2.3 Plasma Membrane, 2.4 Membrane Permeability
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Plasma membrane
separates internal cell environment from external environment
compromised primarily of phospholipids
phospholipids are ampiphatic (have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions),forms a bilayer
polar hydrophilic heads (phosphate regions) are oriented TOWARD aqueous environment
nonpolar hydrophobic tails(fatty acid regions) are facing inwards, AWAY from aqueous environments
hydrophobic interior causes the membrane to be selectively permeable
structure is described by the fluid mosaic model
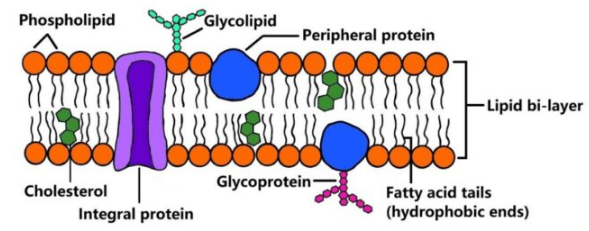
Fluid mosaic model
a model to describe the structure of the cell membrane
fluid: membrane is held together by weak hydrophobic interactions and can therefore move and shift
temperature affects fluidity
unsatured hydrocarbon tails help maintain fluidity at low temps(kinked tails prevent tight packing of phospholipids
cholesterol helps maintain fluidity at high and low temps
at high temps, cholesterol reduces movement so the phospholipids don’t spread too far
at low temps, cholesterol reduces tight packing of phospholipids
mosaic: comprised of many macromolecules
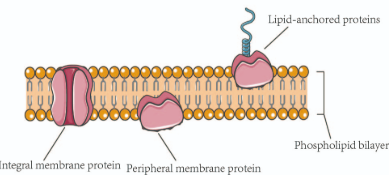
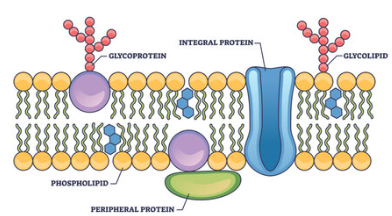
Membrane proteins
Integral proteins and peripheral proteins
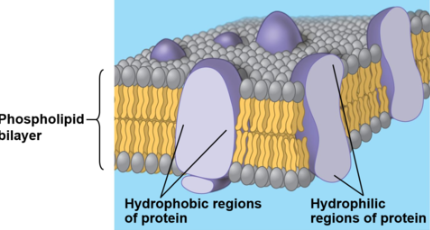
Integral proteins
proteins that are embedded into the lipid bilayer
can be hydrophilic, hydrophobic, or both (determined by R groups/side chains)
hydrophilic= polar or ionic side chains, hydrophilic regions make up the interior of the channel or pore
hydrophilic regions are exposed to the cytosol
hydrophobic= nonpolar side chains
hydrophobic regions make up the protein surface and interact with fatty acids
Peripheral proteins
proteins that are not embedded into the lipid bilayer
loosely bonded to the surface
Membrane Carbohydrates
important for cell to cell recognition
glycolipids are carbohydrates bonded to lipids
glycoproteins are carbohydrates bonded to proteins,most abundant
Selective permeability
the ability of membranes to regulate the substances that enter and exit
this is due to the hydrophobic interior(non polar hydrophobic tails)
small,non polar, hydrophobic molecules have easy passage across the membrane ex. hydrocarbons,CO2,O2,N2(gases)
hydrophilic polar molecules, large molecules, and ions have difficult passage or protein assisted passage across the membrane due to the non polar hydrocarbon tails
small polar, uncharged molecules (like water and ammonia) can pass through in small amounts
Cell wall
some organisms also have cell walls that cover their plasma membrane like bacteria,archaea,fungi and plants
function is to provide structural boundary (defines and supports the cell’s shape), provide a permeability barrier for some substances, and protection from osmosis lysis(cell bursting when excess water goes into cell)
in plants, the cell wall is composed of cellulose, it’s thicker than plasma membranes, contains plasmodesmata(hole like structures in the cell wall filled with cytosol that connect with adjacent cells)