9.1/ ES 2- Redox
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What are there high levels of in the dead sea?
Bromide ions- ideal source of bromine
What are the uses of bromine?
Used in pharmaceuticals- bromine is found in some drugs currently trialled for Alzheimer's disease
Also used as a flame retardants- saves lives
How can bromide ions easily be removed from solution?
Simple chemistry- bromide ions in solution + chlorine solution makes bromine
What sort of compounds are the halides?
Oxidising agents- without other atom/ ion another atom would not lose its electrons
Draw a diagram for the industrial production of bromine
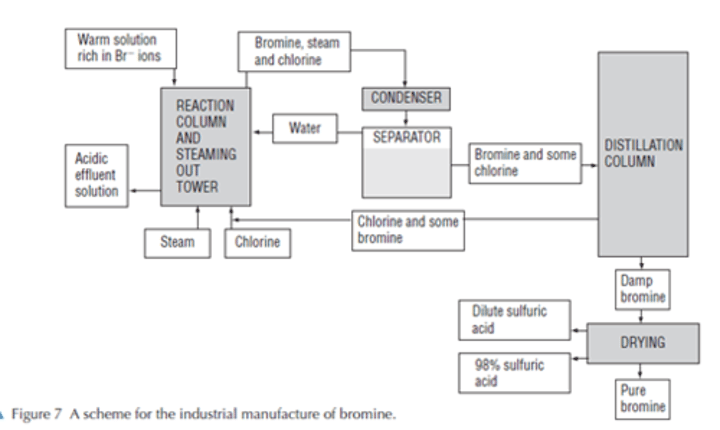
Give the 9 step method for the industrial production of bromine
· Chlorine added to warm water, partially evaporated, acidified sea water to displace the bromine the bromide ions
· Bromine is volatile (bp-331K)
· Steam blown through the solution- Bromine vapour and water given off
· Vapours are then condensed/ two layers form because liquid bromine has low solubility in water
· The dense bromine layer if run off from the water layer that floats on top
· Impure bromine is then distilled and dried
· Chlorine needed is produced by electrolysis on site
· Reaction of chlorine and bromide ions is a type of redox reaction
· Redox reaction- both oxidation and reduction occurring
What three ways can oxidation/ reduction be considered in terms of?
1) Oxygen
2) Oxidation states
3) Electrons- most common way of considering it as not all redox reactions involve oxygen
What is oxidation/ reduction in terms of oxygen?
Oxidation: gaining of oxygen
Reduction: loss of oxygen
Define redox
When oxidation and reduction occur at the same time in a chemical reaction
What is reduction nearly always accompanied by?
Oxidation- there is a constant number of oxygen atoms/ electrons (and vice versa)
Define oxidation (redox according to electrons)?
An atom/ particle loses electrons- causing the other to be reduced- reducing agents (adds/ donates electrons to the other species)
Define reduction (redox according to electrons)?
Atom/ particle gains electrons- causing the other to be oxidised- oxidising agent (takes electrons from the other species- the one being oxidised)
What is the mnemonic to remember redox?
OIL RIG
Oxidation Is Loss
Reduction Is Gain
What must be balanced in a redox reaction?
The number of electrons gained by one species must equal the number of electrons lost by the other species- balancing of electrons
What sort of equations must be used to see if a redox reaction has occurred?
Half equations (they show the movement of electrons)
Why are there no electrons seen in ionic equations?
The number of electrons on each side of the half equation is the same- they cancel out
What are oxidation and reduction in terms of oxidation states?
Oxidation- INCREASE in oxidation state
Reduction- DECREASE in oxidation state
Name four uses of oxidation states
1) naming inorganic compounds
2) deciding what is oxidised and what is reduced in a reaction
3) finding oxidising and reducing agents
4) balancing redox equations
What type of reactions are redox reactions?
A type of electron transfer reaction
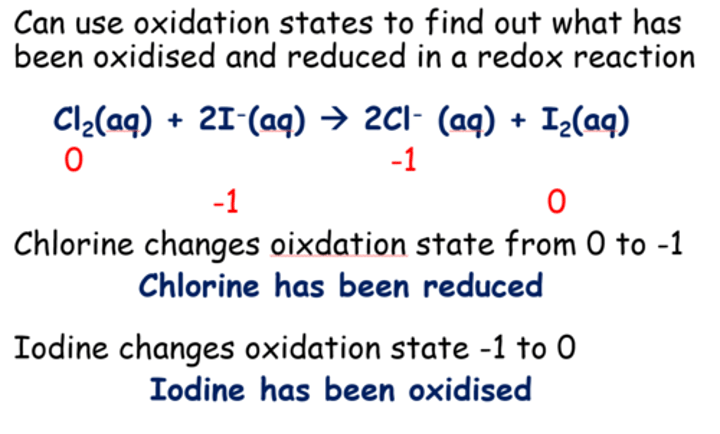
What happens when chlorine solution is added to potassium iodide solution (observations, ionic equations, half equations)?
The pale green solution does brown as the iodide is displaced and forms in solution
Ionic with spectator ions: 2K+I- + Cl2(aq) ----> 2K+Cl-(aq) + I2(aq)
Ionic: 2I- + Cl2(aq) ----> 2Cl-(aq) + I2(aq)
Half equations:
Cl2(aq) + 2e- ----> 2Cl-(aq) - reduced/ oxidising agent
2I- ----> I2(aq) + 2e- -oxidised/ reducing agent
What is an oxidation state?
A number assigned to every atom in an equation- showing how oxidised they are
How would you determined the oxidation state of a pure element?
Always have oxidation state of zero (0)- including diatomic molecules
How would you determined the oxidation state of a simple ion, what is it usually for metals/ non-metals?
Oxidation state= charge on ion
Metals- oxidised, lose electrons, positive ions- increase in oxidation number
Non-metals- reduced, gain electrons, negative ions- decrease in oxidation state
What is the overall charge of a compound?
No overall charge (zero)
Oxidation states of all of the elements added together = zero
What is the oxidation state of all elements?
Zero
How can you work out the oxidation state of an atom in a compound?
Adding up all the known common ones that do not change
How would you determine the oxidation state of bromine in BrF3?
1) Determine known oxidation states- know the oxidation state of fluorine is -1
2) Work out the oxidation state of bromine that is needed to balance this
-1 x 3 = -3
x + (-3) = 0
x = 3
So the oxidation state of bromine is +3
What must all oxidation states include as well as a number?
A +/- sign (comes before the number)
Which element in a substance has a negative oxidation states/ positive oxidation state based on electronegativity?
More electronegative- negative oxidation state
Less electronegative- positive oxidation state
Is the oxidation number just the charge on an ion?
No it is the number of electrons moved
What is the oxidation state of fluorine in a compound?
-1 (always- no exceptions)
What is the oxidation state of oxygen in a compound, what are the exceptions?
-2
Except when combined with F or in the peroxide ion O2^2-
What is the oxidation state of chlorine in a compound, what are the exceptions?
-1
Except when combined with O or F
What is the oxidation state of bromine in a compound, what are the exceptions?
-1
Except when combined with O, F or Cl (when with F= +3)
What is the oxidation state of iodine in a compound, what are the exceptions?
-1
Except when combined with O, F, Cl, Br
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen in a compound, what are the exceptions?
+1
Except when in a metal hydride e.g. NaOH
What is the oxidation state of Group 1 in a compound, what are the exceptions?
+1
No exceptions
What is the oxidation state of Group 2 in a compound, what are the exceptions?
+2
No exceptions
What is the oxidation state of Group 3 in a compound, what are the exceptions?
+3
No exceptions
When is the oxidation state of hydrogen not +1?
When hydrogen is in a metal hydride- H is present as a hydride ion H-
With an oxidation state of -1
When is the oxidation state of oxygen not -2 (two examples)?
Oxygen in peroxides (H2O2)- Electrically neutral sum of oxidation states must be zero
Each H is +1
Each O must be -1 not -2
Oxygen in F2O
Oxygen is not the most electronegative element- fluorine is
F is -1, O is +2
When is the oxidation state of chlorine not just -1?
When in a compound with O or F
Chlorine has many different oxidation states with oxygen and fluorine
What must the oxidation states of all the constituent atoms equal in a complex ion?
The overall charge of the ion (not just 0)
What is the colours of copper (I) oxide and copper (II) oxide?
Copper (I) oxide- organe-powder solid
Copper (II) oxide- black-powder solid
Which elements in compounds are labelled with oxidation states?
Only the elements with variable oxidation states- transition metals, tin, sulphur, nitrogen, halogens
What sort of numbers are used to show the oxidation state, where are they positioned?
Roman numerals, positioned just after the symbol of the atom/ element that they are referring to (do not come before!)
Is there a space/ gap between the numbers and the letters?
No
Are roman numerals showing only positive or only negative oxidation states?
Show the oxidation states for only those atoms with positive oxidation states, all atoms with positive oxidation states must have a roman numeral
What is the 4 step method for naming a compound?
1) Work out the name of the compound
2) Work out which elements have variable oxidation states
3) Work out its oxidation state
4) Add a name after element
What is an oxyanion?
A negative ion with oxygen in it
What does an "ate" ending on an ion show?
It has oxygen present
Which elements in oxyanions should have their oxidation states indicated?
All except for oxygen- the roman numerals refer to the other elements that are not oxygen- always a -2 in oxyanions
Roman numerals do not show the charge for the whole ion only the oxidation state of that element
Why is the oxidation state of chlorine, bromine and iodine not -1 when combined with oxygen?
Because chlorine is more electronegative
Why are there multiple forms of oxyanion for each element?
Because multiple oxyanions exist for each element because multiple formulas/oxidation states exist for each element
What is the formula and oxidation state of a chlorate (I) ion?
ClO-, oxidation state +1
What is the formula and oxidation state of a chlorate (III) ion?
ClO2-, oxidation state +3
What is the formula and oxidation state of a chlorate (V) ion?
ClO3-, oxidation state +5
What is the formula and oxidation state of a chlorate (VII) ion?
ClO4-, oxidation state +7
What happens to the oxidation state when a compound is oxidised?
The oxidation state increases
What happens to the oxidation state when a compound is reduced?
The oxidation state decreases
What sort of reaction is a metal-acid reaction, draw a table to prove this with oxidation states?
Redox, then state: oxidation and reduction both occur at the same time therefor it is a redox reaction
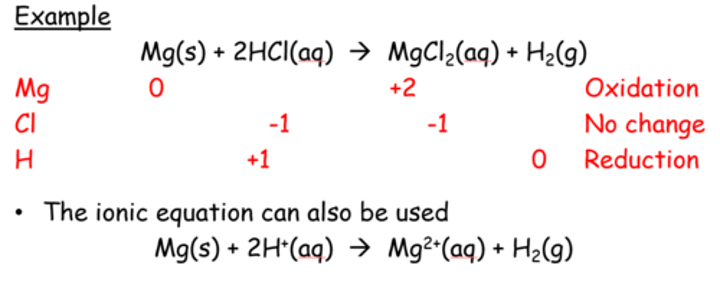
How can equations be balanced with oxidation states?
Balance the equation so that the number of electrons lost equals the number of electrons gained
How can you determined which atom/ elements are oxidised and reduced, what statement must you make?
State oxidised/ reduced with the justification
Oxidised- because the oxidation state increases from A to B
Reduced- because the oxidation state decreases from A to B
If oxidation states increase and decreasing (from different elements) in the same reaction what is it called?
Redox
What is disproportionation?
When the same element is reduced and oxidised in a redox reaction at the same time, element must appear more than once in the equation (diatomic molecules or it is in two compounds)
If there are two sources of the same element and one is e.g. reduced and the other remains the same (such as Cl2 + 2e- --> 2Cl- and 2Cl- already in solution) then does this still count as reduction?
Yes
If the reaction is not redox what statement should you make?
Reaction is not redox because oxidation states stay the same not one decreasing (reduction) and one increasing (oxidation) which is needed to make a reaction a redox reaction
What is the equation for a metal and a dilute acid?
Metal + dilute acid --> Salt + Hydrogen gas
What sort of reaction is a metal and acid reaction?
A redox reaction
In a metal and acid equation which one is reduced and which one is oxidised?
Metal is oxidised- reducing agent, positive metal ion, donates electrons, increases oxidation state
Hydrogen (in acid) is reduced and forms hydrogen gad, 2H+ (in acid) + 2e- ---> H2 (g)
Which acid does not produce the same ionic equation in a metal acid reaction?
Nitric acid-HNO3
With a negative oxidation state is a non-metal ion likely to change?
No
Explain which has been oxidised and reduced in a reaction between chlorine gas and iodide ions using a table to show the oxidation states