Carbohydrates - MCAT
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
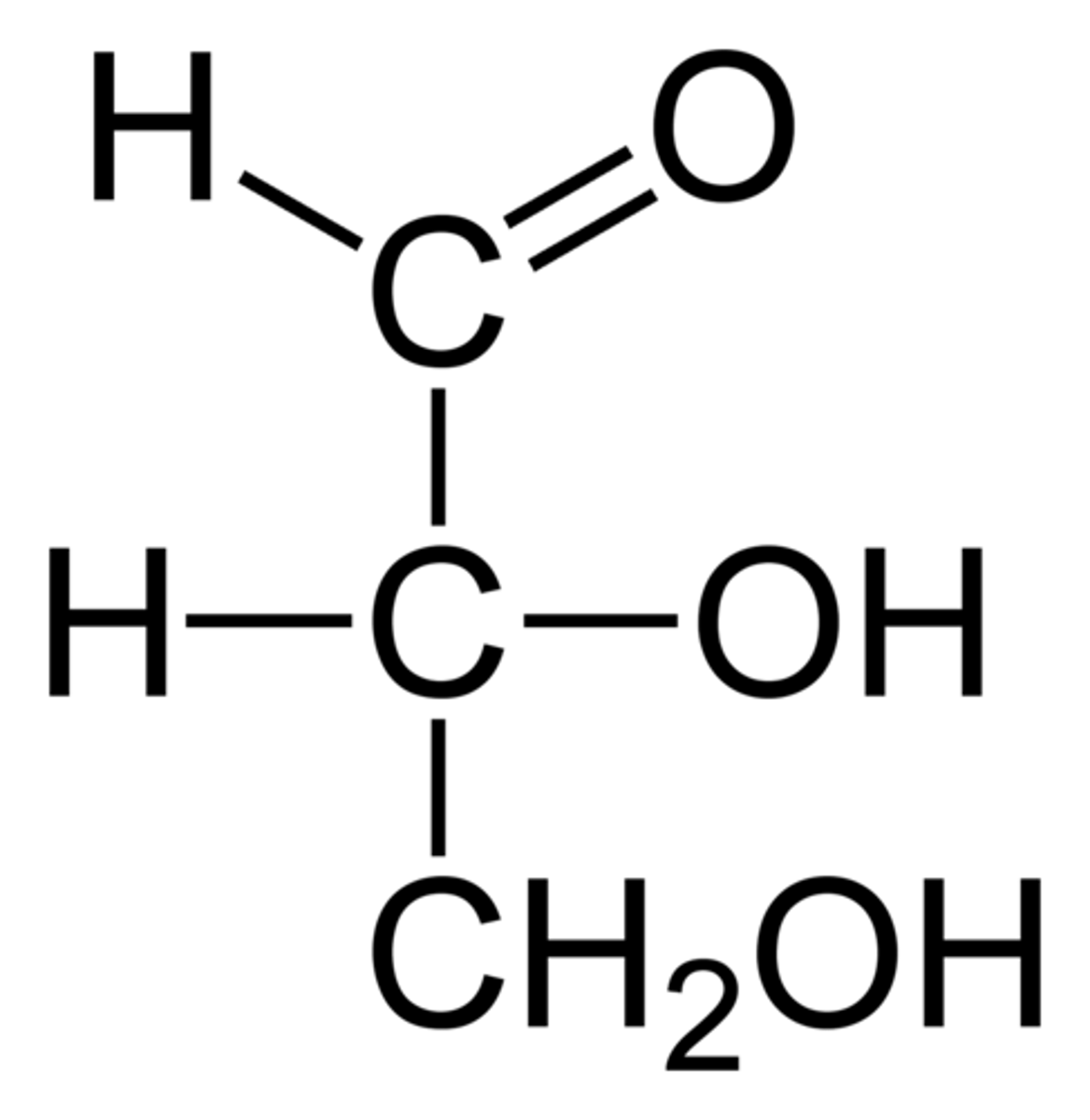
Glyceraldehyde
simplest aldose
Complex sugars
Cn(h2o)m
simple sugars
Cn(h2o)n
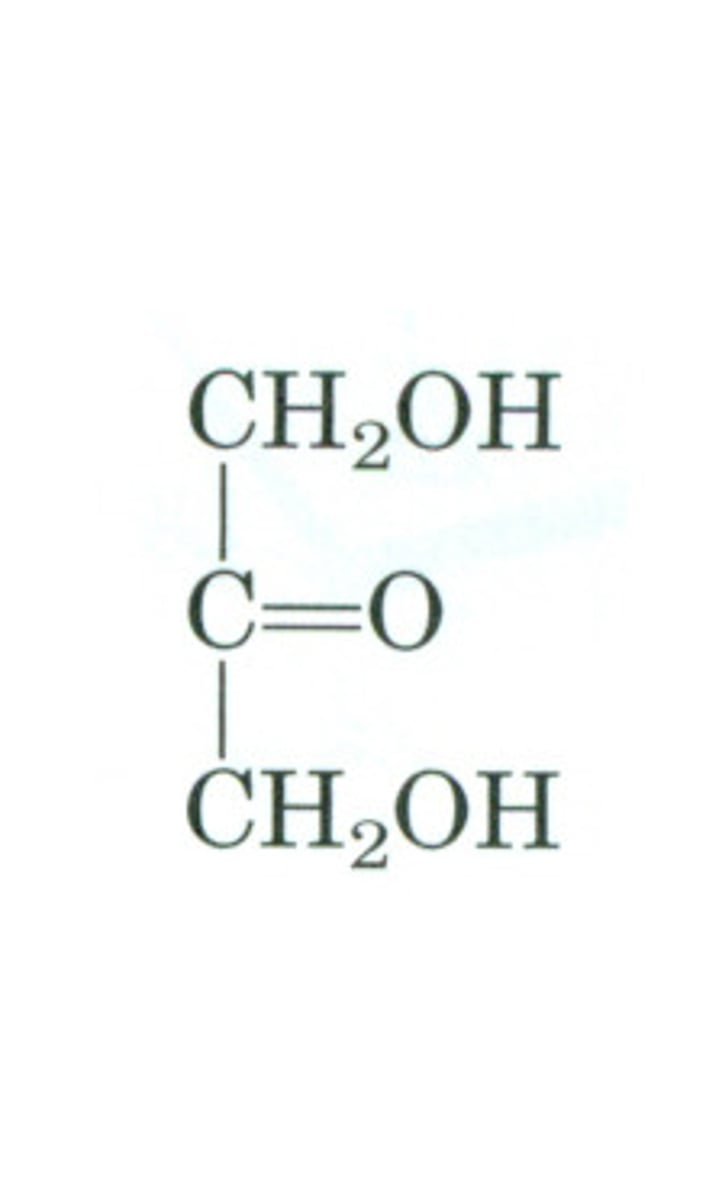
dihydroxyacetone
simplest ketone
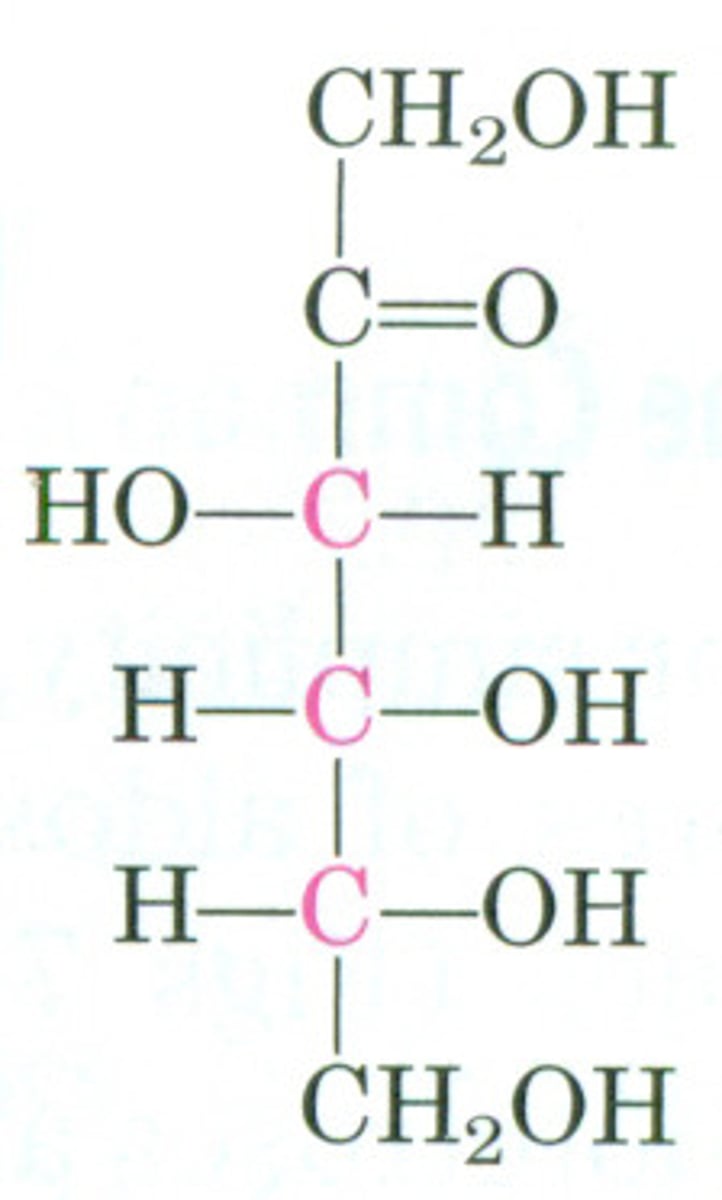
D-fructose
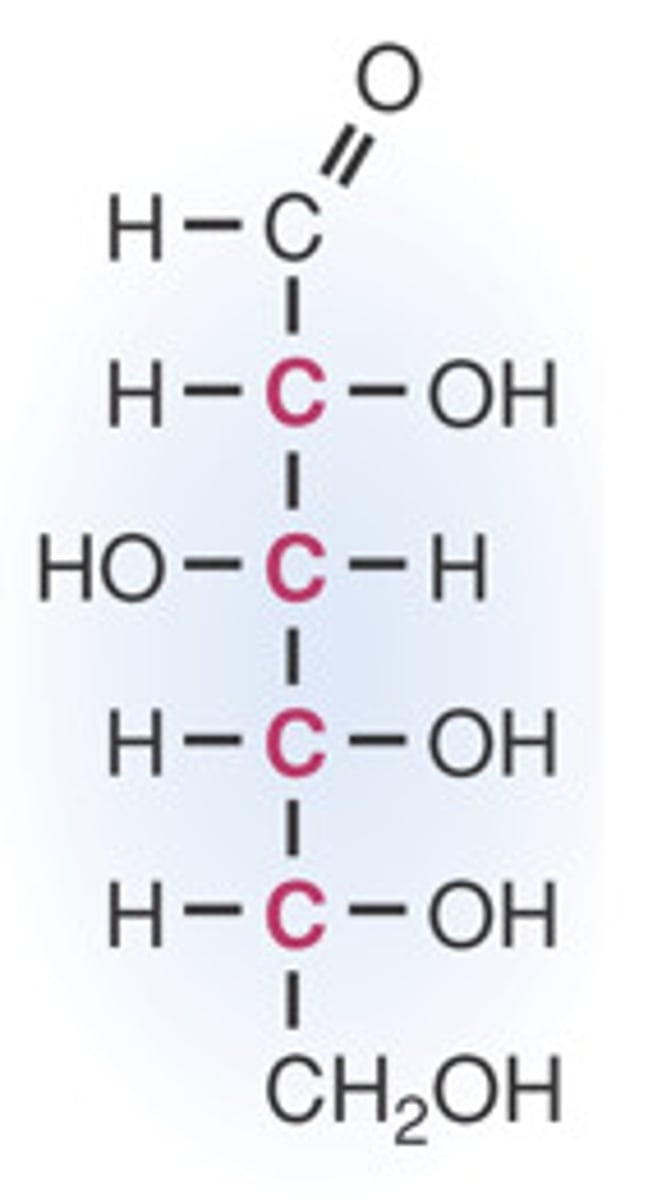
D-glucose
D-galactose
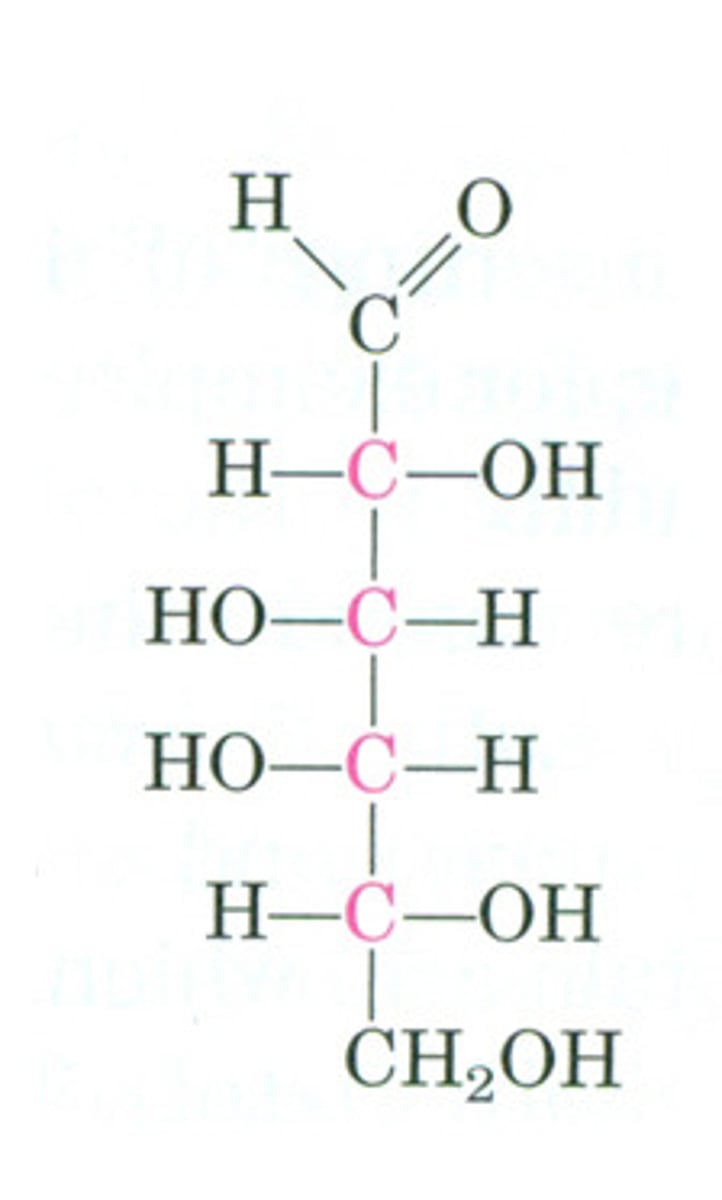
D-mannose
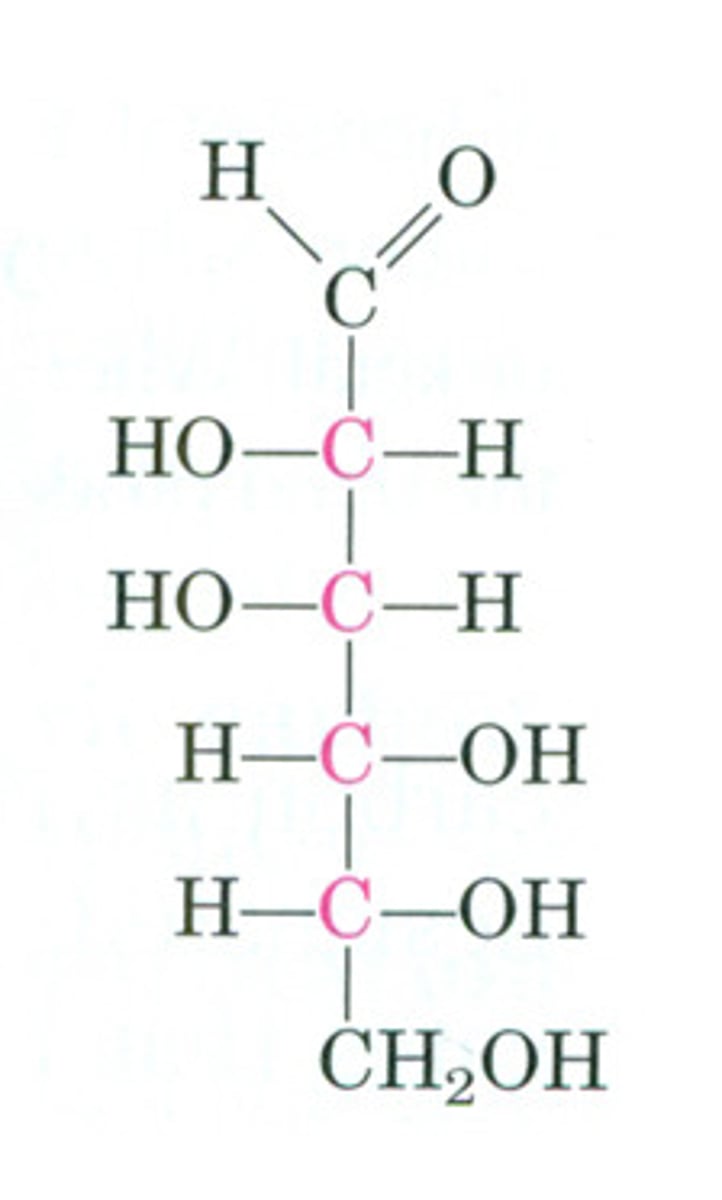
D vs L (anomers)
D - first OH groupi s on the right
L - first OH group is on the left
enantiomers
differ at anomeric carbon!!!
Calculating steroisomers with same backbone
2^n (n=number of chiral carbons)
enantiomers of glucose
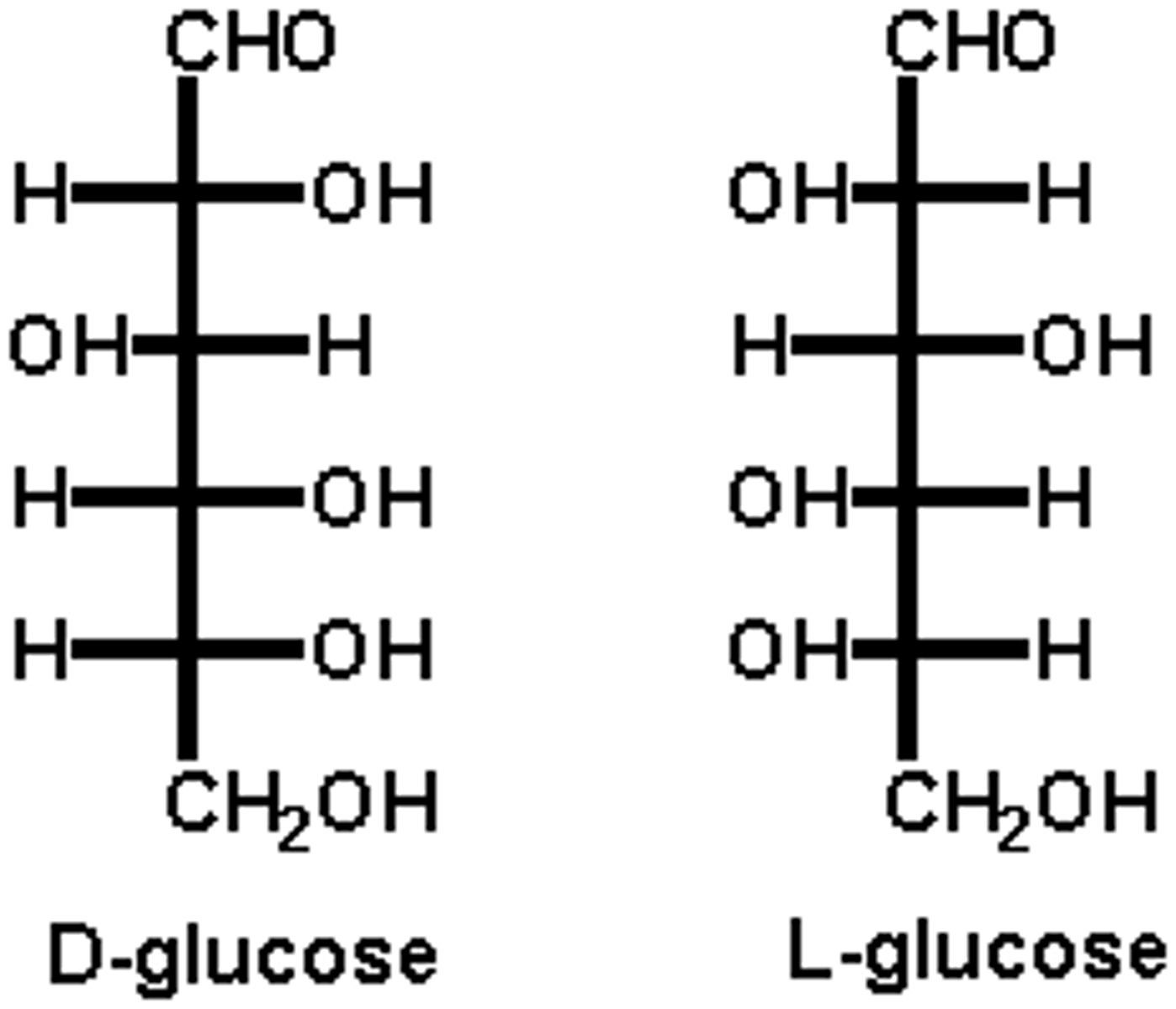
Diasteromer
same fam, same number of carbons, same ald/ke, but not identical
epimer
differs in configuration at only one carbon
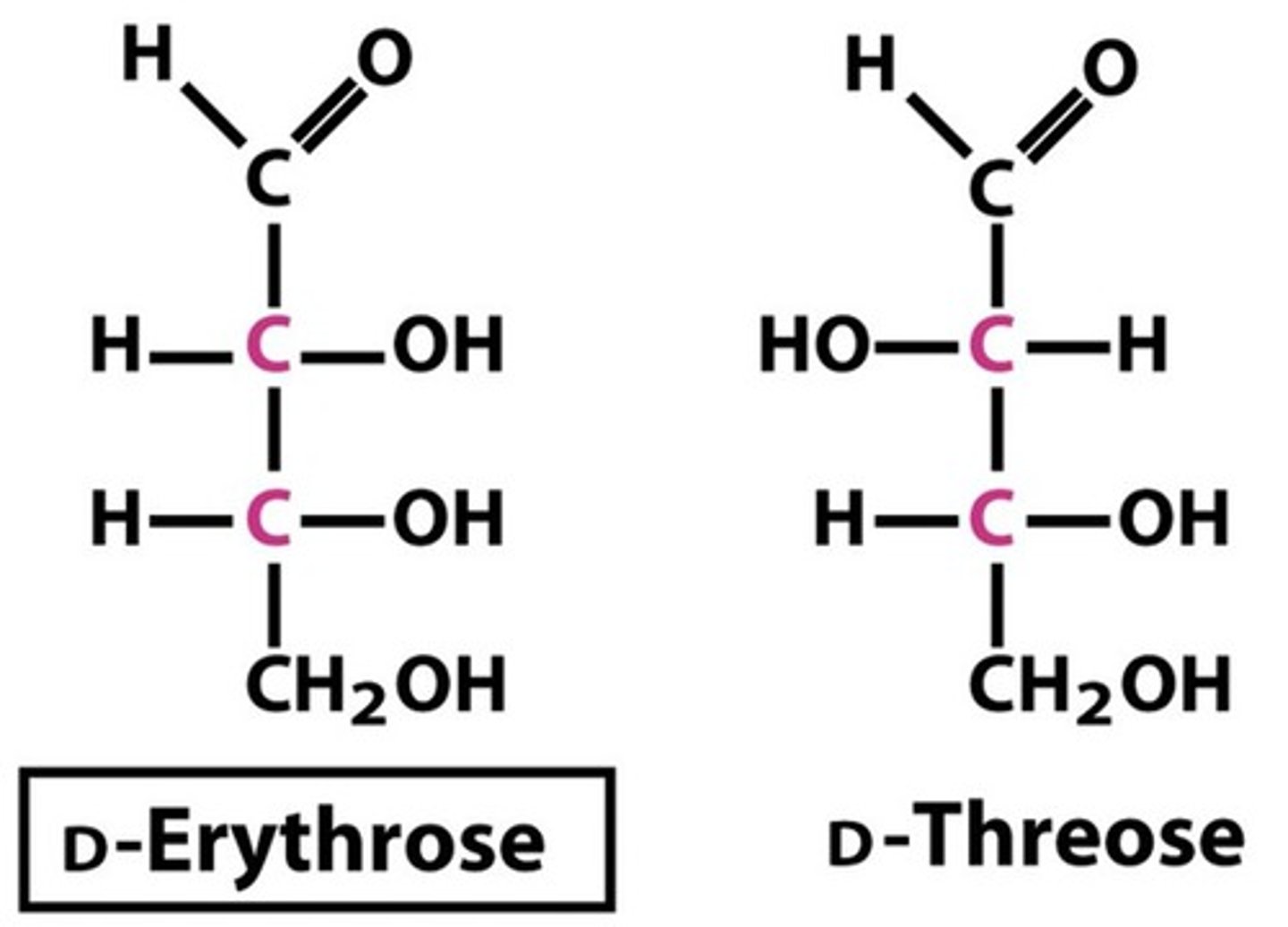
four stereoisomers of an aldotetrose
with their corresponding L mirror images
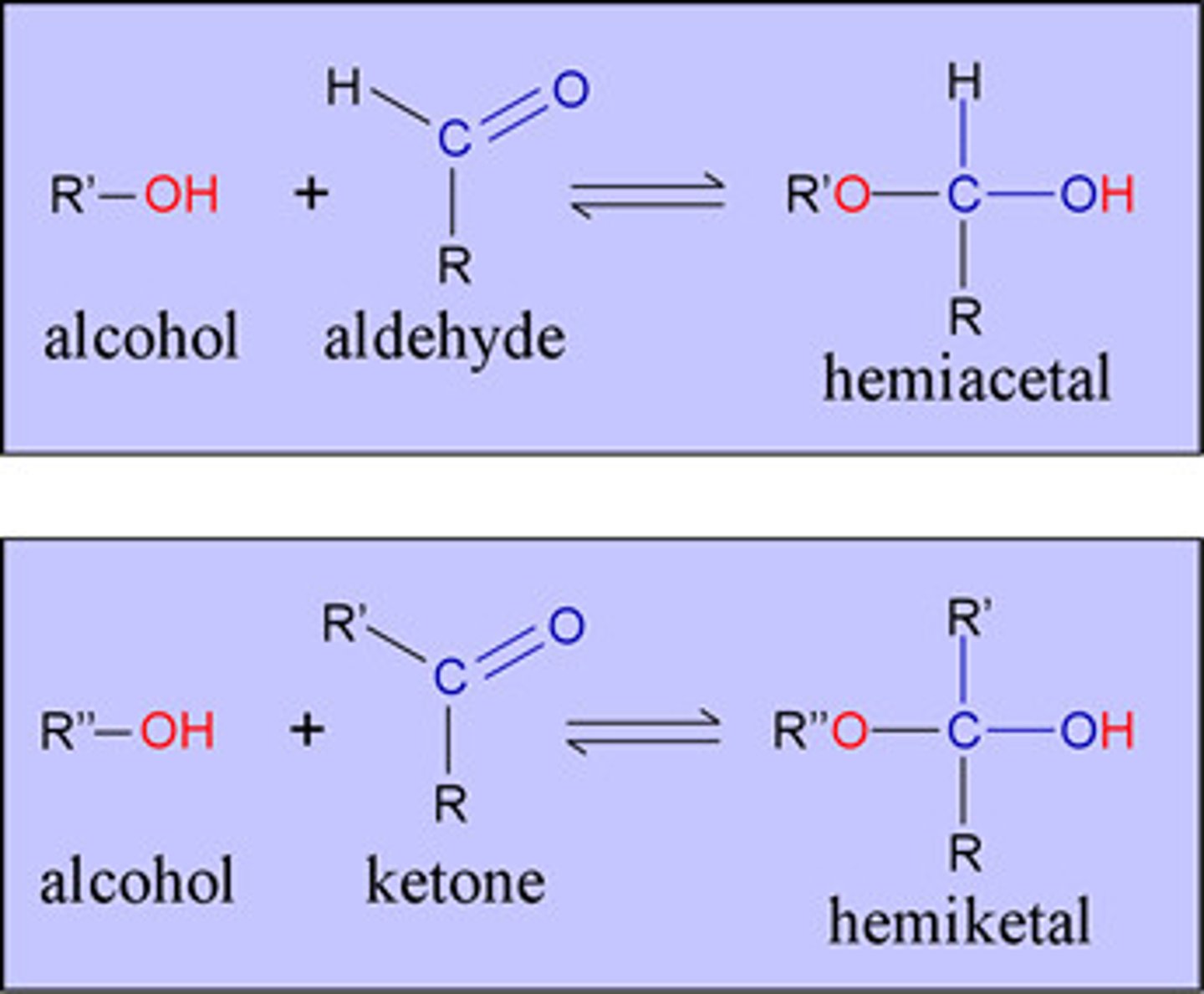
hemiacetals/ketals
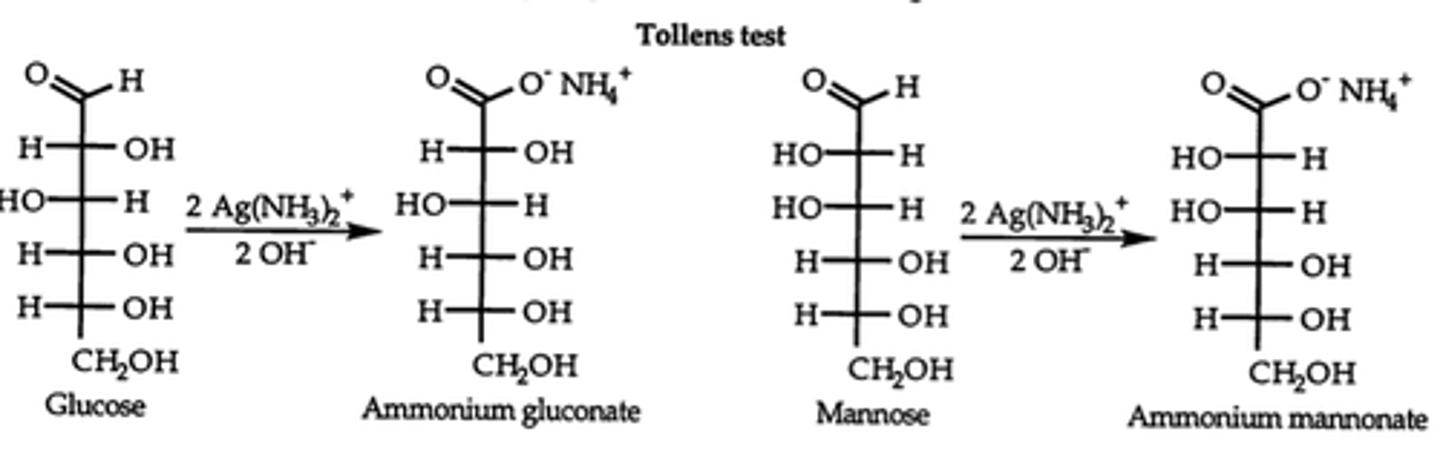
Tollens reagent
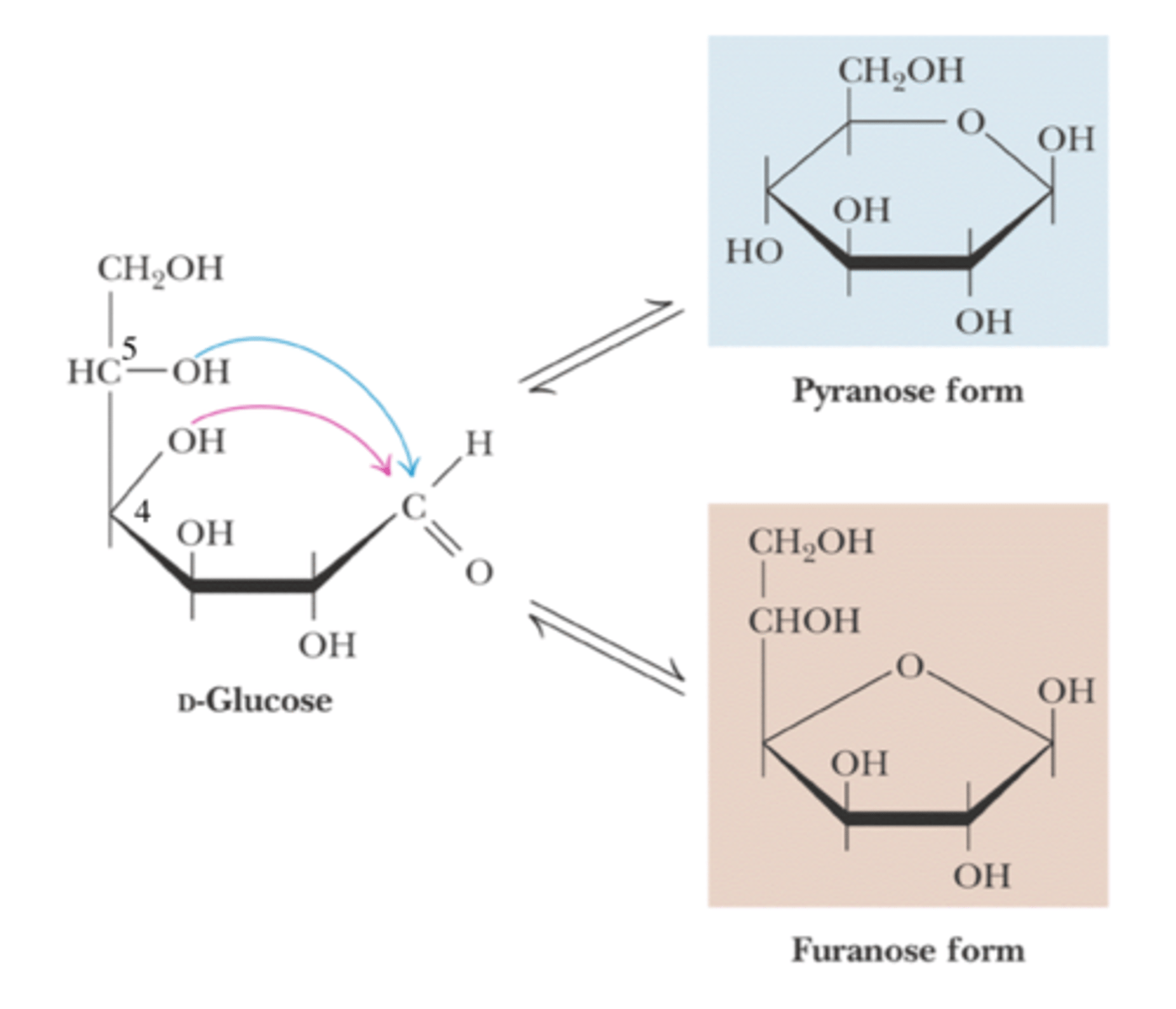
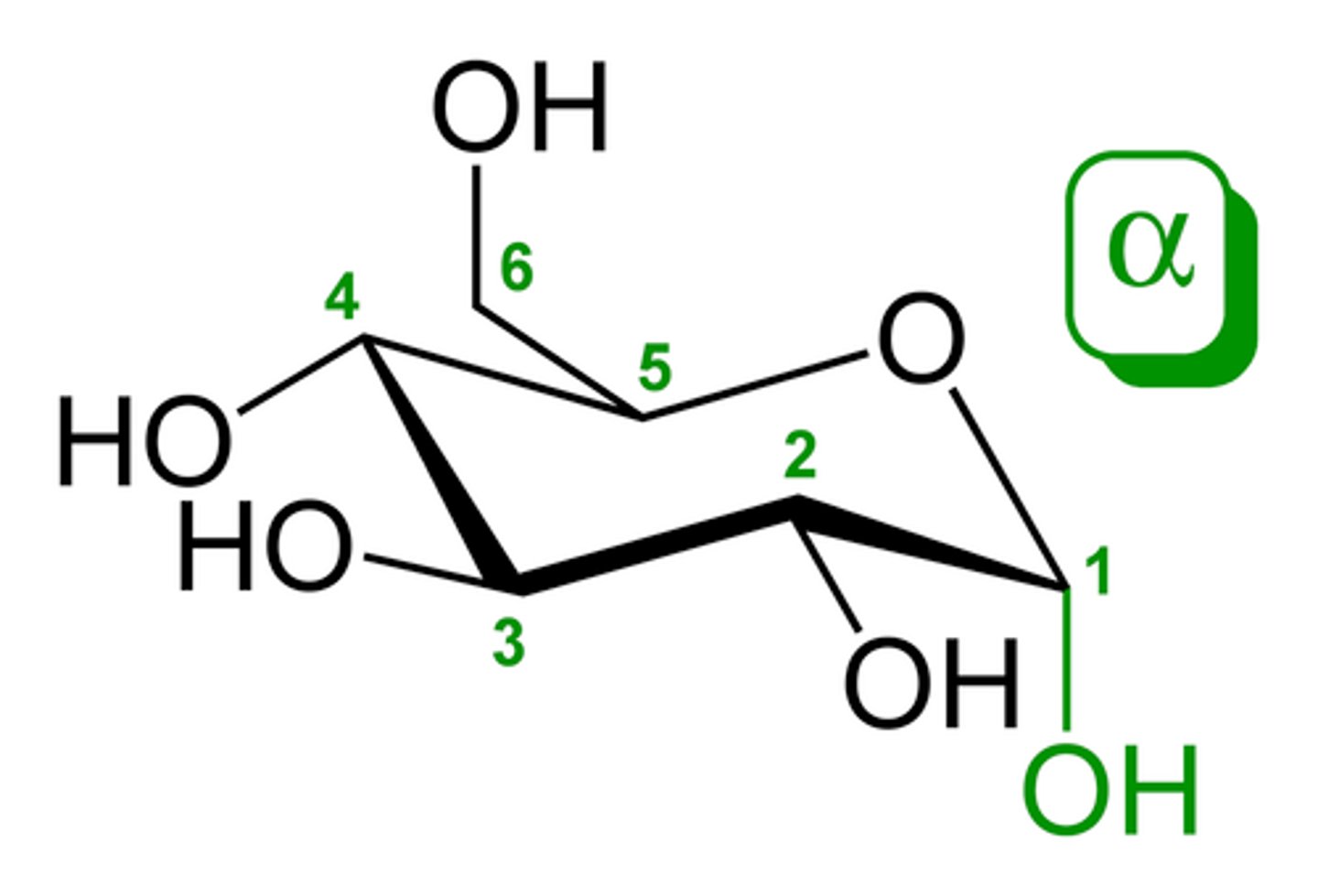
cyclic glucose
anomeric carbon
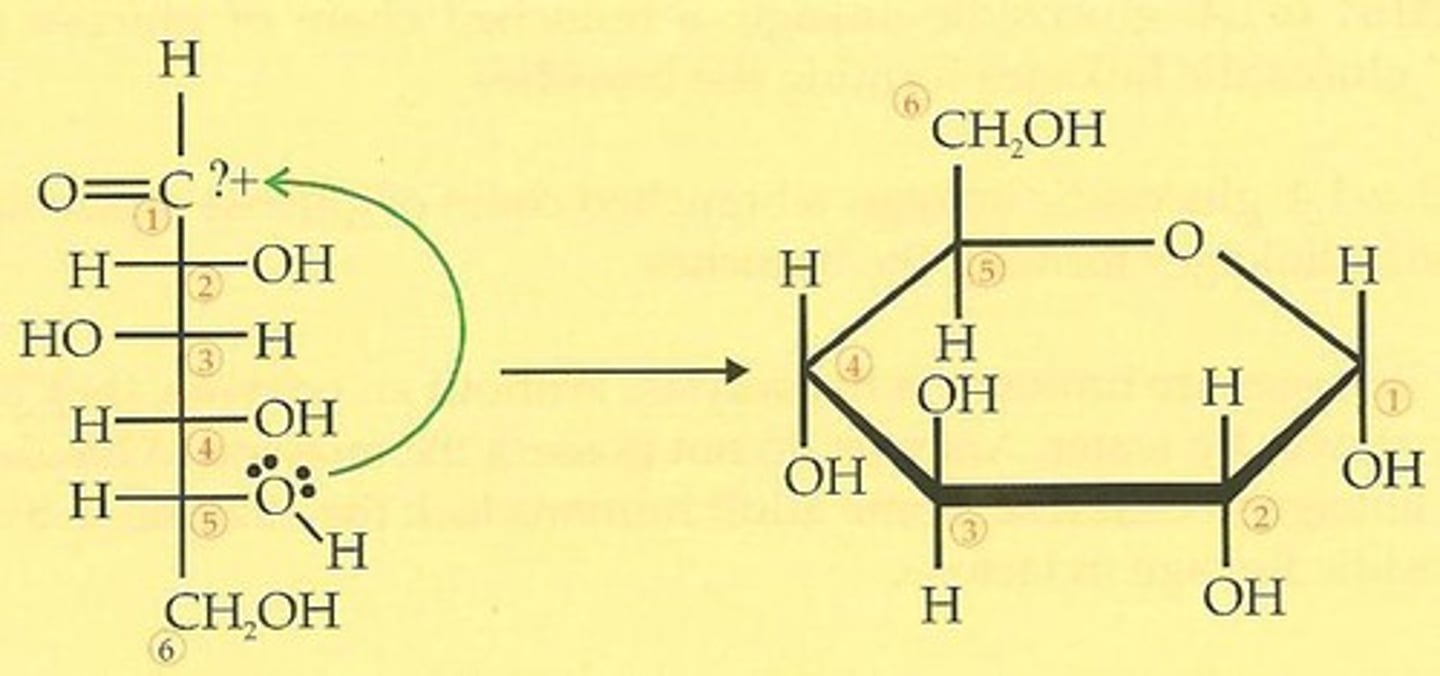
alpha-anomer
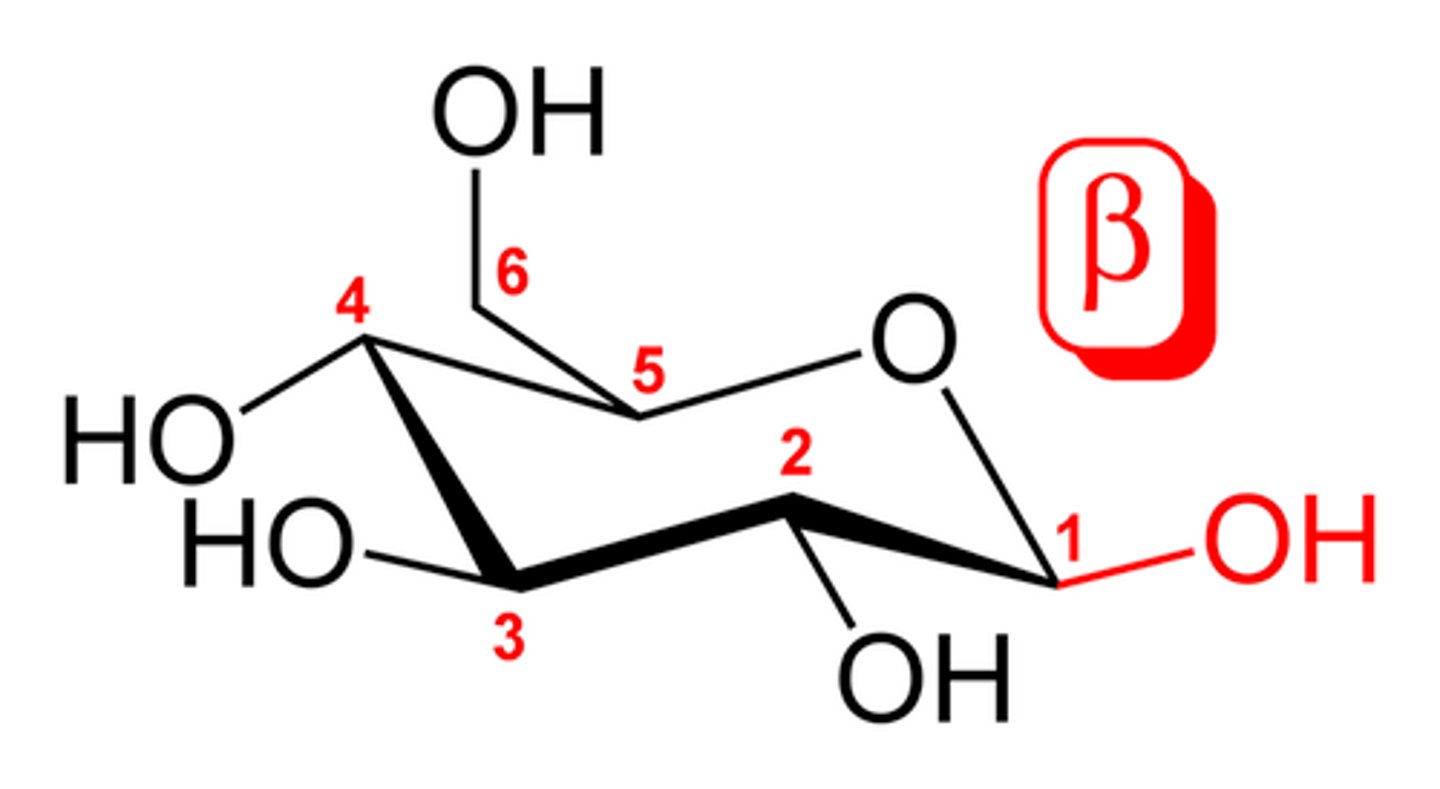
beta-enomer
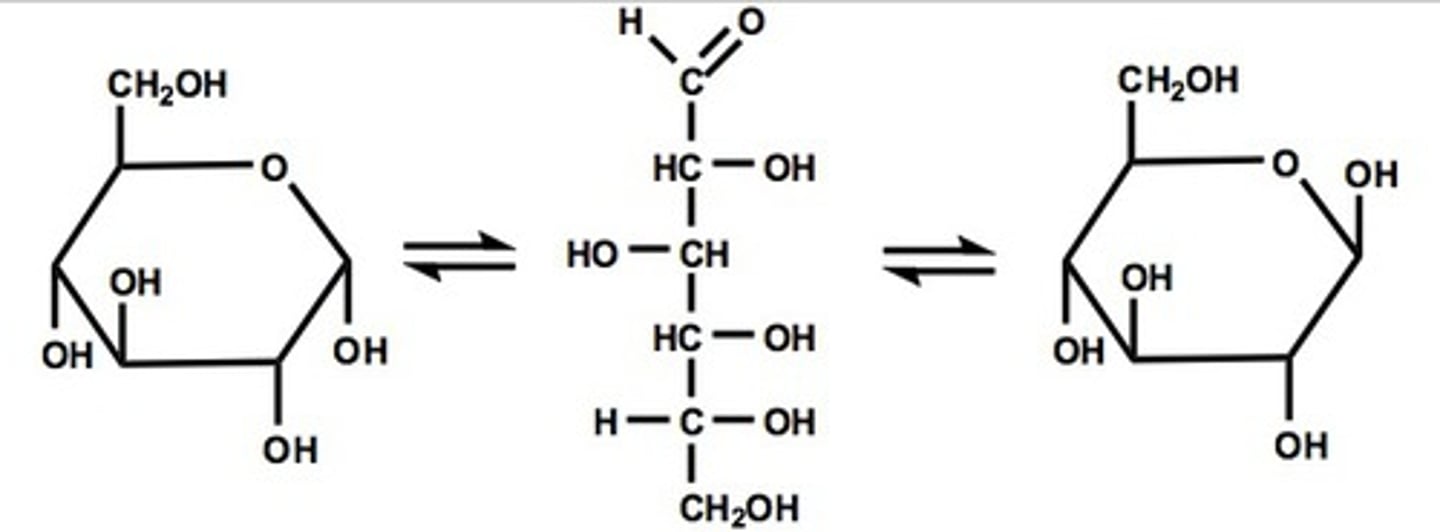
mutarotation
spontaneous change of conformation
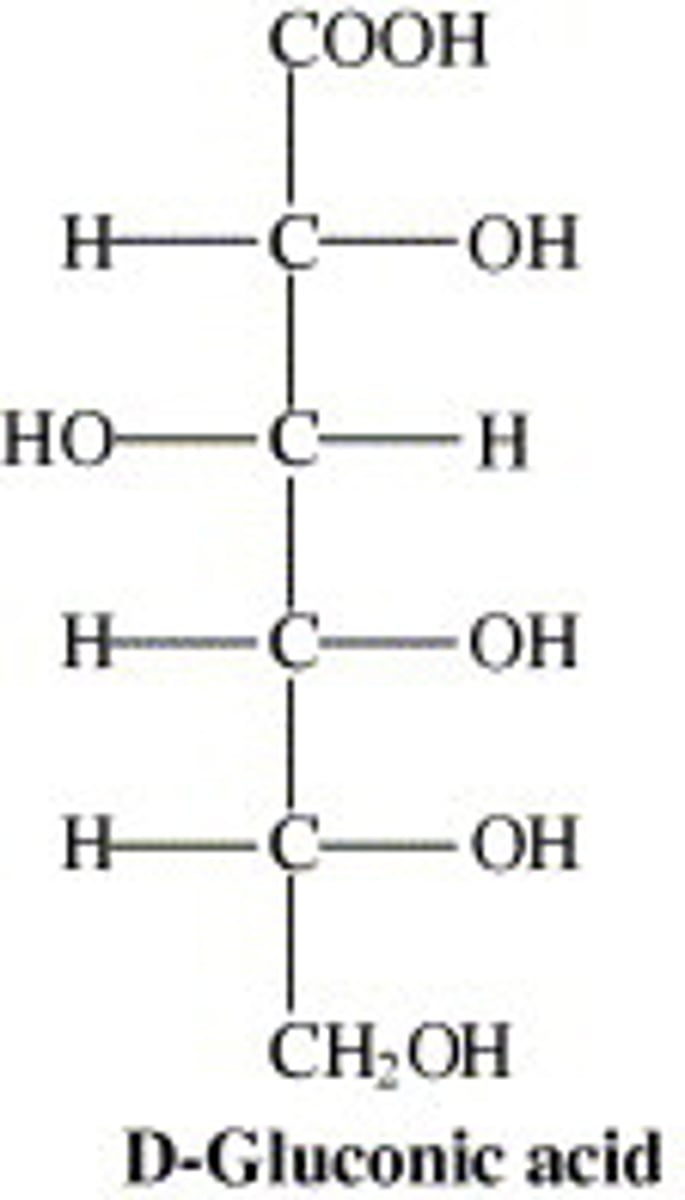
aldonic acids
oxidized aldoses into carboxylic acids
sucrose
glucose-a-1,2-fructose
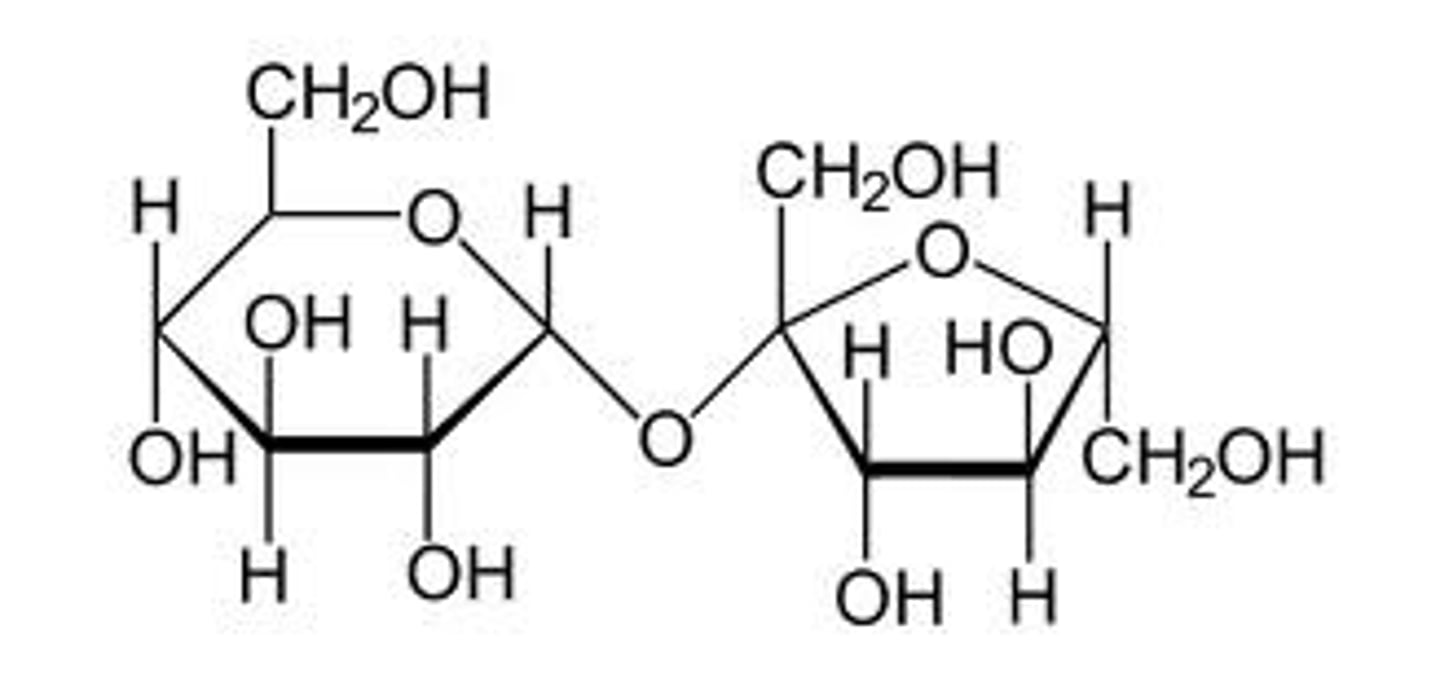
lactose
galactose-b-1,4-glucose
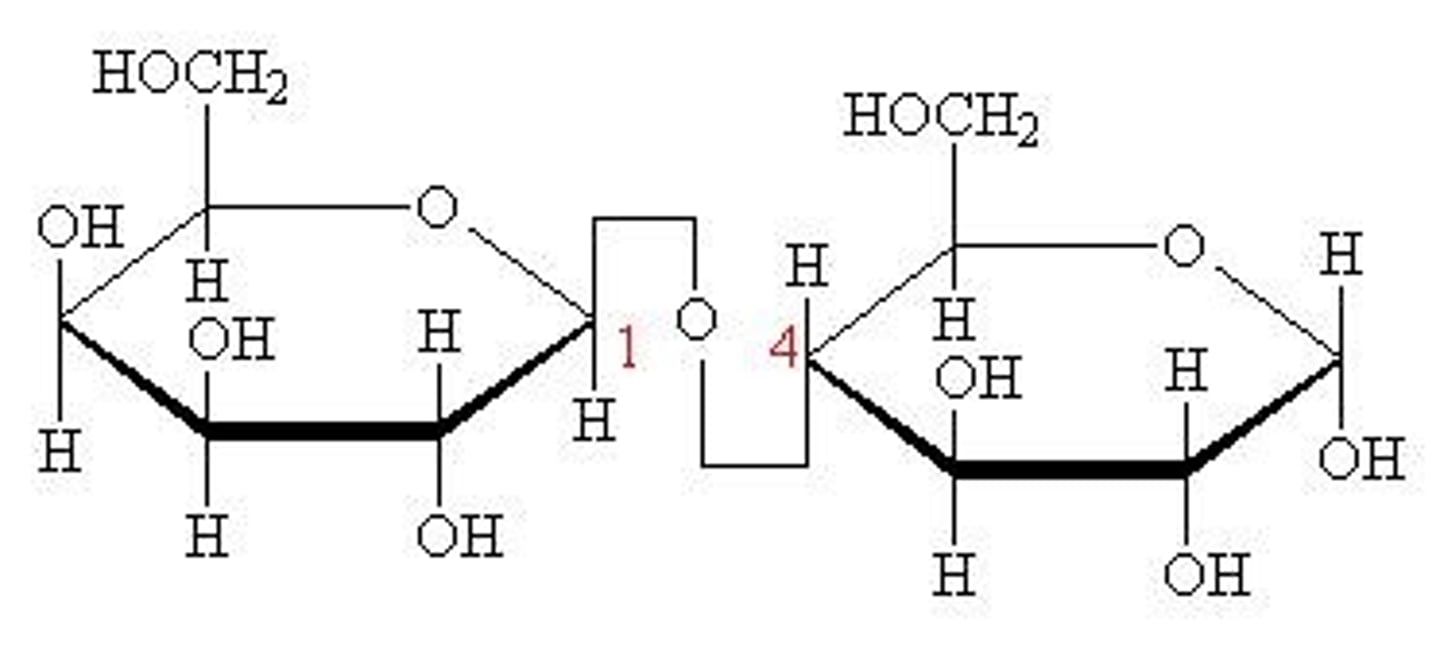
maltose
glucose-a-1,4-glucose
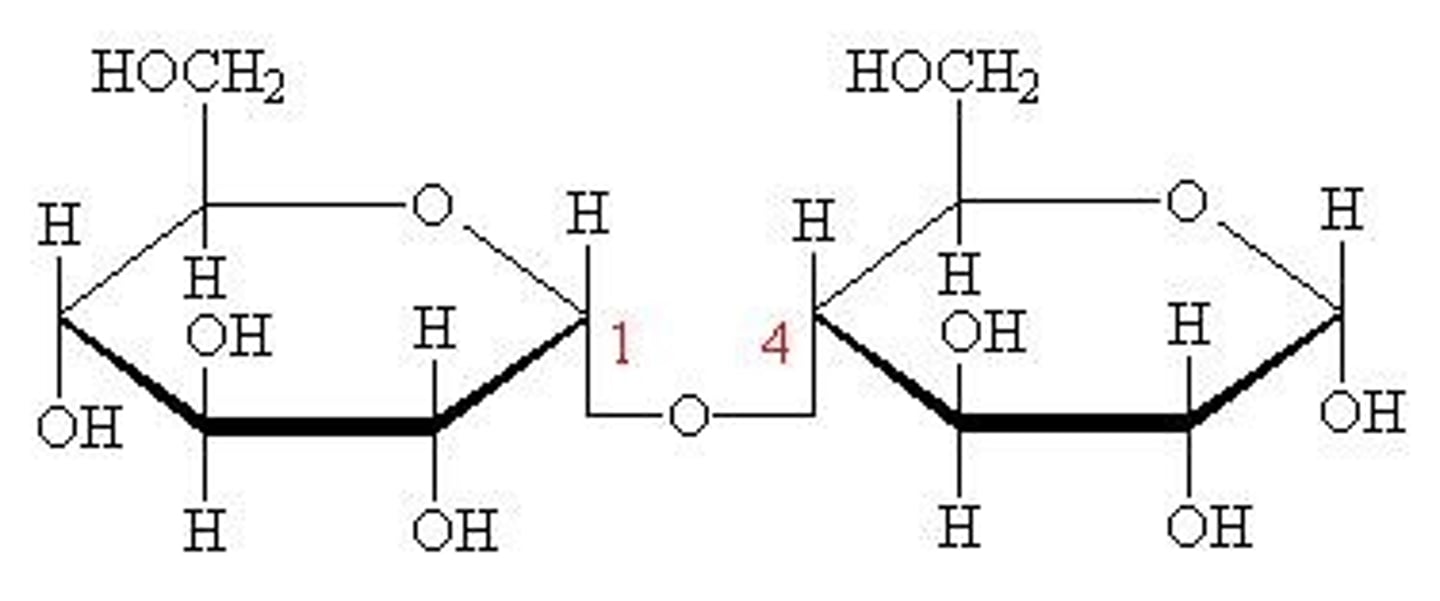
cellulose
polymer of 1,4 linked beta-d-glucose
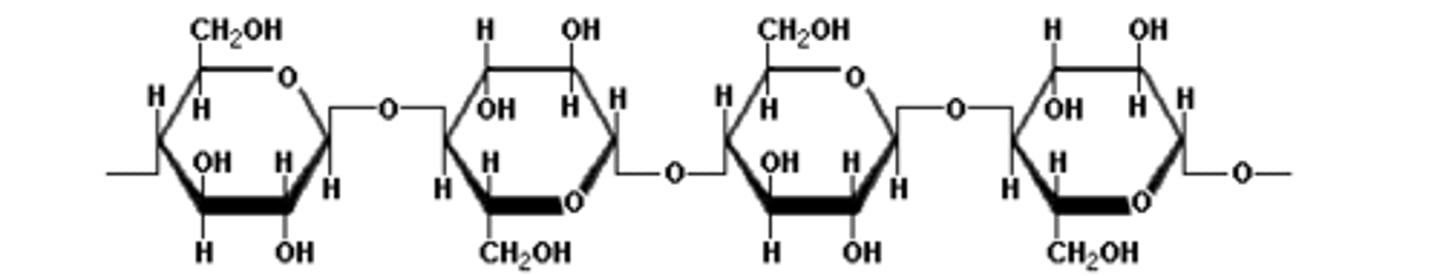
startch
polymers of alpha-d-glucose
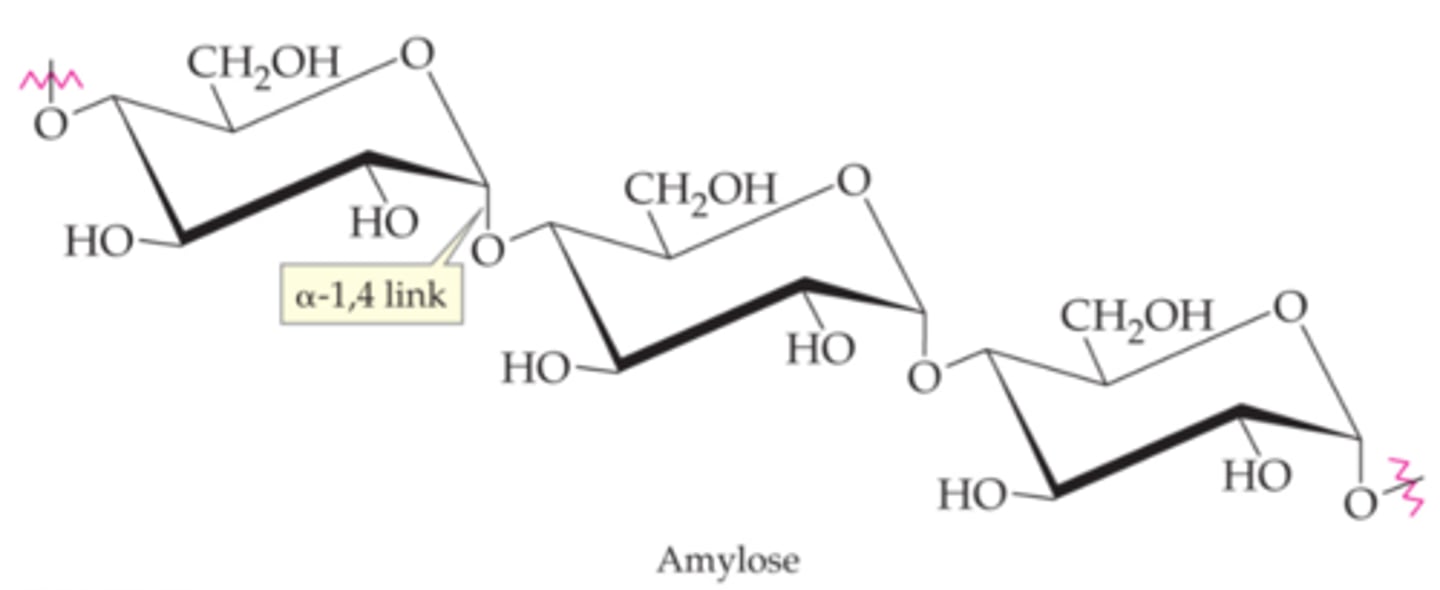
example: amylose
amylopectin also has branches of a-1,6 bonds
iodine tests for the presence of start
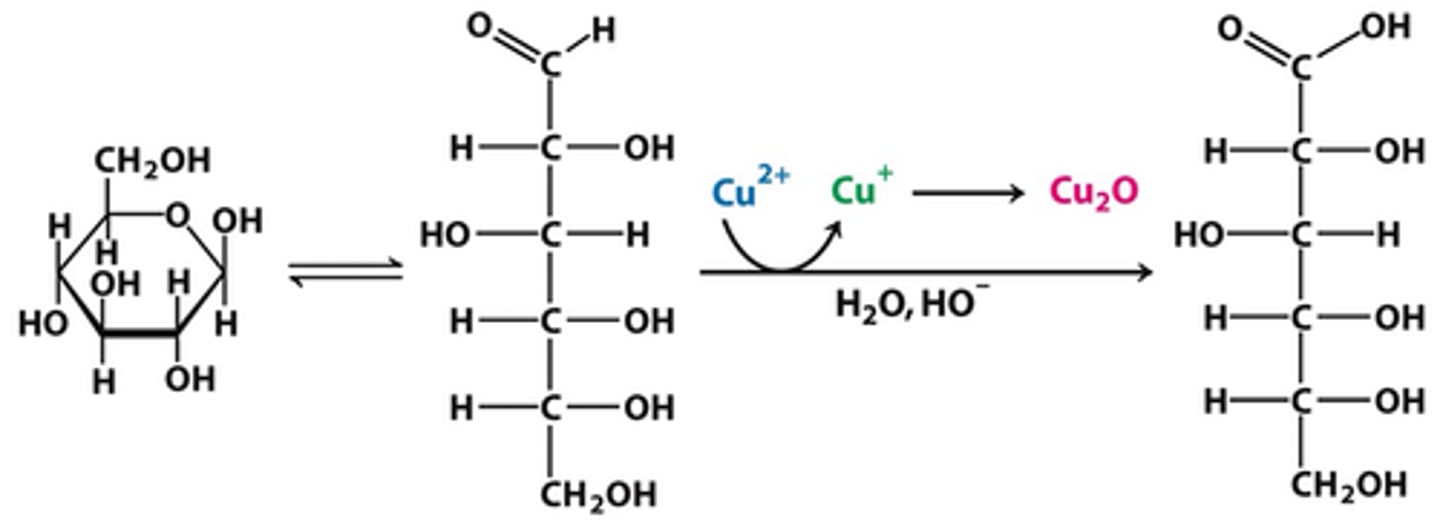
benedicts reagent
detects reducing sugars, red precipitate forms
glucose oxidase
reduces glucose and only glucose
dilute nitric acid
reduces aldehyde and primary alcohol (c-6) to carboxylic acids in reducing sugars