StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.4.3 Genetic diversity can arise as a result of mutation or during meiosis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is meant by gene mutations? (1)
Changes in the sequence of nucleotide bases in the DNA
How can gene mutations occur? (1)
Can arise spontaneously during DNA replication
What are the four different types of gene mutations? (4)
- Substitution
- Deletion
- Addition
- Duplication
Describe the substitution gene mutation (2)
- Replacement of one or more bases
- By one or more different bases
Describe the deletion gene mutation (1)
Removal of one or more bases
Describe the addition gene mutation (1)
Adding of one or more bases
Describe the duplication gene mutation (1)
Where one or more bases is repeated
Describe why a mutation may cause a non-functional protein to be produced (3)
- Mutation results in frame shift
- Which is the alteration in base triplets from the point of
- The sequence of amino acids is altered from the point of
NOTE: The
Why do some substitution mutations not result in changes to the encoded amino acids? (2)
- Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code
- Which means the new base triplet could code for the same amino acid
What are mutagenic agents are used for? (2)
- To increase the rate of mutation
- e.g. benzene, X-rays
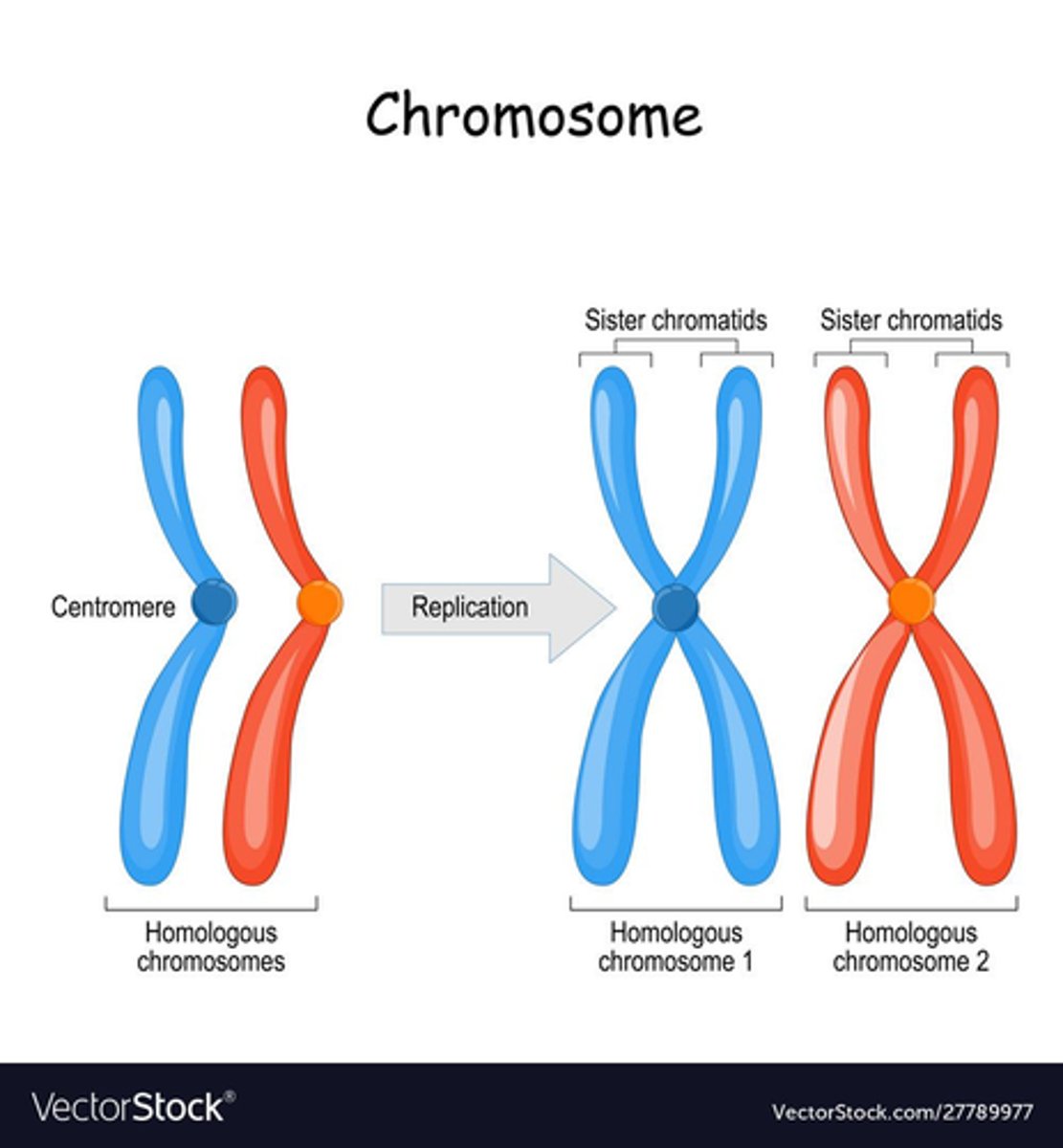
What are homologous chromosomes? (3)
- Two chromosomes
-One parental and one maternal
- That are identical and unpaired
How can mutations in the number of chromosomes arise spontaneously? (2)
- Chromosome non-disjunction
- During meiosis
What is chromosome non-disjunction? (2)
- A mutation that occurs during meiosis
- In which homologous chromosomes do not separate
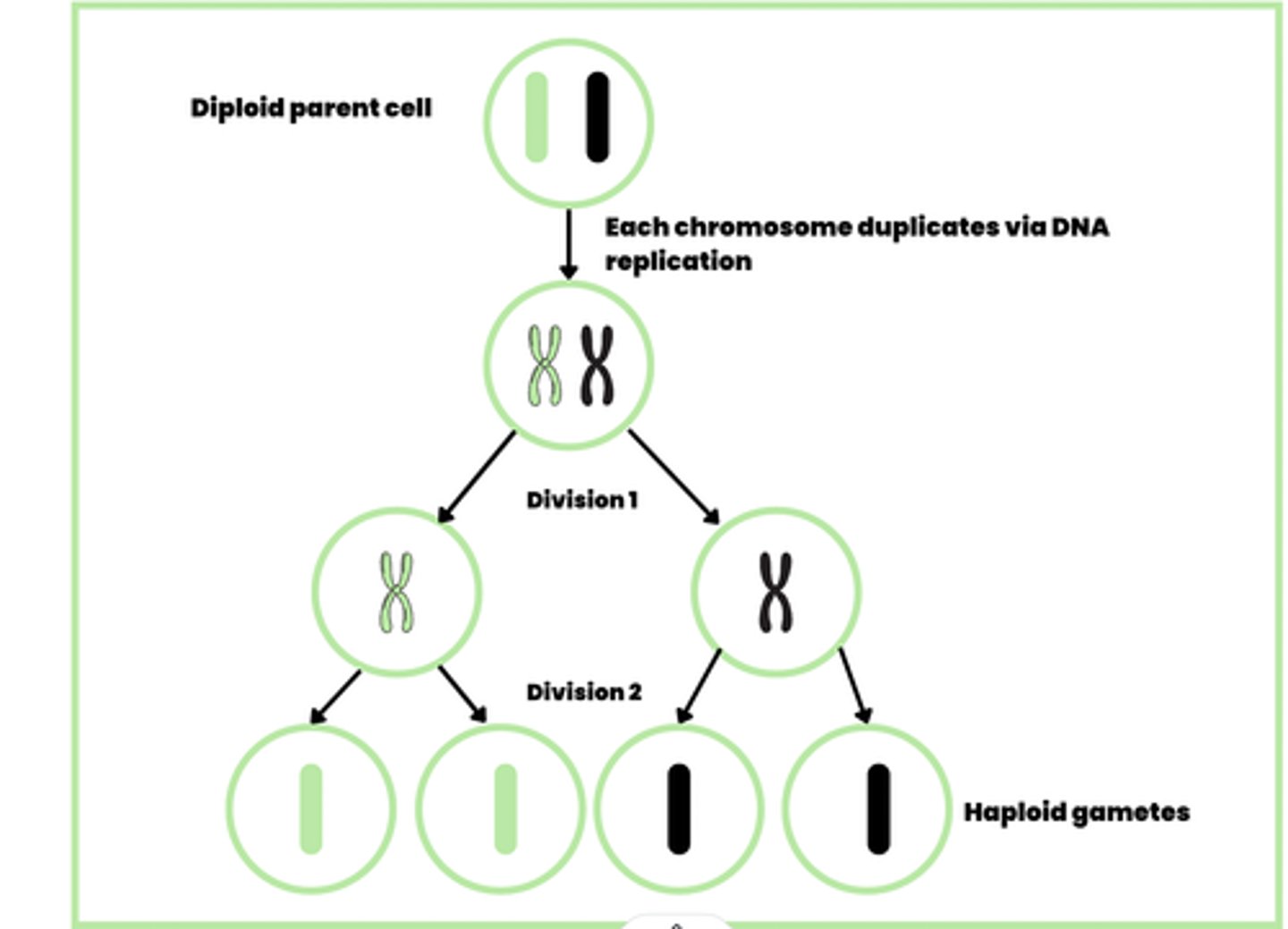
Describe the process of meiosis briefly (3)
- Two nuclear divisions
- Which usually results in the formation of four genetically different haploid gametes
- From a single diploid parent cell
Draw a diagram to describe the process of meiosis
Must know how to draw and interpret this!!
How do genetically different daughter cells (gametes) arise?
The independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
Describe and draw the process of crossing over in homologous chromosomes (4)
Bivalents = Pairs of homologous chromosomes that come together and align side by side
Chiasmata = Points of crossing over
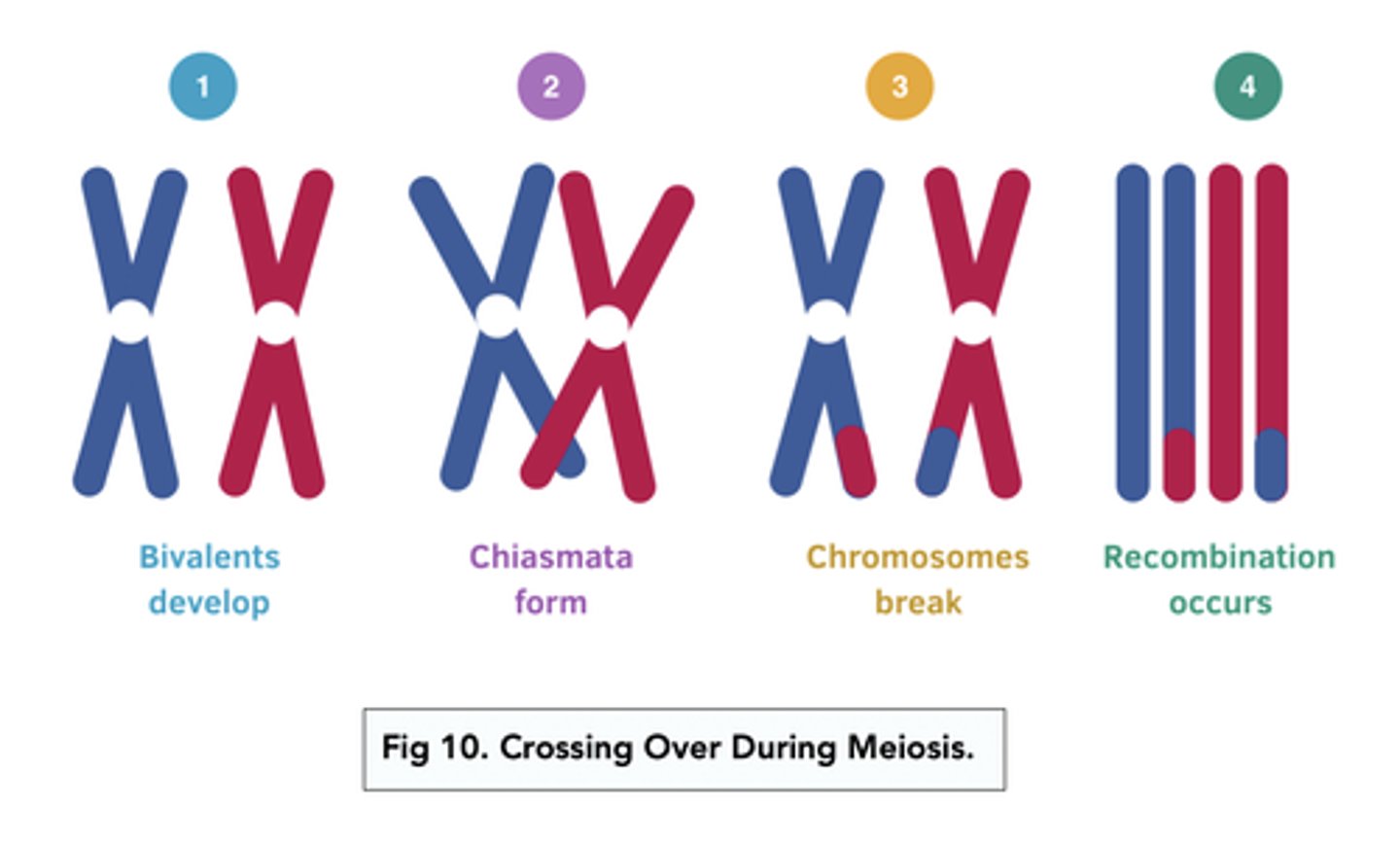
What are the 4 steps in crossing over that you must remember? (4)
1. Bivalents develop
2. Chiasmata forms
3. Chromosomes break
4. Recombination occurs
What does crossing over between homologous chromosomes during meiosis result in? (2)
Results in further genetic variation among daughter cells
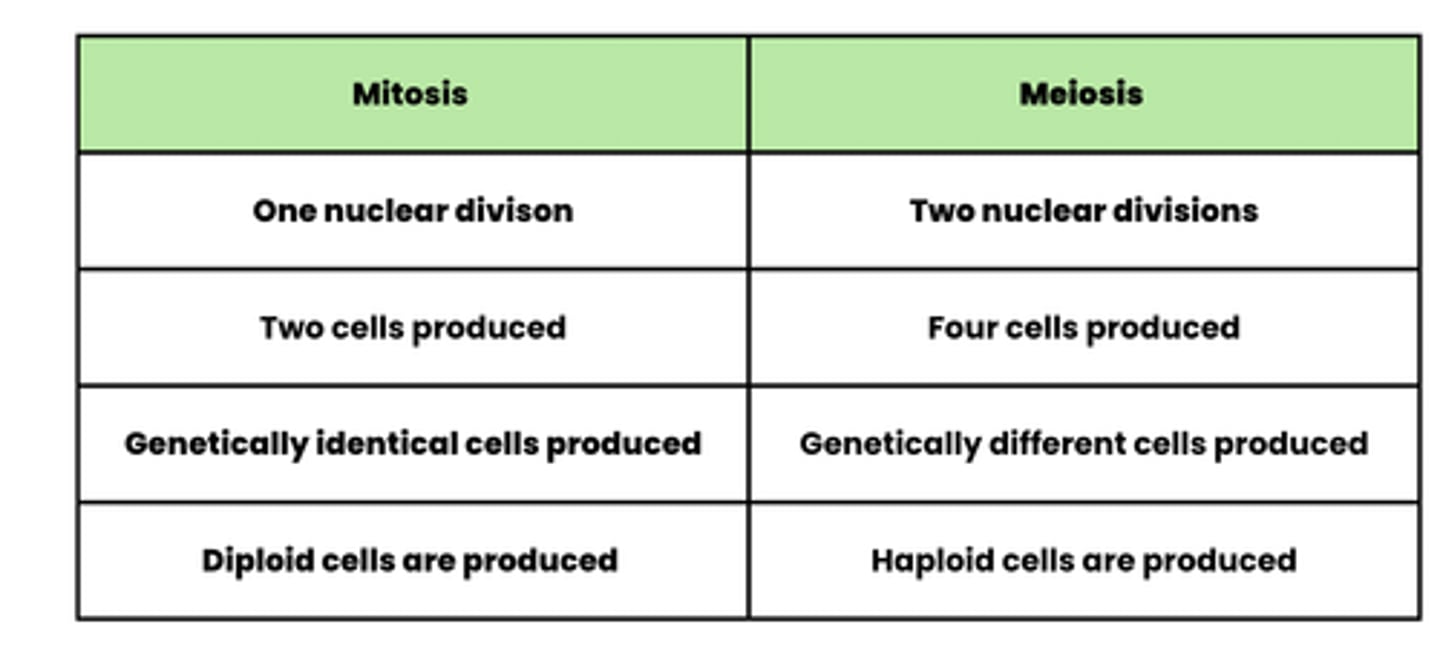
Compare the process of mitosis and meiosis (8)