Hindu Gods, Hindusim and Buddhism
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Brahma
the Creator god with four heads and four arms in Hinduism
Vishnu
the Preserver god in Hinduism, often depicted with blue skin and four arms, holding a conch, discus, club, and lotus
Shiva
the Destroyer/Transformer god in Hinduism, often shown with third eye, a crescent moon, and a trident.
Lakshmi
Hindu goddess of Wealth, Prosperity, Beauty, and Fertility, often depicted sitting on a lotus flower and considered the consort of Vishnu.
Ganesh
elephant-headed Hindu god of Success widely revered as the Remover of Obstacles, the patron of arts and sciences, and the deva of intellect and wisdom
Krishna
a central Hindu deity, considered an avatar (incarnation) of the god Vishnu, and is revered for his teachings on dharma (righteousness), karma, and bhakti (devotion); always carries flute
Saraswati
Hindu goddess, known as the goddess of knowledge, learning, arts, music, and speech, and is also considered the consort of Brahma, the creator; dressed in white for purity; plays the sitar
Kali
Hindu goddess, associated with time, death, destruction, and the cycle of life, considered a symbol of the Divine Mother and of feminine strength; often depicted standing or dancing on her husband, the god Shiva
Surya
The Hindu Sun God; often depicted riding a chariot drawn by seven horses; is considered a vital force in the universe, representing light, energy, and power.
Hindu Trinity
Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva
Temples
a building devoted to the worship, or regarded as the dwelling place, of a god or gods or other objects of religious reverence.

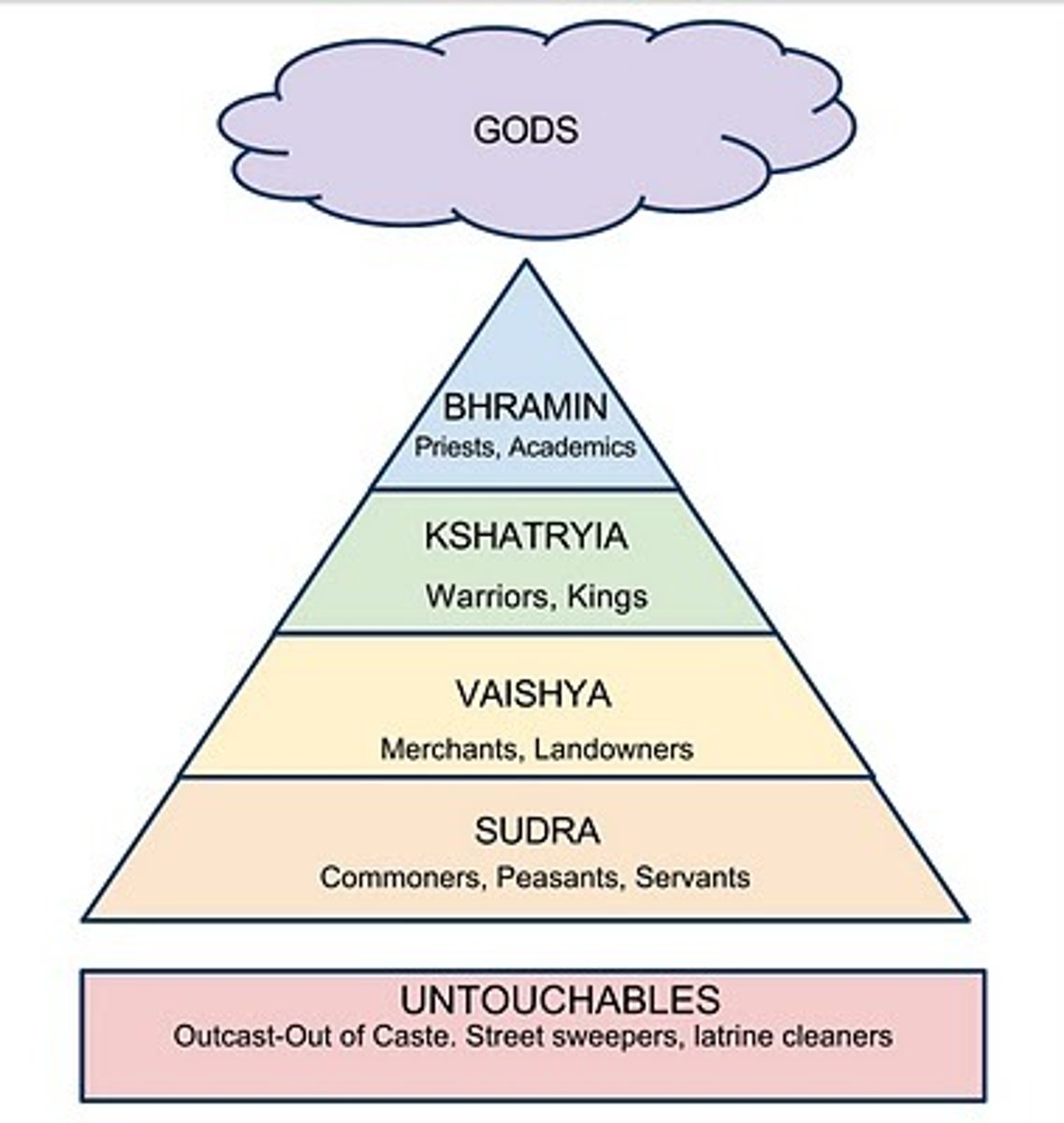
Caste System
A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life
Reincarnation
In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding

Samsara
(Hinduism and Buddhism) the endless cycle of birth and suffering and death and rebirth

Karma
(Hinduism and Buddhism) the effects of a person's actions that determine his destiny in his next incarnation

Vedas
Ancient Sanskrit writings that are the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism. Holy Book.

Dharma
In Hindu belief, a person's religious and moral duties

Nirvana (Buddhism)
Name given to reaching the state of perfect peace in Buddhism.

Buddha
awakened one

4 Noble Truths of Buddhism
Suffering is a part of life, suffering comes from desire, there is no end to suffering unless we end desire, the Noble 8-fold path
Pagoda
The Buddhist place of worship

Siddhartha Guatama (Buddhism)
A prince who founded Buddhism, and gave up his power to become enlightened.
Moksha
Becoming liberated or released from the cycle of reincarnation in Hinduism.
Eightfold Path (Buddhism)
In Buddhism, the basic rules of behavior and belief leading to an end of suffering
Untouchables
LOWEST LEVEL OF INDIAN SOCIETY; not considered a real part of the caste system; often given degrading jobs; their life was extremely difficult
Brahmins
the highest of the four classes of the caste system, traditionally made up of priests
Sudras
Caste that made up most of the Indian population; most were peasants and manual laborers; they had limited rights in society
Vaishyas
farmers, craftspeople, and traders in the caste system
The Upanishads
late Vedic and post-Vedic Sanskrit texts that "document the transition from the archaic ritualism of the Veda into new religious ideas and institutions" and the emergence of the central religious concepts of Hinduism.