Chemistry - 11 Polymers - 11.1 Addition Polymerisation & 11.2 Condensation Polymerisation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
Polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
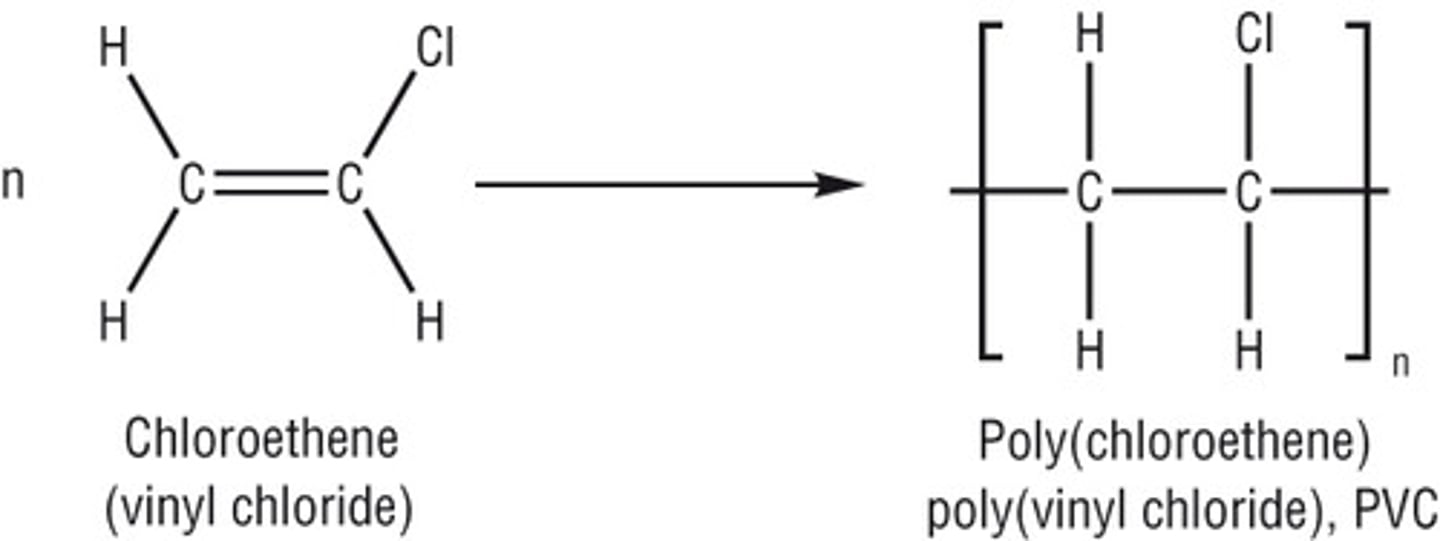
Polymer of alkene
poly(alkene)
Addition polymerisation
combination of a large number of monomers to form a single chain
Why are polyalkenes unreactive?
as they are saturated and contain only single covalent bonds
How does addition polymerisation work?
the C=C double bond is 'broken' so that either end can bond to another carbon
Advantages of polyester fibres [2]:
- hard-wearing
- less wrinkling
Advantages of nylon fibres [3]:
- lightweight
- less wrinkling
- non-absorbent (dries quickly)
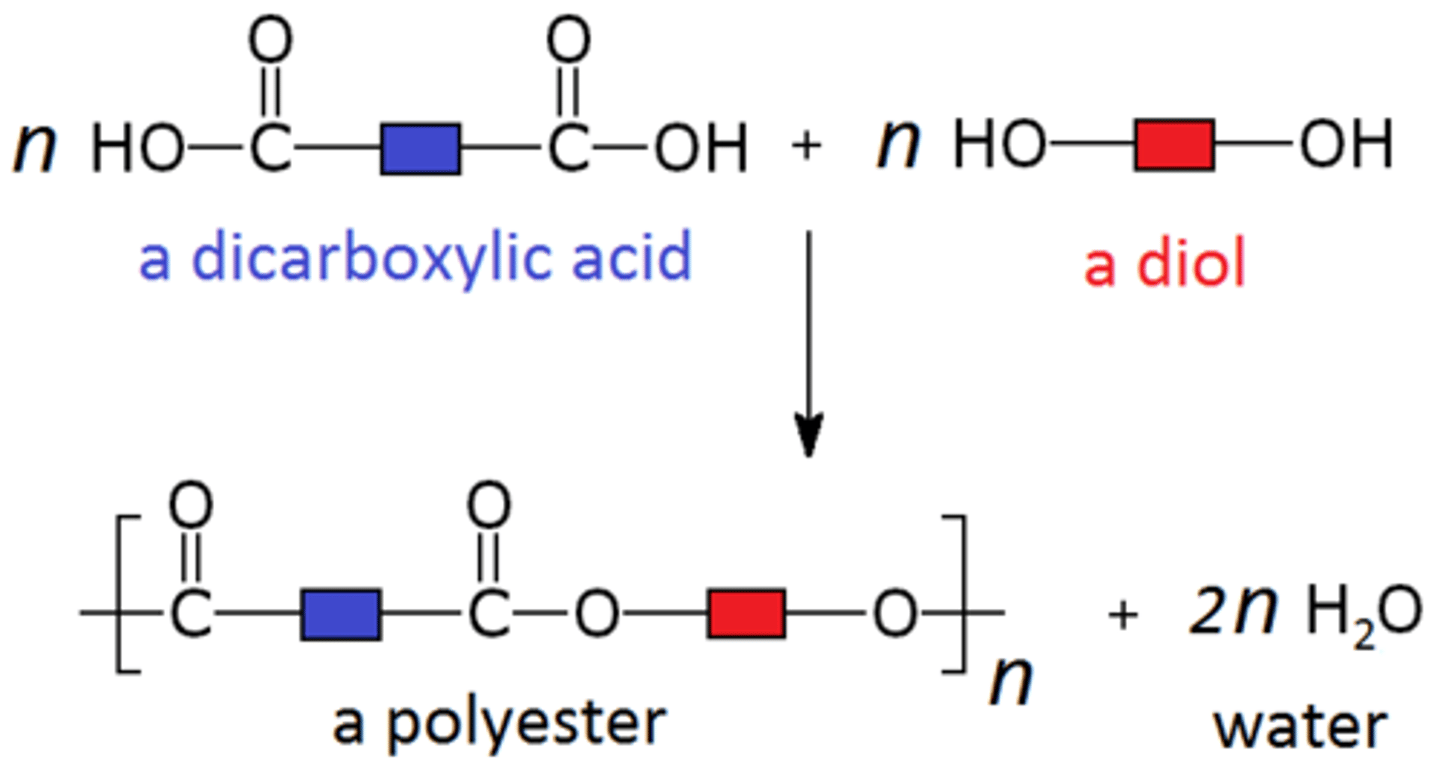
What are the products of condensation polymerisation?
condensation polymer + small molecule (H₂O or HCl)
Two types of condensation polymerisation [2]:
- between two different monomers with different functional groups on both ends (xAx + yBy)
- between the same monomer with two different functional groups on either side of each (xAy + xAy)
Diol
an alcohol containing two -OH groups (e.g. butane diol)
Dicarboxylic acid
a carboxylic acid containing two -COOH groups (e.g. butane dioic acid)
Carbon backbone
the chain or ring upon which the remainder of the molecule is built
Polyesters are made with... [2]
- a diol
- a dicarboxylic acid
Diol + dicarboxylic acid
condensation polymer + water
Amine group
NH₂
Amino acid
monomer of protein
What does the dicarboxylic acid give to the water molecule in condensation polymerisation?
-OH
What does the diol give to the water molecule in condensation polymerisation?
-H
Addition polymers are ... while polyesters are ...
non-biodegradable, biodegradable