GP- esophagus+stomach
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
to pass food from the pharynx to the stomach
the function of the esophagus is..
cervical, thoracic, abdominal
what are the 3 different parts of the esophagus?
striated
dogs have an esophagus composed of _______ muscle
smooth + striated
(cranial 2/3 striated, distal 1/3 smooth)
cats have an esophagus composed of _______ muscle
smooth + striated
(cranial 2/3 striated, distal 1/3 smooth)
horses have an esophagus composed of _______ muscle
two sphincters:
1.pharyngoesophagic/proximal/upper sphincter
2.gastroesophagic/caudal/lower sphincter
the esophagus has _____ sphincters.
closed (constricted)
when resting, how are sphincters?
the UES relaxes, opening to allow food to pass to the LES
when food arrives to the upper esophagic sphincter, what happens?
the LES relaxes, opening to allow food to pass to the stomach
when food arrives to the lower esophagic sphincter, what happens?
closed
in a resting position, are the esophagic sphincters open or closed?
vomiting
if the animal has abdominal contractions, it this vomiting or regurgitation?
vomiting
which, vomiting or regurgitation involves nausea and retching?
regurgitation
if the animal eats and immediately after, the food comes back up- do we think this is regurgitation or vomiting?
no- vomiting can occur any time, even without a link with food ingestion
does the animal vomit immediately after eating?
vomit- partially digested, bilious, acidic
regurgitation- undigested, tube-shaped, alkaline, mucous
how does the appearance of vomit versus regurgitated food appear?
vomit
a dog lets out a partially digested, irregularly shaped lump of food- do we assume this is regurgitated or vomit?
vomit
which has an acidic pH- regurgitated food or vomit?
regurgitated food
which has an alkaline pH- regurgitated food or vomit?
esophagic- because this is regurgitated food (tube-shaped, undigested, mucous)
a dog has released this from its mouth... do we assume this is an esophagic or gastric issue?
esophagus
regurgitation is a sign of a problem with the _____
regurgitation
what is the MAIN symptom of esophagic disease?
-repeated attempts to swallow
-dysphagia
-odynophagia (pain when swallowing)
-cough
-regurgitation
what are the signs of esophagic disease?
pain when swallowing
what is odynophagia?
painful:
esophagitis
esophagic stenosis
gastroesophagic reflux
neoplasia
foreign bodies
not painful:
megaesophagus
esophageal diverticulum
esophageal fistula
what are the most common esophageal disorders?
esophagitis
esophagic stenosis
gastroesophagic reflux
neoplasia
foreign bodies
which esophagic disorders are painful for the animal?
esophagitis
the MOST COMMON esophageal disorder is...
narrowing of the esophagus
what is esophageal stenosis?
intramural causes:
trauma, causing scar tissue to form
intraluminal causes:
foreign bodies or tumors blocking the lumen
extramural causes:
cardiomegaly, lymphadomegaly, neoplasia
what might be the cause of esophageal stenosis?
intramural esophageal stenosis
what is the name of this disorder?
the narrowing of the esophagus due to the thickening of the esophageal wall (ex: scar tissue)
what is intramural esophageal stenosis?
the narrowing of the esophagus due to an obstruction (ex: foreign body, neoplasia)
what is intraluminal esophageal stenosis?
the narrowing of the esophagus due to something externally compressing it (ex: cardiomegaly, lynphadomegaly, neoplasia, etc)
what is extramural esophageal stenosis?
cardiomegaly- this is an extramural cause
what is the cause of this esophageal stenosis?
-anorexia/hyporexia
-adipsia/hypodipsia
-lethargy
-ptyalism/sialorrhea
-can lead to esophagitis
what are the main symptoms of esophageal stenosis?
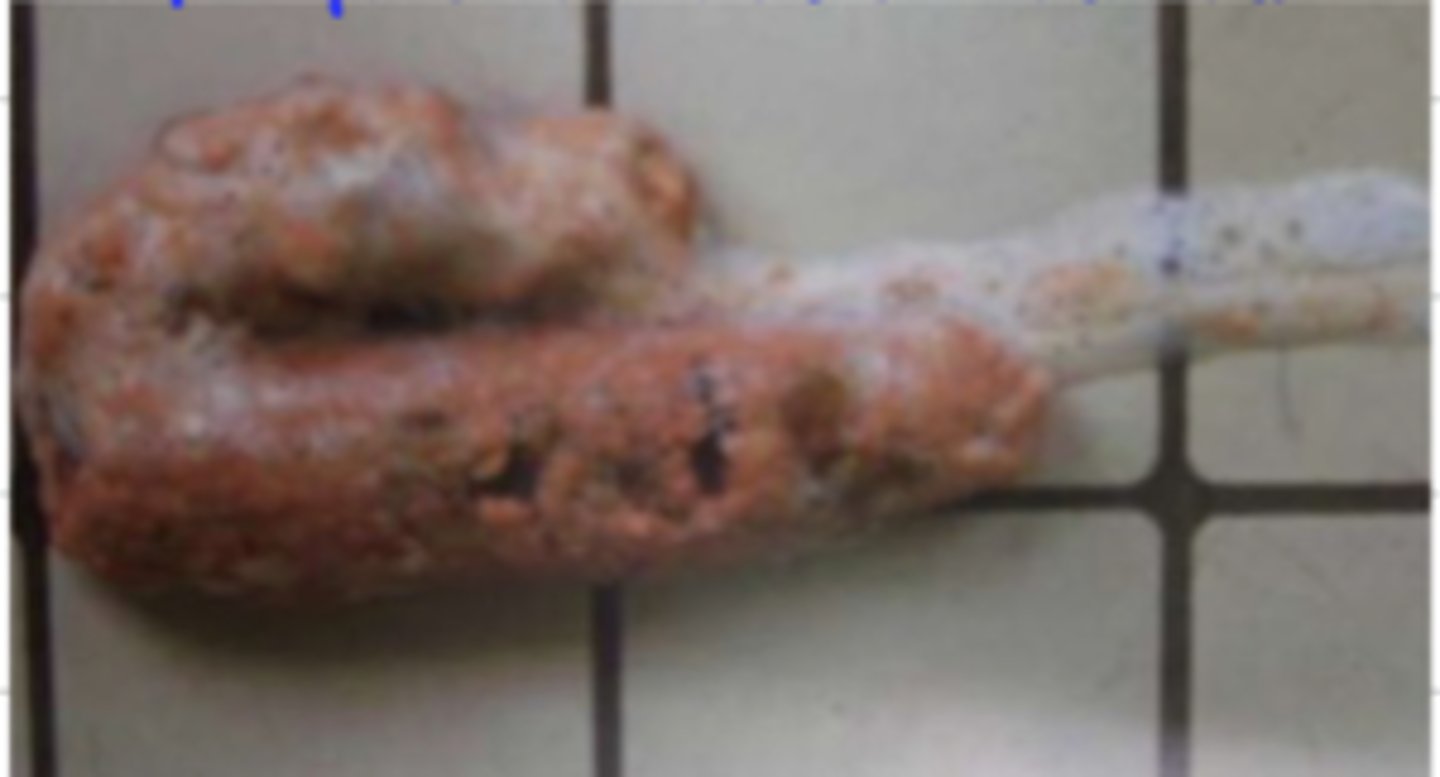
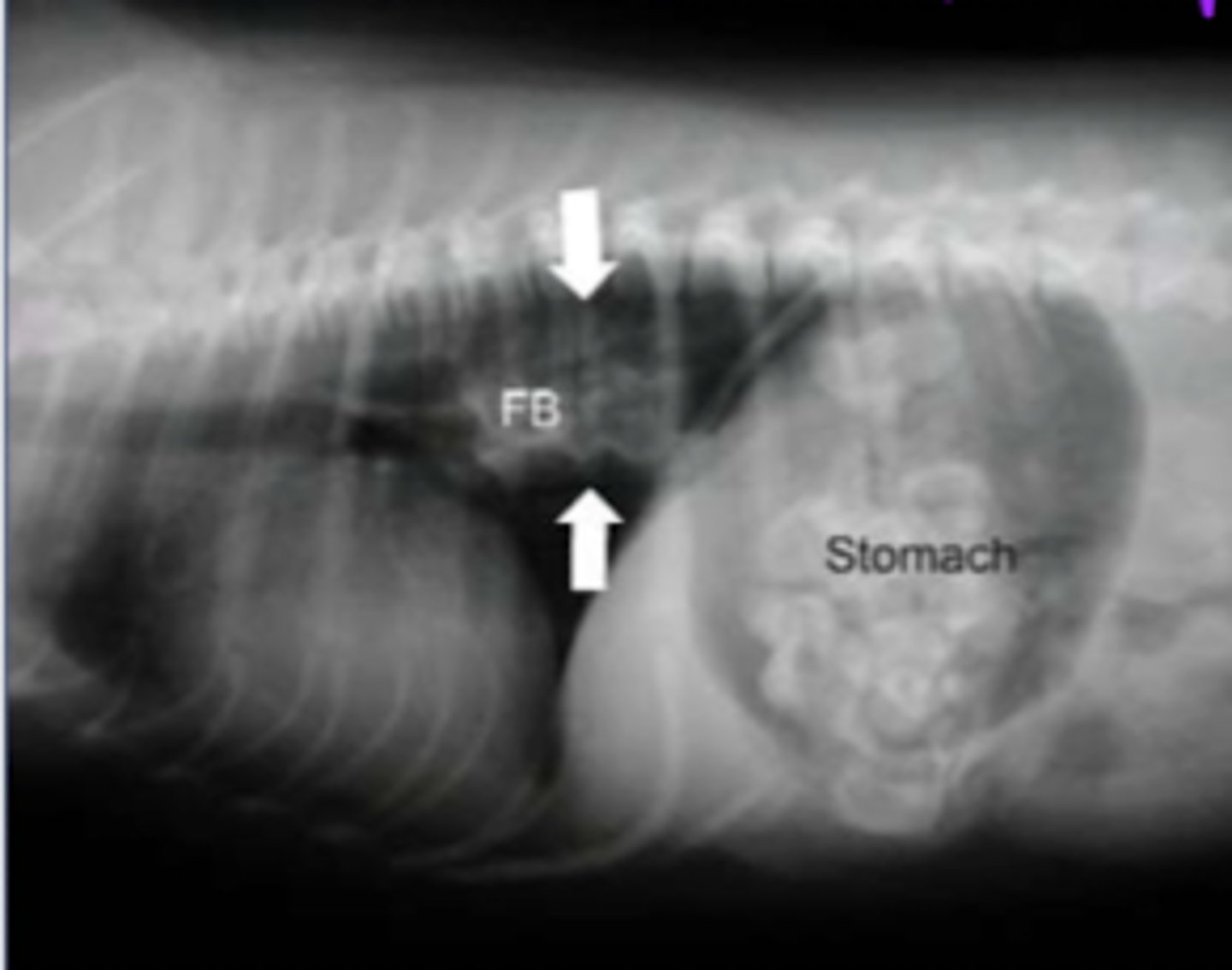
intraluminal esophageal stenosis (due to a foreign body)
what is the disorder we see here?
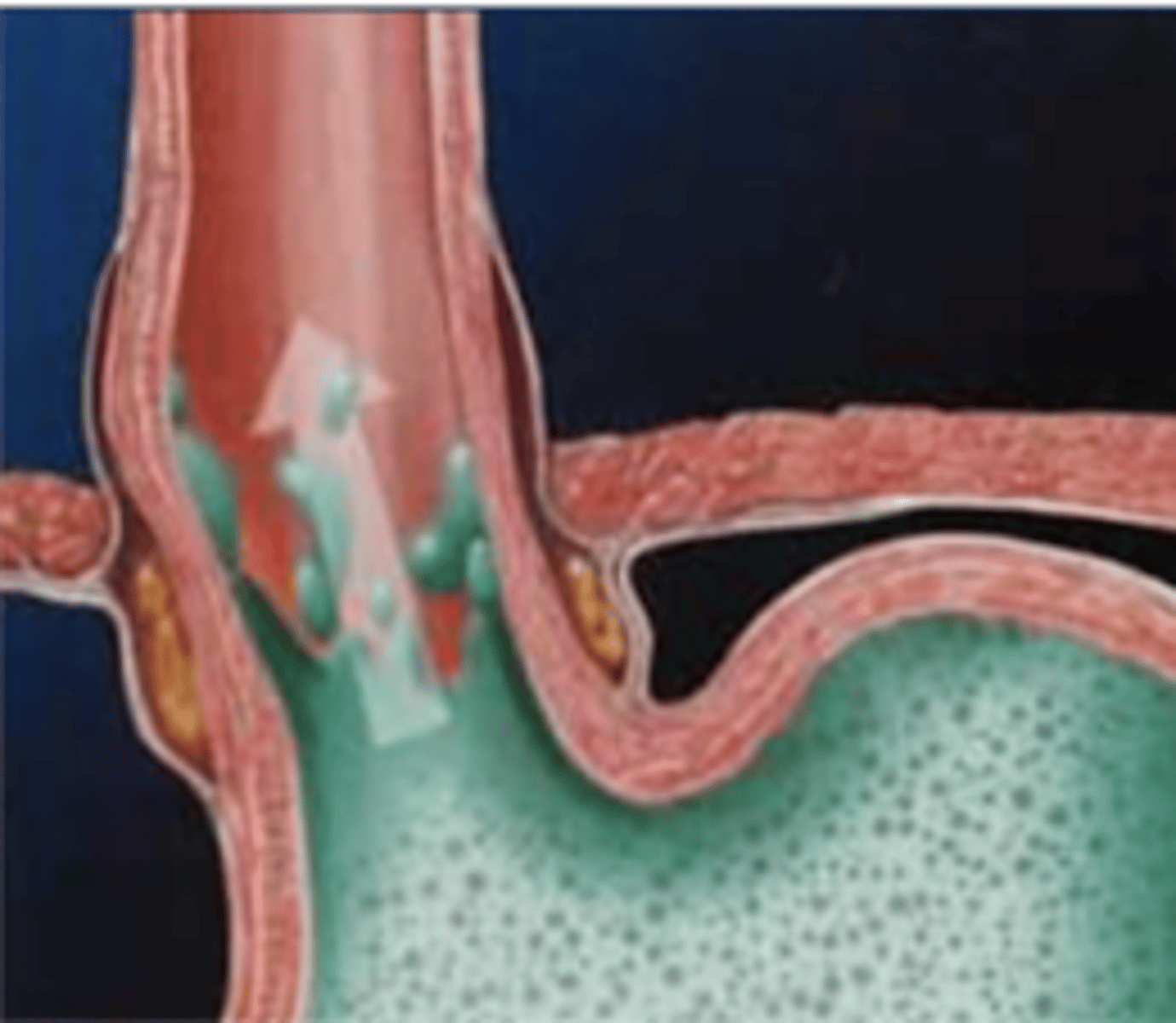
when gastric content passes to the esophagus
what is gastroesophagic reflux?
no- but if it is, it is with brachycephalic breeds
is gastroesophagic reflux commonly seen in dogs?
gastroesophagic reflux
the disorder where gastric content passes to the esophagus is called...
-LES disorders
-chronic vomiting
-hiatal hernia
-delayed gastric emptying
what are the possible etiologies of gastroesophagic reflux?
gastroesophagic reflux
an LES disorder will most likely lead to what problem in the esophagus?
-odynophagia
-hypersalivation/ptyalism
-extension of the head and neck when swallowing
-hyporexia/anorexia- weightloss
-cough
-regurgitation
what are the symptoms of gastroesophagic reflux?
regurgitation
will a gastroesophagic reflux cause vomiting or regurgitation?
gastroesophagic reflux
what type of disorder is characterized here?
leiomyoma- smooth muscle tumor
carcinoma- epithelial tissue tumor
sarcoma- bone/soft tissue tumor
what are the possible types of neoplasia we might see in the esophagus?
neoplasia in the esophagus
what is the problem we see here?
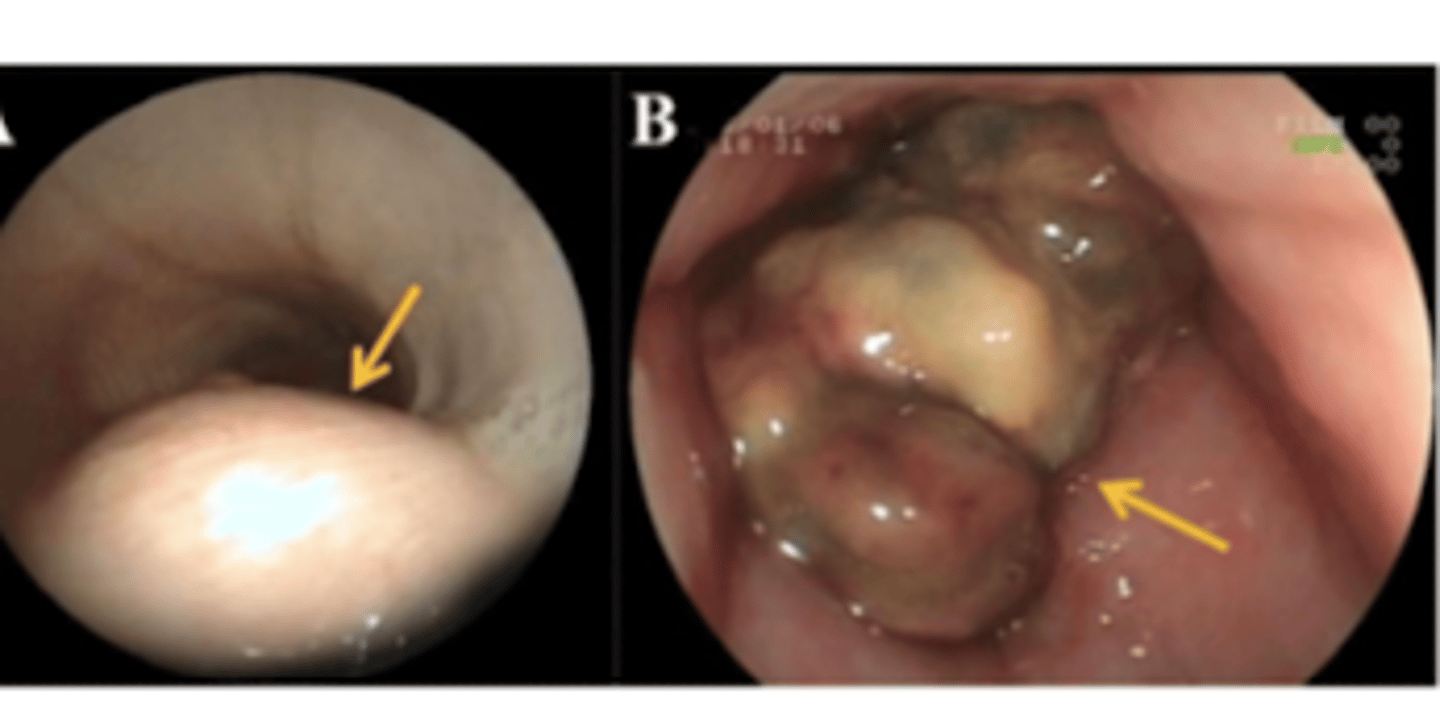
parasite in the esophagus (Spirocerca lupi)
what is the problem we see here?
Spirocerca lupi
what is the most common parasite we will find in the esophagus of a dog?
very slow onset (the clinical signs appear very slowly)
how fast is the onset of clinical signs of an esophagic neoplasia?
the diffuse dilation of the esophagus
what is megaesophagus?
megaesophagus
the most common cause of regurgitation in dog is...
megaesophagus
the diffuse dilation of the esophagus is medically called...
congenital (after weaning, vagal nerve disorder)
acquired
idiopathic muscular or neural disorder
or secondary to another disease
what are the possible reasons that an animal might have megaesophagus?
german shepherd, great dane, labrador, siamese
what small animal breeds are predisposed to congenital megaesophagus?
-CNS disorders (distemper, brainstem lesion)
-peripheral neuropathy (polyneuritis, dysautonomy)
-neuromuscular junction disease (myasthenia gravis, botulism, tetanus)
-piloric stenosis
-esophagic muscle disturbances (esophagitis, endocrine disease)
-mediastinitis
an acquired megaesophagus can be secondary to what diseases?
-regurgitation
-dyphagia
-anorexia/hyporexia
-pain (if caused by esophagitis)
-ptyalism
-halitosis
-aspiration pneumonia
what are the symptoms of an animal with megaesophagus?
-megaesophagus
-esophageal stenosis
-gastroesophagic reflux
-esophageal diverticulum
-neoplasia
-foreign body
-esophageal fistula
-esophagitis
if an animal comes in to the clinic because it is regurgitating, what disorders would we add to our differential diagnosis?
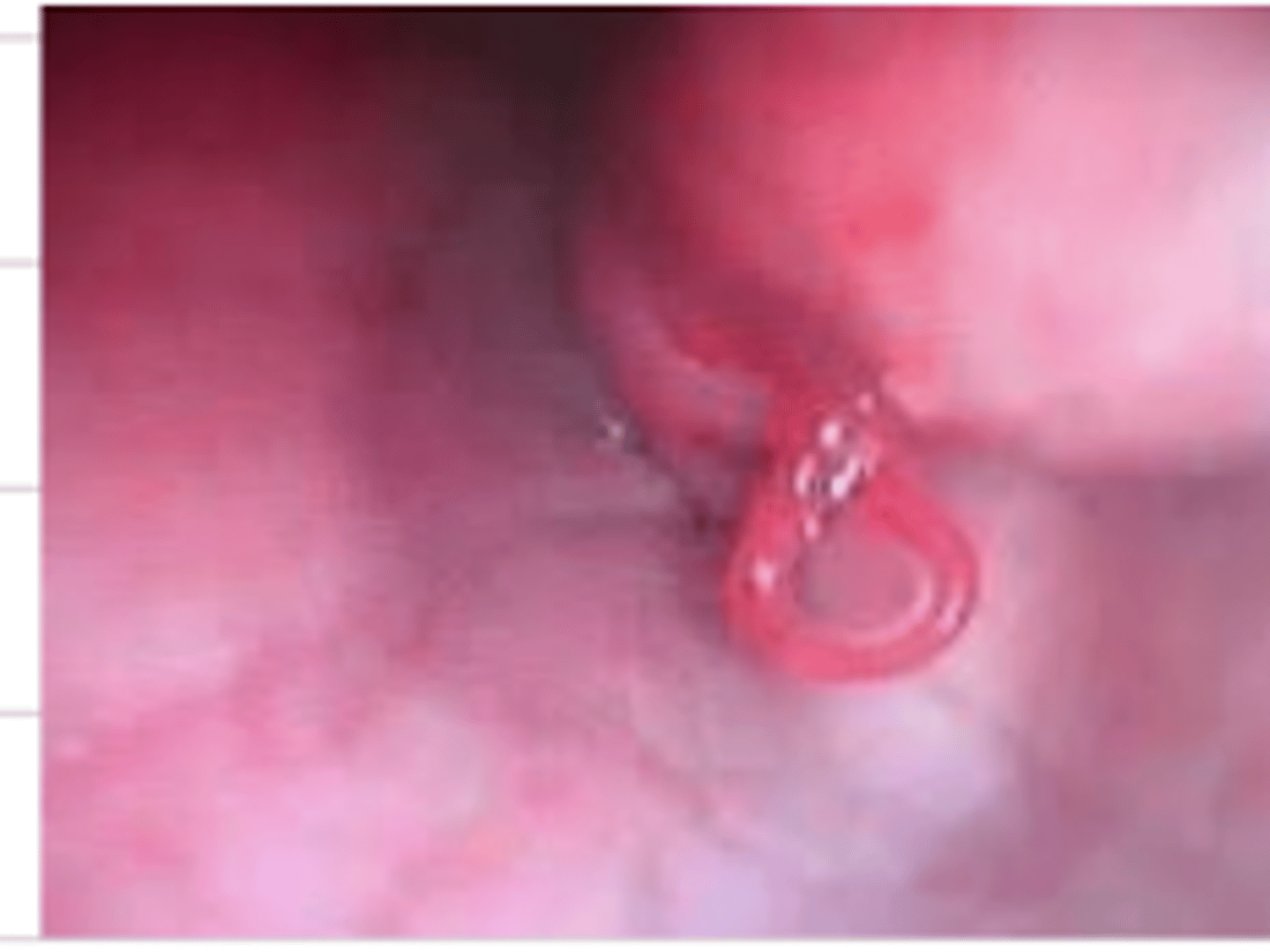
megaesophagus
after performing tests on this animal, we receive this image- what is the diagnosis?
a pouch-like dilation of the esophageal wall
what is an esophageal diverticulum?
esophageal diverticulum
a pouch-like dilation of the esophageal wall is called a...
no
are esophageal diverticulums common in small animals?
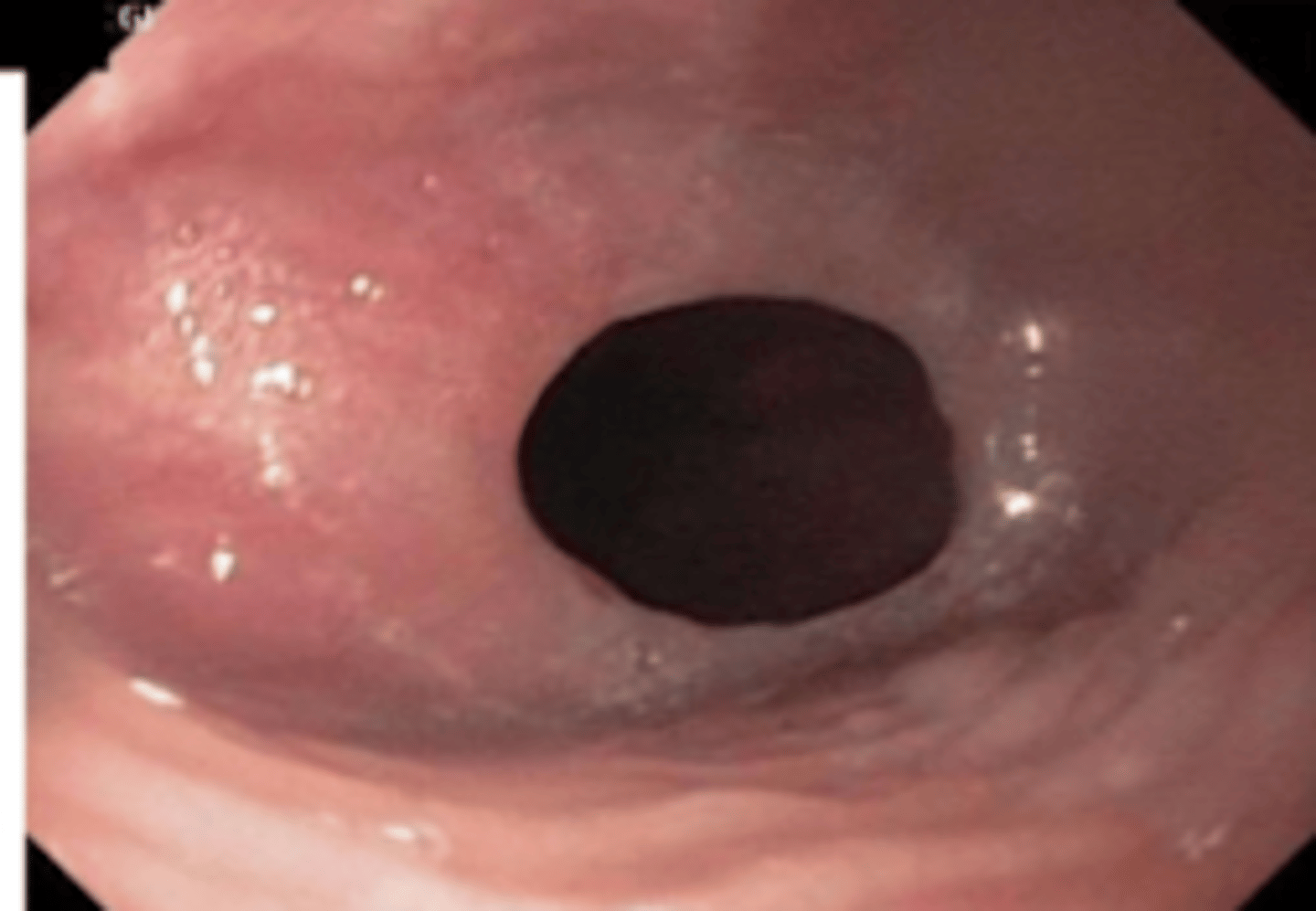
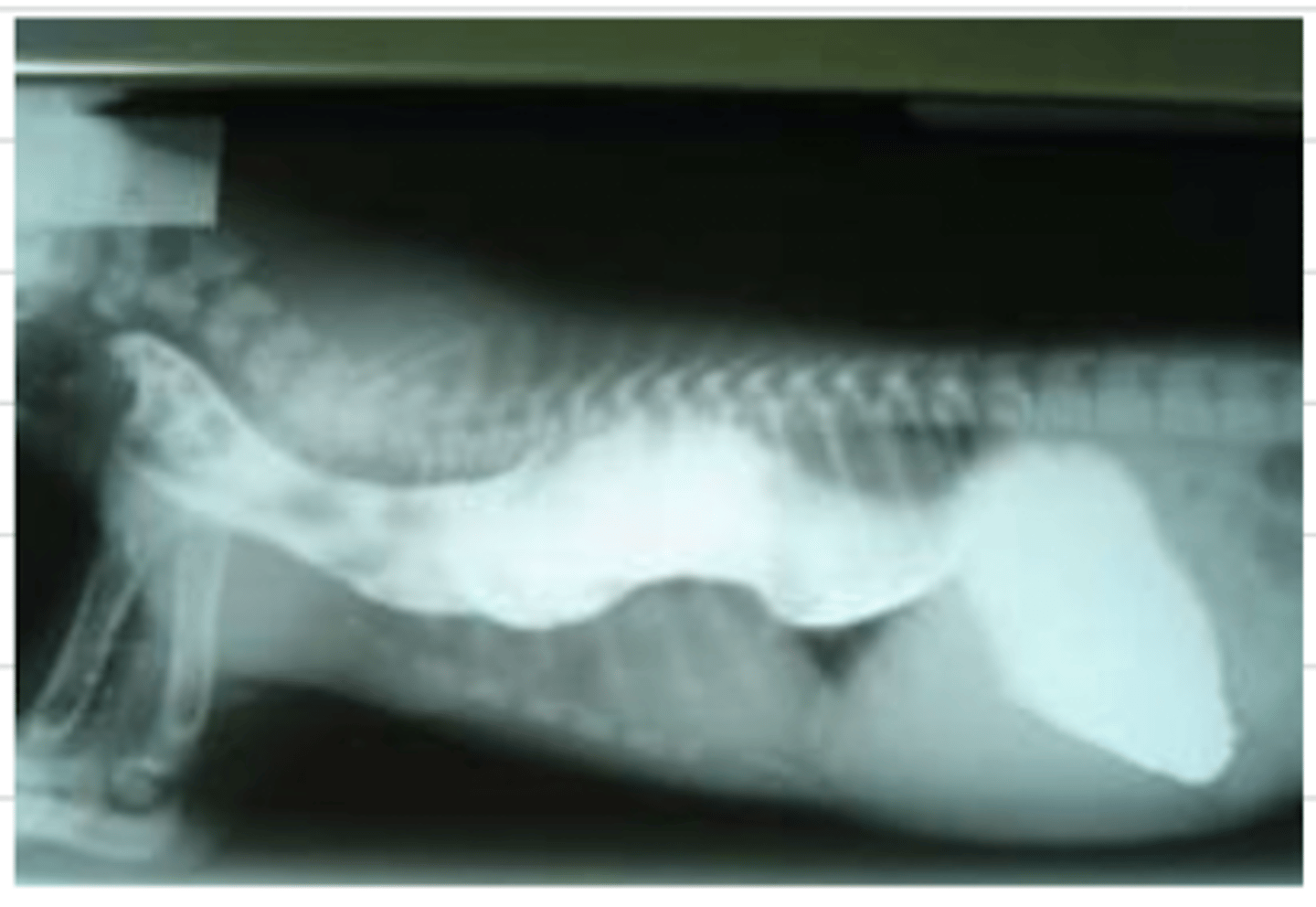
esophageal diverticulum
an endoscopy and xray of this animal reveals these findings- what is the diagnosis?
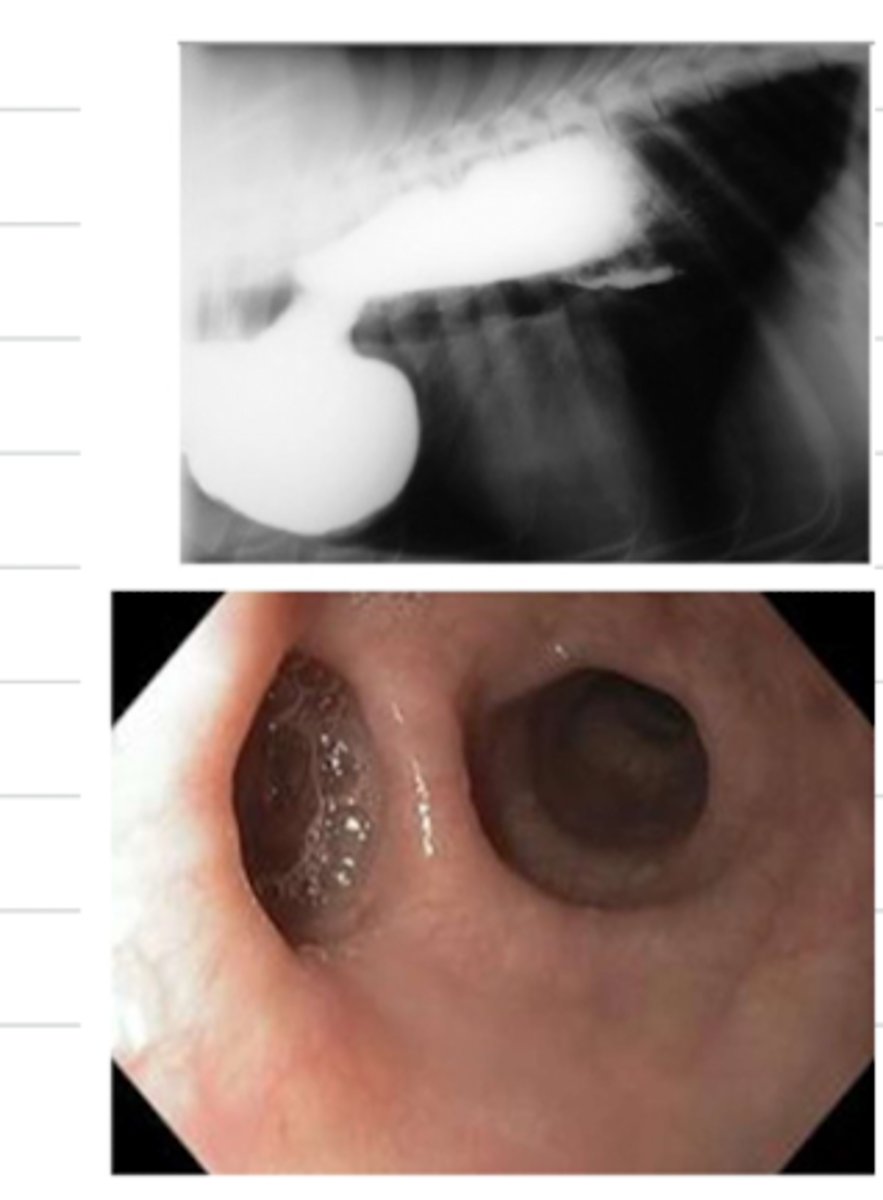
-regurgitation
-retching
-anorexia
(usually unpainful)
what are the symptoms of an animal with an esophageal diverticulum?
-control the size and frequency of food passing to the intestines
-start protein and fat digestion
-vitamin and mineral absorption
what are the functions of the stomach?
-vomiting
-abdominal pain
what are the 2 main symptoms of a gastric disorder?
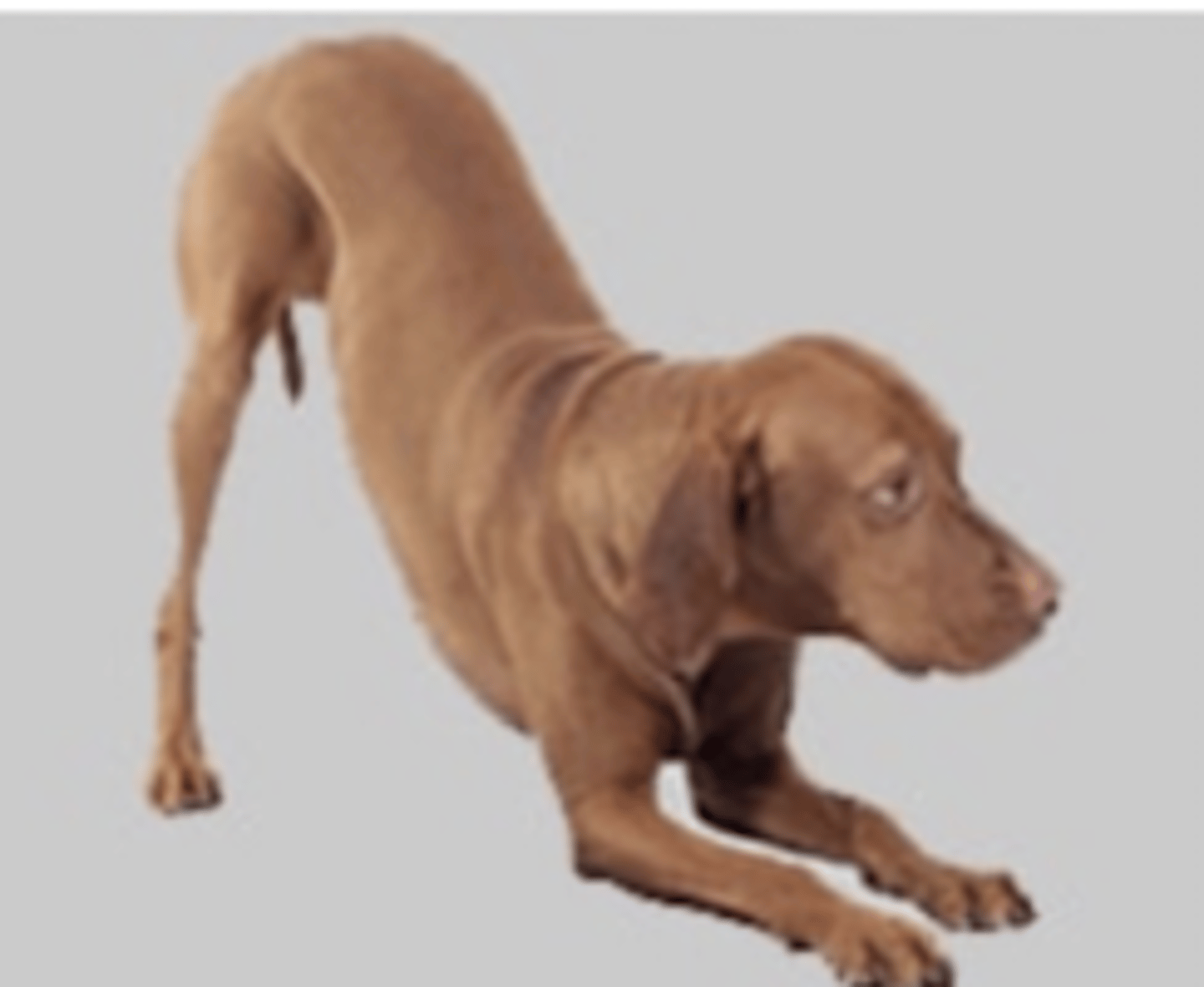
prayer position
abdominal pain due to gastric dysfunction
this position is called _______, and it is a sign of what?

false- vomiting does not indicate that the problem is ONLY in the stomach, it can be secondary to another disorder
true or false- vomiting always is due to a primary gastric disorder
the active ejection of the contents of the stomach and upper intestine
define vomit
common- dogs, pigs, cats
uncommon- horses
vomiting is common in what animals? it is uncommon in what animals?
no, it is a symptom
is vomiting a disease?
1. sickness/nausea
2. retching
3. vomit
what are the phases of vomiting?
rhythmic inspirations with a closed glottis
-intrathoracic pressure decreases while intraabdominal pressure increases
-inhibition of gastric motility
-retrograde contraction of the small intestine and pylorus
-cardia and LES dilation- content is transferred to the esophagus
what is retching?
small intestine and pylorus (they contract in a retrograde manner)
what structures contract in order to retch?
abdominal muscles and diaphragm
during vomiting, what muscles are mainly contracting?
CNS centers
peripheric receptors
chemoreceptors- by emetic substances
what 3 different categories can stimulate the vomit center in the brainstem?
-trauma
-hydrocephalus
-vestibular system
-psychological reasons
-acute pain
what problems can stimulate the CNS to stimulate the vomiting center?
-abdominal musculature
-salivary glands
-sphincters, stomach, esophagus, duodenum
when the vomit center in the brainstem is stimulated, what structures are then stimulated?
-duodenum
-pancreas
-liver
-kidney
-genitals
peripheric pain receptors located in the ___________, when stimulated, trigger the vomit center.
vagus nerve
vomit center in the brainstem
when peripheric pain receptors located in the duodenum, pancreas, liver, kidney, or genitals are stimulated, the ______ nerve stimulates the ______
because the vestibular system can stimulate the vomit center- they are very close to eachother
how can motion cause vomiting?
by triggering the CTZ (chemoreceptor trigger zone)
how can drugs induce vomiting?
-gastritis
-ulcers
-neoplasia
-flow obstruction
-foreign bodies
what gastric issues can cause vomiting?
-IBD (inflammatory bowel disease)
-neoplasia
-foreign bodies
-intussusception
-functional disorders
what intestinal issues can cause vomiting?
anything that causes pain in the kidneys, liver, pancreas, spleen, or urogenital tract
-genitourinary disease
-peritonitis
-pancreatitis, pancreatic neoplasia
-hepatitis, colangiohepatitis, bile obstruction
-splenic torsion
-nephritis, pielonephritis, nephrolithiasis, urinary obstruction, prostatitis, pyometra
what intraabonimal but unrelated to the GI tract issues can cause vomiting?
-uremia
-hypoadrenocorticism
-diabetic ketoacidosis
-hyperthyroidism
-hypercalcemia
-septicemia
what endocrine/metabolic disorders cause vomiting?
-strychnine
-ethylene glycol
-lead
what are the most common toxins that cause vomiting?
-vestibular disease
-encephalitis
-neoplasia
-increased intracraneal pressure
what neurological disorders commonly cause vomiting?
-fluid loss (causing dehydration and hypovolemia)
-electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia, hypochloremia)
-metabolic alkalosis
-aspiration pneumonia
-reflux esophagitis
the consequences of vomiting are...
alkalosis
can vomiting cause metabolic acidosis or alkalosis?
-gastritis
-gastric ulcer
-gastric neoplasia
-foreign bodies
-gastric retention
-gastric dilation/torsion
the main monogastric stomach disorders are....
the inflammation of the gastric mucosa
gastritis is...
acute- sudden onset, short duration
chronic- persistent, prolonged, slowly evolving lesions
different etiologies!
what is the difference between acute and chronic gastritis?
-nutrition (greediness)
-coprophagia
-drugs
-chemicals
-foreign bodies
-secondary to acute nephropathy or hepatophaty, virus, bacteria, or parasites
acute gastritis might be caused by...
-long term injury
-chronic irritation due to foreign bodies
-virus (distemper, parvovirus)
-chronic nephropathy and hepatopathy
-food allergy
-chemical substances (fertilizers, pesticides)
what might cause chronic gastritis?
distemper, parvovirus
what viruses commonly cause chronic gastritis in dogs?
NSAIDs
what drug type commonly causes acute gastritis?
-abdominal pain
-vomit (severe and frequent in acute gastritis)
-appetite loss
-diarrhea (leads to dehydration)
-lethargy, weakness
-pale/yellow mucosa
the symptoms of gastritis include...
no, they are not common in dogs
are gastric ulcers a common cause of vomit in dogs?
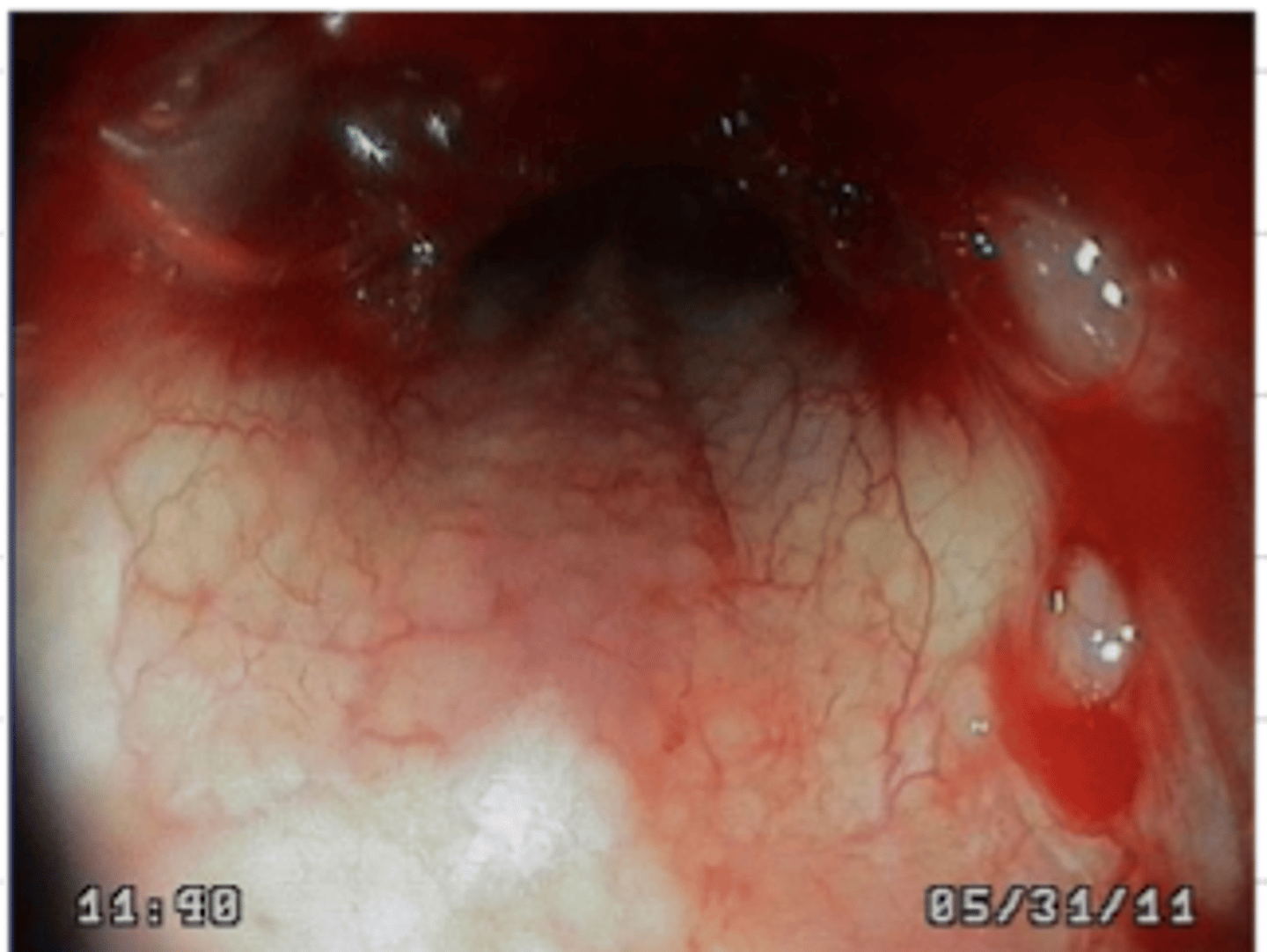
gastritis
stomach endoscopy. what disorder do we see here?
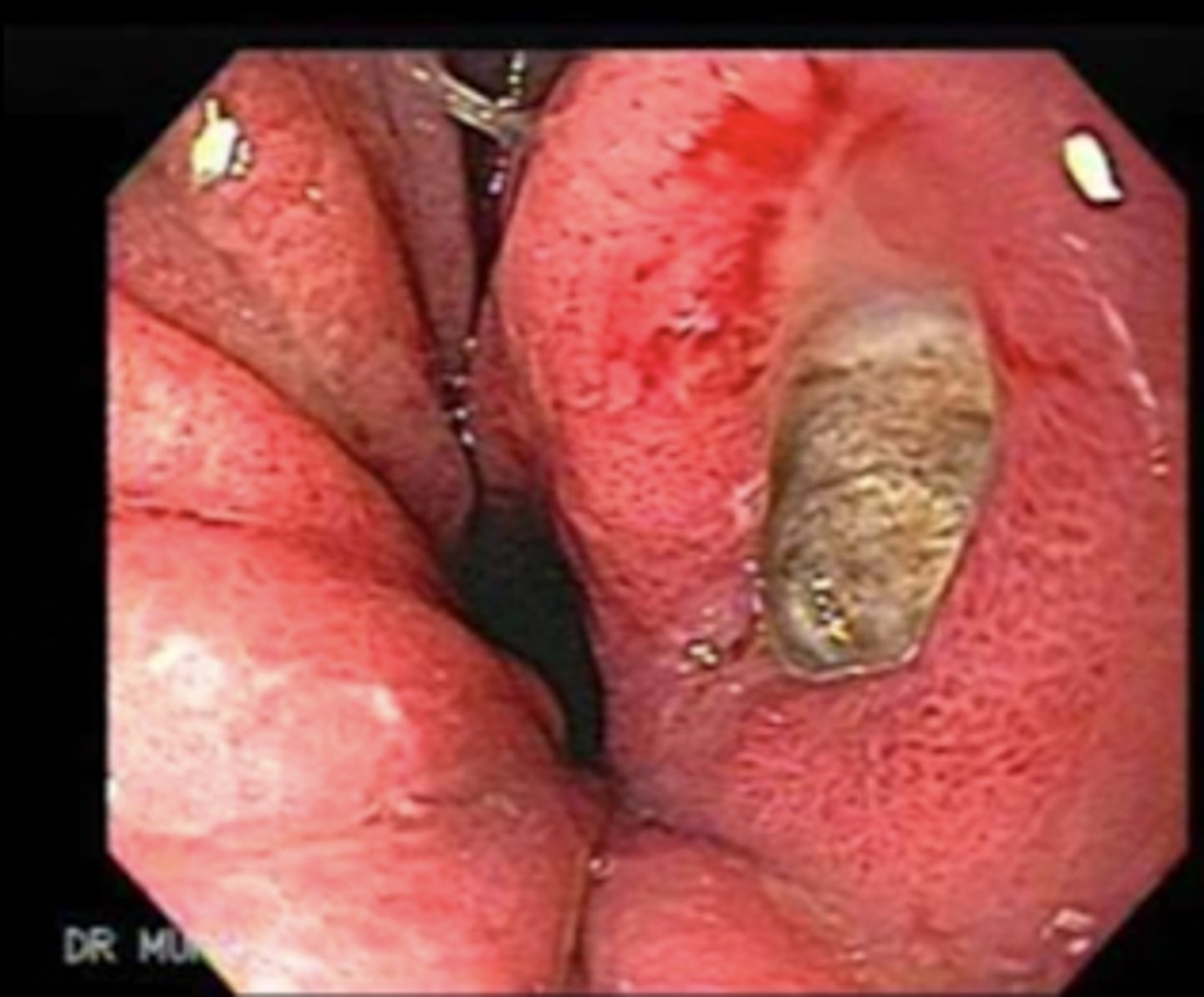
gastric ulcer
stomach endoscopy. what disorder do we see here?
-mucosa
-prostaglandins
-high blood flow
-HCO3- secretion
-inhibition of gastrin release in the antrum
how does the stomach naturally defend itself against acid to prevent ulcers?