9.1 Properties of Metals, 9.2 Uses of Metals
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the physical properties of metals?
Thermal & electrical conductor when solid,
Malleable & ductile
High melting point and boiling point.
Note: For all substances, Boiling point > Melting point.
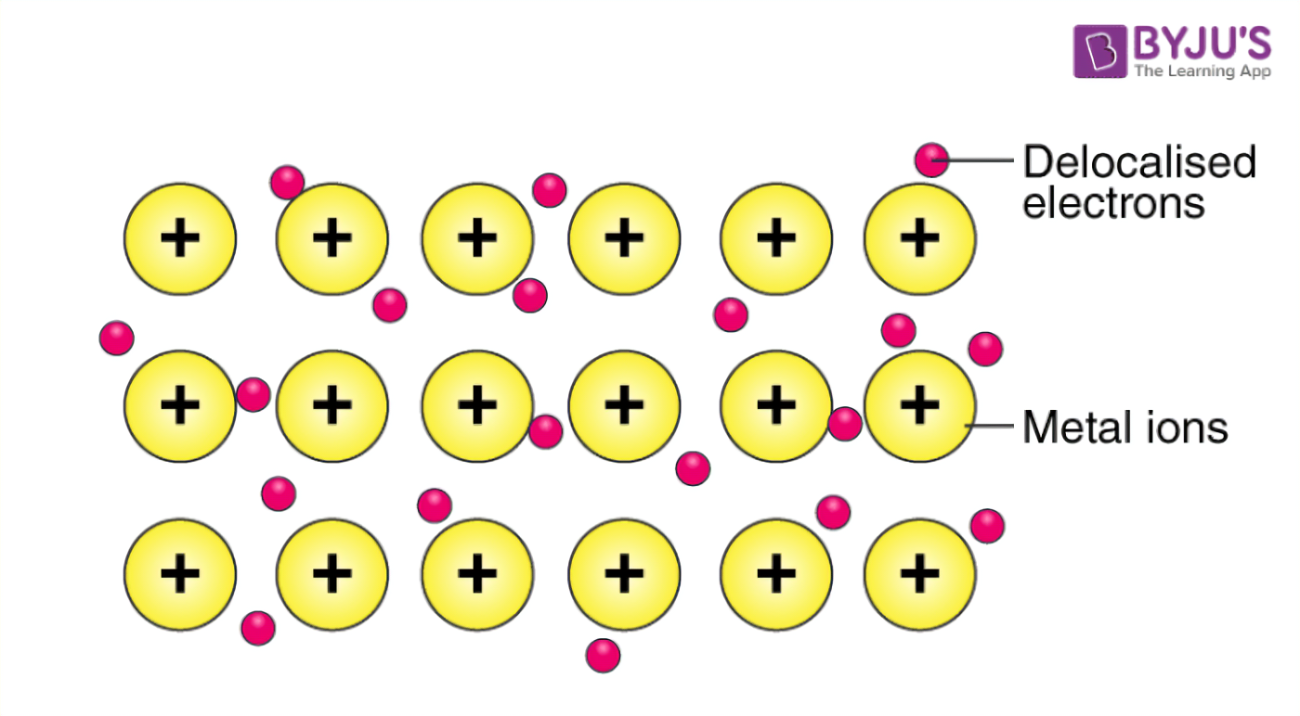
Why do metals conduct electricity?
Metals have metallic bonding in layers with delocalized electrons that can move freely and carry charge —> allows the transfer of electricity.
Note: Non-metals lack metallic bonds and act as insulators. Covalent and ionic bonds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
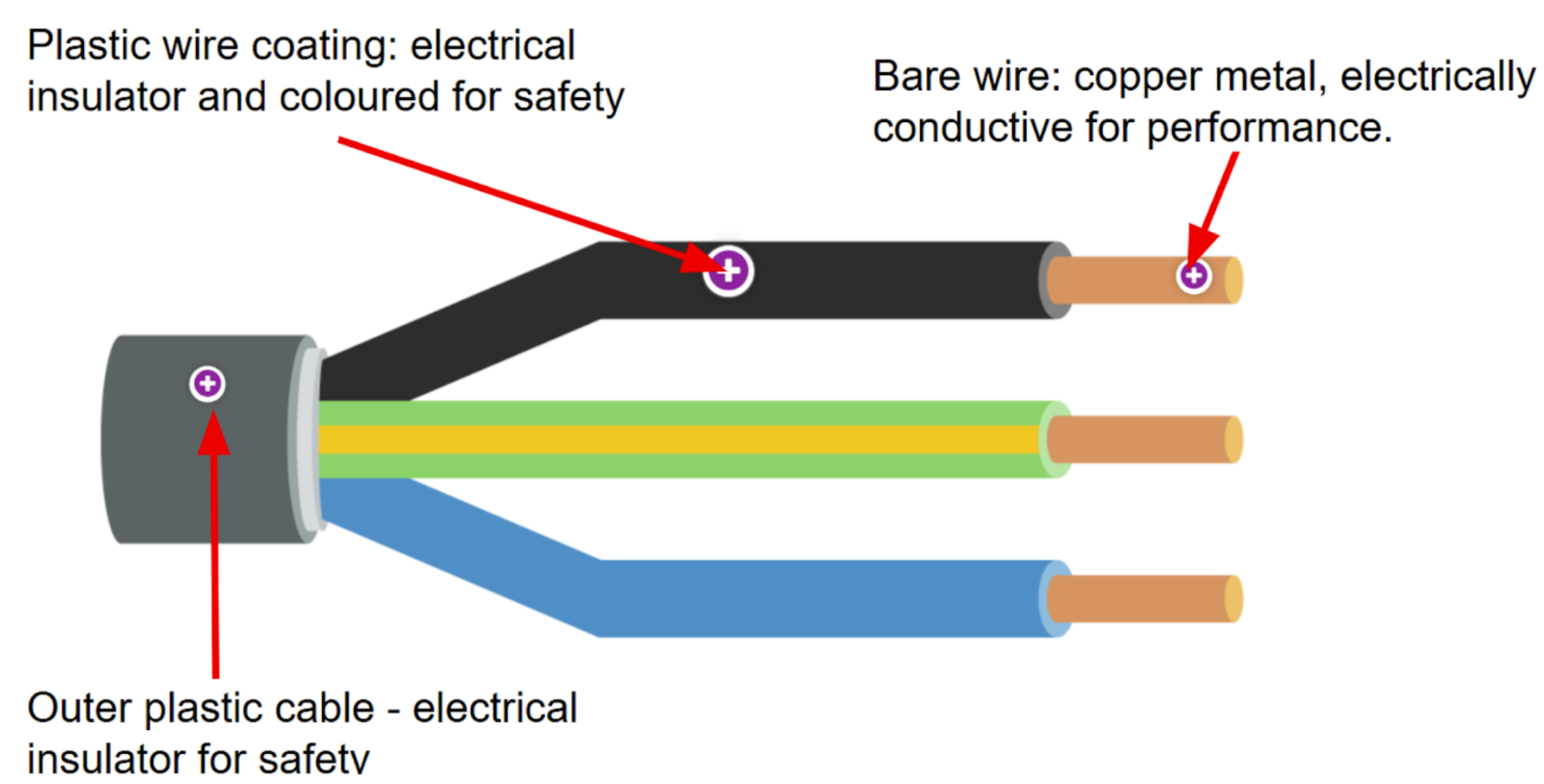
Why are copper wires coated in plastic?
Plastic, made from covalent bonds, is an electrical insulator.
—> prevents electricity from escaping and protects objects from the current flowing through copper wires.
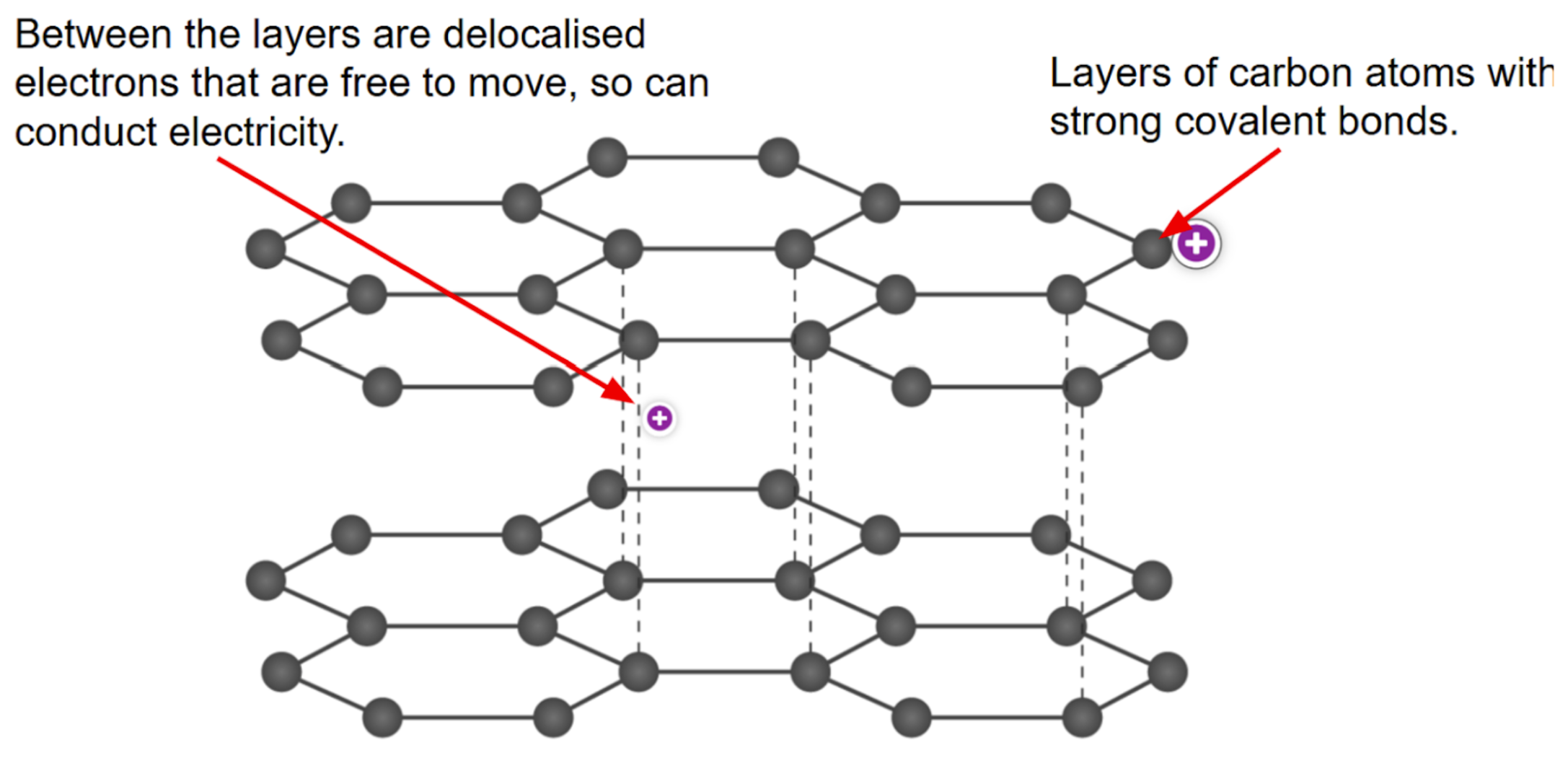
How does graphite's atomic structure enable it to conduct electricity?
Graphite has strongly bonded layers separated by delocalized electrons, allowing electrical conductivity.
How does a metal cooking pot demonstrate thermal conductivity?
The pot's metal allows heat to pass through easily to cook food.
Plastic handles are insulators, ensuring the pot can be held safely.
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points?
Requires high energy to overcome metal’s strong intermolecular forces.
Note: Metals remain solid at high temperatures due to these strong forces.
Define malleable and give an example.
Can be easily bent or shaped without breaking.
Example: Gold can be shaped into coins.
Define ductile and give an example.
Being stretched into wires.
Example: Copper wires.
How do non-metals like glass differ from metals in terms of malleability?
Non-metals are brittle, meaning they break easily.
What is the general equation for the reaction of metals with dilute acids?
Metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Zinc + hydrochloric acid → ?
Zinc + hydrochloric acid → zinc chloride + hydrogen
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
Zinc + sulfuric acid → ?
Zinc + sulfuric acid → Zinc sulfate + hydrogen
Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂
How can hydrogen gas be tested?
Using the squeaky pop test.
What is the general equation for the reaction of metals with water?
Metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Calcium + water → ?. What are the observations?
Calcium + water → calcium hydroxide + hydrogen Ca + 2H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ + H₂.
Observations: Calcium disappears, and hydrogen bubbles form on the metal surface.
How does sodium react with oxygen?
Sodium + oxygen → sodium oxide
4Na + O₂ → 2Na₂O
Why are Group I metals stored in oil?
Group I metals are stored in oil to prevent reactions with oxygen due to their high reactivity.