Pain Perception
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
Pain
\- defined as the most reason why people visit a healthcare provider as well as the PT
\- unpleasant sensory and emotional experiences associated with actual or potential tissue damage
\- can affect emotions
\- unpleasant sensory and emotional experiences associated with actual or potential tissue damage
\- can affect emotions
2
New cards
Acute Pain
usually fast and can last for a few days.
3
New cards
Chronic Pain
\- pain felt lasted for weeks, months, years
\- severe pain
\- severe pain
4
New cards
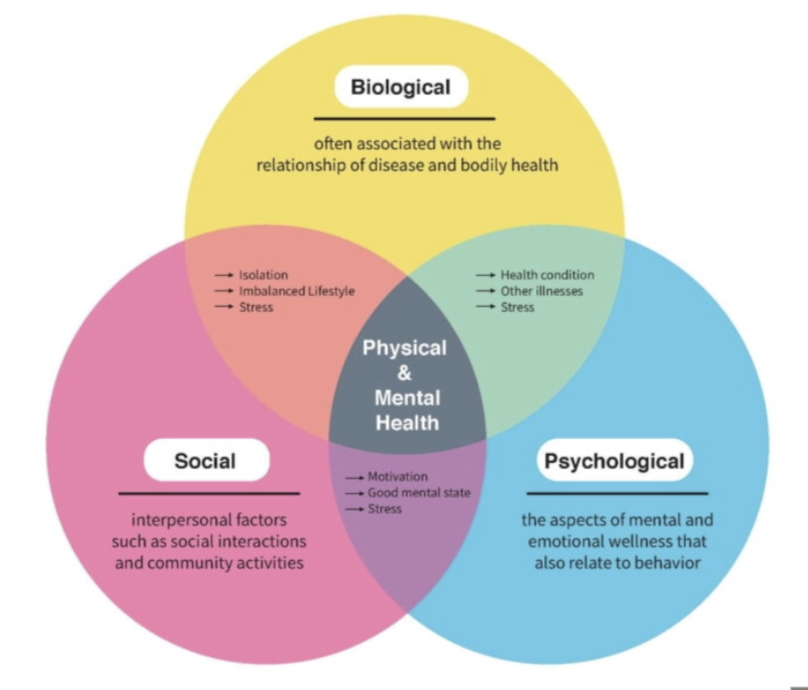
Biopsychosocial Model
\- correlate tissue damage to pain sensation
\- recognizes the physical, interactive, personal, and environmental factors that can affect body functions, structures, activity, and participation in the life activities of your pt
\- recognizes the physical, interactive, personal, and environmental factors that can affect body functions, structures, activity, and participation in the life activities of your pt
5
New cards
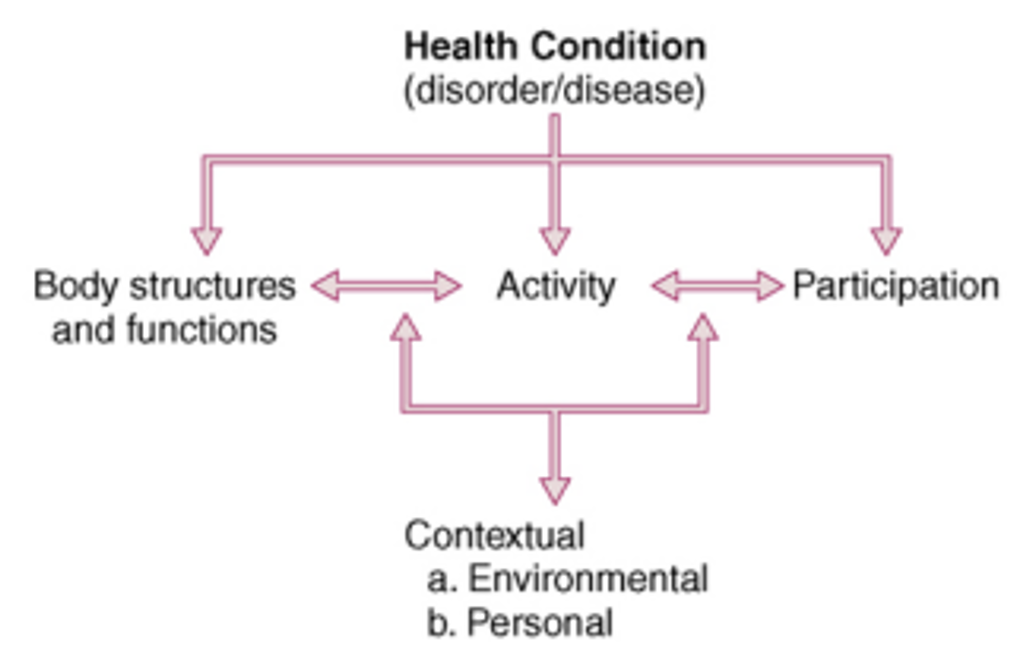
ICF Model
PT visualizes the entire scenario of the pt, because of his/her condition and enables the PT to think what he/she can do to improve and help the pt to get back to their previous state.
6
New cards
Causalgia
a syndrome of sustained burning pain, allodynia, and hyperpathia after a traumatic nerve lesion, often combined with vasomotor and sudomotor dysfunction and later trophic change
7
New cards
Dysesthesia
an unpleasant abnormal sensation, whether spontaneous or evoked
8
New cards
Hyperpathia
a painful syndrome characterized by an abnormally painful reaction to a stimulus, especially a repetitive stimulus, as well as an increased threshold.
9
New cards
Paresthesia
an abnormal senstion, whether spontaneous or evoked.
10
New cards
Suffering
\- refers to the affective component of pain
\- includes both emotional and cognitive components, and may be due to a combination of unpleasantness and catastrophizing
\- usually caused by emotional damage
\
\- includes both emotional and cognitive components, and may be due to a combination of unpleasantness and catastrophizing
\- usually caused by emotional damage
\
11
New cards
Psychogenic
an older term for pain believed to be caused by psychological factors when organic factors were absent or not severe enough to explain the pain complaint.
12
New cards
* Severe unremitting pain
* Pain unaffected by medication or position
* Severe night pain
* Severe pain with no history of injury
* Severe spasm
* Pain unaffected by medication or position
* Severe night pain
* Severe pain with no history of injury
* Severe spasm
red flags in pain.
13
New cards
Spasm
is a normal response of our body, it is a protected contraction of muscle to limit motion.
14
New cards
Musculoskeletal Pain
\- pain is lessened at night because structures are rested
\- pain is also superficial or sharp
\- pain decreases with cessation of activity
\- pain can be either or intermittent and is aggravated by mechanical stress
\- pain is also superficial or sharp
\- pain decreases with cessation of activity
\- pain can be either or intermittent and is aggravated by mechanical stress
15
New cards
Systemic
\- other organs or structures involved other than the root cause of the pain
\- deep aching and throbbing
\- constant type of pain; spasm is constant
\- not aggravated by mechanical stress as compared to the msk system
\- associated with the following:
* Jaundice
* Migratory arthralgias
* Skin rashes
* Easy fatigability
* Sudden weight loss
* Low grade fever
* Generalized weakness
* Slightly progressive symptoms
* Tumors
\- deep aching and throbbing
\- constant type of pain; spasm is constant
\- not aggravated by mechanical stress as compared to the msk system
\- associated with the following:
* Jaundice
* Migratory arthralgias
* Skin rashes
* Easy fatigability
* Sudden weight loss
* Low grade fever
* Generalized weakness
* Slightly progressive symptoms
* Tumors
16
New cards
Jaundice
yellowish discoloration.
17
New cards
Temporal Pattern
duration and chronicity.
18
New cards
Muscle
aching, dull, and cramping.
19
New cards
Ligament
dull and aching.
20
New cards
Nerve Root
sharp, shooting, radiating, and lightning-like.
21
New cards
Bone
deep, nagging, and dull.
22
New cards
Fracture
sharp, deep, and excruciating.
23
New cards
Vasculature
throbbing and diffuse.
24
New cards
* Degree of physical damage
* Personality of the patient
* Social context
* Cultural context
* Attitude and behavior of health professional
* Past experience
* State of mind
* Personality of the patient
* Social context
* Cultural context
* Attitude and behavior of health professional
* Past experience
* State of mind
factors that influence pain.
25
New cards
Verbal Report Scale
\- adjectives are used to describe different levels of pain
\- purely verbal
\- “from 0 to 10, gaano kasakit yung pain na nararamdaman?”
\- purely verbal
\- “from 0 to 10, gaano kasakit yung pain na nararamdaman?”
26
New cards
Visual Analog Scale
allows the patient to visually gauge the amount of pain along a solid 10-cm line.
27
New cards
Numerical Rating Scale
the patient rates the pain from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain).
28
New cards
Body Diagram
\- ipapa-plot mo kay pt. kung saang part ng katawan masakit
\- lagyan ng “X” sa (R) shoulder para ma-visualize ‘yong location ng pain
\- lagyan ng “X” sa (R) shoulder para ma-visualize ‘yong location ng pain
29
New cards
Faces Pain Rating Scale
\- use of emoji
\- hospitals usually have these
\- hospitals usually have these
30
New cards
Temperature Rating Scale
\- “ituturo ni pt kung anong level of pain”
31
New cards
Outcome Measure Tool
\- assessing the pain and sensory of the pt
\- to determine whether the pain is due to neuropathic in nature or not
\- to determine whether the pain is due to neuropathic in nature or not
32
New cards
LANSS Pain Rating Scale
\- Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs
\- 2 areas
● Pain Questionnaire
● Sensory Testing
\- Total score is 24,
* < 12 = the cause is not neuropathic in nature
* > 12 = the cause is neuropathic in nature
\- 2 areas
● Pain Questionnaire
● Sensory Testing
\- Total score is 24,
* < 12 = the cause is not neuropathic in nature
* > 12 = the cause is neuropathic in nature
33
New cards
* Physiological
* Sensory
* Affective
* Cognitive
* Behavioral
* Cultural
* Sensory
* Affective
* Cognitive
* Behavioral
* Cultural
common causes that can contribute to the paint.
34
New cards
Therapeutic Exercises
\- to address the pain
\- e.g. peripheral joint mobilization
* using a grade 1 or 2 dose for pain relief
* grade 3 and 4 for stretching maneuvers
\- e.g. peripheral joint mobilization
* using a grade 1 or 2 dose for pain relief
* grade 3 and 4 for stretching maneuvers
35
New cards
Manual Therapy
include manipulation techniques.
36
New cards
Neuromuscular Reeducation
\- NMES
\- electrical stimulation
\- electrical stimulation
37
New cards
Assistive Device
to unload the pt’s weight.
38
New cards
Physical and Electrotherapeutic Modalities
\- TENS
\- Ultrasound
\- Hot and cold compress
\- IRR
\- Ultrasound
\- Hot and cold compress
\- IRR