Acids, bases & salt preparations
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
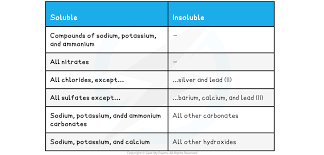
What are the rules of predicting the solubility of ionic compounds?
Compounds of sodium, potassium and ammonium are soluble
All nitrates are soluble
All chlorides except silver and lead (II) are soluble
All sulfates except barium, calcium and lead (II) are soluble
Only sodium, potassium and ammonium carbonates are soluble
Only sodium, potassium and calcium hydroxides are soluble
Describe acids & bases in terms of proton transfer
Acids are proton donors
Alkalis are proton acceptors
What is produced when an acid & a base react together?
salt + water
What is produced when an acid & a metal oxide react together?
salt + water
What is produced when an acid & a metal hydroxide react together?
salt + water
What is produced when an acid & a metal carbonate react together?
salt + carbon dioxide + water
What is produced when an acid & ammonia react together?
ammonium salt
What are 5 common laboratory acids & their formulas?
Hydrochloric acid → HCl
Nitric acid → HNO3
Sulfuric acid → H2SO4
Ethanoic acid (vinegar) → CH3CO2H
Phosphoric acid → H3PO4
(all acids have hydrogen in their formula because acids are hydrogen donors)
What is an alkali?
a base that is soluble in water
What substances can act as bases?
metal oxides
metal hydroxides
ammonia
Describe an experiment to prepare a pure dry sample of a soluble salt starting from an insoluble reactant (e.g. copper II oxide)
- add insoluble base to an acid
- continue to add base until there is excess base remaining to ensure that all acid has reacted
- use a filter funnel & paper to remove any unreacted base from the acid
- heat the solution with a Bunsen burner so that the water evaporates & only crystals of the salt remain
- place the salt crystals on some paper towel & leave them to dry somewhere warm
Describe an experiment to prepare a pure dry sample of a soluble salt starting from an acid & an alkali
- use a titration to calculate the exact volume of the alkali that reacts with the acid
- mix the exact volumes of the acid & the base
- warm the solution with a Bunsen burner so that water evaporates and crystals of the salt remain
- place the salt crystals on some paper towel & leave them to dry somewhere warm
Describe an experiment to prepare a pure dry sample of a soluble salt starting from 2 soluble reactants (e.g. lead II sulfate)
- mix 2 solutions of soluble reactants together
- insoluble salt crystals will form, so use a filter funnel & paper to separate them from the mixture
- wash the salt crystals with distilled water & leave them to dry