
What is the role of the pancreas?
The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions, producing digestive enzymes and hormones to regulate blood sugar levels.
What digestive enzymes does the pancreas produce?
Amylase, lipase, and proteases (such as trypsin and chymotrypsin).
What hormones does the pancreas produce?
Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
What is immunization?
Immunization is the process by which an individual is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine.
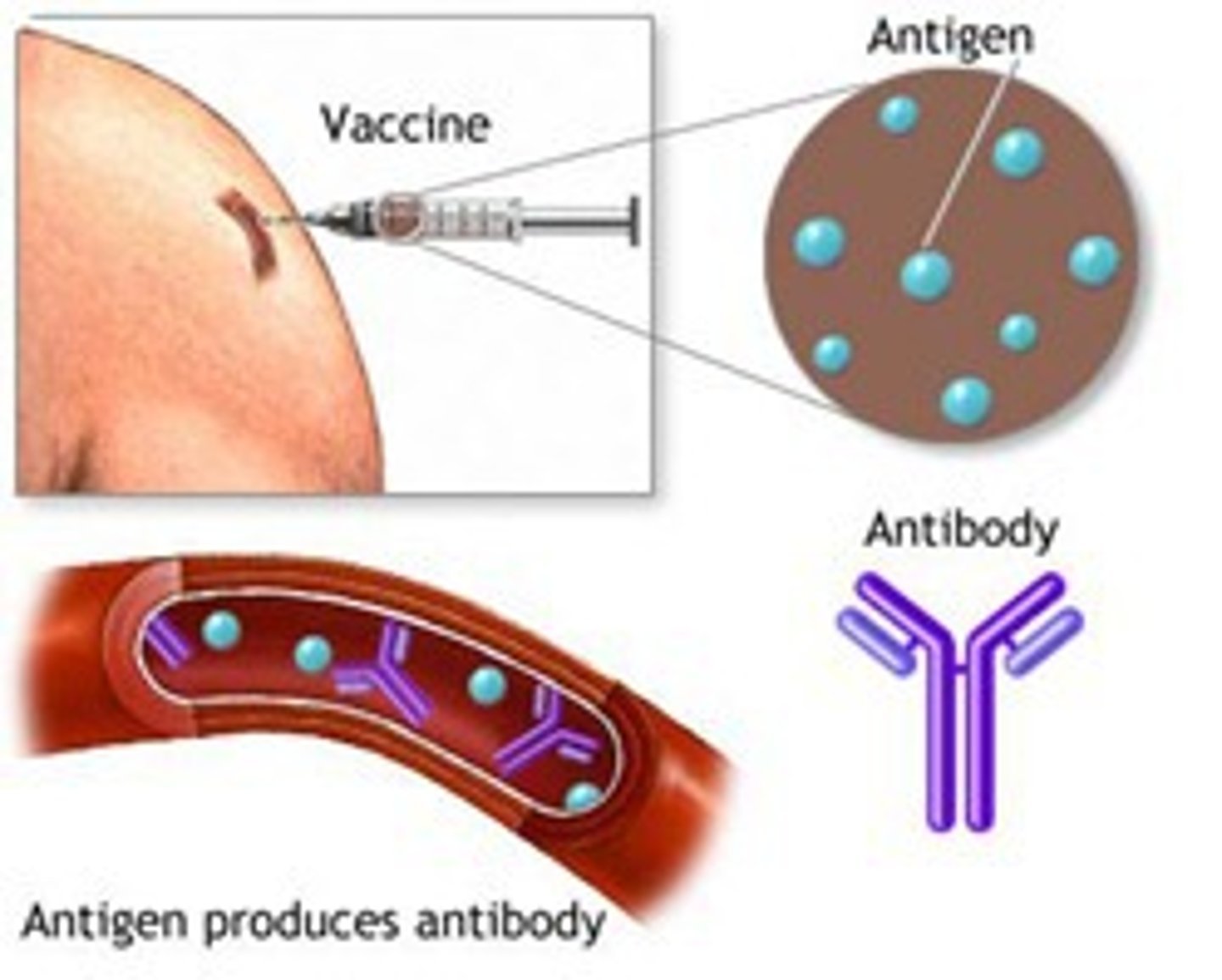
How is immunization helpful in general health
Immunization prevents diseases, reduces disease spread, protects vulnerable groups, lowers healthcare costs, and improves quality of life.
What is the green substance stored in the gallbladder?
Bile.
Why is BMI not a good indicator of health?
BMI does not account for muscle mass, fat distribution, age, sex, or overall health factors.
What does the large intestine digest?
The large intestine does not digest food; instead, it absorbs water and stores food for a short period before it leaves the body.
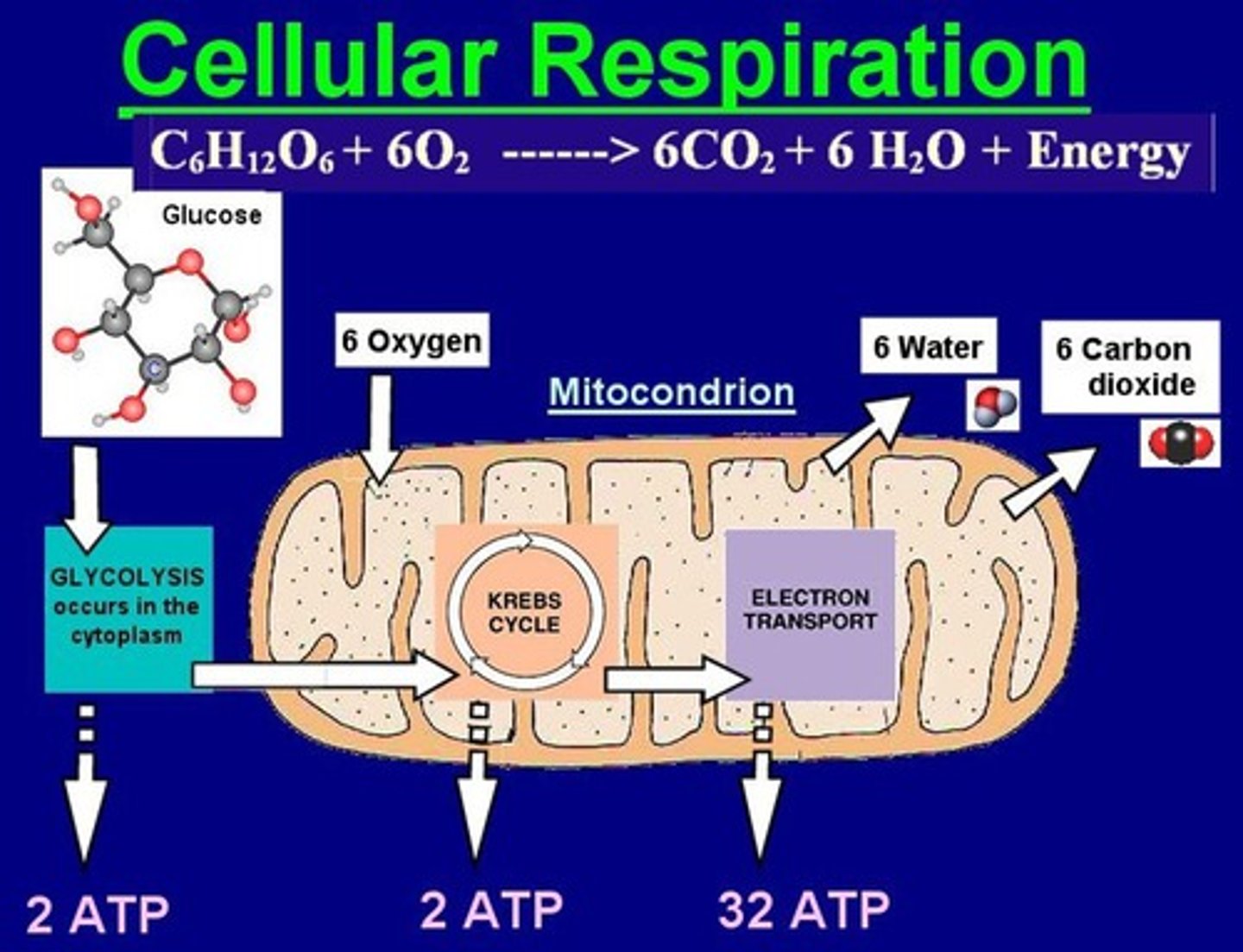
What is the order of respiration?
Respiration involves glucose and oxygen being converted into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. The process generally follows these steps:
1. Oxygen is transported to cells.
2.Glucose is converted into energy within cells.
3.Carbon dioxide and water are produced as by-products and transported out of cells.
Path of de-oxygenated blood
Lungs -- Left Atrium -- Left Ventricle -- Cells
Select the best definition for a healthy diet.
A healthy diet is one that contains a balanced amount of food from each food group, providing necessary nutrients for healthy growth and activity.
Describe two common causes of high blood pressure and explain how to reduce blood pressure.
Cause 1: Unhealthy Diet - Consuming too much salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol can lead to high blood pressure.
Cause 2: Lack of Physical Activity - Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and increased blood pressure.
HOW TO FIX: Engage in regular physical exercise (30 minutes most days) and adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while reducing salt, saturated fats, and cholesterol to maintain a healthy weight and lower blood pressure.
What is Matter
Something that takes up mass and volume, making up everything.
Define a Solid
State of matter with tightly packed particles, fixed shape and volume. Particles can vibrate in place. Examples: Ice, Metal, Wood.
Define Liquid
State of matter with loosely arranged particles, fixed volume but variable shape. Particles can move from one place to another. Examples: Water, Gasoline, Mercury.
Define Gas
State of matter with widely spaced particles, no fixed shape or volume. Particles move freely in random directions. Examples: Air, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide.
Define Mass
Measure of the amount of volume in an object. The greater the mass, the more matter it contains and the heavier it is.
What is Volume
Amount of space an object occupies.
What is Density
Measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume. Solids are the most dense, followed by liquids, then gases.
Melting
Process of a solid becoming a liquid.
Freezing
Process of a liquid changing to a solid.
Boiling
Rapid change of a liquid to a gas by adding lots of heat.
Evaporation
Slow change of a liquid to a gas at lower temperatures.
Sublimation
Change of a solid directly to a gas. Examples: Iodine, Dry Ice (frozen CO2).
Conduction
Heat transfer through direct contact between objects, flowing from hotter to cooler objects.
Convection
Heat transfer through the movement of a fluid, such as air or water, where warmer fluids rise and cooler fluids sink.
Radiation
Heat transfer through the emission and absorption of electromagnetic waves without the need for a physical medium.
Heat
Transfer of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one, driven by temperature difference.
Temperature
Measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance, indicating the hotness of the substance.
Thermal Energy
Form of energy due to an object's temperature.
Insulation
Using materials to prevent heat transfer between objects by conduction, convection, or radiation.
Dry Ice
Solid carbon dioxide at -79 degrees Celsius, changing from solid to gas by absorbing thermal energy.
Convection Current
Constant cycle of warmer fluid rising and cooler fluid sinking, occurring in liquids and gases.
Heat Transfer Sources
Natural sources like volcano/sun, man-made sources like lighter/heater, and nuclear energy.
Thermal Conductors
Objects with the ability to transfer heat energy efficiently, such as metals like steel or copper.
Thermal Insulators
Objects that resist heat conduction, such as polystyrene and plastics.
Substance Heating
Adding energy to a substance, causing particles to move more and change states.
Independent Variable
An independent variable is exactly what it sounds like. It is a variable that stands alone and isn't changed by the other variables you are trying to measure. For example, someone's age might be an independent variable.
Substance Cooling
Removing energy from a substance, causing particles to slow down and change states.
What minimizes heat loss?
silvered surfaces
Changing States of Matter
Matter can change from one state to another by gaining or losing heat energy, with specific temperature points for state changes.
Light
A form of energy visible to the human eye.
White Light
Light composed of a spectrum of colors.
Reflection
Bouncing of light off a surface.
Incident Ray
Ray of light hitting a surface.
Reflected Ray
Ray of light bouncing off a surface.
Angle of Incidence
Angle between incident ray and normal line.
Angle of Reflection
Angle between reflected ray and normal line.
Normal Line
Line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
Concave Mirror
Mirror with shiny surface on the inside curve.
Convex Mirror
Mirror with shiny surface on the outside curve.
Laws of Reflection
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
Refraction
Bending of light as it passes through different media.
Primary Colors of Light
Red, Green, Blue; cannot be made by mixing.
Secondary Colors of Light
Colors made by mixing primary colors.
Diverging Lens
Lens that spreads light rays apart.
Converging Lens
Lens that focuses light rays to a point.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Energy stored due to an object's position in a gravitational field.
Measurement Units
Standard units used for quantifying physical quantities.
Zero Error
Difference between measured value and true value.
Speed of Light
Approximately 3.0 x 10^8 m/s in vacuum.
Spectrum of Colors
Range of colors produced by light dispersion.
Microscopes / Magnifying Glass
Instruments that magnify small objects using lenses.
Color Absorption
Objects absorb all colors except their own.
Light Source
Object that emits or produces light.
Curved Mirrors
Mirrors that are either concave or convex.
Plane Mirror
Flat mirror that reflects light without distortion.
SI Prefixes
Standardized prefixes for metric units.
Formula for Gravitational Potential Energy
Ep = m g h.
Acceleration Due to Gravity
Constant at approximately 10 m/s².
Kinetic Energy
Energy associated with motion of objects.
Kinetic Energy Formula
Ek = 0.5 m v².
Air Resistance
Opposing force when moving through air.
Speed
Change in distance over change in time.
Speed Measurement
Measured in meters per second (m/s).
Prism Spectrum
Different colors bend differently through a prism.
Cornea
Transparent front part of the eye.
Pupil
Dark hole allowing light into the eye.
Iris
Colored part controlling light entry into pupil.
Lens
Bi-convex disc focusing light onto retina.
Retina
Layer of light-sensitive cells at the eye's back.
Optic Nerve
Carries visual information to the brain.
Translucent
Allows light to pass but not clear images.
Opaque
Does not allow light to pass through.
Refracted Ray
Light ray that has changed direction in a medium.
Energy Transfer
Movement of energy through different forms.
Dependent Variable
the variable that changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation. It's the outcome you're interested in measuring, and it "depends" on your independent variable. In statistics, dependent variables are also called: Response variables
Controlled Variable
A controlled variable is a component kept constant in a scientific experiment to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. It is a key factor in the scientific method, as it allows researchers to isolate the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.