BIOL 3000 Exam 3
1/454
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
455 Terms
Chromatin
DNA and protein complex that compacts DNA
T or F: Chromatin is only found in eukaryotes
True
Histones
Proteins found in chromatin, provides structure, shape and gene regulation of chromosomes
Euchromatin
Lightly packed chromatin rich in gene concentration. Is most often under active transcription
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed chromatin consisting mainly of genetically inactive sequences
In chromosomes, when gene transcription occurs, what is likely the chromatin formation?
Euchromatin
Facultative heterochromatin
Gene silencing; Barr bodies
The condensed, inactive X chromosomes found in females is an example of
Barr bodies
Constitutive heterochromatin
VERY gene poor; centromeres and telomeres
Folded fiber model
DNA and protein model that proposed a single, long chromatin fiber makes up each chromosome
Folded fiber model: Type A fiber
Chromatin fiber 1-10 nm. DNA packing ratio is 6:1
Folded fiber model: Type B fiber
Chromatin fiber 20-25 nm. DNA packing ratio 10:1
According to the folded fiber model, what type of fiber is folded more tightly?
Type B
According to the folded fiber model, extensive folding of Type __ forms a chromatid
B
Nucleosome model
Most accepted DNA packing model. Proposes nucleosomes to be the packing unit of eukaryotic chromatin, made up of a double DNA strand wrapped core histones.

Which DNA packing model is better fit for protein biosynthesis?
Nucleosome model
Which of the following statements is true regarding core histones? I. H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 are core histones II. They were highly conserved during evolution III. Have a very basic charge due to being made of cystine and arginine IV. Consist of approximately 120 amino acids each
I, II, and IV
Which of the following statements is true regarding linker histones? I. Consists of 200 animo acids II. They were highly conserved during evolution III. Tissue specific expression IV. Closely associated with core particle
I and III
H1 is in what histone class?
Linker histones
How many core histones are in a nucleosome?
8, two of each type
How many linker histones are in a nucleosome?
1
What is the importance of 10 nm fiber in nucleosome formation?
They are the primary packing of chromatin
Solenoid formation
Helical coiling of 10 nm fibers consisting of 6 nucleosomes
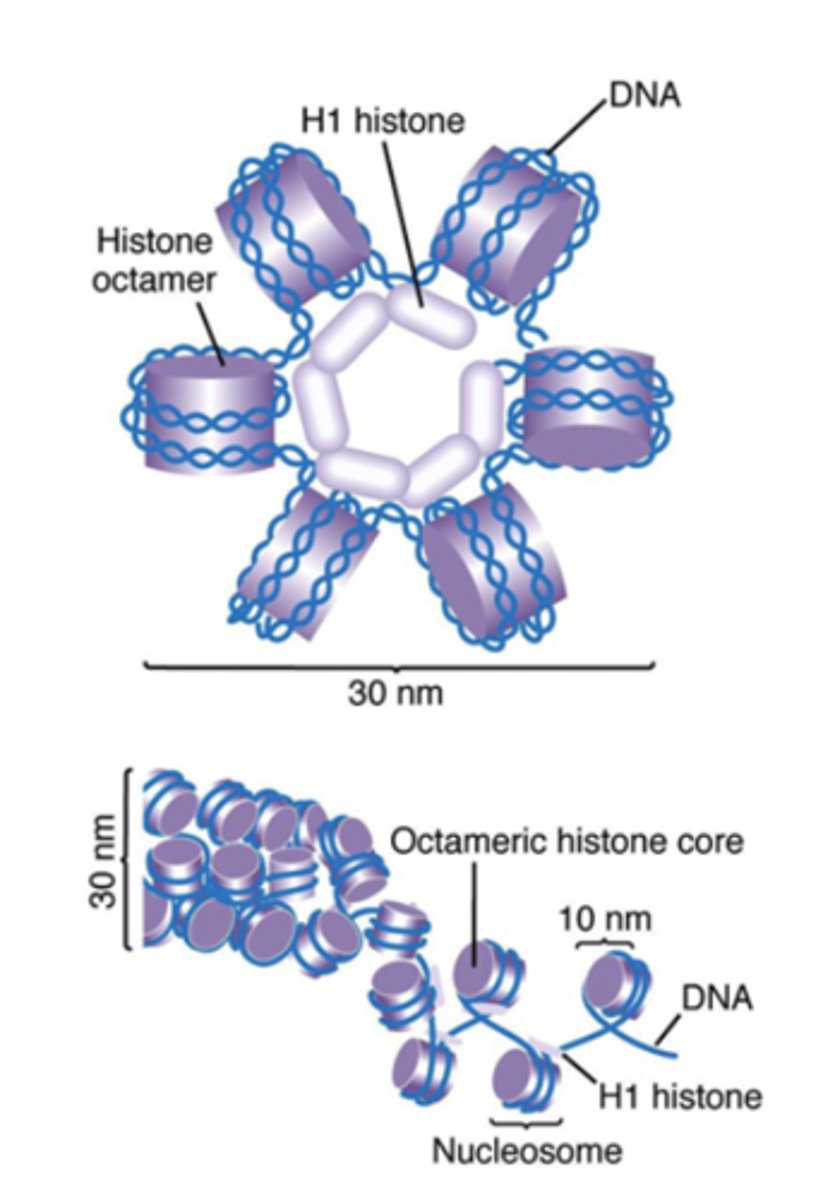
What histone is found in the center of a solenoid, and what is it used for?
H1, used for packing
How does H1 histone work?
Binds linker DNA and 146 bp portion of central core DNA, compacts up to 40x!
Zig Zag model formation
Due to the limited flexibility of DNA, straight linker DNA connects opposite nucleosomes
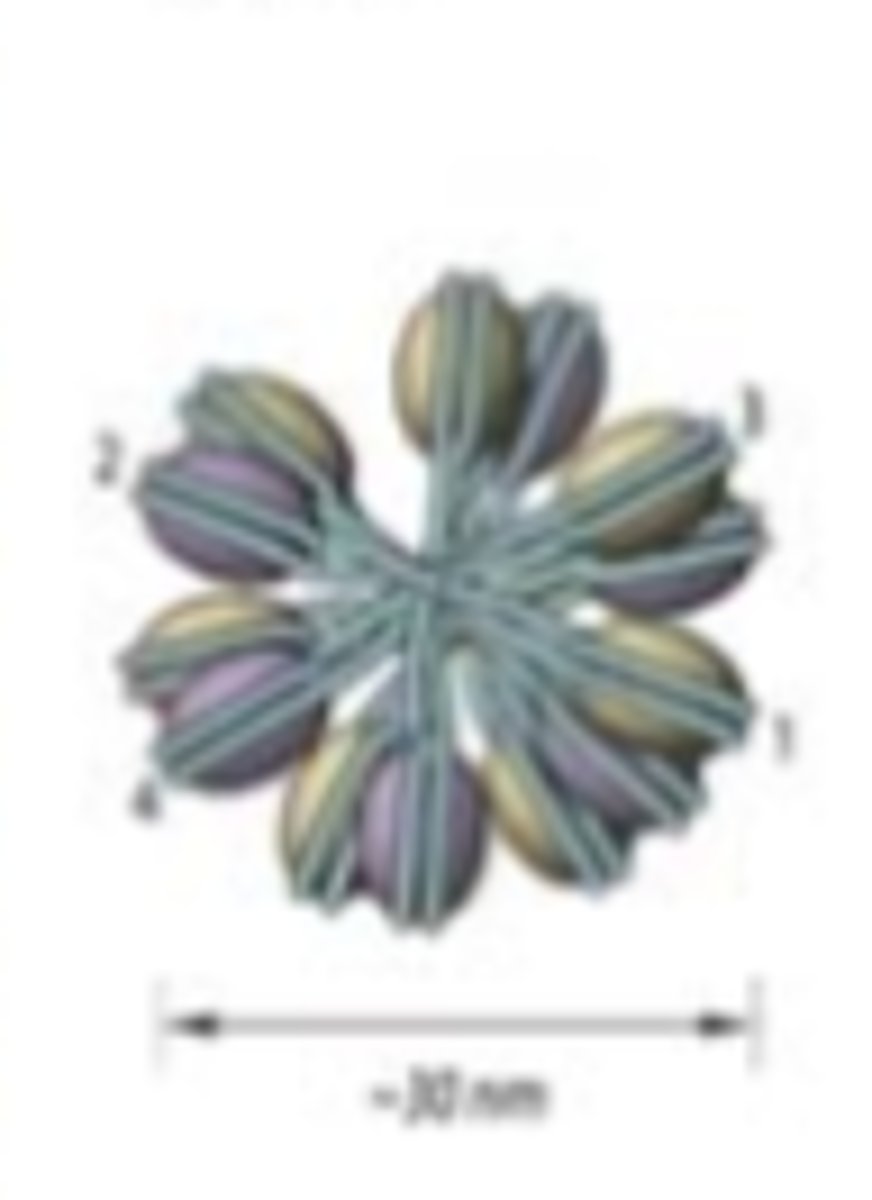
T or F: both solenoid and zig zag typologies may both simultaneously be present in chromatin fiber
True
Chromatin loops
Higher order of coiling with 300 nm chromatin fiber built around scaffold of topoisomerase II
Chromatin loops share the same level of compaction as...
Euchromatin
Metaphase chromosome
condensed chromatin loops looped around spiral scaffold composed of Topoisomerase II and about 15 non‐histone proteins.
Metaphase chromsosomes have the same level of compaction as...
Heterochromatin
2 nm-10 nm fibers are known as ___ and are found in the ___ phase
DNA and nucleosomes; G1
30 nm fibers are known as ___ and are found in the ___ phase
chromatin; early G2
300 nm fibers are known as ___ and are found in the ___ phase
Chromatin loops; late G2
700 nm fibers are known as __ and are found in the __ phase
condensed chromatin loops; beginning prophase
Chromosomes contain __ nm fibers, and are found in the ___ phase
700; metaphase
What are the phases of DNA condensation?
Nucleosomes > Solenoids > Chromatin Loops > Condensed Chromatin > Chromatin folded around protein scaffold
C value paradox
excess DNA present in genome that does not seem to be essential for development or evolutionary divergence of an organism
G value paradox
Number of genes does not correlate with organismal complexity
Types of DNA in the genome
Highly repetitive (HR), moderately repetitive sequence (MR), unique
Highly repetitive DNA sequences make up _% of the human genome
10
T or F: Highly repetitive DNA sequences are located in euchromatic regions around the centromere/telomere
False, heterochromatic
HR DNA function
Structural and organization to nothing more than junk
Where is HR DNA found?
Present at >10^6 copies per genome
What type of DNA sequence occurs as variable length motifs (5-100 bp) in long tracts of up to 100 Mb?
Highly repetitive
"noncoding/junk DNA" is known as what sequence type?
Highly repetitive
Alpha satellite DNA
consists of 2-30+ repeats of 171 bp tandem repeats, HR DNA
moderately repetitive sequences make up about ____% of the human genome
30
T or F: MR sequences are found throughout the euchromatin
True
Where are Moderately Repetitive sequences present?
Between 10-10^5 copies per genome
MR sequences are about __ bp in size
300
'redundant' genes for histones, and ribosomal RNA and proteins is a trait of which DNA sequence type?
Moderately repetitive
Microsatellite DNA
Variable number of tandem repeats typically occurring in non-coding regions of the genome
Interspersed repetitive DNA
Transposable elements
What are two examples of MR sequences?
Interspersed repetitive DNA and microsatellite DNA
Microsatellites occur through what type of mutation?
Slippage recognition
___ are useful genetic markers because they tend to be highly polymorphic
Microsatellites
Microsatellites are uses as genetic markers for what purposes?
To sequence the human genome, to marker certain disease/conditions, markers for DNA testing in forensic cases
Unique DNA makes up ___% of the human genome
1-5
T or F, Unique DNA sequences are found throughout the heterochromatin around centromeres/telomeres
False, they are found throughout euchromatin (not near centromeres and telomeres!)
"coding DNA regions = GENES" describe what DNA sequence type?
Unique sequences
T or F: about 40,000 protein coding genes can be found in Unique sequences
False, only about 20,000 can be found
Where are unique sequences present?
Single or low copy number per genome
Gene
Sequence of unique nucleotides (GENOTYPE) that carry the genetic information which is to be expressed (PHENOTYPE)
Molecular genes contain which of the following: I. Promoter II. Operator III. Terminator IV. Transcribed Region V. Regulatory Sequence
I, III, IV, and V
Promoter
DNA sequence onto which the transcription machinery binds and initiates transcription
transcribed region
Contains the information that specifies an amino acid sequence
Regulatory sequence
Binding site for regulatory proteins that regulate rate of transcription
Exon
Expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
Intron
Sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
Flanking regions
5' untranslated region and 3' untranslated region
5' untranslated region
mRNA that is directly upstream from the initiation codon.
3' untranslated region
section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon
TATA box
highly conserved sequence in DNA serving as the binding site for transcription factor binding.
Which of the following is a core DNA sequence
5'‐TATAAA‐3'
Do promoters or enhancers have a basal level of transcription?
Promoters
Enhancer sequences
CAAT box and GC box
CAAT box
(5'‐GGCCAATCT‐3') consensus sequence that occurs upstream by 60‐100 bases to the initial transcription site
GC box
region of DNA that can be bound with proteins (activators)to activate transcription of a gene or genes
Do promoters or enhancers have a ramped up level of transcription?
Enhancers
Terminators
section of nucleic acid sequence that marks the end of agene or operon in genomic DNA during transcription
What are the types of genes?
Solitary Genes (Unique), Duplicated Genes, Multigene Families, Pseudogenes, and Repeated Genes
Solitary genes (unique)
A single copy of a gene (in haploids, 2 copies in diploids), comprises the bulk of euchromatin
Duplicated genes
Process by which a portion of a chromosome is duplicated resulting in an additional copy of a gene (paralog gene
Paralog gene
A copy of the original gene
In Duplicated Genes, _____ of the two genes may mutate and change the original function of the gene
Either
T or F: Duplicated genes usually occur due to an error during Meiosis
True
Multigene families
Set of several similar genes, formed by duplication of a single original gene, and generally with similar biochemical functions
What gene type(s) are most often located in similar regions of the chromosome?
Multigene families
T or F: Multigene Families are most often used or synthesized at different times
True
Pseudogenes
Dysfunctional relatives of genes that have lost their protein‐coding ability, often the result of multiple mutations within a gene
Repeated genes
Multiple copies of small genes clustered throughout the genome at specific sites
What gene type(s) are present in high copy number?
Repeated genes
T or F: Repeated genes are few times present in a "head‐to‐tail" configuration
False, they are many times present
What are two examples of repeated genes?
genes for tRNA and rRNA
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
1 GENE (genotype) -> 1 mRNA (intermediate) -> 1 "PROTEIN" (phenotype)
DNA to mRNA is called
transcription
Where does transcription occur?
Cell nucleus in eukaryotes
When does transcription occur?
Either G1/S or G2/M
Template strand
DNA strand that mRNA is built from