Unit 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
the properties of a molecule depend on…
the shape and nature of the bonds
a model for the geometry of molecules
valence-shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory
a model about WHY molecules form bonds and WHY they have the shape they do
valence-bond theory
a model of chemical bonding that deals with the electronic structure of molecules
why they look the way they do
molecular orbital (MO) theory
bond angles
the angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of a molecule’s atoms
connects nucleus between lines
electron domain
a region in which at least two electrons are found
bonds = 1
why do electron domains repel each other?
because they’re negatively charged (optimizes space)
bonding domain
2-6 e- that are shared by TWO atoms, this forms a COVALENT BOND
nonbonding domain
2 e- that are located on a single atom; aka a LONE PAIR
VSEPR for NH3
(ammonia); 3 bonding domains, 1 nonbonding domain = 4 e- domains
how do domains arrange themselves?
so as to minimize their repulsions—they’re always pushing(b/c they’re all negative)
electron-domain geometry
one of five basic arrangements of domains
depends only on the total # of e- domains not the kind of domain
overall # of domains
molecular geometry
describes the orientation of the atoms in space
depends on how many of each kind of e- domain
depends on TYPES of domains
to find the EDG and/or MG….
draw the LS
multiple bonds count as single domain
total number of domains:
electron-domain geometry:
possible Molecular geometries:
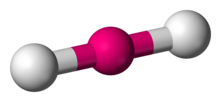
2; linear; linear (e.g: CO2)
molecules with more than one central atom…. (predicting the EDG and MG)
apply the VSEPR model to each individual/part
nonbonding domains are attracted to…
only ONE nucleus
are more spread out
i.e. “lone pairs”
COMPRESS bond angles—pushes on other bonds because its not really bonded, causes fluctuation in IBA
bonding domains are…
less spread out
a molecules polarity is determined by…
its overall dipole, which is the vector sum of the dipoles of each of the molecule’s bonds
total # of domains: 3
electron-domain geometry:
possible Molecular Geometries:
IBA:
trigonal planar;
all 3 bonding: trigonal planar (e.g BF3)
1 nonbonding: bent (e.g. NO2)
120
total # of domains: 4
EDG:
possible MG:
IBA:
tetrahedral
all 4 bonding: tetrahedral (e.g CH4)
2 non bonding