Comparative Male Reproductive Anatomy
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Perineal hernia
escape of pelvic viscera due to weakness or atrophy of muscles of pelvic diaphragm
presents as swelling to side of anus
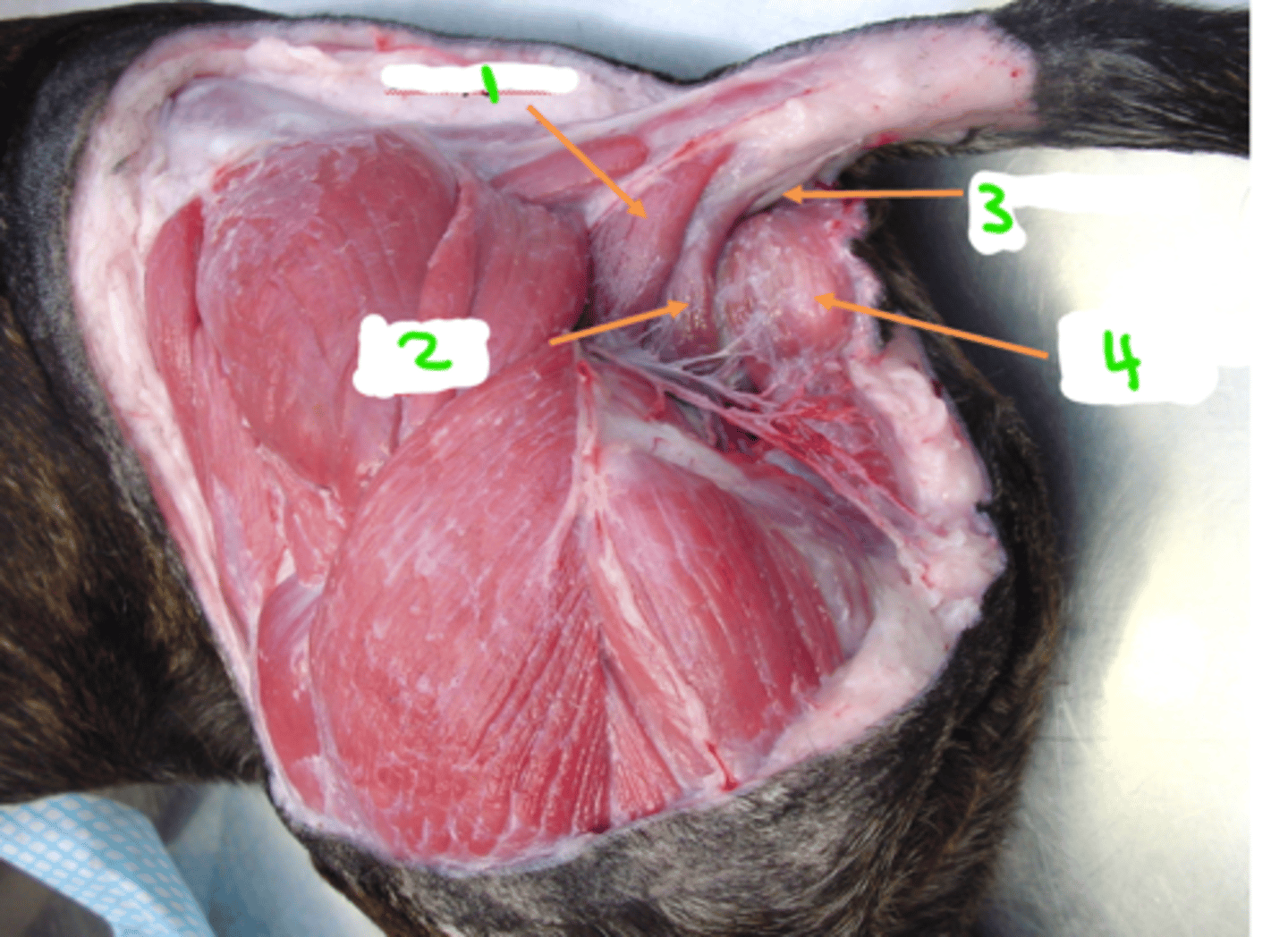
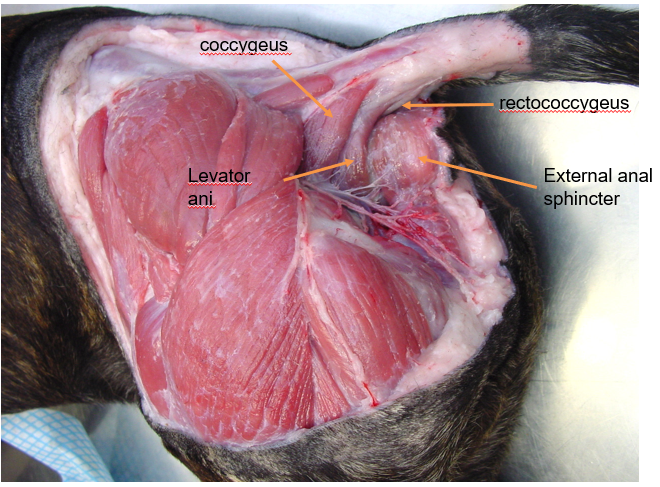
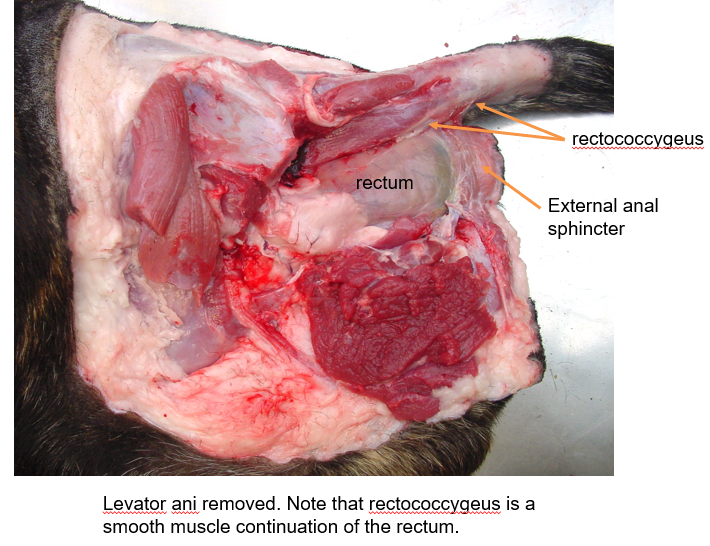
Male perineal anatomy
1 = coccygeus —> depresses tail
2 = levator ani —> depresses tail
3 = retrococcygeus —> continuous with rectus
4 = external anal sphincter
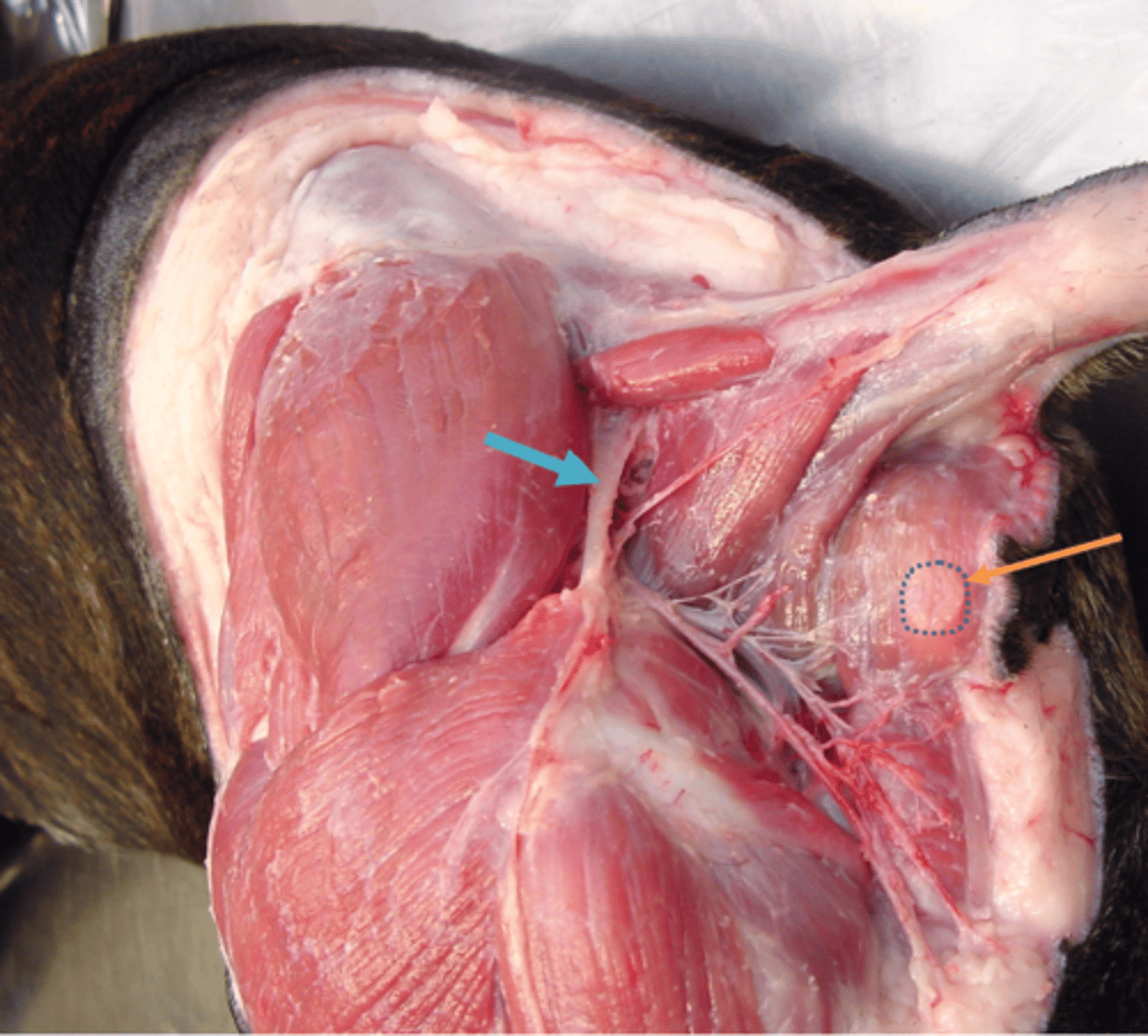
What are the blue arrow and orange arrow pointing to?
Blue = sacrotuberous ligament
Orange = anal sac —> lies between internal & external anal sphincters
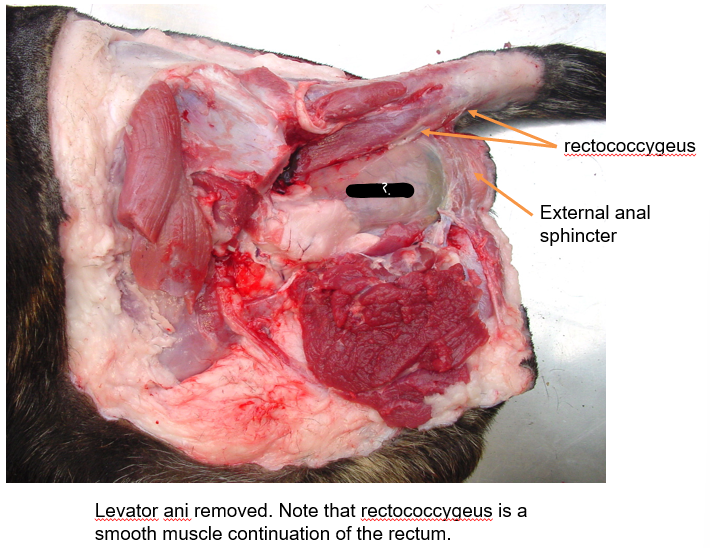
What is this structure?
Rectum
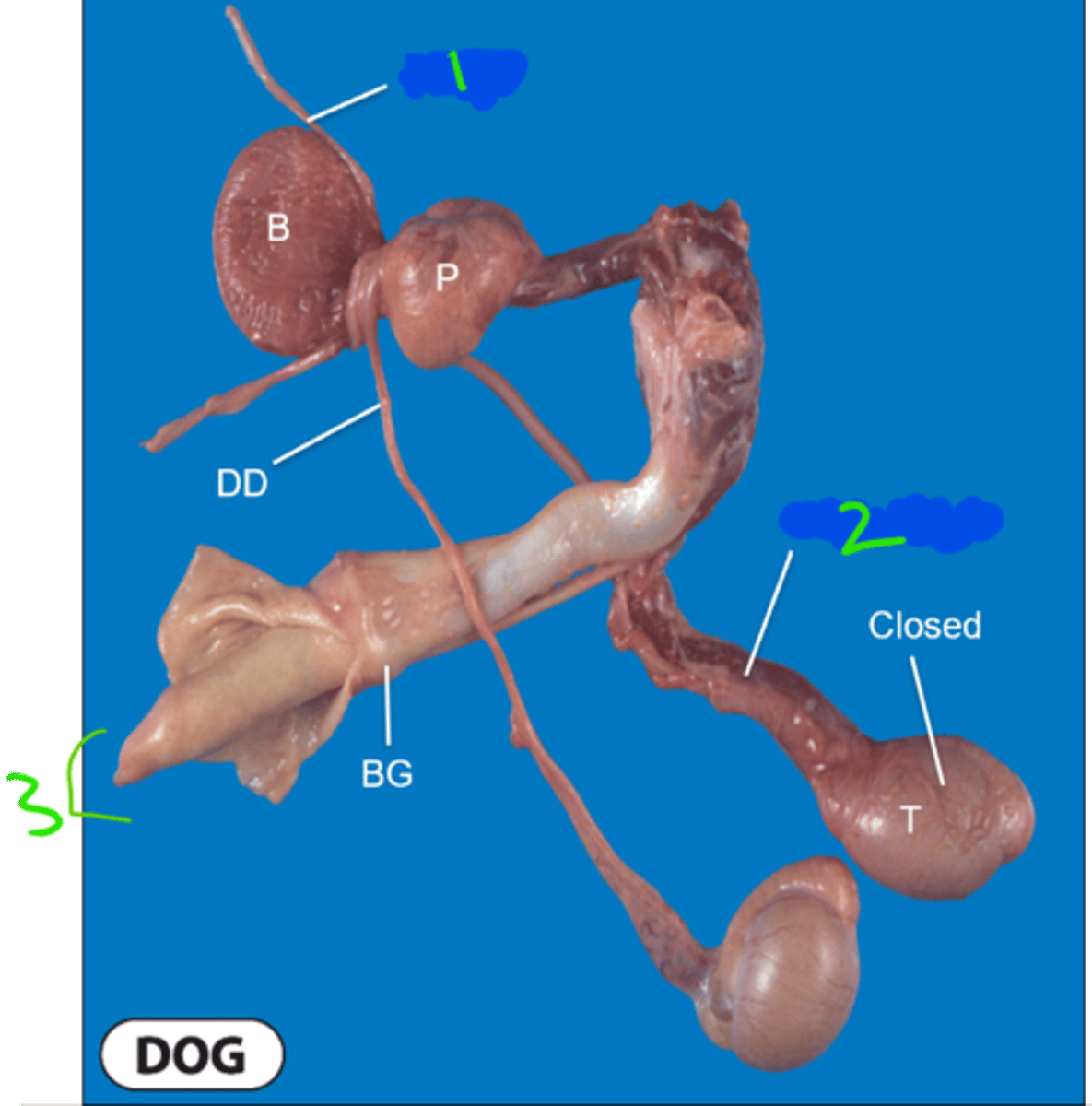
Dog Penis Anatomy
Name 1-3 and all other parts
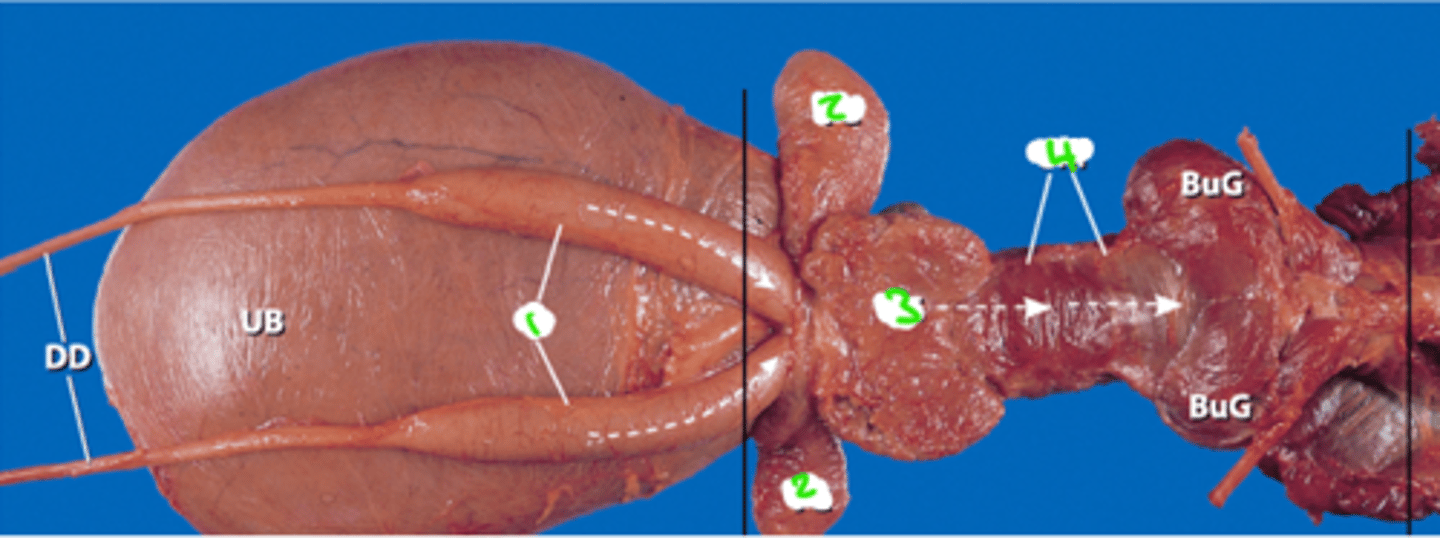
1 = ureter
2 = cremaster muscle
3 = glans penis
B = bladder
P = prostrate
DD = ductus deferens
BG = bulbus glandis
T = testes
What are the three parts of a penis?
Base (root) - attaches to ischial arch
Shaft - main proportion
Glans penis - end tip (variable morphology between species)
What are the two basic penile anatomy models?
Which species exhibit these?
Musculocavernous - dog & stallion
Fibroelastic - boar, bull & ram
Key features of musculocavernous penis
Erection dependent upon sinusoids that fill with blood
No sigmoid flexure
What is unique about a dog's bulbus glandis?
Allows them to face in opposite direction during intraomission
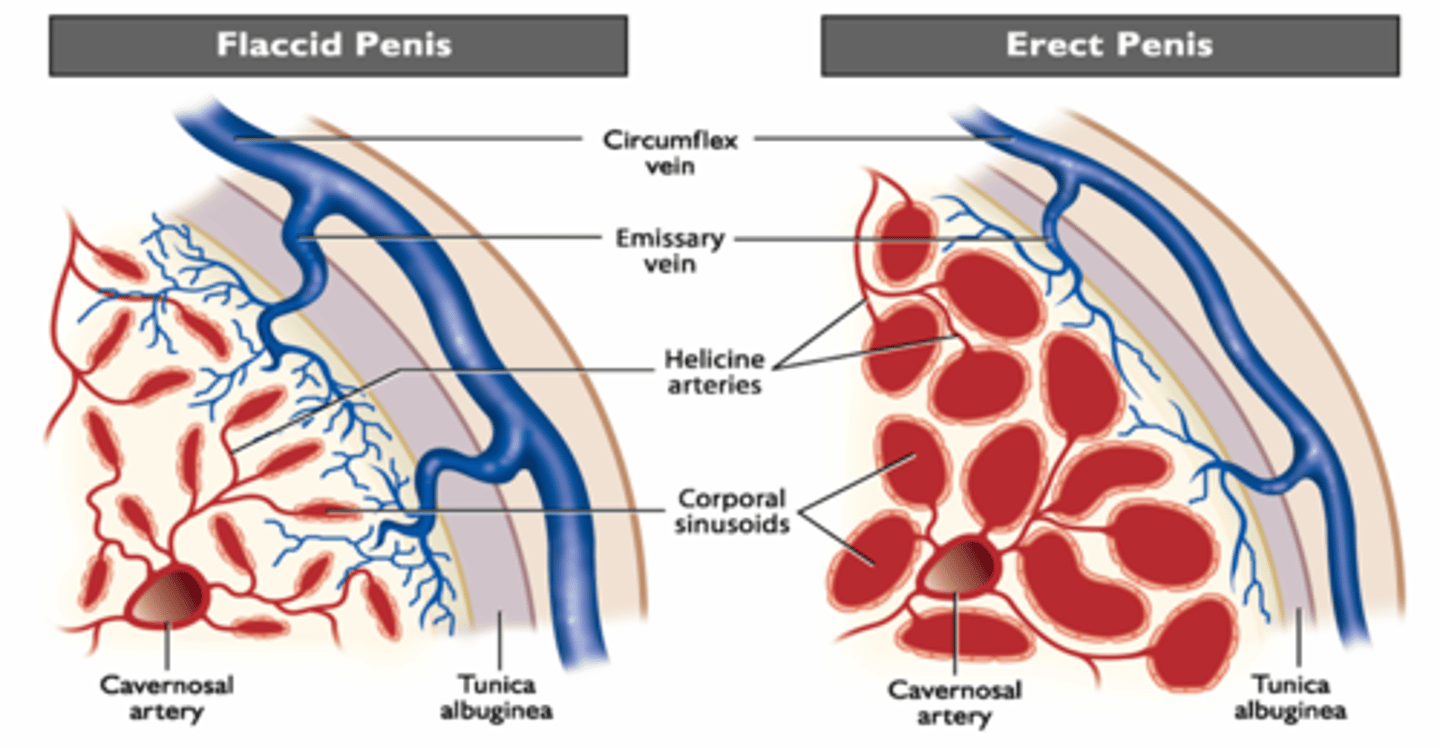
Mechanism of erection in musculocavernosus penises
- increased arterial blood inflow
- sinusoids dilate (parasympathetic NANC neurones)
- restricted venous flow
- increased intrapenile pressure
- penis diameter increases (in horse & dog)
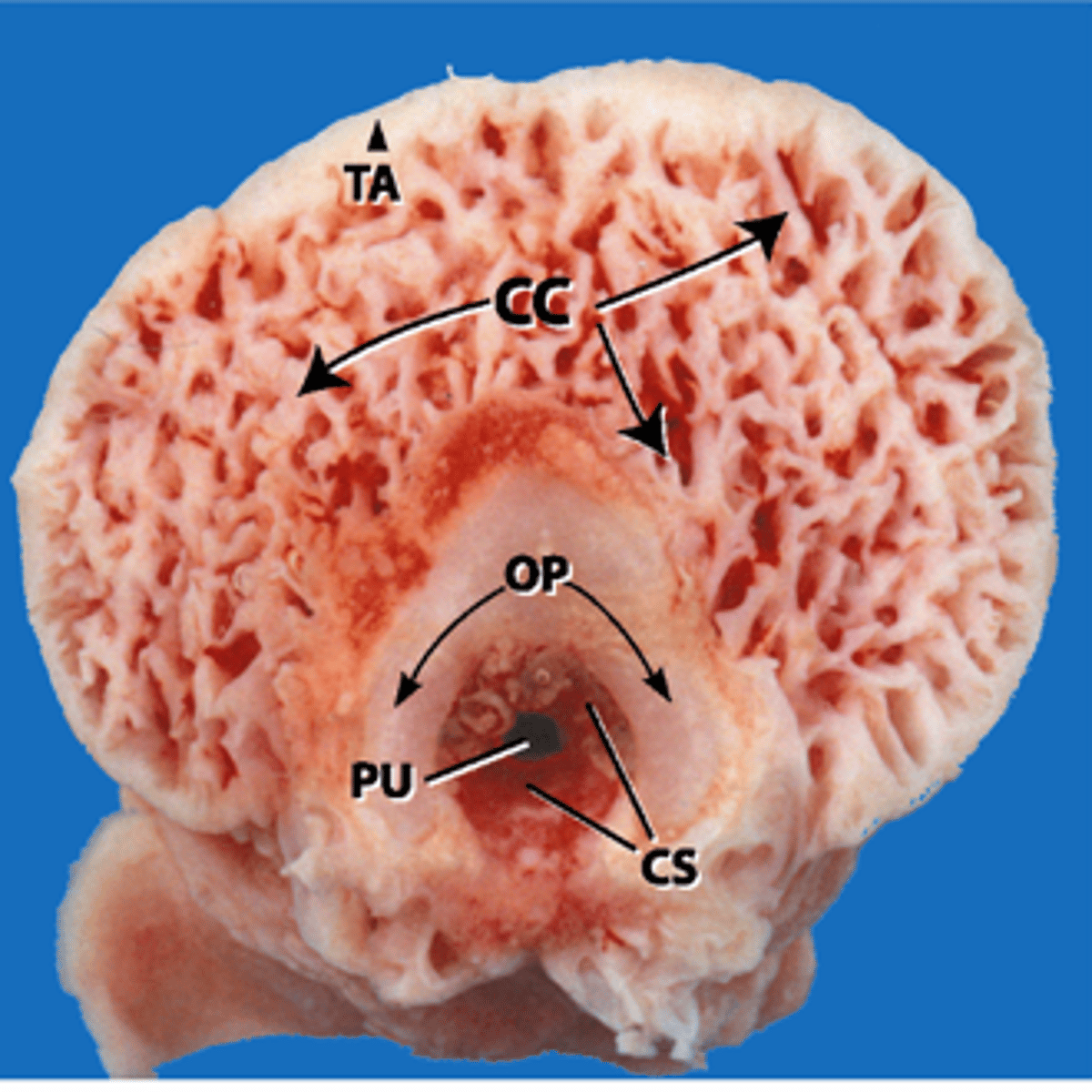
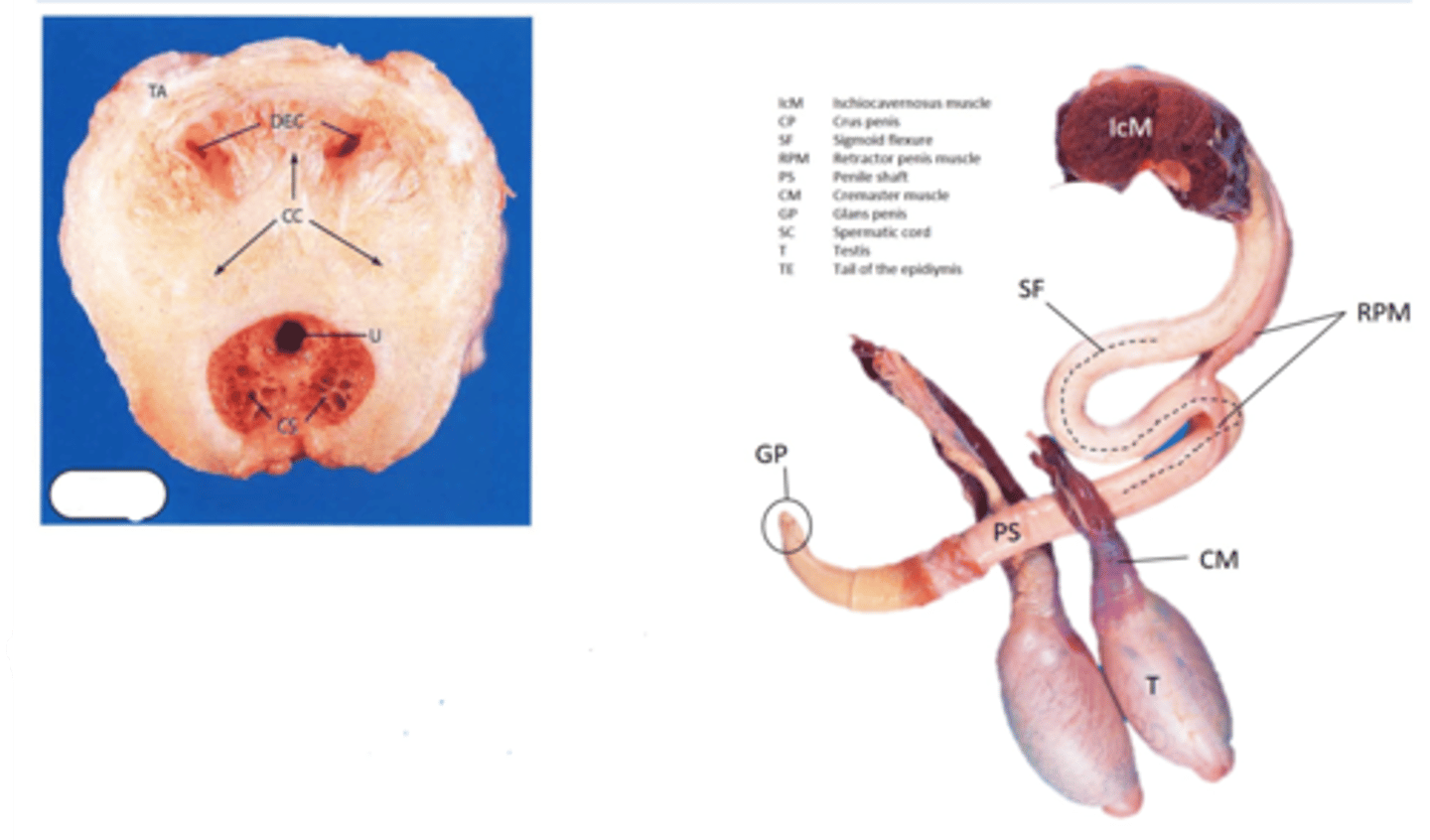
Name tissues within glans penis
TA = tunica albugenia
CC = corpus cavernosum
OP = os penis
PU = penile urethra
CS = corpus spongiosum
Fibroelastic penis key features
- limited erectile tissue from dense tunica albuginea
- sigmoid flexure —> S-shaped configuration along shaft allows to be retracted within sheath until erection
- erection is stiffening without significant change in diameter
- sigmoid flexure maintained by pair of retractor penis muscles
Mechanism of erection in a fibroelastic penis
relaxation of retractor penis muscles & blood filling corpus cavernosum & corpus spongiosum
What species does this penis belong to? What are its key features?
Bull
retractor penis holds sigmoid flexure
retractor penis m. is a lot bigger
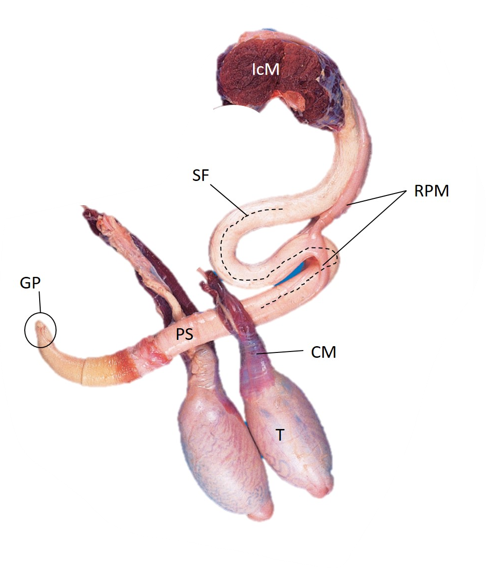
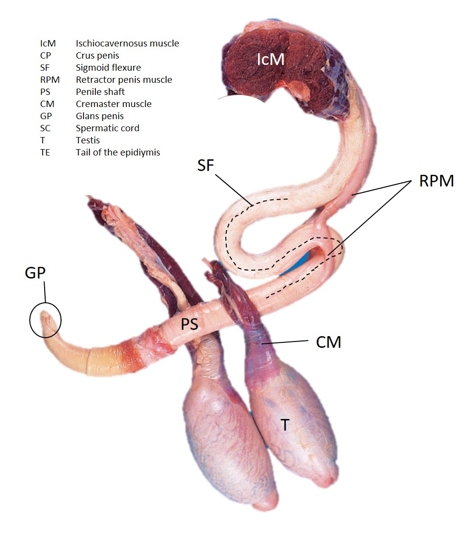
Name the parts of the bull penis
What species does this penis belong to? What are its key features?
Boar
Fibroelastic
Sigmoid flexure is prescrotal
corkscrew shape enables it to lock within sow cervix
Name muscles 1-4 associated with the penis (dog)
1 = Urethralis —> striated, surrounds pelvic urethra, moves semen into penile urethra
2 = Ischiocavernosus —> paired, short muscles in root of penis
3 = Bulbospongiosus —> overlaps root of penis, extends down caudal & ventral surfaces to cover bulbourethral glands
4 = Retractor Penis —> smooth muscle
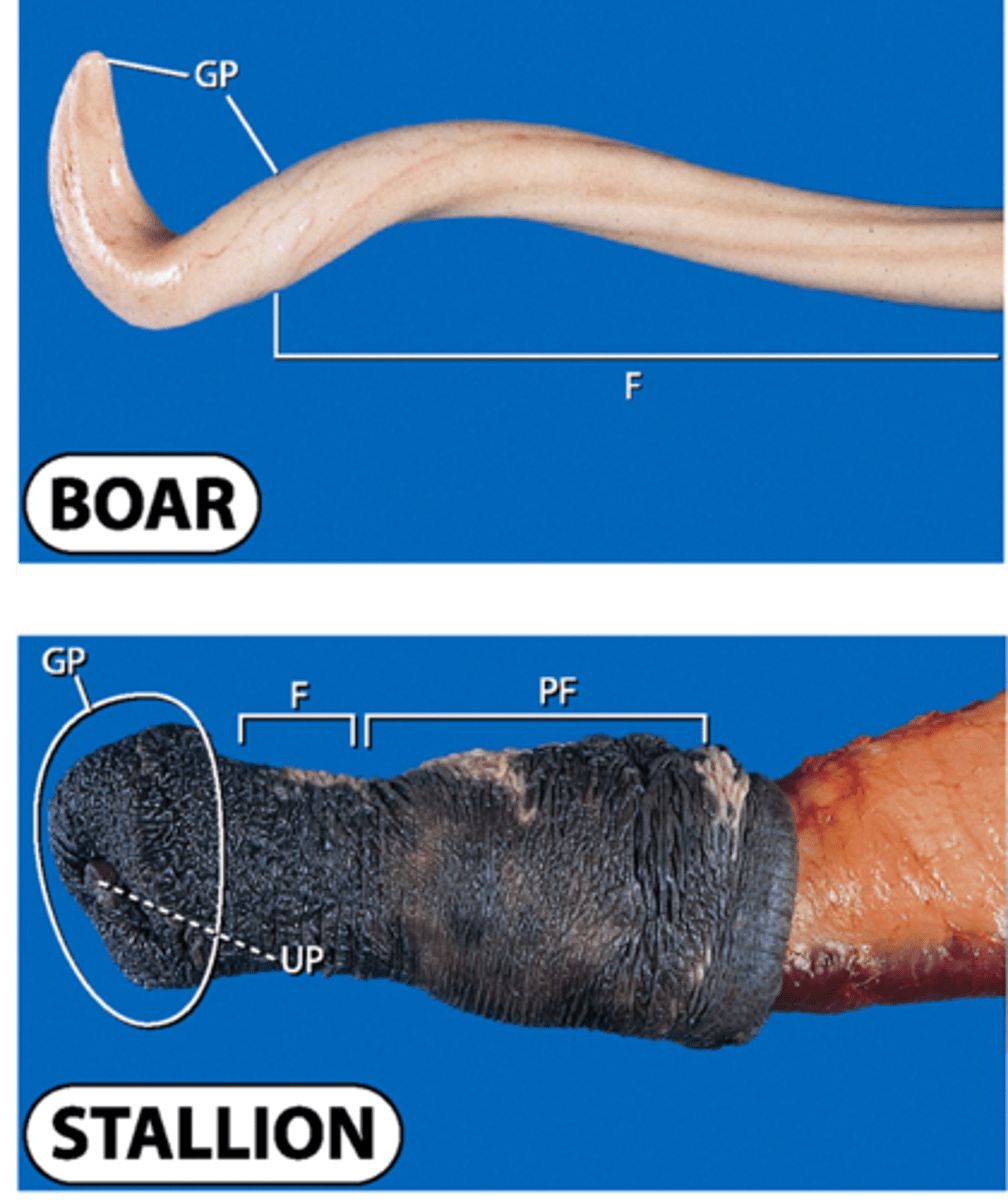
Comparative glans anatomy of boar & stallion
Boar
No glans - terminates in spiral
Locks into sows cervix —> forces ejaculation into uterus
Stallion
Urethral process is sunk into deep fossa glandis
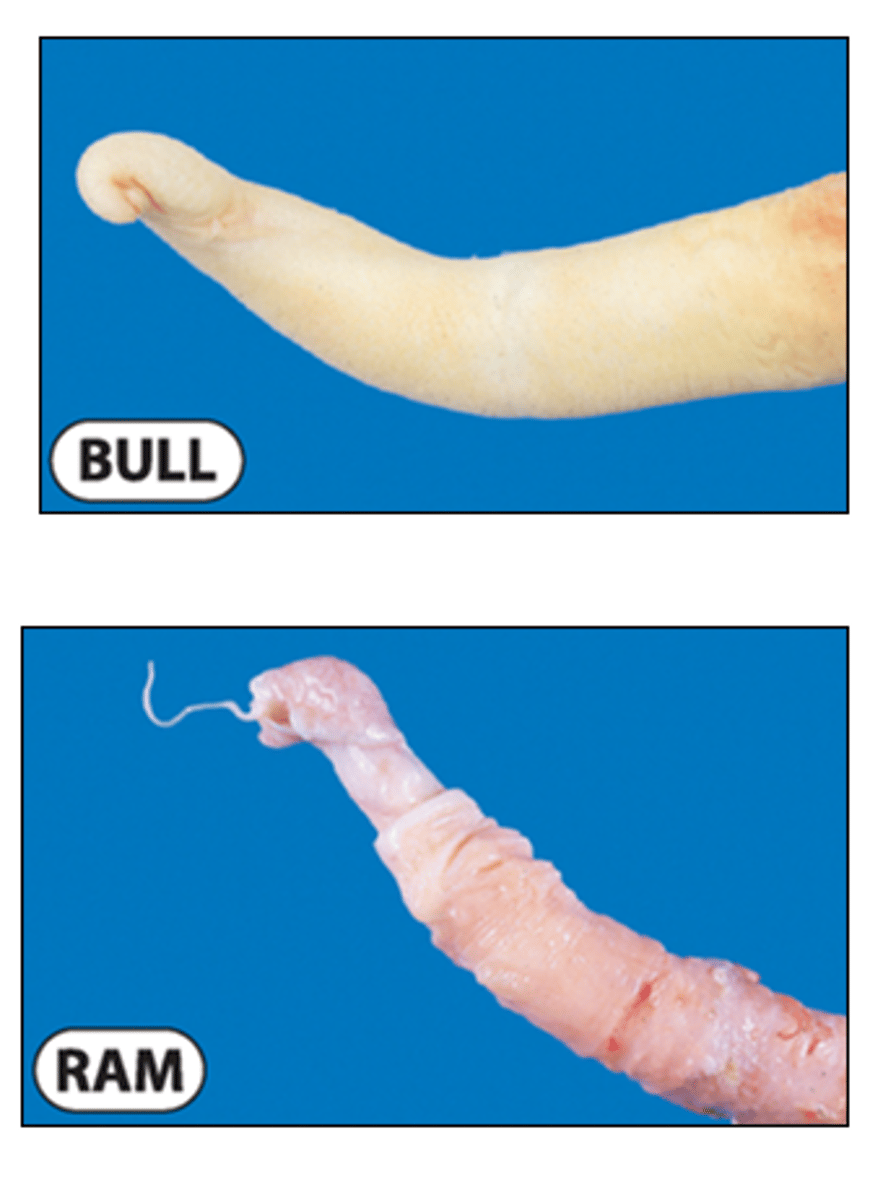
Comparative glans anatomy of bull & ram
Bull
penis tapers to a point
Ram
similar but has vermiform appendage (worm-like urethral process —> extention of urethra)
No bulbus glandis or os penis (unlike dog)
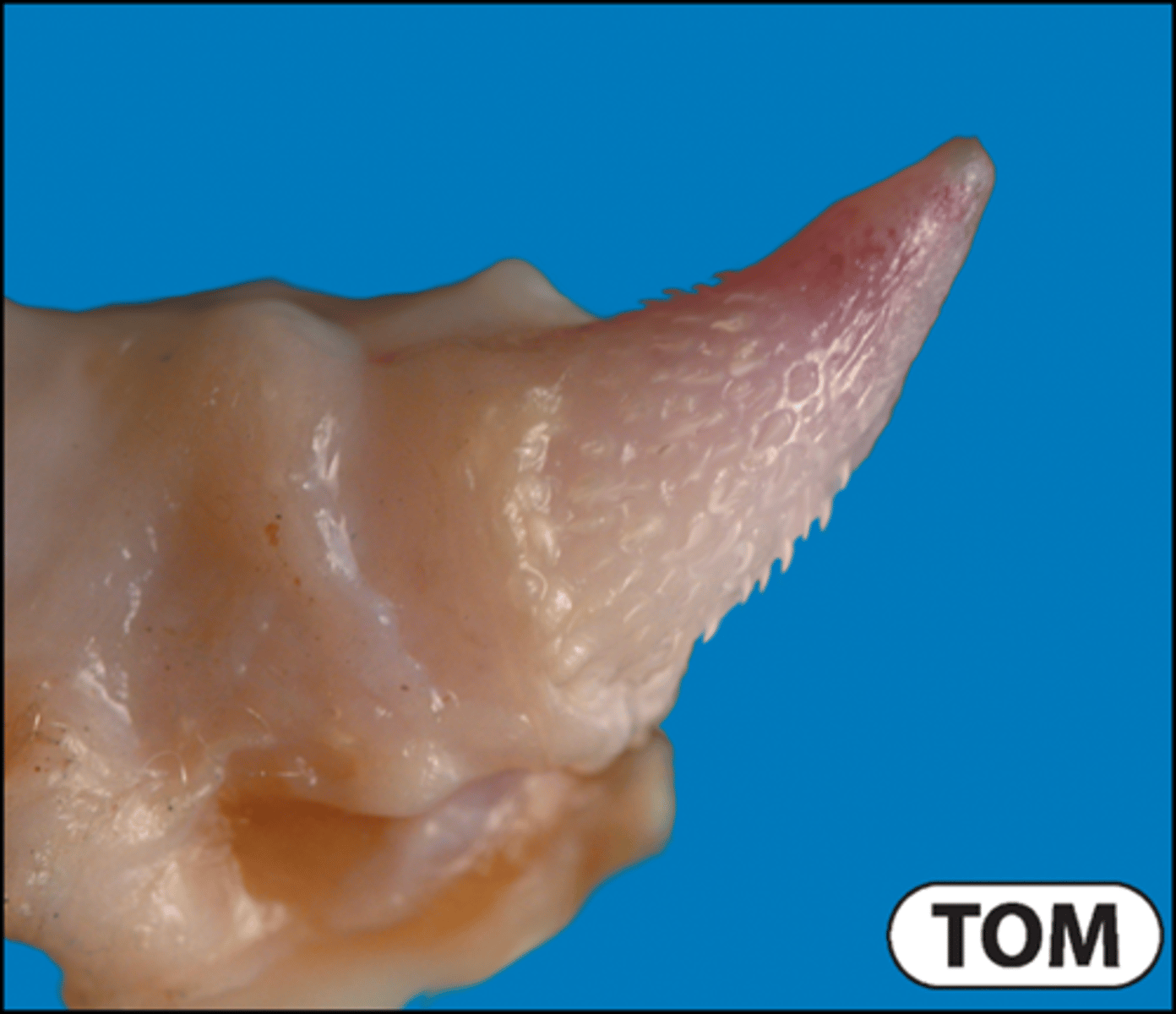
Anatomy of the tom cat glans penis
Cornified spines - stimulate reflex ovulation
Dependent upon androgens (disappear in neutered animals)
Describe urethral calculi (stones)
From bladder
Can get caught in penile urethra —> unable to pass urine
Common “pinch points” where urethral calculi obstruction occurs in:
Dogs
Bulls
Rams
Dogs —> base of os penis
Bulls —> proximal end of sigmoid flexure/ischial arch
Rams —> vermiform appendage
What is the function of the accessory sex glands?
Produces seminal plasma —> correct pH, ionic content and with nutrients for survival
small in immature animals & animals castrated prior to puberty
Post-pubertal castration leads to atrophy of glandular component
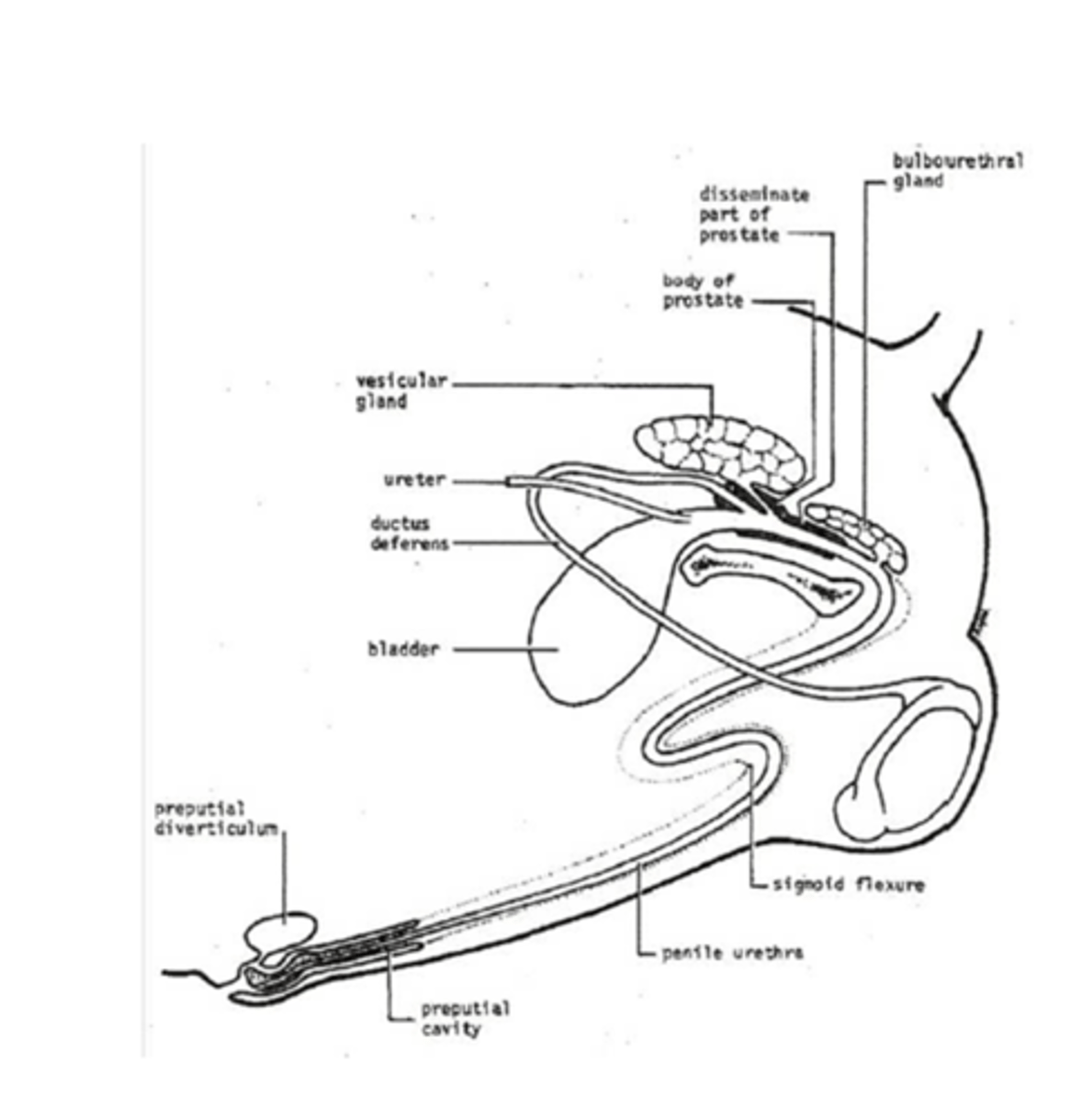
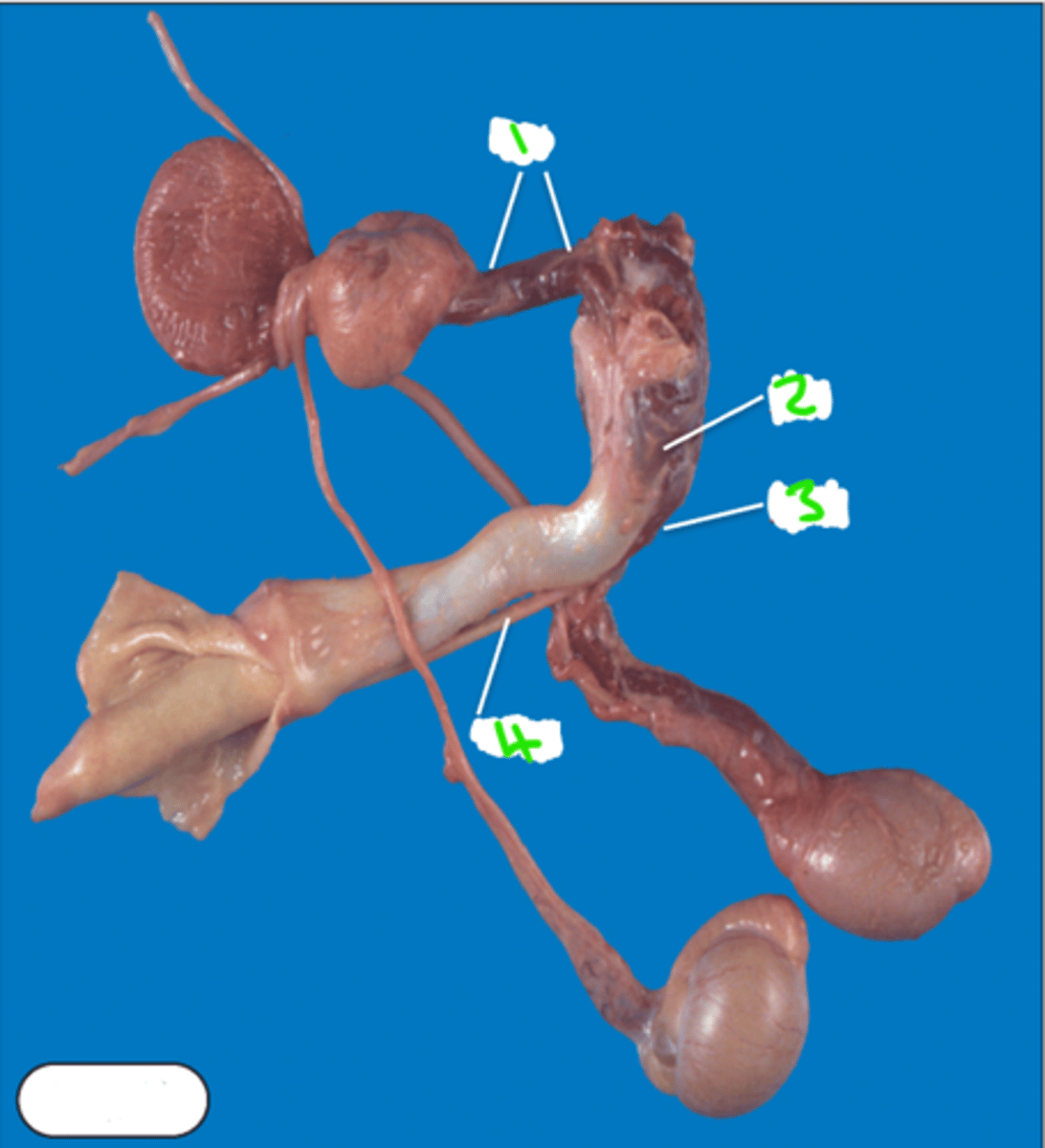
Label the accessory sex glands of the stallion
1 = ampulla —> enlargments of ductus deferens, open directly into pelvic urethra
2 = vesicular glands
3 = prostrate —> consists of compact body & diffuse tissue within wall of pelvic urethra
4 = bulbourethral gland
Comparative scrotum anatomy of bulls, stallions and boars
Bull
long/pendulous marked neck
Stallion
globular with poorly defined neck
Boar
subanal, close to caudal thigh surface
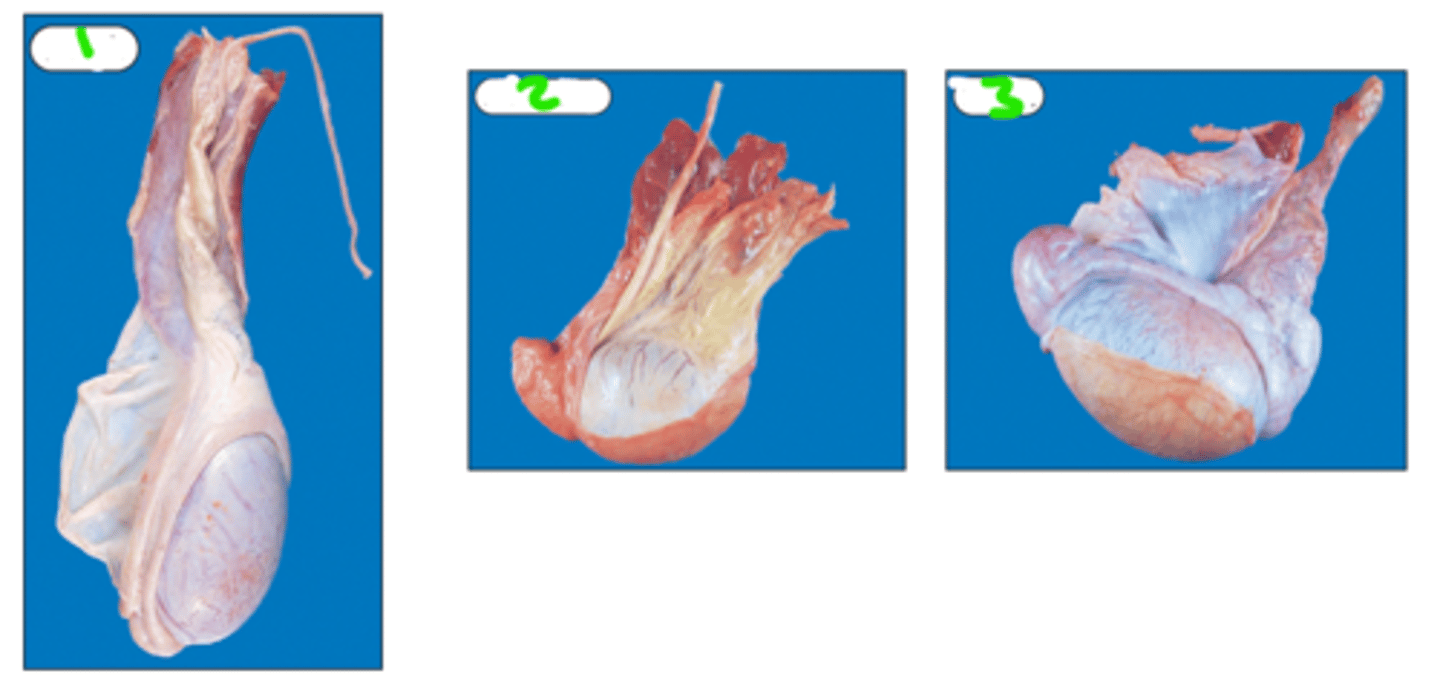
Which testes belong to which species
1 = bull
2 = stallion
3 = boar
Comparative kidney anatomy:
Cats/Dogs/Sheep
Cows
Pigs
Horses
Kidney bean shaped
12 lobed shape
Dorsoventrally flattened
L & R different shapes —> more cranial kidney (i.e. right kidney) more heart shaped
Which species have all 4 male accessory glands present?
Cow, Horse & Sheep
In what situation is the rupture of the bull penis most likely to occur?
At natural service if the female suddenly drops down
Why does the scrotum of bulls (and many other species) not heal well?
They contain lots of sebaceous glands