Pulmonary Exam 1: Physiology Mechanics of breathing (Dr. Leavis)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1/3 of the lung's tendency to collapse is due to:
elastic fibers

2/3 of the lung's tendency to collapse is due to:
alveolar surface tension

_________ results from electrostatic forces between water molecules lining the alveolar walls
Surface tension

On the surface, water molecules interact _______ and with subsurface molecules but are not pulled toward the air interface
laterally
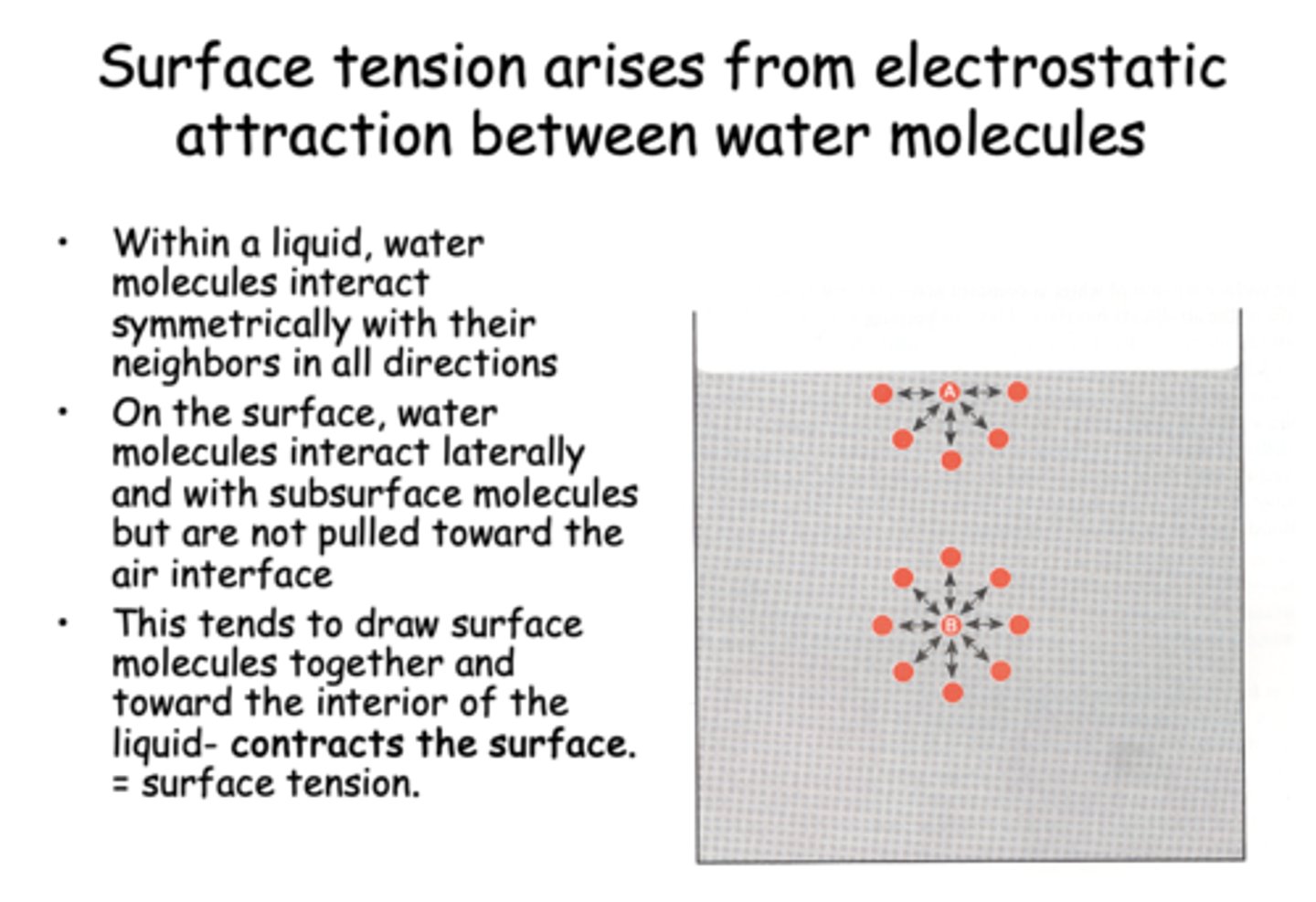
Within a liquid, water molecules interact ______ with their neighbors in all directions
symmetrically
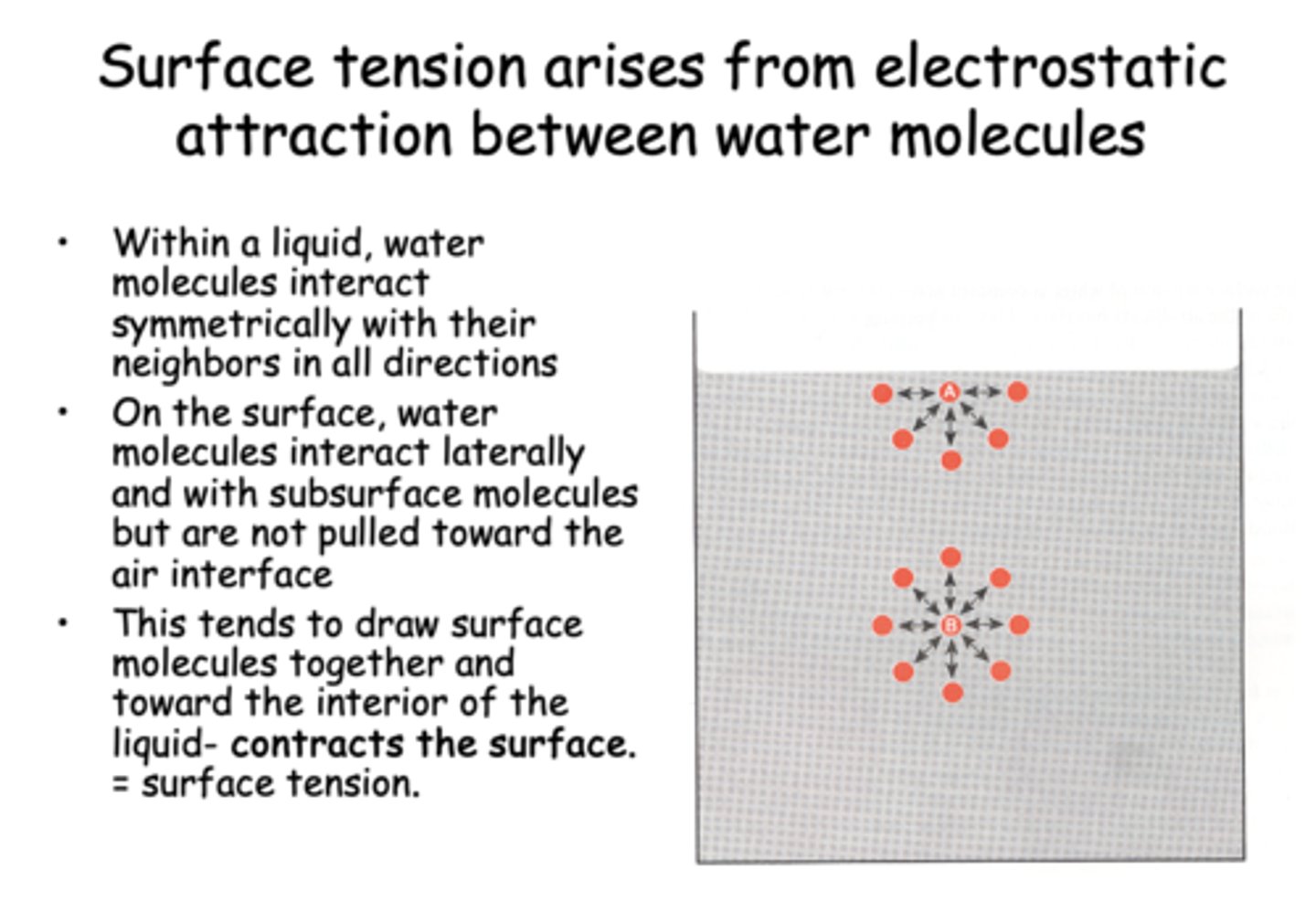
On the surface, water molecules interact laterally and with subsurface molecules but are not pulled toward the air interface. This tends to draw surface molecules together and toward the interior of the liquid- contracts the surface, known as...
Surface tension
In an alveolus, the surface tension created by the thin film of water lining it is directed toward the __________
center
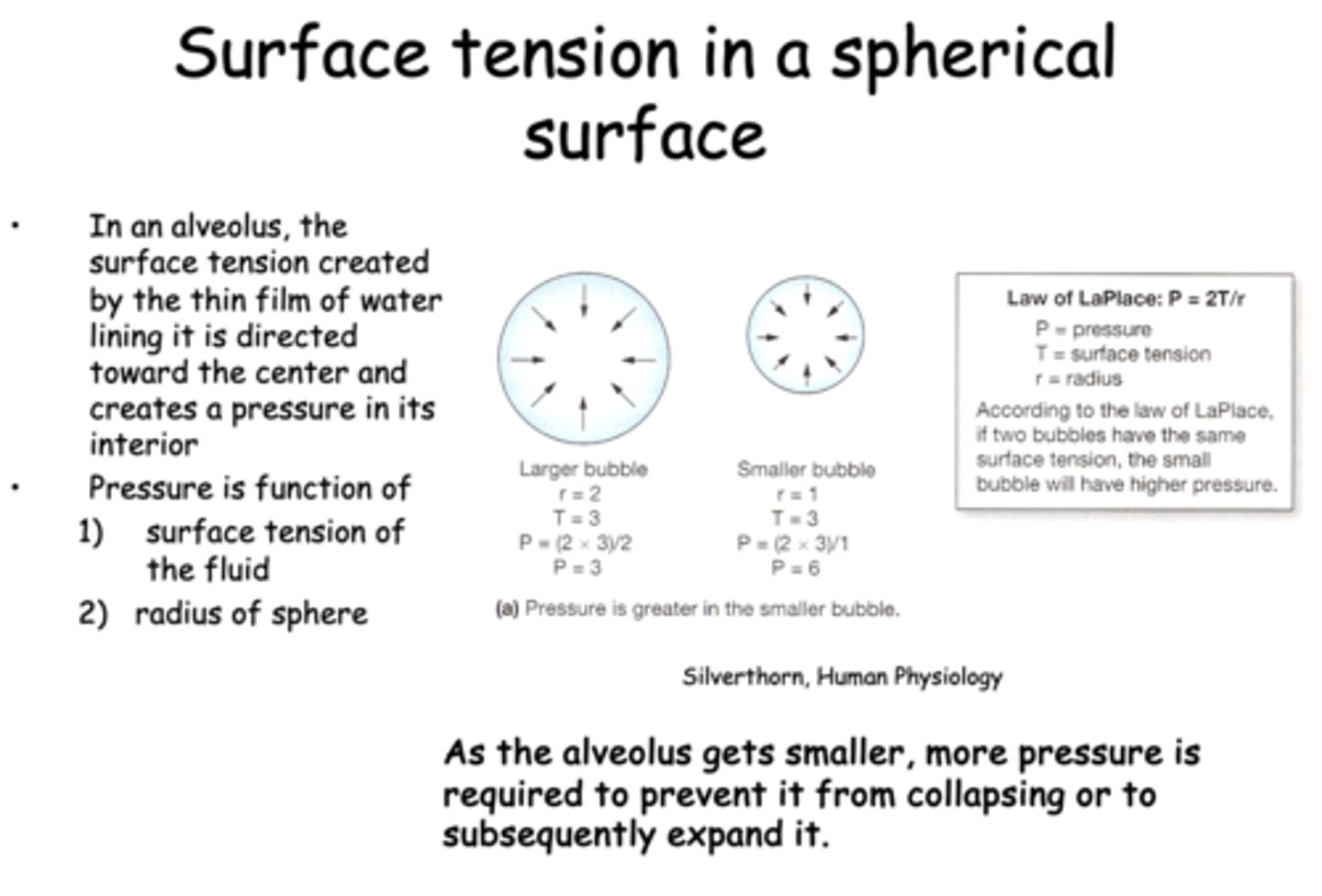
according to the law of LaPlace, if two bubbles have the same surface tension, the one with the _____ radius will have a higher pressure
smaller
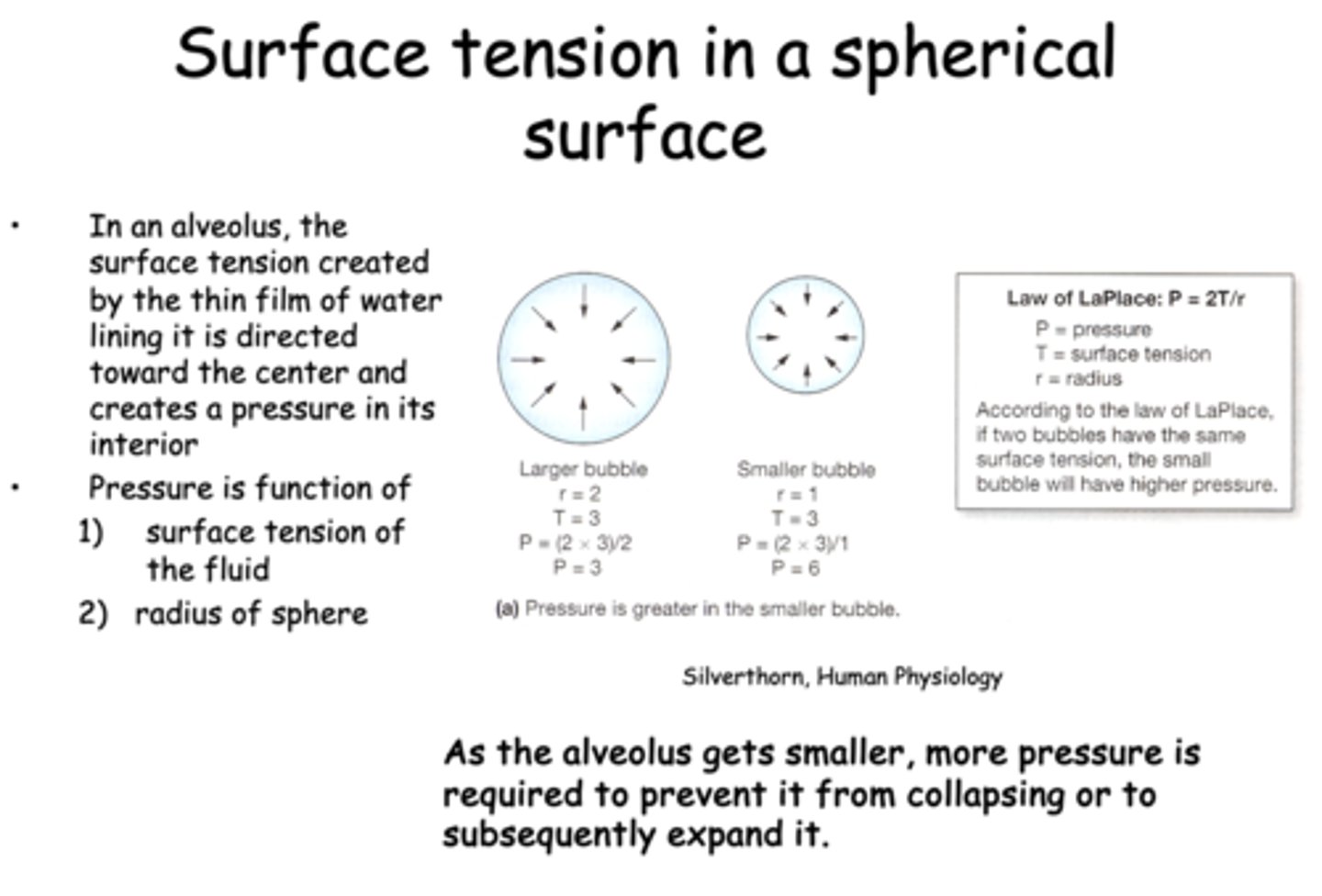
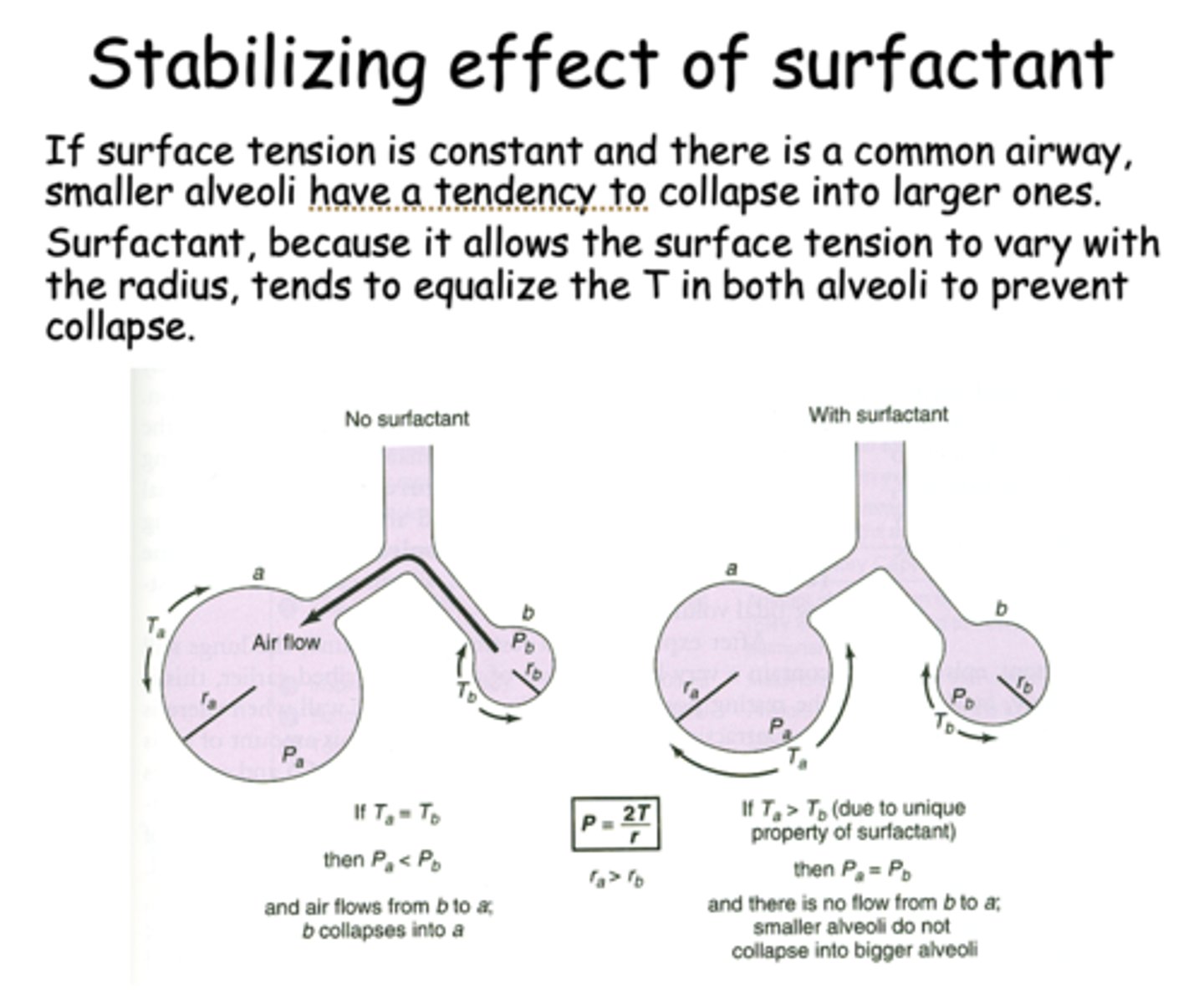
what is the law of LaPlace?
P = 2T/r
pressure inside an alveoli is a function of:
- Surface tension
- Radius
Surfactant is a mixture of:
- Lipids
- Proteins
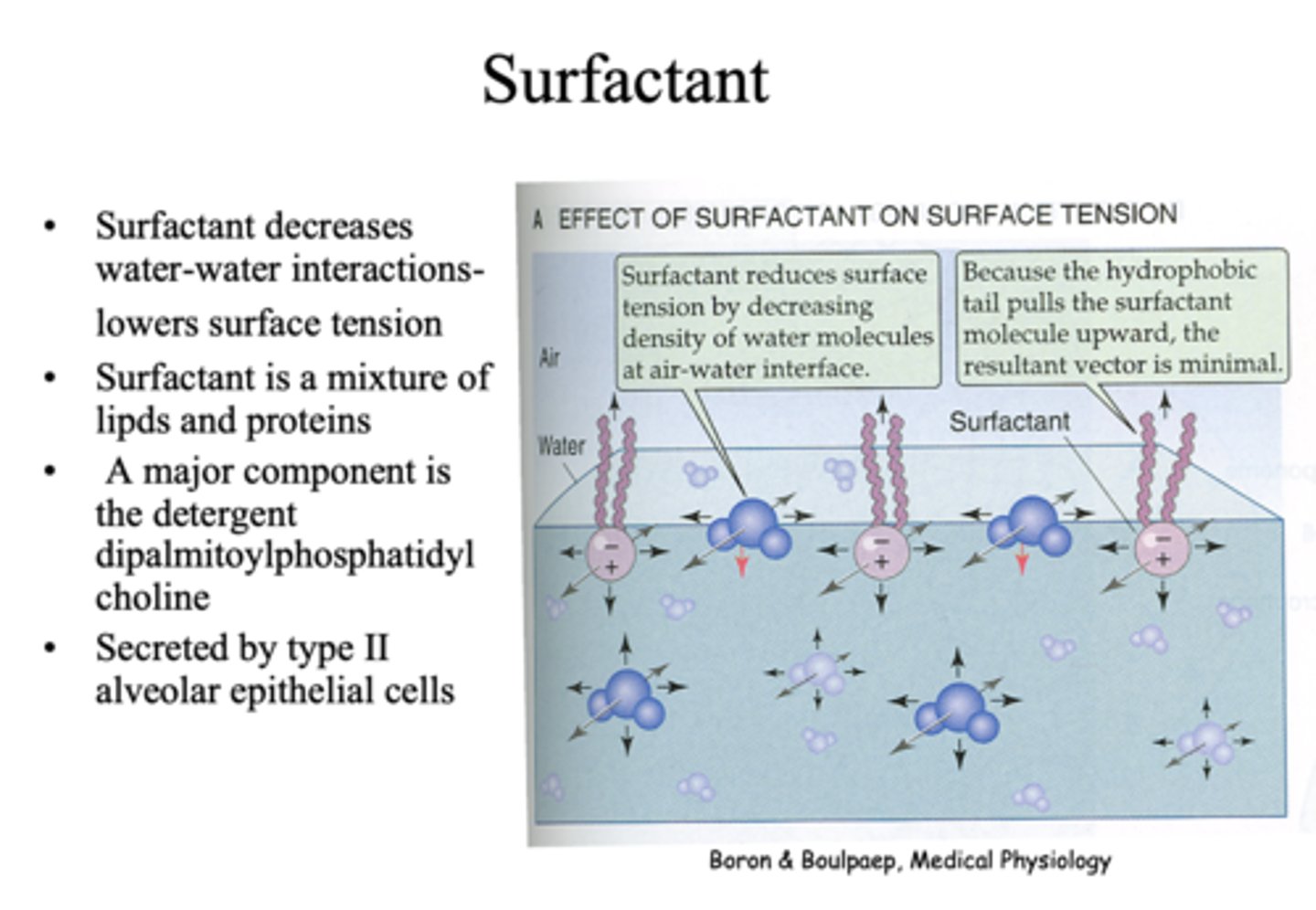
_______ in alveoli decreases water-water interactions- lowers surface tension
surfactant
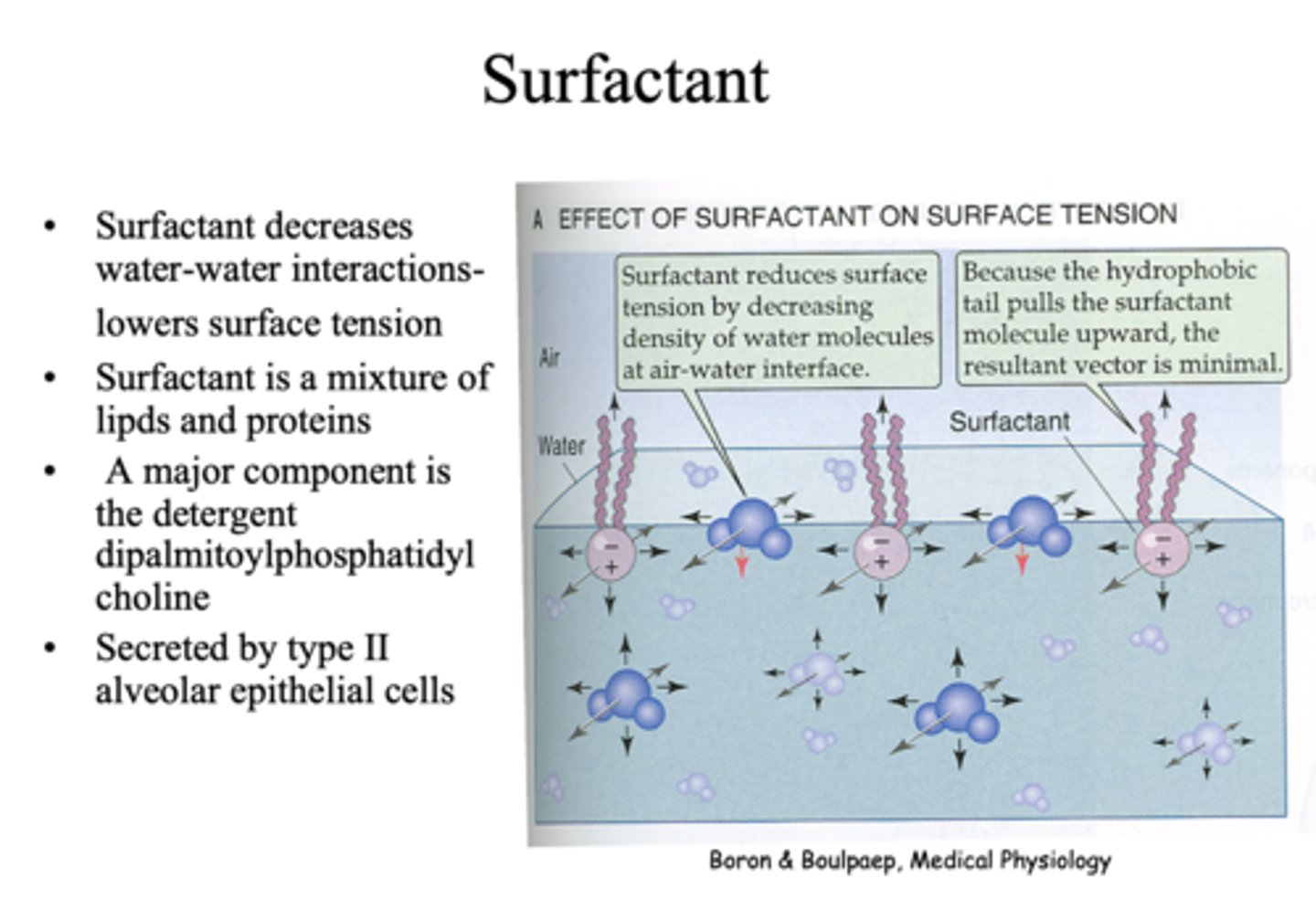
functions of surfactant:
- Water-water interactions/ lowers surface tension
- Equalize the T in alveoli w/ different radii to prevent collapse (allows aveoli of different size to be near each other)
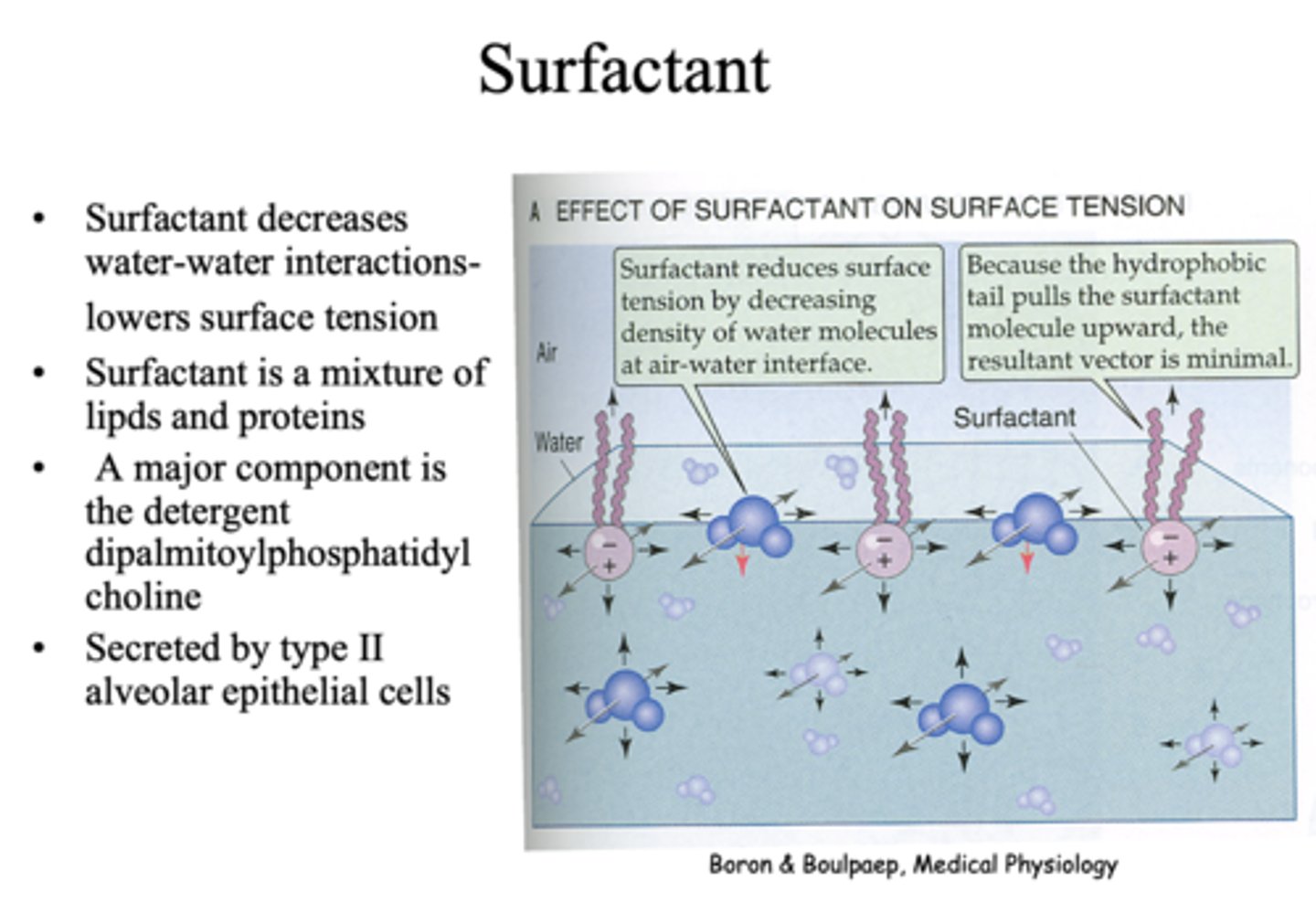
What has the following characteristics?
- A major component is detergent dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine
- Secreted by type II alveolar epithelial cells
surfactant
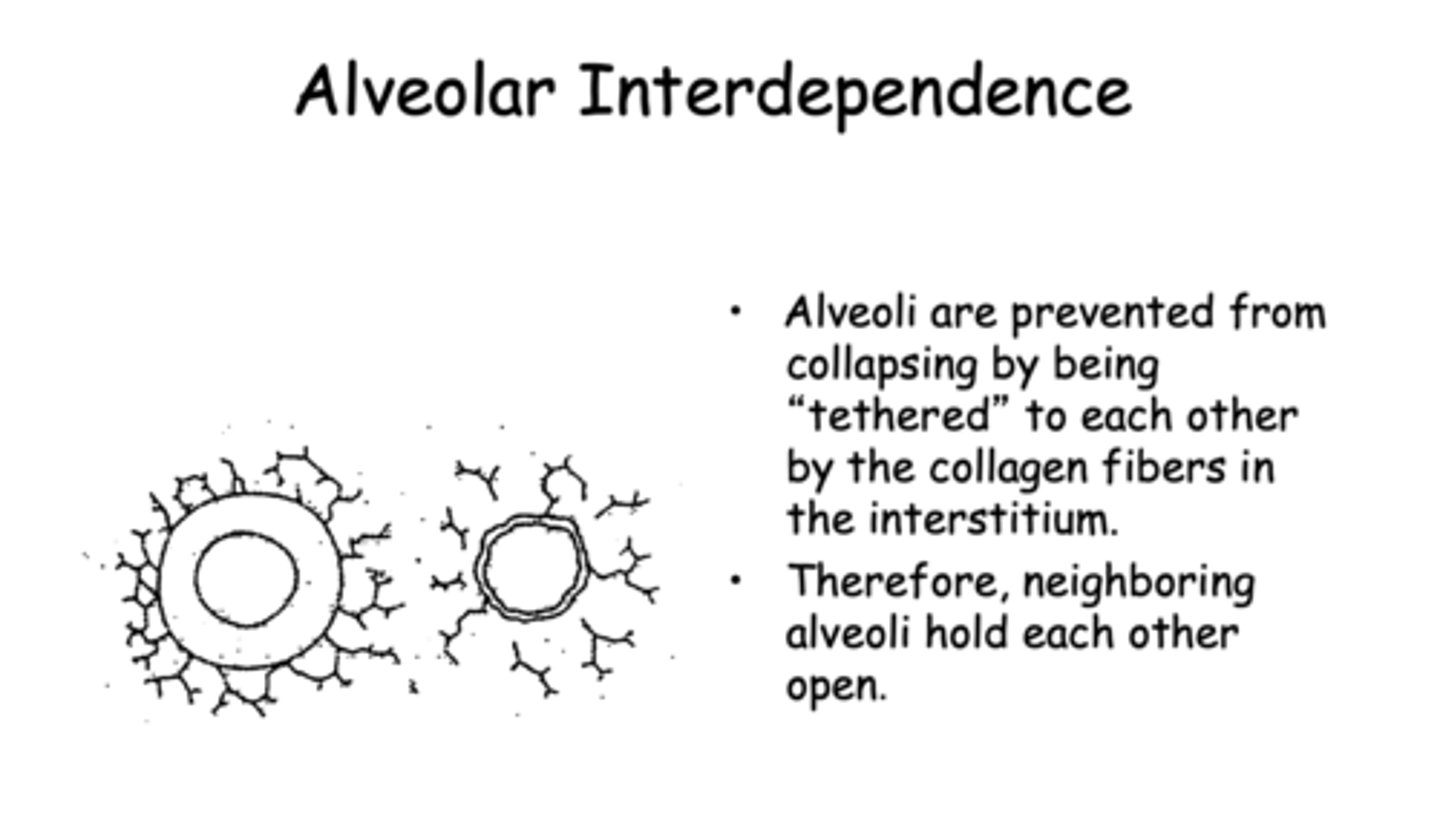
t/f: alveoli can hold each other open due to being tethered by collagen fibers, this also prevents collapsing
true
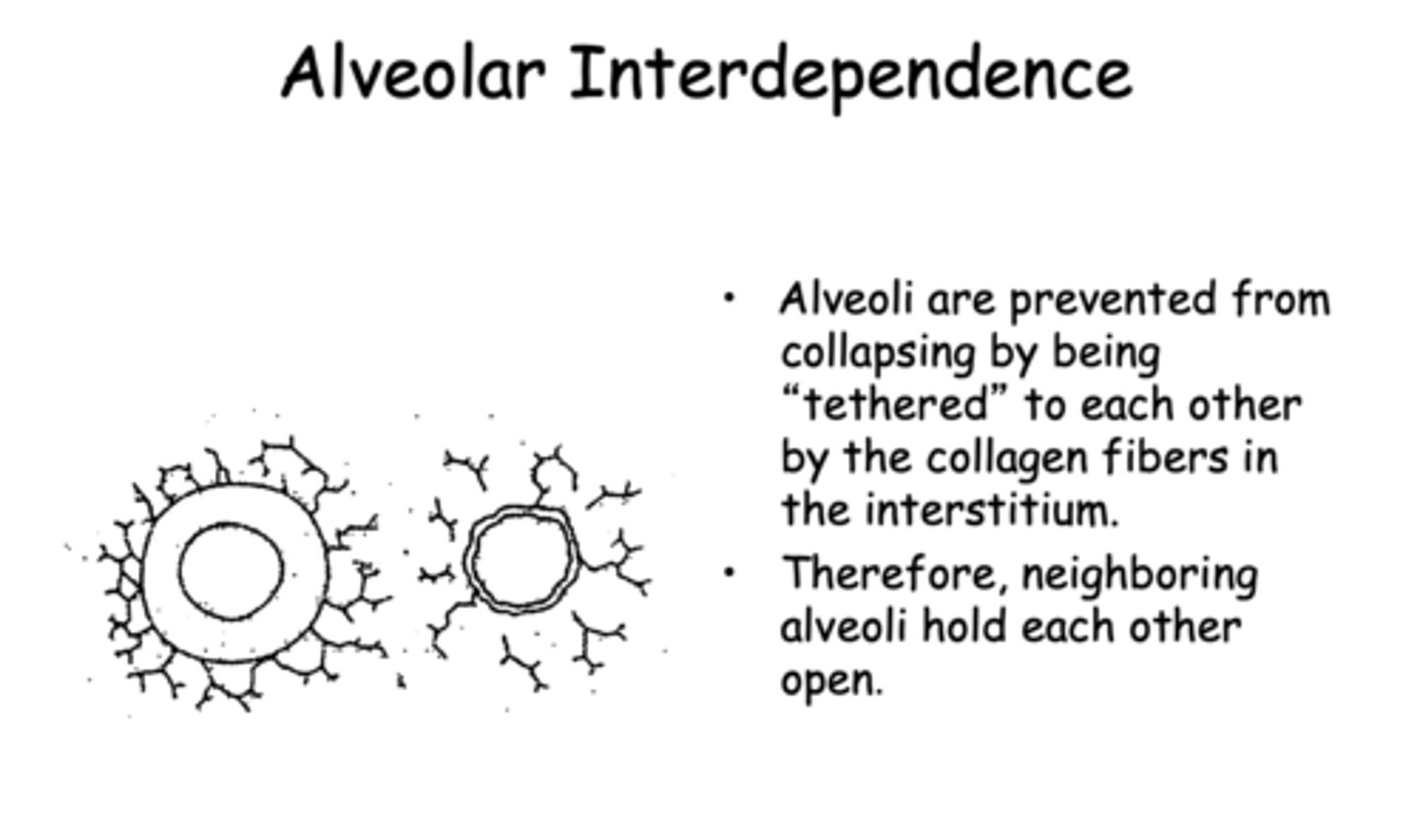
Alveoli are prevented form collapsing by being "tethered" to each other by the collagen fibers in the intersitium. therefore, neighboring alveoli hold each other open, known as _____________
alveolar interdependence
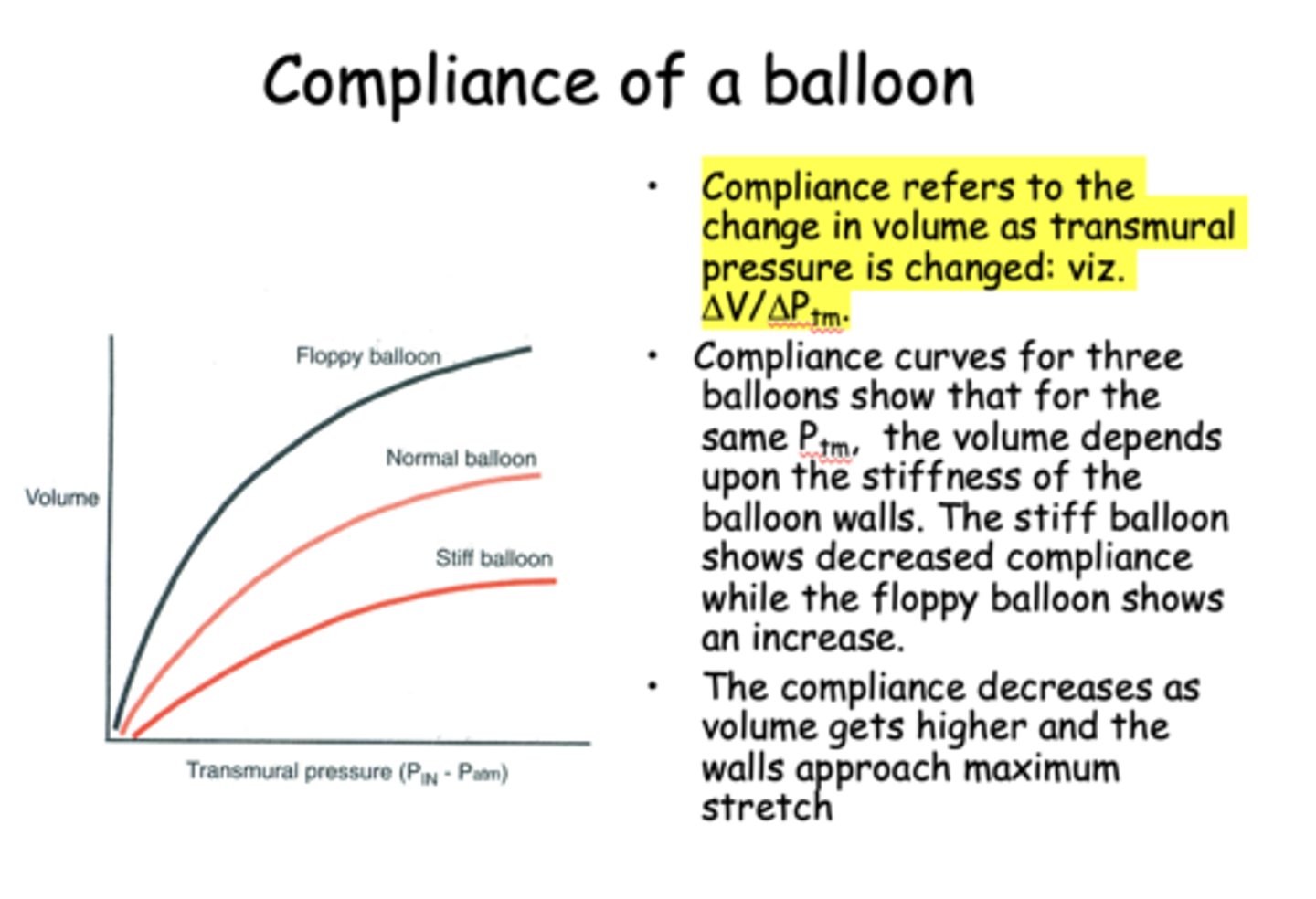
___________ refers to the change in volume as transmural pressure is changed
Compliance
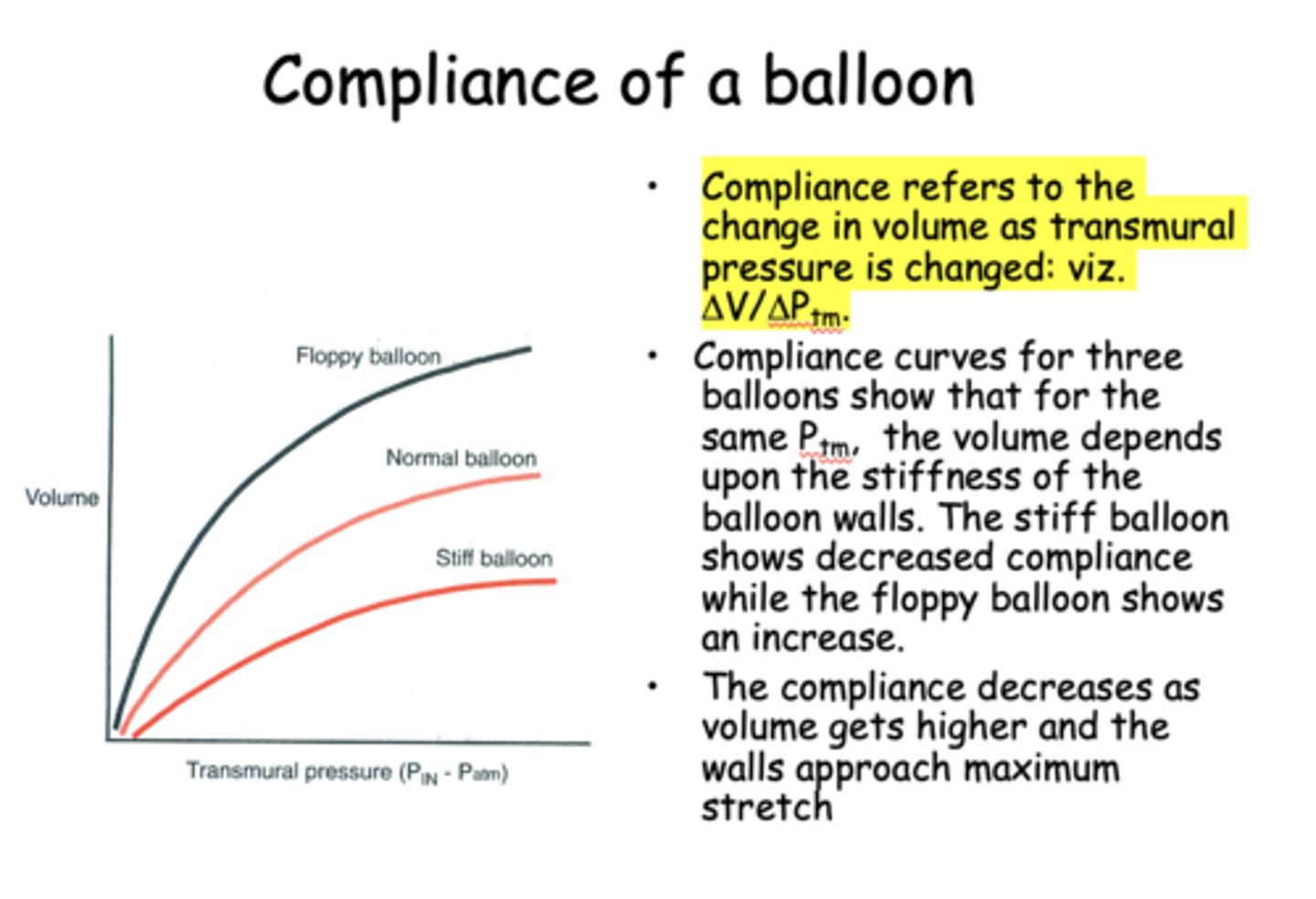
what is the formula for compliance?
change in volume/change in pressure
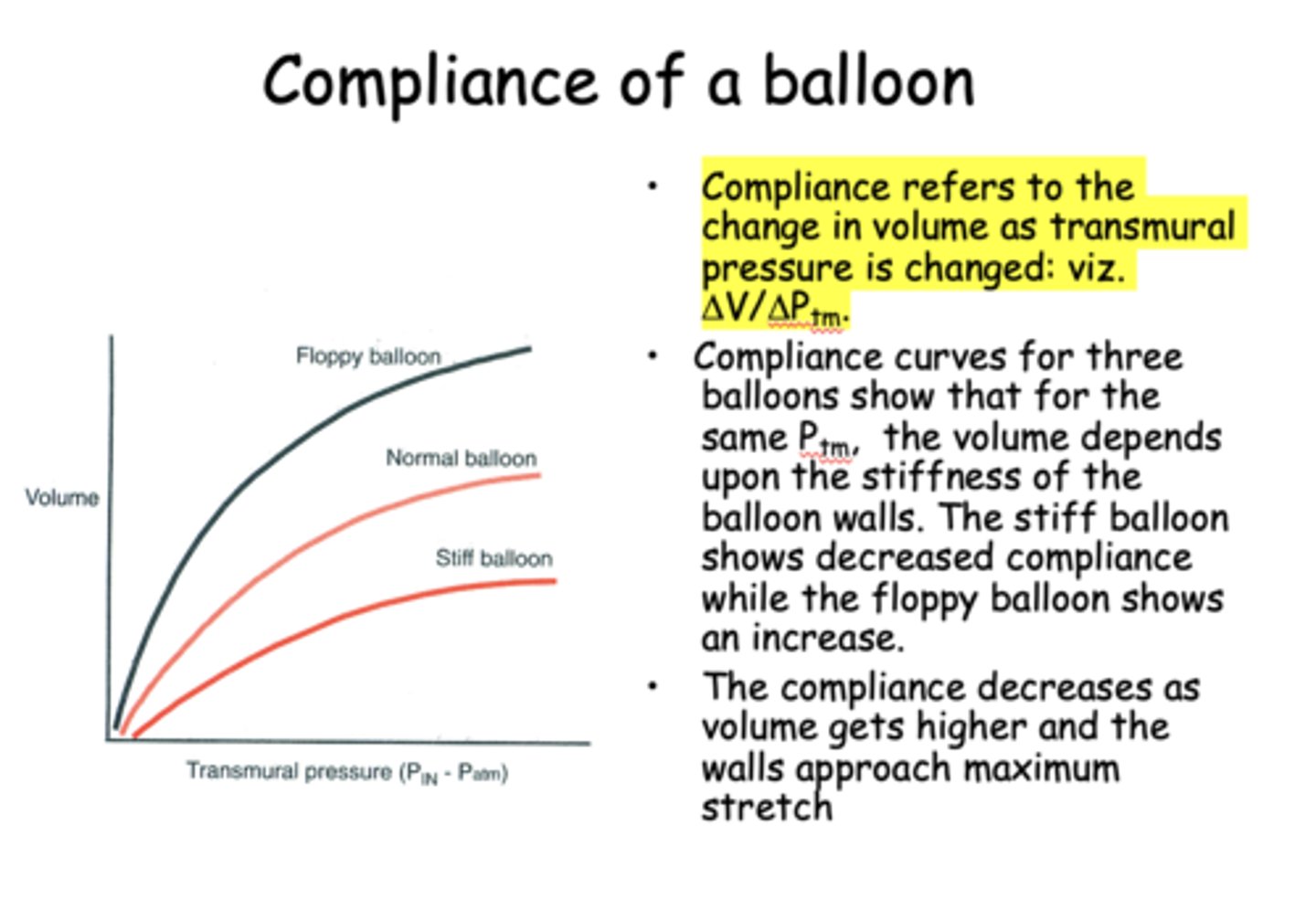
The compliance ____________ as volume gets higher and the walls approach maximum stretch
Decreases
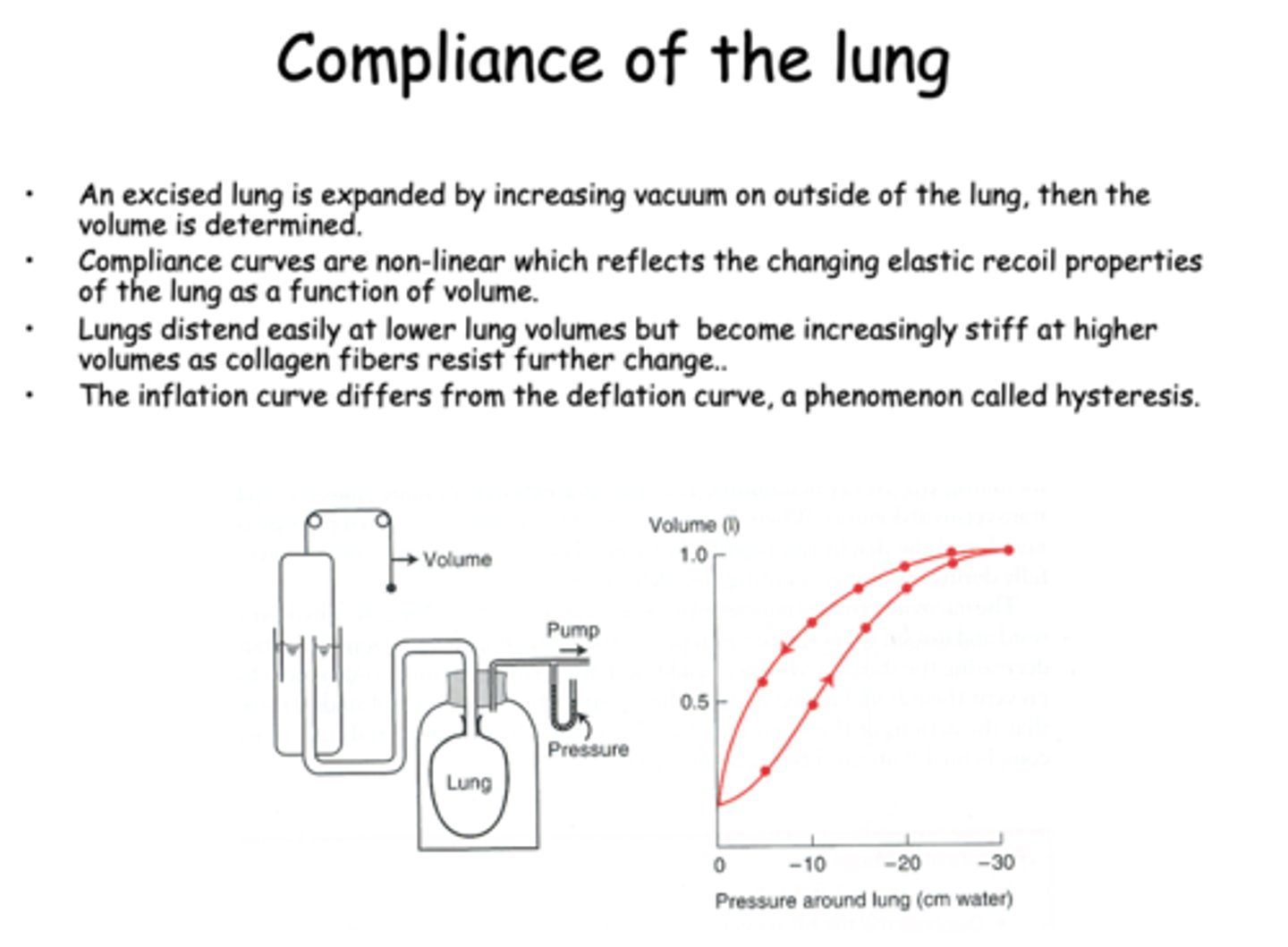
Compliance curves are ___________ which reflects the changing elastic recoil properties of the lung as a function of volume
non-linear
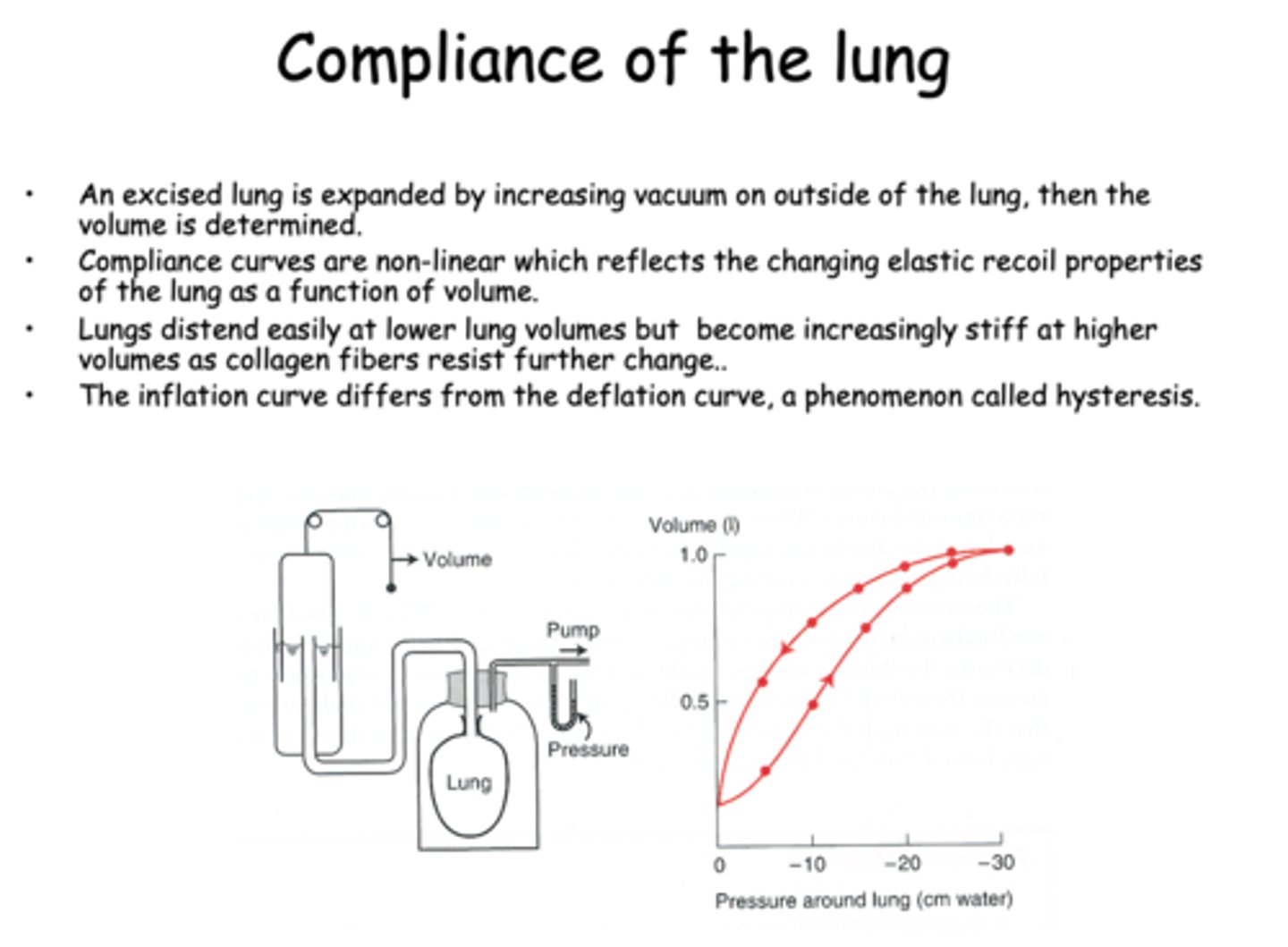
Lungs distend easily at lower lung volumes but become increasingly _________ at higher volumes as collagen fibers resist further change
Stiff
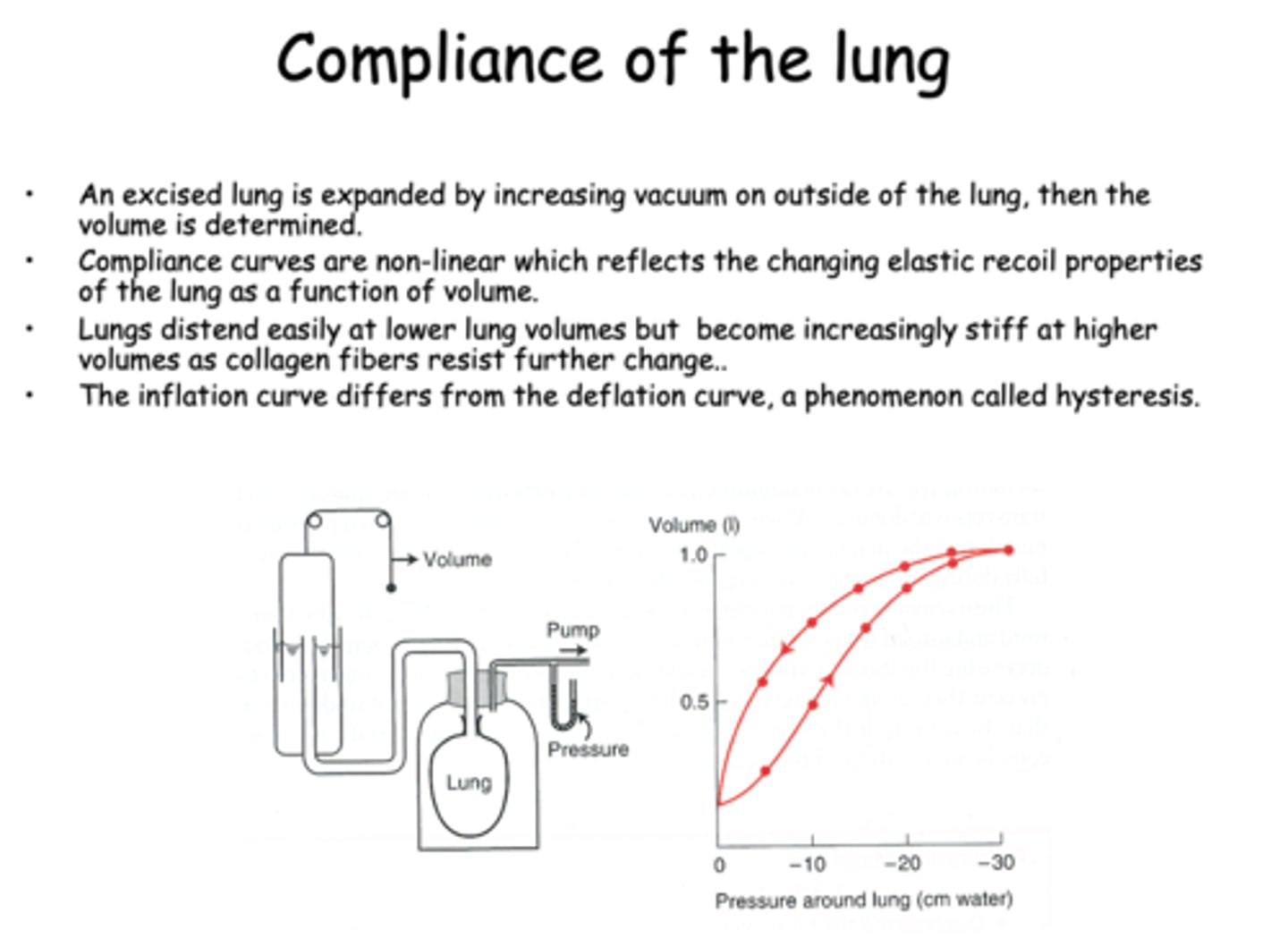
The inflation curve differs from the deflation curve, a phenomenon called _______
hysteresis
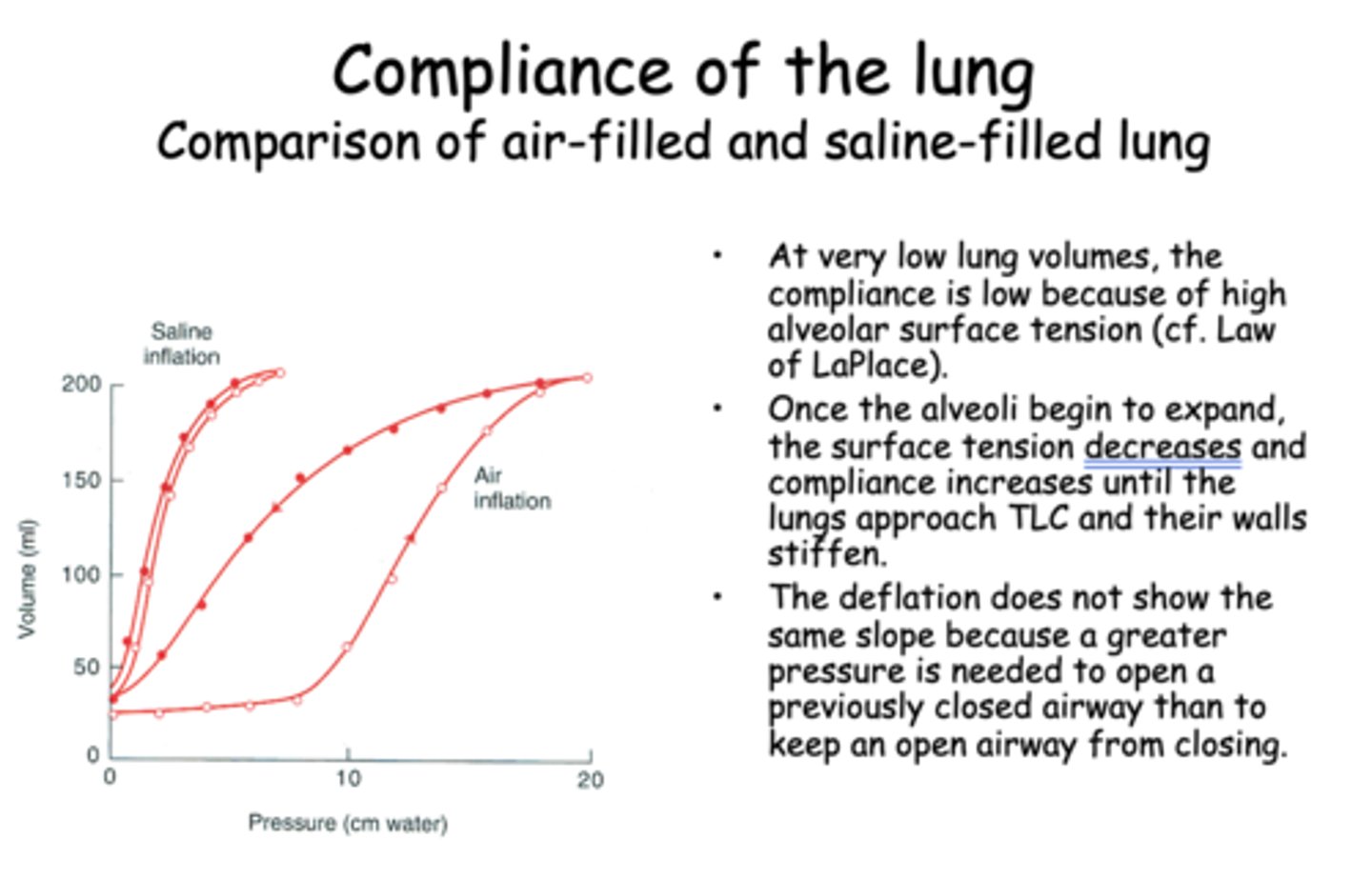
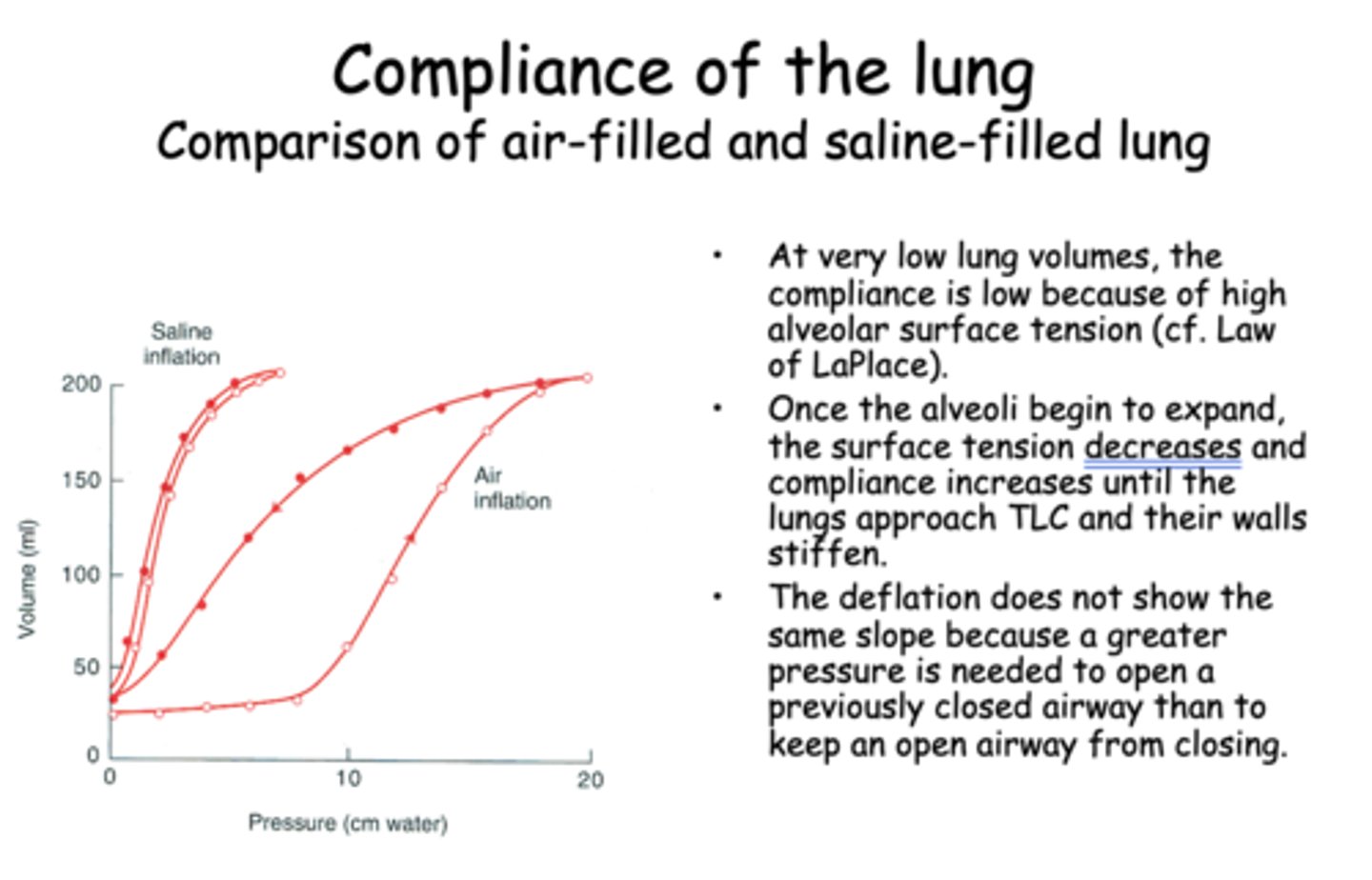
At very low lung volumes, the compliance is low because of high alveolar ________
surface tension
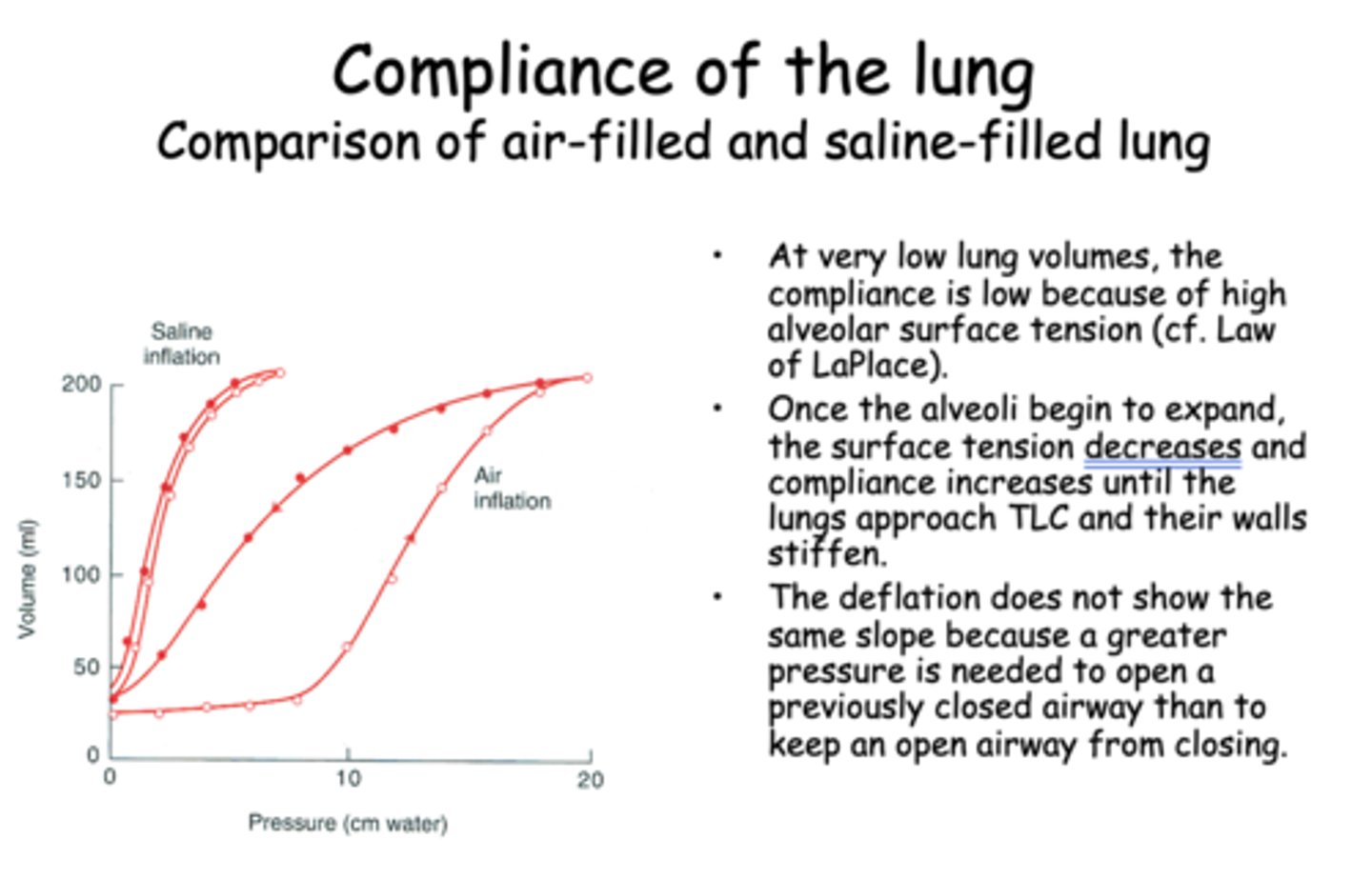
Once the alveoli begin to expand, the surface tension __________ and compliance __________ until the lungs approach TLC and their walls stiffen.
decreases, increaes
T/F: Inflation and deflation show the same curve for compliance of the lung
False
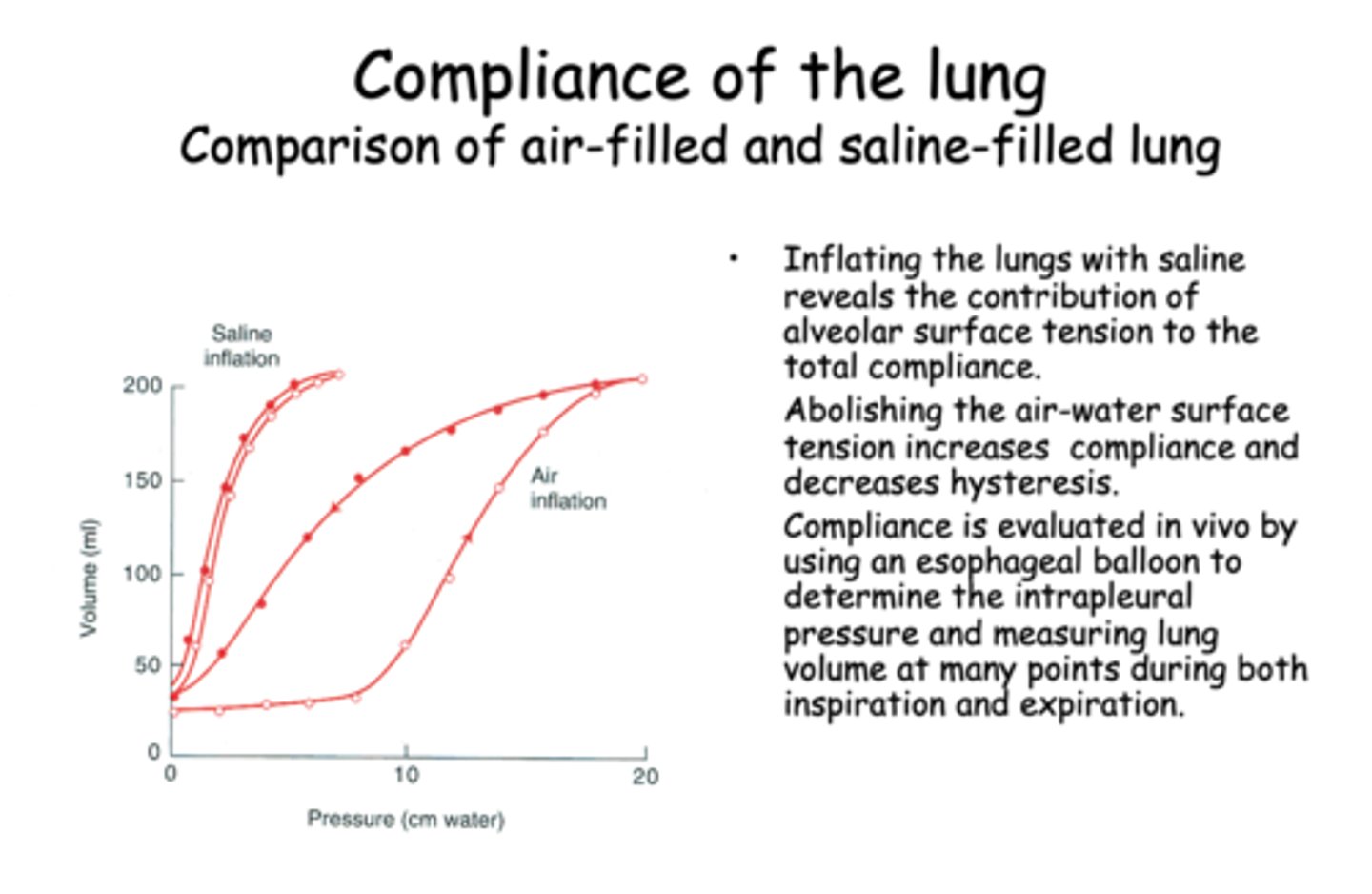
Abolishing the air-water surface tension will_______ compliance
increase
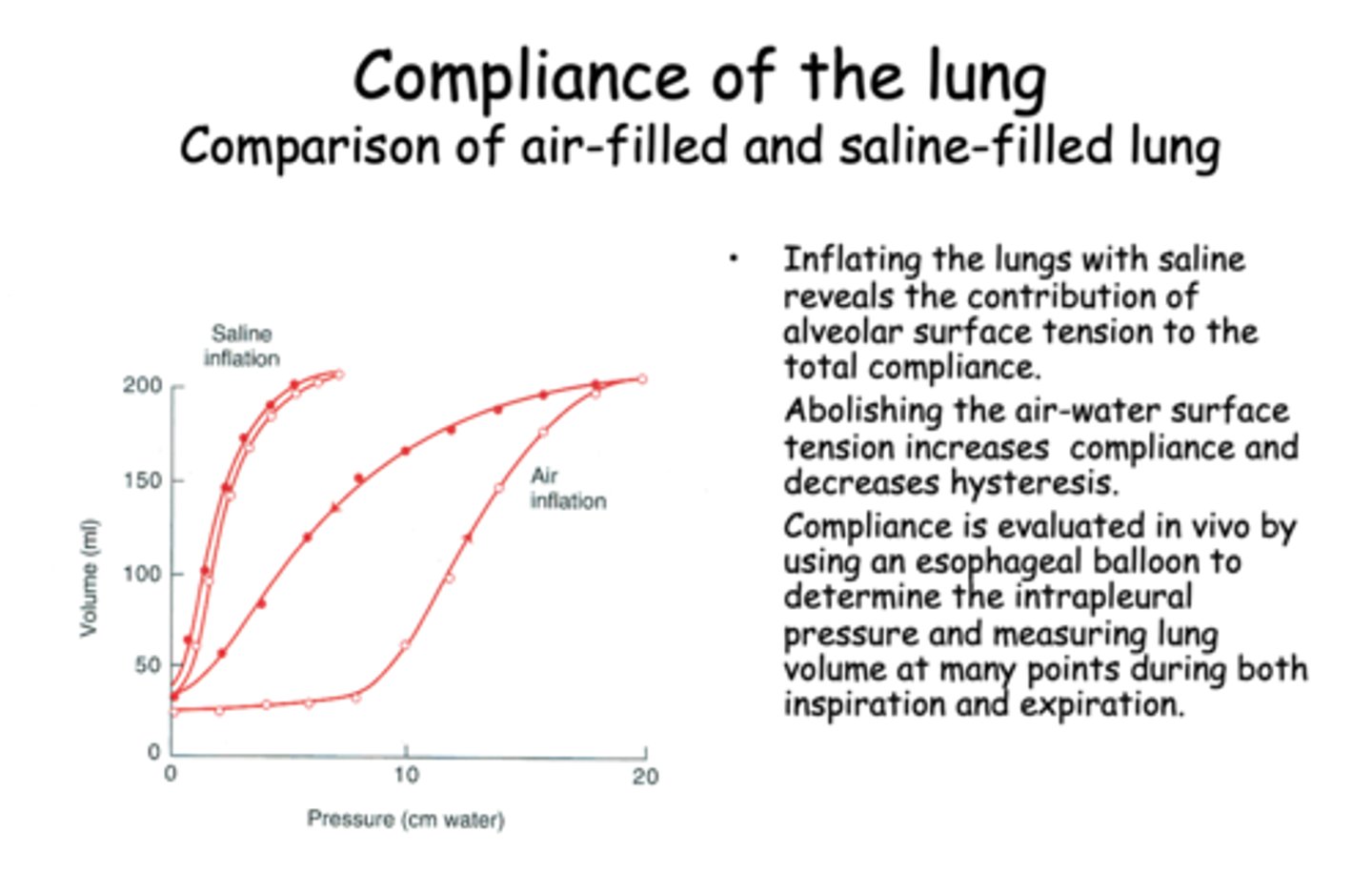
Abolishing the air-water surface tension will ________ hysteresis
decrease
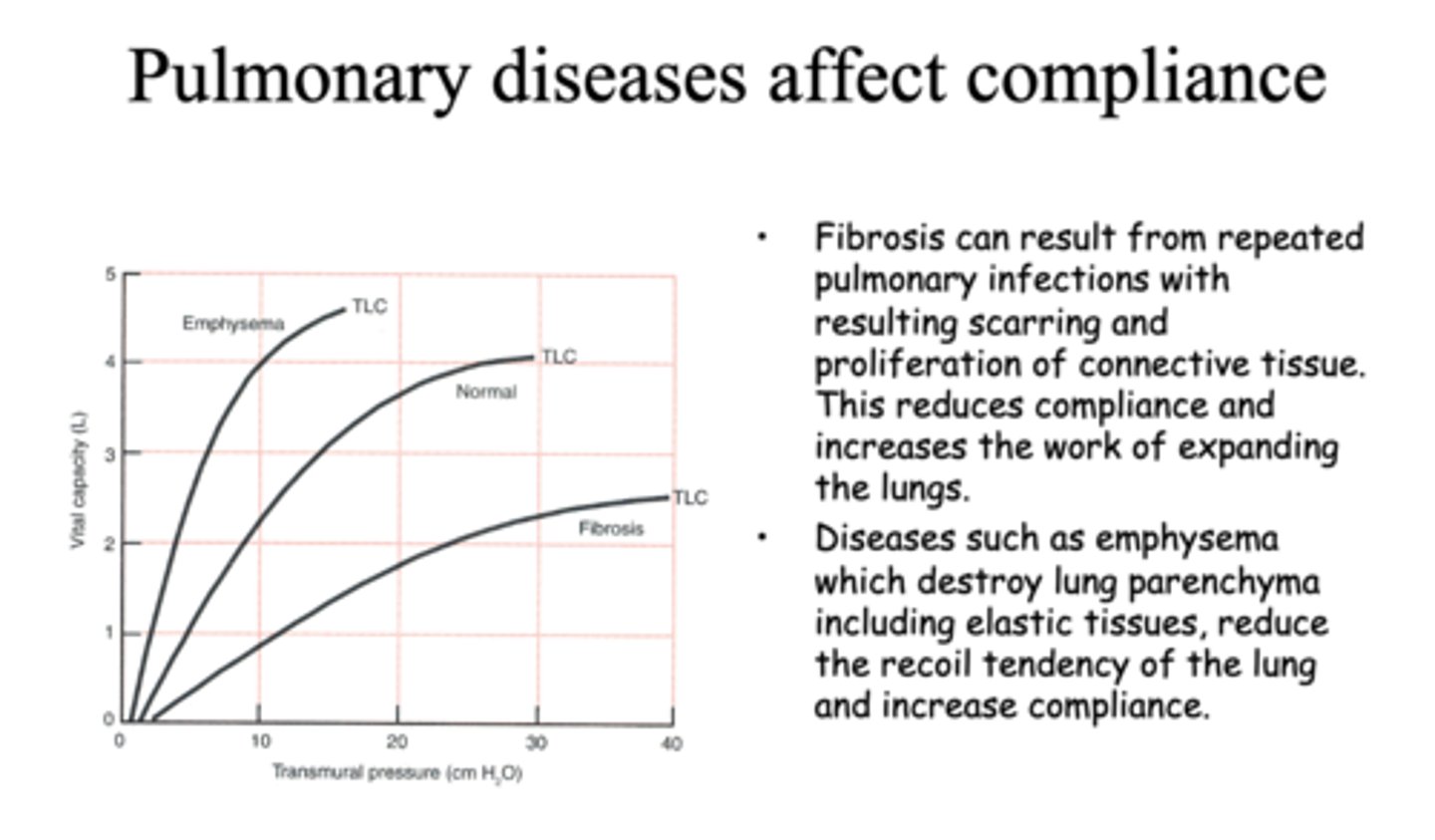
Fibrosis of the lungs can result in a _______ in compliance and total lung capacity, increases work in expanding lungs
decrease
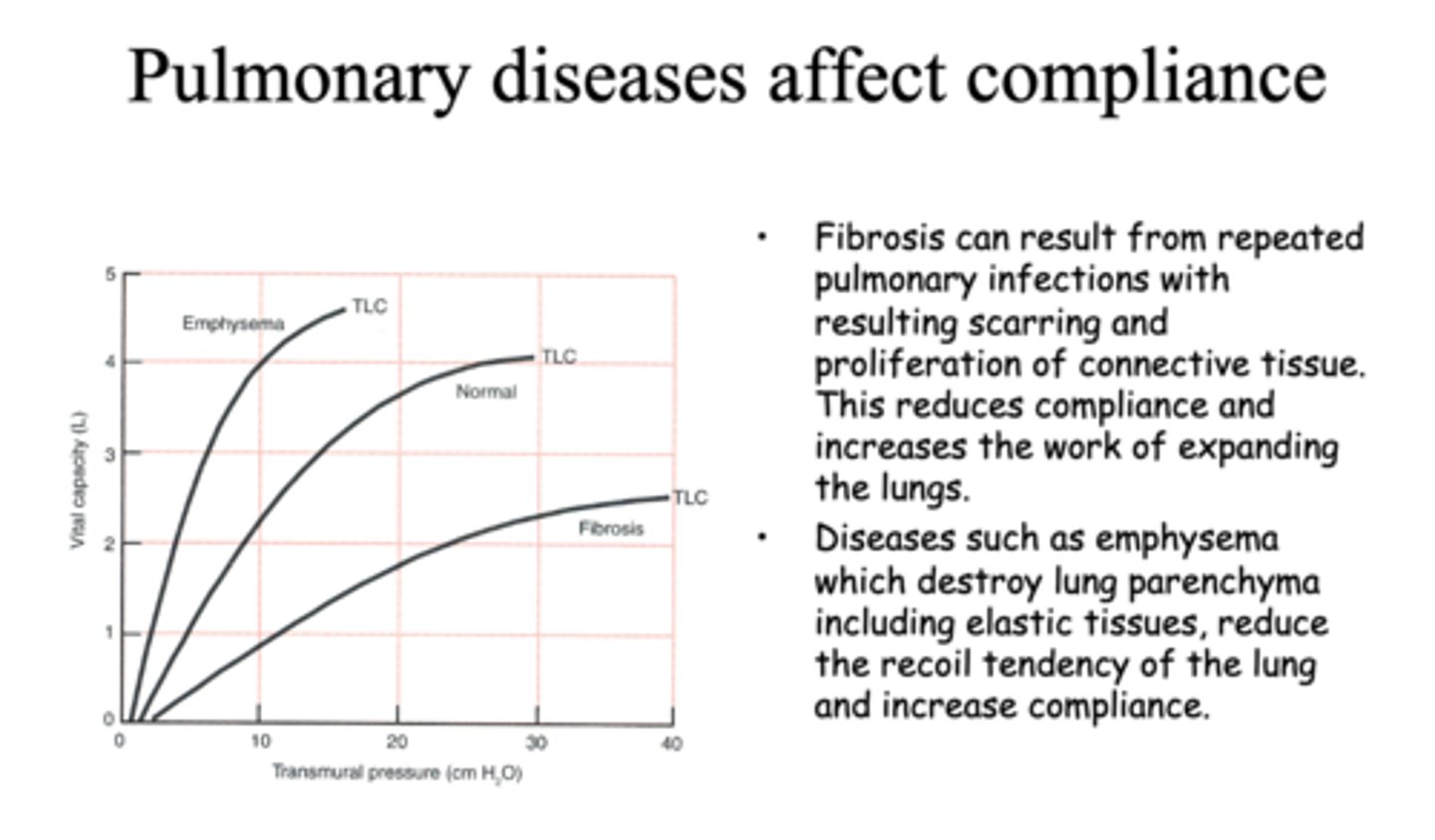
emphysema of the lungs result in a _______ in compliance and total lung capacity
increase
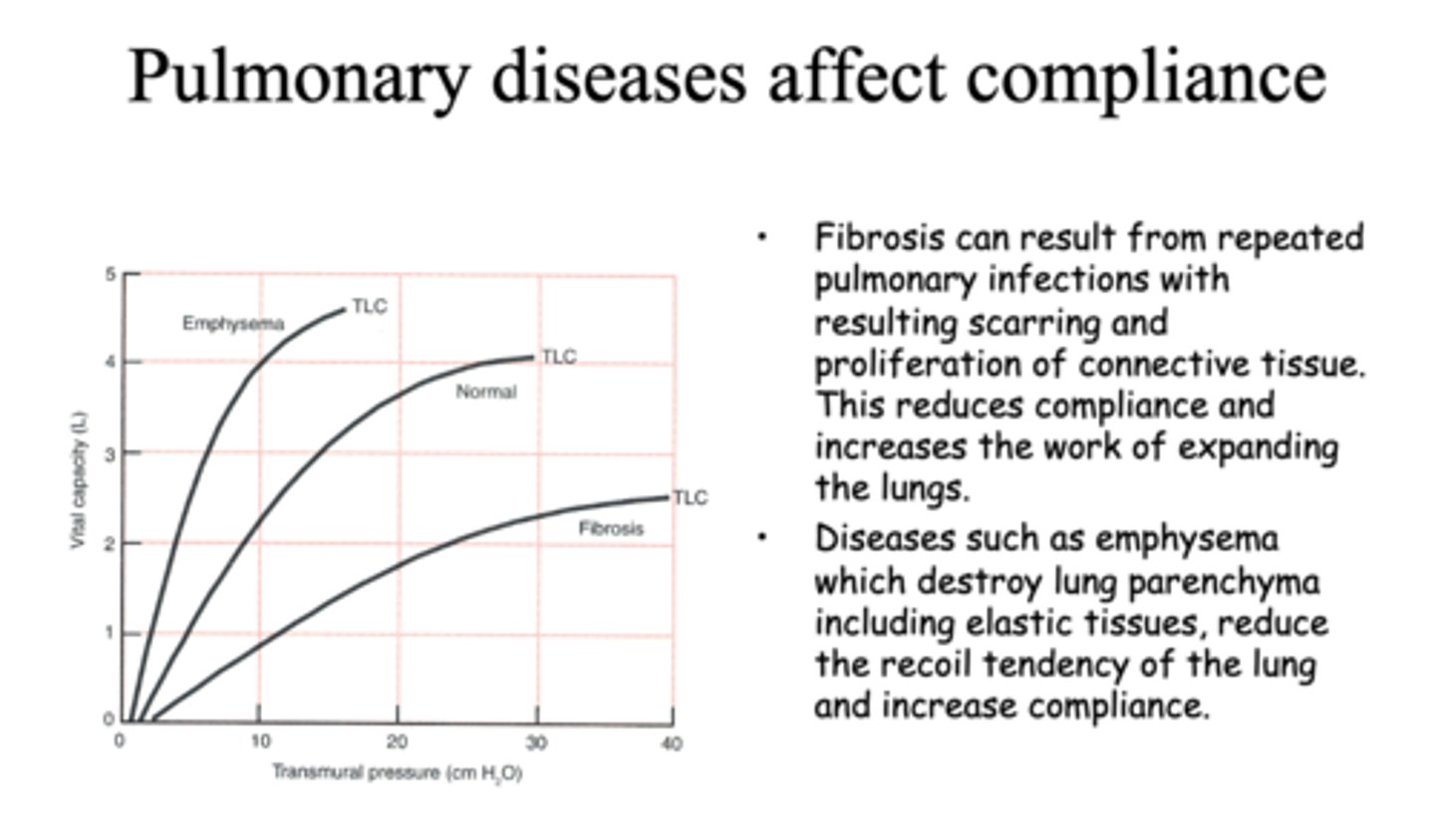
Define the following:
Destroy lung parenchyma including elastic tissues, reduce the recoil tendency of lung
emphysema
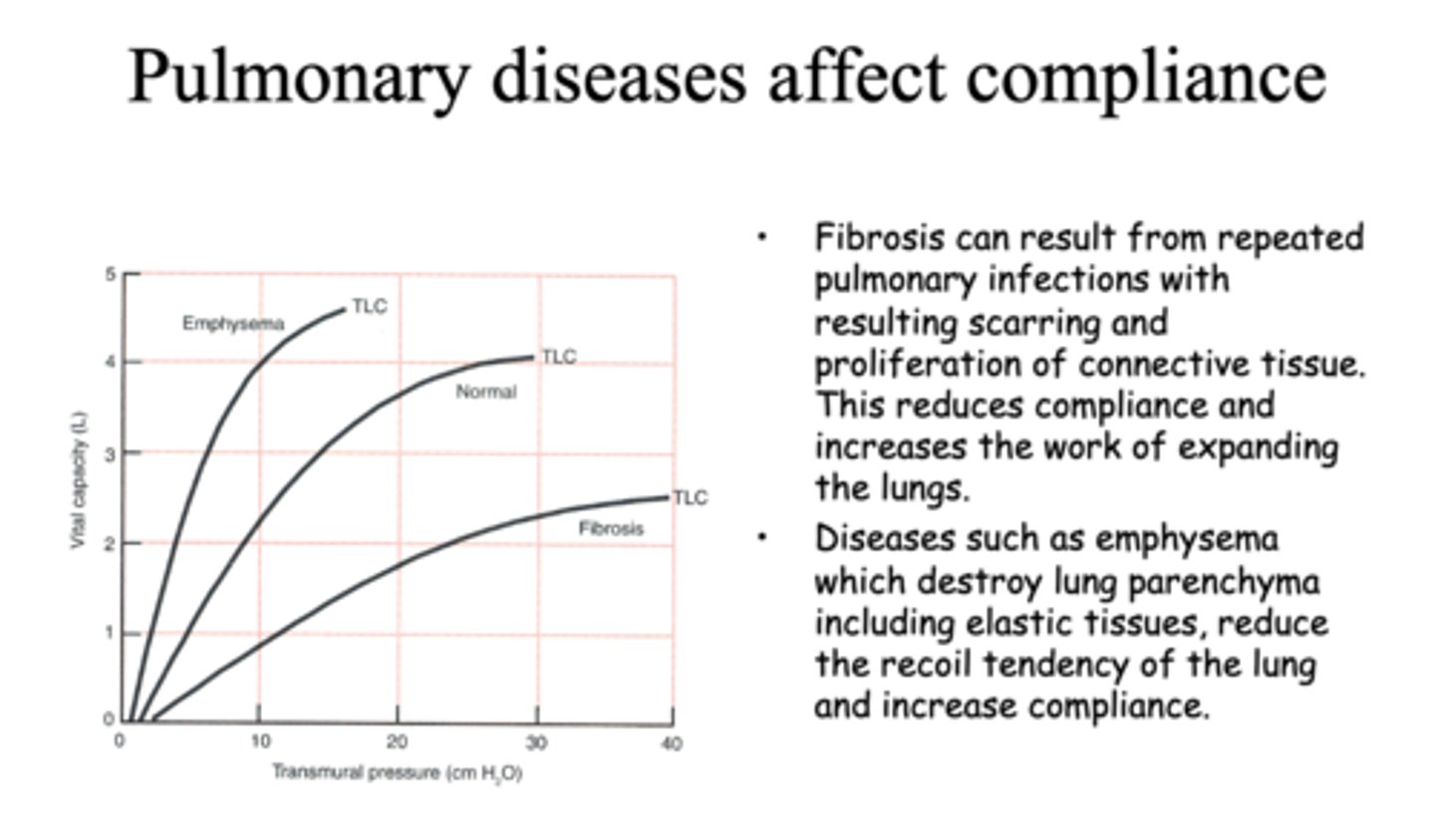
Define the following:
Result from repeated pulmonary infections with result scarring and proliferation of connective tissue
fibrosis
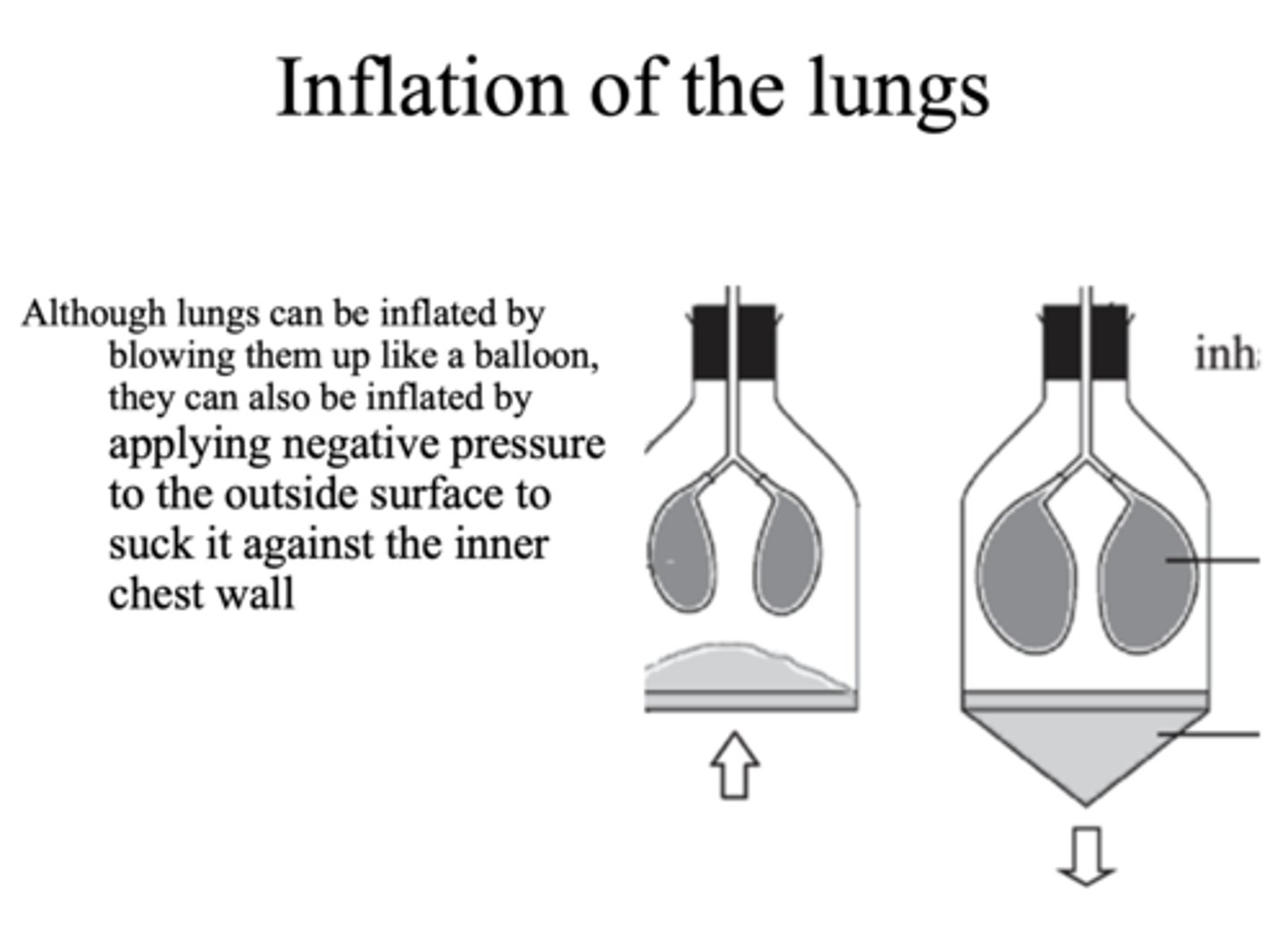
Lungs can be inflated by either:
- Positive pressure inside
- Negative pressure outside (normal mechanism)

Although lungs can be inflated by blowing them up like a balloon, they can also be inflated by applying ___________ pressure to the outside surface to suck it against the inner chest wall
Negative
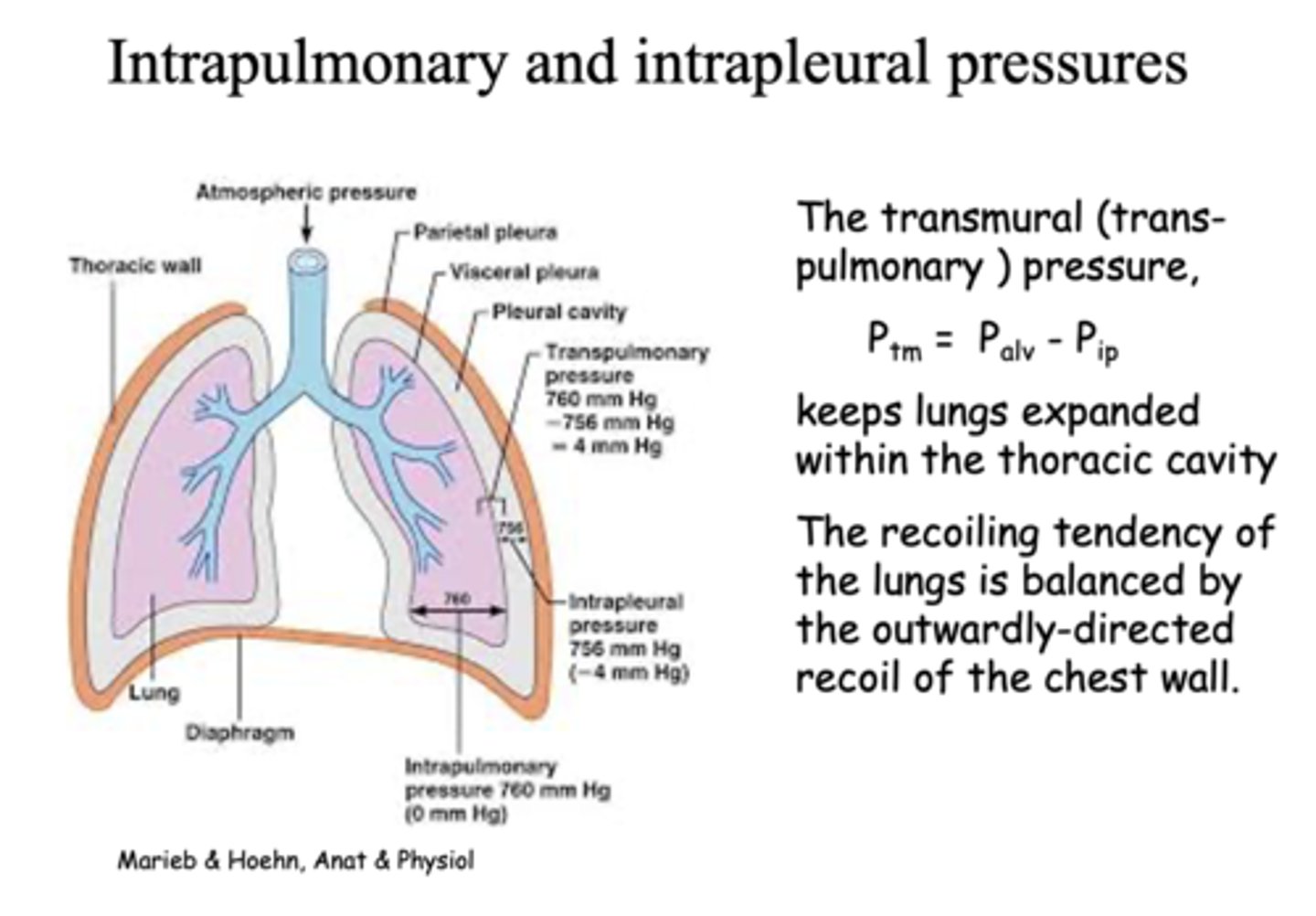
this pressure keeps lungs expanded within the thoracic cavity and prevents it from collapsing:
transmural pressure
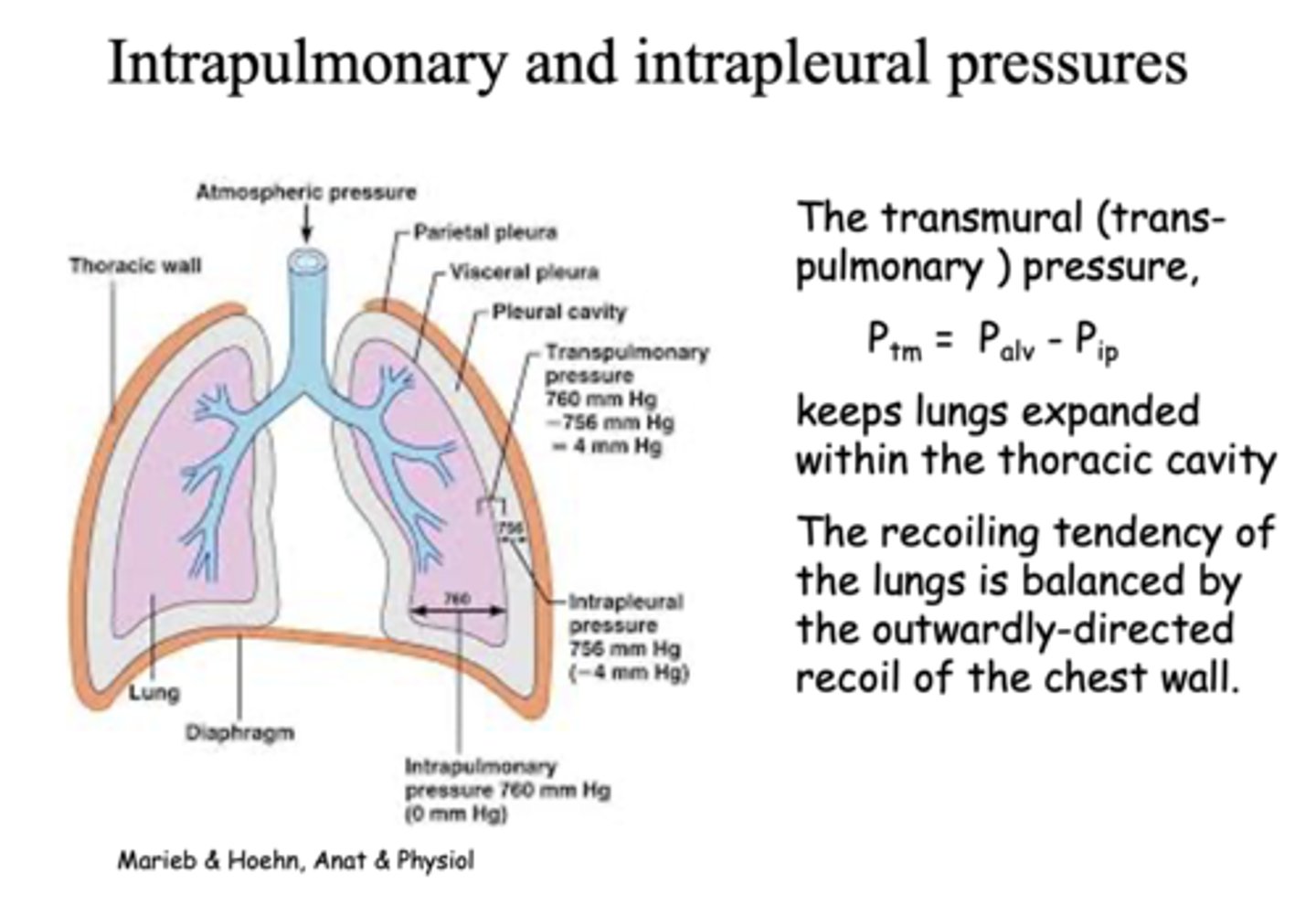
the pressure within the pleural cavity is slightly _____ than alveolar pressure
lower
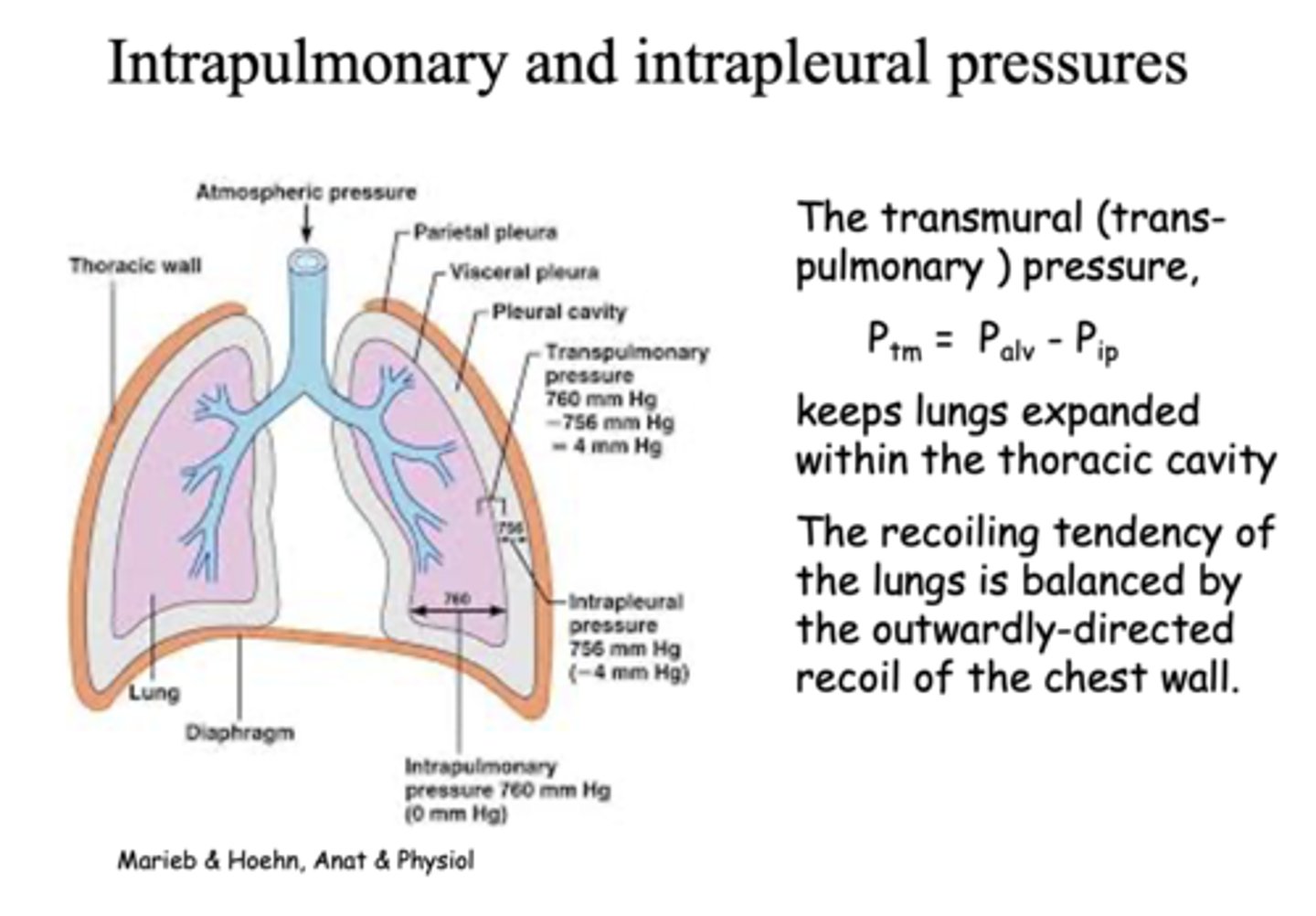
how do you calculate normal transmural pressure?
Palv - Pip
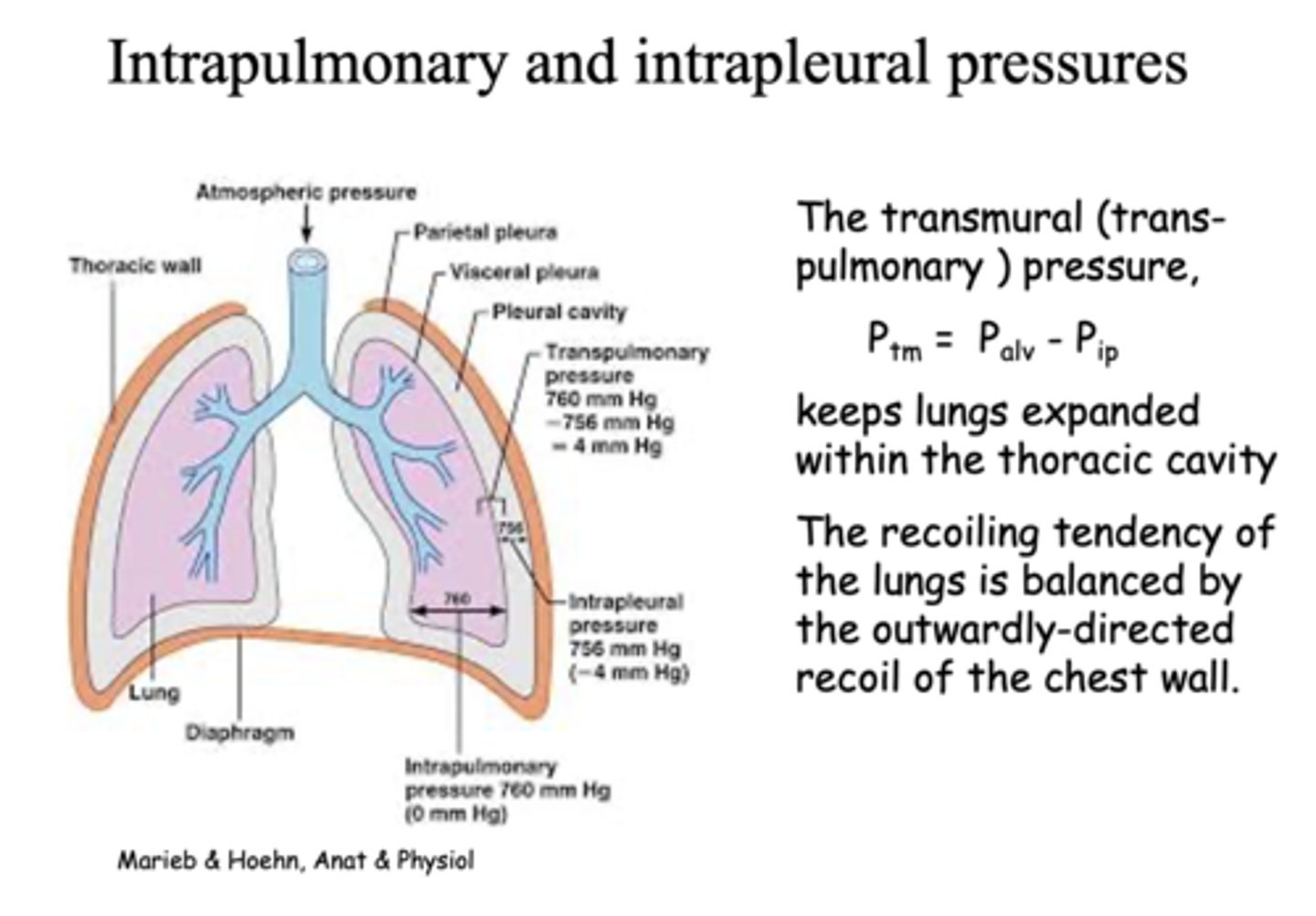
What is the intraplueral pressure between the visceral pleural and thoracic wall?
-4 mm Hg
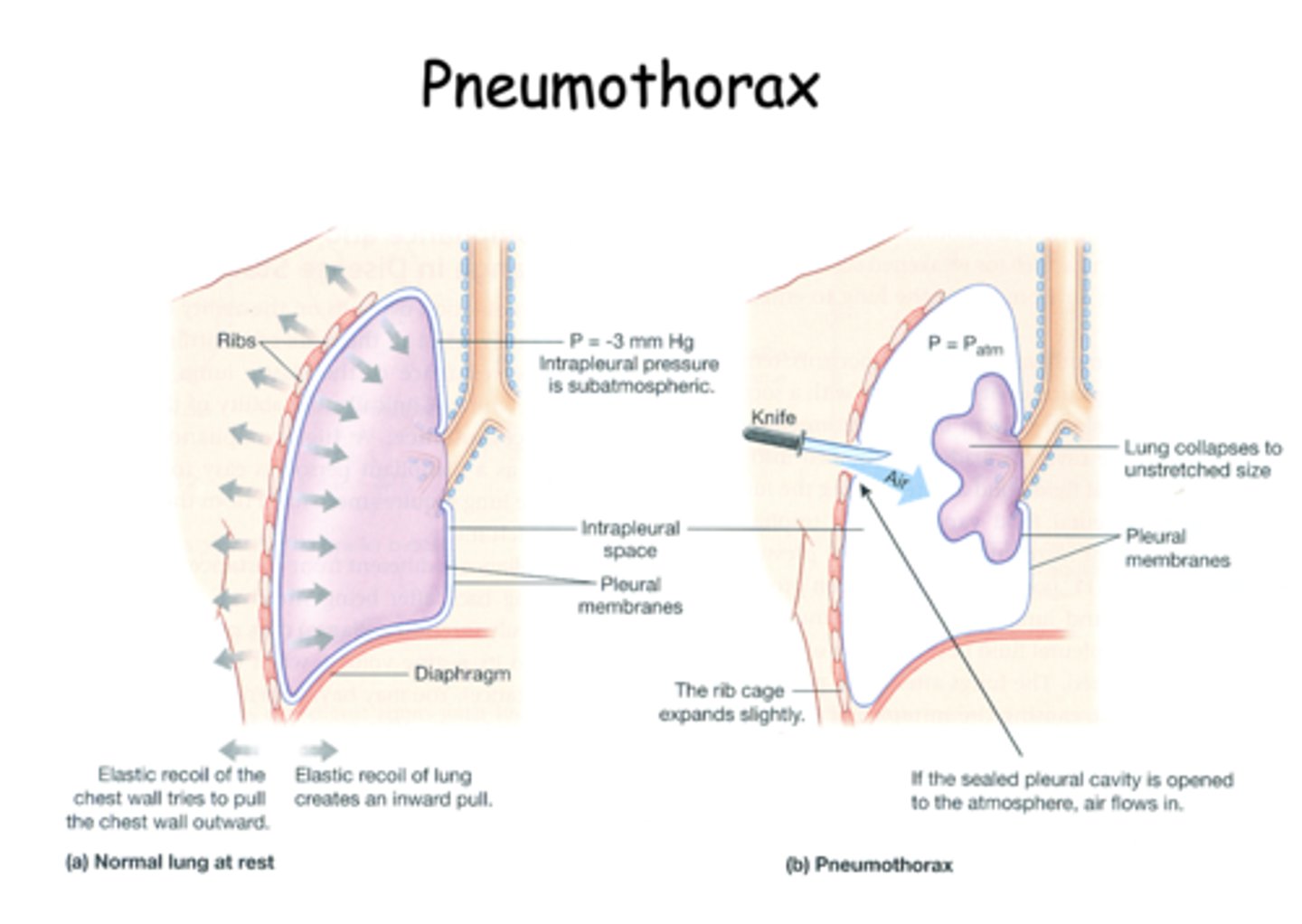
if the pleural cavity was opened by a knife wound, the lungs would _______ due to intrapleural pressure becoming equal to atmospheric pressure
collapse
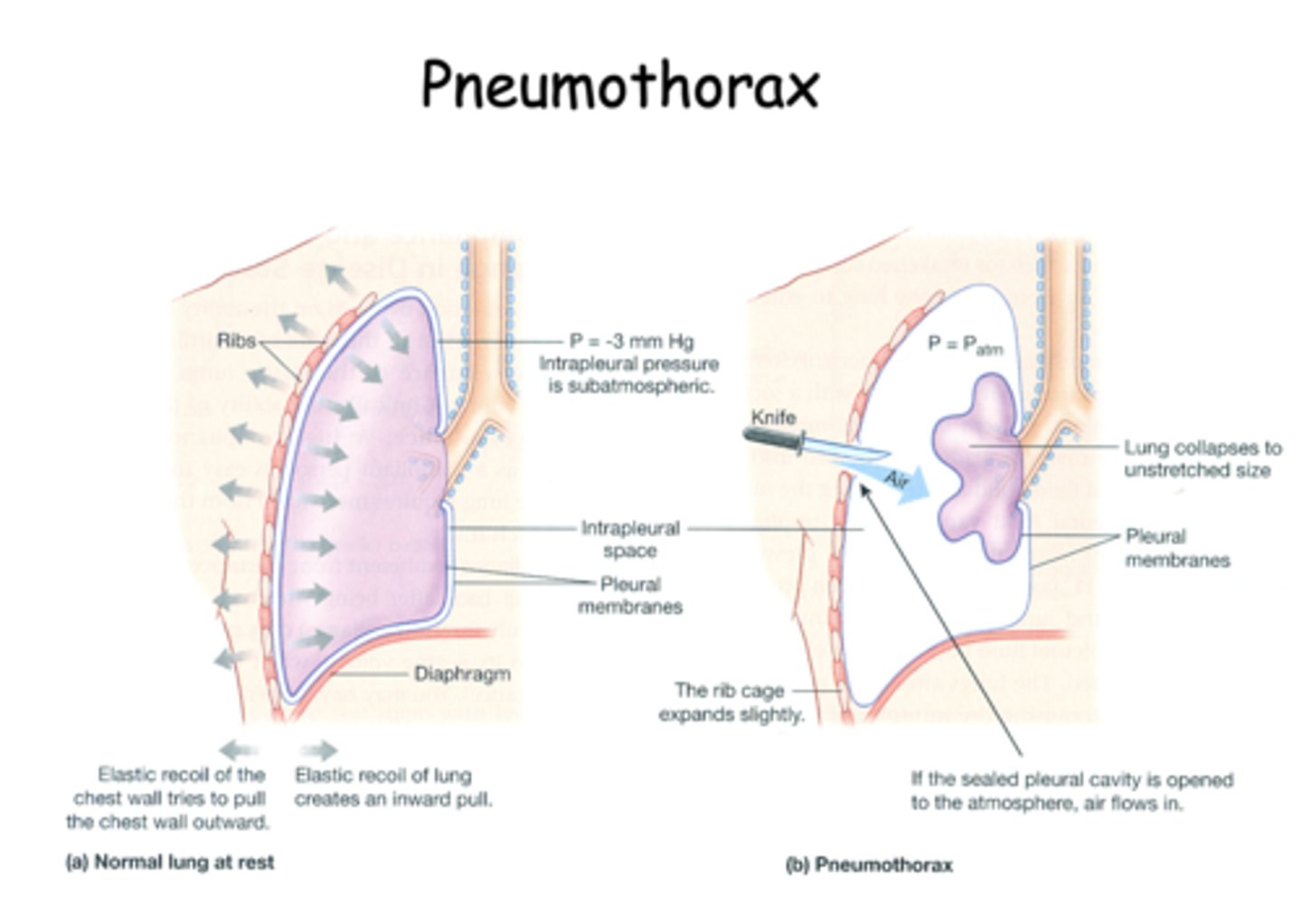
air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall, possibly resulting in a collapsed lung and deflation of alveoli
pneumothorax
Reduction in the size of a container containing an amount of gas will result in a _________ in pressure
increase
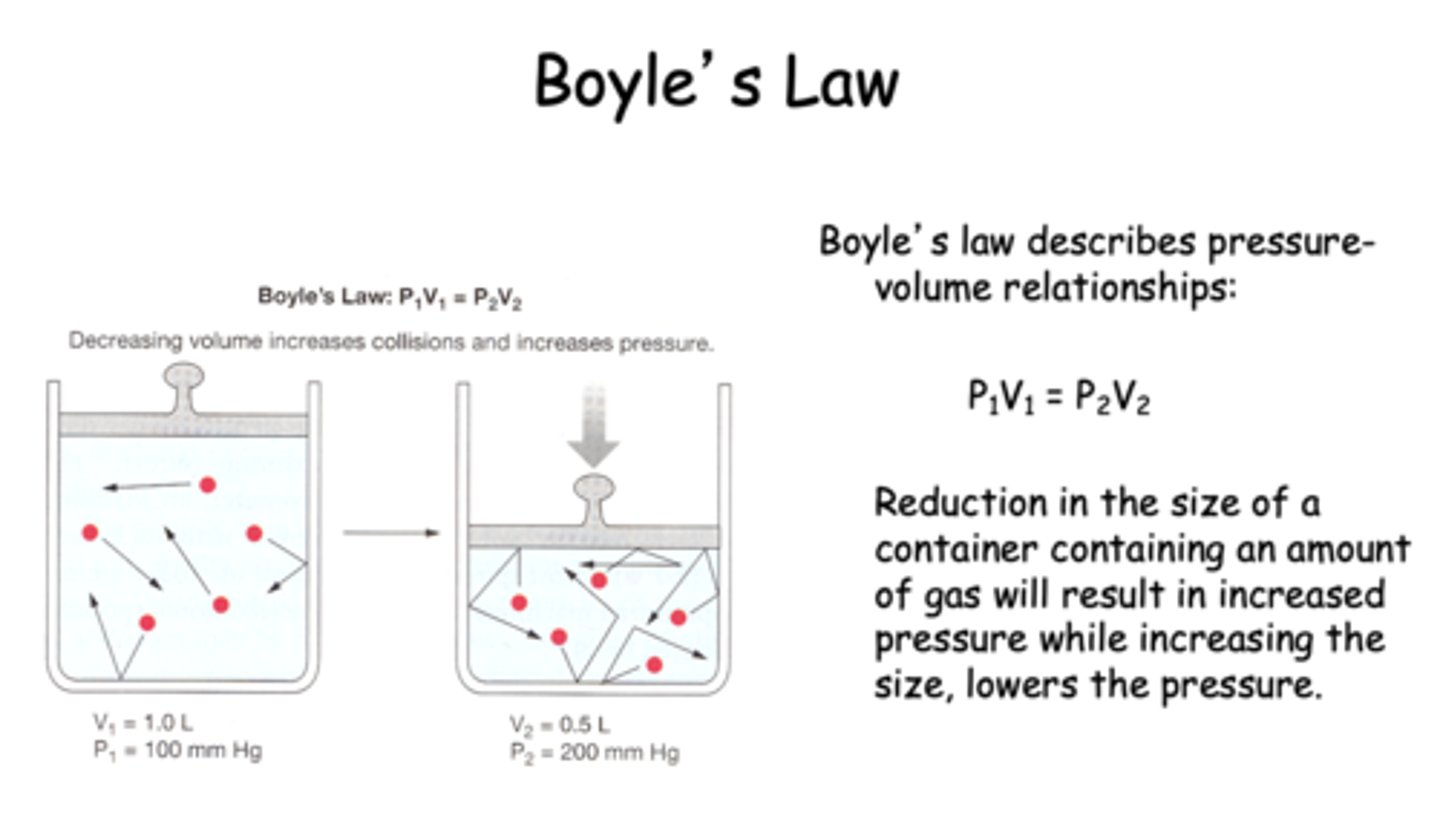
Boyle's law formula:
P1V1=P2V2
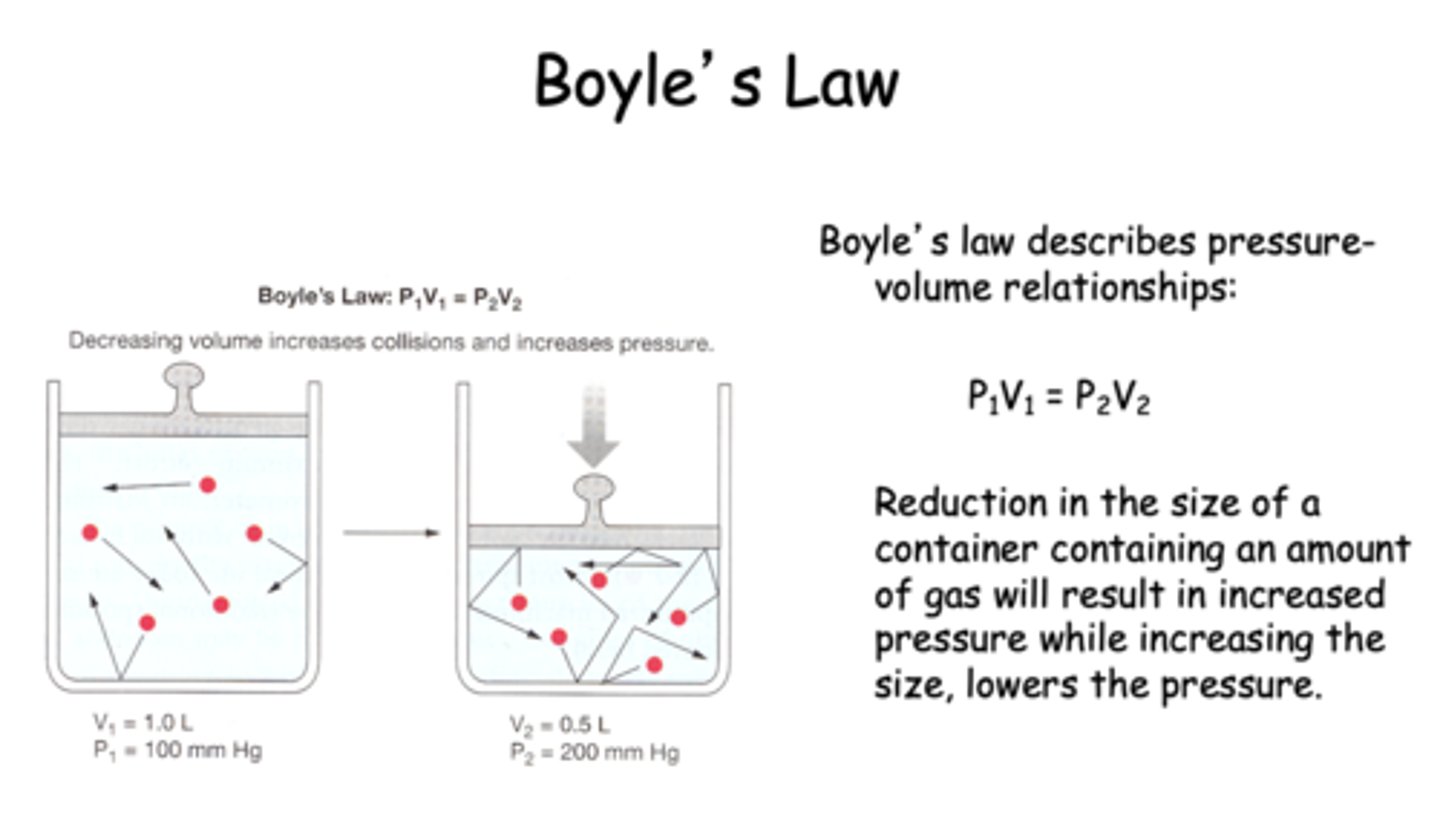
increasing the volume of a closed container would _____ the pressure
decrease
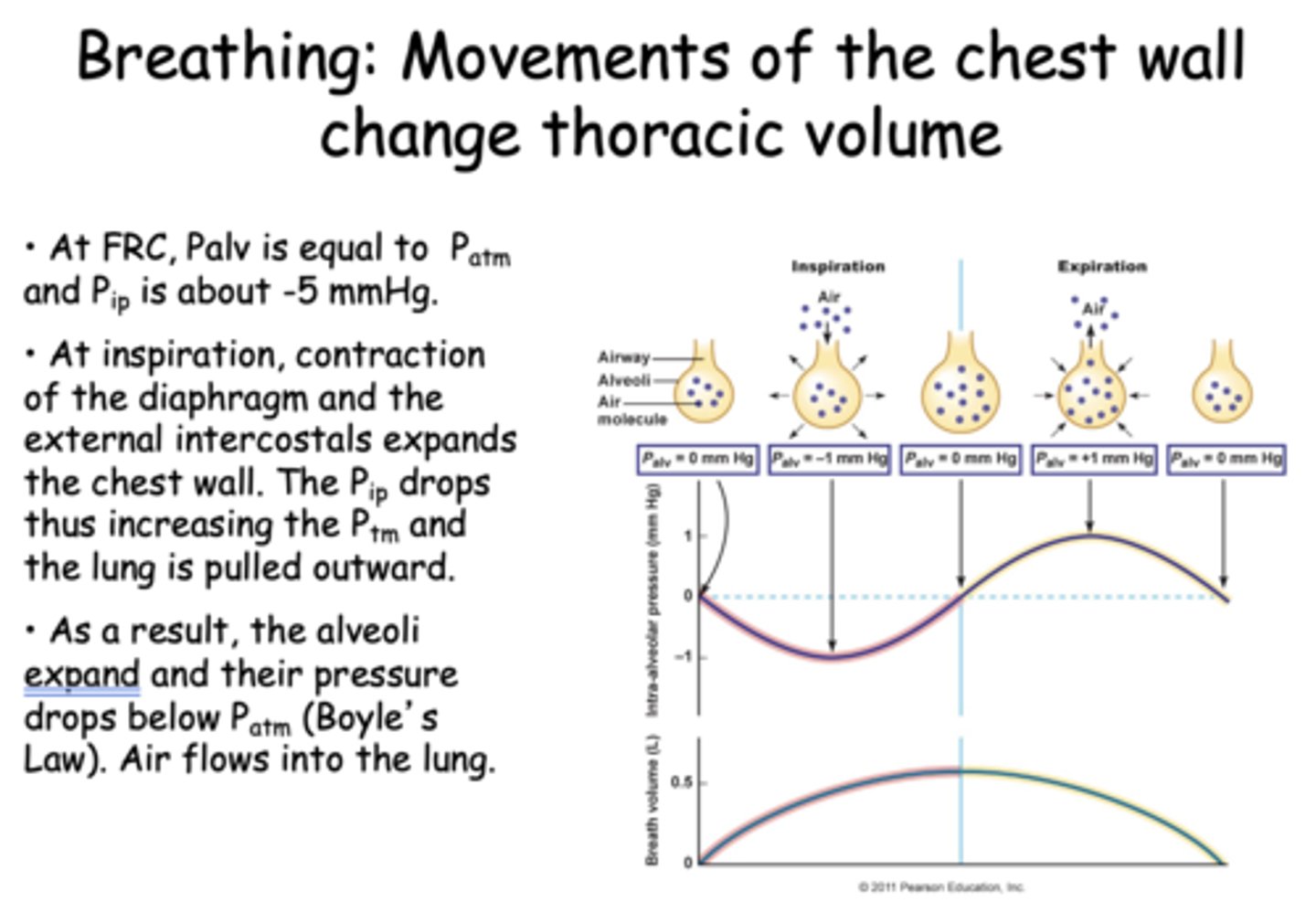
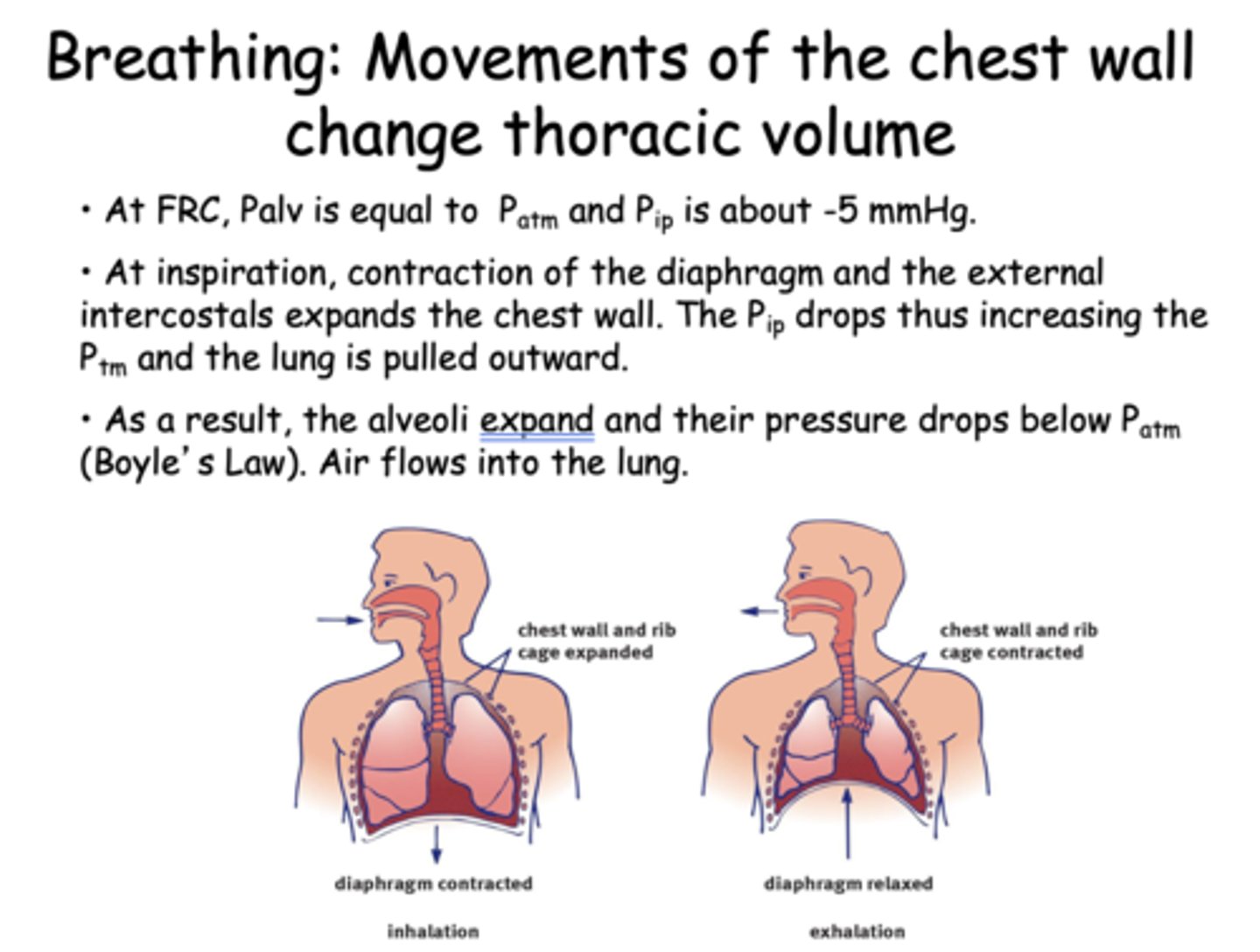
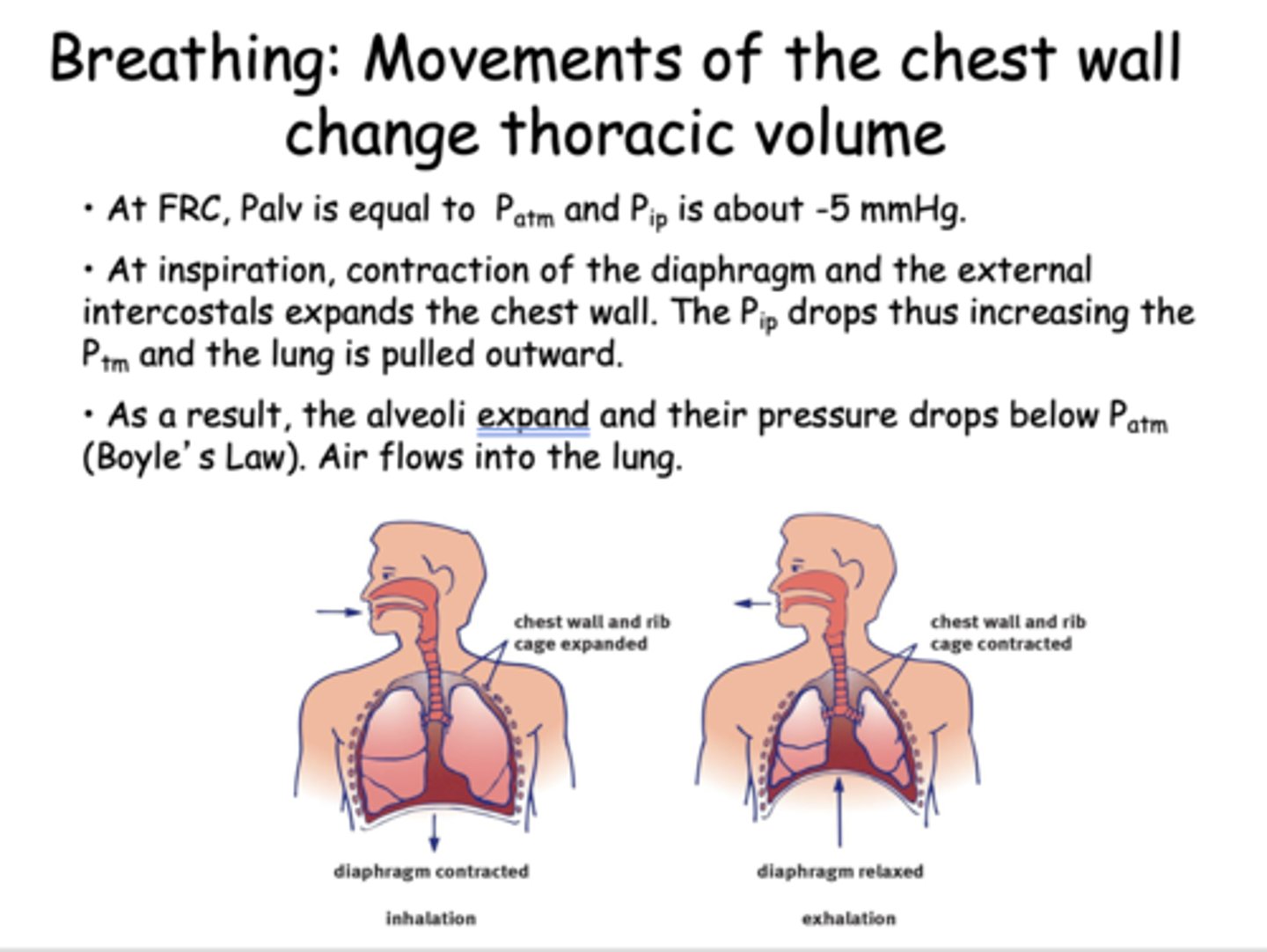
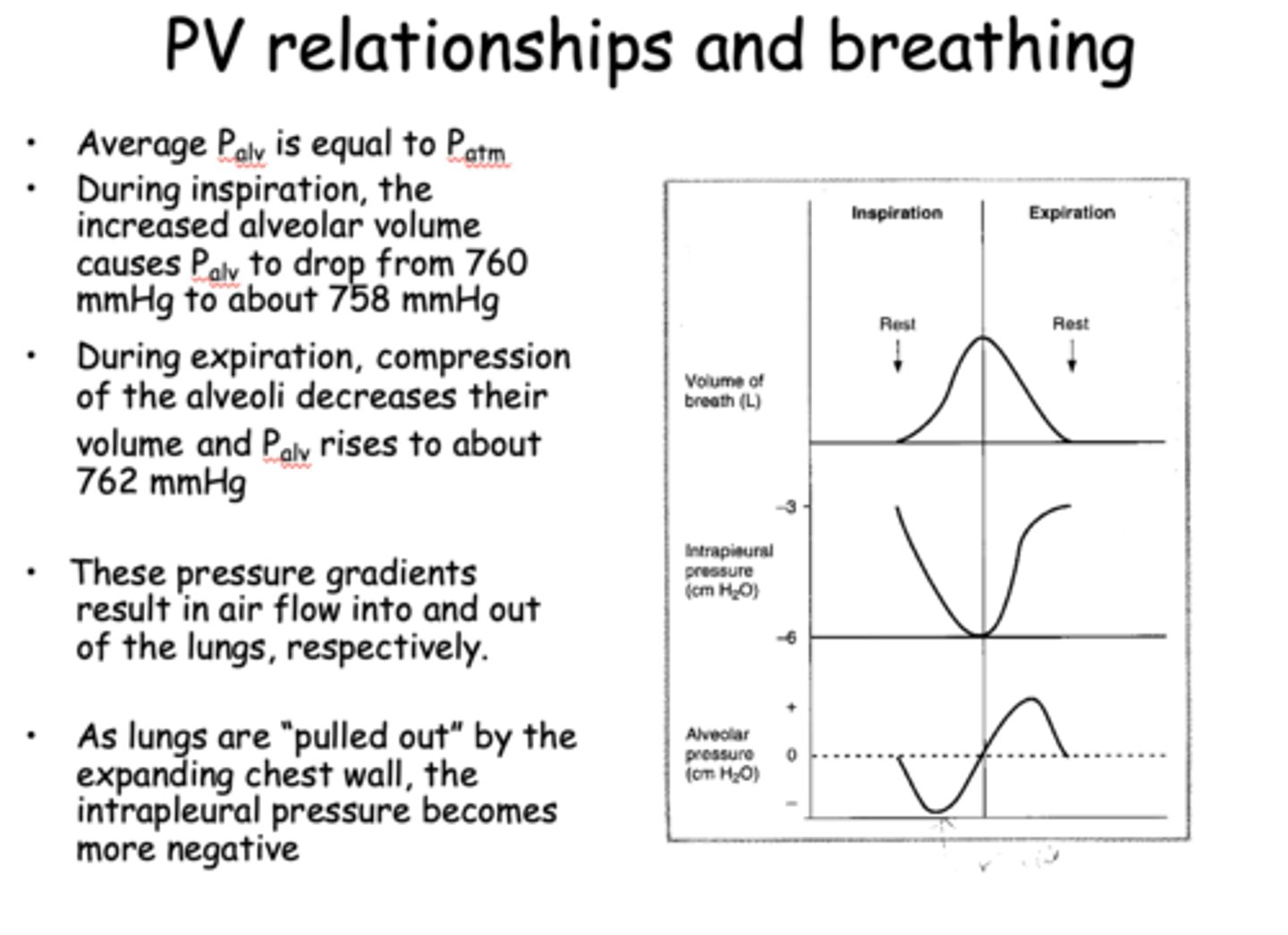
At inspiration, contraction of the diaphragm and the external intercostals expands the chest wall. The Pip drops thus increasing the Ptm and the lung is pulled outward. As a result, what. happens to the alveoli and pressure?
The alveoli expand and their pressure drops below Patm (Boyle’s Law). Air flows into the lung
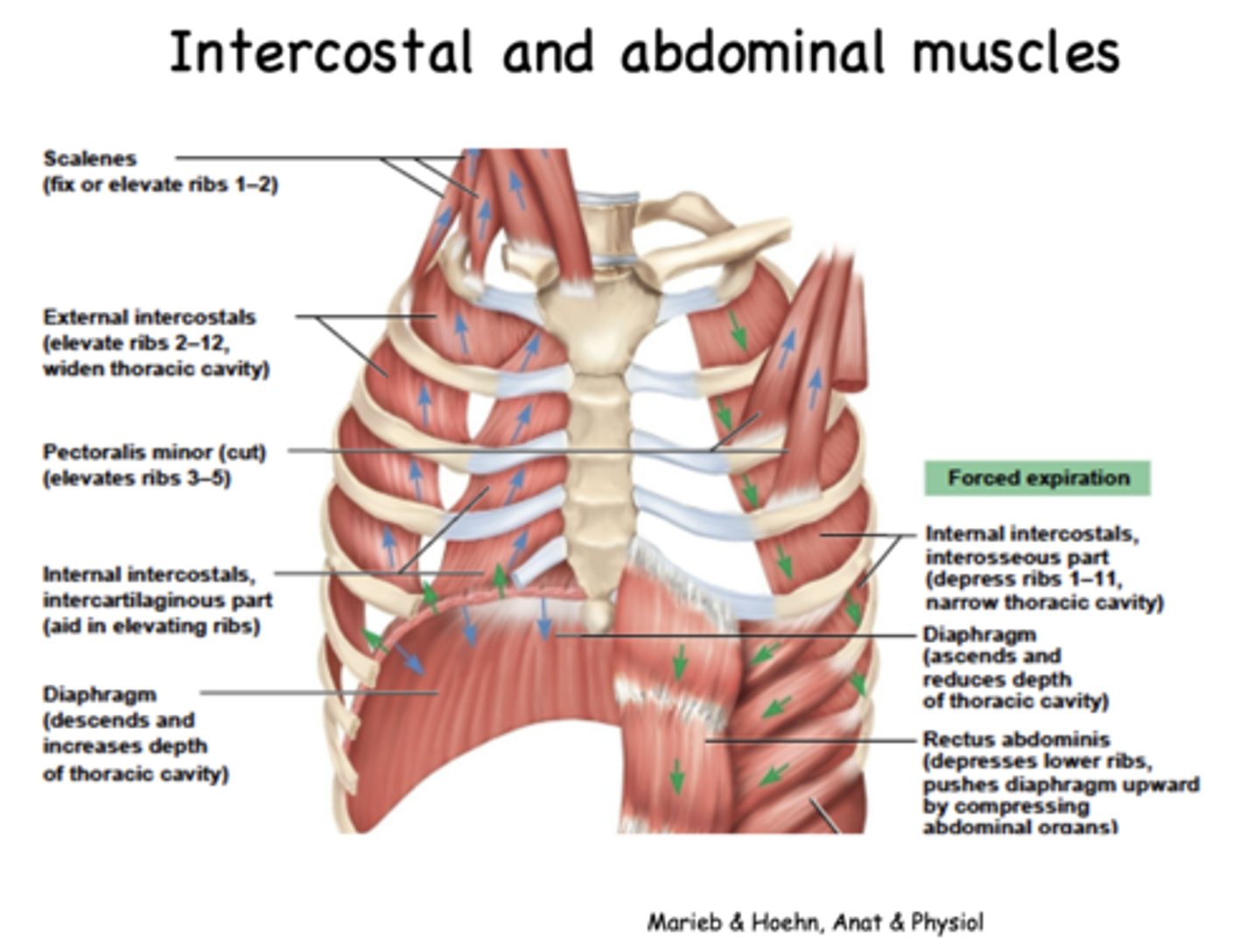
what are the muscles responsible for inspiration?
- Diaphragm
- External intercostals
- Scalenes
- SCM (?)
what muscles are responsible for forced expiration?
- Internal intercostals
- Diaphragm
- Abdominal muscles
- Rectus abdominis
_______ is normally a passive process driven by the elastic recoil of the lungs
expiration
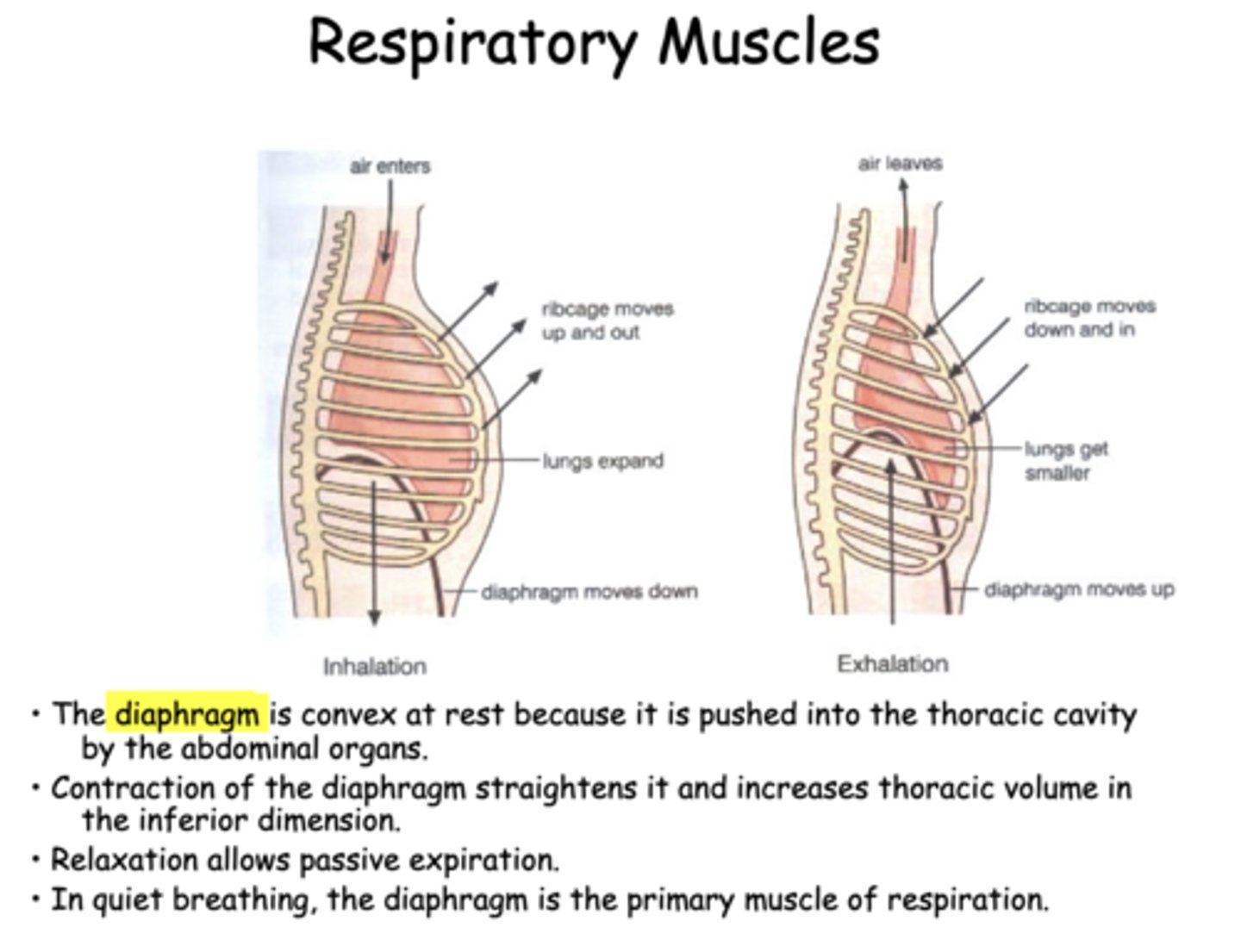
Expiration is normally a passive process driven by the:
elastic recoil of the lungs
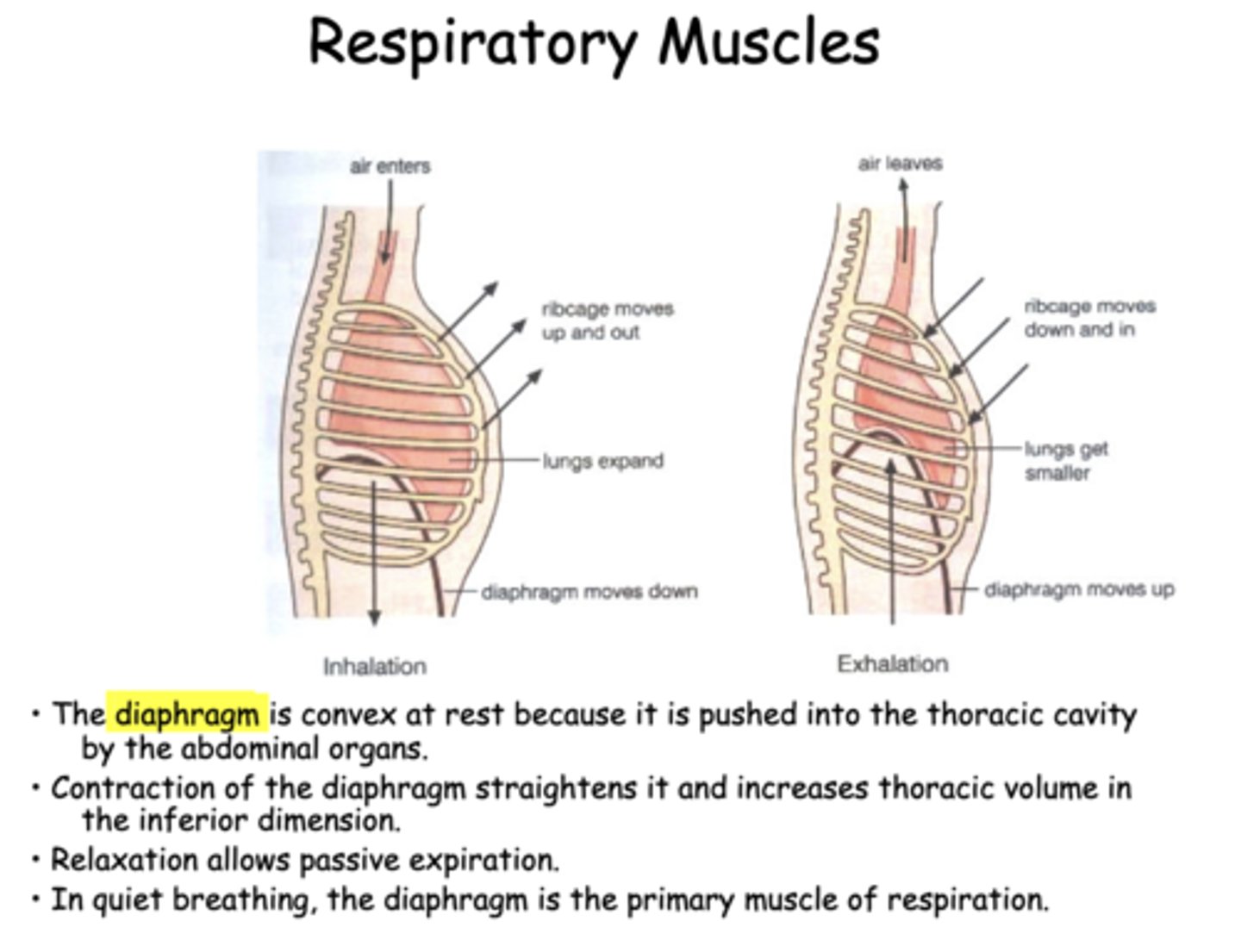
during inhalation, the diaphragm ________
contracts and moves downward
during inhalation, the chest wall and rib cage is
expanded
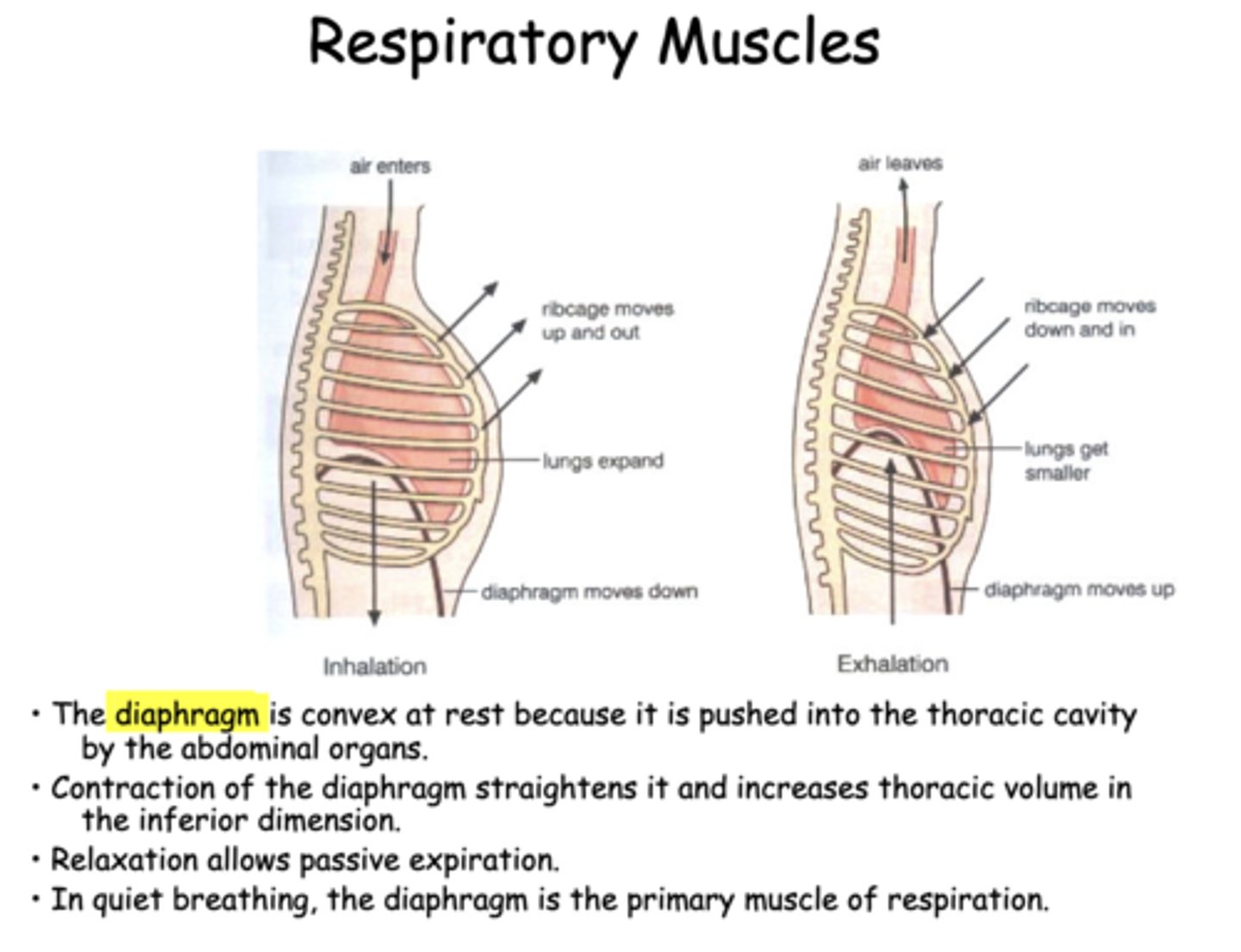
during exhalation, the chest wall and rib cage is
contracted
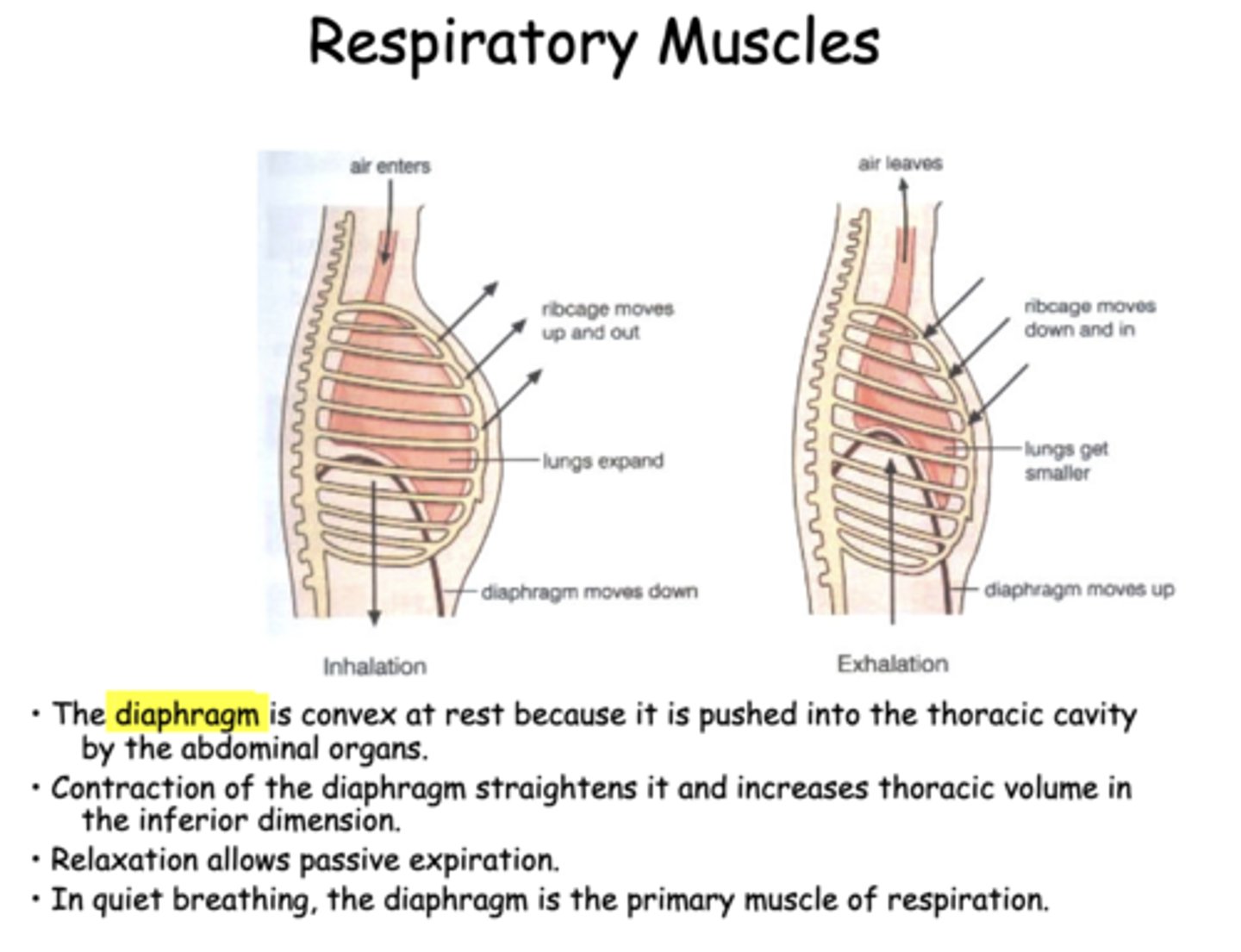
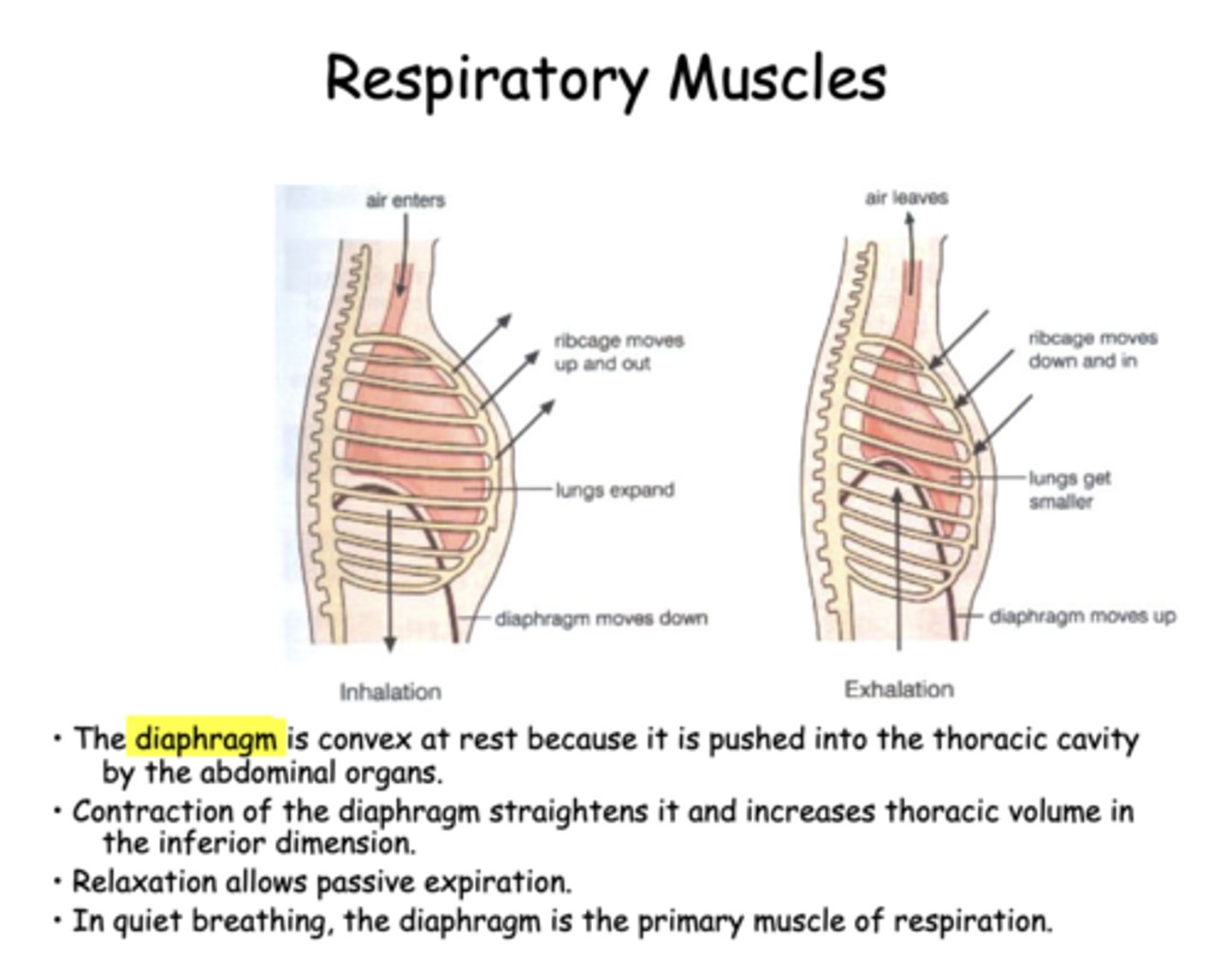
the diaphragm is _________ at rest because it is pushed into the thoracic cavity by the abdominal organs
Convex
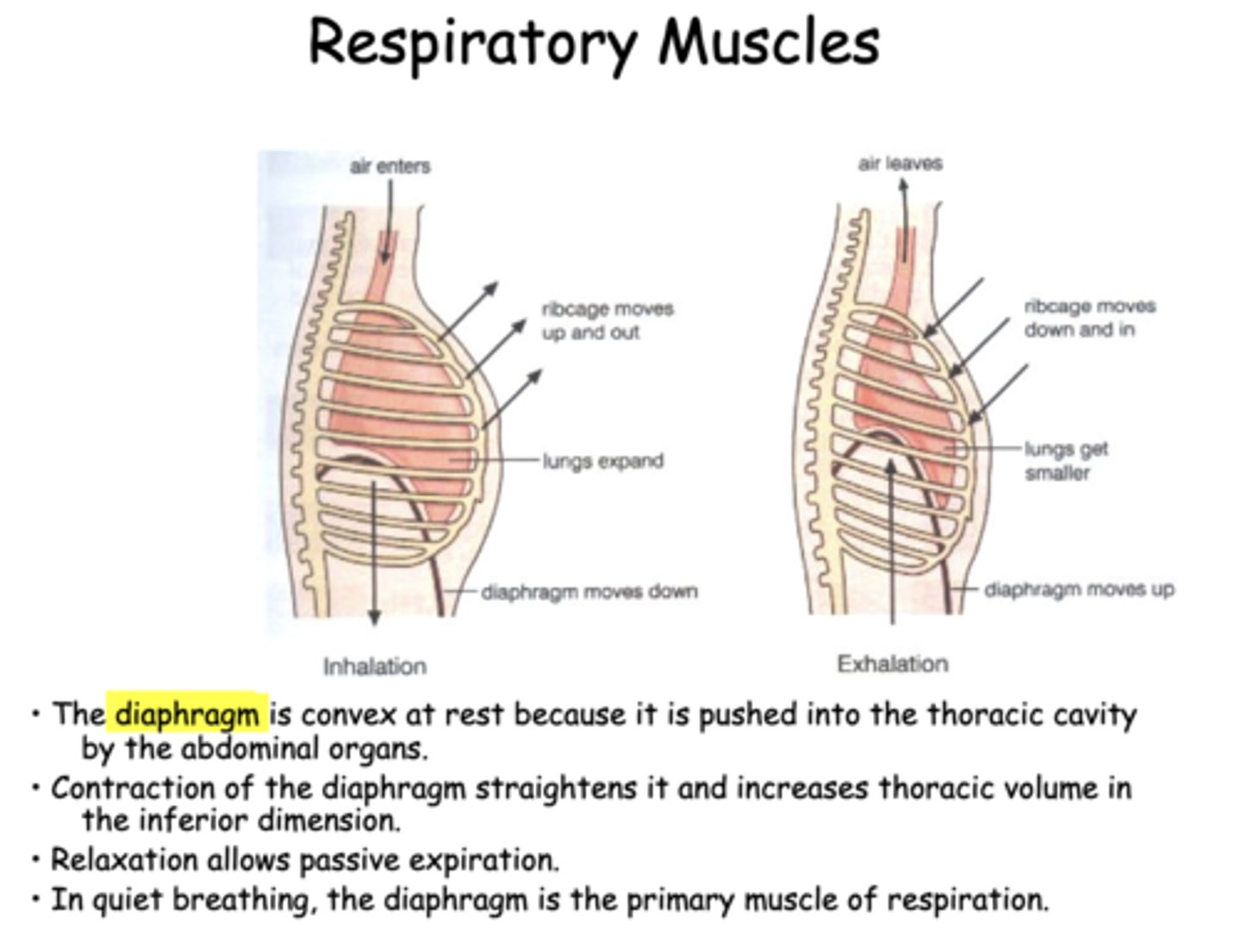
in quiet breathing, the _________ is the primary muscle of inspiration
diaphragm
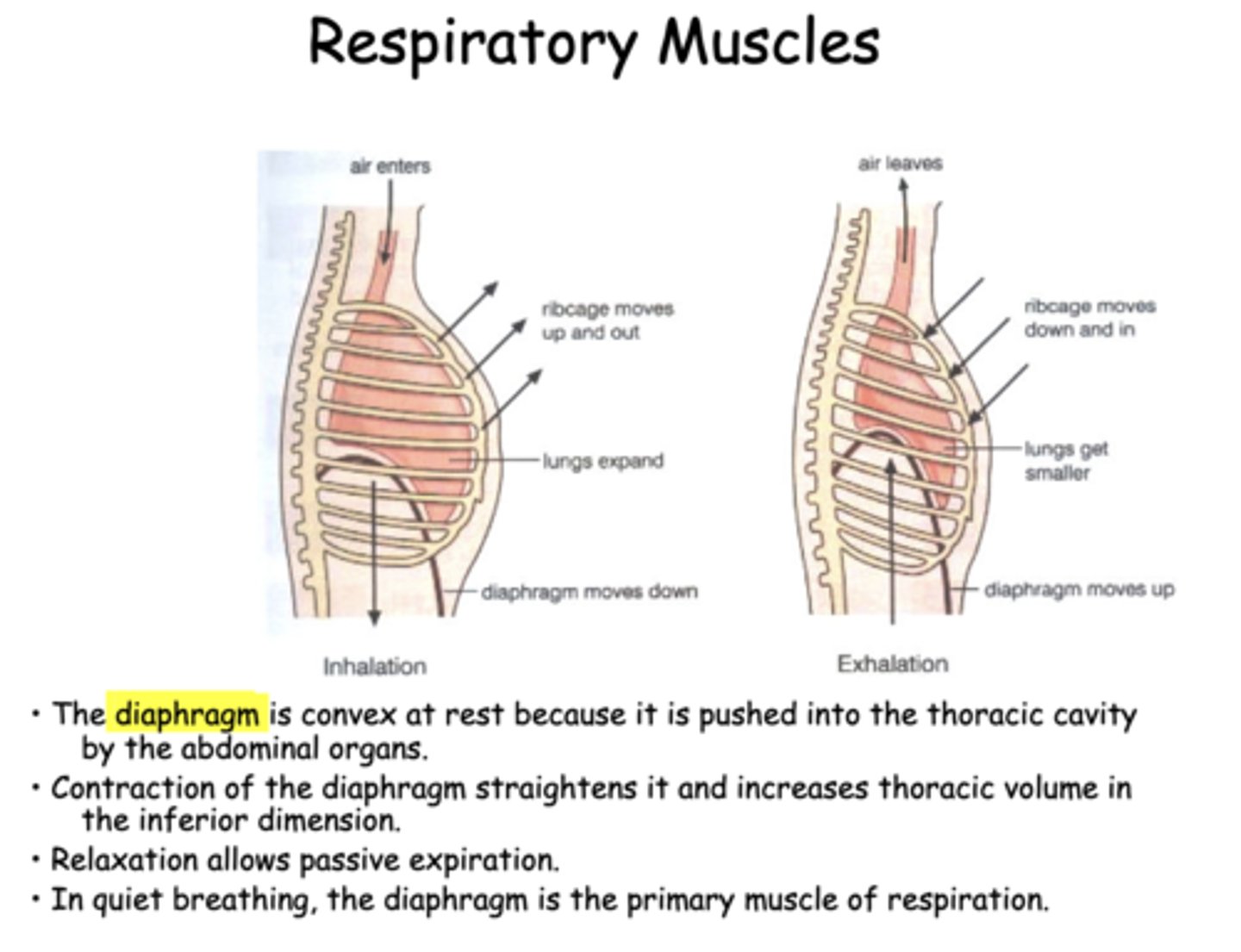
As lungs are "pulled out" by the expanding chest wall, the intrapleural pressure becomes more ___________
Negative
contraction of the diaphragm will ________ thoracic volume
increase
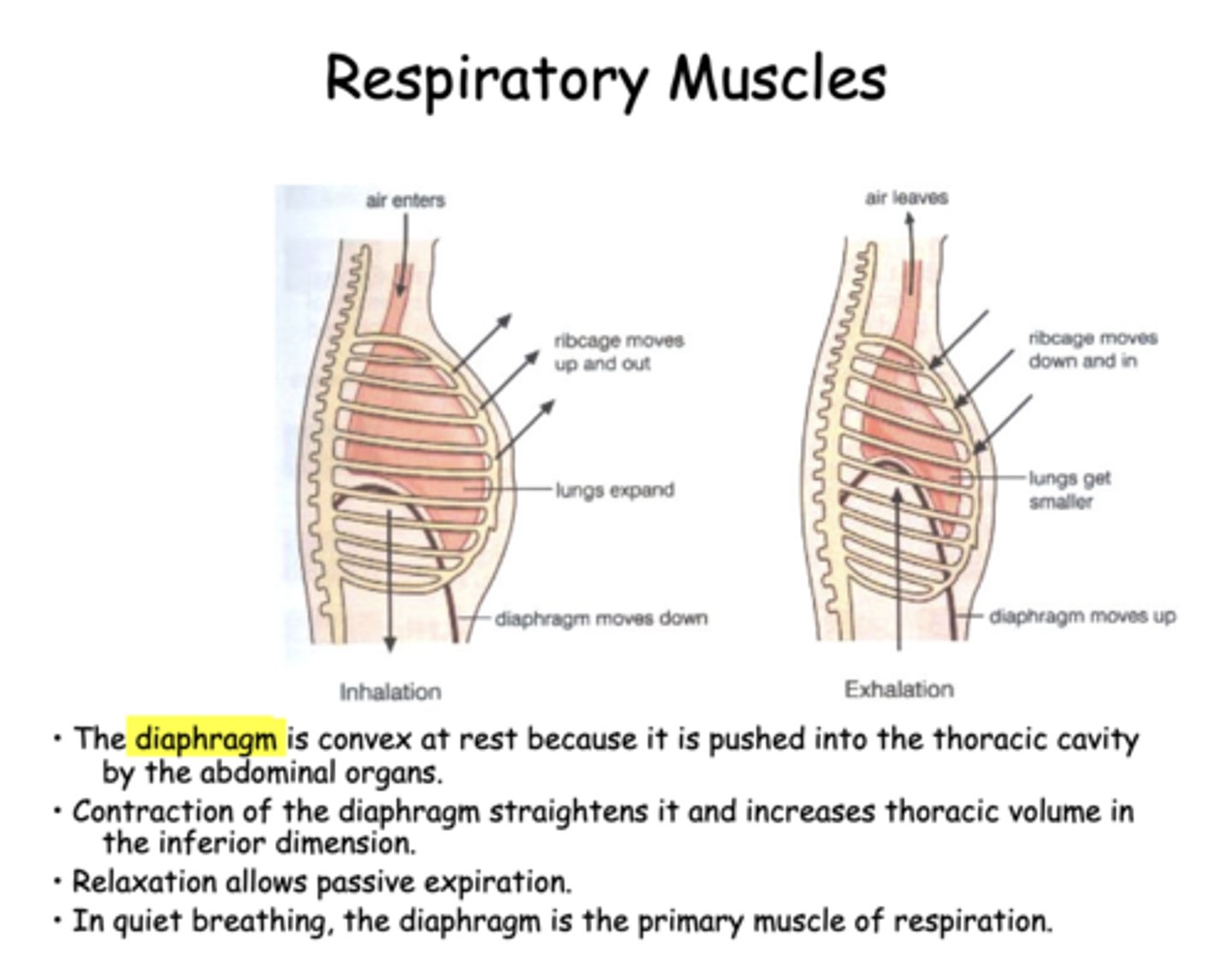
relaxation of the diaphragm allows for _______
passive expiration
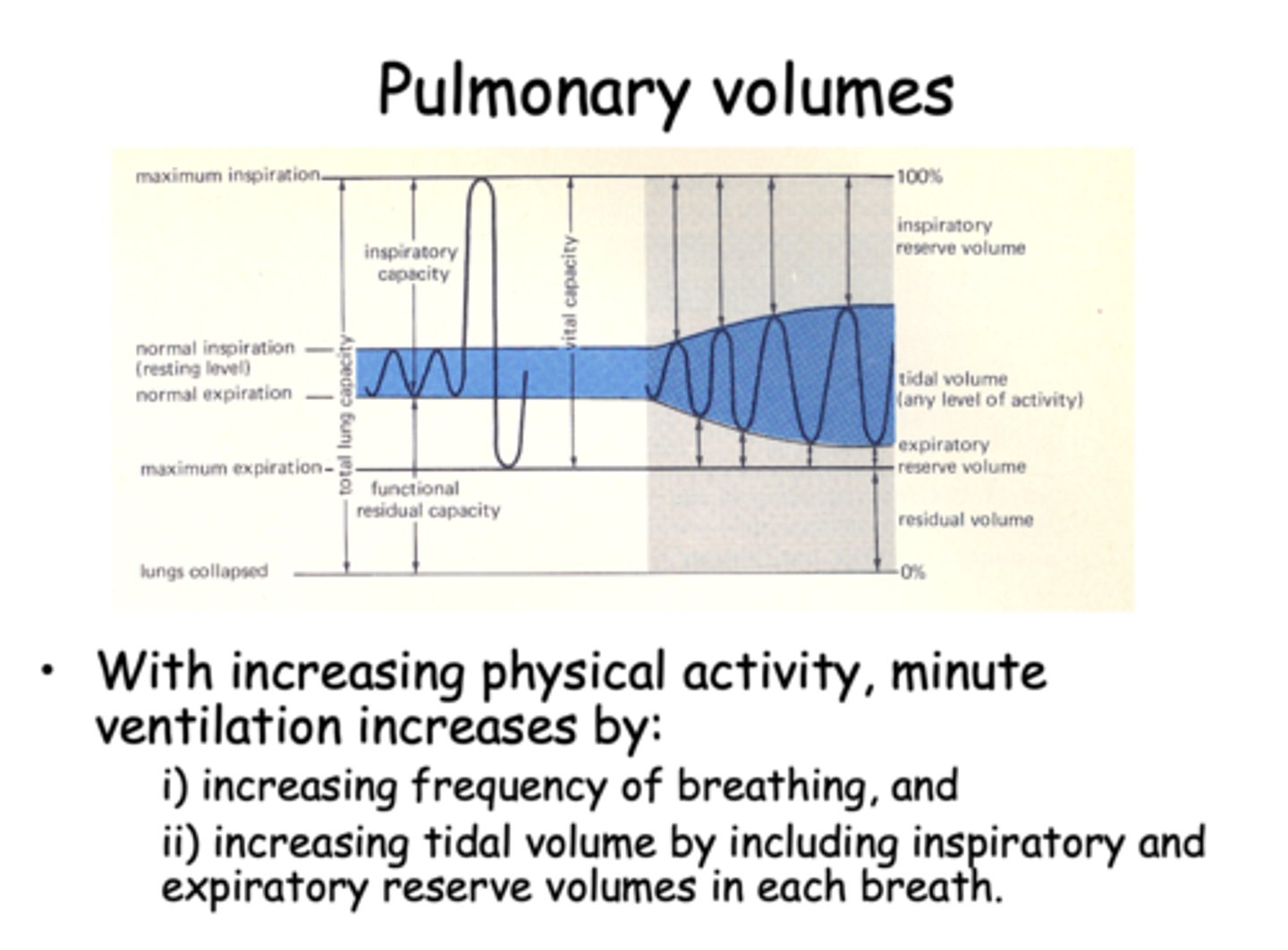
At very low lung volumes, the compliance is ______ because of high alveolar surface tension
low
At Functional Residual Capacity, Palv is equal to _____
Patm
At Functional Residual Capacity, Pip is about ______
-5 mmHg
With changes in physical activity, minute ventilation increases in what two things?
- Frequency of breathing
- Tidal volume
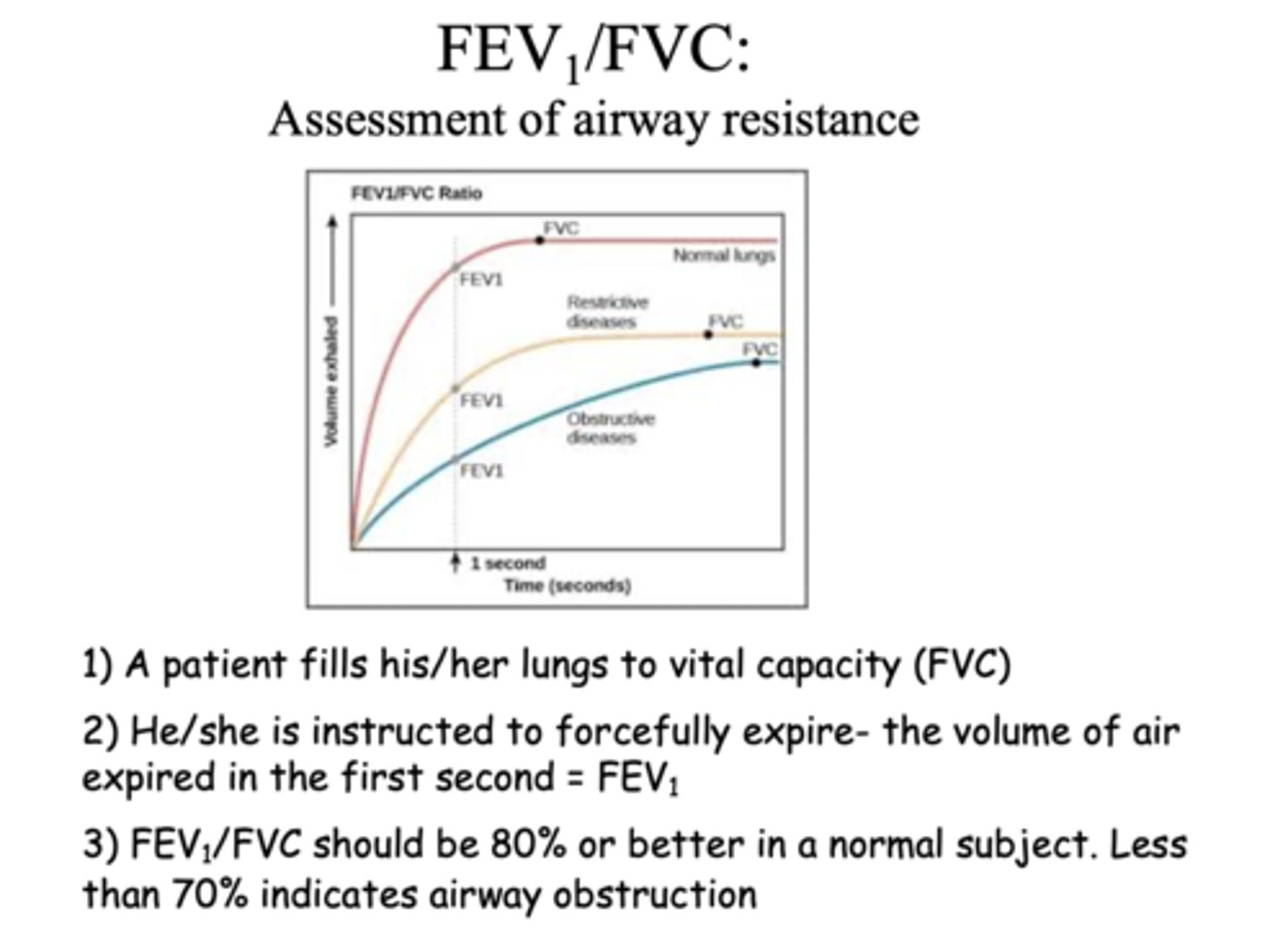
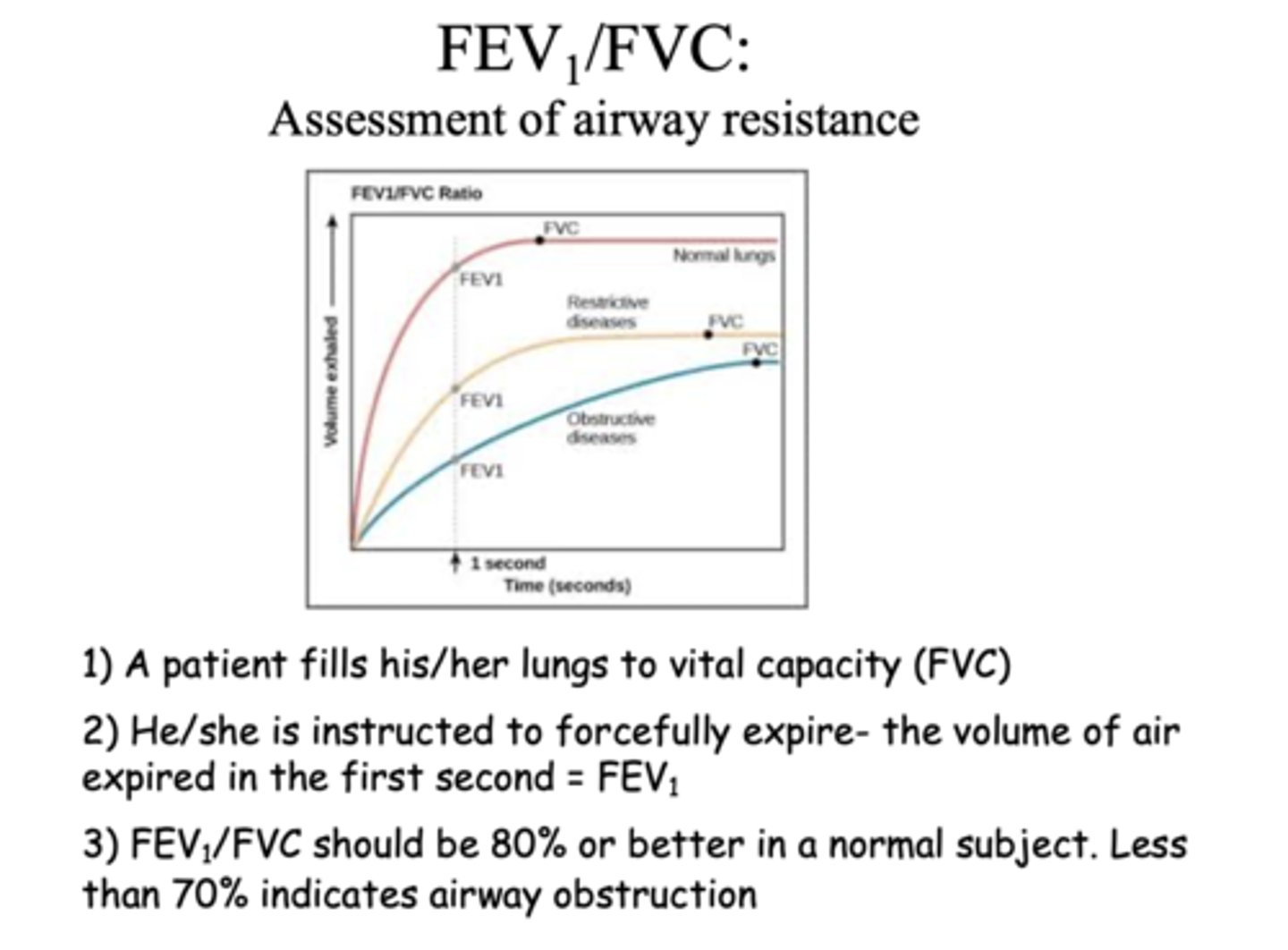
FEV1/FVC should be ___ or better in a normal subject
80%
tidal volume increases from
inspiratory residual volume & expiratory residual volume
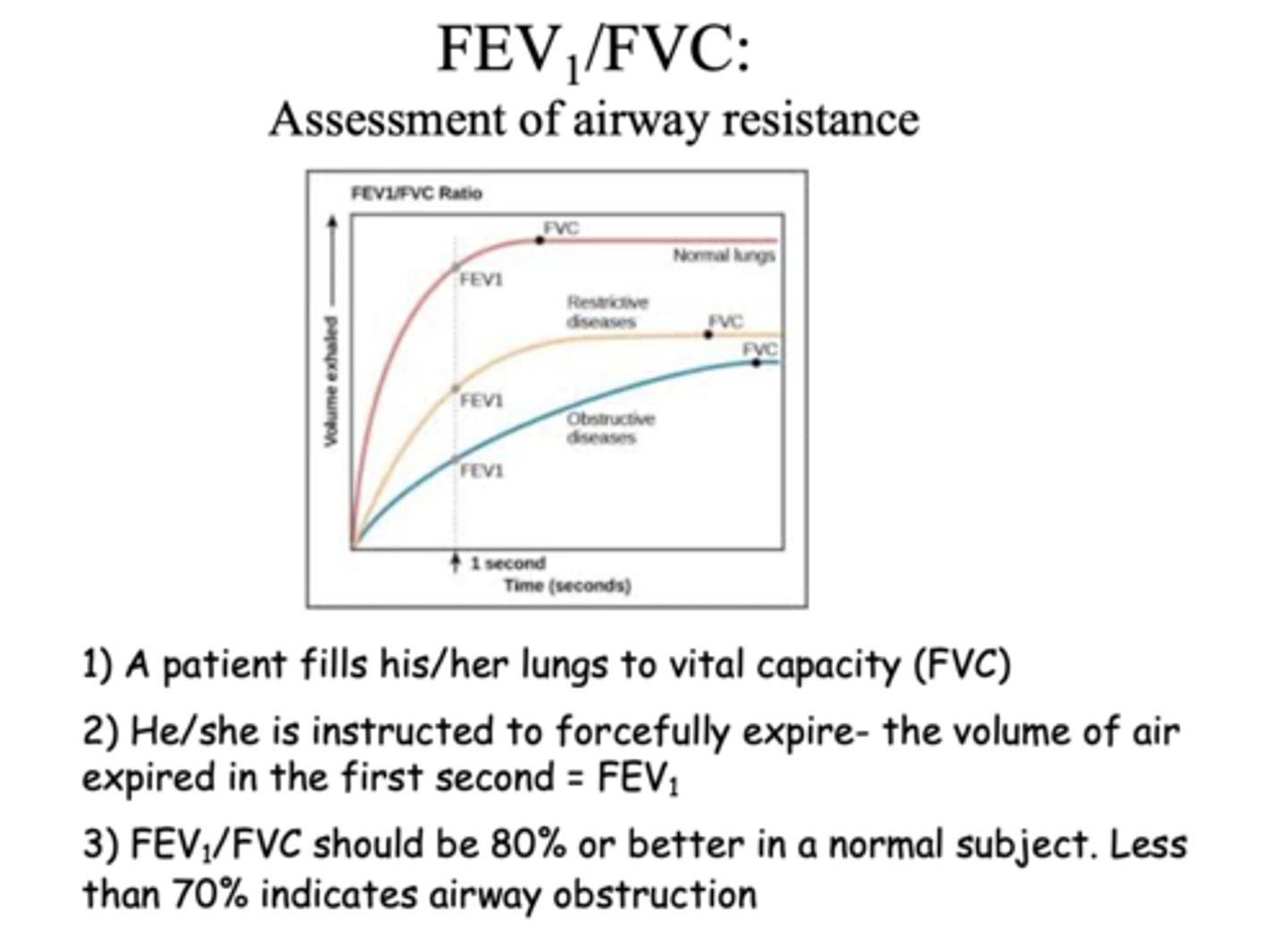
-patient fills his/her lungs to vital capacity (FVC)
-he/she is instructed to forcefully expire, the volume of air expired in the first second (FEV1)
FEV1/FVC is an assessment of ____________
airway resistance
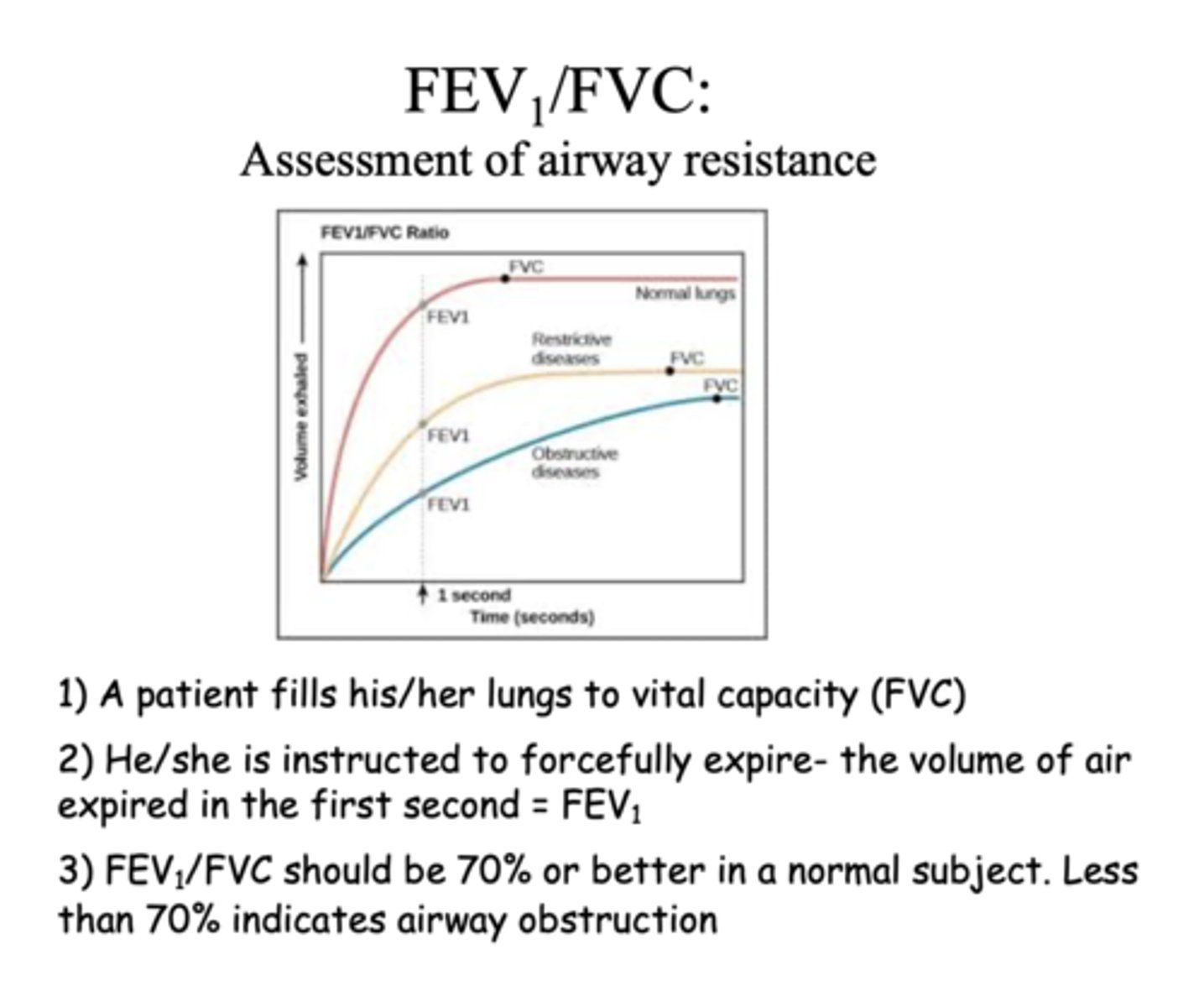
FEV1/FVC less than 70% indicates
airway obstruction
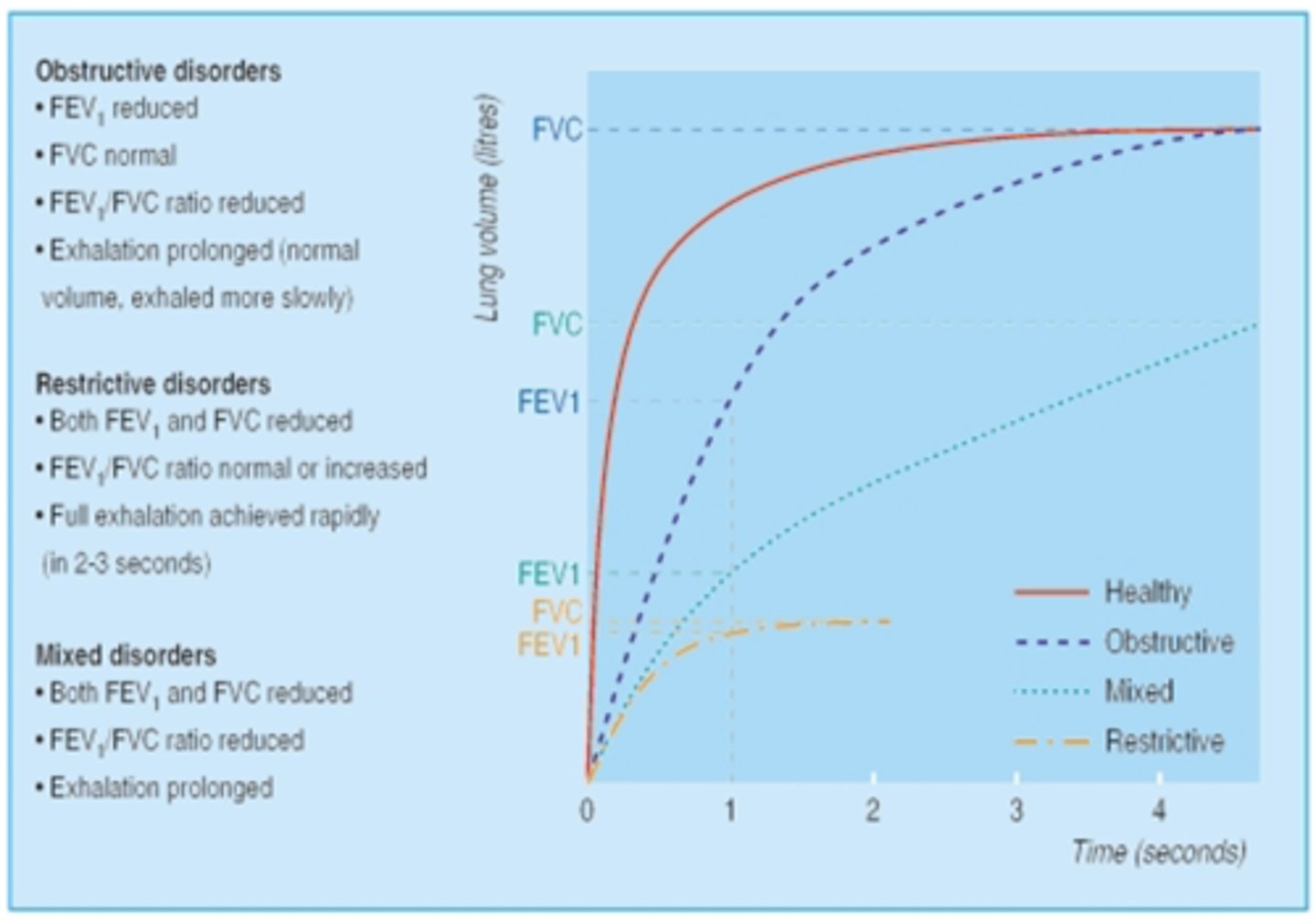
Which disorder is the following: Restrictive, obstructive, or mixed?
- FEV1 reduced
- FVC normal
- FEV1/FVC ratio reduced
- Exhalation prolonged (normal volume, exhaled more slowly)
Obstructive disorders
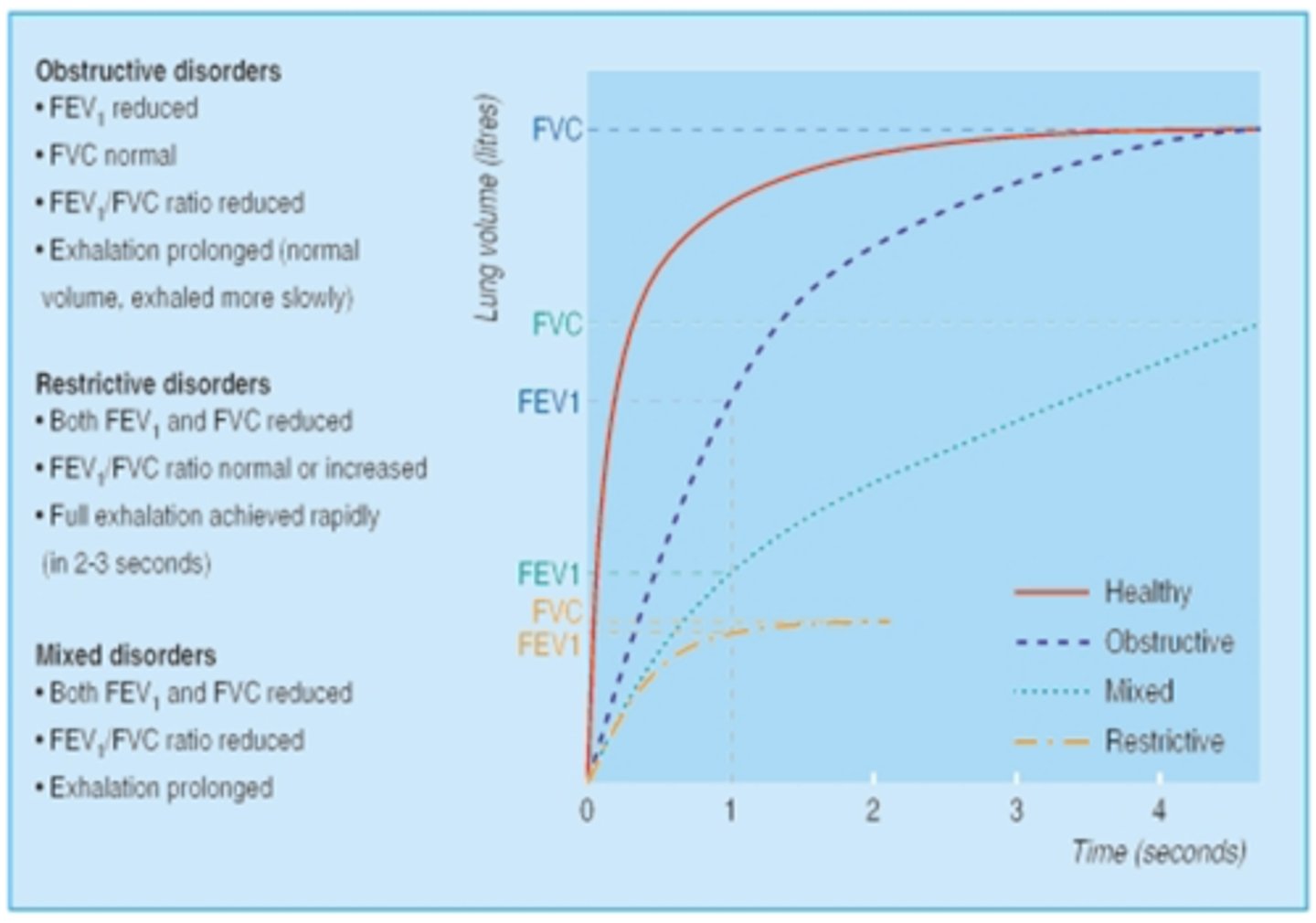
Which disorder is the following: Restrictive, obstructive, or mixed?
- Both FEV1 and FVC reduced
- FEV1/FVC ratio normal or increased
- Fill exhalation achieved rapidly (2-3 seconds)
Restrictive disorders
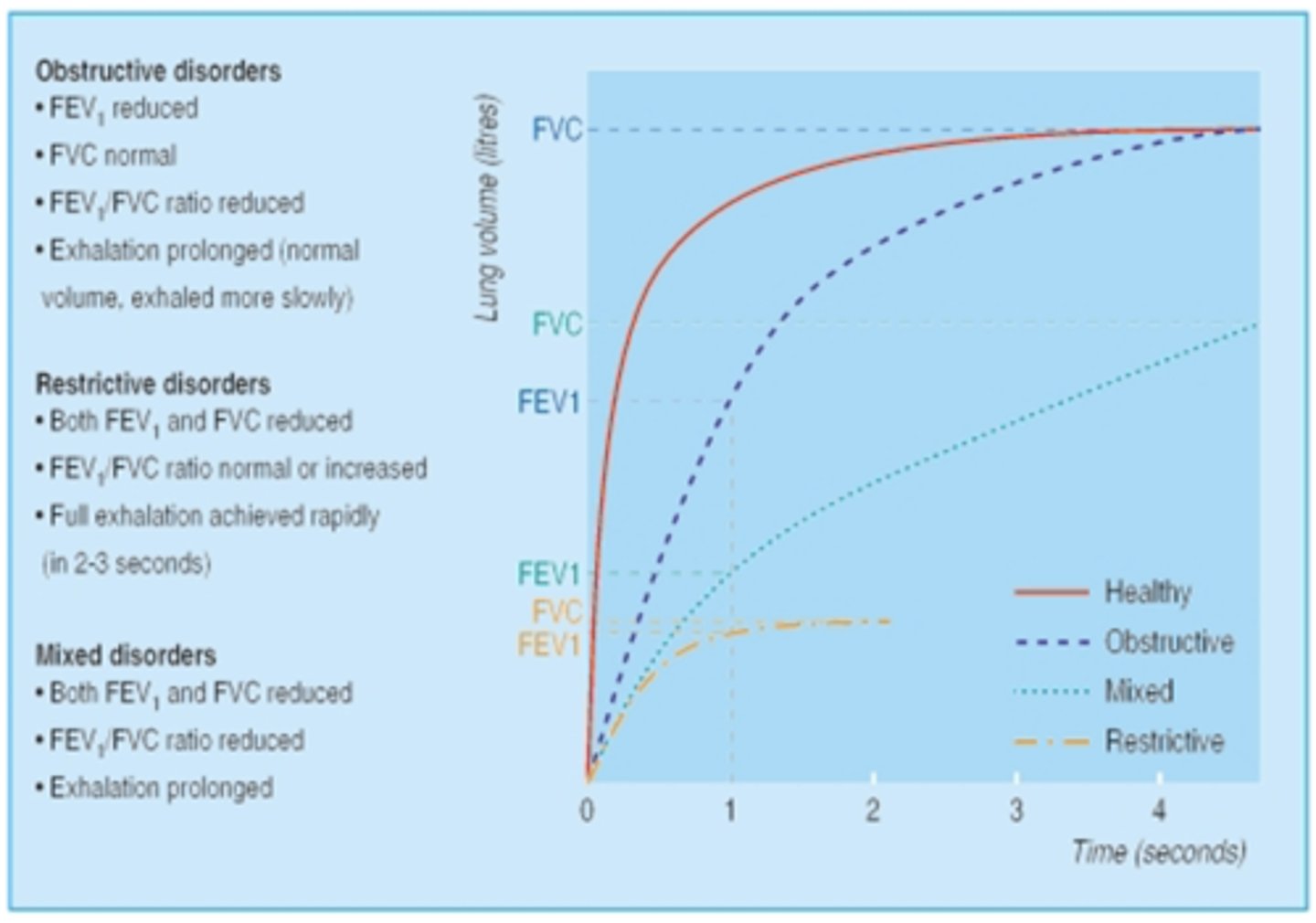
Which disorder is the following: Restrictive, obstructive, or mixed?
- Both FEV1 and FVC reduced
- FEV1/FVC ratio reduced
- Exhalation prolonged
Mixed disorders
_______ diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, commonly result in reduced lung volumes owing to loss of lung compliance
restrictive
________ diseases such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, cause increase in residual volume, functional residual capacity & total lung capacity due to increased airway resistance or decreased elastic recoil
obstructive