Periodic Table Trends and Bonding (Unit 1 Grade 11 Chemistry)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Carbonate Formula
CO3 2-
Hydroxide Formula
OH -
Phosphate Formula
PO4 3-
Bromate Formula
BrO3 -
Ammonium Formula
NH4 +
Permanganate Formula
MnO4 -
Nitrate Formula
NO3 -
Sulfate Formula
SO4 2-
Chlorate Formula
ClO3 -
What does the prefix “Per______ic acid” represent?
X + 1 (Gained an oxygen atom)
What does the prefix “_____ic acid” represent?
X (Base acid formula)
What does the prefix “_____ous acid” represent?
X - 1 (Lost an oxygen atom)
What does the prefix “Hypo____ite acid” represent?
X - 2 (Lost two oxygen atoms)
What are the elements associated with HOFBrINCl?
The elements hydrogen, oxygen, fluorine, bromine, iodine, nitrogen, chlorine, which exist as diatomic molecules in their natural state.
(H, O, F, Br, I, N, Cl)
Why does HOFBrINCl exist?
These elements exist as diatomic molecules because they are more stable when bonded to another atom of the same element, forming pairs to achieve a full valence shell.
What is an Atomic Radii?
Atomic Radii is the size of an atom, similar to the word “Radius”, It’s chemistry’s unit of measurement to find the radius of an atom.
What is the Atomic Radii Trend?
On the Periodic Table, there’s a trend that shows that any element that progresses furthest to the bottom left of the periodic table will have a larger atomic radius than those on the top right.
Which Group consists of the biggest atomic Radius?
The Alkali Metals group, located in Group 1 of the periodic table, consists of the biggest atomic radius due to their low effective nuclear charge and high number of electron shells.
What is Effective Nuclear Charge?
Known as “Zeff” or just “Z”, It’s the positive charge of pulling electrons towards the nucleus. To not confuse you, it is completely different from its actual nuclear charge as it’s based on the attraction close to the positively charged nucleus (relying on the amount of protons existing) rather than the amount of electrons it’s attempting to attract to satisfy its valence.
How do you determine “Zeff” Value?
It’s determined by the outer shell amount of electrons, representing itself as “Zeff.” To discover this we must set an example, Carbon (C) will be our example. Carbon has a charge of 4+ or - but to answer its effective nuclear charge, we must subtract its inner rings worth of electrons to find our Z. Formula is built off as “Zeff = #protons - #inner electrons.” Giving us the answer that Carbon’s Zeff is 4.
What is Ionization energy?
It’s the measurement to see the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom to acquire a negative or positive charge.
What’s the Electron Affinity?
A measurement of the attraction between the incoming electron and nucleus. It’s basically the opposite of ionization energy on the periodic table as instead of measuring the amount of energy change after gaining an electron.
Electron affinity Trend/Ionization Energy shown on the Periodic Table
On the Periodic Table, There’s a trend that is shown that any element that is closest to the top right of the periodic table will have the highest amount of ionization energy/Electron Affinity.
Which Group has the highest amount of energy required for Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy?
Example would be the Noble gases as they are the only elements with a complete valence shell, hence why you almost never see them mixed with other elements as it requires a lot of energy to remove/add a single electron from its shell.
What is Reactivity?
Metals react by losing electrons and the lower the attraction for outer electrons, the greater reactivity.
Metals react by losing electrons, meaning losing electrons will increase the force.
Non metals react by gaining electrons, meaning gaining electrons will increase the force
What Trend does Reactivity have?
Bottom Left for reactivtiy of Metals, Top right for reactivity of non-metals.
What is a bond?
It’s the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals or other structures.
What is a Dipole?
A molecule that has both positive and negative charges, commonly seen when a bond is polar.
Imbalance of atoms that have positive or negative charges. (May be more positive charges than negative or more negative charges than positive charges
What is Electronegativity? (EN)
The tendency of an atom that is in a molecule to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself.
What is a polar bond and how high is their electronegativity?
When two different elements form a bond by sharing electrons and there’s an unequal balance of electrons, most of the time, there’s lone pairs.
Comes from the differences between electronegatvitiy if the EN is higher than 0.5 but less than 2, confirming the bond to be polar.
Higher electronegativity results in a greater attraction for electrons
What is a nonpolar bond and the difference of electronegativity?
A balanced amount of electrons are distributed to all atoms within the molecule, sharing electrons equally and creating no positive or negative poles, no lone pairs.
Comes from the differences between the electronegativity if the EN is lower than 0.5
What is a Partial Charge?
Non-integer or determined charge value when measured in “elementary” charge units.
Represented in the symbol Delta
What is ionic bond?
It’s the process of 2 or more atoms transferring its electrons to another atom in order to complete their desired valence shell amount. This bond only happens between a metal and non-metal atom.
Note that an electron transfer will cause a negative charge (Known as anion, an ion that is negatively charged) or positive charge (known as a cation, an ion that is positively charged).
All electrons lost by the metal are gained by the non metal
If EN is higher than 2 then it is an ionic bond
Properties of ionic substances/compounds
Crystal lattice when solid at room temperature
High melting/ boiling points
Hard but very brittle in water
What is covalent bonding?
A bond that happens between a non metal and nonmetal. Main difference from ionic bonds is that they share electrons rather than transfer their electrons creating a new type of compound which is called “Covalent Compound.”
No ions are formed from the creation of the compounds.
Formula for drawing Lewis Dot Diagram
# of atoms • electron amount +... = total number of electrons
Properties of non-metal substances/compounds
Form molecules that can turn into any state of matter (Solids, liquids, gasses)
Low melting/ boiling points
What do double bonds look like?
What does Resonance Structure mean?
If you’re not certain where the bonds need to go so you show all possible solutions.
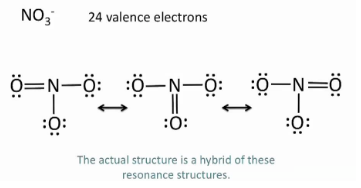
What does Expanded Valance?
Octet rule allows a max of 4 bonds but some allow 8, only for those with an atomic number greater than 10.
What is VSEPR?
VSEPR stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion and it presents us with the idea that electron pairs repel each other whether or not they are in bond pairs or in lone pairs.
Formula for VSEPER is AB#E#
A represents Central Atom
B represents Bonding Electron Pairs
E represents non bonding lone electron pairs
# represents the amount of Bonding electrons there are or lone pairs.
What are the three dimensional representations in VSEPR?
Lines represent it’s across 2 dimensionally
Triangle represents it’s towards you
Dotted Triangle represents it’s behind the central atom
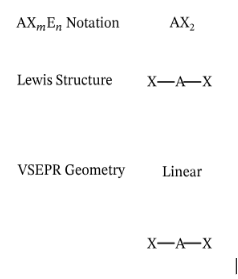
Describe and give me the formula for a Linear Diagram (AX#E#)
A straight line
Formula = AB2E0
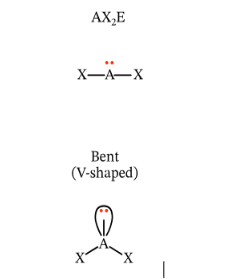
Describe and give me the formula for a Bent Angular Diagram
Bent shape
Formula = AX2E1 or AX2E2
Describe and give me the formula for a Trigonal Planar
Triangle Shape
Formula = AX3E0
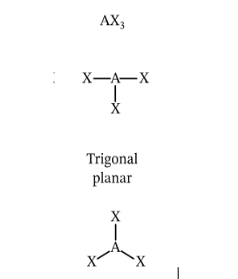
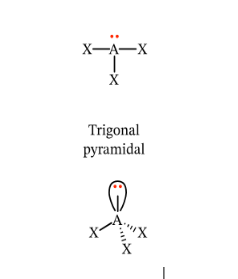
Describe and give me the formula for a Trigonal Pyramidal
Will have 4 points, resembling a pyramid.
Formula = AX3E1
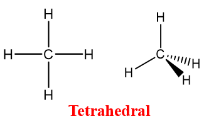
Describe and give me the formula for a Tetrahedral
Similar to a trigonal pyramidal but no lone pairs and exact same shape.
Formula = AX4E0
What is are Intramolecular Forces?
The force of electrostatic attraction inside a molecule
Bonds that hold the atoms together to form a molecule, including Ionic Bonds, Polar covalent, non polar covalent.
Extremely strong and in order to be broken, must have chemical means.
What are the 3 types of Intramolecular forces?
London Dispersion Forces, Dipole, and Ionic Forces
What is London Dispersion Forces?
These forces exist between all molecules
Weakest type of Intramolecular force
Because electrons move around, some spaces will be asymmetrical
The greater # of electrons and protons, the greater the force.
Dominant Force in non polar molecules
Non-metals, higher the mass, higher the force
Metals, higher the EN, higher the force
What is Dipole - Dipole Interactions?
Occur between polar molecules that already have dipoles.
Oppositely charged ends
Unequal distribution of charges on the molecule.
What is Hydrogen Bonds?
Specific type of Dipole Force.
Occurs between hydrogen atoms and high electronegativity valued atoms (F, O, N) within a molecule.
What is Ionic Forces?
Can be both inter or Intra forces.
Strongest overall force
Non Metal + Metal
What is Intermolecular Forces?
Forces of attraction between two molecules
Much weaker than Intramolecular forces
Due to how fragile this force is compared to Intramolecular Force, Physical changes can break or weaken these forces.
How can you predict the boiling point using the strength of intermolecular forces?
The more polar molecule present, the stronger dipole-dipole and higher boiling point.
You can determine the boiling point by discovering the EN
Higher the EN, the higher boiling point.