BU111 Tech Factors Finals Prep
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What is Technology?
Equipment, material, and Information technology advancements
What are Equipment & material advancements?
They substitute/magnify human effort, Reduce cost, improve performance, increase flexibility
What is an example of Equipment & material advancements?
Robots used to automate tasks and enhance production efficiency
What is information technology advancements?
Devices & software for creating, storing, exchanging, and using information
What is an example of Information technology advancements?
Cloud; data analytics; video calls
What are elements of Technological Factors?
Internet, Information technologies, Materials & equipment
What is the significance of Technological Factors?
It demands constant scanning & learning, It changes sources of competitive advantage and barriers to entry, It creates opportunities for new products and efficiency, and legacies/Compatibility make change challenging
What five industries are radically changed by technology?
Music, Travel, Transportation, Publishing, Retail
In the Automobile industry, what are ways that technology has impacted it?
Heads-up display (AR) and voice control, Functions/ autonomous, Design & testing, Service booking & diagnosticsResearch & Purchasing, 3D printing customization
How has technology impacted research and development?
You used to have to go to the drawing board, make sketches, make a prototype and then go make to the drawing board to make adjustments and repeat this cycle until the product is complete. Now it can all be done digitally, saving time.
How has technology impacted power?
It has enabled more efficient generation, storage, and distribution of power, including smart grids, renewable energy integration, and advanced battery technologies.
How has technology impacted building and moving?
Through assembly lines that increase productivity, and through innovations in planes, trains, and cars that improve transportation efficiency.`
How has communication been impacted by technology?
Through mass media, telecommunications, and digital platforms that allow instant global sharing of information.
How has technology impacted information?
Computers and internet have enabled rapid collection, storage, analysis, and sharing of vast amounts of information through digital databases, cloud computing, and advanced analytics.
What is an example of an advancement in information?
i-robots learning where to go when vacuuming
How has technology impacted smart tech?
Through autonomous machines and devices that can act, learn, and make decisions using AI and machine learning.
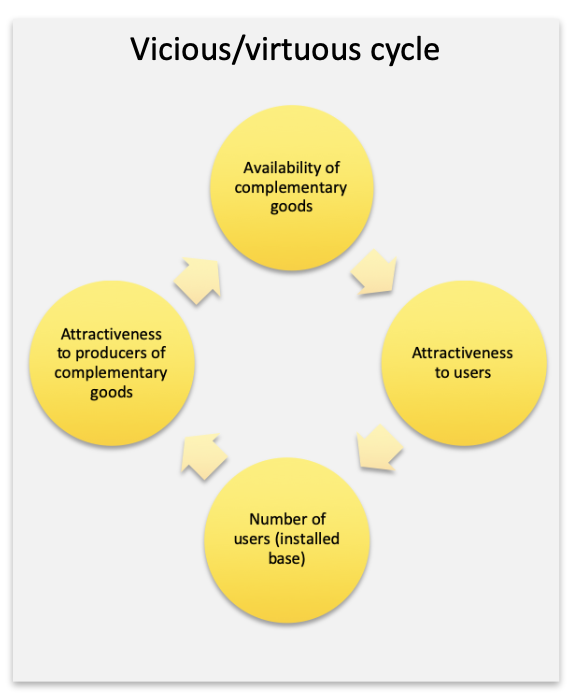
What cycle is this an image of?
Vicious/Virtuous Cycle
What are complementary goods?
Products that are typically used together, so that the demand for one increases the demand for the other
What is an example of a complementary good?
Printers and ink cartridges.
Which of these is not an example of a complementary good?
Coffee and tea
Which of these is an example of a substitute good?
Butter and margarine
What is a technology standard?
A specification that ensures compatibility between complementary goods, allowing them to work together efficiently.
What is an installed base?
The total number of a company’s products or systems currently in use by consumers, which can influence the adoption of complementary goods.
What is an example of an installed base?
Apple, because the large number of existing devices encourages the use of complementary products like apps, chargers, and accessories.
What is the Network Effect?
When a product or service becomes more valuable as more people use it, such as social media platforms or messaging apps.
What is an example of the Network Effect?
Social media platforms like Snapchat, because the more users join, the more valuable the platform becomes for everyone.
What is customer lock in?
The extent to which a customer is “committed” to a product or service, making it difficult or costly to switch to a competitor
Large customer lock in creates _________ switching costs
higher
Small customer lock in creates _________ switching costs
lower
What does larger customer lock in create?
Greater resistance to switch
What are common causes of customer lock-in?
Habit or system familiarity, learning, investment in the product or service, and switching costs that make changing difficult.
How does customer lock-in connect to Porter’s Five Forces?
Customer lock-in reduces the threat of new entrants and rivalry among existing competitors by making it harder for customers to switch to alternative products or services.
How has technology impacted e-commerce and omnichannel retail?
It enables seamless integration across online and offline channels, allowing customers to shop, browse, and receive support through multiple platforms efficiently
What is E-Commerce?
The buying and selling of goods and services over the internet, including online shopping, electronic payments, and digital marketplaces.
What is Omnichannel?
A retail strategy that integrates multiple channels-online, mobile, and physical stores—to provide a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints.
What is a big player in E-commerce and Omnichannel?
Amazon, because it operates both an extensive online marketplace and integrates physical retail, logistics, and digital services for a seamless customer experience.
What is an example of a business that uses E-commerce and Omnichannels?
Disney
What is the benefit of E-commerce and Omnichannel?
Enhanced marketing, service, and consistency; improved operational efficiency; enhanced data collection; and higher profit margins.
What is Virtual and Augmented Reality?
Technologies that replicate an environment (virtual reality) or overlay digital information onto the real world (augmented reality) to enhance user experiences.
What is the benefit of Virtual and Augmented Reality?
Allows users to experience products, environments, or events without purchase or physical presence, reduces costs, and enhances the overall user experience.
Which of these is an example of Virtual and Augmented Reality?
Sephora, because it allows customers to “try on” makeup virtually using augmented reality technology.
Which of these is an example of Virtual and Augmented Reality?
Clearly glasses, because they use augmented reality technology to overlay digital information onto the user’s view of the real world.
What is an example of Virtual and Augmented Reality in use?
Experiences such as training simulations, virtual travel, immersive games, and enhanced product demonstrations using VR/AR technology.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Machines that are programmed to think like humans, capable of rapidly gathering and processing data, recognizing patterns, making decisions, and executing tasks, and are being used in most industries.
What is the benefit to Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Task automation, reduced bias (though bias can still be programmed in), faster and better decision-making, predictive capabilities, and a higher likelihood of top-quartile financial performance.
Which of these is an example of when Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used?
Improved customer targeting, finance (fraud detection), self-driving cars and autonomous machines, personalization, healthcare (diagnostic assistance), and creative applications like writing, music, and images.
Which of these is an example of a business using Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
A tire manufacturer using data-driven selling to optimize tire stocks across stores, leveraging AI to predict demand and improve inventory management.
Which of these is an example of a business using Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Apple Health, because it uses AI to analyze health data, provide insights, and offer personalized recommendations to users.
What are Opportunities that Technology can provide?
Product innovation, uniqueness, added value, improved information use and sharing, competitive advantage, barriers to entry, and customization.
What are Threats that Technology can provide?
Why is information overload and security a threat to technology?
Because information is now stored digitally on the cloud rather than in a secure physical location, making it more vulnerable to overload, breaches, and misuse.
Why is disconnected employees and customers a threat to technology?
Because it can be difficult to retain human resources, leading to high employee turnover and a lack of peer connections, which reduces collaboration and organizational efficiency.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is achieving financial performance an Opportunity?
Technology can improve efficiency, reduce costs, increase revenue, and enable data-driven decisions, all of which contribute to stronger financial performance and competitive advantage.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is achieving financial performance a Threat through technology?
Pursuing financial performance with technology can be risky because investments in new tools, systems, or capabilities are costly, and failure to adopt or implement them effectively can hurt profitability.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is Meeting customer needs an opportunity through technology?
Technology allows businesses to better understand and anticipate customer needs, personalize products and services, enhance engagement, and improve satisfaction, creating competitive advantage.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is Meeting customer needs a threat in technology
Failing to meet customer needs with technology can lead to dissatisfaction, lost loyalty, negative reviews, and reduced competitiveness, which can threaten a company’s market position.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is Building quality products and services an opportunity for technology?
Technology enables better design, precision, testing, and customization, allowing companies to create higher-quality products and services that enhance reputation and customer satisfaction.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is Building quality products and services a threat for technology?
Investing in technology to build high-quality products and services can be costly, require ongoing R&D, and create risks if the technology fails to deliver expected standards, potentially harming reputation and profitability.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is encouraging innovation and creativity an opportuntiy for technology?
Technology provides tools, platforms, and data that enable employees to experiment, generate new ideas, streamline R&D, and create innovative products and services, enhancing competitive advantage.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is encouraging innovation and creativity a threat for technology?
Pursuing innovation and creativity with technology can be costly, risky, and time-consuming, and failed experiments or poorly implemented ideas can harm reputation and reduce ROI.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is gaining employee commitment an opportunity for technology?
Technology can engage employees through collaborative tools, learning platforms, and transparent communication, increasing commitment, productivity, and overall organizational performance.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is gaining employee commitment a threat for technology?
Relying on technology to engage and retain employees can be risky, as improper implementation, lack of training, or over-reliance on digital tools may lead to disengagement, high turnover, and reduced productivity.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is creating distinctive competitive advantage an opportunity for technology?
Technology can provide unique capabilities, innovative products, efficient processes, and superior customer experiences, helping a company differentiate itself and gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
Tech impact on KSF:
How is creating distinctive competitive advantage a threat for technology?
Pursuing a competitive advantage through technology can be risky, as it often requires significant investment, rapid adaptation, and ongoing innovation; failure to maintain it can result in lost market position and financial strain.
What are the four types of innovations that create varying challenges for large firms?
Radical/Disruptive, Architectural, Modular, and Incremental/Sustaining innovations, each presenting different strategic and operational challenges.
What is Radical/Disruptive Innovation?
Innovation that significantly changes an industry or market, often allowing a small, young firm to challenge established players and gain a foothold, requiring a large change in knowledge and structure
What is an example of a Radical/Disruptive Innovation?
A calculator compared to a slide rule, because it fundamentally changed how calculations were performed, disrupting the existing market.
What is an Architectural Innovation?
An innovation that changes the way components of a product or system are linked together, often altering the overall design or process while keeping core components largely the same.
What is an example of an Architectural Innovation?
A smartphone that integrates existing components (camera, processor, screen) in a new configuration to enable new functionality or form factors.
What is a Modular Innovation?
An innovation that changes one or more components of a product or system without altering the overall architecture, improving functionality or performance of individual modules.
What is an example of a Modular Innovation?
A digital camera compared to a film camera, because it replaces the imaging component while keeping the overall camera structure and use familiar.
What is an Incremental/Sustaining Innovation?
Innovation that improves a product or service in small, continuous steps, helping to sustain existing advantages and maintain competitiveness over time.
What is an example of an Incremental/Sustaining Innovation?
A new model of a smartphone with improved battery life and camera performance, building on the previous version to maintain competitive advantage.
What is an incumbent?
A company or organization that is currently established and dominant in a particular market or industry.
With Incremental/Sustaining Innovations, the _________ wins.
Incumbent
With sustaining Innovation, who are you trying to serve?
Existing customers, by improving products or services incrementally to maintain satisfaction and loyalty.
Apple releases a new product every year. What would happen if they didn’t?
Other competitors would gain market share by offering newer, more innovative products, potentially reducing Apple’s dominance and sales.
Increase performance and productivity means ___________ profit.
an increase in
Decreased performance and productivity means ___________ profit.
a decrease in
With ______________ innovations, you don’t know it is ____________ until it __________ the industry
disruptive, disruptive, transforms
_______________ innovations improve at a faster rate that ___________, and incumbents cannot keep up
Disruptive, sustaining
In a niche market, you are likely to sell ___________.
Fewer products, but highly specialized to meet the unique needs of a small, targeted customer segment.
What kind of innovation is AirBnB?
Disruptive innovation, because it began by offering a low-cost, alternative lodging option that initially served a different market segment than hotels, and later expanded to overlap with traditional hotel customers.
What kind of innovation is Uber?
Disruptive innovation, because it started by offering a convenient, app-based ride service that initially targeted underserved segments and later expanded to compete with traditional taxis.
If Uber creates a car-sharing service, is it disruptive?
Yes, it would be disruptive innovation because it targets a new or previously underserved market segment, providing an alternative to traditional car ownership and mobility services.
What are key considerations with innovations?
Initial target market, initial performance, and later performance and market
Why do large firms sometimes fail?
Organizational structure and capabilities slow response time and influence choices, organizational processes weed out ideas that don’t address current customer needs, and they focus on satisfying mainstream customers, ignoring new technologies and higher-margin opportunities.
How can the Diamond-E create a problem for innovation?
By blocking or slowing down ideas that don’t align with existing resources, strategy, or management preferences
What KSF connects to Organizational processes weeding out ideas that don’t address current customer needs?
Meeting Customer needs
Why do large firms sometimes fail?
They avoid small, uncertain, unfamiliar markets
What type of markets do large firms often avoid?
Niche markets that are small and financially unattractive, with uncertain growth, lower profit margins, and a higher risk of criticism if they fail
What is a niche market?
A small, specialized segment of a larger market with unique customer needs
Diamond-E
How do technological factors connect to management preferences?
Management preferences shape which technologies are adopted and prioritized
Diamond-E
How do technological factors influence a firm’s strategy?
Technology can open opportunities for new products, services, or efficiency, guiding strategic choices
Diamond-E
How do technological factors relate to a firm’s resources?
Technology can enhance or require new resources, such as skills, equipment, or capital
Diamond-E
How do technological factors impact organizational structure and processes?
Technology can require new processes, workflows, or reporting structures
Diamond-E
How do technological factors connect to a firm’s environment?
Technology creates opportunities and threats in the external market, shaping how a firm responds to competitors and customers