Lab 6 Green Algae & Seedless Plants
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Green algae (protists) and land plants are ____ that share a common ancestor.
photosynthetic eukaryotes
Similarities of green algae (protists) and land plants
Photosynthetic eukaryotes
cells walls made of cellulose
sugar stored as starch
chlorophyll as green pigment
What are the 2 evolutionary lineages of green algae
Chlorophytes and charophytes
Charophytes (Chara)
more closely related to land plants because they both have gametangia
makes and protects gametes
allows transition from water → land
antheridia: make sperm which has flagella
archegonia: makes eggs
Has sterile jacket: protects gametes from drying (water needed to fertilize)
Alternation of generation
Algae, moss, and fern switch between haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte)
for survival and evolution
importance: helped plants go from water → land
Alternation of generation in algae
default reproduction is asexual (diploid, 2n)
switch to sexual reproduction (haploid, n) when in unfavorable conditions → making zygospores which break into spores
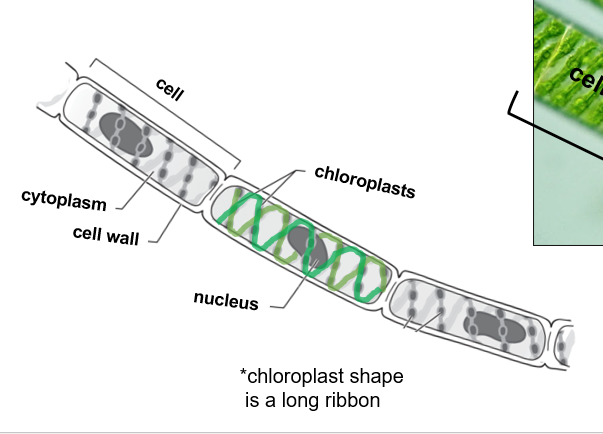
What is Spirogyra?
Filamentous, colonial green algae
Contains ribbon chloroplasts
Asexual Reproduction in Spirogyra
Good conditions (warm, sunlight, nutrients)
haploid (n) and divide through mitosis/fragmentation → filaments elongate and attach to each other by the cell wall
Bad conditions
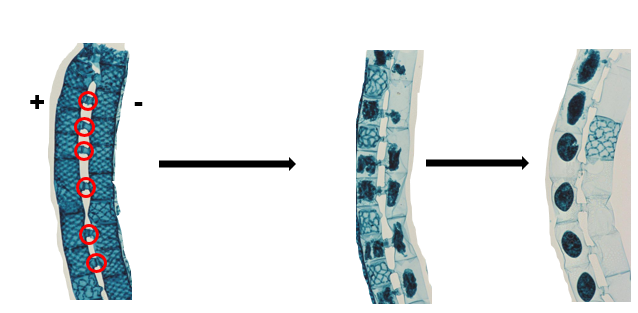
Conjugation: haploid (n) cells come tg to make diploid (2n) zygotes = zygospores
filaments line up (n) → forming conjugation tube in order to condense (n) (-) strain into (+) strain → zygospore (2n)
Zygospores does meiosis to make haploid cells (n)
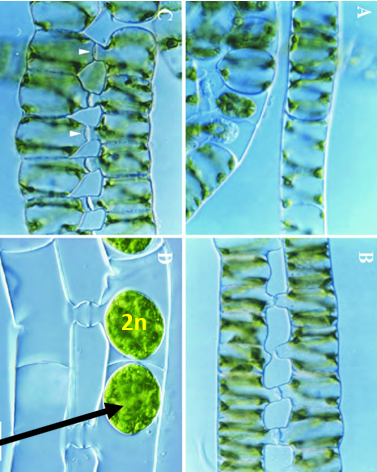
What is this a picture of?
Asexual reproduction in spirogyra
Land plant evolution
diploid phase as sporophyte
haploid phase as gametophyte
terrestrial, primary producer
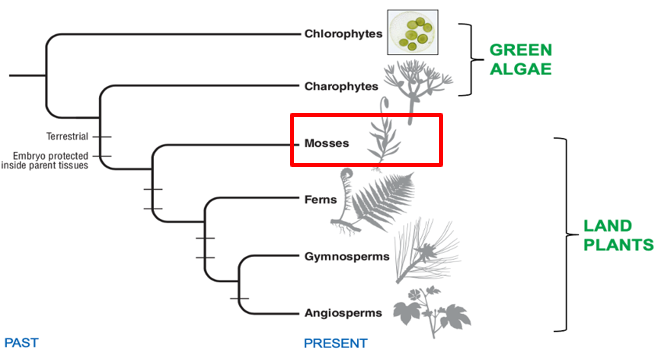
Mosses: Nonvascular Land Plants
no vascular tissue, therefore no tissue to transport water and nutrients → make plants grow tall
Also considered bryophytes
Moss (alternation and generation)
dominant stage when just leafy (gametophyte)
Non dominant stage when produces stalks
Moss asexual reproduction
Gamete producing parts: archegonium(egg), antheridium (sperm)
Spore producing parts: capsule which the sporangium (filled with spores) consist inside of the capsule
spores burst out of capsule
sporophyte attached to gametophyte
Vascular Land Plants
sporophyte: dominant stage
Has vascular tissue (true roots, stems, leaves) to transport water (xylem) and nutrients for plant growth
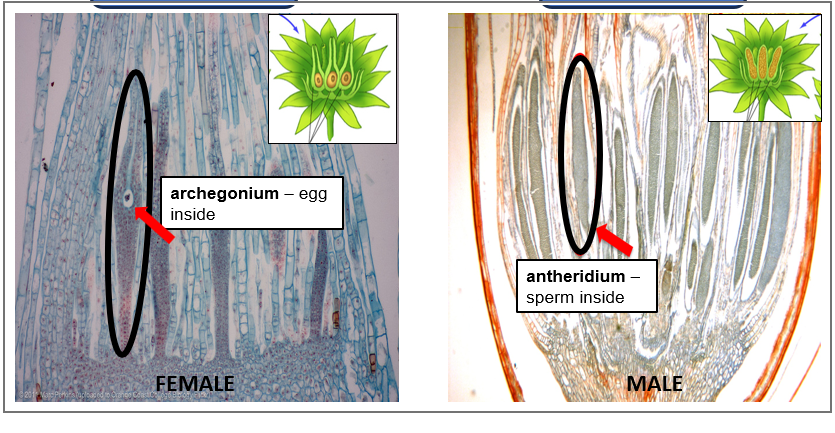
What is this image of?
gamete producing parts in moss
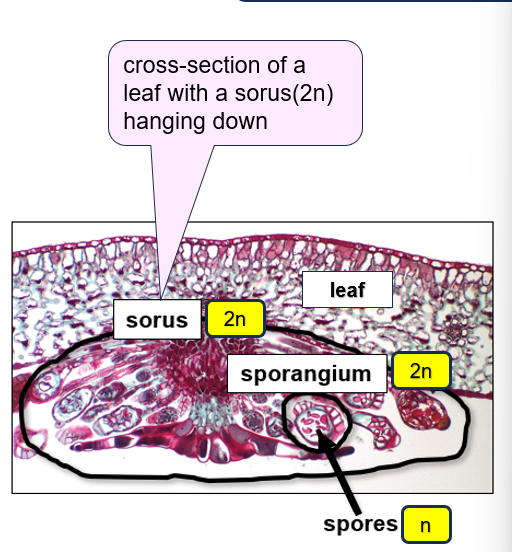
Ferns (vascular seedless land plant)
dominant phase: sporophyte (2n) → grows on gametophyte
Non dominant phase: gametophyte (n) → VERY small/almost microscopic
Ferns Reproduction
Gametophyte (n) - haploid
antheridia: sperms that has flagella
archegonia: eggs waiting for sperm for fertilization
rhizoids: hair like projections for anchoring
Sporophyte (2n) - diploid
Sorus: cluster of sporangia (found underside of leaf)
purplish looking cross-sections