AMBULATORY ANESTHESIA
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
The international Association for Ambulatory Surgery was formed in
1995
→Surgery performed on an outpatient basis
→Maybe hospital based or performed in an office or surgicenter
Ambulatory surgical procedures
PLACES
● Within the hospital
● Freestanding satellite facility affiliated with or independent from a hospital.
● Physician’s office
Maximum duration of surgery
4 HOURS
PROCEDURES
● Maximum duration of surgery (4hrs)
● Does not pose a significant safety risk
● Do not require an overnight stay
● Associated with post-operative care manageable at home ● Low rates of postoperative complications
● Blood transfusions requiring procedures are not contraindicated.
Age infants should be monitored .
12hrs post op.
Appropriate candidate for some ambulatory surgical procedures if their systemic diseases are medically stable
ASA Physical Status III or IV
A normal healthy patient
ASA I
A patient with mild systemic disease
ASA II
A patient with severe systemic disease
ASA III
A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life
ASA IV
A morbund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation
ASA V
A declared brain-dea d patient whose organs are being remove for donor purpose
ASA VI
Mild disease only without substantive functional limitations. Examples include (but not limited to): current smoker, social alcohol drinker, pregnant, obesity (30
ASA II
Substantive functional limitations. one or more moderate to severe diseases. Examples include (but not limited to): poorly controlled DM/HTN, COPD, morbid obesity (BMI≥40), active hepatitis, alcohol dependence or abuse, implanted pacemaker, moderate reduction or ejection fraction, ESDR undergoing regularly scheduled dialysis, premature infant PCA<60 weeks, history (>3 months) of MI, CVA, TIA, or CAD/stents.
ASA III
Examples include (but not limited to): recent (<3 months) MI
ASA IV
Examples include (but not limited to): ruptured abdominal/thoracic aneurysm, massive trauma, intracranial bleed with mass effect, ischemic bowel in the face of significant cardiac pathology of multiple organ/system dysfunction
ASA V
→Higher incidence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Obese patients
Obese patients
→Can be done in the ambulatory center if done under local anesthesia or regional anesthesia
High risk of hypoxemia post operatively
OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA
● Each outpatient facility should develop its own method of preoperative screening
1. Visit the facility
2. Phone call
3. Complete medical history, medications, medical problems, family history.
● Adult →Following viral URI’s, surgery should be delayed because airway flow obstruction persists up to
6 weeks
● Children→Survey showed that URI associated with an increased risk of perioperative respiratory adverse events only when
symptoms were present or had occurred within the 2 weeks before the procedure
● Independent risk factors for adverse respiratory events:
→Use of ETT
→Presence of copious secretions
→Hx of prematurity
→Nasal congestion
→Hx of reactive airway disease
→Hx of paternal smoking
→Surgery involving the airway
Clear fluids
2
Breast milk
4
Formula milk
6
Nonhuman milk
6
Light meal
6
Meals that include fried or fatty food or meat
8
● Medications that should be taken on the day of surgery:

● Medications that should be avoided on the day of surgery:
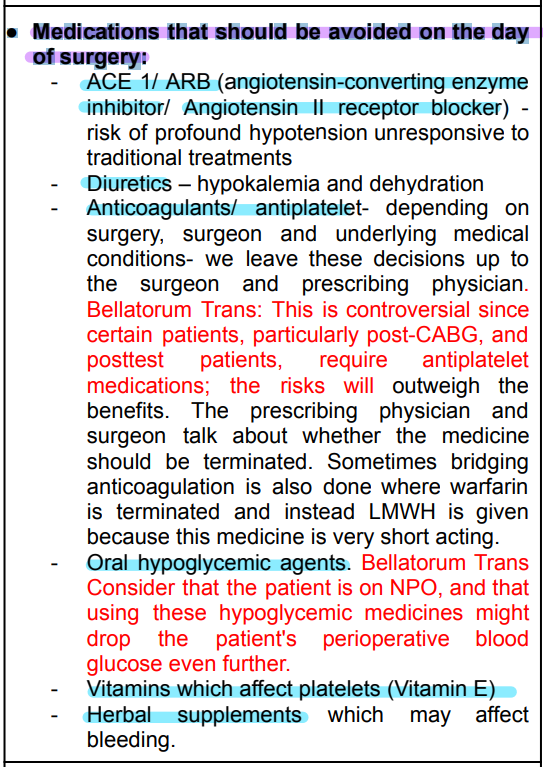
● Nonessential medications that can be continued on the day of surgery

drug most used to reduce anxiety and induce sedation
Midazolam
Dose of Midazolam
0.25 mg/kg - 0.5 mg/kg

- Can be administered preoperatively to sedate the patient, control HPN during tracheal intubation and decrease pain before surgery
● Opioids and NSAIDs
can be given post op shivering
Meperidine (also clonidine, tramadol, ketamine)
- Use most commonly for ex-premature infants undergoing hernia repair
SPINAL ANESTHESIA
General Anesthesia as back up for
SPINAL ANESTHESIA
only predictor of spinal anesthesia failure
Bloody tap on 1st attempt
Anesthesia Suitable for pelvic, lower abdominal, lower extremities etc.
SPINAL ANESTHESIA
Medication for Spinal anesthesia
Lidocaine and Bupivacaine
may cause transient neurologic symptoms
Lidocaine
: longer duration of action (usually 2-3 hours has a predictable effect)
Bupivacaine:
● Treatment of post-epidural headache
- bedrest - analgesia - oral hydration - IV caffeine - epidural blood patch
● Longer to perform
● Slower onset
● Advantageous when duration or surgery is unclear
● Decrease risk of post dural puncture headache
EPIDURAL AND CAUDAL ANESTHESIA
- form of epidural anesthesia in children having infraumbilical operation as a supplement to GA
- Difficult in obese children or those more than 10kg.
CAUDAL ANESTHESIA
Total elbow arthroplasty
● Infraclavicular block
Foot surgery
Sciatic nerve block:
Breast surgery
● Paravertebral Block
THRA
● Femoral Nerve Block
Shoulder surgery
● Interscalene Block
Hand and Forearm surgery
● Axillary Block:
● Levels of sedation
(Ramsay Sedation Scale)
Consciousness is minimally depressed
Light
(asleep patients that when touched is they can respond, or easily aroused)
● Moderate/ Conscious Sedation
Protective reflexes are partially blocked and response to physical stimulation or verbal command may not be appropriate
Deep
Maintenance drugs for general anesthesia
Propofol and Sevoflurane
T ½ of propofol
1-3 hours
Sweet smelling inhalational agent, can be given in pediatrics before IV access
Sevoflurane
Brief paralysis to facilitate tracheal intubation
Succinylcholine
Nondepolarizing drugs can also be used for neuromuscular blocking (Longer DOA: 45mins)
Rocuronium
Neuromuscular blocking Drugs
Succinylcholine and Rocuronium
● Higher Incidence for PONV
-After Nitrous oxide use
- Women
- Previous Hx of PONV/ Motion sickness
- Surgical procedures (Laparoscopy, Lithotripsy, Operations on EENT)
- Monozygotic twins
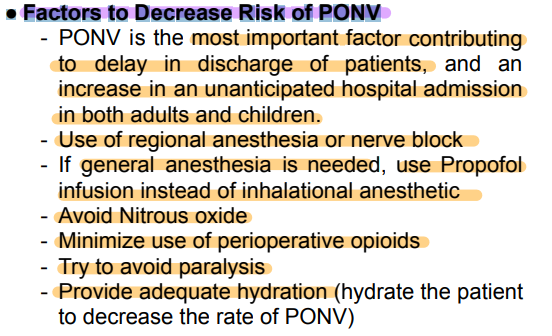
● Factors to Decrease Risk of PONV
● Reasons for delays of discharge
- Drowsiness
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Pain
- A Benzodiazepine receptor antagonist
Flumazenil
- Use to reverse the effects of sedation after endoscopy
Flumazenil
Flumazenil
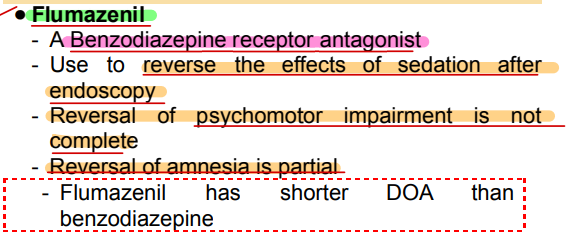
- Reversal of opioids may also be necessary
Naloxone
● Post-surgical pain should be differentiated from the discomfort of
hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and full bladder.
● Post op pain must be treated effectively. Medications should be given in small intravenous doses, with short acting opioids like
fentanyl
Pain management

. PREPARATION FOR DISCHARGING THE PATIENT
• PACU
• Phase II Recovery
• Home
PHASE II RECOVERY
● Day surgery unit
● Patients remain until they are able to tolerate liquid, walk, and/or void
● Direct transfer when patients awakened in the OR
● Test higher level of function
- Ability to use one's hands
- Drive a car (Do not recommend to a patient sedated to drive within 24 hours
- Remain alert long enough to drive
● Before discharge
- Dressings should be checked
- Include responsible person for discharge instructions
- Inform patients the side effects of all drugs used
- Discuss where the patient can return in case of a problem