Psychology: Memory - The multi-store model
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) MSM layout
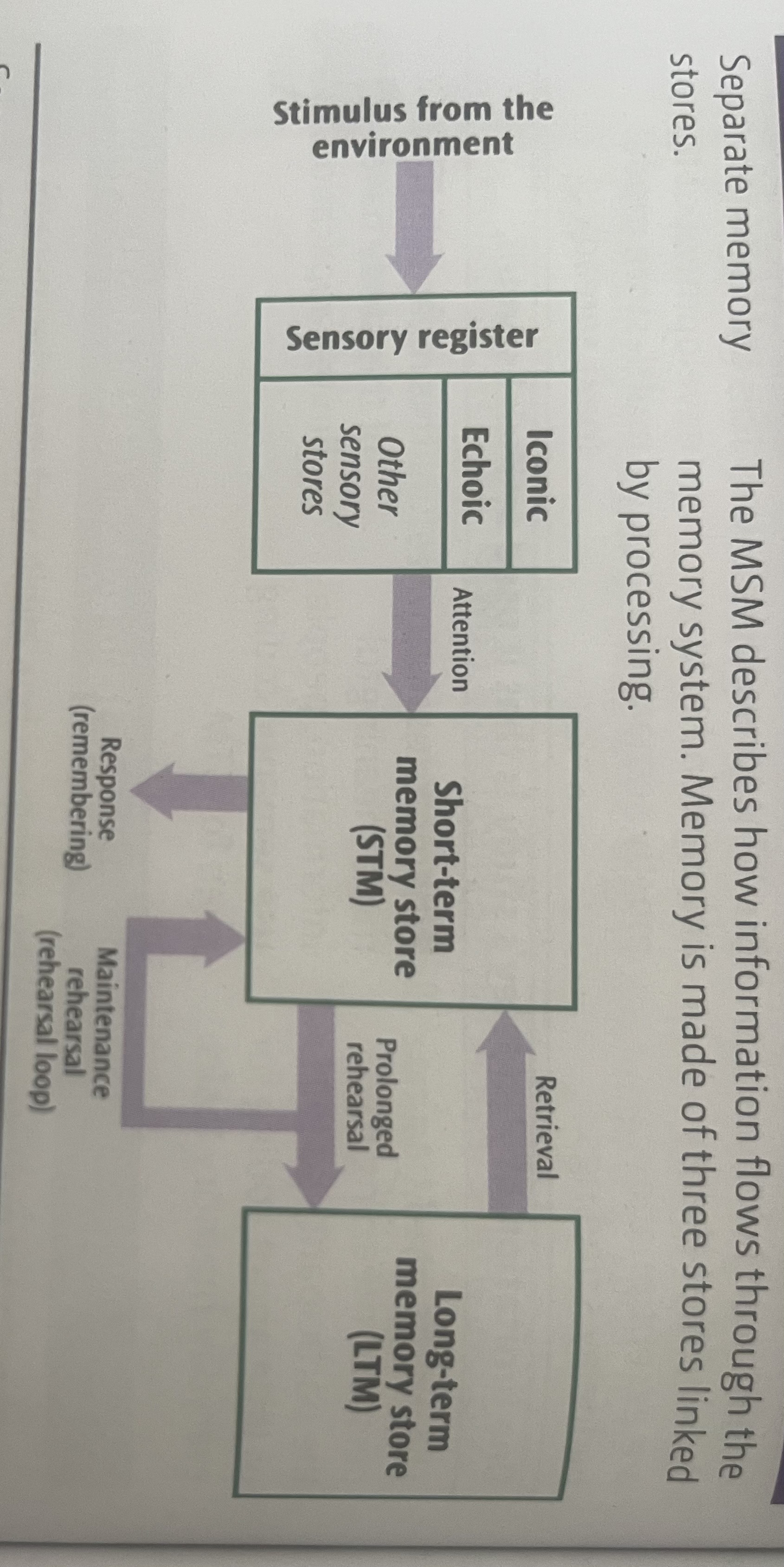
Sensory register (SR)
All stimulus passes through the SR There are five stores, one for each sense.
Coding = depends on the sense e.g. visual in iconic, acoustic in echoic
Duration = very brief, less than 0.5s
Capacity = very high
If attention was payed, the info passes into the STM
Short term memory (STM)
Coding = acoustic
Duration ≈ 18s unless rehearsed
Capacity = 7 ± 2 before some forgetting occurs
Through maintenance rehearsal, info passes onto LTM
Long term memory (LTM)
Coding = mostly semantic
Duration = potentially up to a lifetime
Capacity = potentially unlimited
When we want to recall info, it must be retrieved from LTM to STM
Strength of MSM - Research support showing difference of LTM and STM
Baddeley (1966) - we tend to mix up words that are acoustic when using STM
We mix words for semantics when using LTM
Supports view that the two memory stores are separate and independent
However studies tend not to use everyday info, they use meaningless stimuli
MSM may not be valid of how memory works in everyday life
Limitation of MSM - Evidence suggesting there is more than one STM store
(Shalice and Warrington) KF had amnesia, STM recall was poor when he heard digits but was better when he read them
Other studies confirm there may also be a seperate STM store for non-verbal sounds
MSM is wrong to claim there is only one STM store processing info
Limitation of MSM - Prolonged rehersal not necessary for STM-LTM transfer
Craik and Watkins argued there are 2 types of rehersal: maintenance and elaborative
Elaborative is needed for long-term storage. Occurs when you link information to existing knowledge or think ahout its meaning
Suggests MSM doesn't fully explain how long-term storage is achieved