BiologyCards (copy)
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
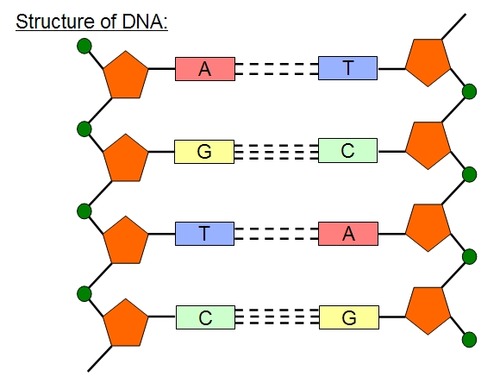
DNA base pairing.
dna is made of 2 chains of nucleotides connected by hydrogen bonds
Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) make 2
Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) make 3
Genetics
the study of heredity and genes
DNA structure
DNA: polymer Nucleotide: monomer
sugar-phosphate backbone
nitrogen base pairs
DNA composition
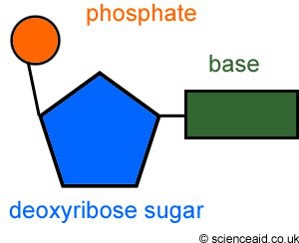
dna contains deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar) dna is a nucleic acid (molecule made up of nucleotides)
nucleotides have 3 parts: sugar, nitrogen base, phosphate
Chromosomes
threadlike structures found in nuclei of cells
each chromosome is 1 long dna molecule wrapped around proteins
chromosomes contain large numbers of genes among them, and the physical position of a gene is called a "Locus"
proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues
RNA
ribonucleic acid sugar: ribose instead of thymine (T), RNA has uracil (U) forms of RNA include: Messenger RNA (mRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA)
DNA: location, shape, chemical composition
location: is found in the nucleus of cells shape: is shaped as a double helix chemical composition: "deoxyribonucleic acid"
dna vs rna
deoxyribose sugar vs. ribose sugar, thymine vs. uracil , double strand vs. single strand
transcription
dna is unzipped at the desired gene (done by enzyme called helicase)
its copied by making a molecule of mRNA that complements 1 side of the dna strand
mRNA molecule can leave the nucleus to make a protein
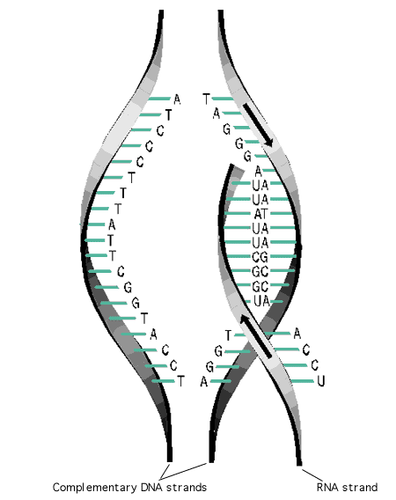
translation
the copied mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome to make protein
the mRNA is read in sequences of 3 nucleotide bases (codons)
UAA, UAG, UGA in codon sequence means STOP
codons
each codon (mRNA readers) codes for an Amino acid.
as the mRNA is read more amino acids are joined together to form protein
4 nitrogen bases in DNA
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
somatic cells / body cells
diploid (2n)
contains 46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
most cells in the body
sex cells / gametes
haploid cells contains 23, only 1 pair of each chromosome sperm and egg cells
somatic vs sex cells
somatic: diploid, 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs sex: haploid, 23 chromosomes, 1 of each
sex chromosomes
somatic cells have a pair of these, either XX (F) or XY(M)
autosomes (somatic chromosome)
all chromosomes except sex chromosomes somatic cells have 44 autosomes 22 pairs
homologuous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Mitosis: one division forming 2 identical cells (clones) (somatic cells)
Meiosis: two divisions forming 4 genetically different cells (sex cells)
mitosis
duplicated chromosomes line up along the cell equator single file
the copies of the chromosomes then pull apart and go to opposite ends of the cell
the cell pinches inwards and makes 2 new identical cells
mitosis phases (4)
Prophase
chromosomes condense and become visible
Metaphase
chromosome lines up single file at the equator
Anaphase
sister chromatids pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase
2 new nuclei form around the 2 new sets chromosomes
cytokinesis: cell pinches inwards and splits into 2 new daughter cells
meiosis
division of sex cells
occurs in the testes and ovaries
it divides diploid germ cells into haploid gametes
daughter cells only have 23 chromosomes
meiosis divisions
first: the pair of chromosomes separate
second: the copied chromosomes separate like mitosis
fertilisation
fusion of a sperm and egg zygote = diploid, with 23 chromosomes from each parent, total of 46 zygote rapidly divides by mitosis to form an embryo
identical/non-identical twins
identical:
zygote splits and forms 2 embryos
non identical:
more than one egg is released and is fertilised
Gregor Mendel: peas
mendel grew pea plants and would keep detailed records of each plants different traits
he would breed certain plants together, taking notes on traits and traits of offspring
saw patterns in how traits were passed on
allele
Different forms/versions/combinations of a gene
e.g.: Gene: eye colour Alleles: brown, blue, green
Genotype
the combination of alleles genotypes are normally written as a letter per allele allele 1 - (b) allele 2 - (B)
Phenotype
the physical expression of a gene This is affected by the genotype and environmental factors e.g.: petal colour gene - purple petal
Heterozygous alleles
alleles are different (Bb)
Homozygous alleles
alleles are the same (BB), (Bb)
carriers
a carrier is one wo has the recessive heterozygote allele, but does not express it in their phenotype.
if 2 carriers have children, their offspring could:
have the trait
be a carrier
not have the trait
dominance: alleles
one allele codes for a dominant phenotype and one codes for a recessive phenotype
if the allele for the dominant trait is in the genotype it's expressed in the phenotype
the allele for the recessive trait is ONLY expressed when it is the only allele present (bb)
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
Dominant: will always display in offspring- even heterozygous
Recessive: only displayed when homozygous recessive
punnett squares
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
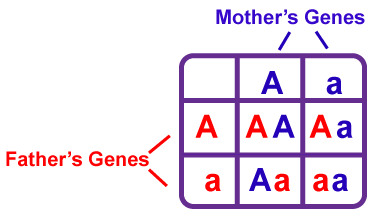
genetic crosses
Where 2 organisms with specific traits are bred together and the traits of their offspring are recorded
co-dominance
in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism
mutations
errors or changes in the dna squence or an entire chromosome
they can lead to proteins not being made or producing different/non-functional proteins
causes of mutations
spontaneous mutation: the cause is unknown induced mutation: the cause (mutagen) can be identified
mutagen
factor that triggers mutations in cells examples: uv rays nuclear radiation x-rays certain chemicals some pathogens
types of point mutations
SUBSTITUTION of a different nucleotide DELETION of a nucleotide INVERSION of a small group nucleotides INSERTION of a nucleotide
consequences of point mutations (3)
silent: no change in amino acid used
missense: change in amino acid used
nonsense: no more amino acids added to the protein
chromosomal abnormalities: structural
DUPLICATION: part of the chromosome is duplicated DELETIONS: a portion of the chromosome is flipped around INVERSIONS: a segment of a chromosome is flipped around TRANSLOCATIONS: segments of two chromosomes are exchanged
chromosomal abnormalities: number
too many or too few chromosomes
this can be lethal and/or cause a genetic disorder
examples of beneficial mutations
mutation that cause resistance to pesticides or antibiotics
"heterozygote advantage": this is where having a copy of both alleles (the normal and mutated version) for a trait provides a survival advantage
passing on mutations
not all mutations can be inherited only mutations found in sex cells will be passed on to an offspring
what is a pedigree
a family record that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations
Trait Inheritance: autosomal
inheritance not connected to sex
trait inheritance: sex-linked
Y-linked trait only ever affect males
x-linked may affect one gender more than the other
4 types of inheritance
autosomal dominant autosomal recessive sex linked dominant sex linked recessive
Y-linked traits
type of sex-linked only ever affects males there's only ever 1 copy of the gene present and as such there isn't a need for dominant/recessive
genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
genetic organisation of the cell
cell -> nucleus -> chromosome -> gene -> dna
haploid vs diploid
Haploid (23 chromosomes) means cell has one set of DNA, diploid has 2 sets and 46 chromosomes

test
test