OSU Anatomy 2300 Unit 4
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
Overview of the skull
-part of the axial skeleton
-composed of 22 bones total
-8 bones form cranium
-14 associated w/ face
-7 additional bones associated w/ skull
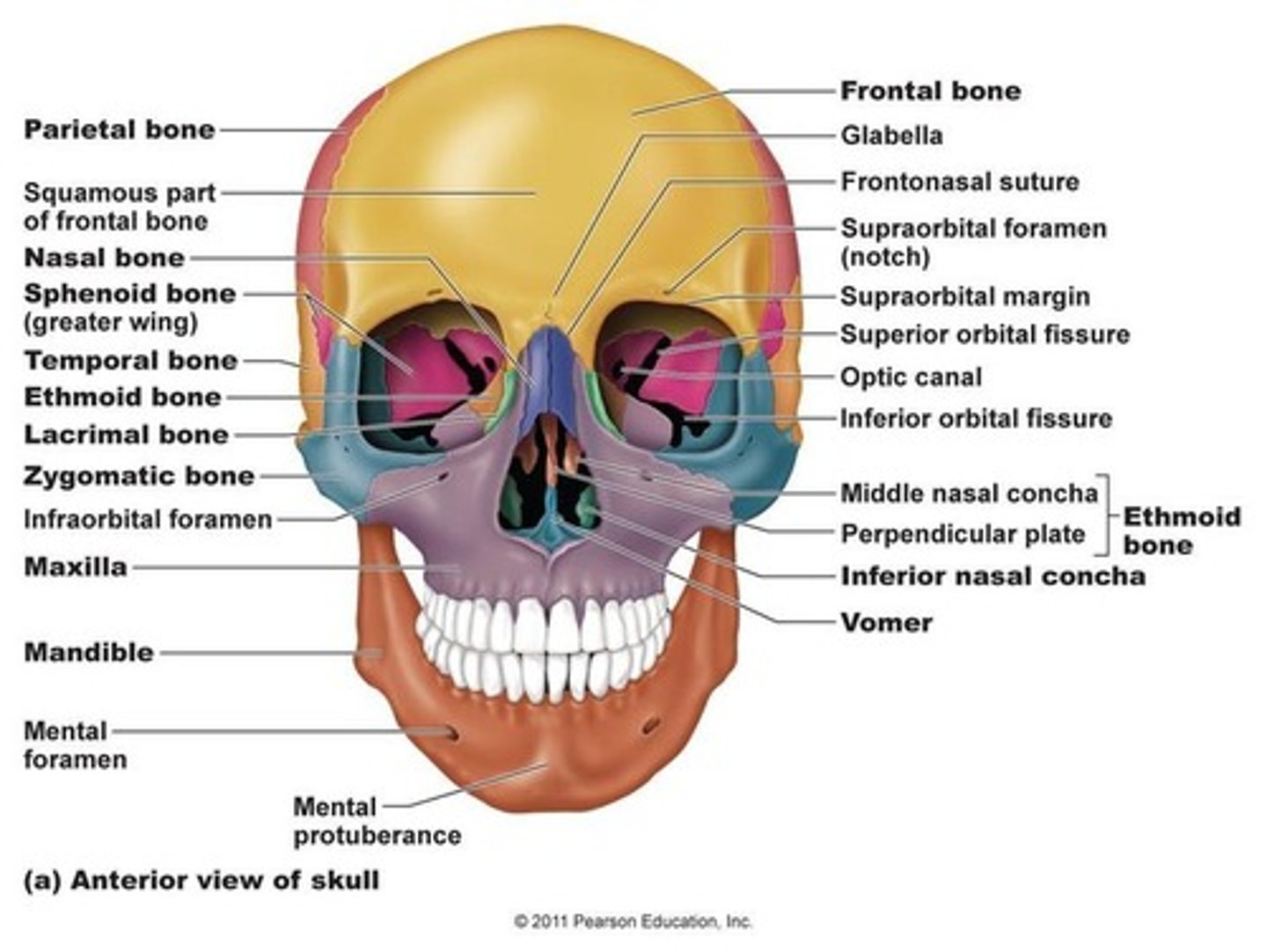
What are the bones of the cranium?
-frontal bone (1)
-occipital bone (1)
-sphenoid bone (1)
-ethmoid bone (1)
-parietal bones (2)
-temporal bones (2)
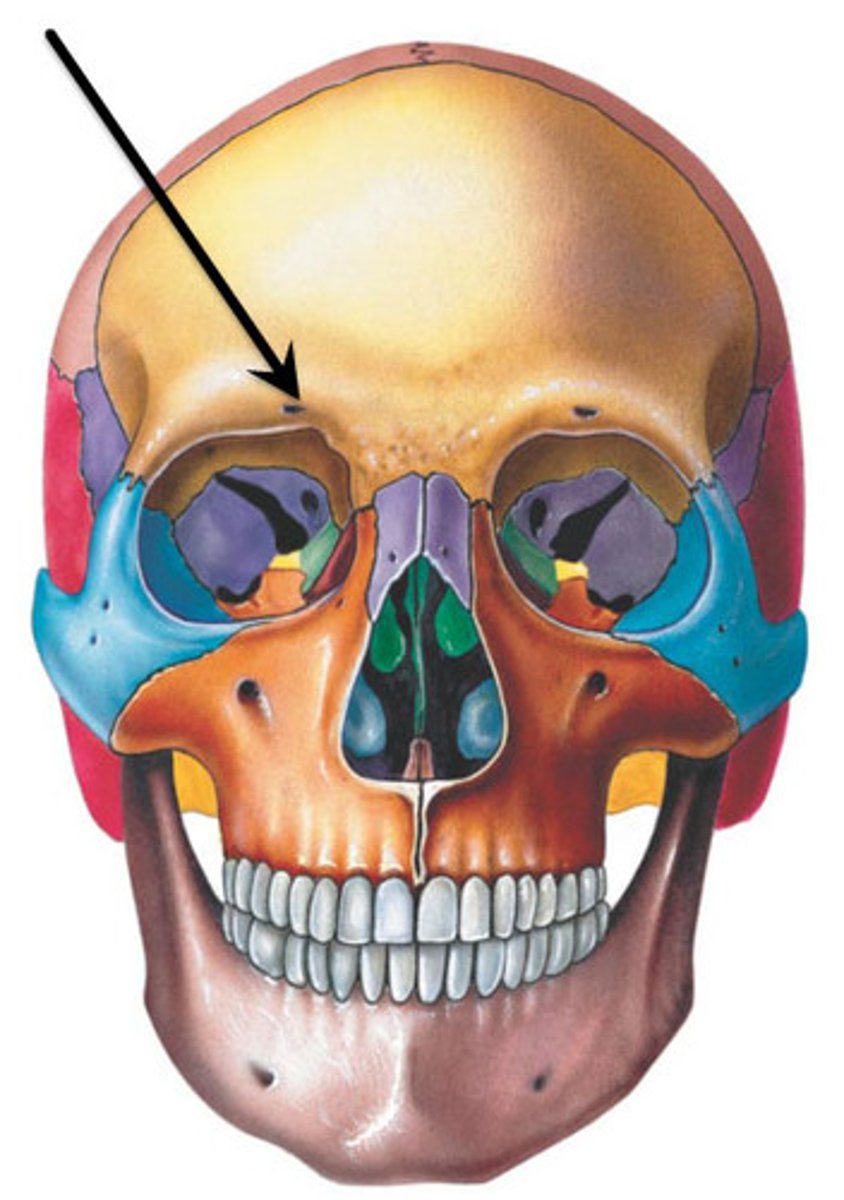
Frontal bone of skull
forehead bone; protects cranium (yellow on fig.)
-supra-orbital notch (foramen)
-supra-orbital nerve travels through notch
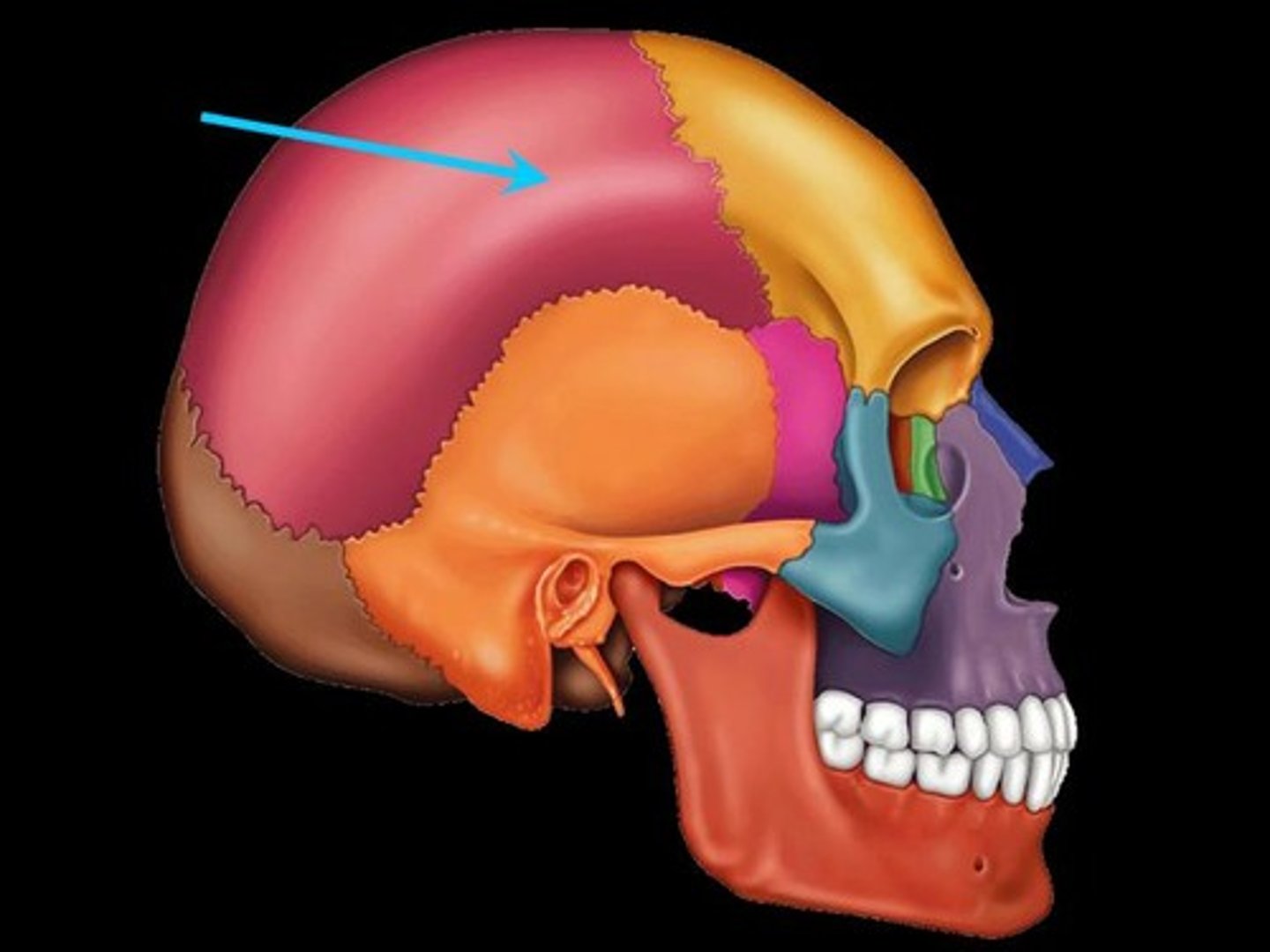
Parietal bones of skull
Bones that form the sides and top of the cranium
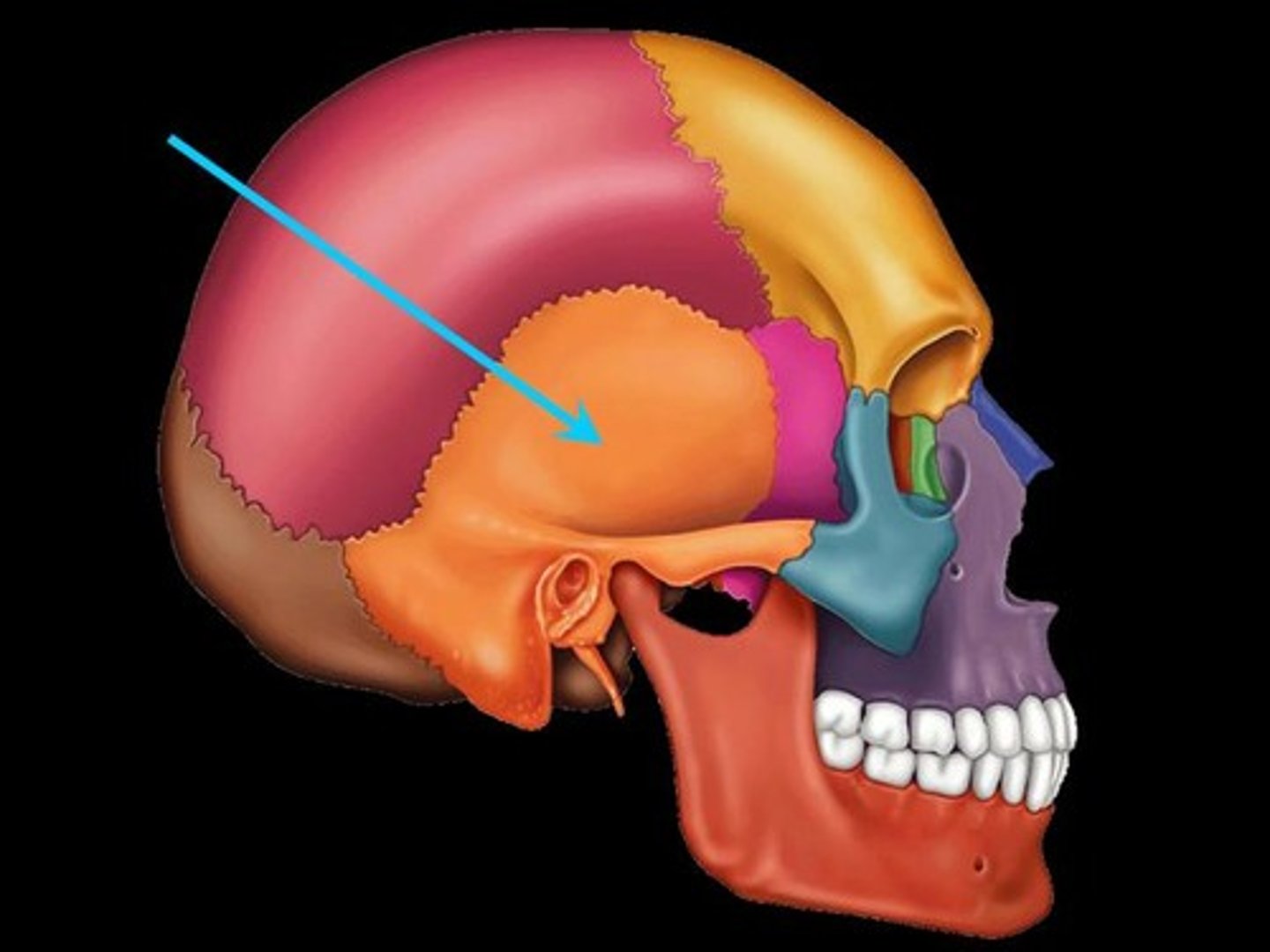
Temporal bones of skull
-contains external acoustic meatus
-mastoid process
-styloid process
-zygomatic process
carotid canal of temporal bone
for internal carotid artery
stylomastoid foramen of temporal bone
contains facial nerve
mandibular fossa of temporal bone
articulates with the mandible

internal acoustic meatus of temporal bone
Facial n. (CN VII)
Vestibulocochlear n. (CN VIII)
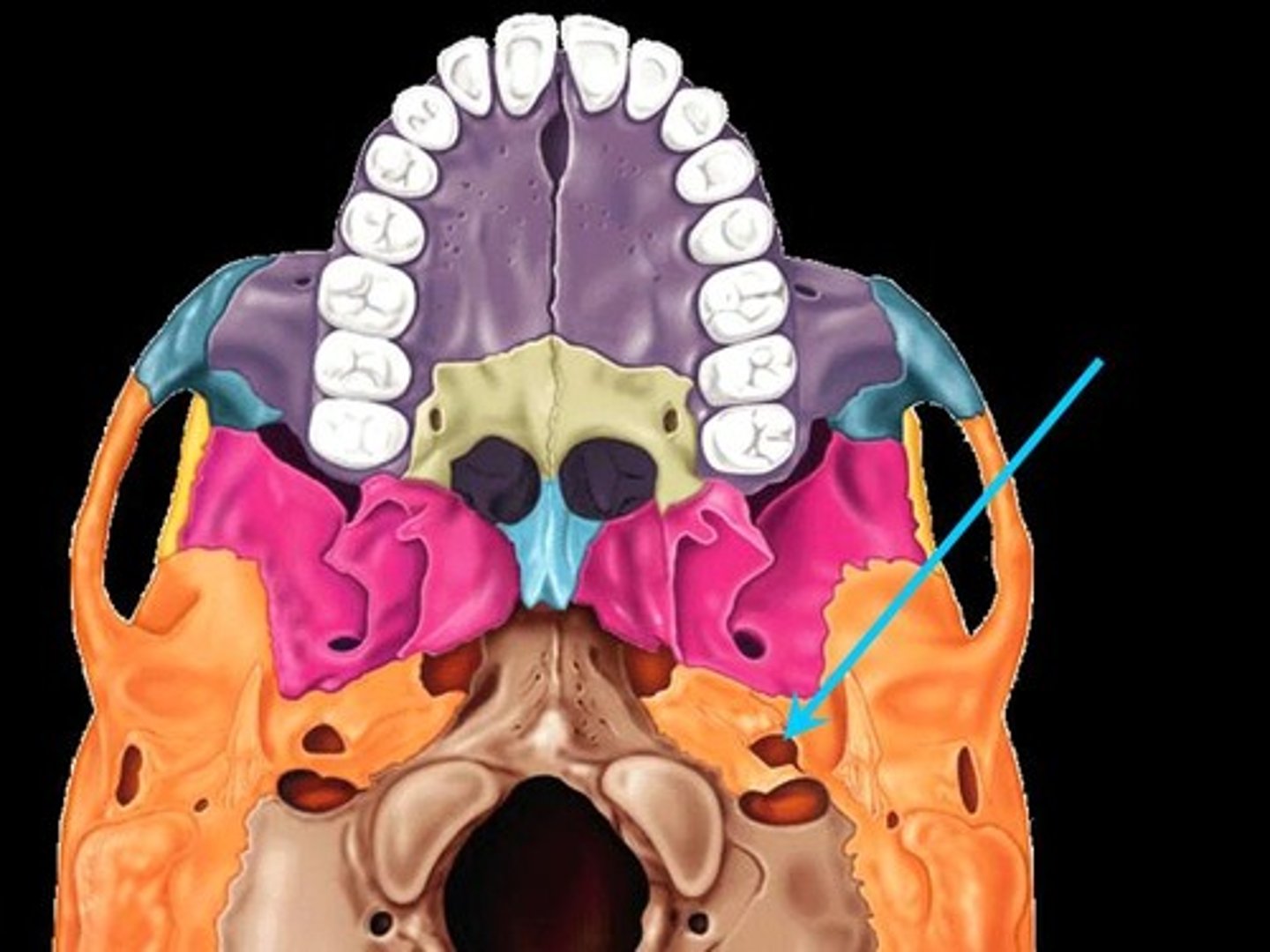
jugular foramen of temporal bone
foramen for internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI
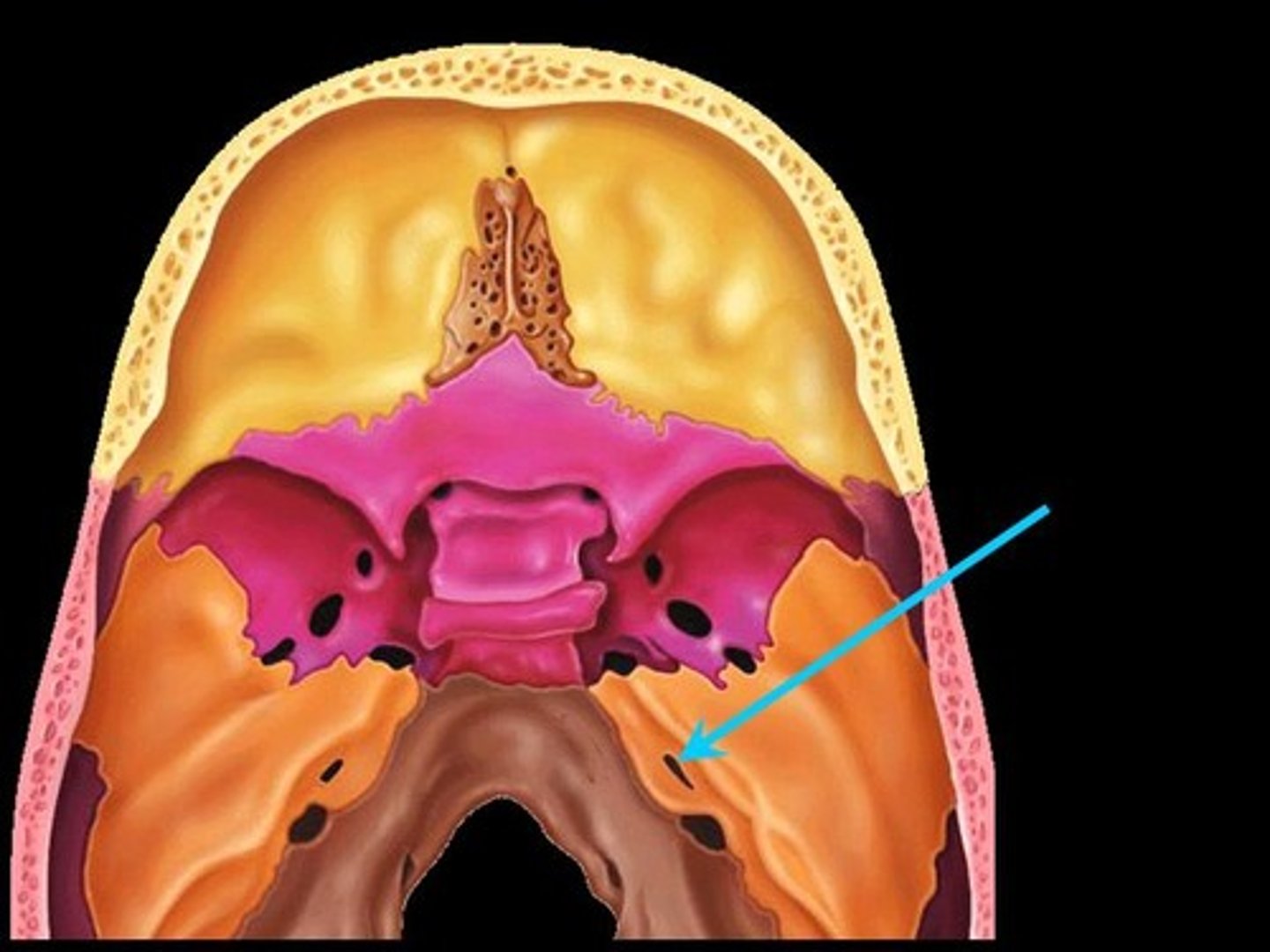
occipital condyles of occipital bone
rounded processes that articulate with the atlas (C1)
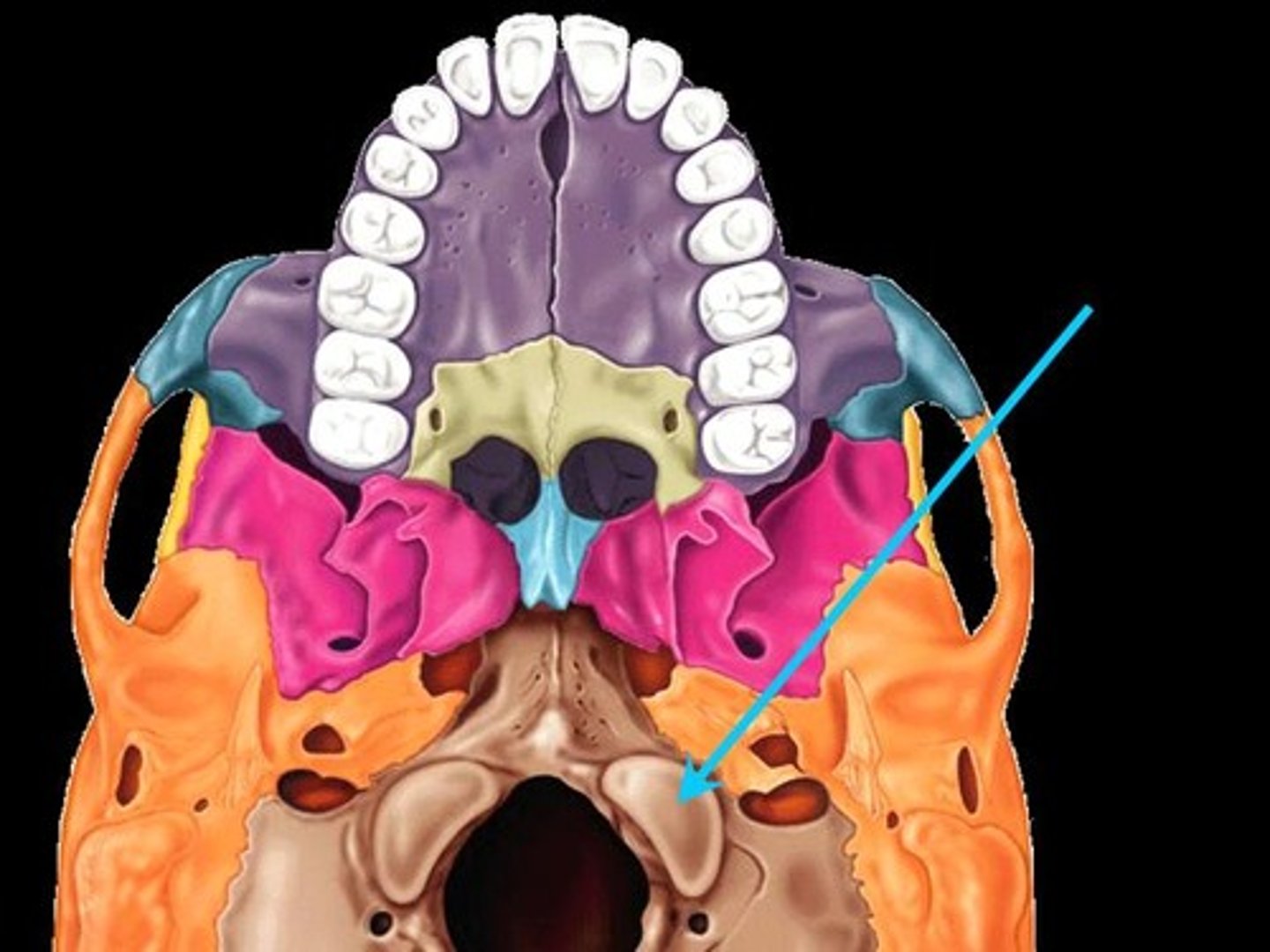
foramen magnum of occipital bone
-spinal cord exist via foramen magnum
-vertebral arteries enter via foramen magnum

external occipital protuberance of occipital bone
projection at base of skull posterior to foramen magnum
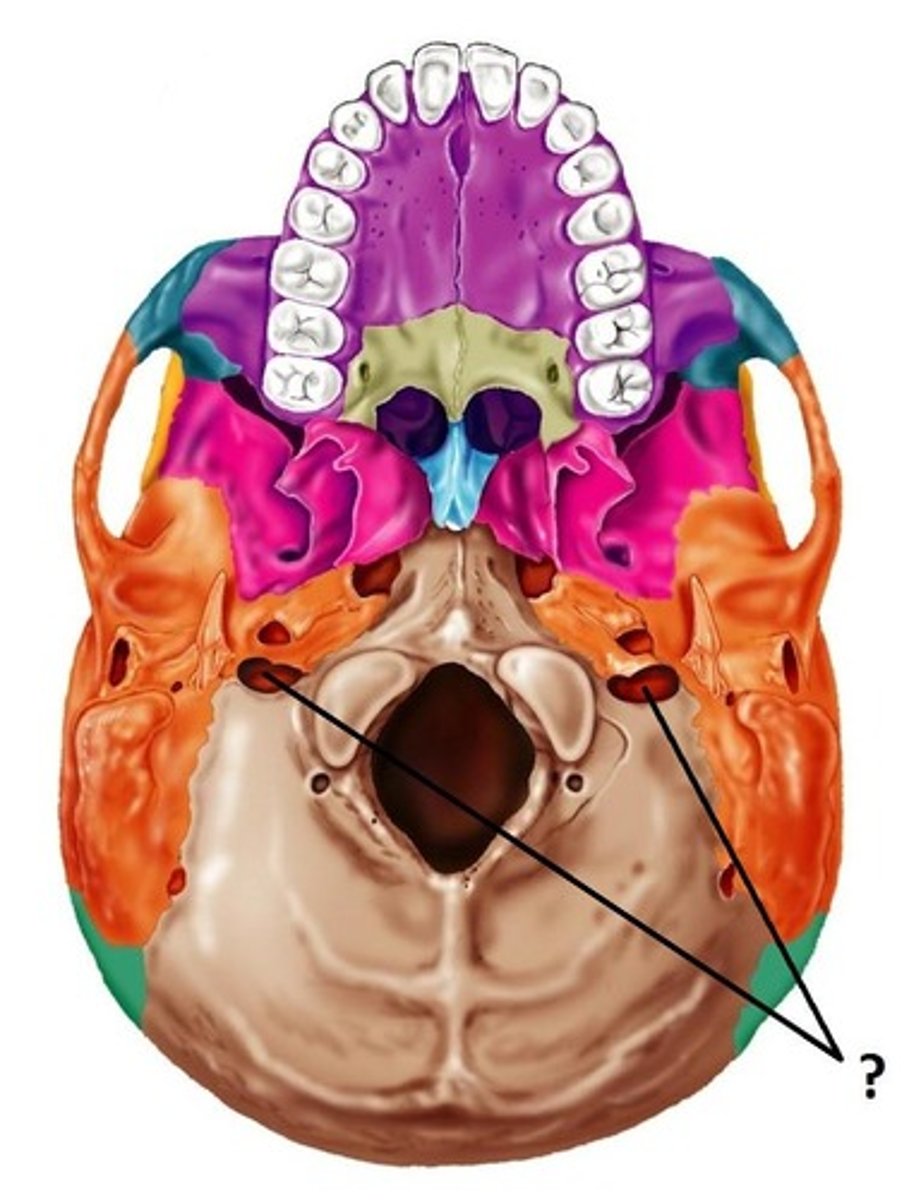
hypoglossal canal of occipital bone
contains hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
What are the main structures of sphenoid bone (8)
(1) lesser wing
(2) greater wing
(3) sella turcica
(4) foramen lacerum
(5) optic canal
(6) foramen rotundum
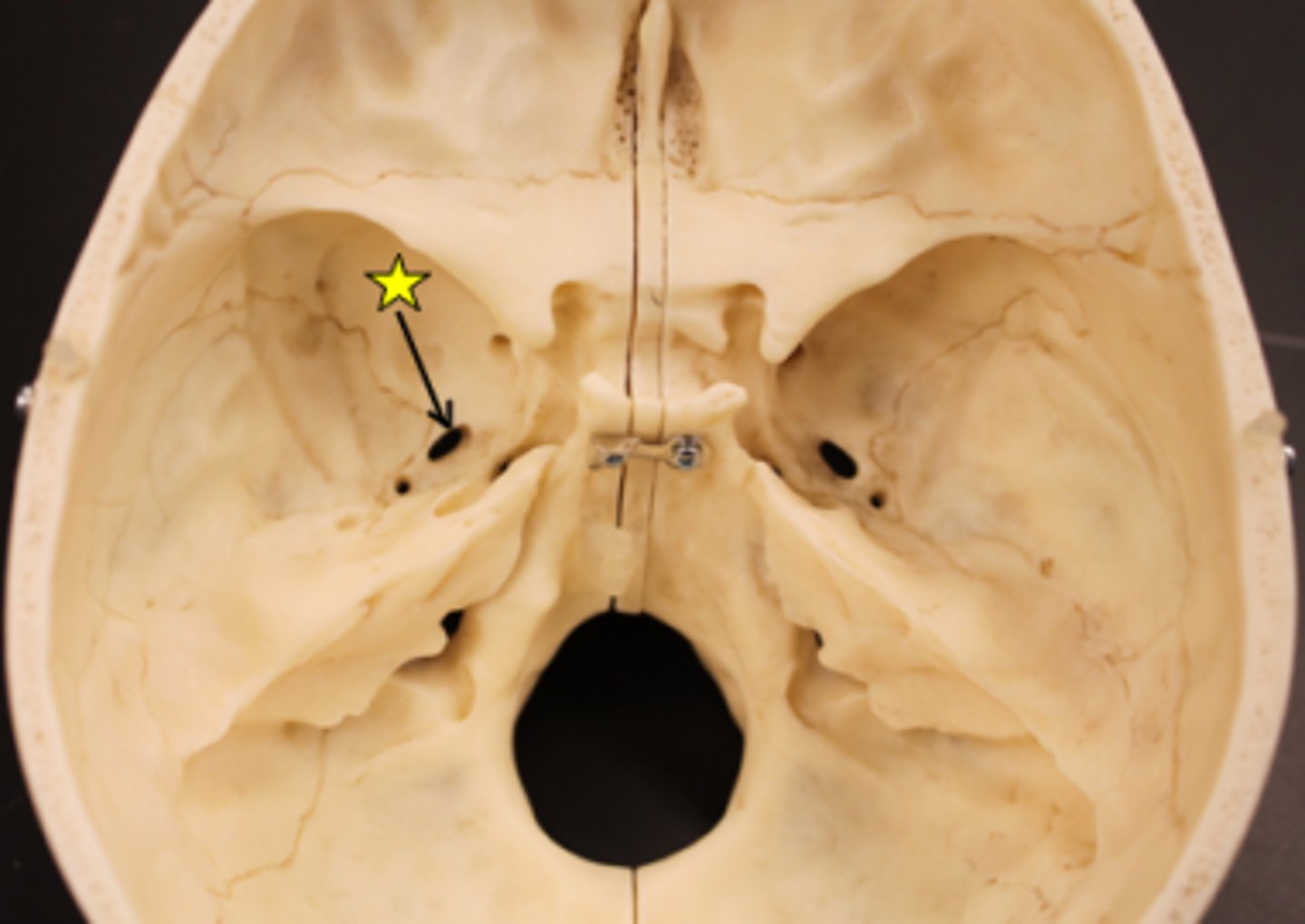
(7) foramen ovale
(8) foramen spinosum
Sella Turcica ("Turkish Saddle") of the Sphenoid Bone
(inferior view)
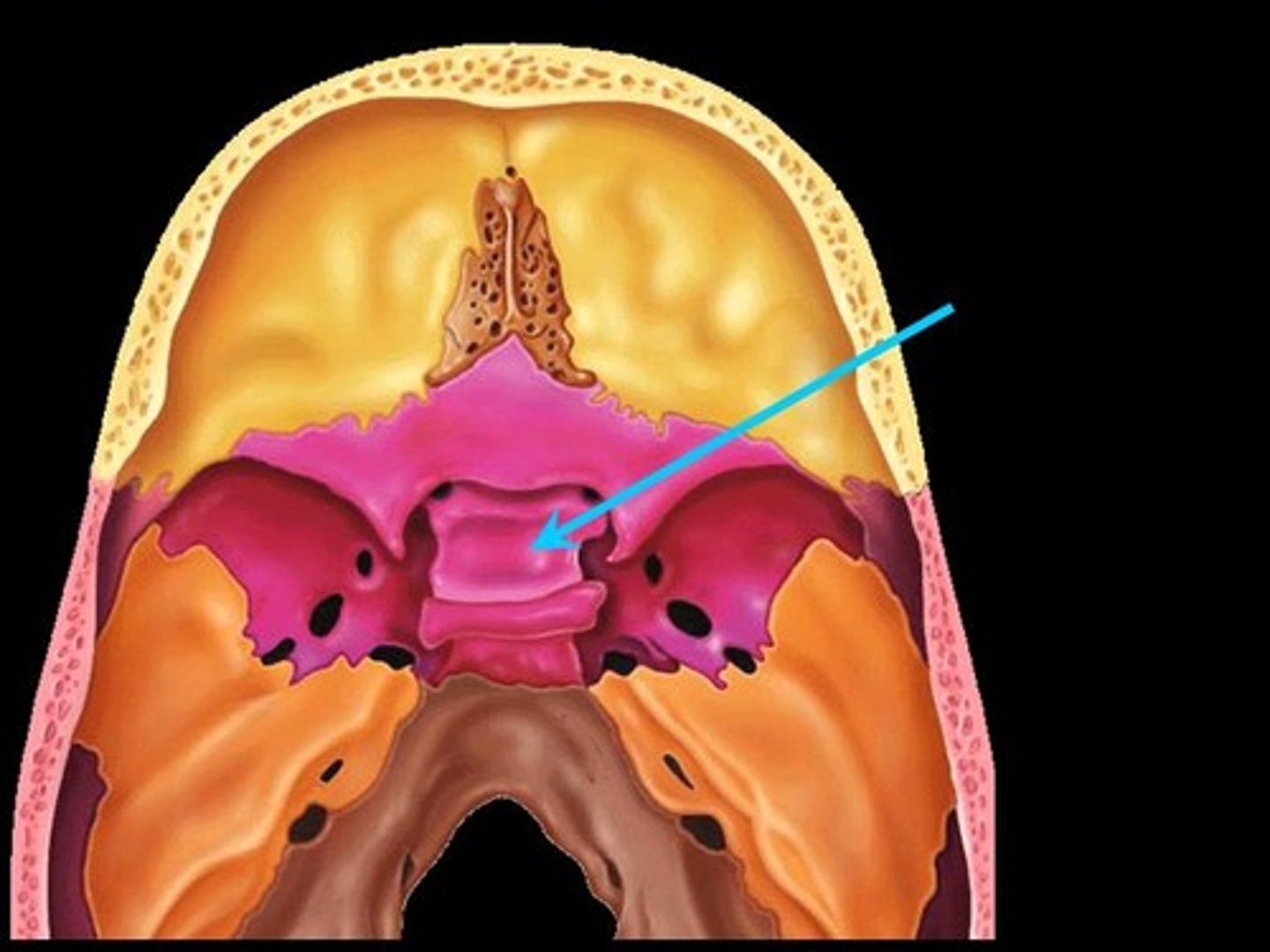
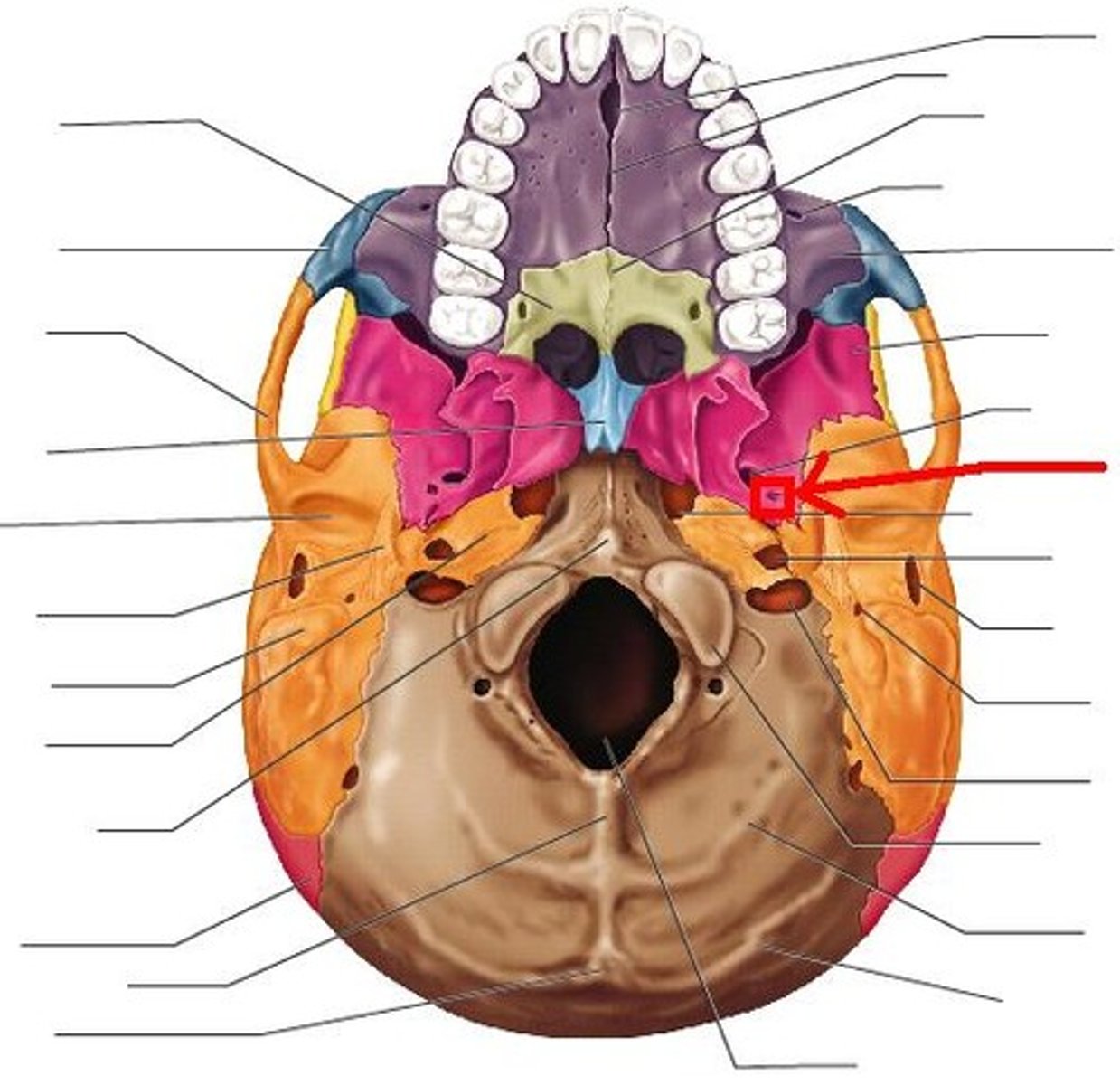
foramen lacerum of sphenoid bone
-opening for the internal carotid artery
-lateral to Sella Turcica

optic canal of sphenoid bone
contains optic nerve (CN II)
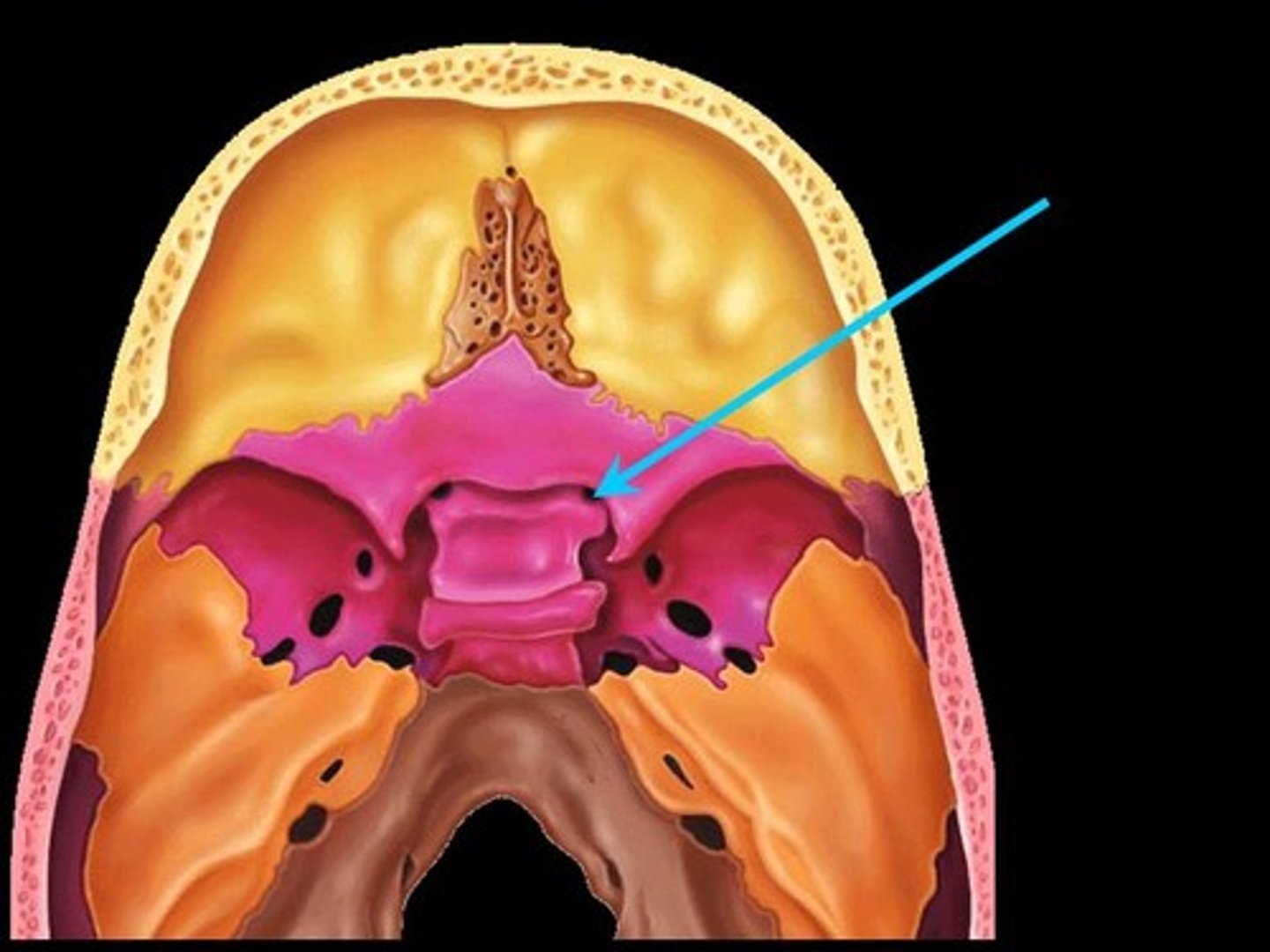
foramen rotundum of sphenoid bone
First part of Cowboy Ros, transmits maxillary branch CN V2 (part of trigem)
Foramen ovale
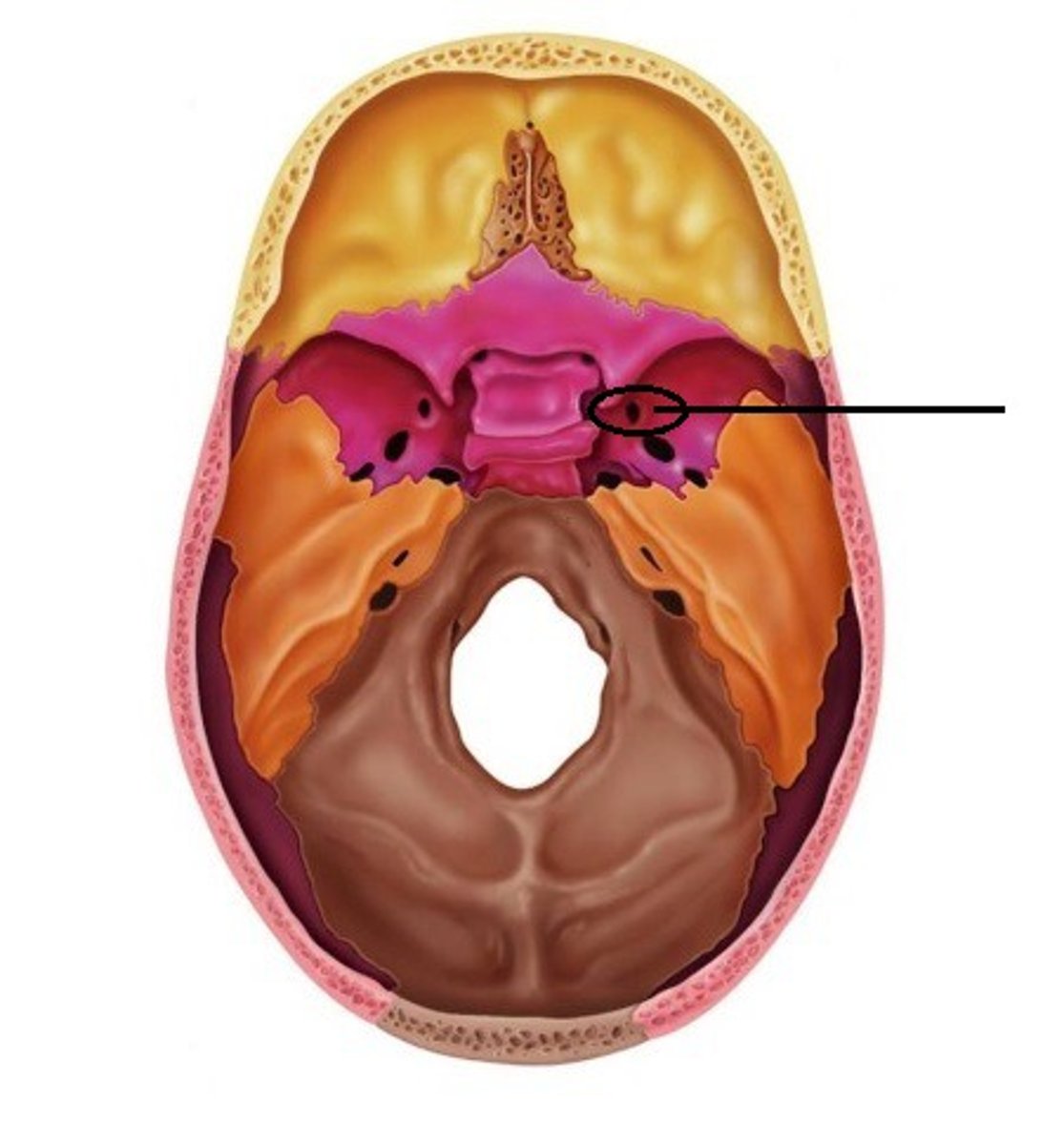
foramen spinosum of sphenoid bone
(red circle); inferior to foramen rotundum; lateral to foramen ovale
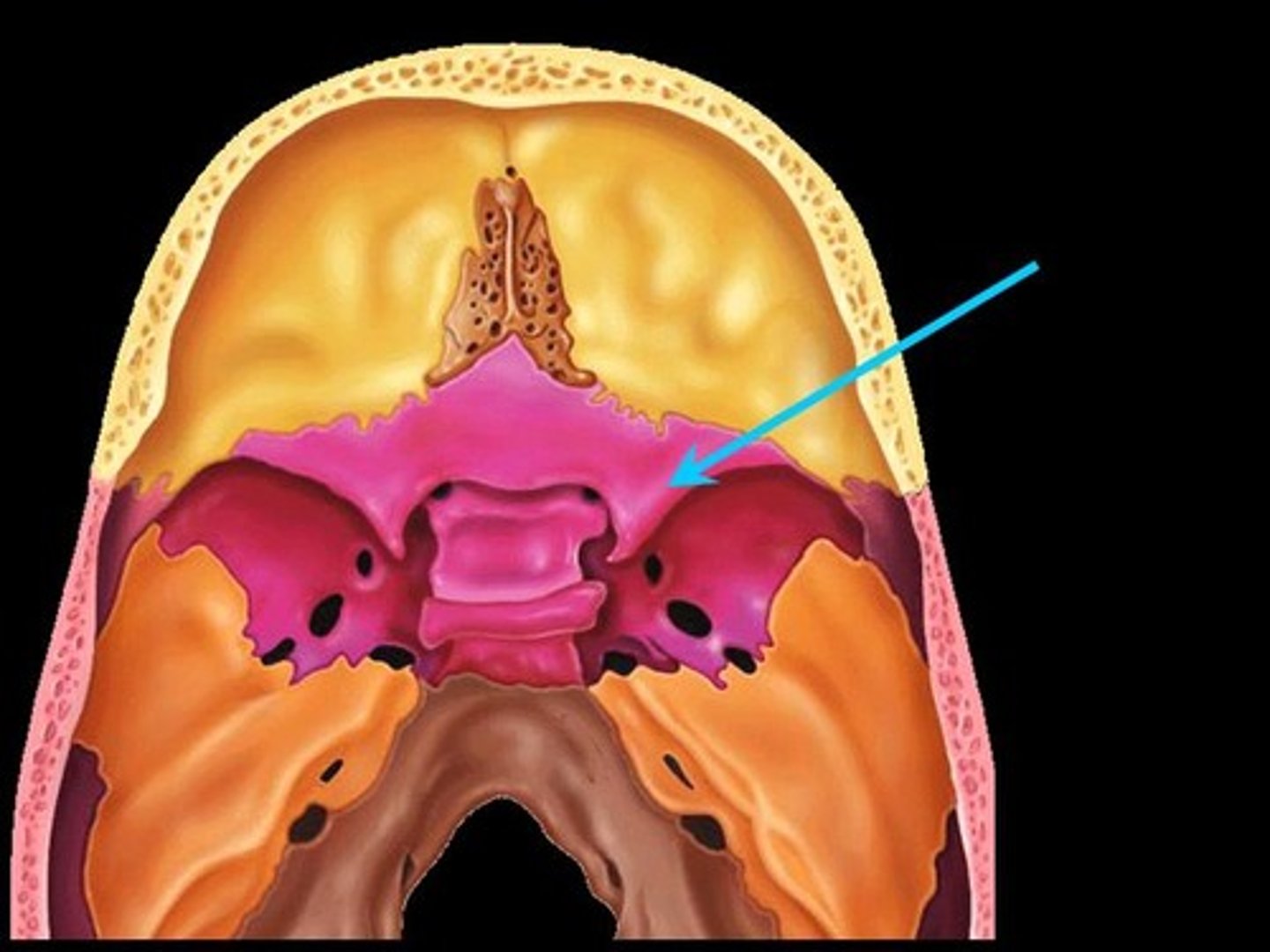
Greater wing of sphenoid bone
posterior & inferior to lesser wing on the interior of the skull; also visible in the posterior orbit and lateral side of the skull
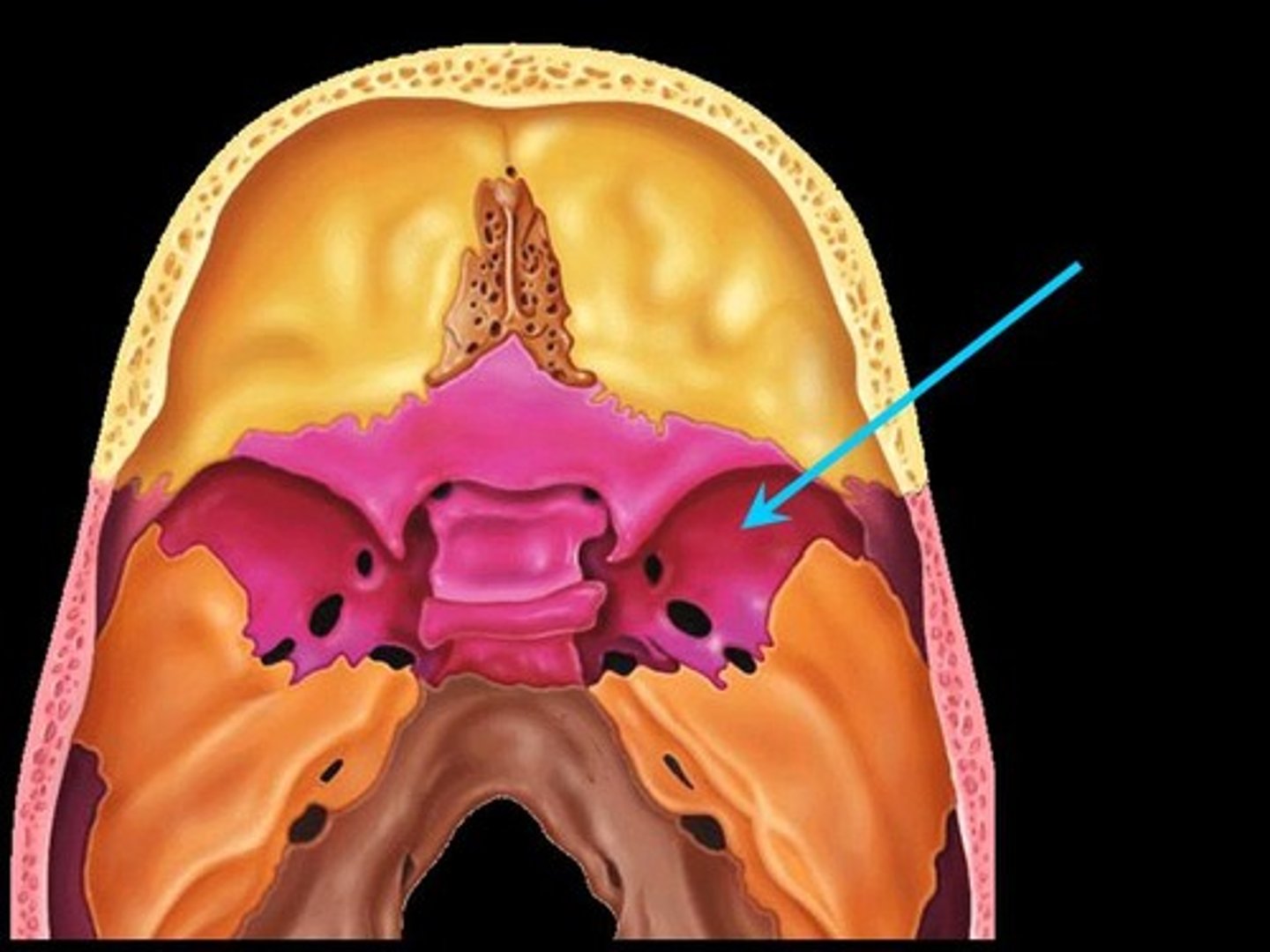
Lesser wing of sphenoid bone
anterior & superior to greater wing on the interior of the skull
Cowboy Ross Mnemonic
Cowboy: sits in the saddle (Sella turcica)
R: foramen rotundum
O: foramen ovale
S: foramen spinosum
ROS: medial --> lateral
What nerve runs through foramen rotundum?
Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
-second division of trigeminal
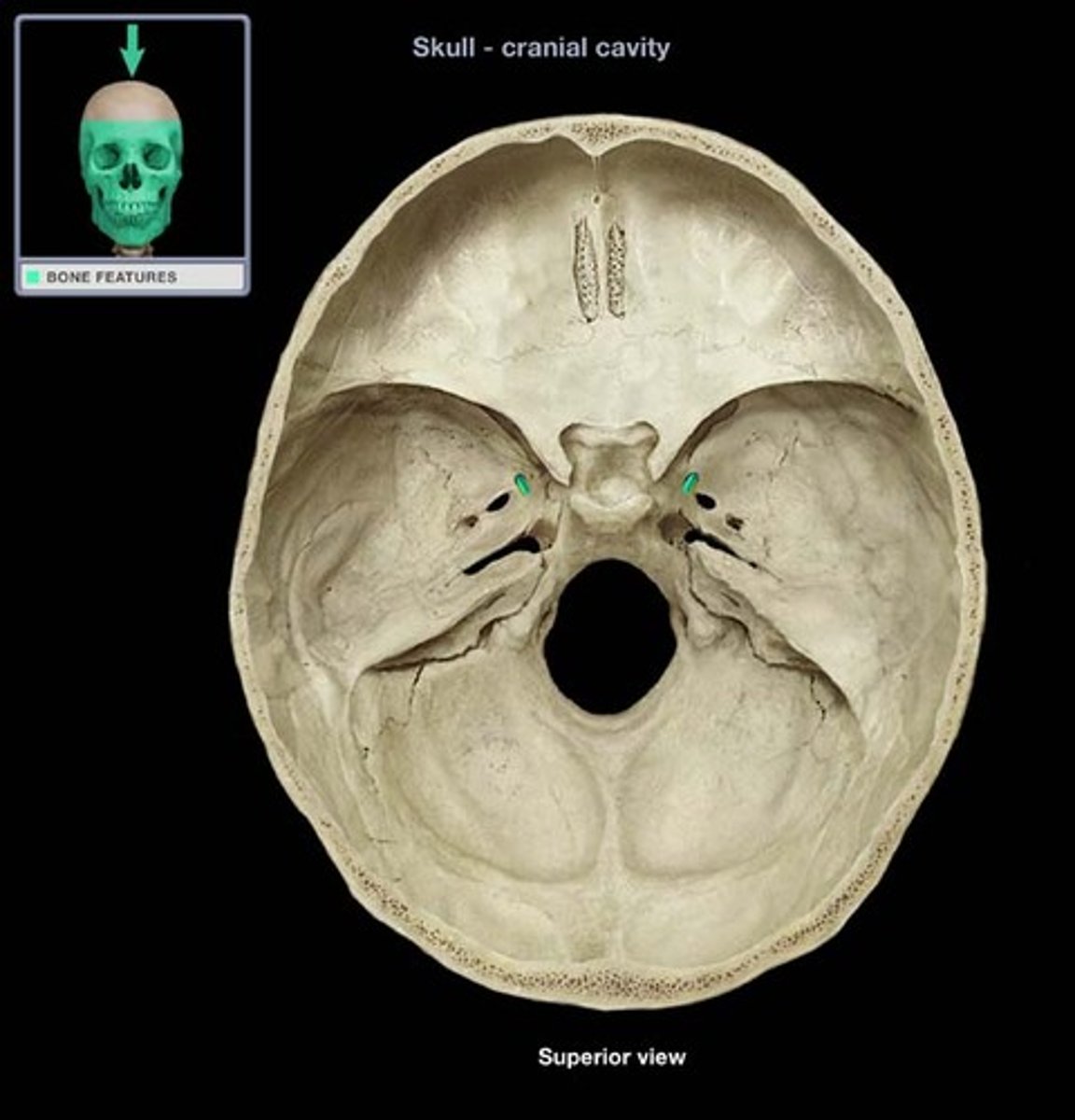
What nerve runs through foramen ovale?
Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
-third division of trigeminal

What runs through foramen spinosum?
middle meningeal artery
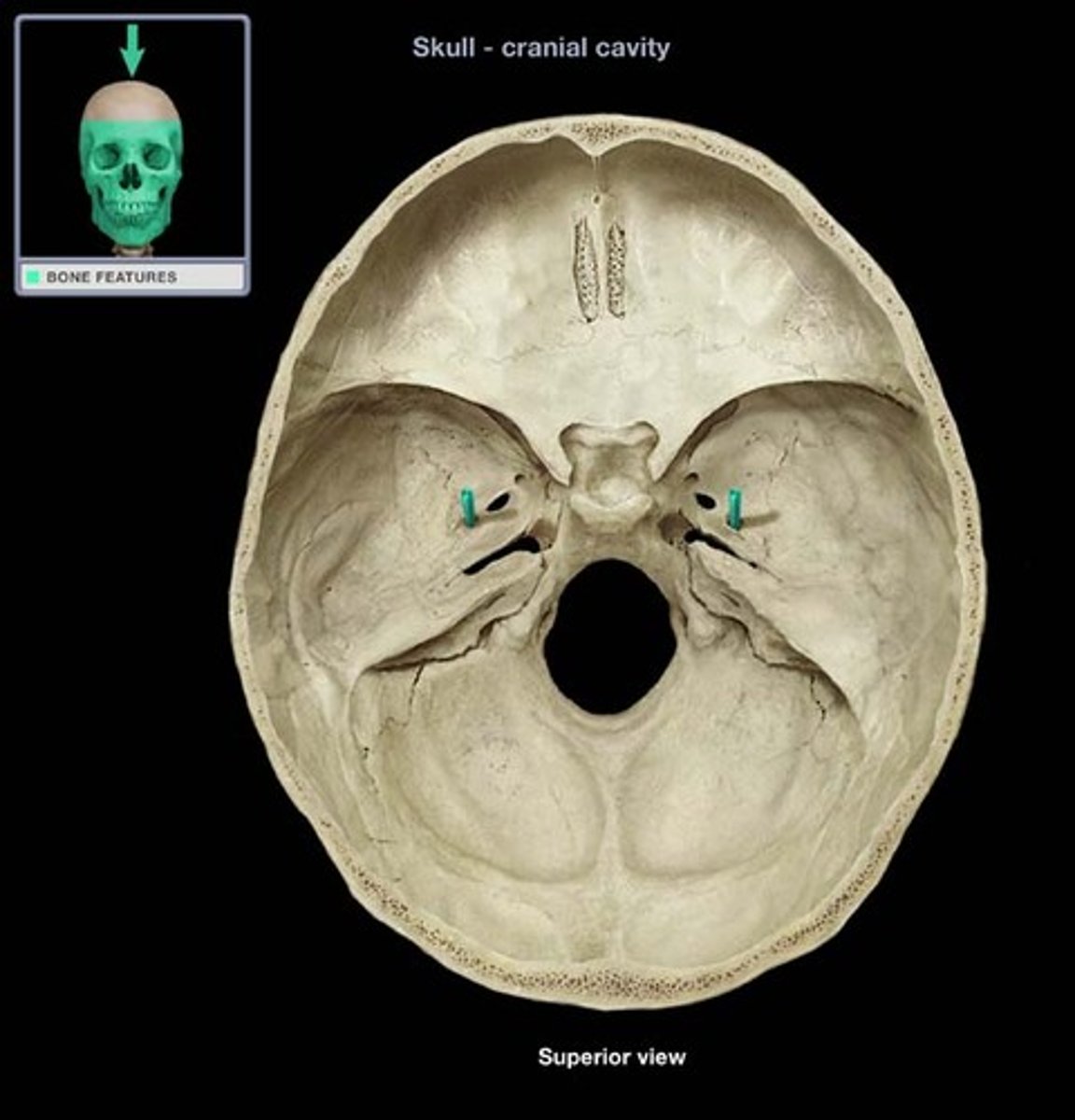
What runs through foramen lacerum?
Nothing; it is covered w/ cartilage
Sphenoid bone (anterior view): optic canal
Identify this structure:
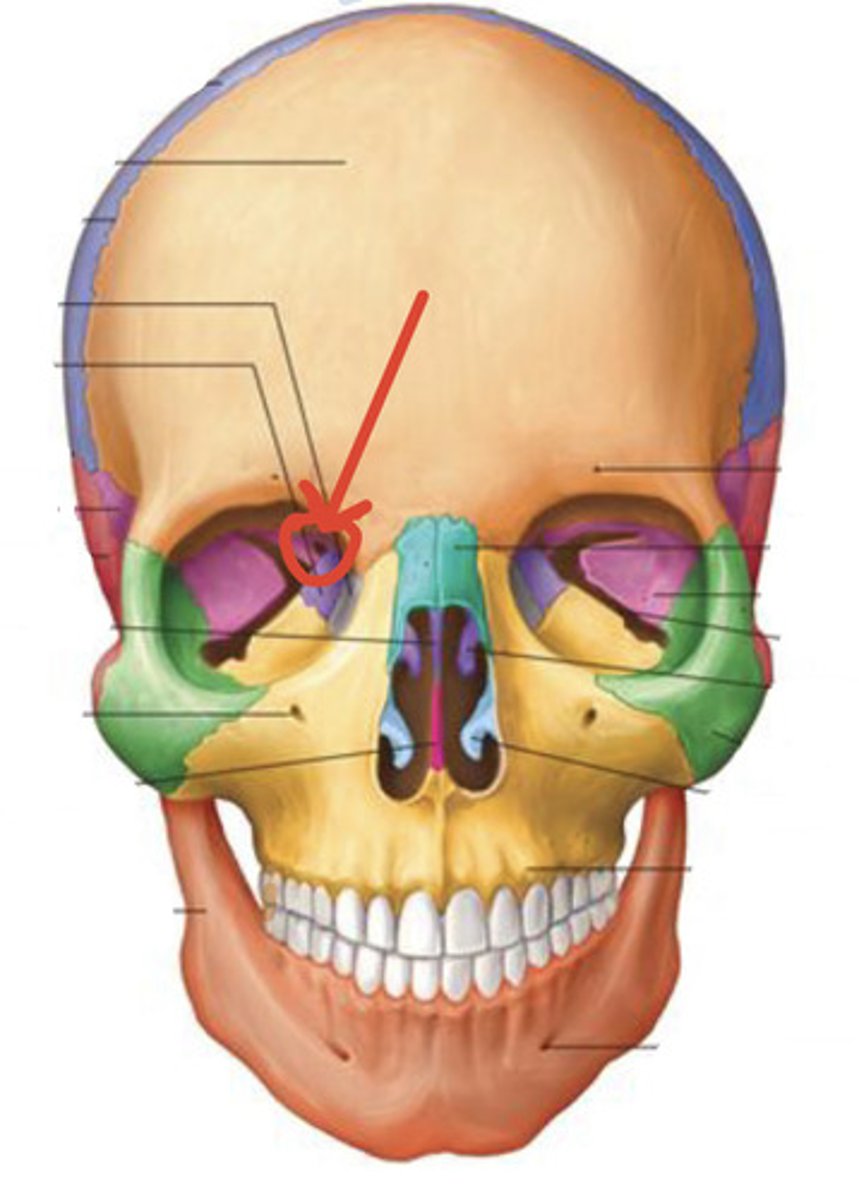
Sphenoid bone (anterior view): superior orbital fissure
Identify this structure:
What travels through the superior orbital fissure?
CN III, IV, V (1st part), VI and the superior ophthalmic vein
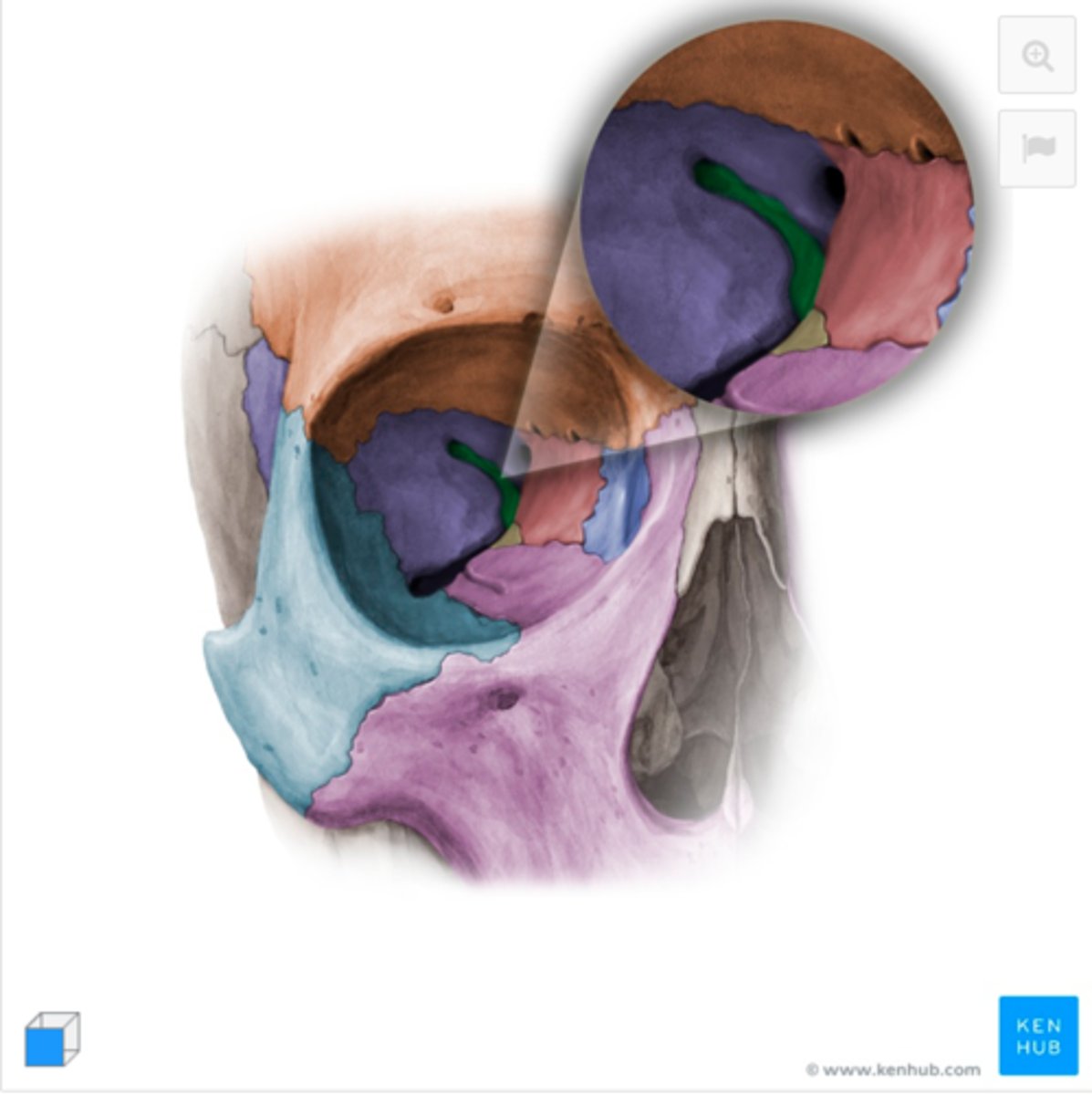
Medial pterygoid plate
Lateral pterygoid plate
Crista galli of ethmoid bone
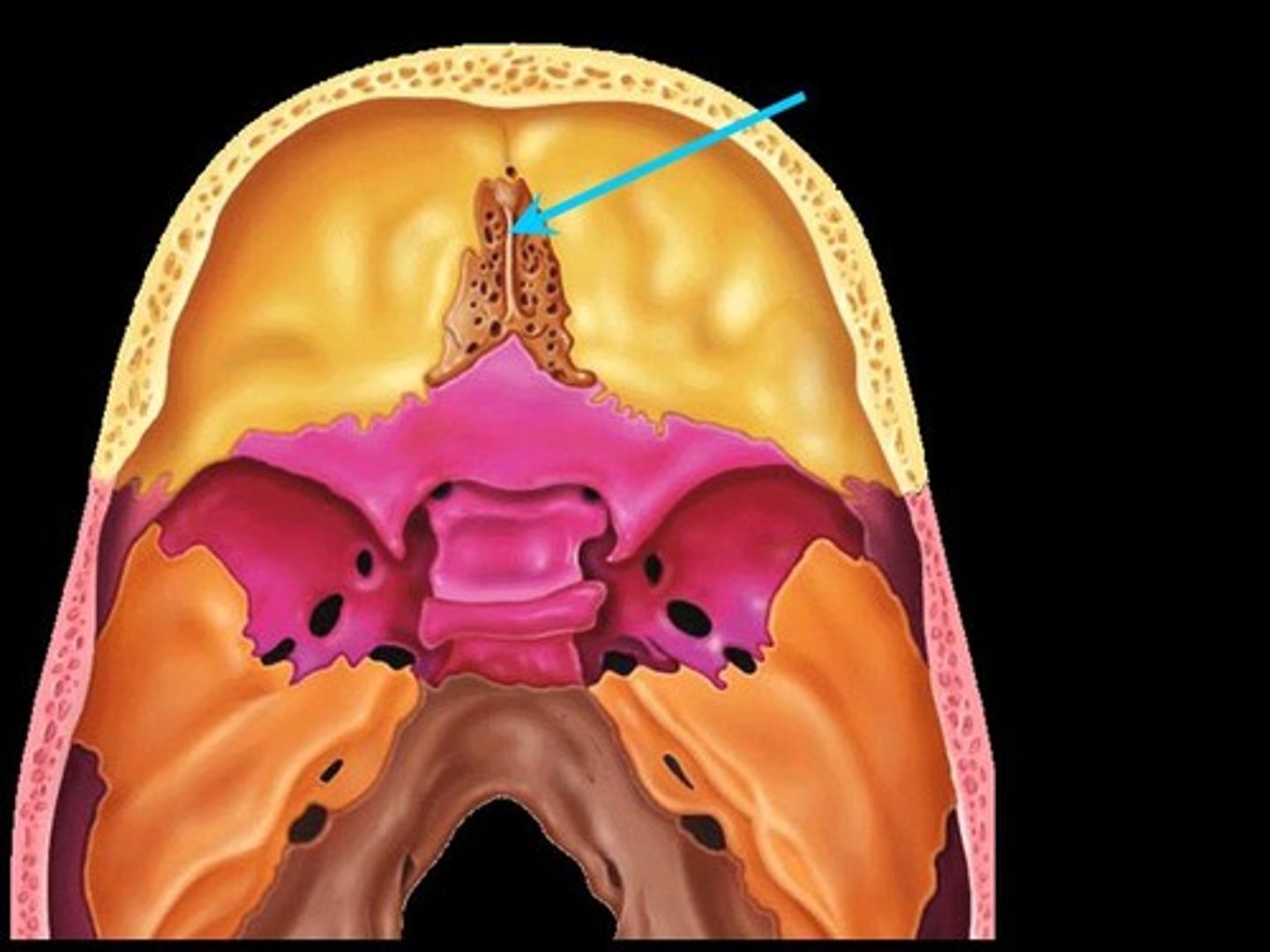
Cribriform plate & cribriform foramina of ethmoid bone
innervated by CN1 / olfactory nerve
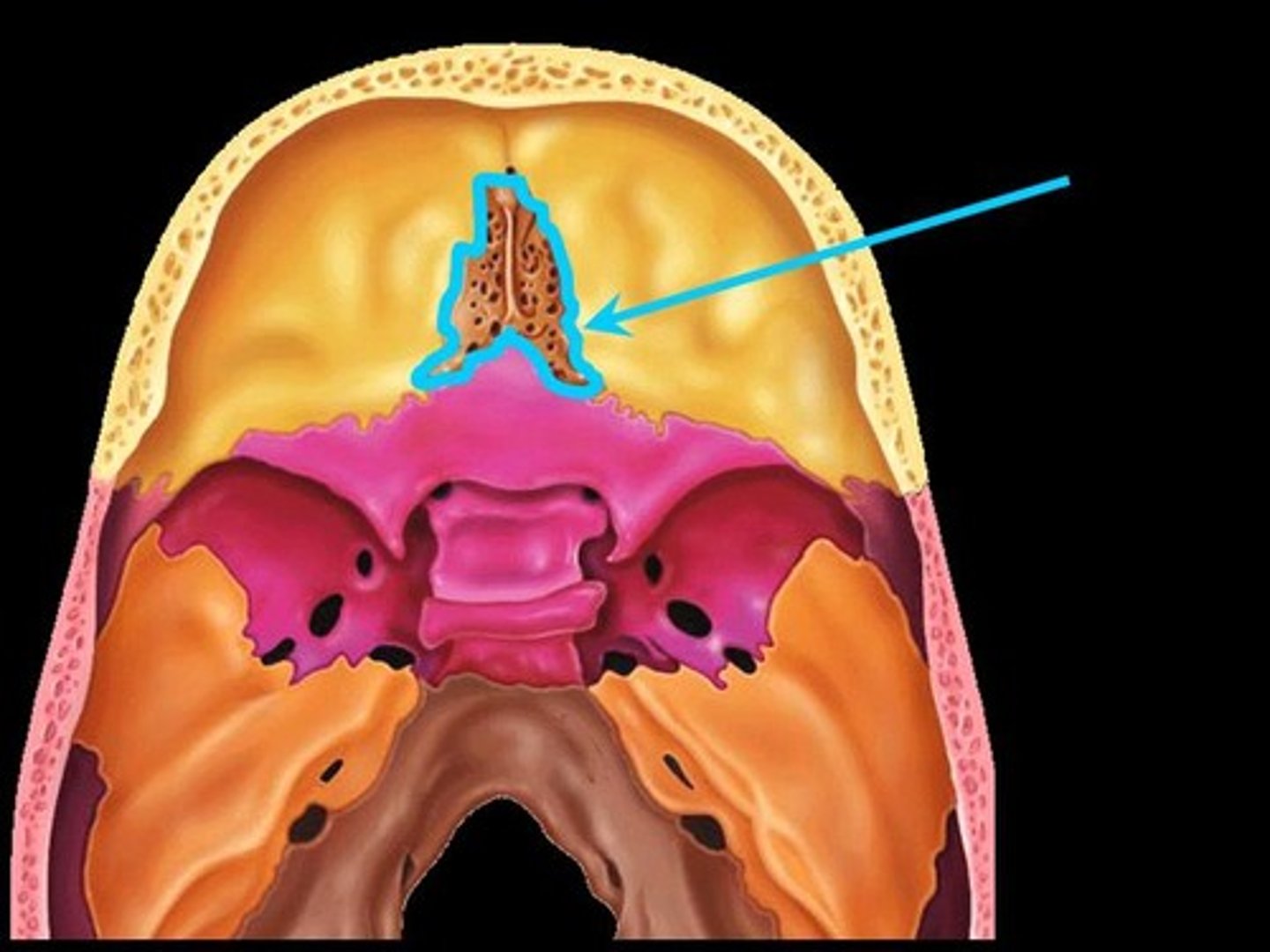
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
forms superior part of nasal septum

middle nasal concha of ethmoid bone
Bone between the superior and inferior conchae

Describe characteristics of suture joints?
Fibrous joints
-very short fibers connect the interlocking edges of articulating bones
-joints between bones of skull
4 major sutures of the skull
(1) coronal suture
(2) squamous suture
(3) lambdoidal suture
(4) sagittal suture
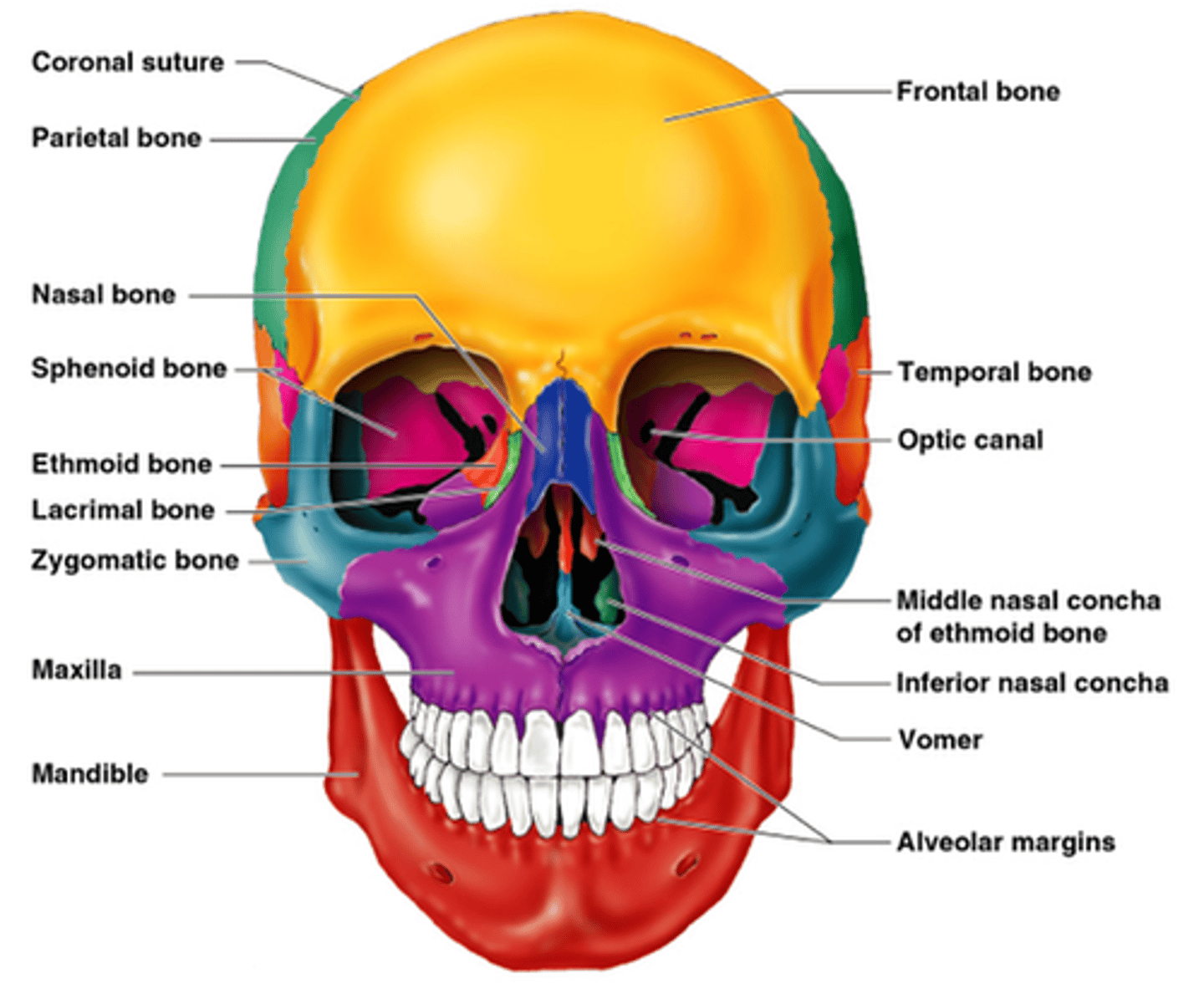
coronal suture of the skull
separates frontal and parietal bones
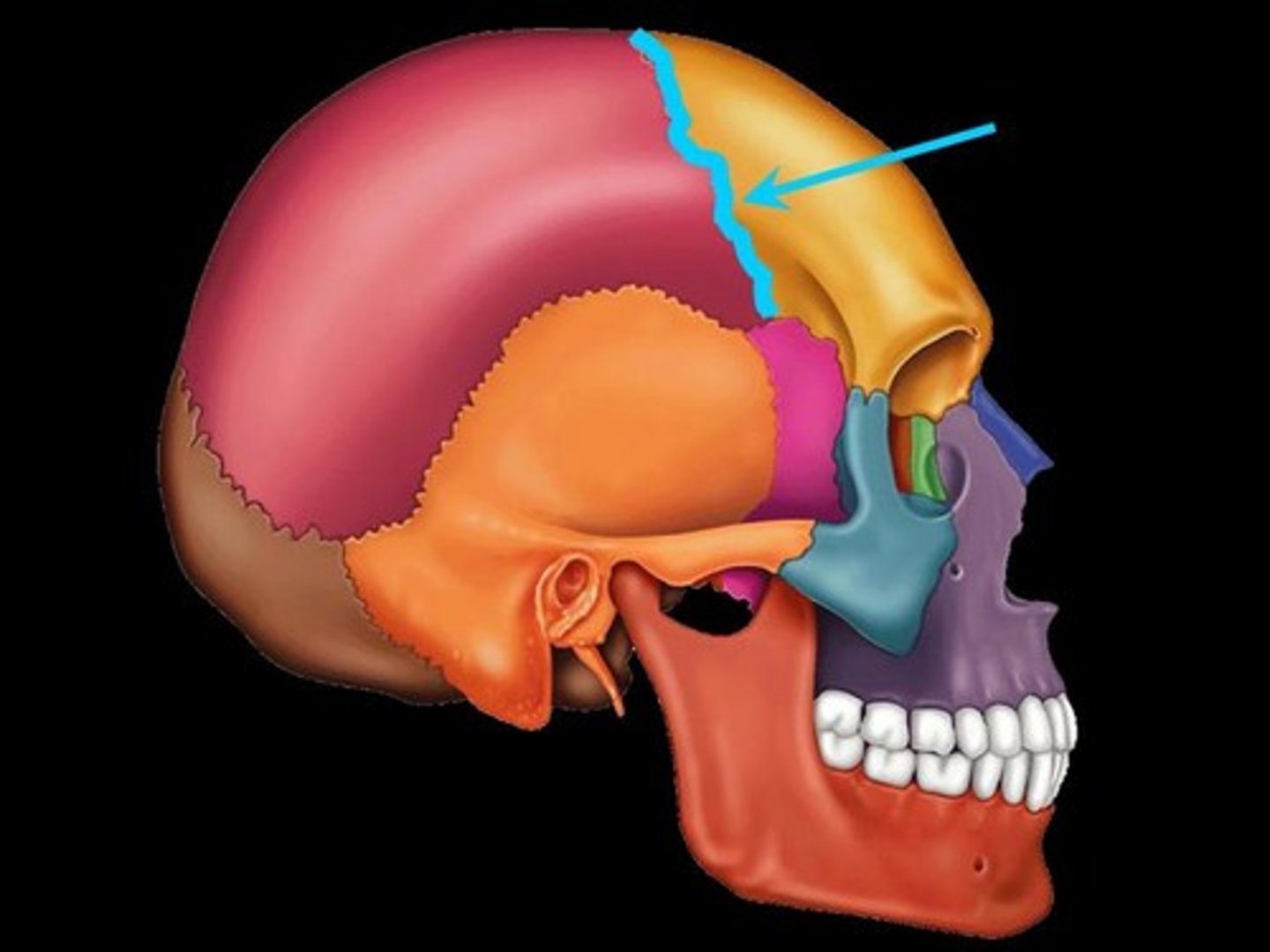
squamous suture of skull
separates parietal from temporal
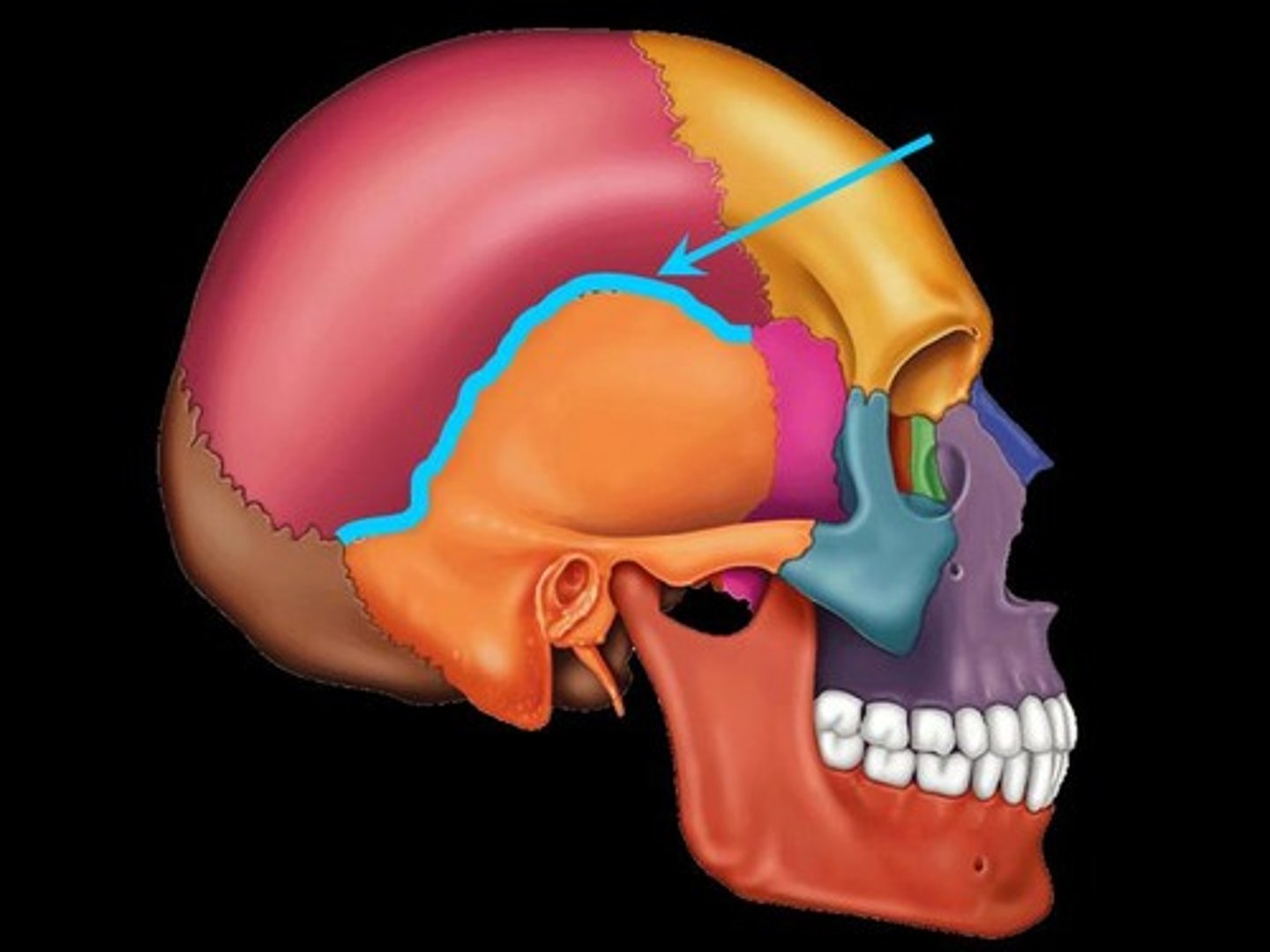
lambdoidal suture of skull
between parietal and occipital bones
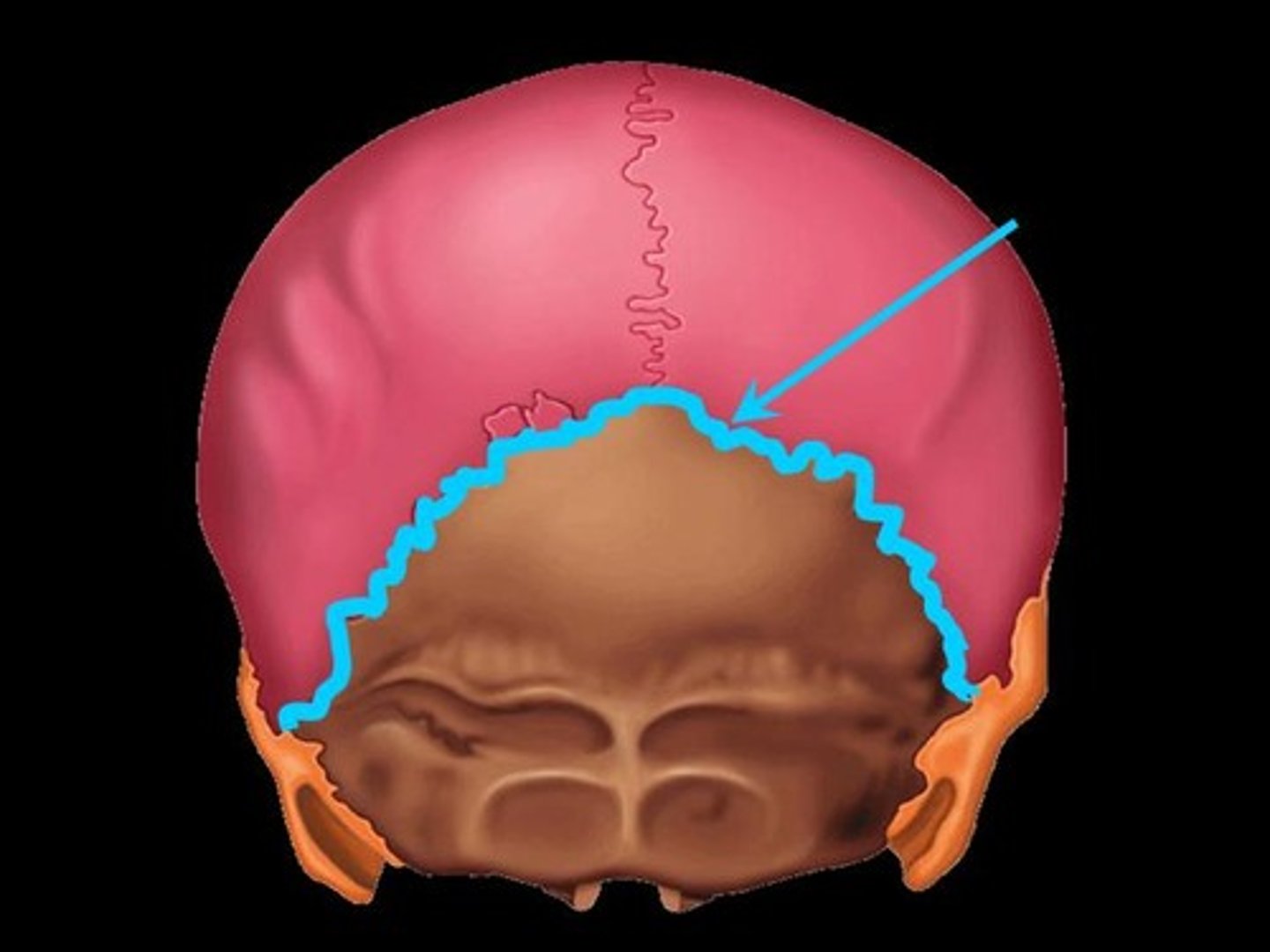
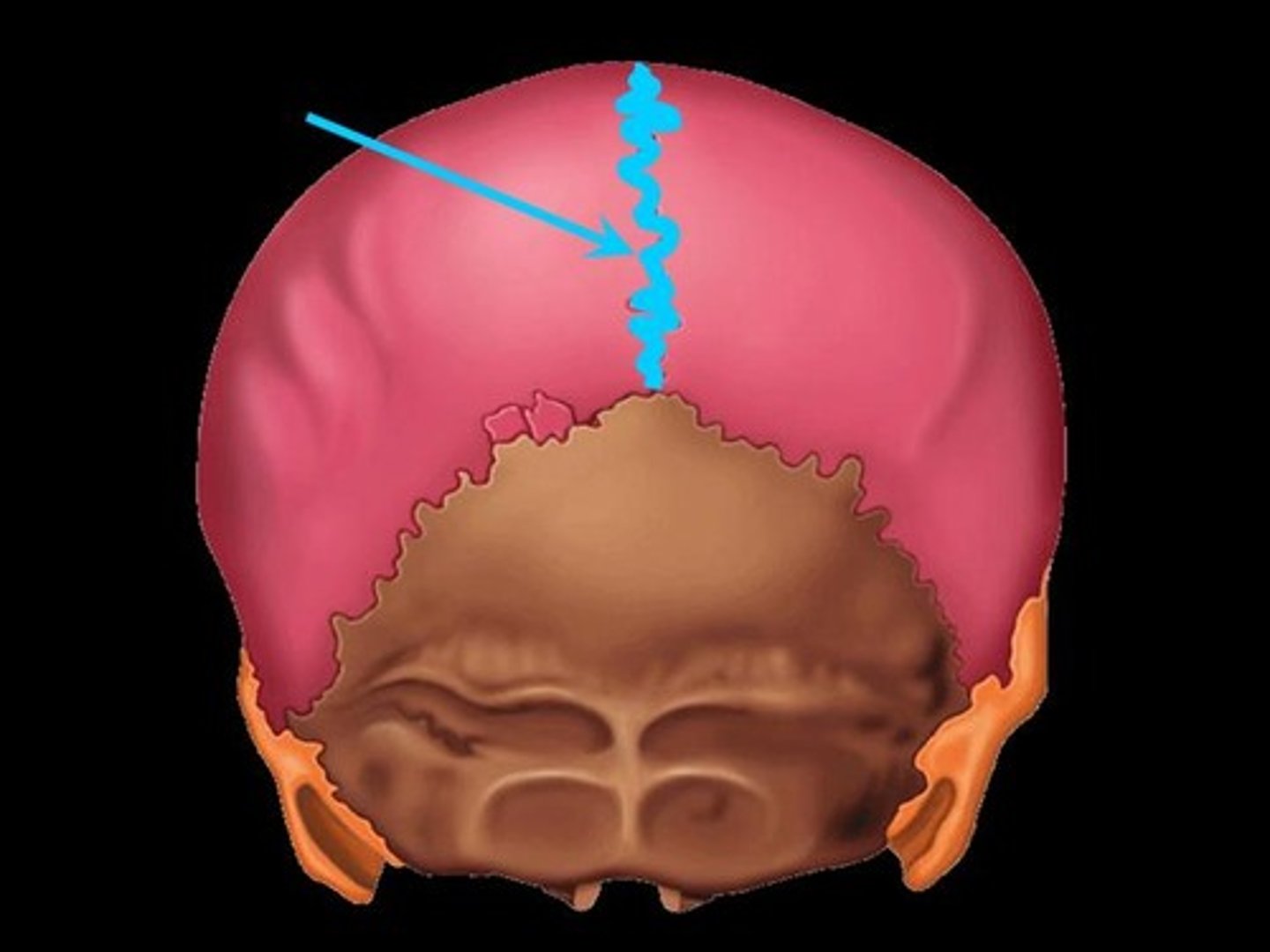
sagittal suture of the skull
between parietal bones
Identify the bones of the face (14)
-maxillae (2)
-nasal (2)
-zygomatic (2)
-lacrimal (2)
-palatine (2)
-inferior nasal conchae (2)
-vomer (1)
-mandible (1)
Infra-orbital foramen of maxilla
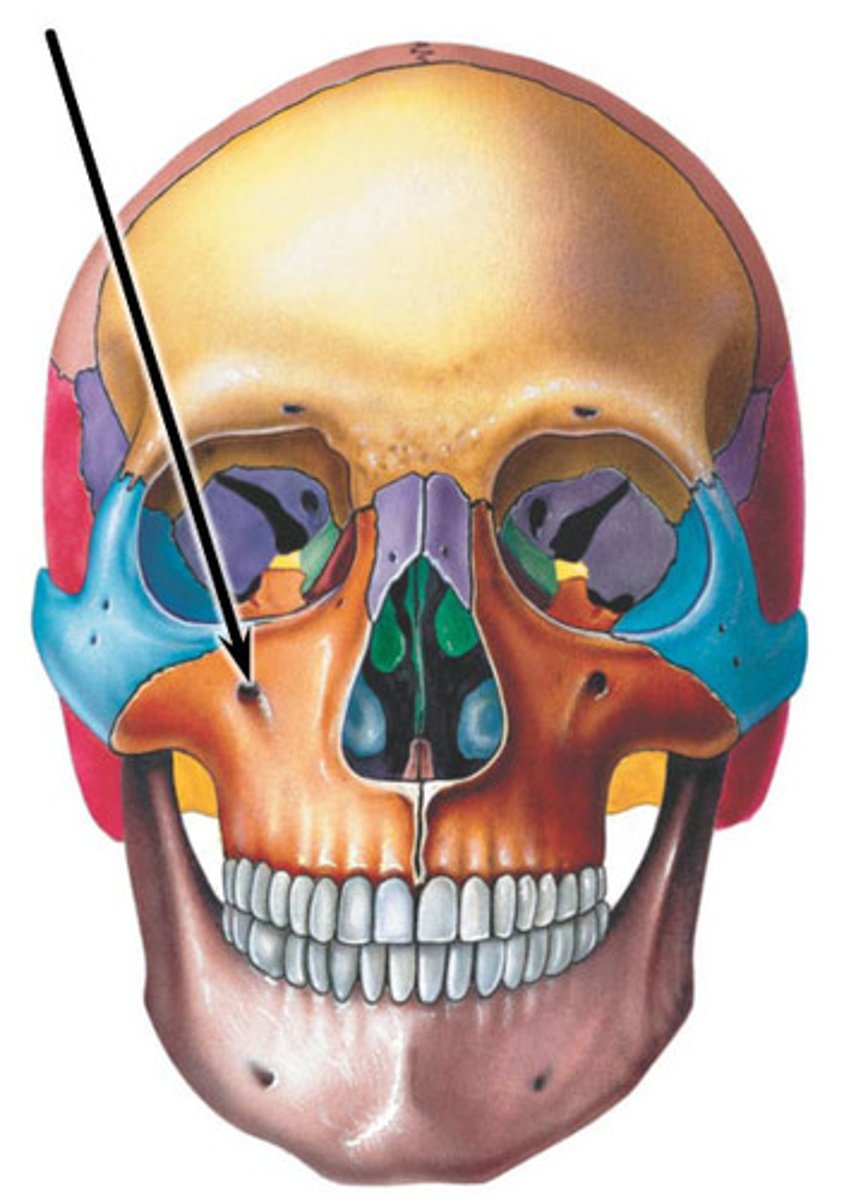
What goes through the infra-orbital foramen?
Infra-orbital nerve (V2) and Infra-orbital artery (maxillary artery, pterygopalatine segment)
Alveolar process of maxilla
curved, inferior margin of the maxilla that supports & anchors the upper teeth
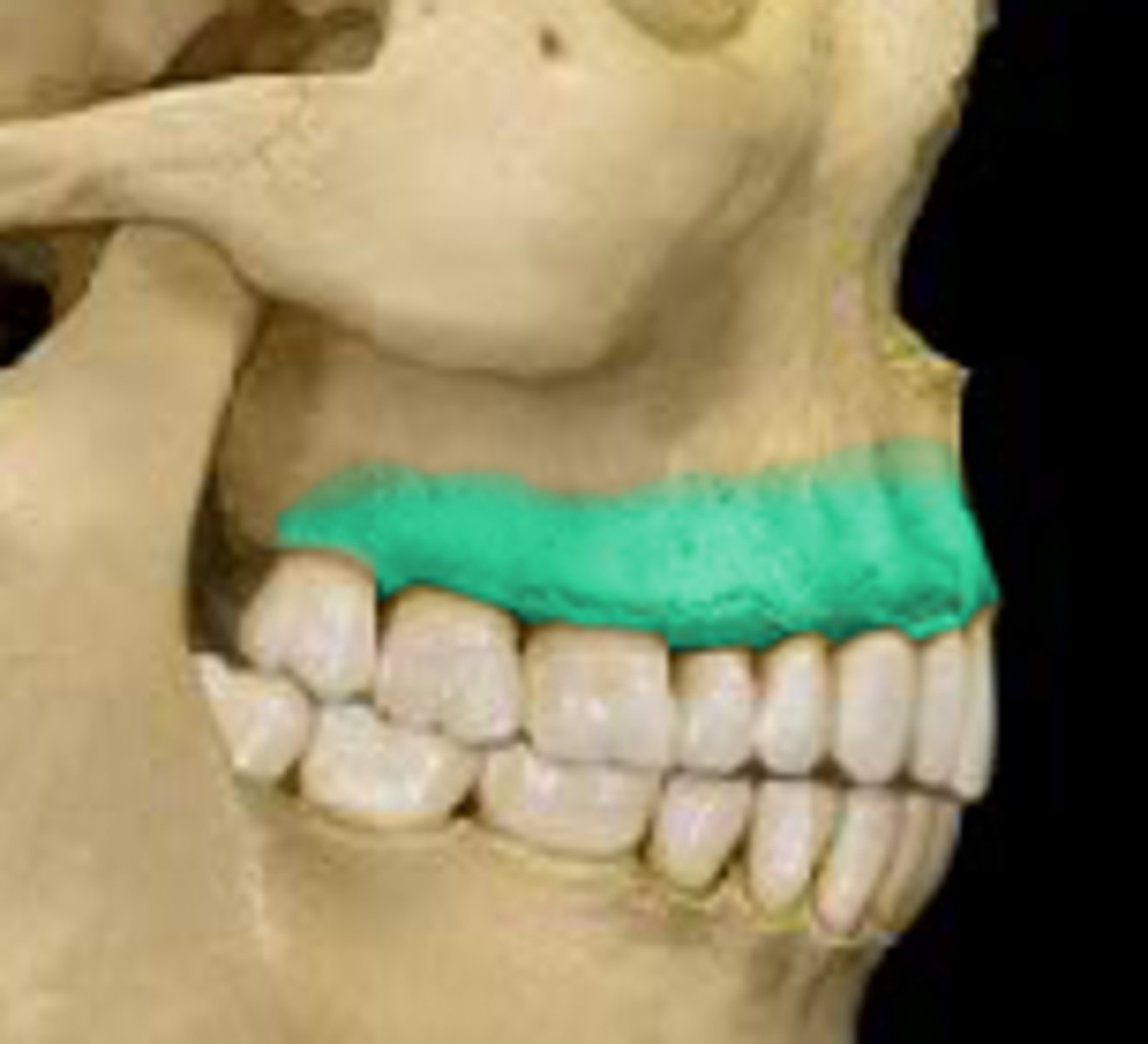
Palatine processes of maxillary bone
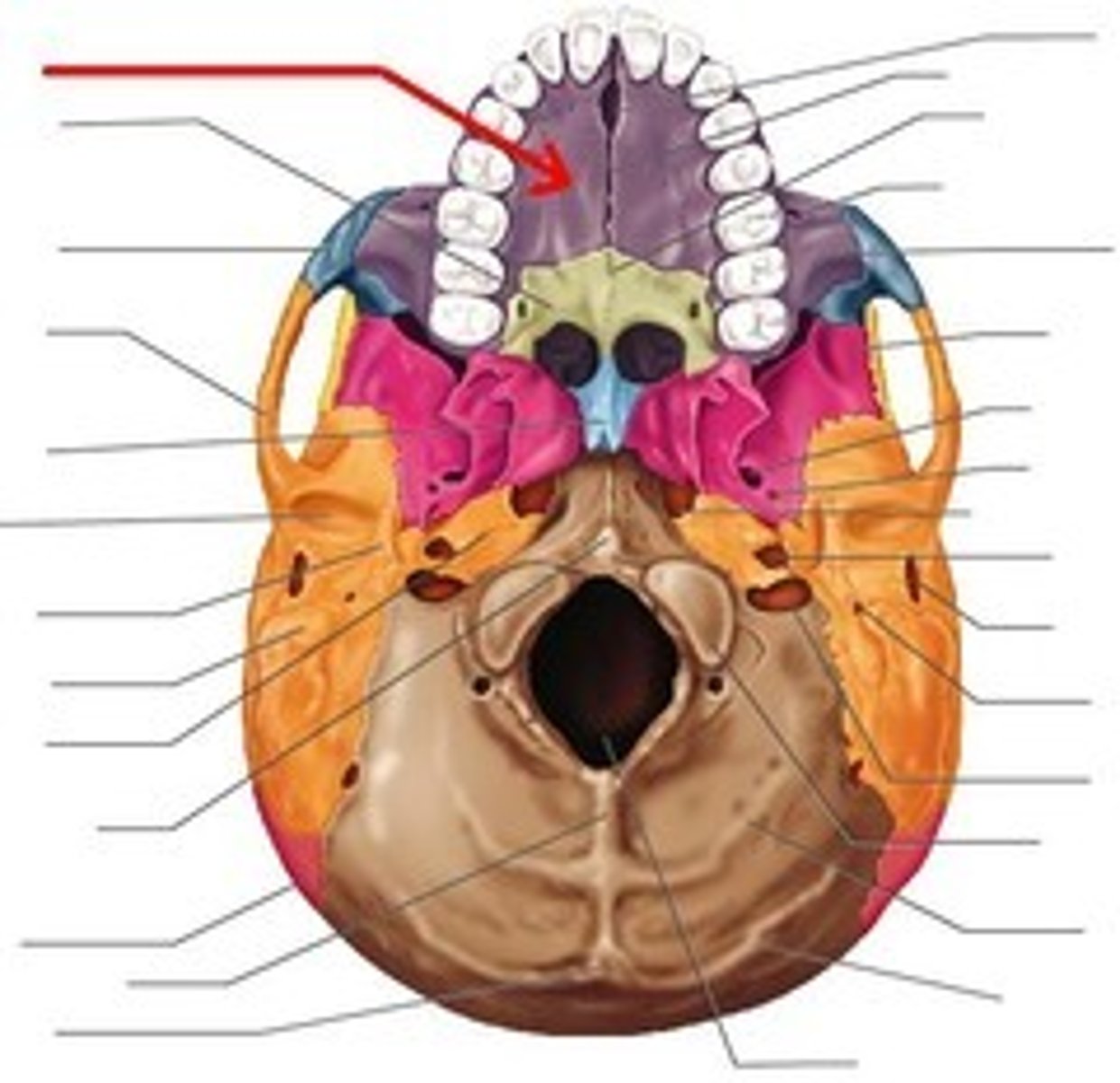
Identify the paranasal sinuses (4)
(1) frontal sinus
(2) sphenoid sinus
(3) ethmoid sinus
(4) maxillary sinus
What is the function of paranasal sinuses?
lighten the skull, act as a resonance chamber for speech, produce mucus, help to moisten the air
Horizontal plate of palatine bone
form the posterior part of the hard palate of the mouth & the floor of the nose
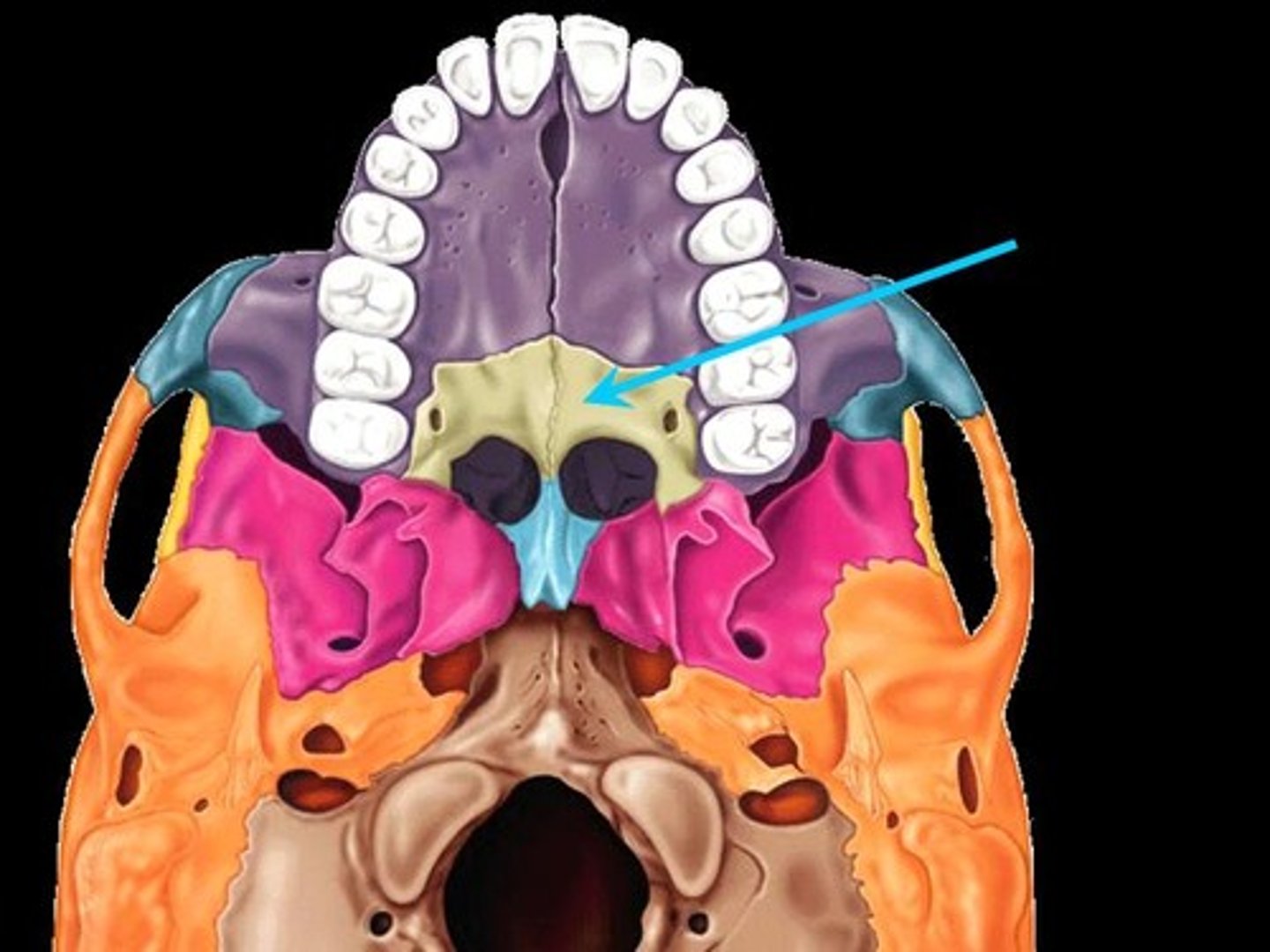
What 2 structures form the hard palate?
(1) palatine processes of the maxillae
(2) horizontal plates of the palatine bones

Zygomatic bone
the arch of bone beneath the eye that forms the prominence of the cheek
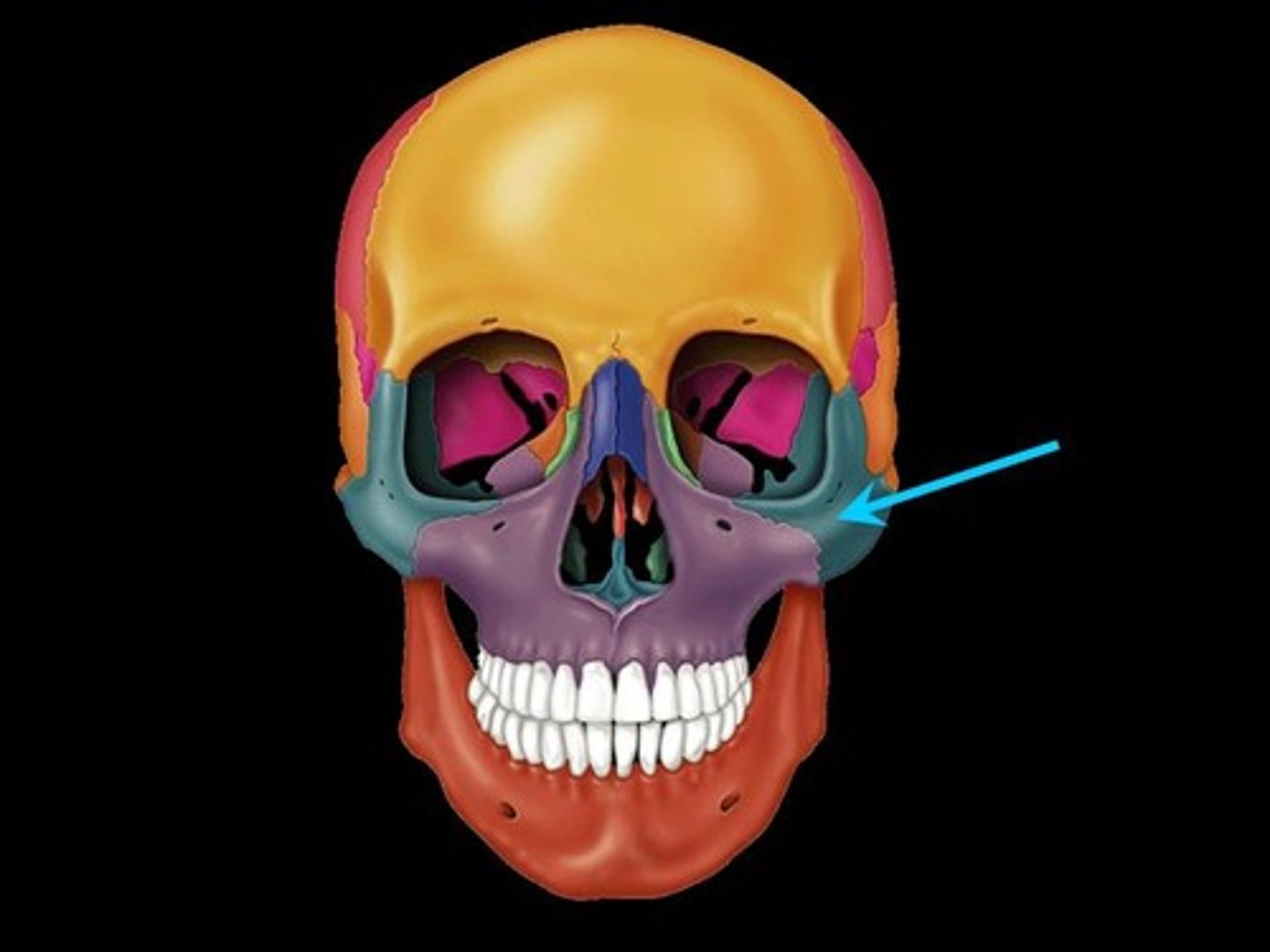
Temporal process of zygomatic bone
Name this part of the zygomatic bone.
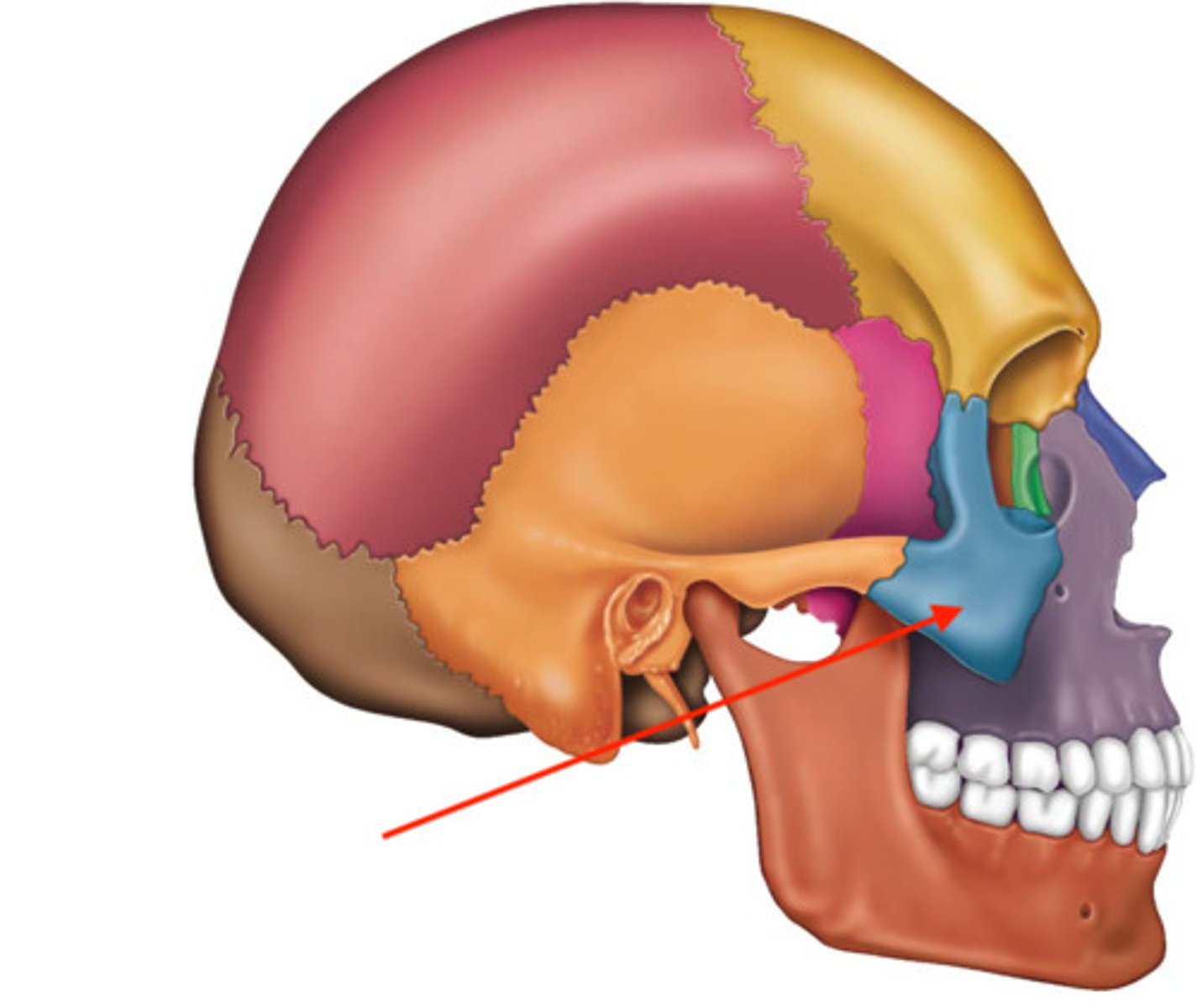
What 2 structures form the zygomatic arch?
temporal process of zygomatic bone + zygomatic process of temporal bone
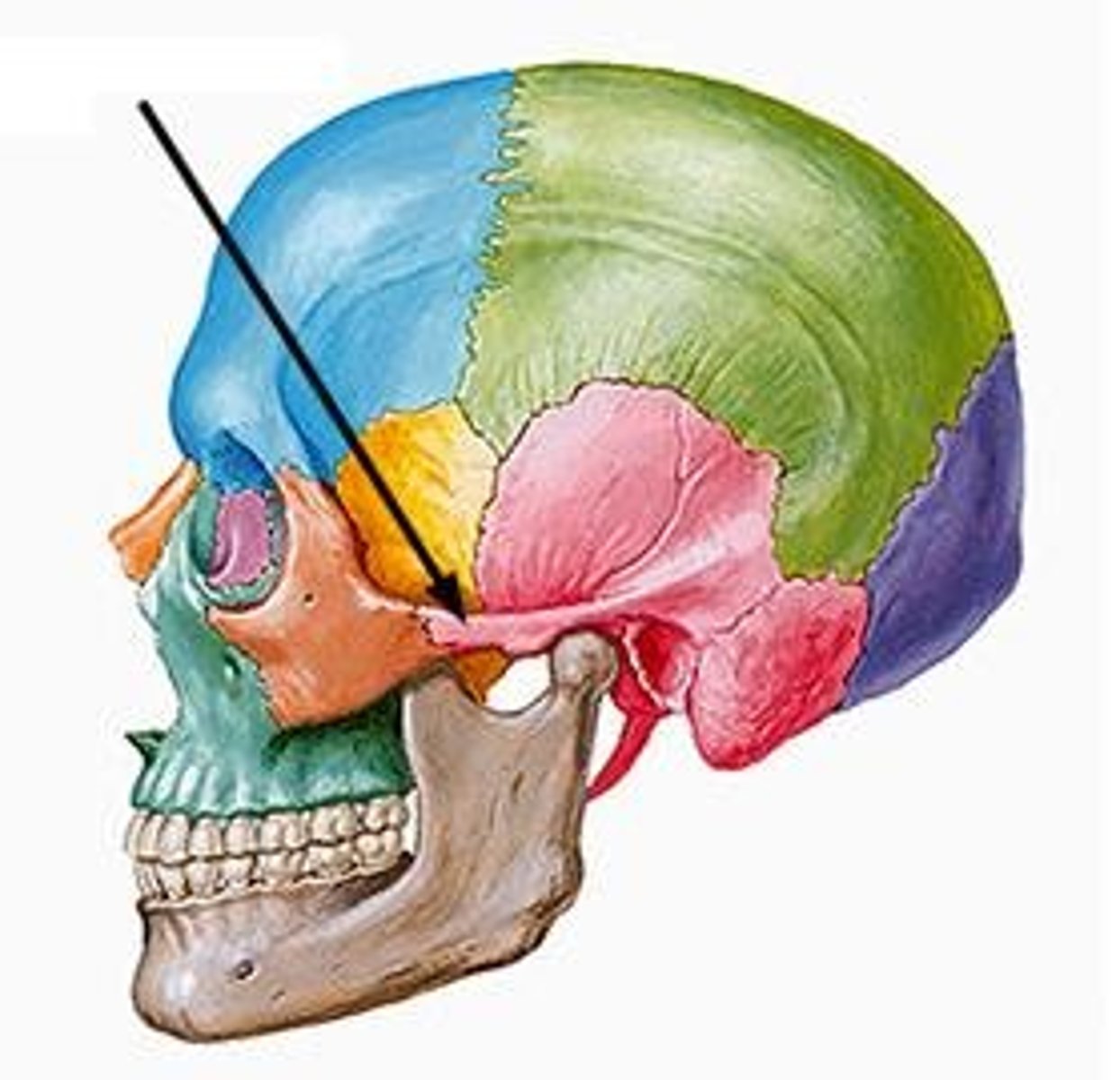
lacrimal bones
paired bones at the corner of each eye that cradle the tear ducts
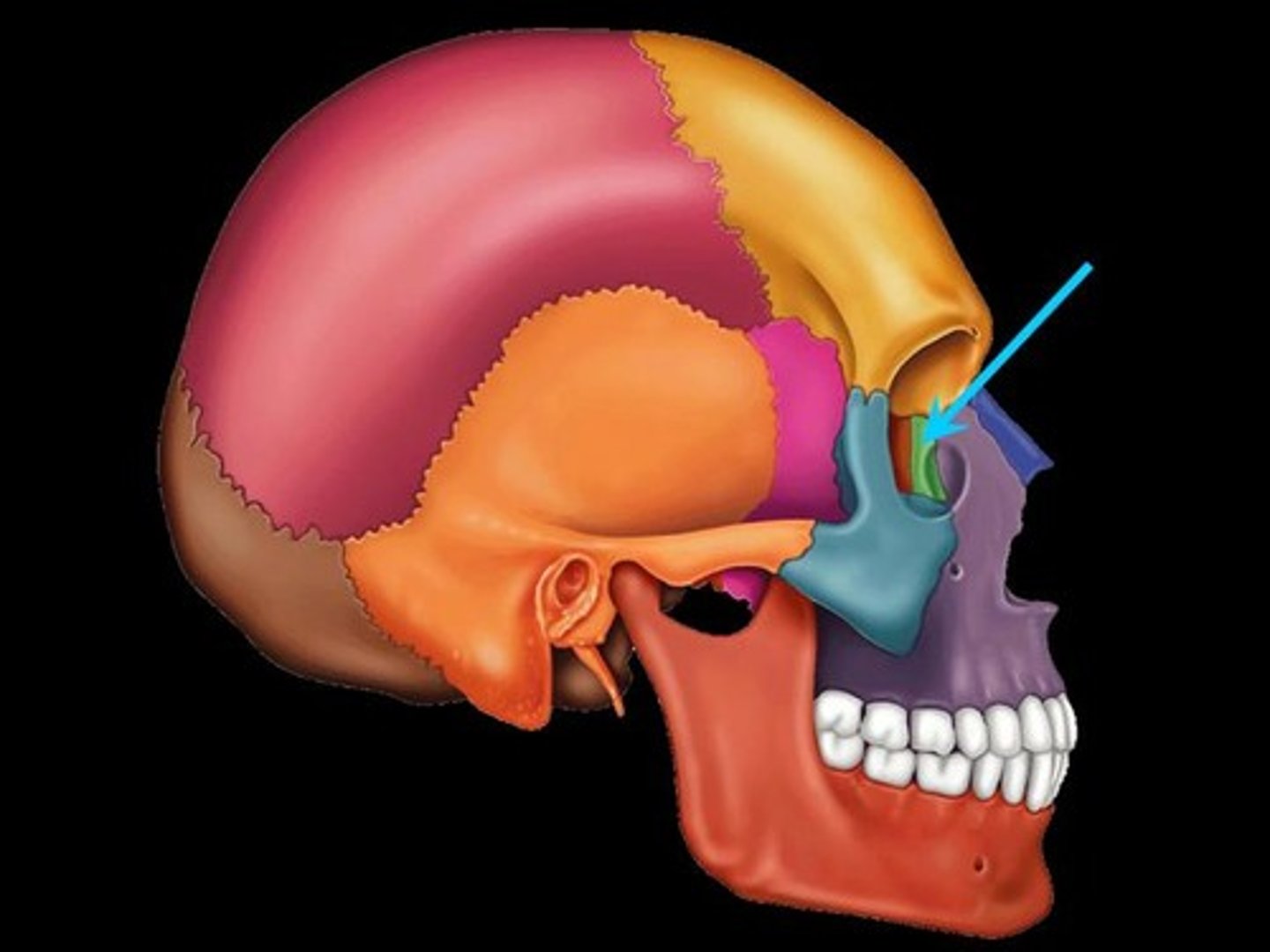
What 7 bones make up the orbit of the eye?
(1) frontal bone
(2) zygomatic bone
(3) maxillary bone
(4) sphenoid bone
(5) ethmoid bone
(6) lacrimal bone
(7) palatine bone
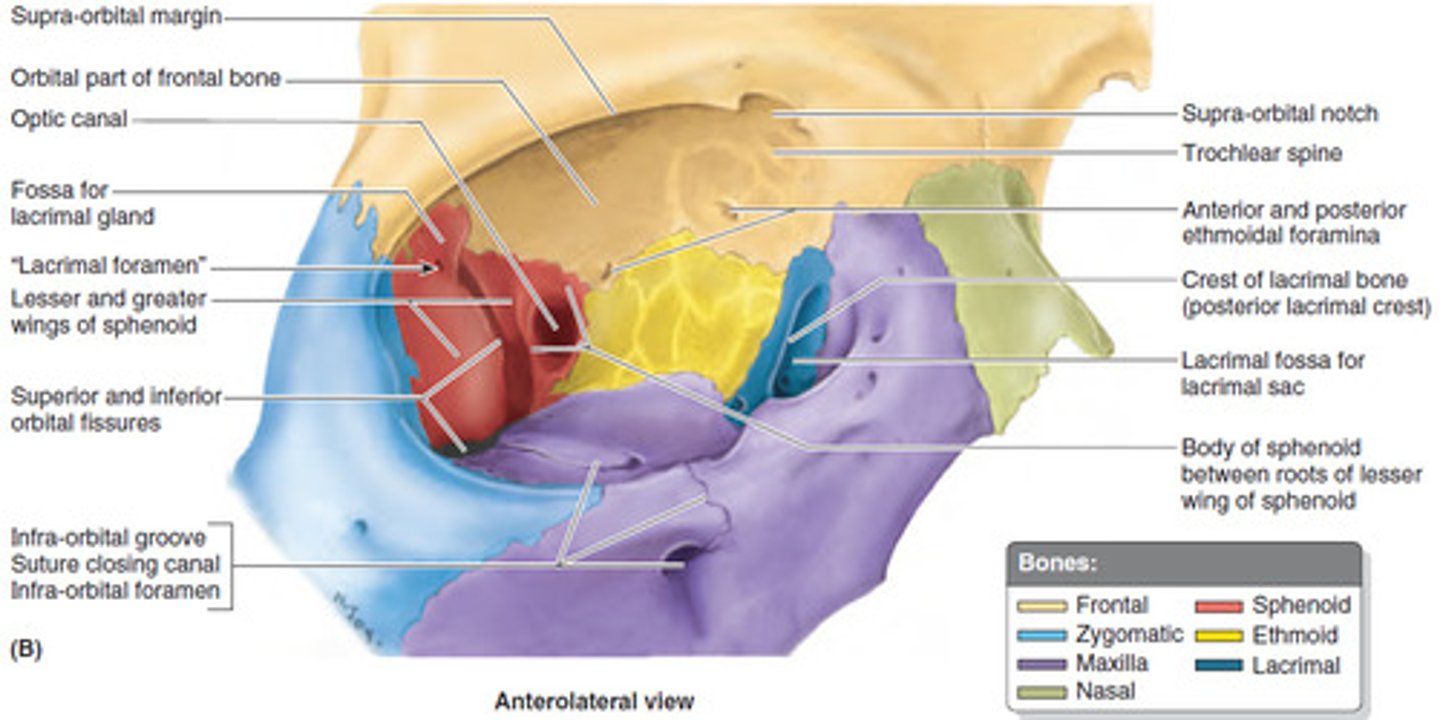
Inferior nasal conchae
-most inferior within nasal cavity
-help to warm/clean air before it enters lungs
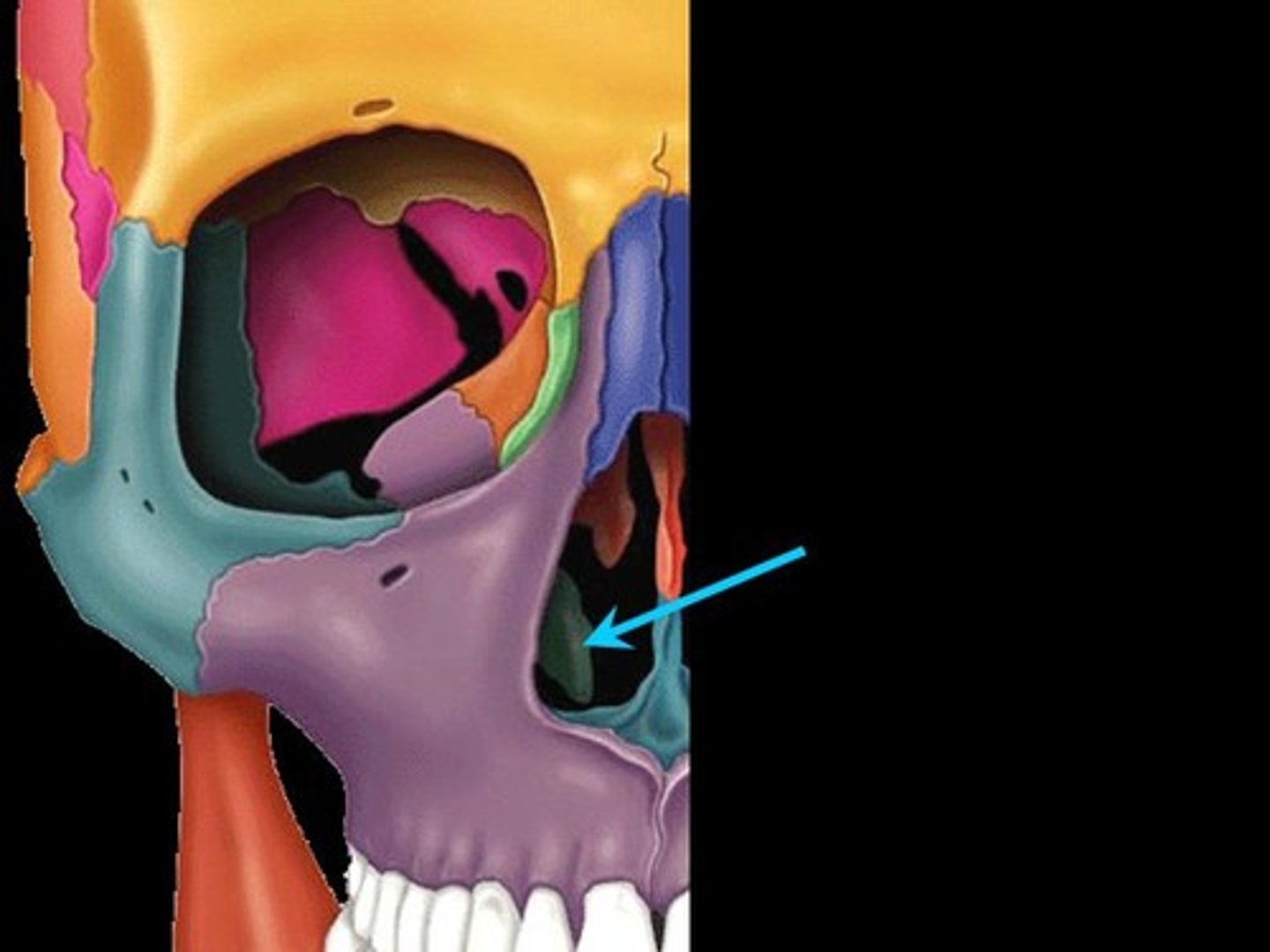
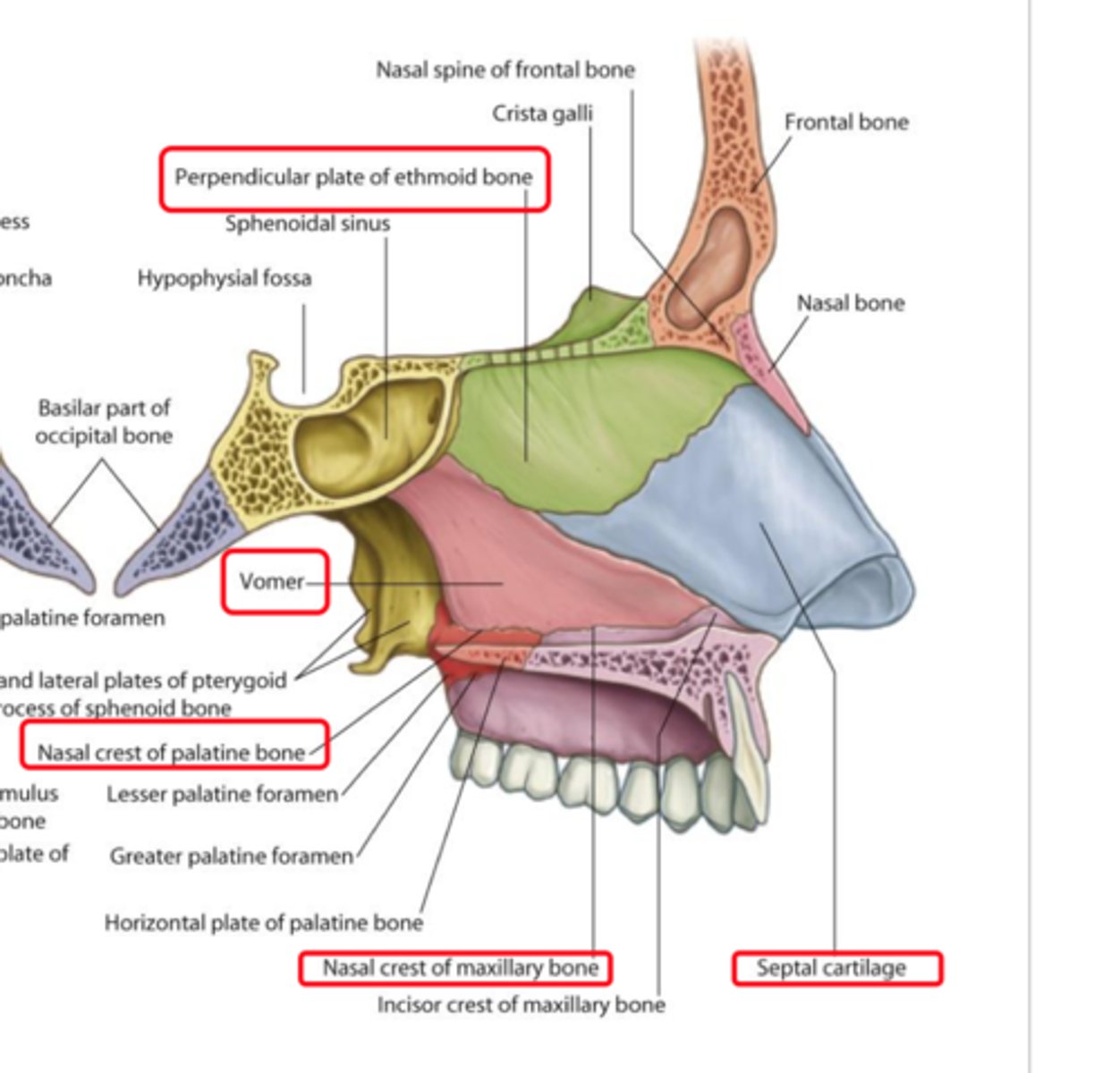
What 3 structures form the nasal septum?
(1) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
(2) vomer bone
(3) septal cartilage
What is a deviated septum?
-occurs when nasal septum is displaced to one side
-often present at birth / can occur due to injury
Symptoms: nosebleeds, congested nostril, noisy breathing during sleep
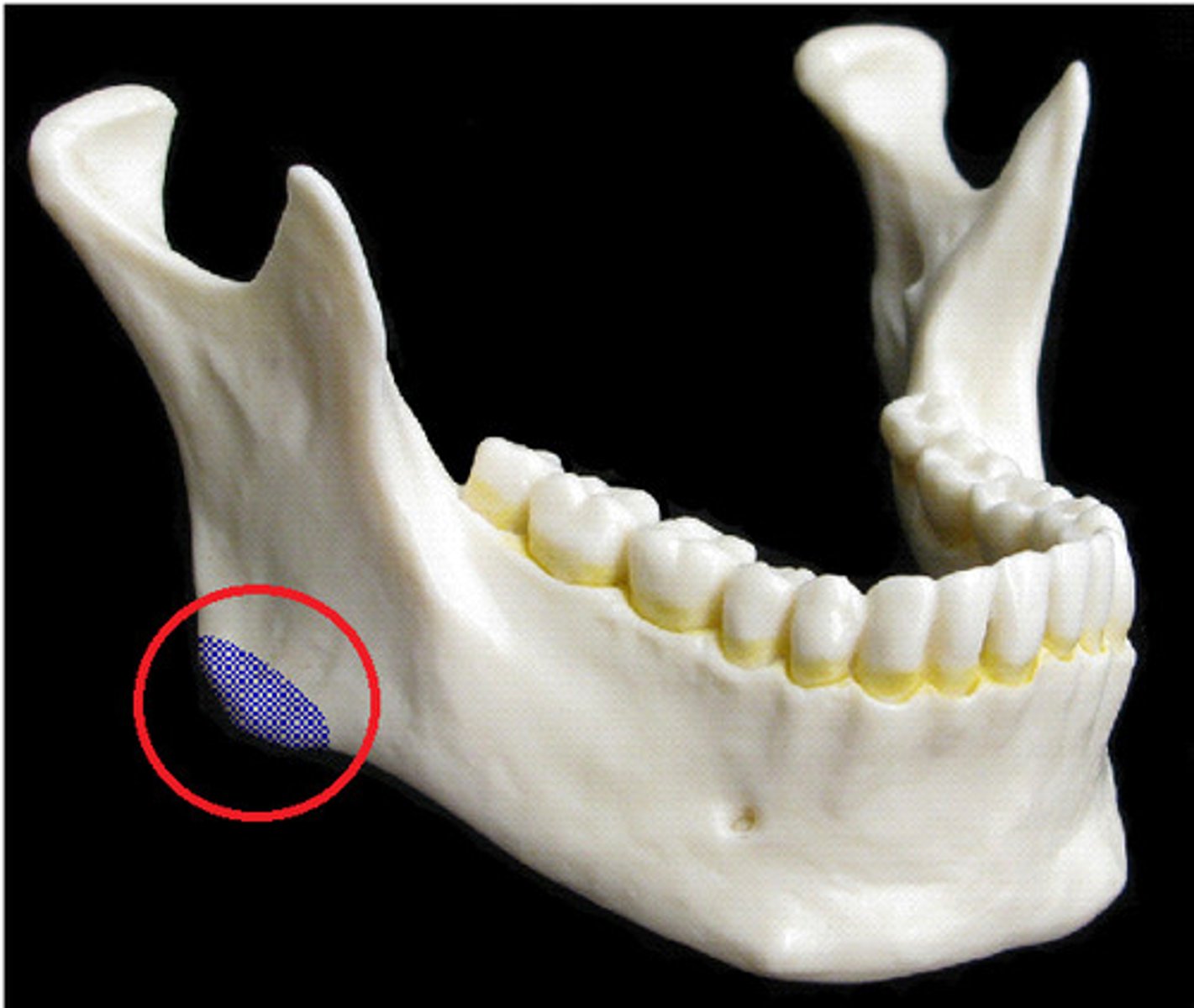
Angle of the mandible
Name this bony landmark.
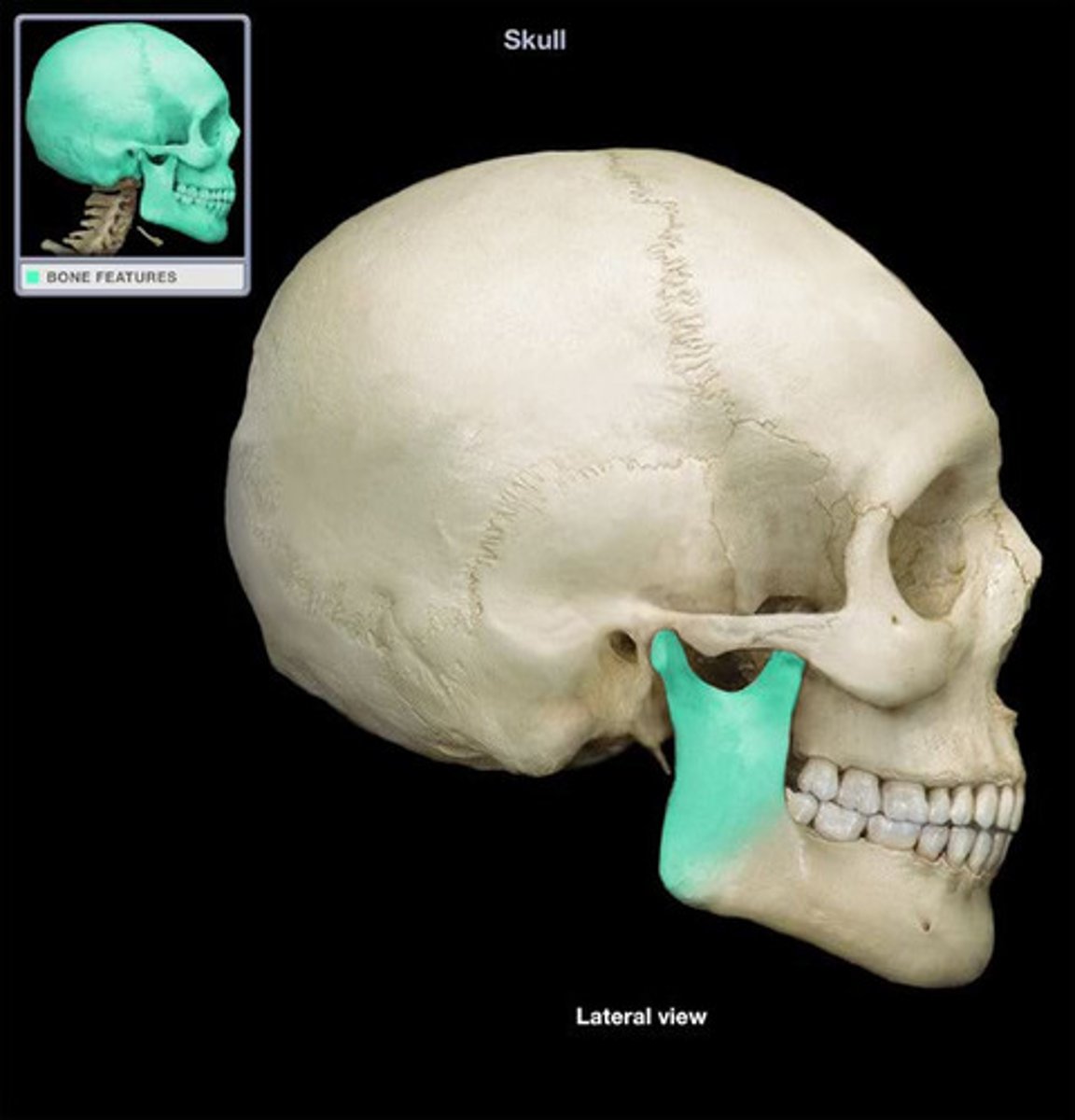
Ramus of the mandible
vertical portion of the mandible
Condylar process of mandible
articulates with temporal bone forming the temporomandibular joint at mandibular fossa
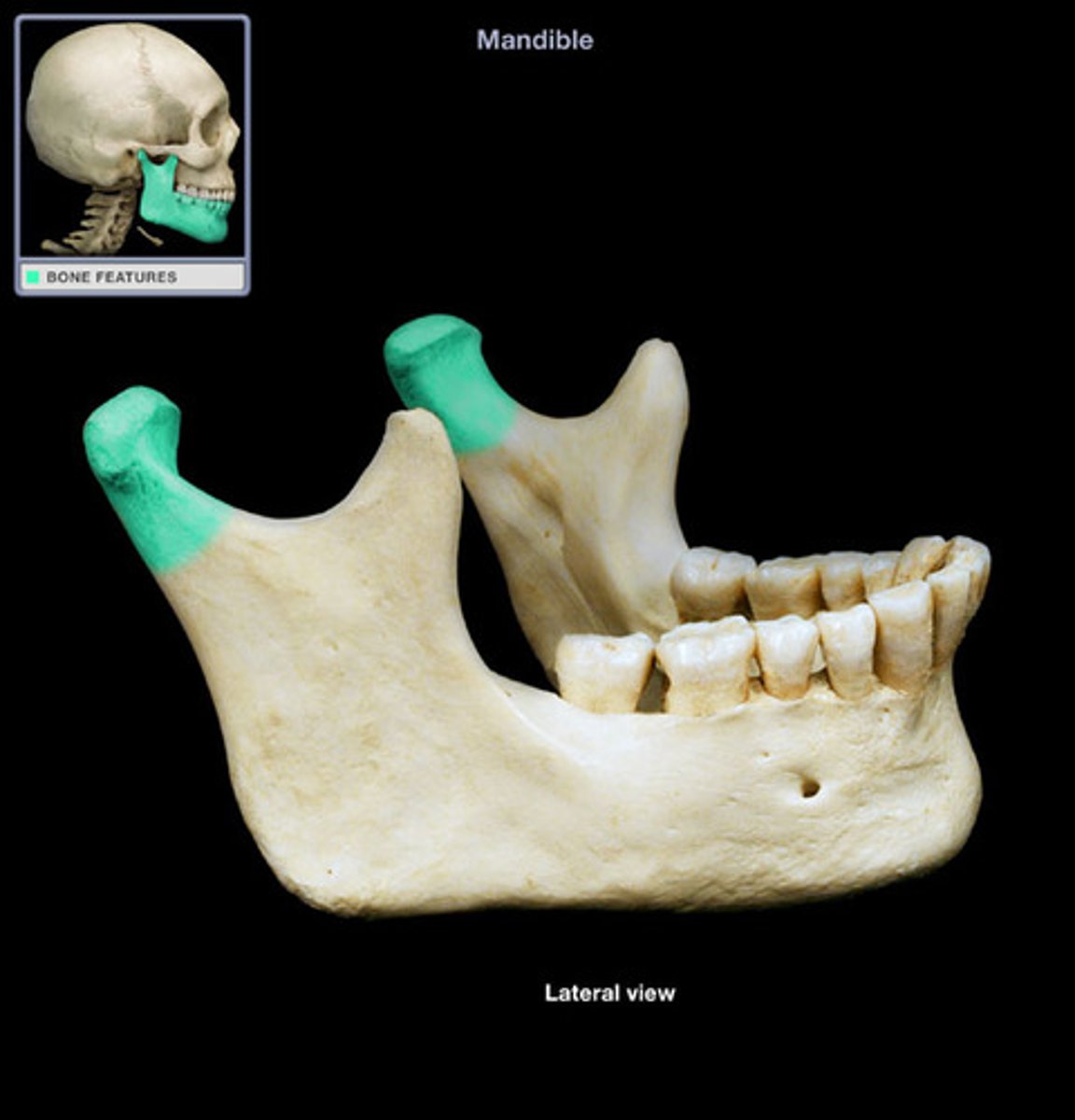
Coronoid process of mandible
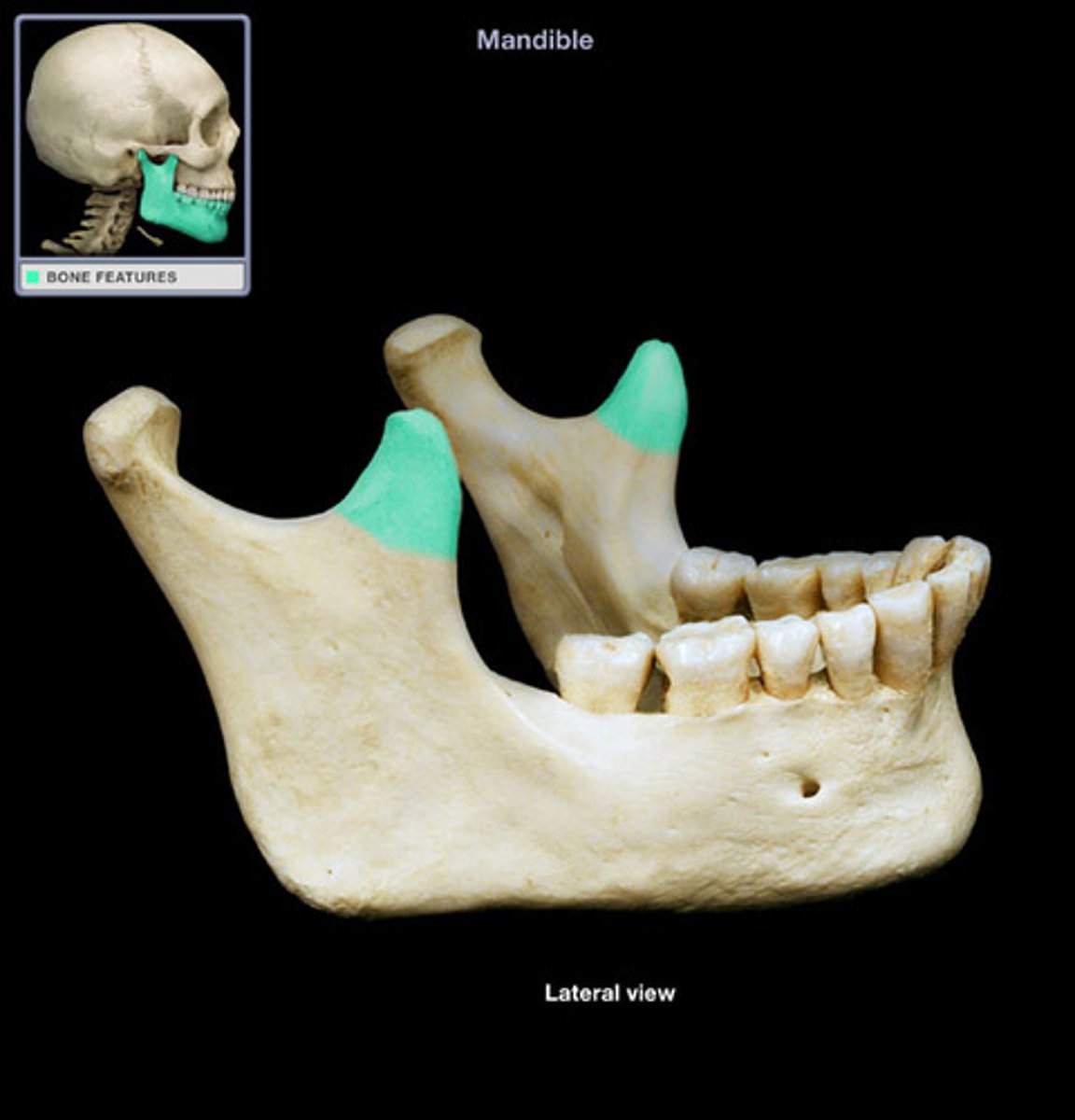
Mental foramen of mandible
one of two holes located on the anterior surface of the mandible
-permits passage of the mental nerve and vessels
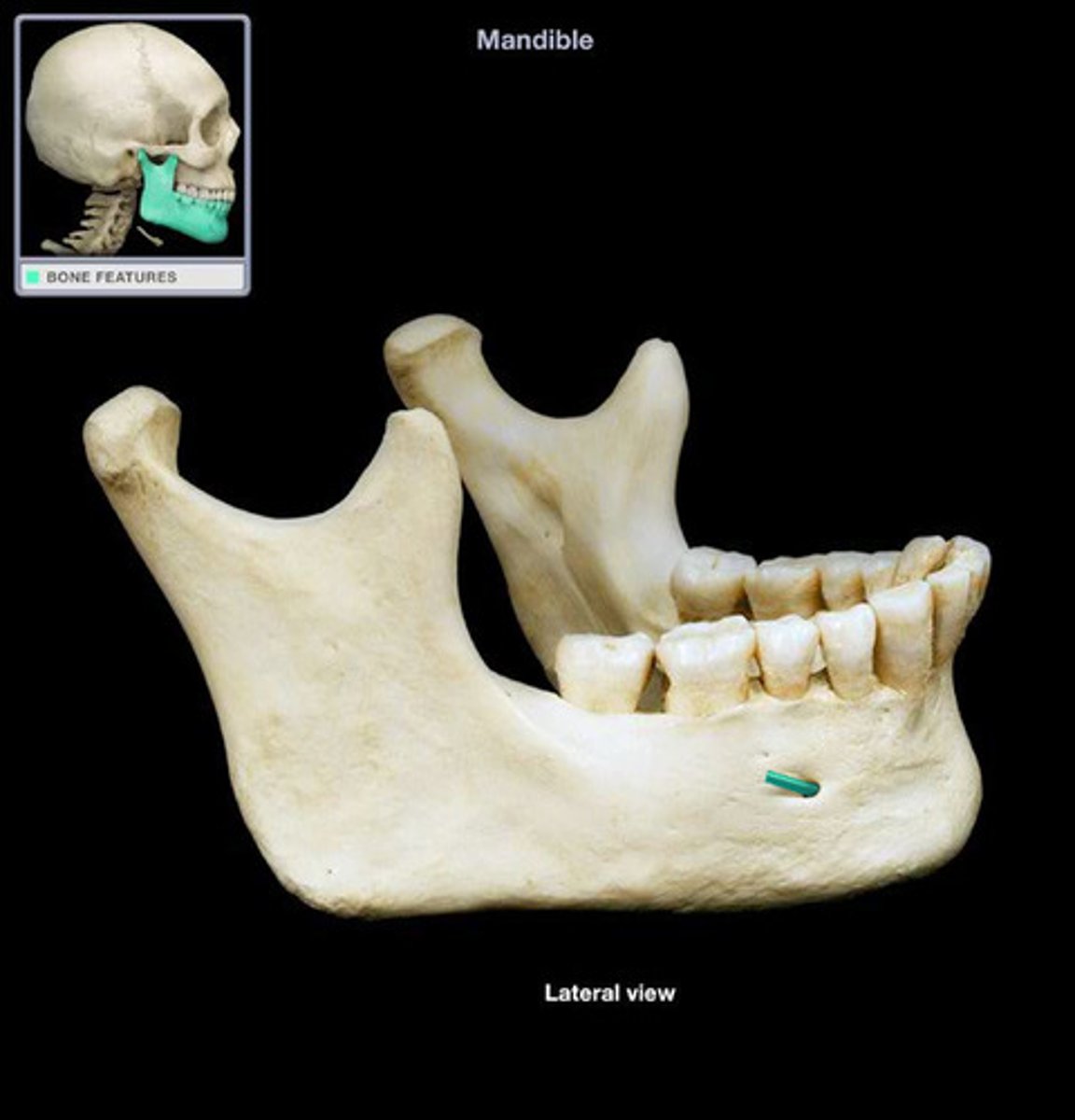
Mandibular foramen of mandible
Located on the medial surface of each ramus; passageway for the nerve involved in tooth sensation
(Dentists inject anesthetic into this foramen before working on the lower teeth)
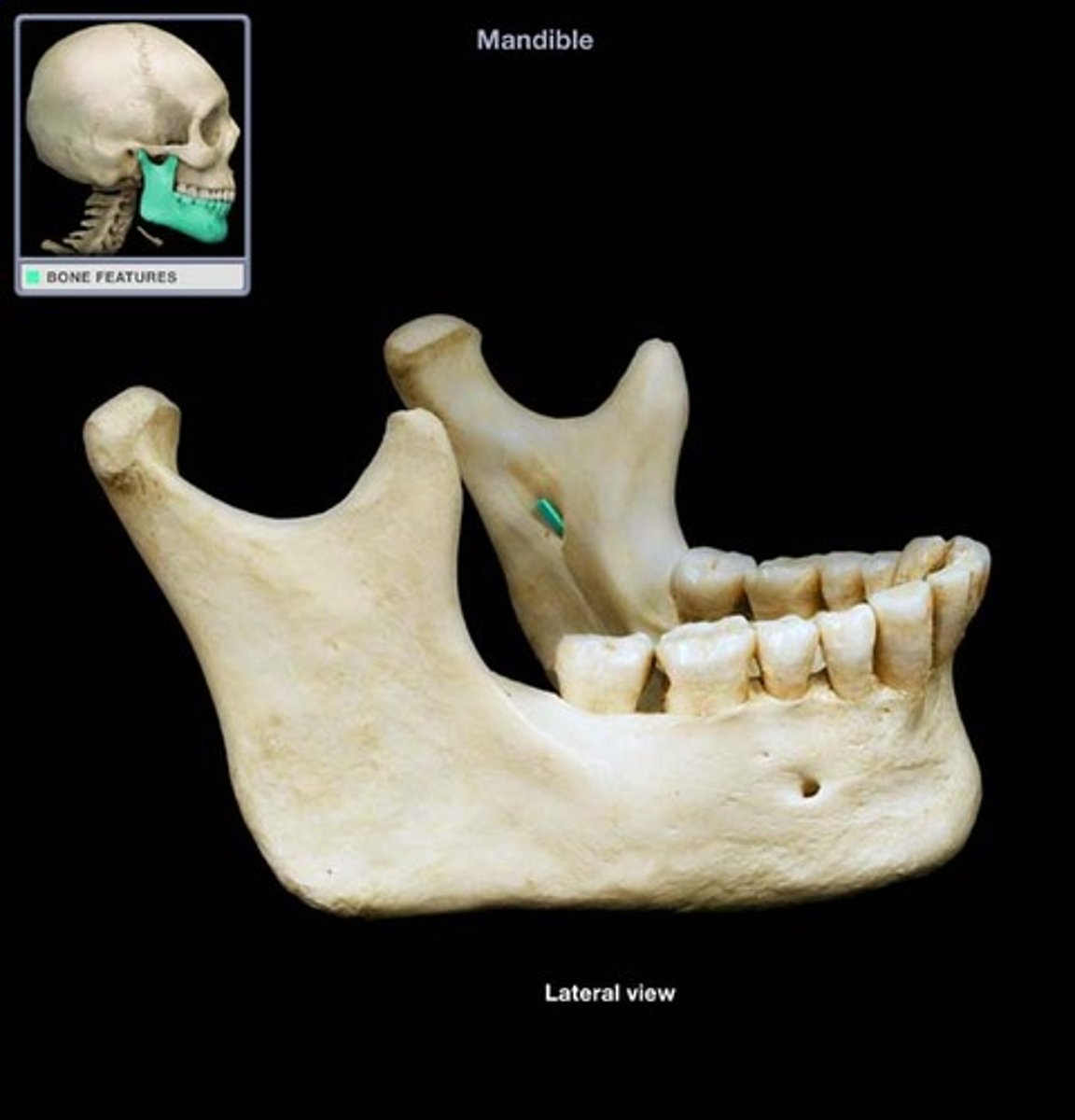
Genoid tubercle of mandible
attachment point for muscles of tongue

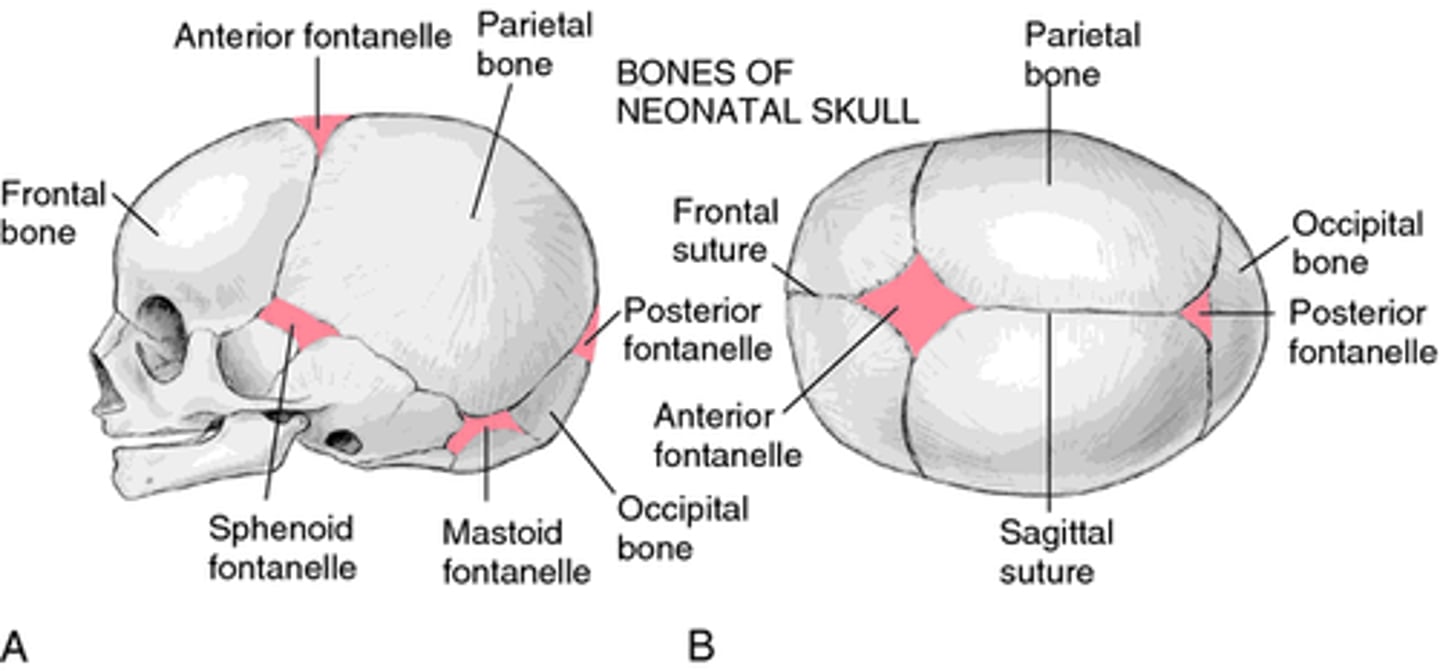
What are fontanelles?
-soft fibrous areas where several sutures unite
-allow for molding & remodeling
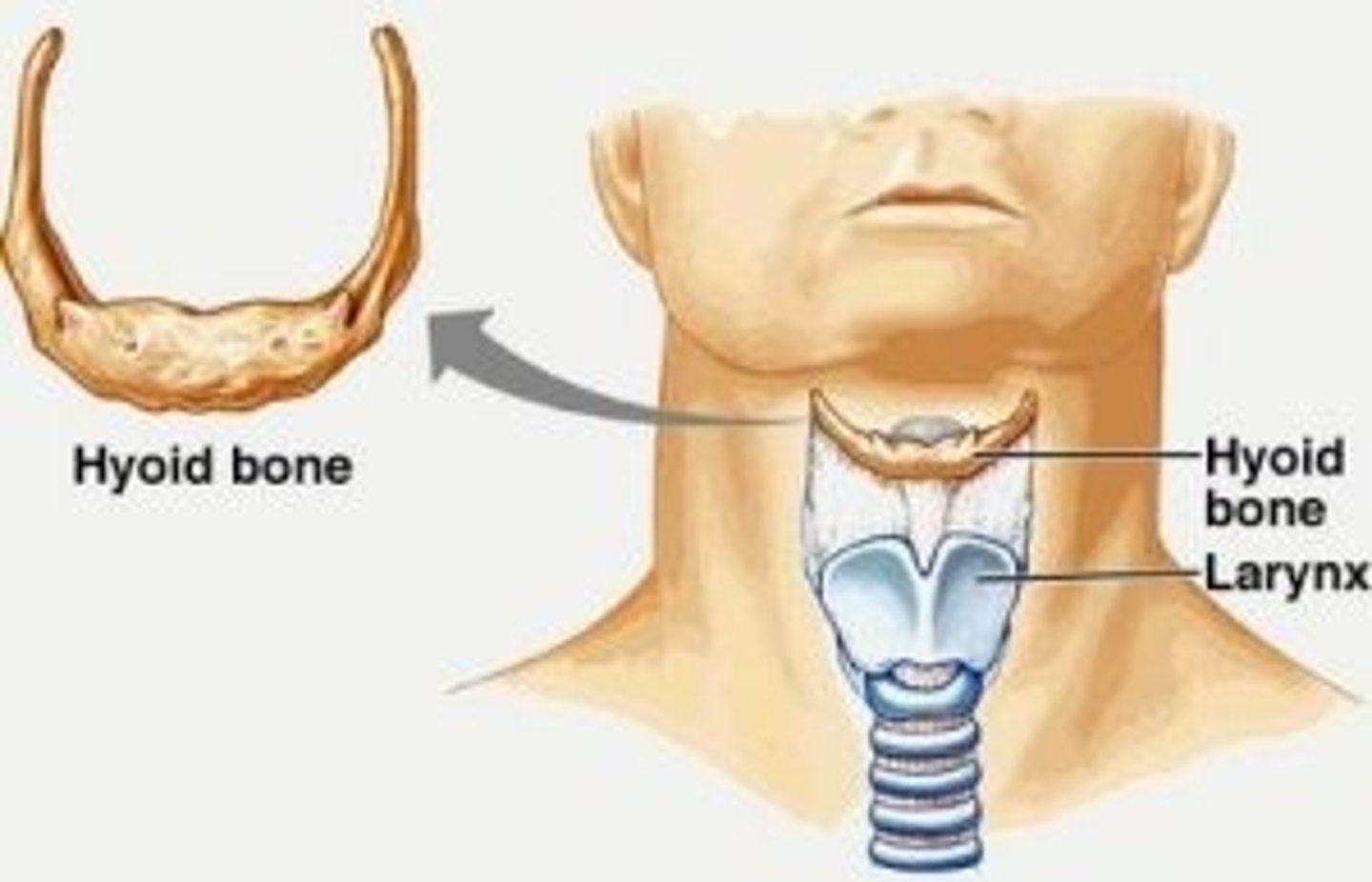
Hyoid bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles
What are the 4 lobes of the cerebral hemispheres?
(1) frontal
(2) parietal
(3) temporal
(4) occipital

Gyrus
elevated fold of the brain
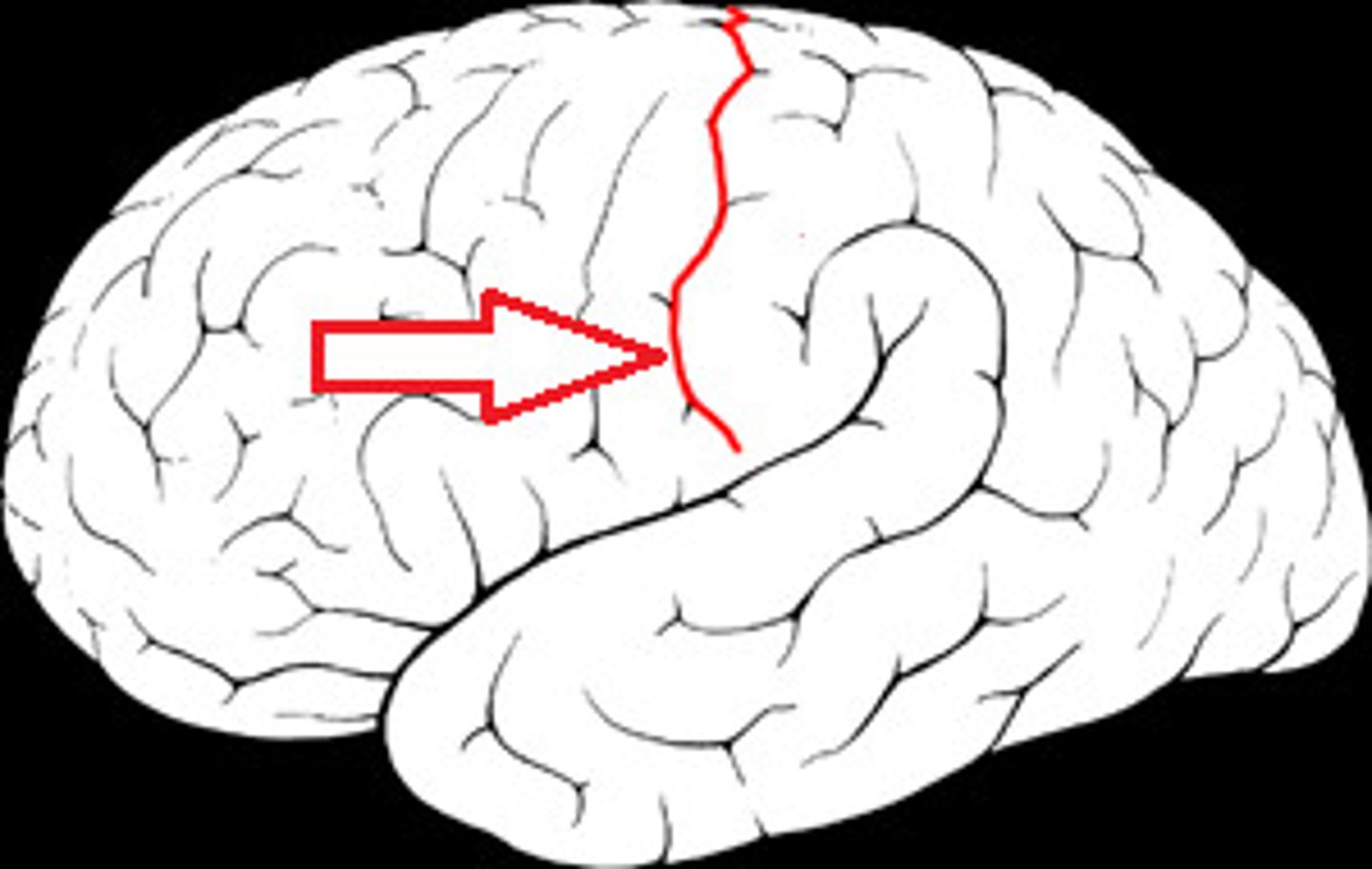
Sulcus
shallow groove between gyri
Fissure
deep groove between gyri
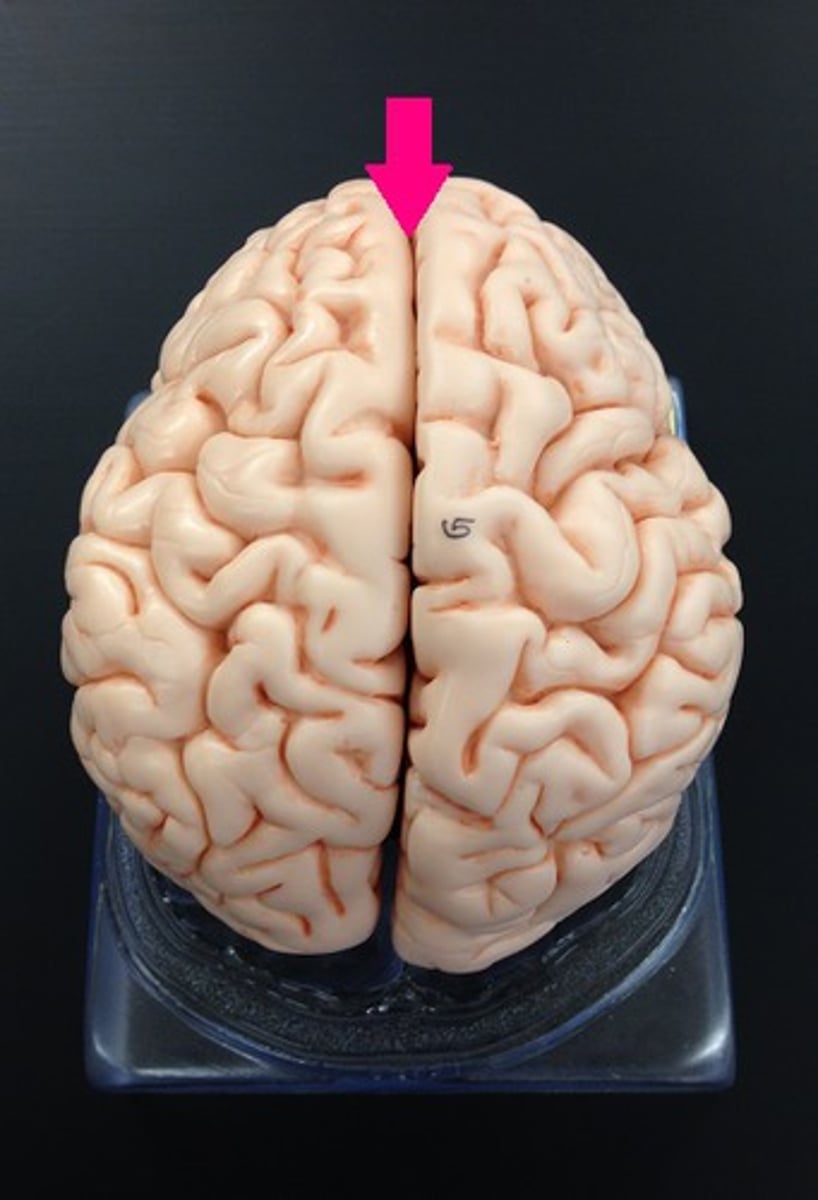
Longitudinal fissure of brain
deep groove down the brain; separates left & right hemispheres
Sylvian/lateral fissure of brain
separates frontal & parietal from temporal lobes
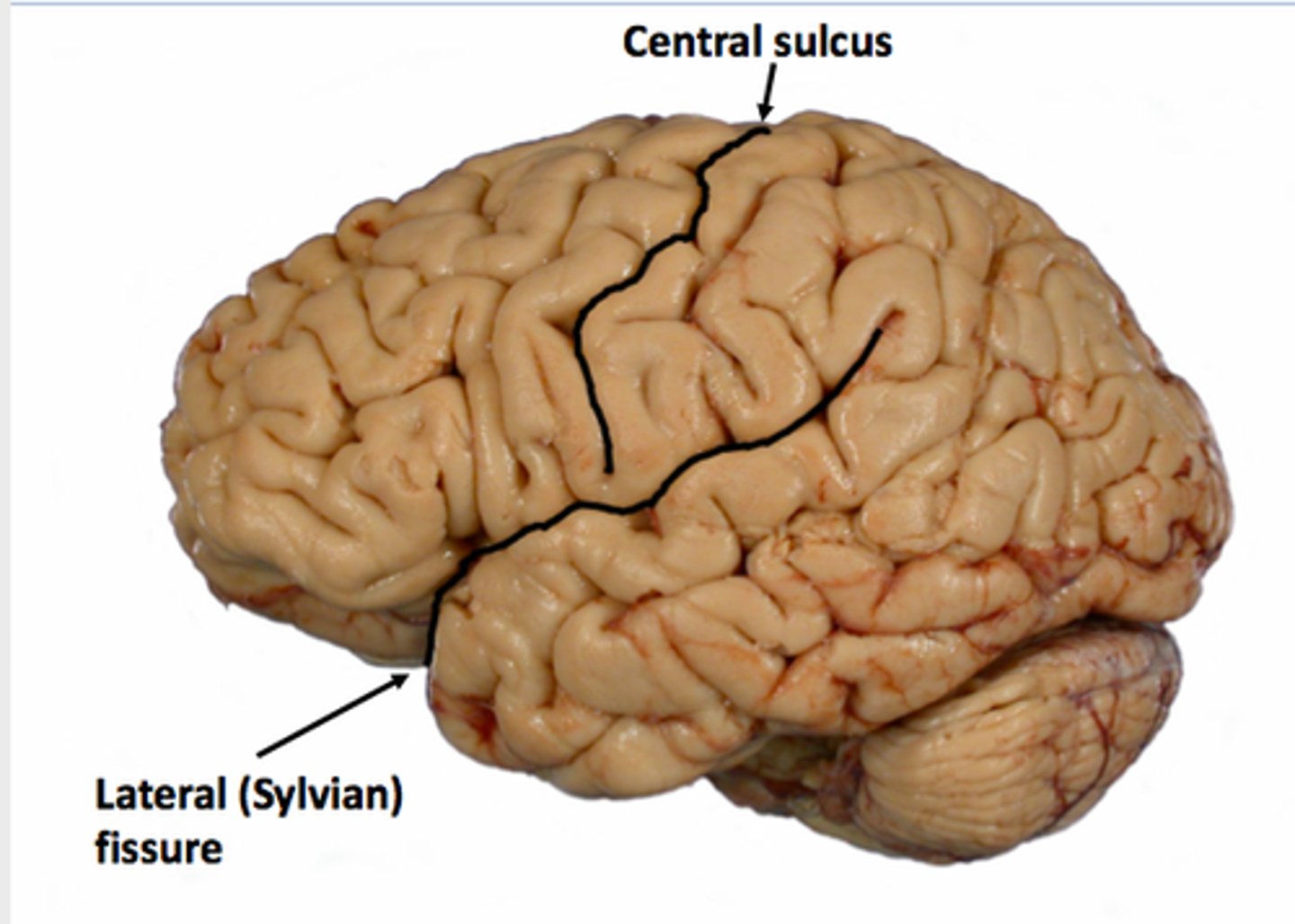
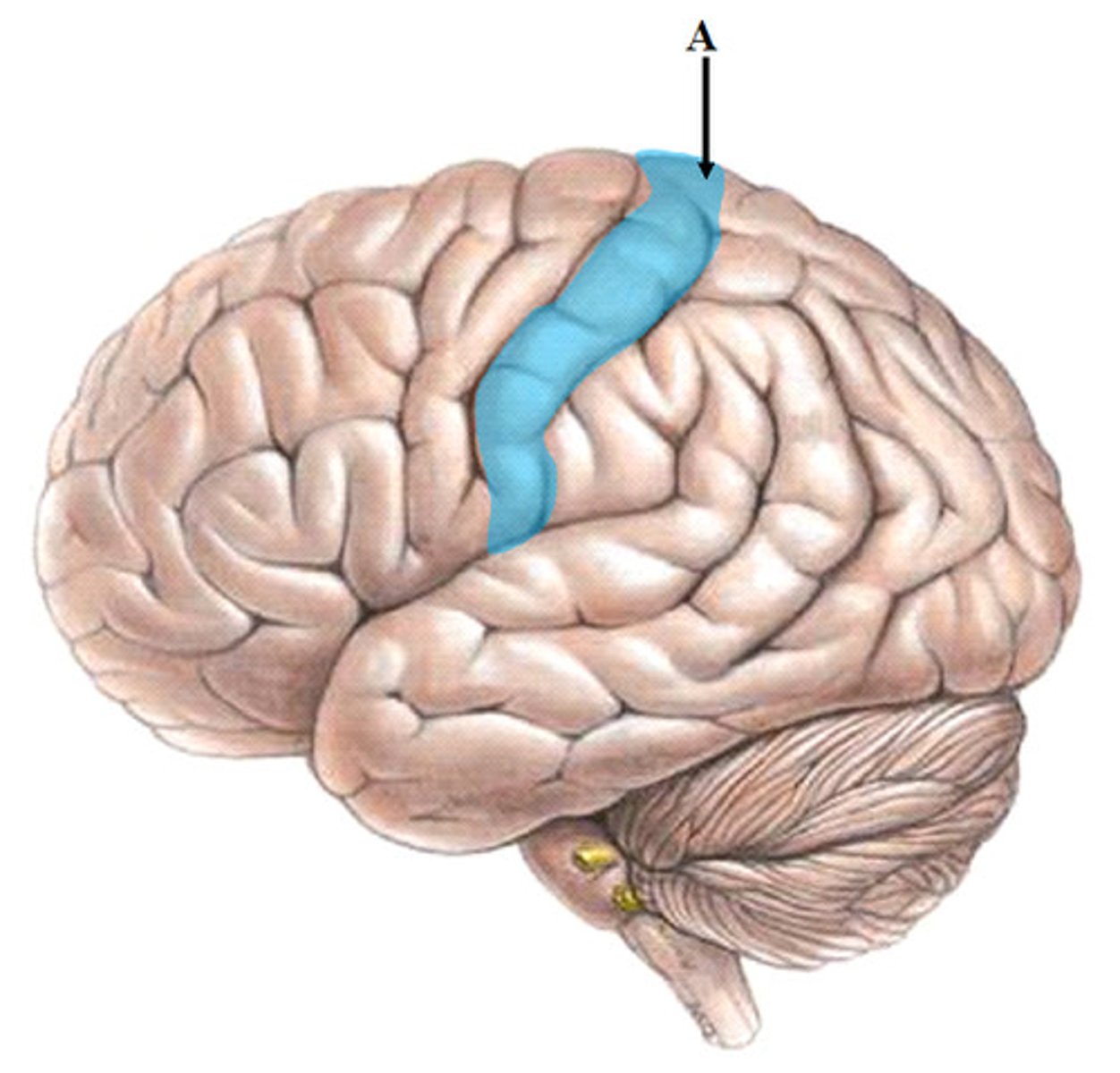
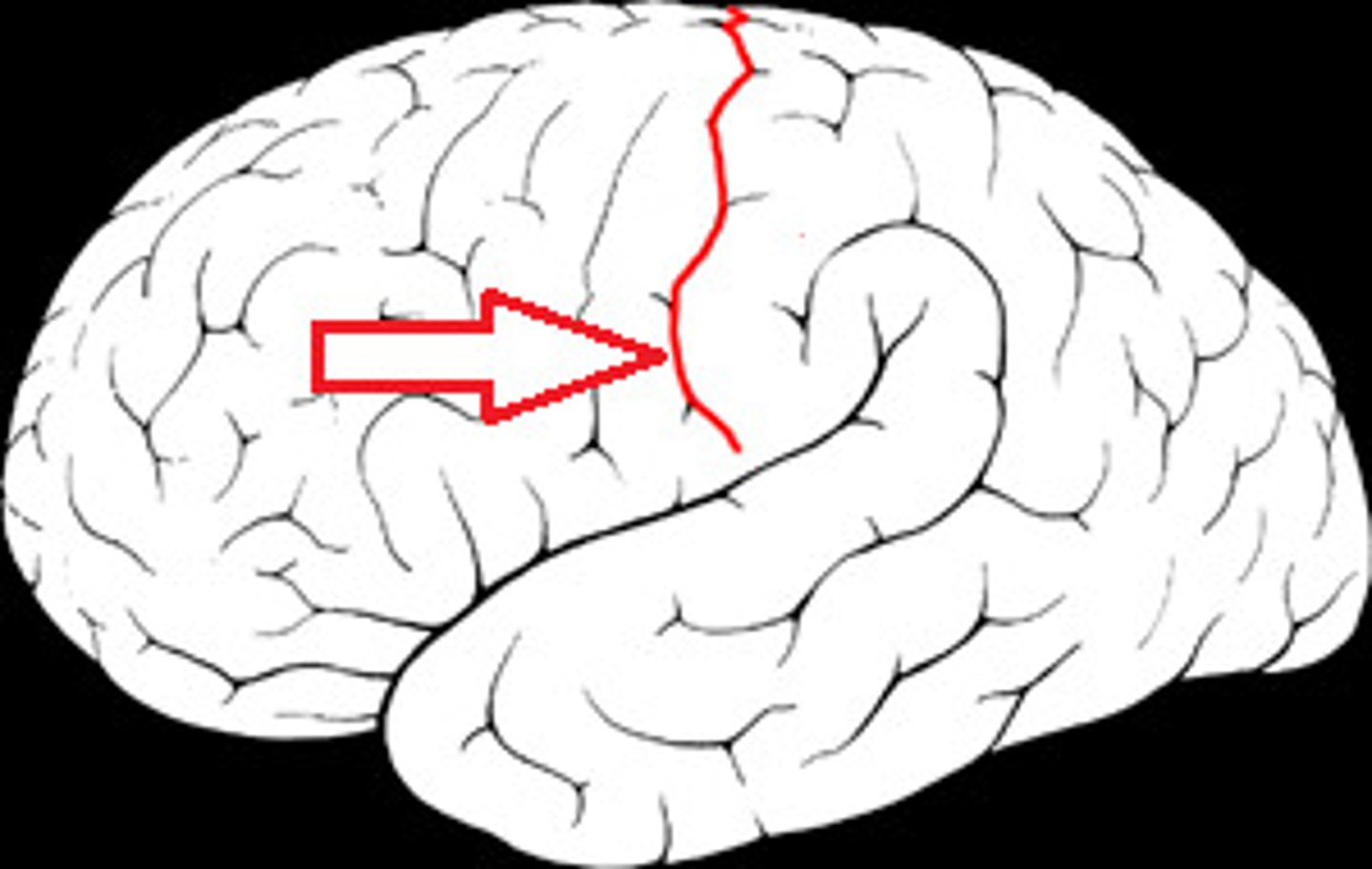
Central sulcus of brain
separates frontal & parietal lobes
Transverse fissure of brain
separates cerebrum from cerebellum

What is located in the anterior cranial fossa?
frontal lobe
What is located in the middle cranial fossa?
temporal lobe
What is located in the posterior cranial fossa?
cerebellum
What are the 3 basic regions of each hemisphere?
(1) cerebral cortex
(2) internal white matter
(3) basal nuclei
What comprises grey matter of the brain?
cell bodies, dendrites & unmyelinated axons
What comprises white matter of the brain?
myelinated axons
What are the 3 main functions of the cortex?
(1) motor areas: initiation of movement
(2) sensory areas: sensory info. reception/ perception
(3) association areas: complex integrative functions
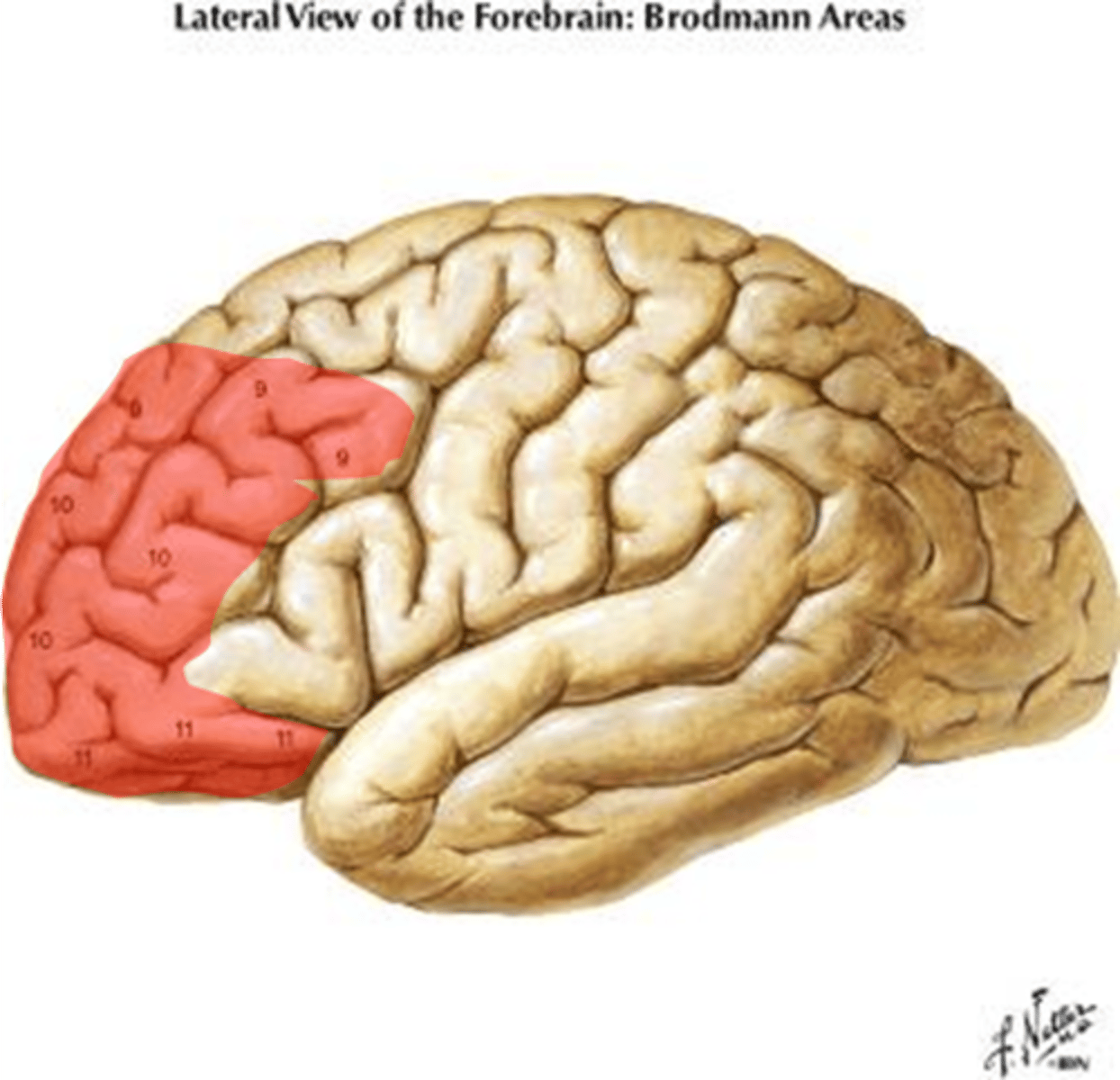
Prefrontal cortex
Location:
Function:
Location: frontal lobe
Function: personality & character traits
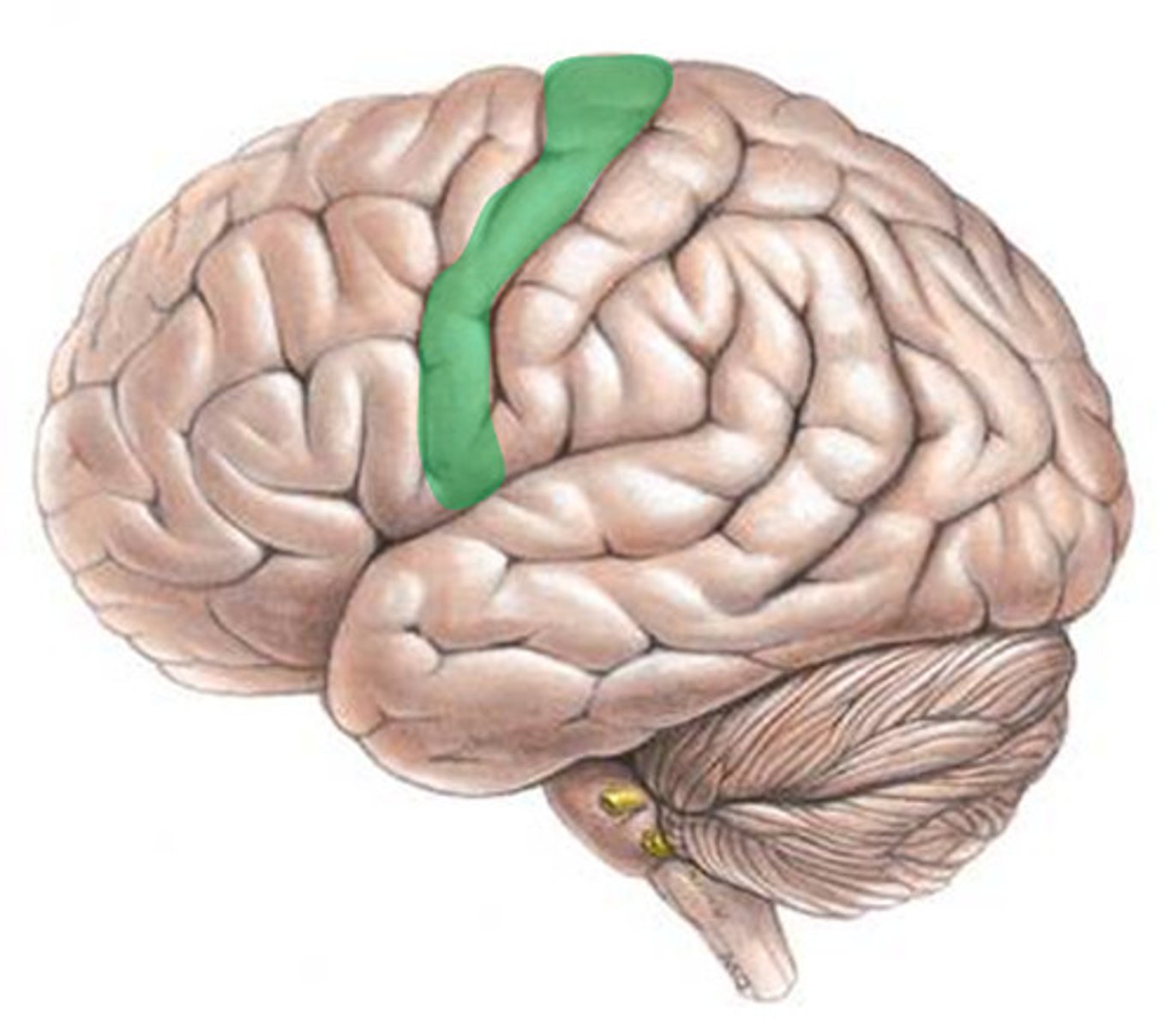
Primary motor cortex
Location:
Function:
Location: precentral gyrus (frontal lobe)
Function: fine motor control
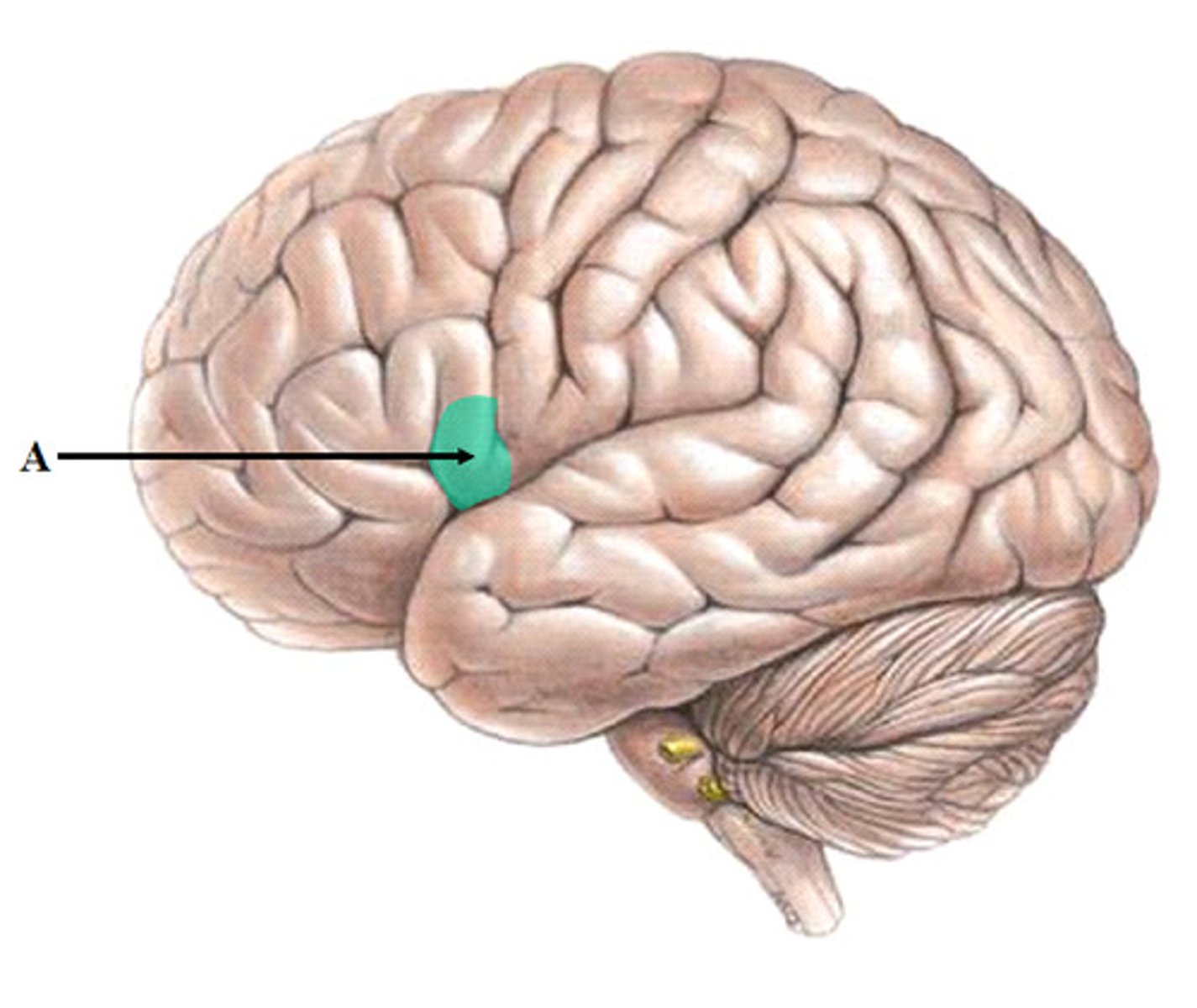
Broca's area
Location:
Function:
Location: frontal lobe (dominant hemisphere only)
Function: speech production
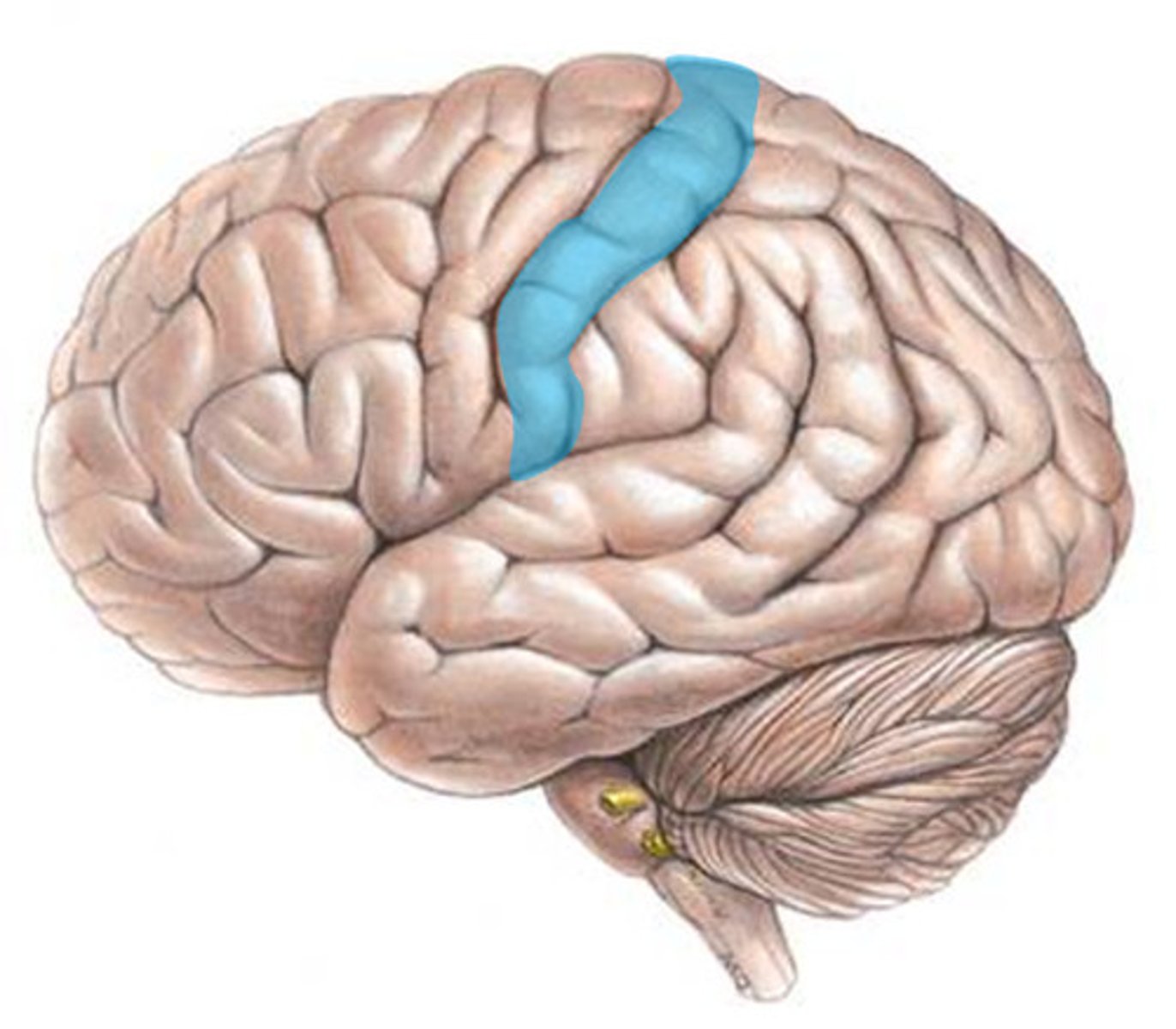
Primary sensory cortex
Location:
Function:
Location: postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe)
Function: sensory
Primary auditory cortex
Location:
Function:
Location: temporal lobe
Function: hearing
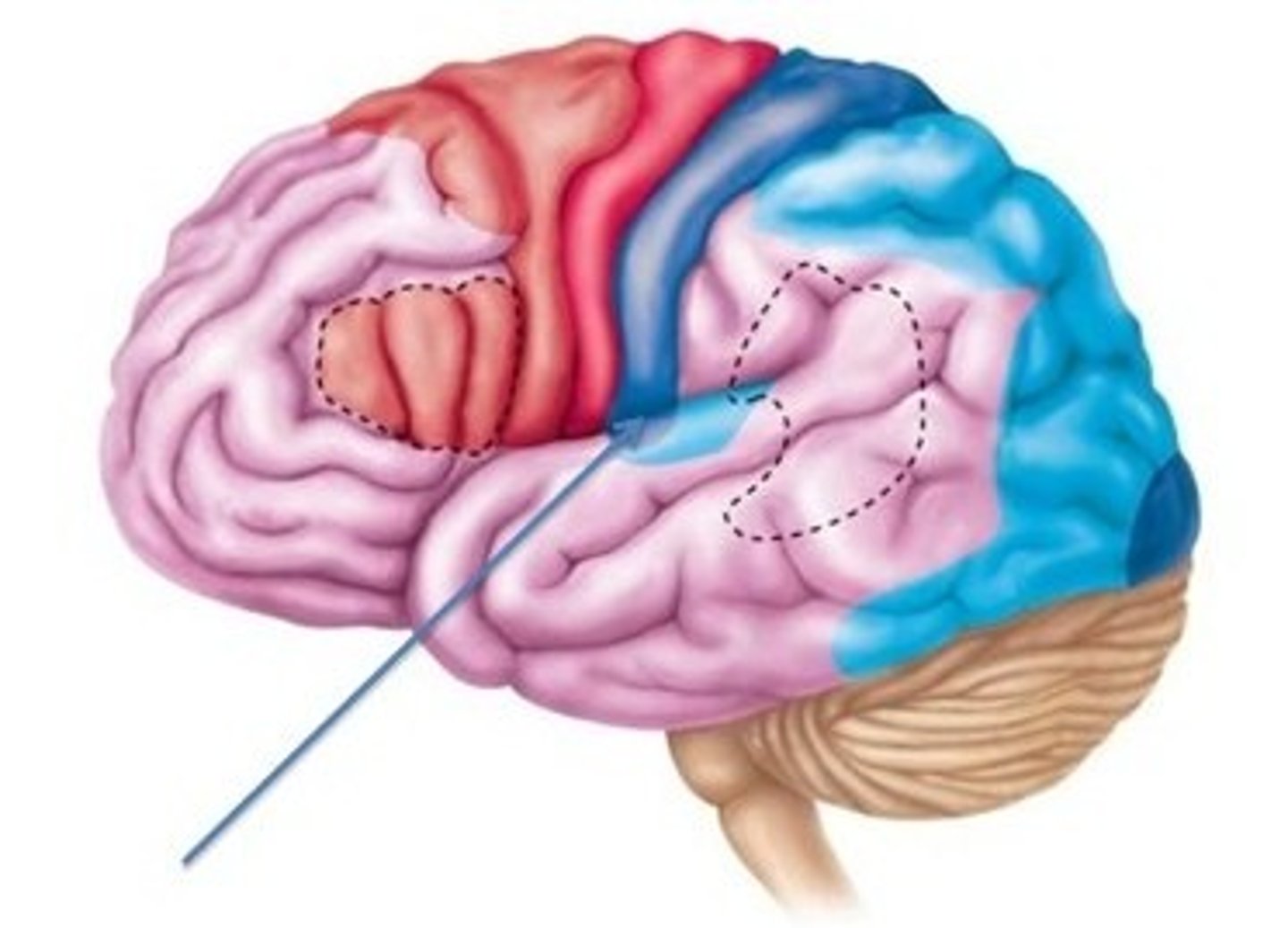
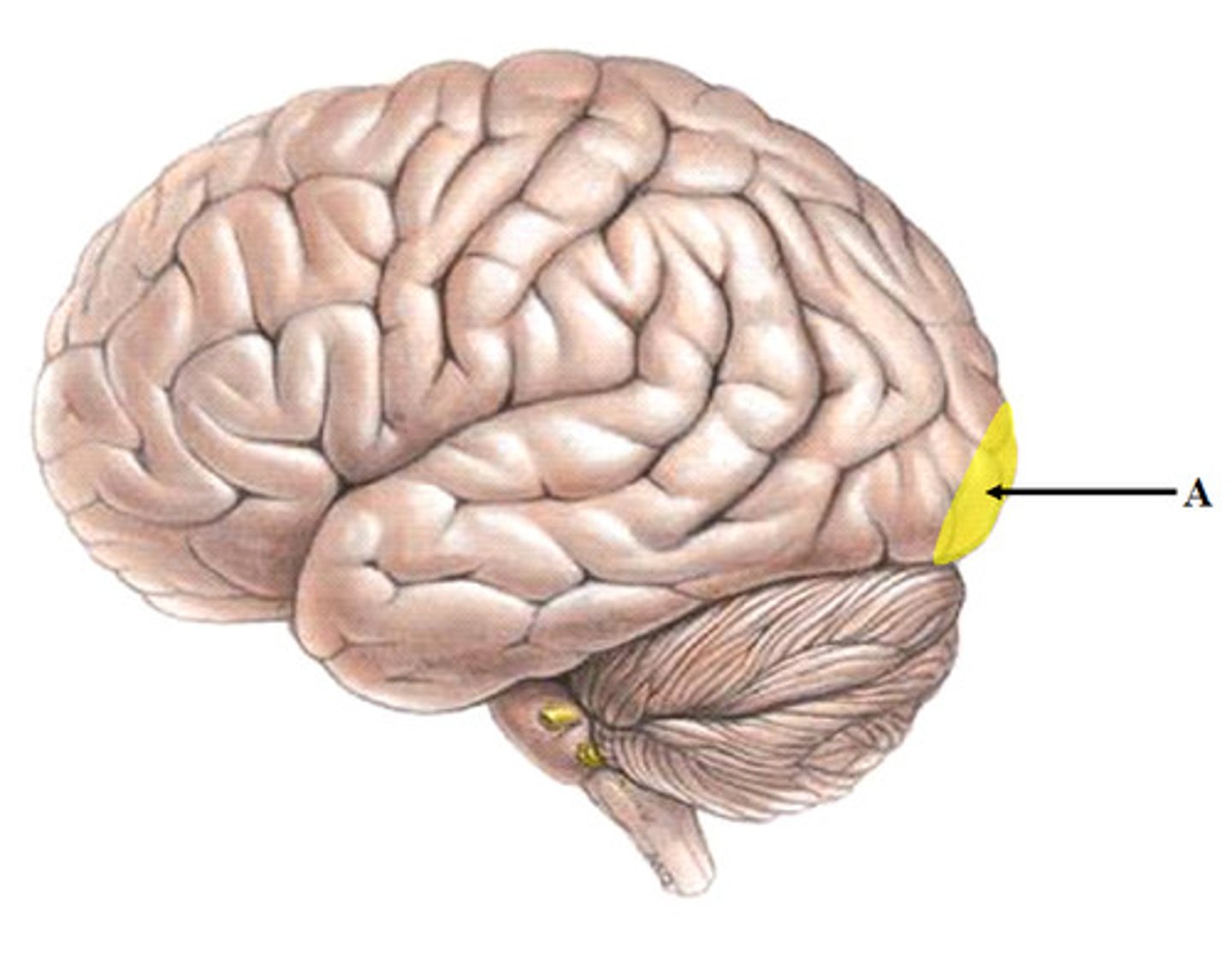
Primary visual cortex
Location:
Function:
Location: occipital lobe
Function: vision
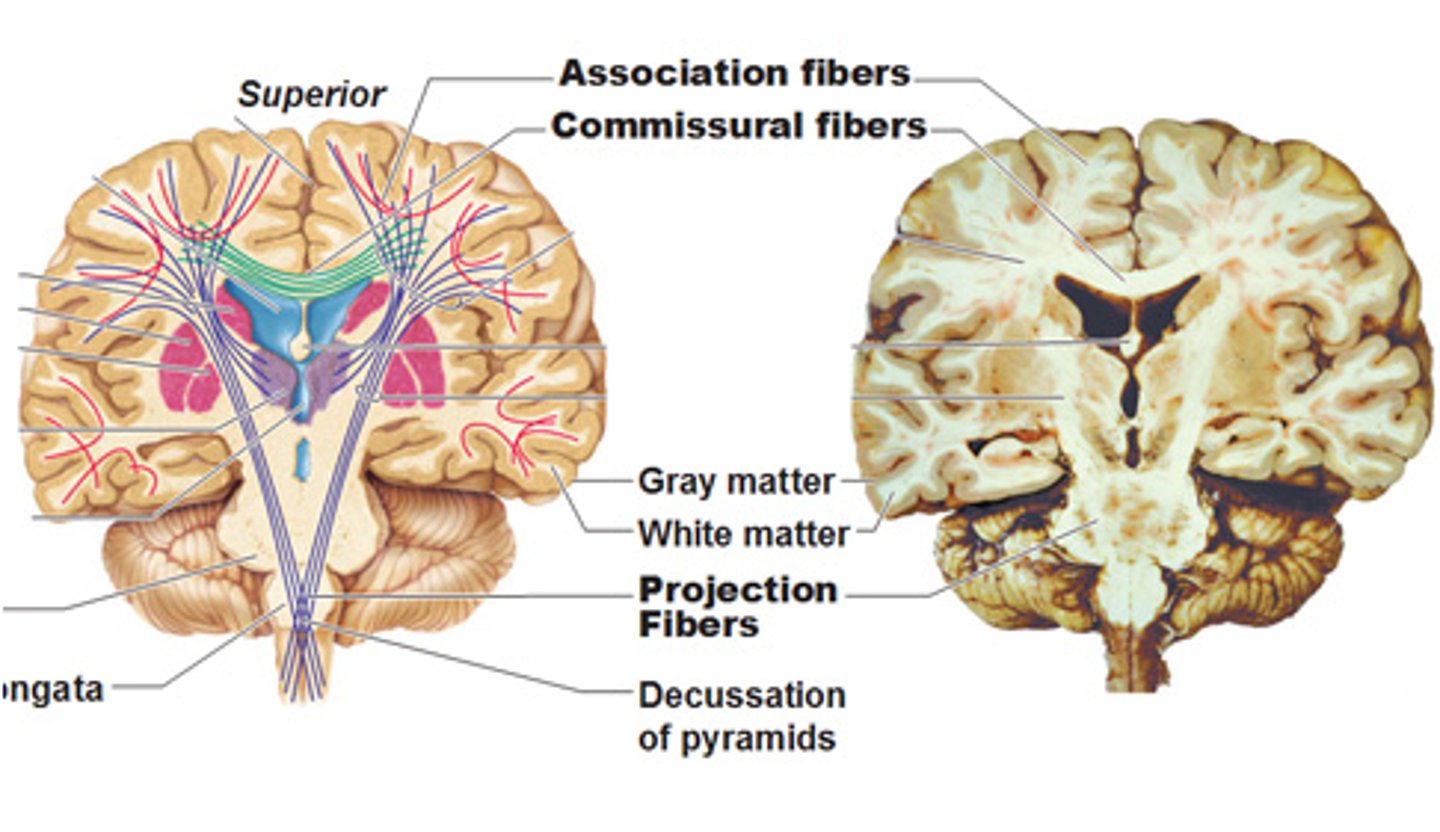
What are commissural fibers?
fibers connecting grey area matter between the two hemispheres
Ex. corpus callosum
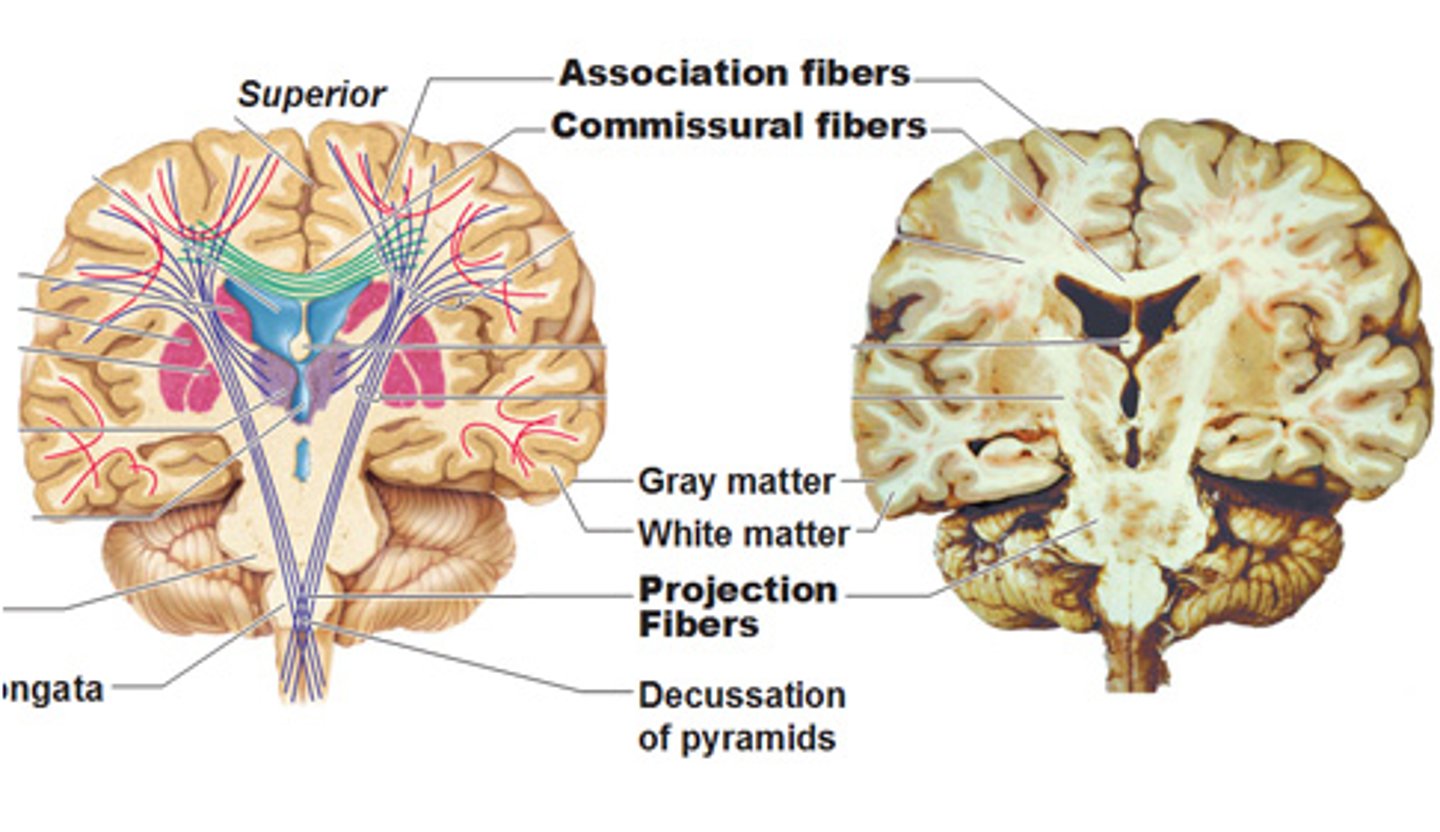
What are association fibers?
fibers connecting parts of the same hemisphere
Ex. general cerebral white matter

What are projection fibers?
fibers connecting the cerebral cortex to other parts of the CNS
Ex. spinal tracts
What are basal nuclei?
collection of nerve cell bodies deep in the cerebellum
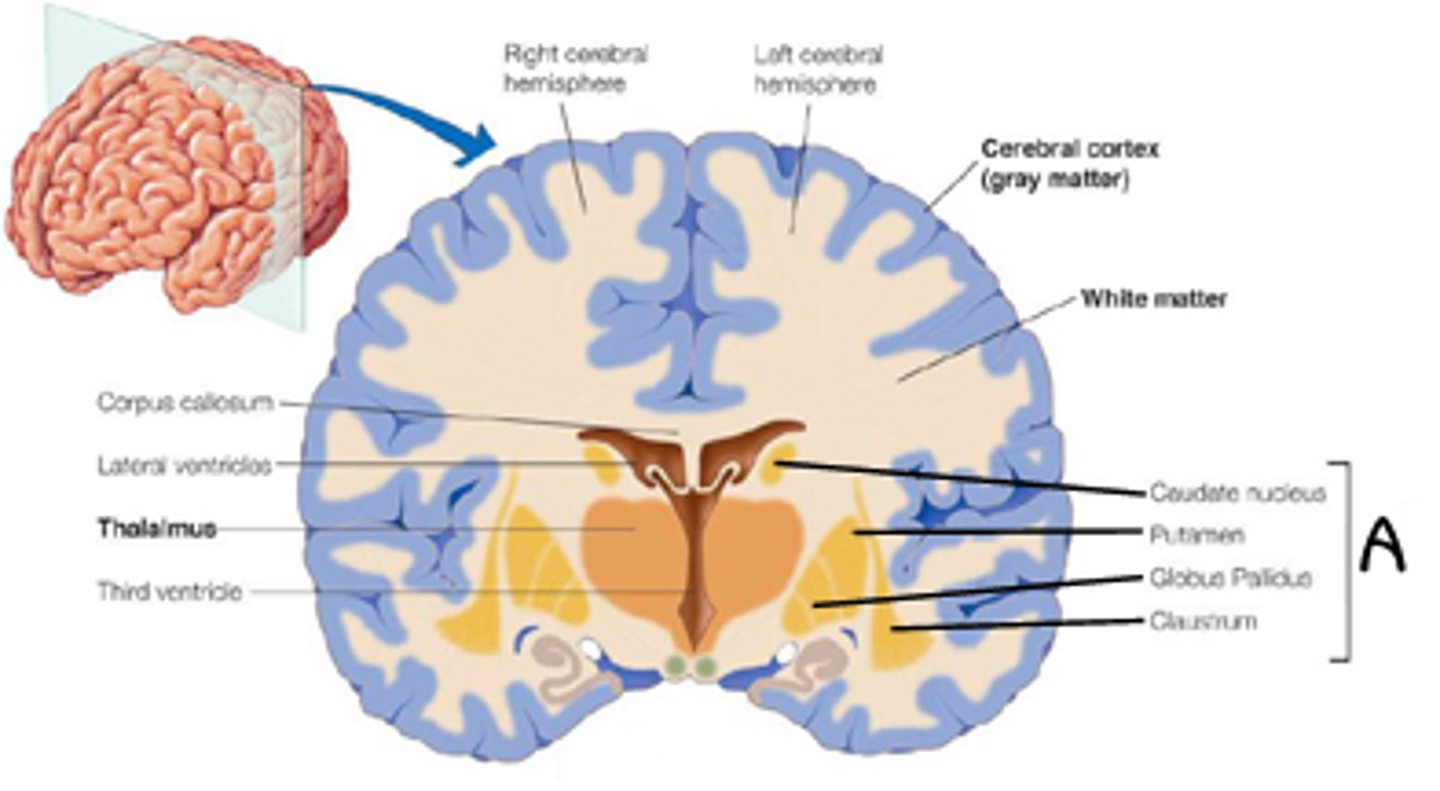
What is the function of basal nuclei?
Influence motor function by regulating the initiation and termination of movement. Inhibits extraneous muscle contraction and helps to maintain motor control
*damage can lead to muscle rigidity and/or resting tremors
Thalamus
major relay center for all sensation entering the cerebral cortex except olfaction; aids in motor activity

Hypothalamus
major regulator of the body's internal environment, through the autonomic, limbic, and endocrine systems
Epithalamus
regulates sleep/wake cycle w/ hypothalamus
-main projection called pineal body secretes melatonin hormone
Identify the 3 parts of the brain stem:
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Function of brain stem:
(1) produces autonomic behaviors vital to survival
(heart rate, respiration)
(2) pathway for descending & ascending axons
(3) contains nuclei for CN3-12