head and neck anatomy pin test
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
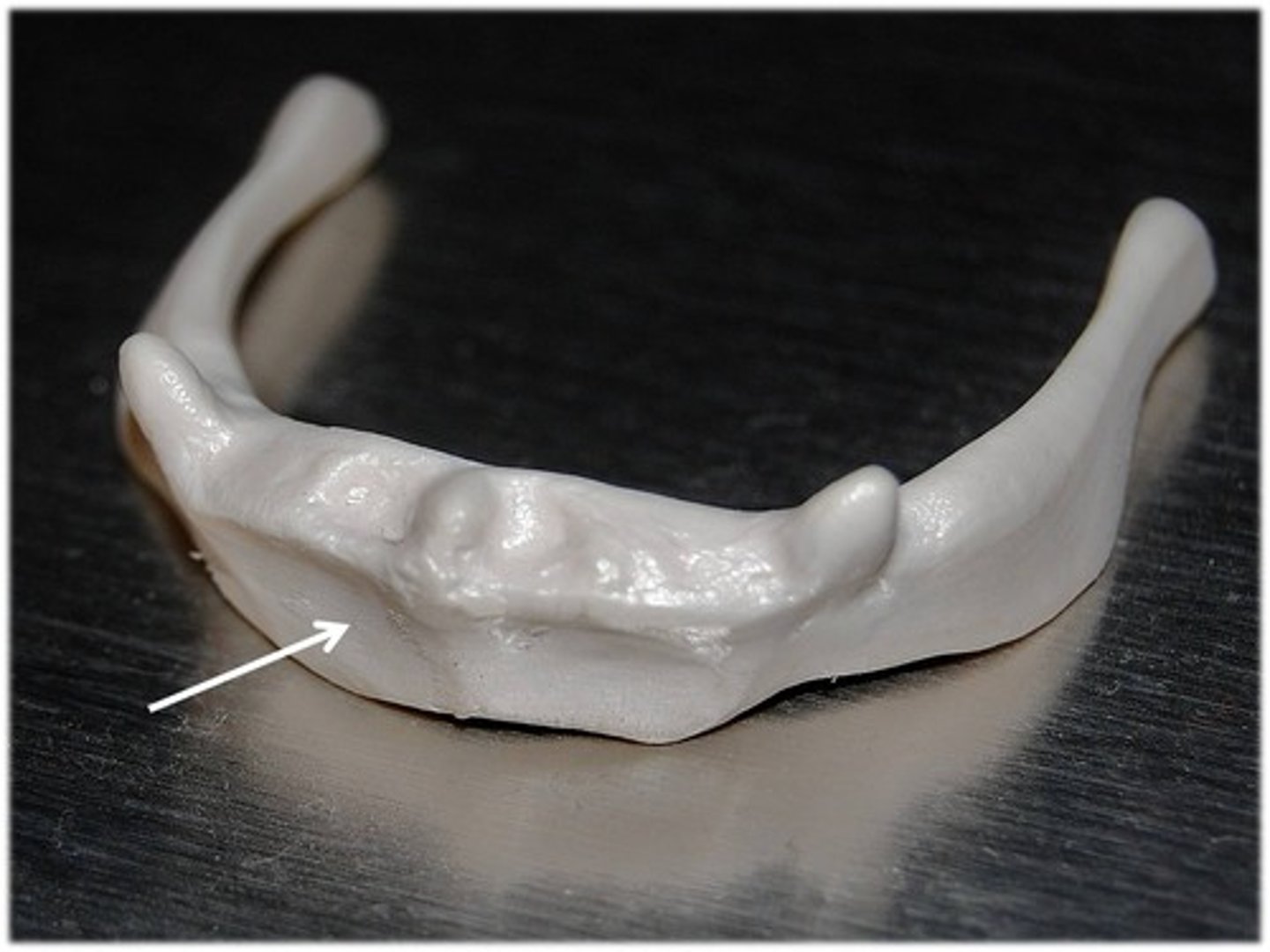
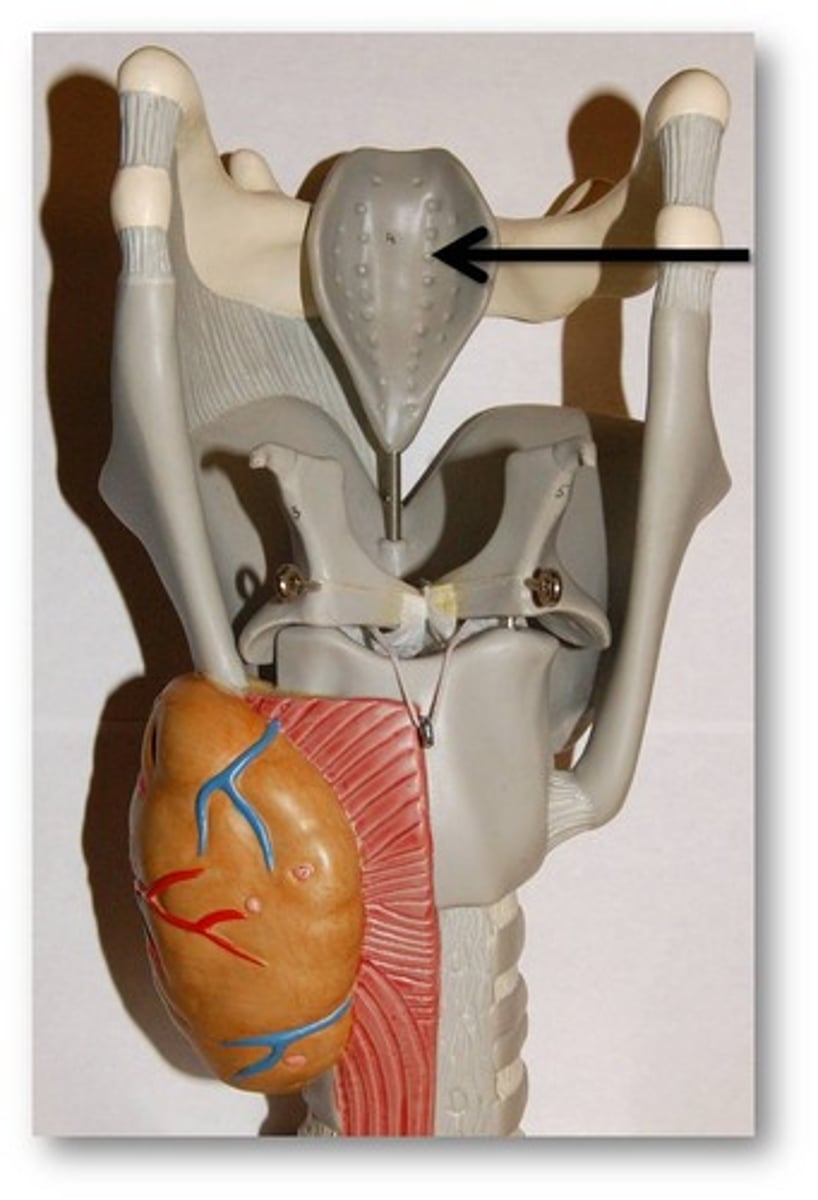
body of hyoid
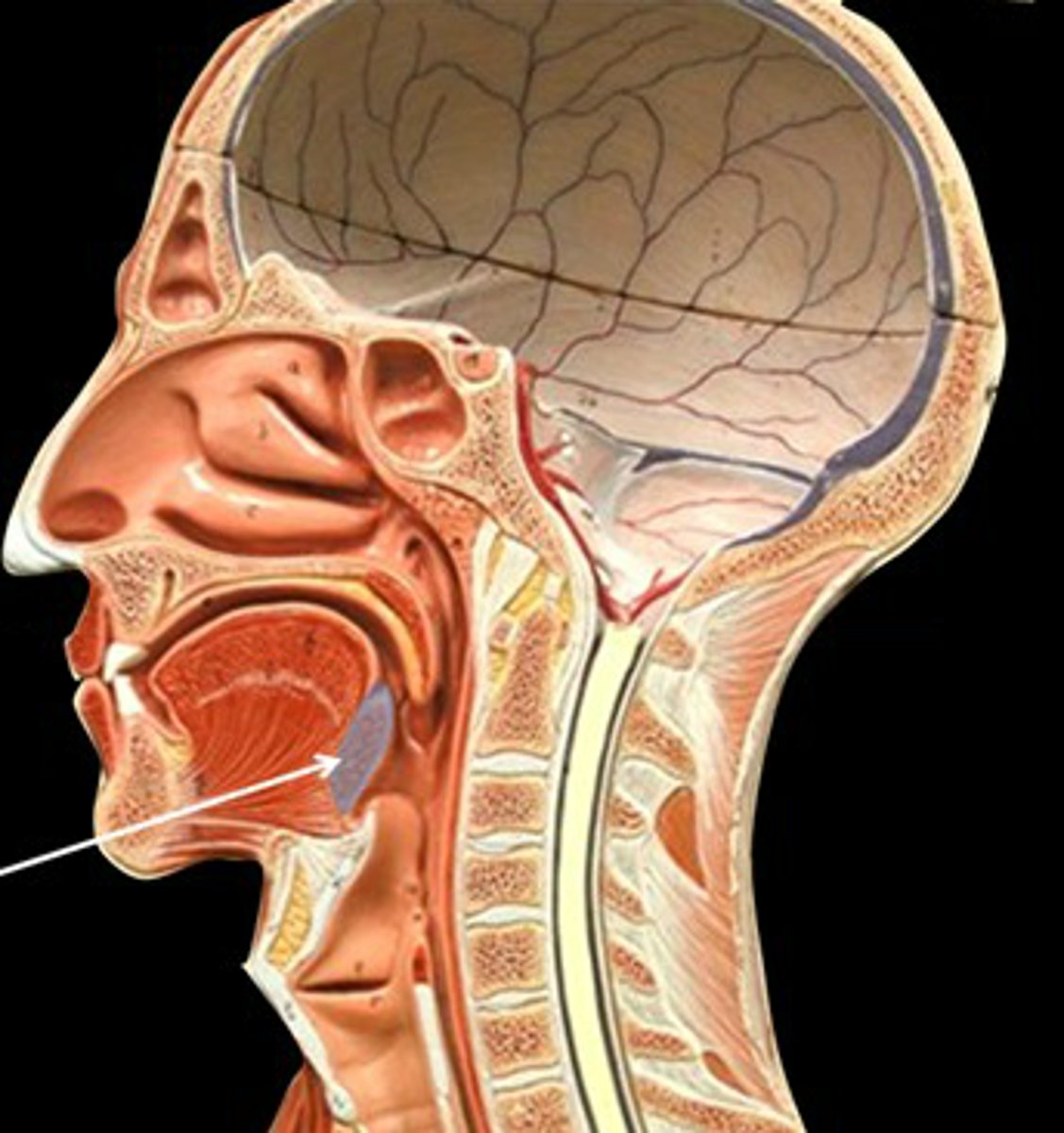
what is this structure
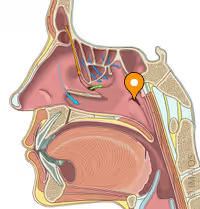
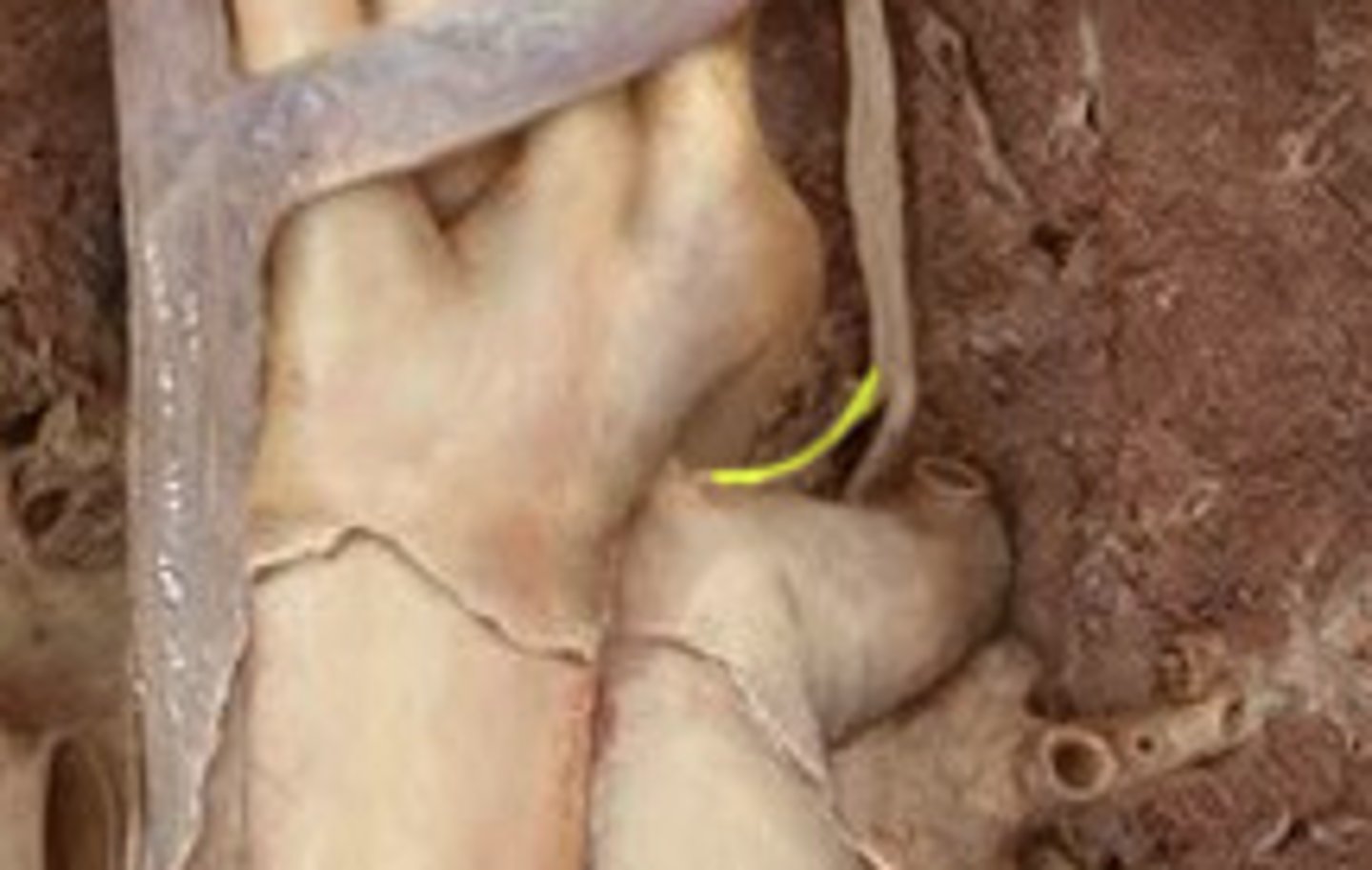
pharyngotympanic tube (eustachian tube)
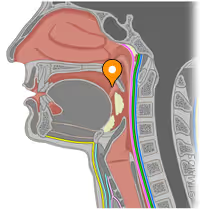
isthmus of oral fauces
what is this opening in the back of the oral cavity
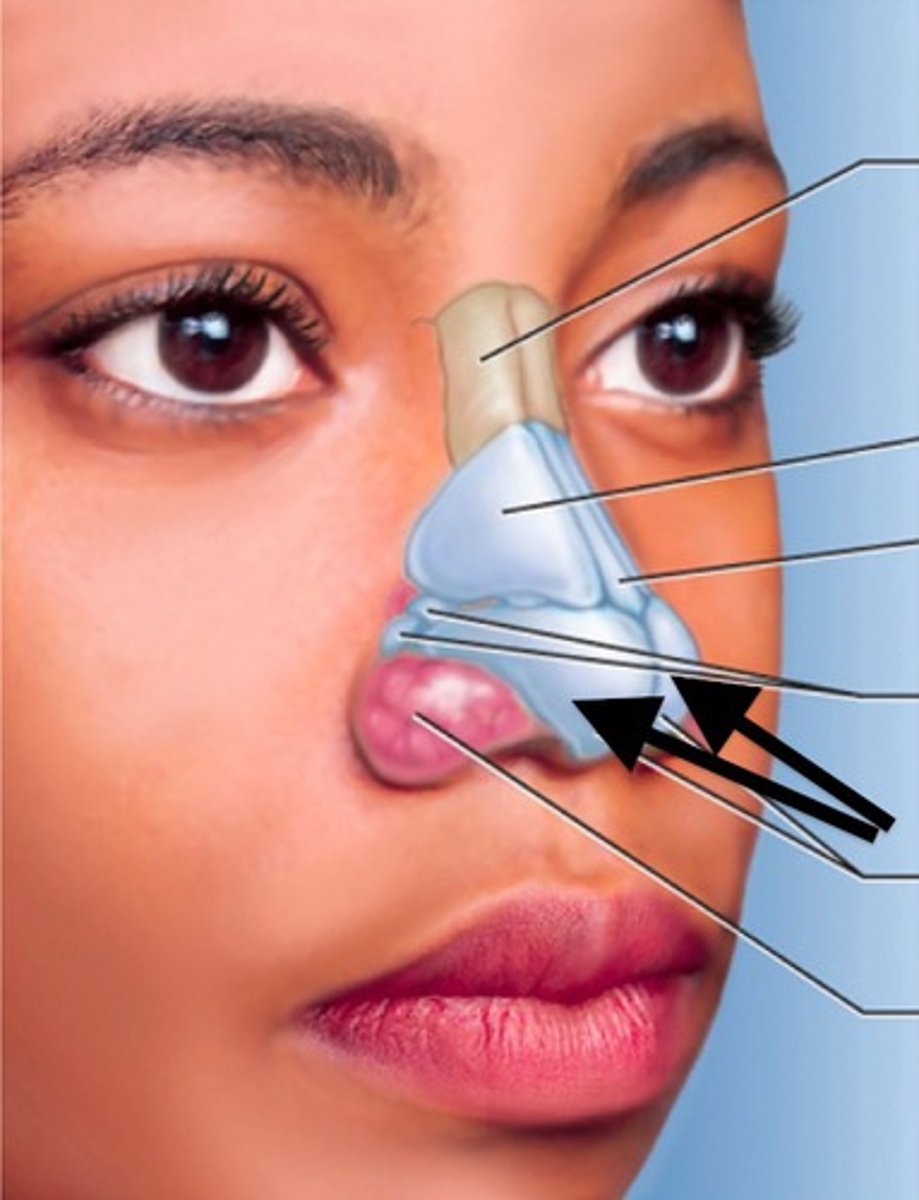
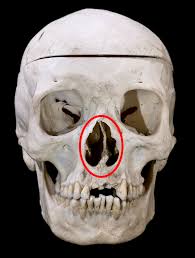
piriform apeture
internal laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal artery
what is the innervation and blood supply ABOVE the vocal cords
recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior laryngeal artery
innervation and blood supply BELOW the vocal cords
lesser horn of hyoid, stylohyoid ligament
structure and what attaches here
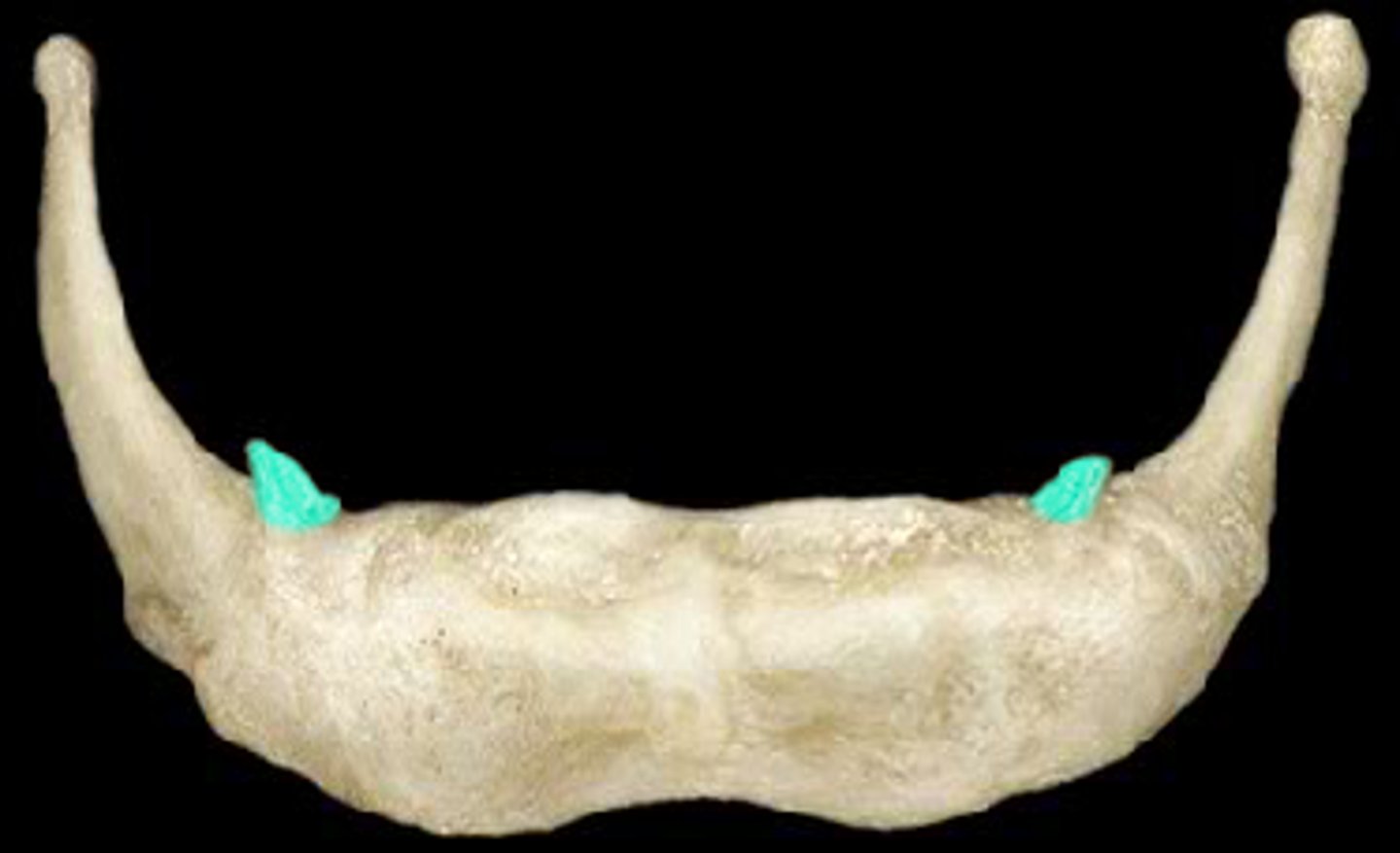
pharyngeal tubercle, superior constrictor muscle
structure, what attaches here
greater horns of hyoid, middle constrictor muscle
structure and what attaches heree
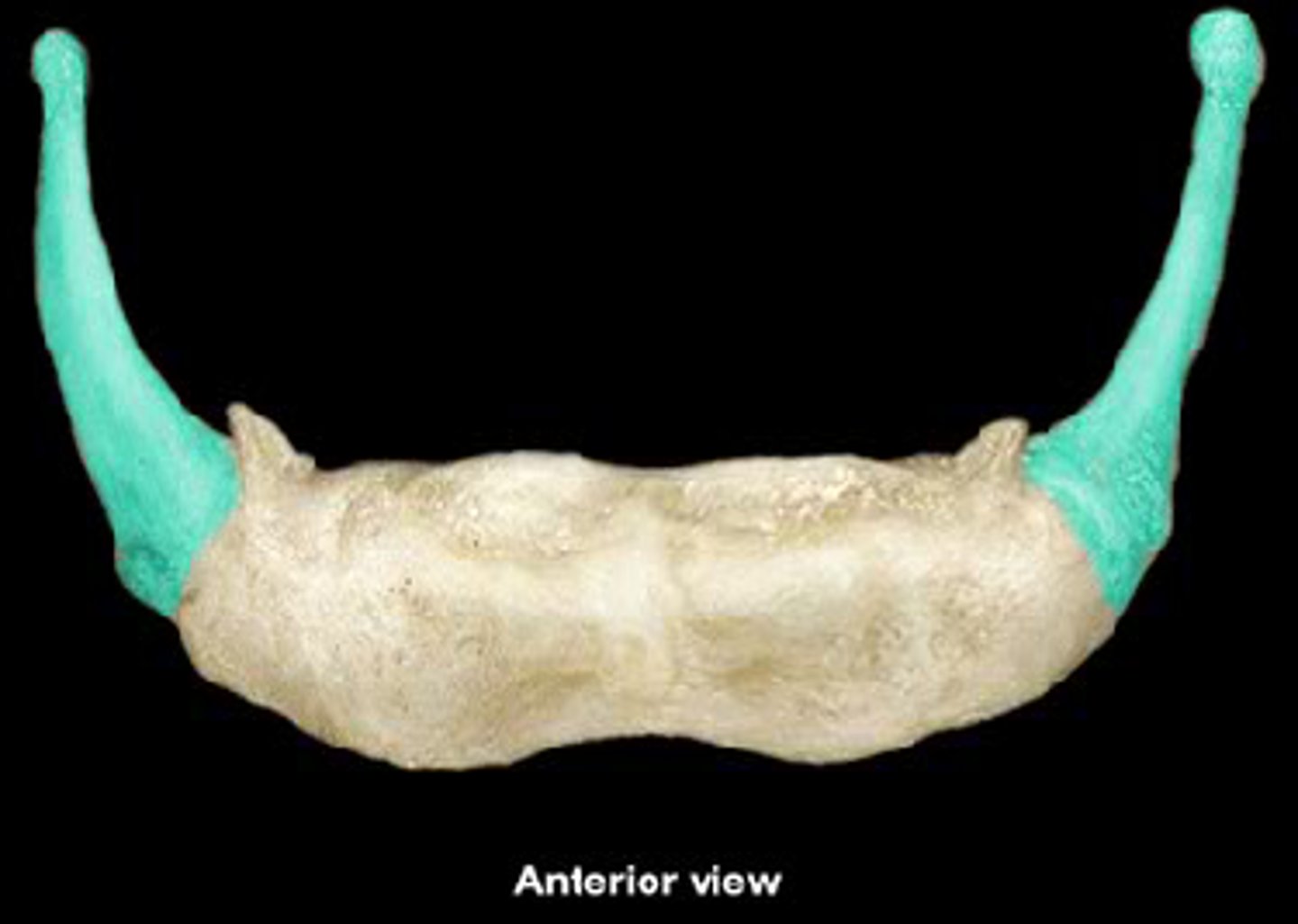
thyroid cartilage, inferior constrictor
structure and what attaches here
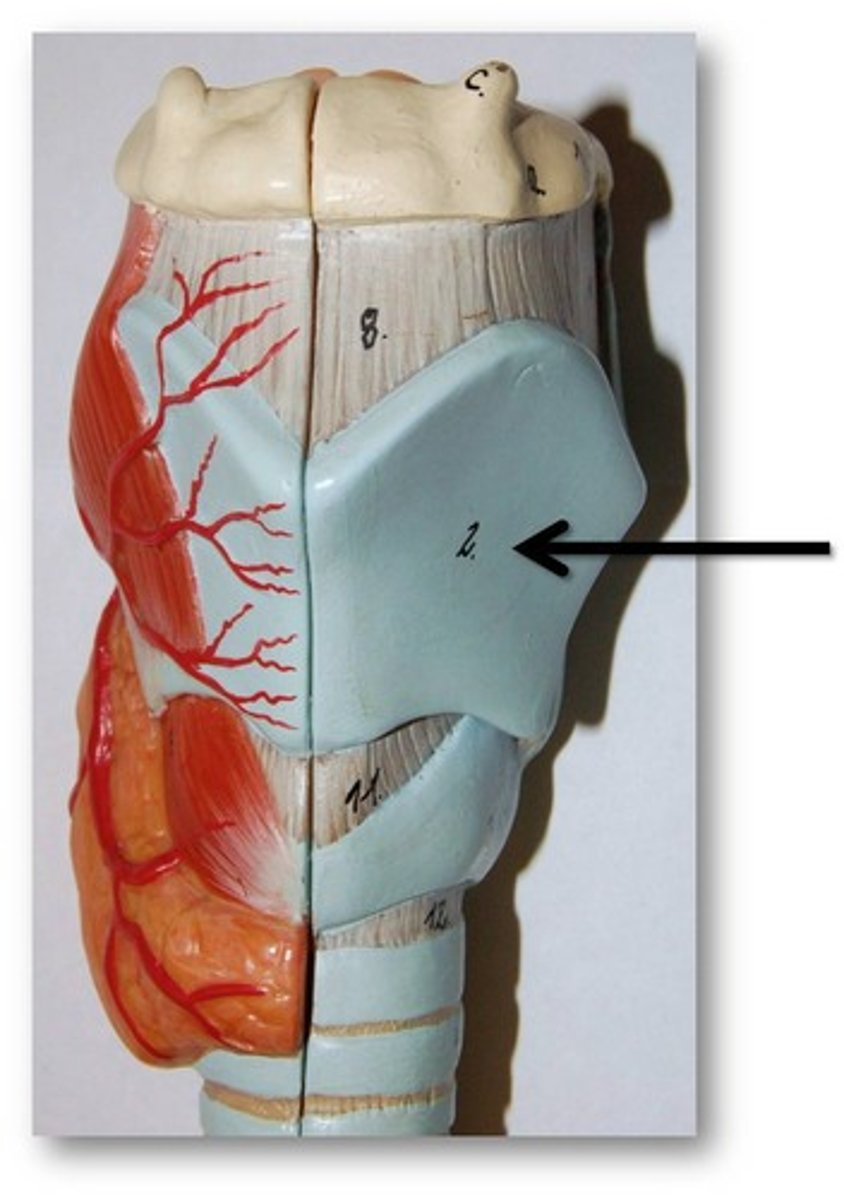
cricoid cartilage
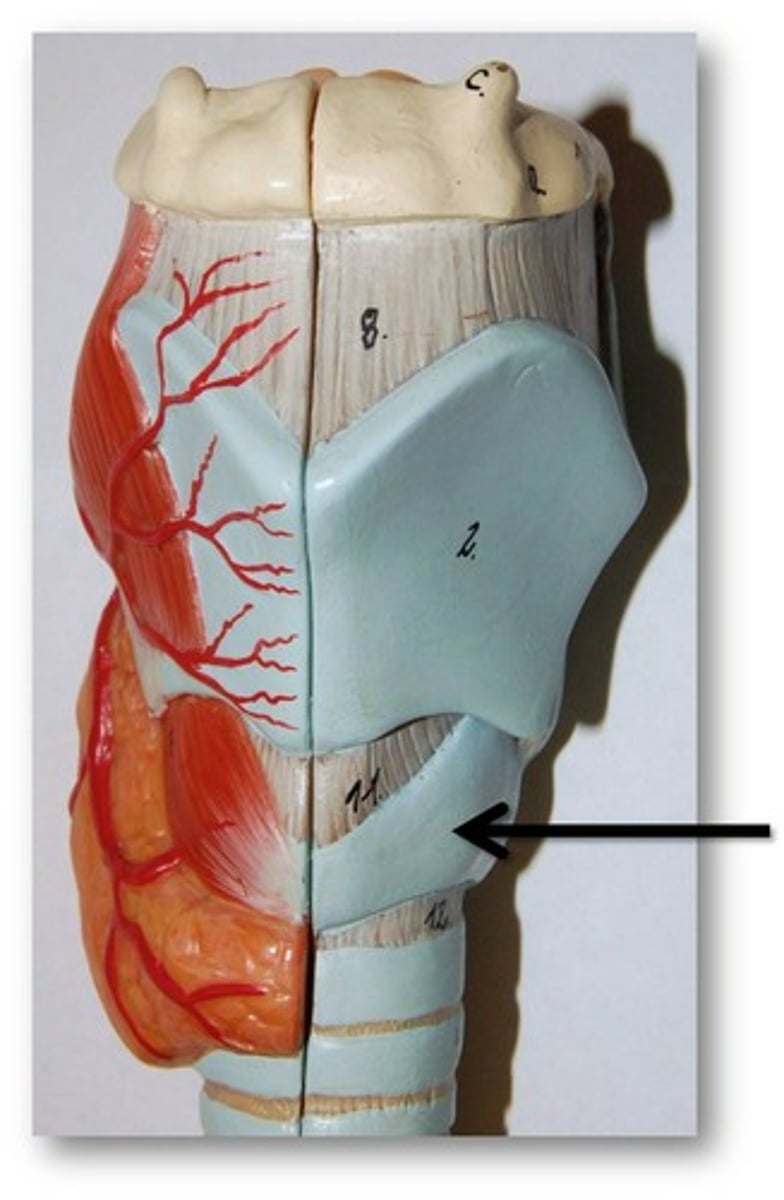
tracheal rings
pharyngeal raphe
Posterior midline attachment for the constrictors

stylohyoid ligament
holds the hyoid bone in place.
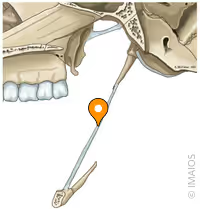
pterygomandibular raphe, superior constrictor
structure and what attaches here
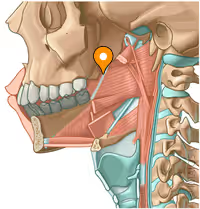
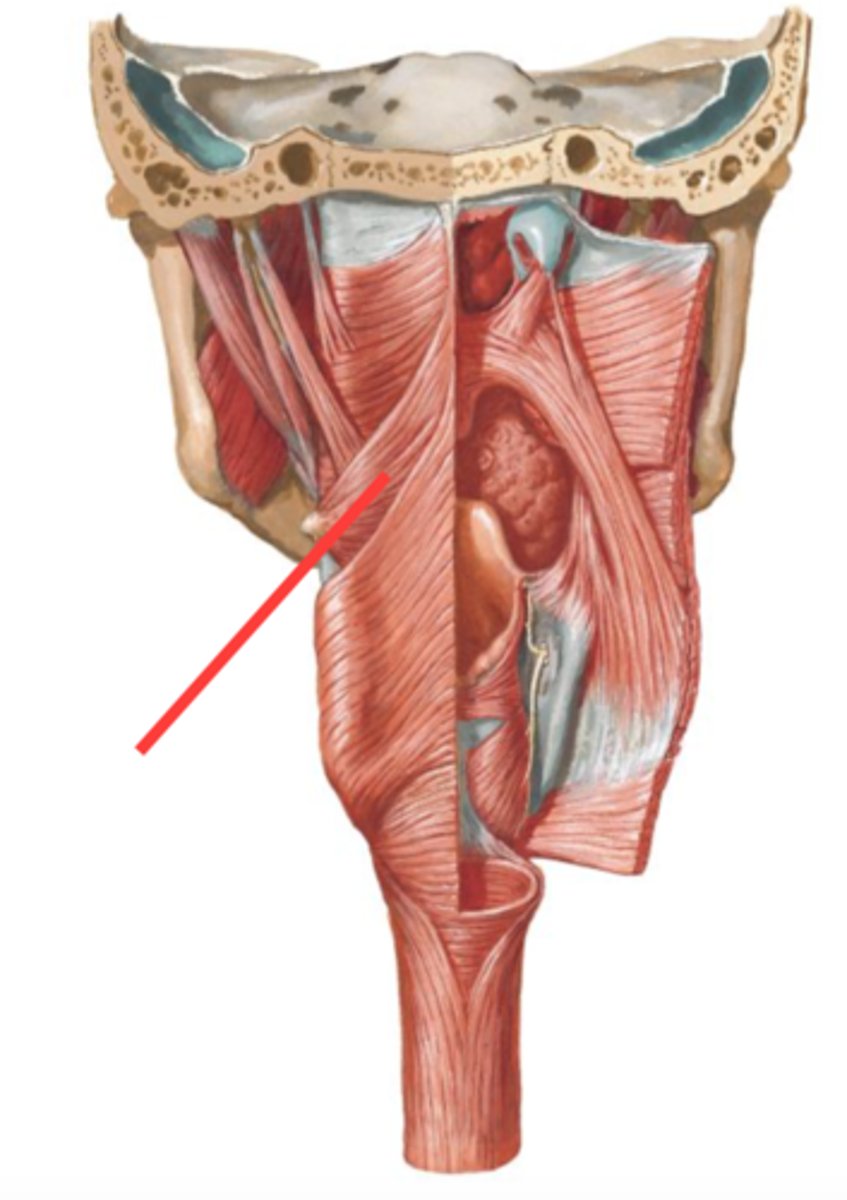
thyrohyoid membrane, internal laryngeal nerve and superior laryngeal artery
structure and what passes through it
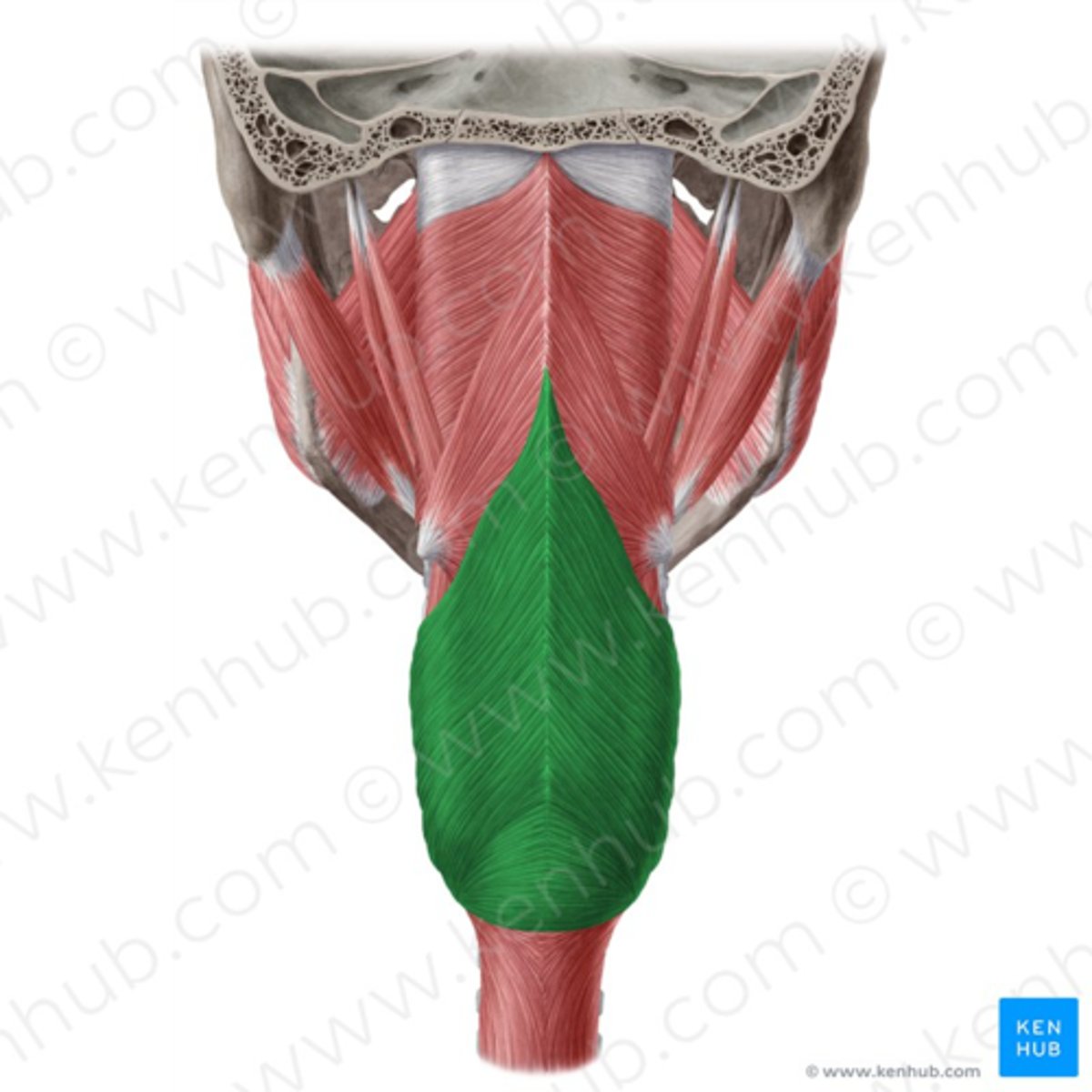
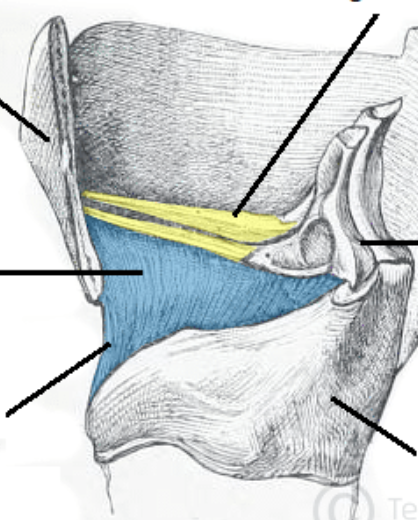
superior constrictor (CN X)
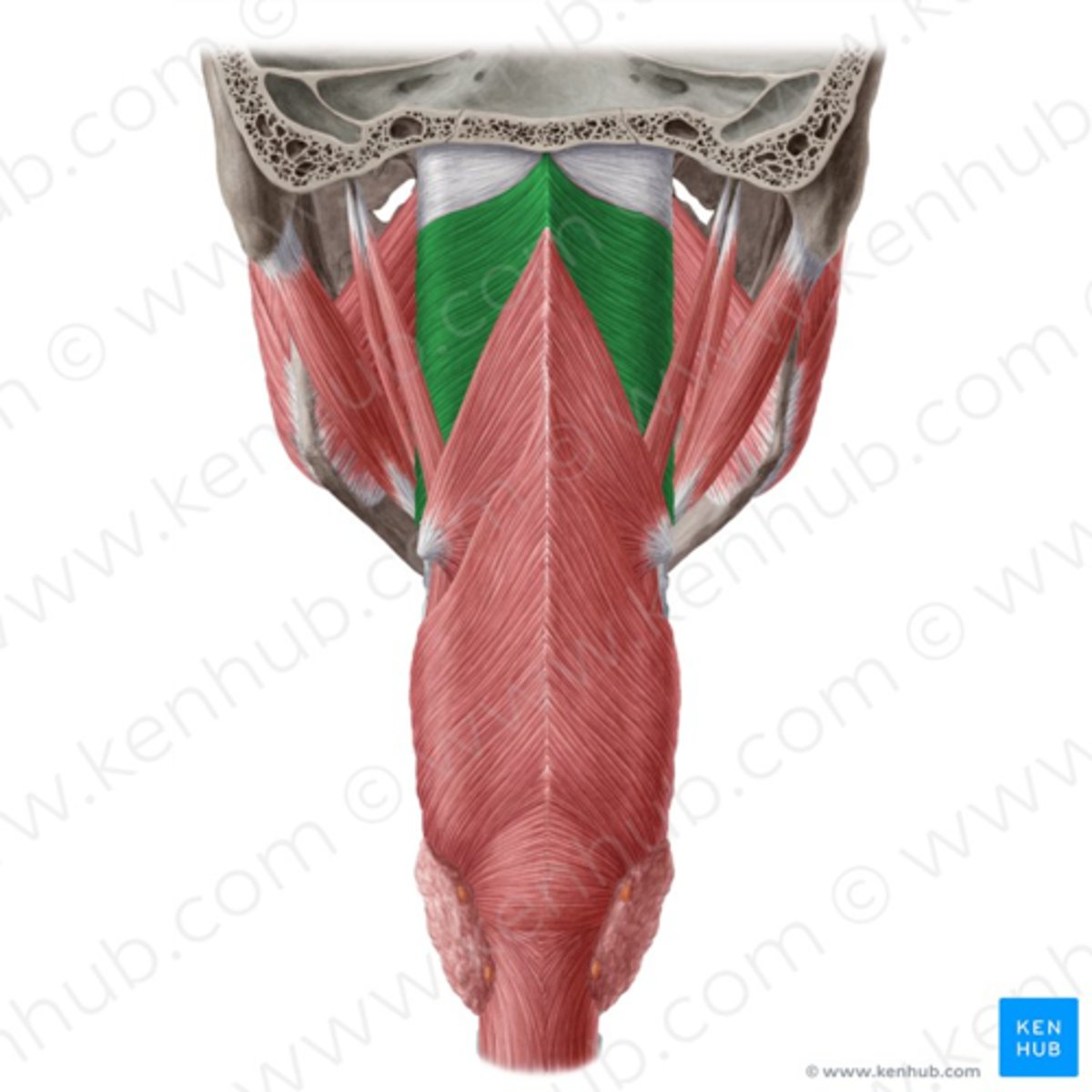
middle constrictor (CN X)
inferior constrictor (CN X)
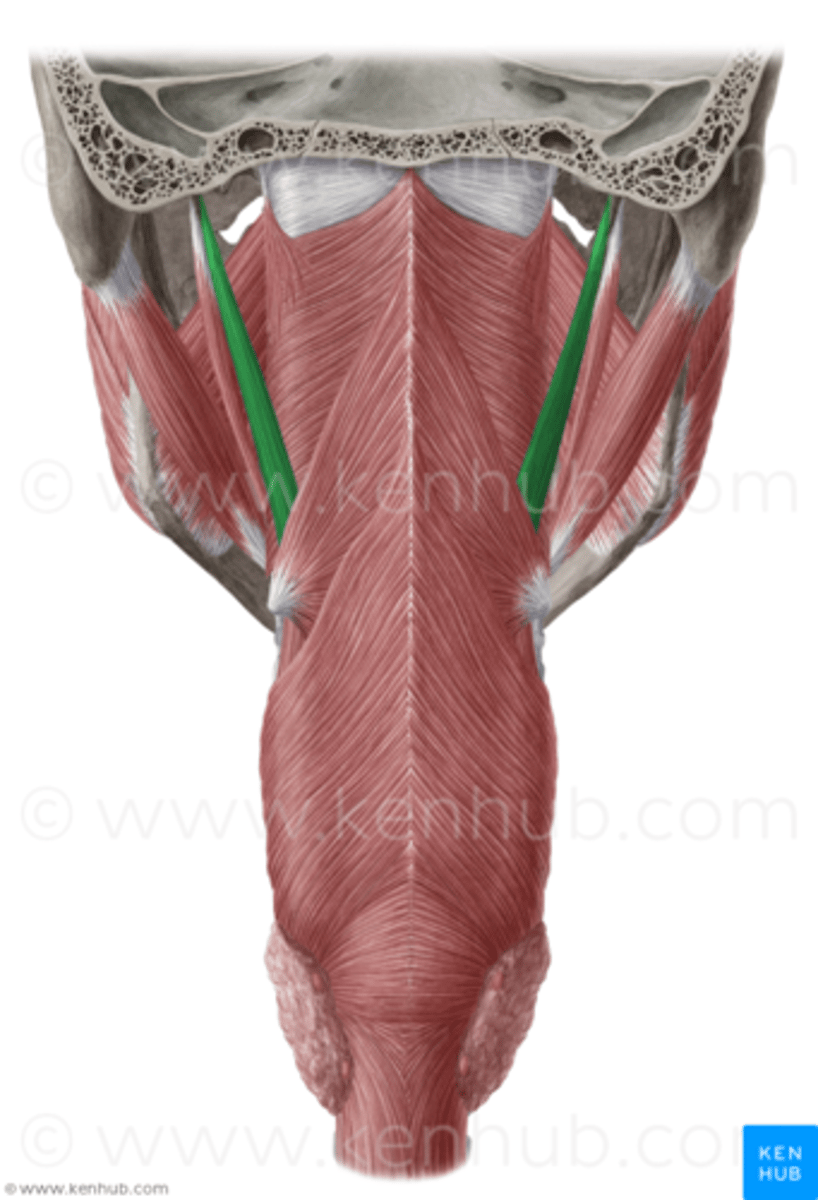
Stylopharyngeus (CN IX)
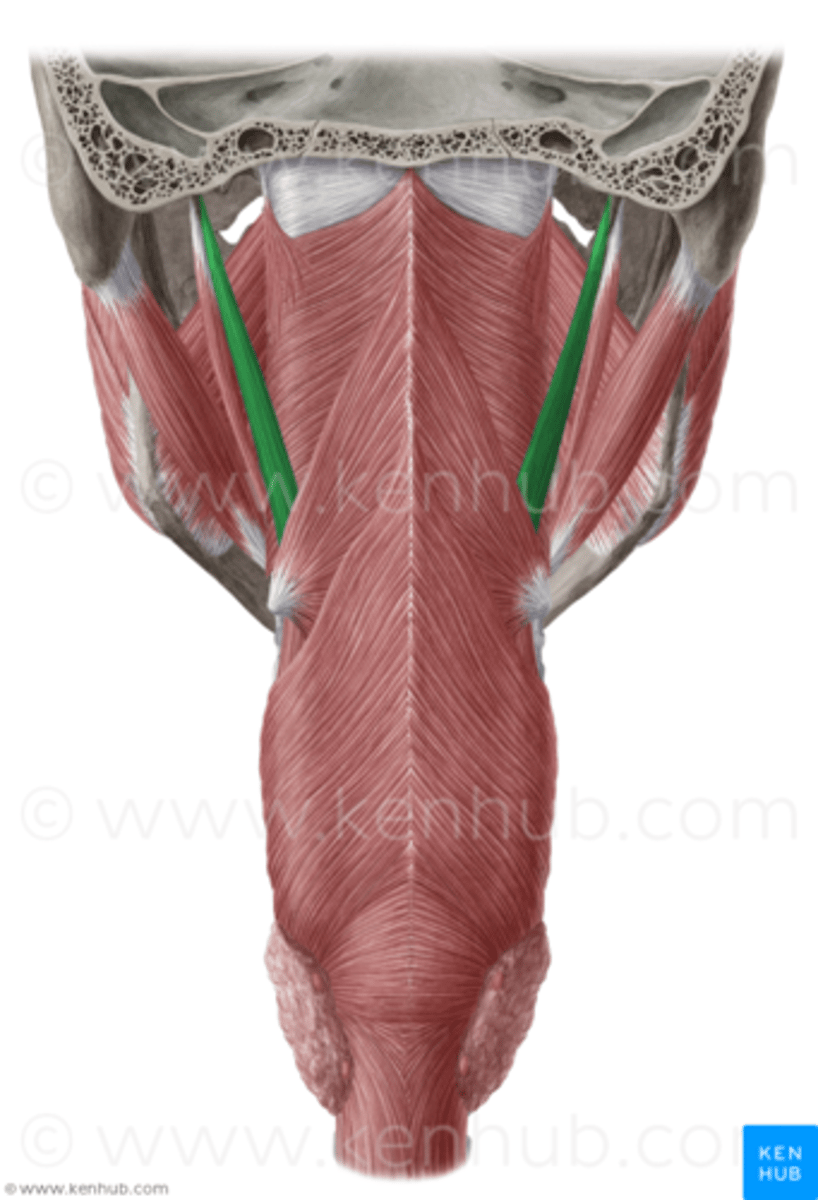
CN IX (glossopharyngeal)
what innervates this muscle?
internal laryngeal nerve
SENSORY innervation to larynx ABOVE vocal cords
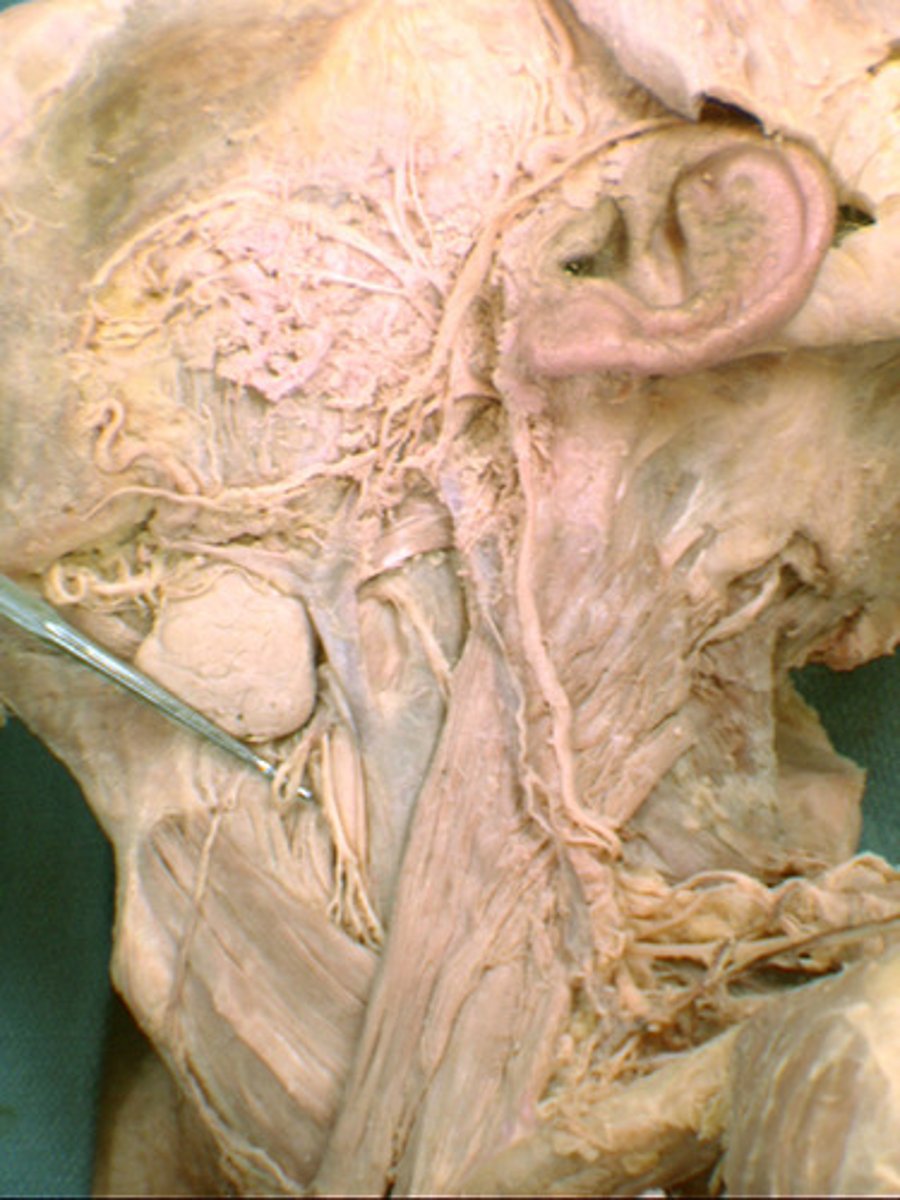
recurrent laryngeal
SENSORY nerve to larynx BELOW to vocal cords
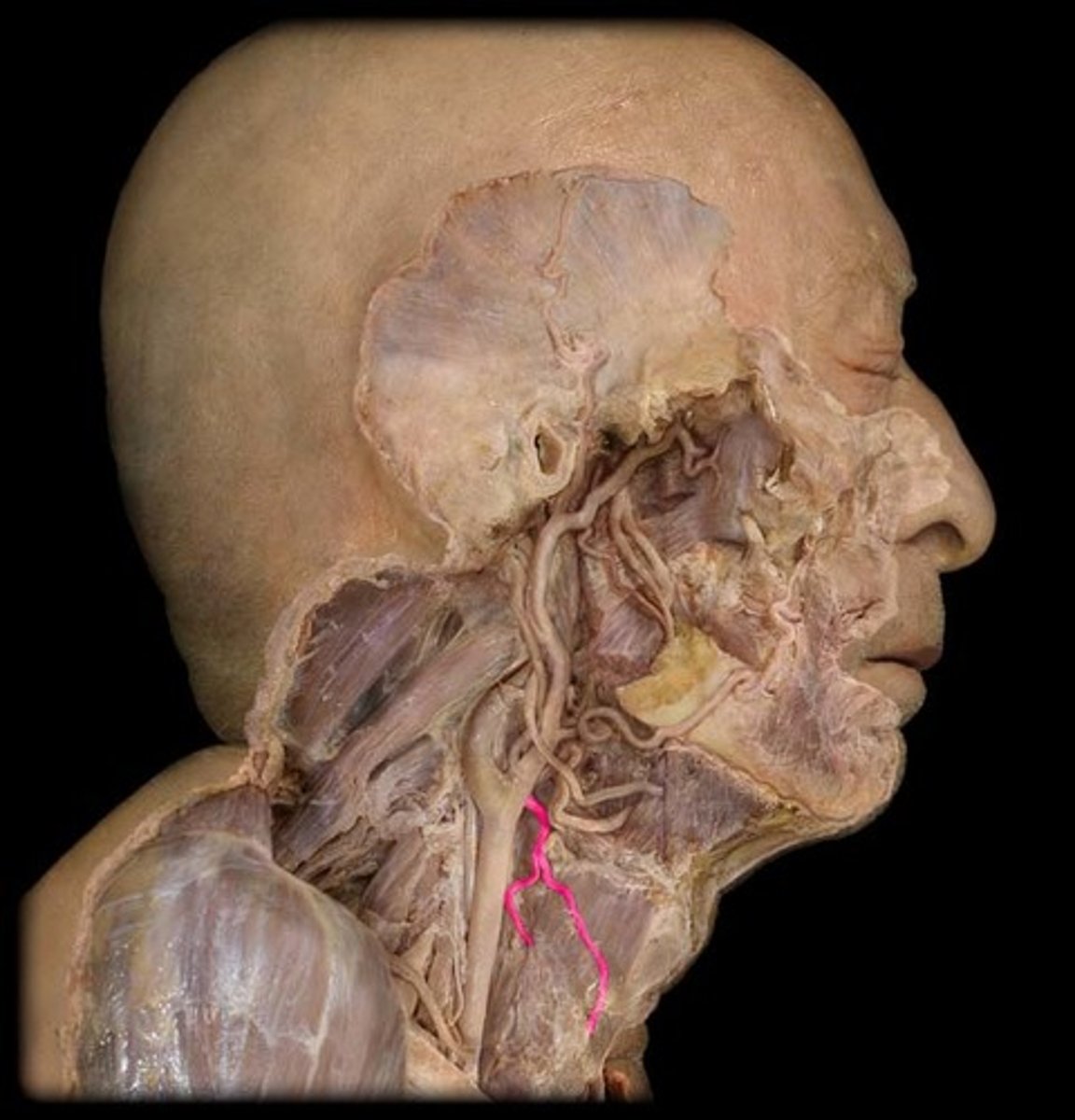
sympathetic trunk and superior cervical sympathetic ganglion
supplies postganglionic sympathetic innervation to the smooth muscle and glands in the head
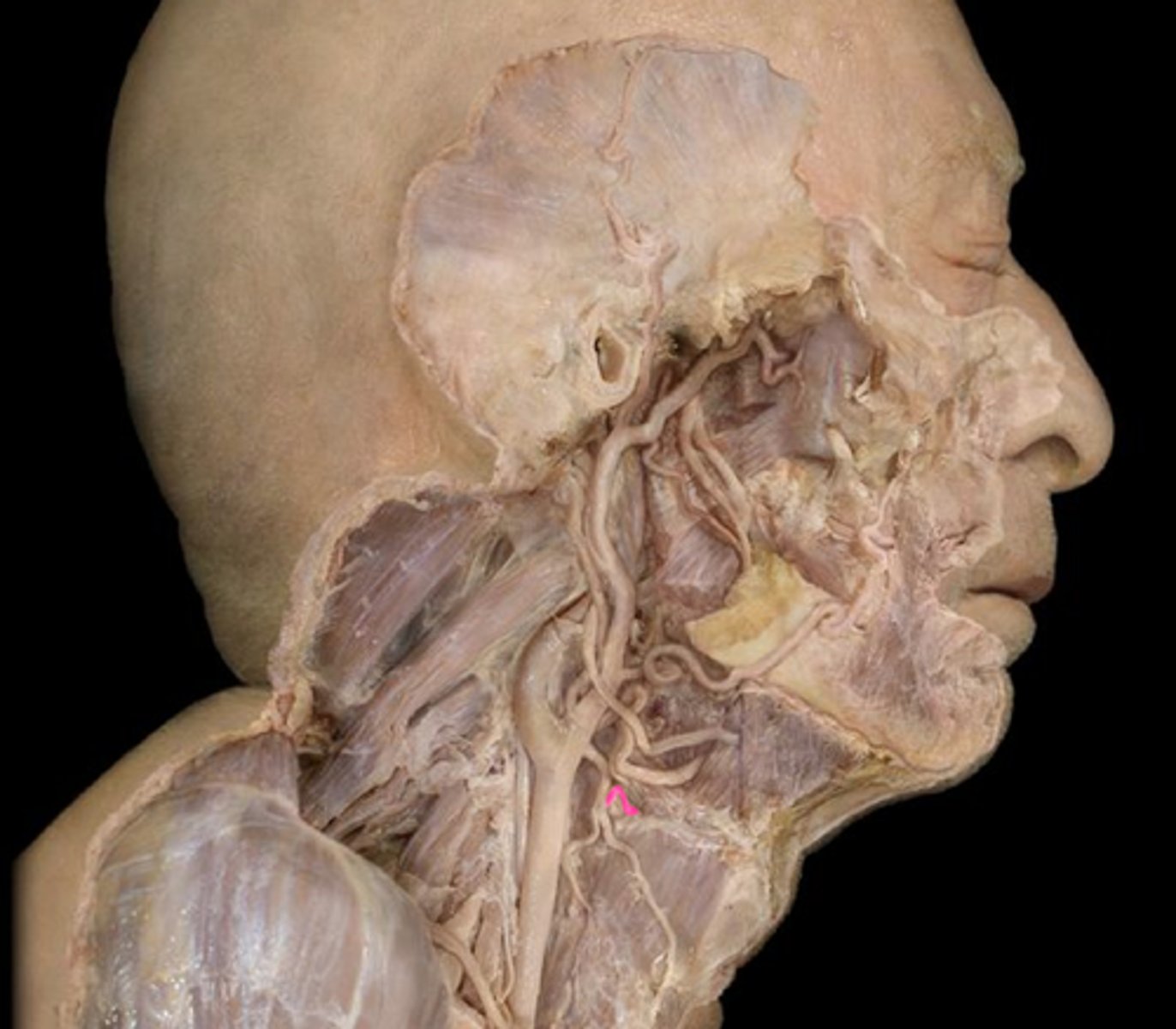
superior thyroid artery
superior laryngeal artery
Travels with internal laryngeal nerve through the thyrohyoid membrane
epiglottis
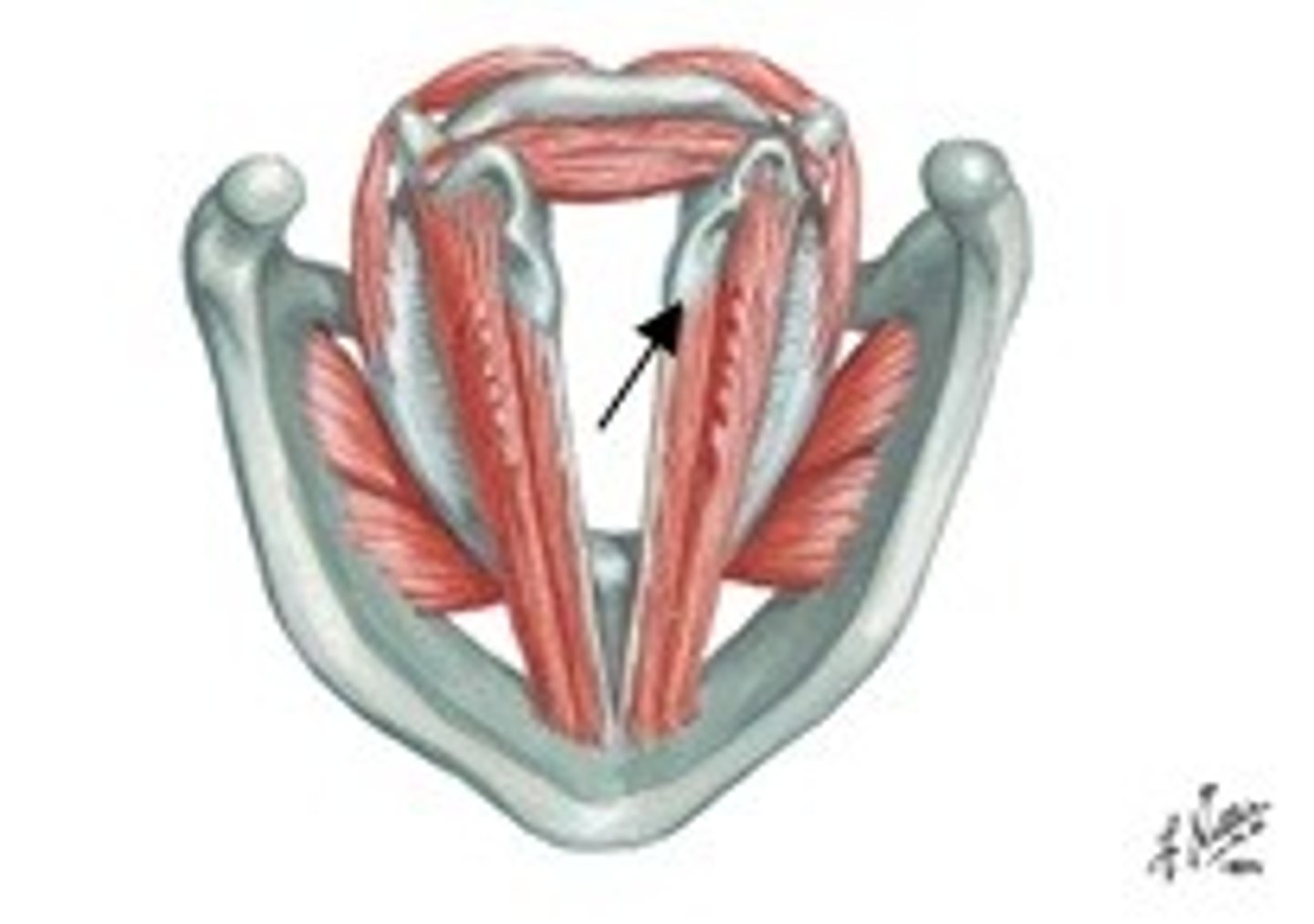
muscular process of arytenoid
Attaches to posterior and lateral cricoarytenoid muscles
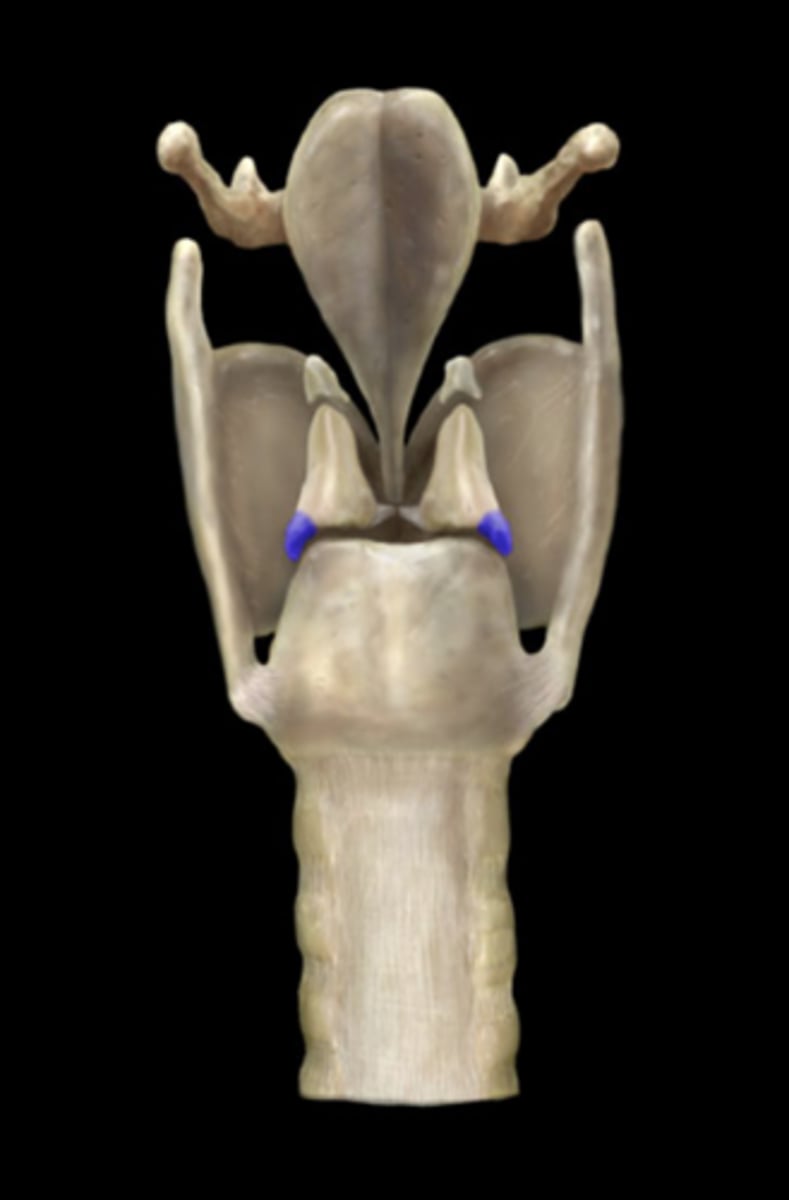
vocal process of arytenoid
Attached to vocal ligament
arytenoid cartilage
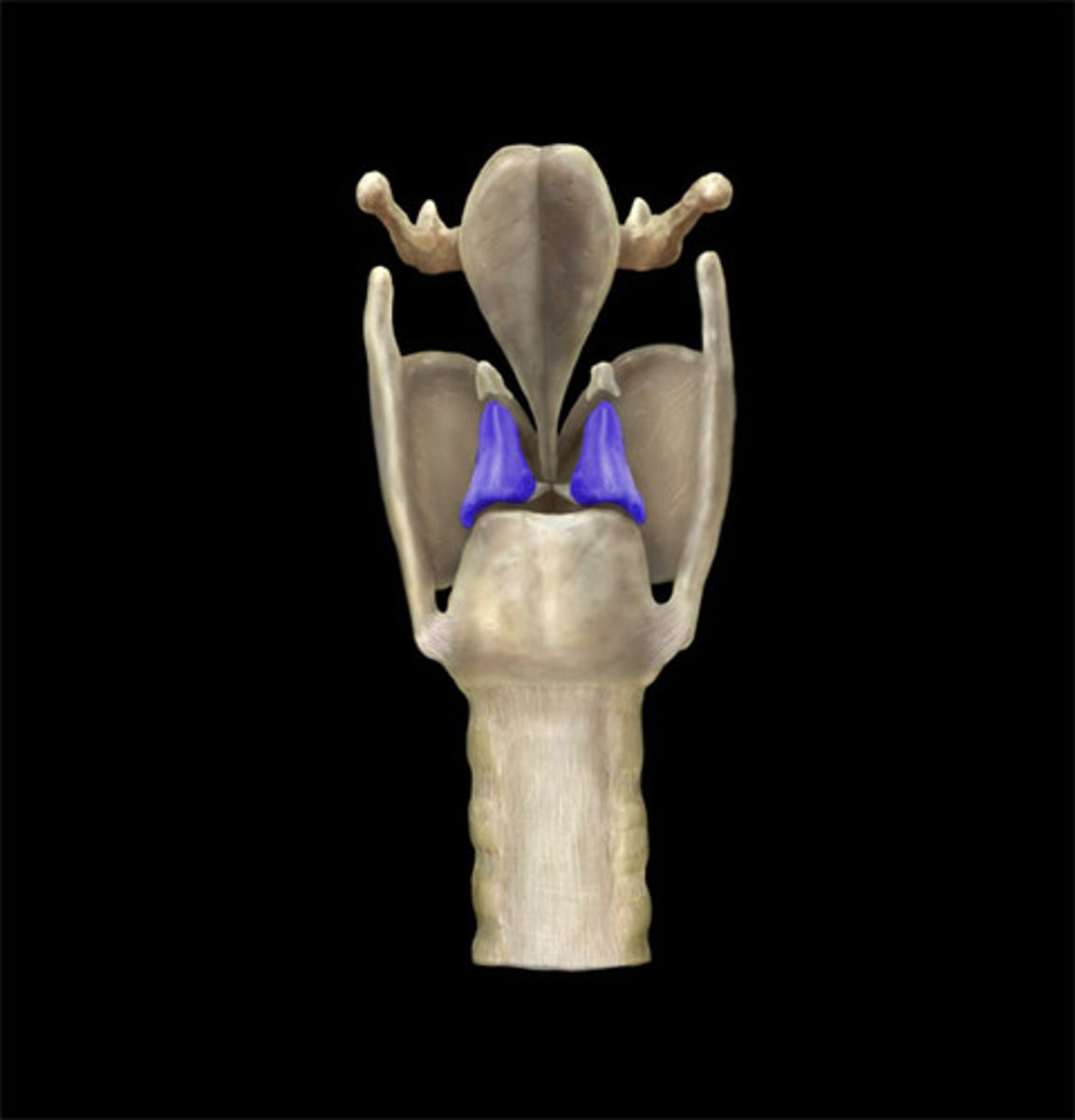
cricoarytenoid joint
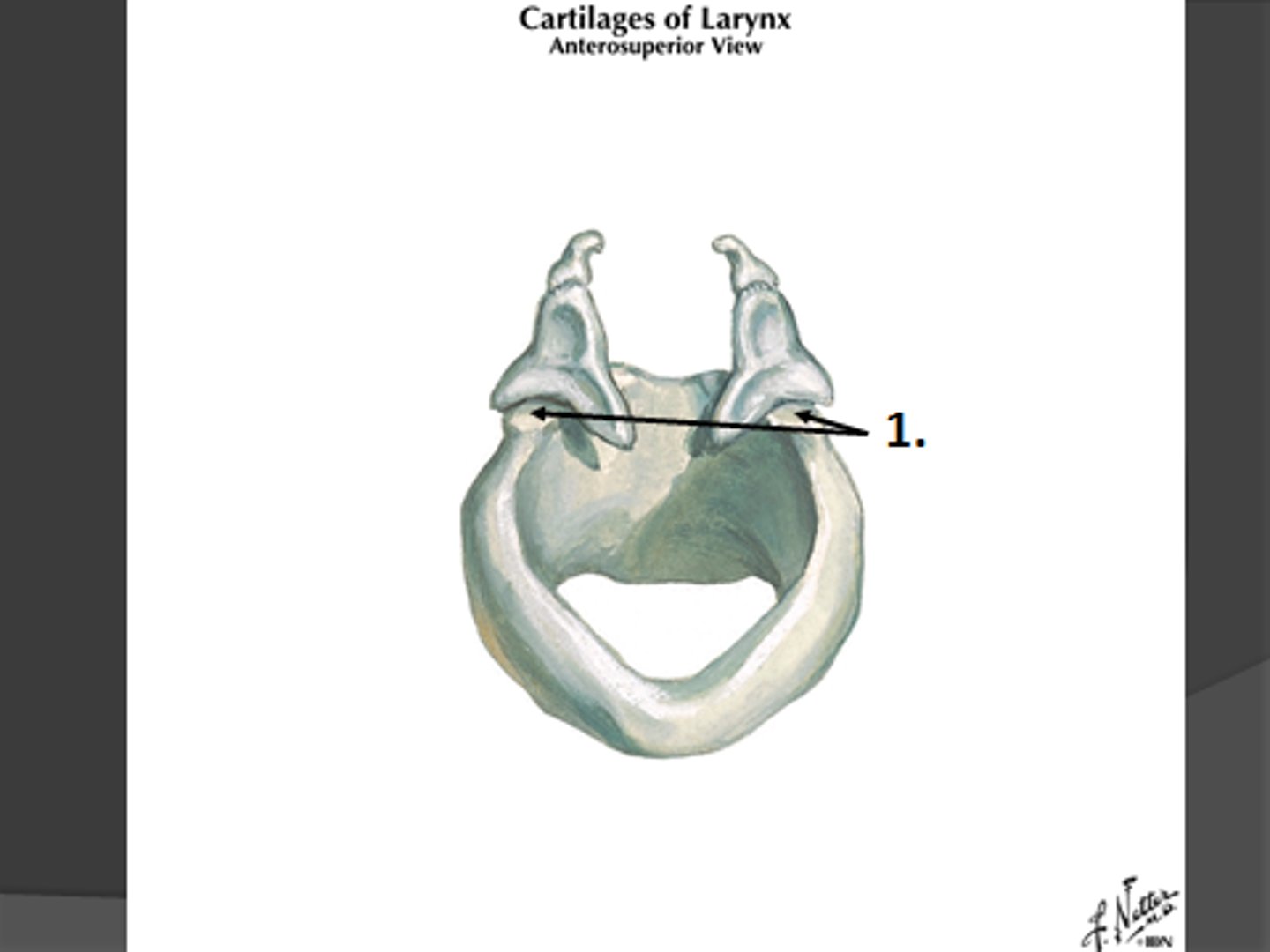
quadrangular membrane
lateral side of the epiglottis all the way to the ventricular fold
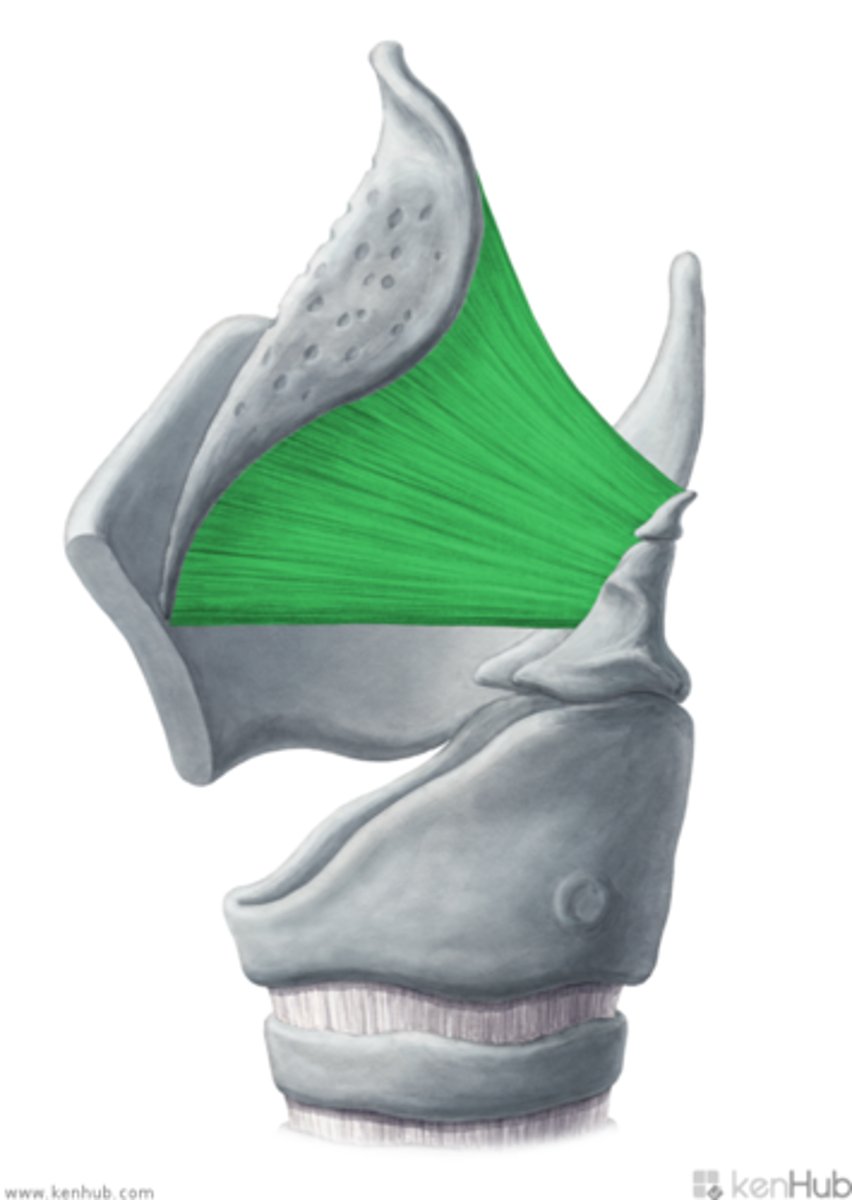
aryepiglottic fold/ligament
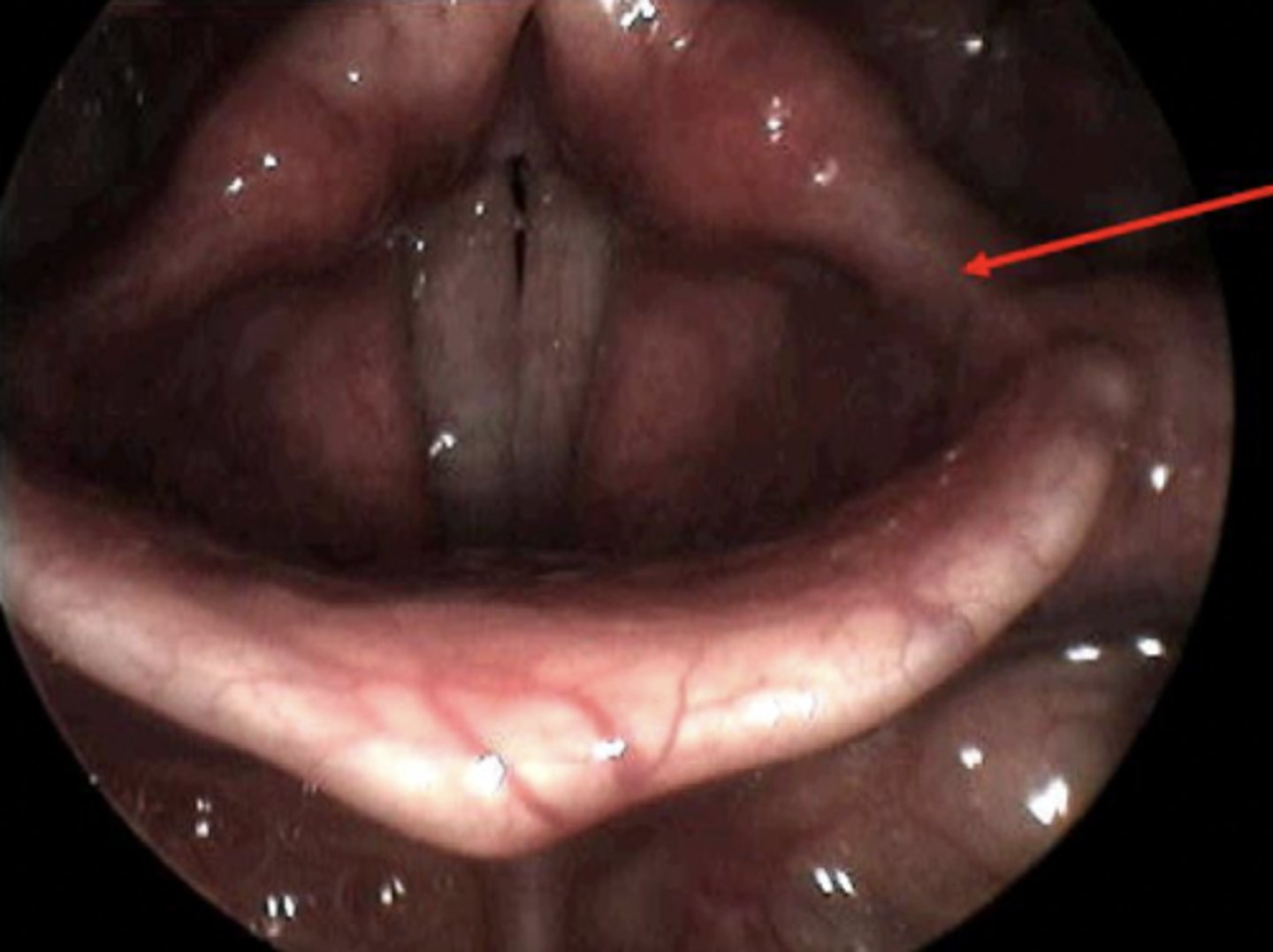
vestibular fold/ligament
false vocal cord
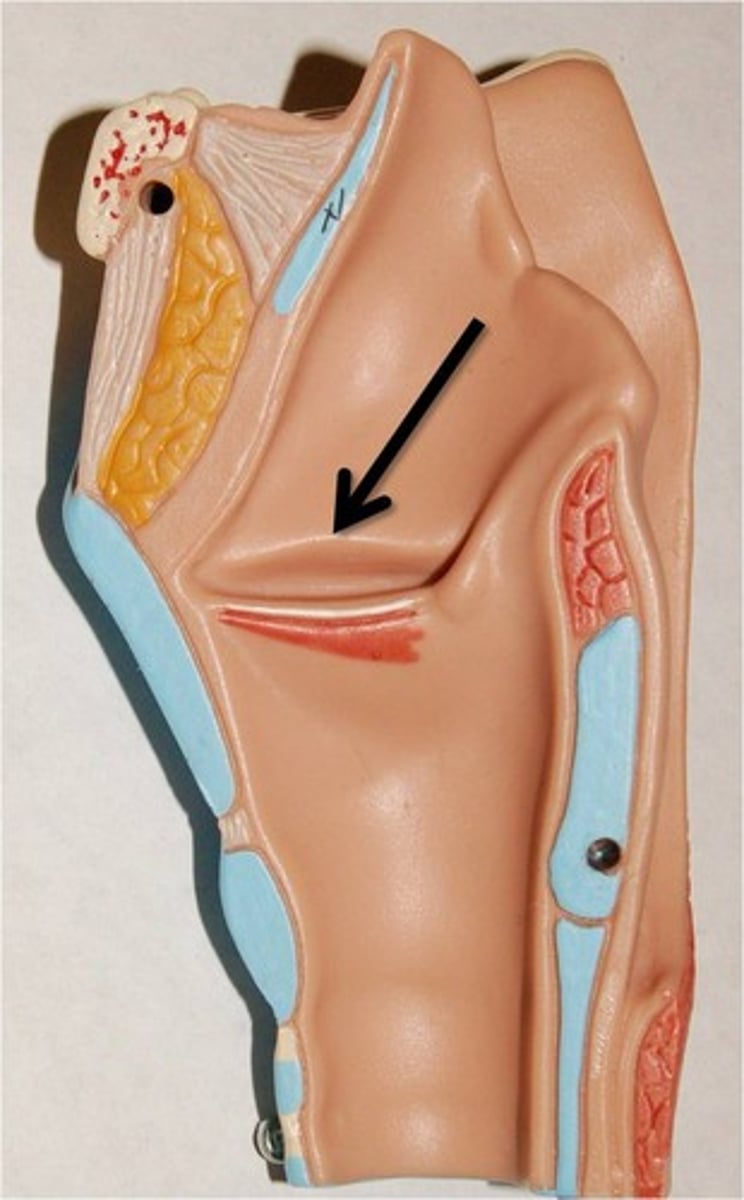
vocal fold/ligament
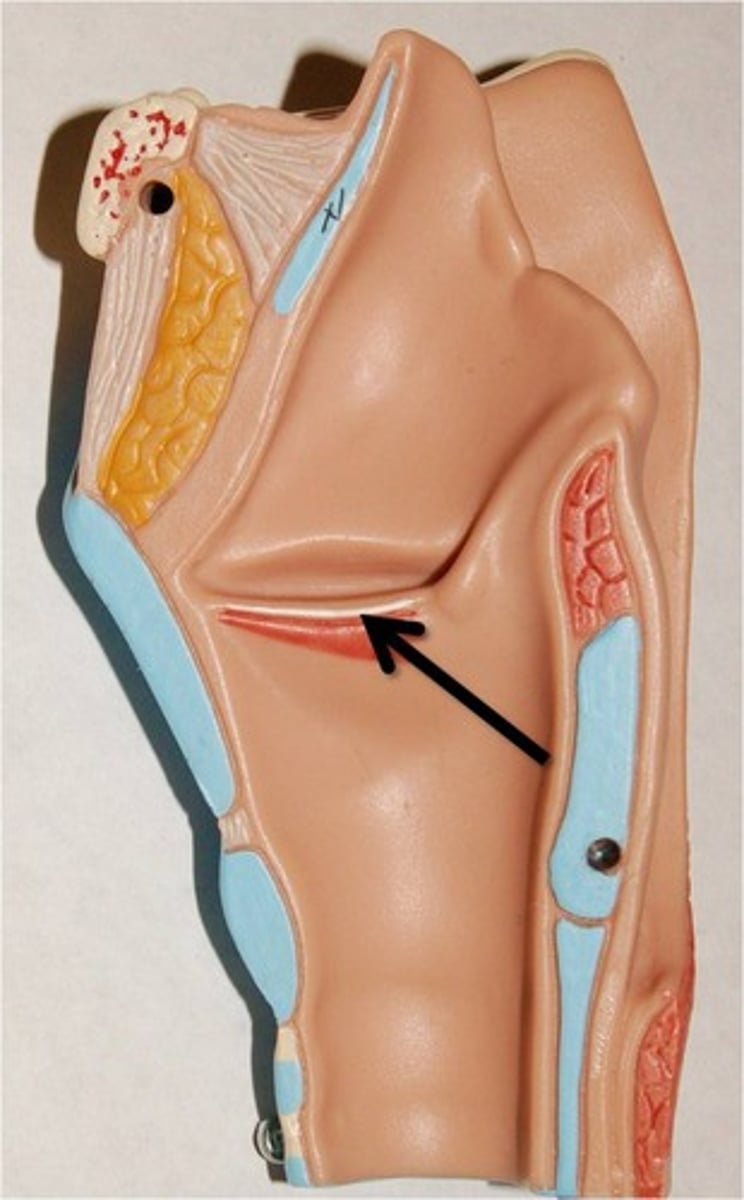
cricothyroid membrane
laryngeal inlet
opening that connects the pharynx and larynx
valleculae
space between tongue and epiglottis
piriform fossa
hollow pockets on the lateral sides of the glottic opening
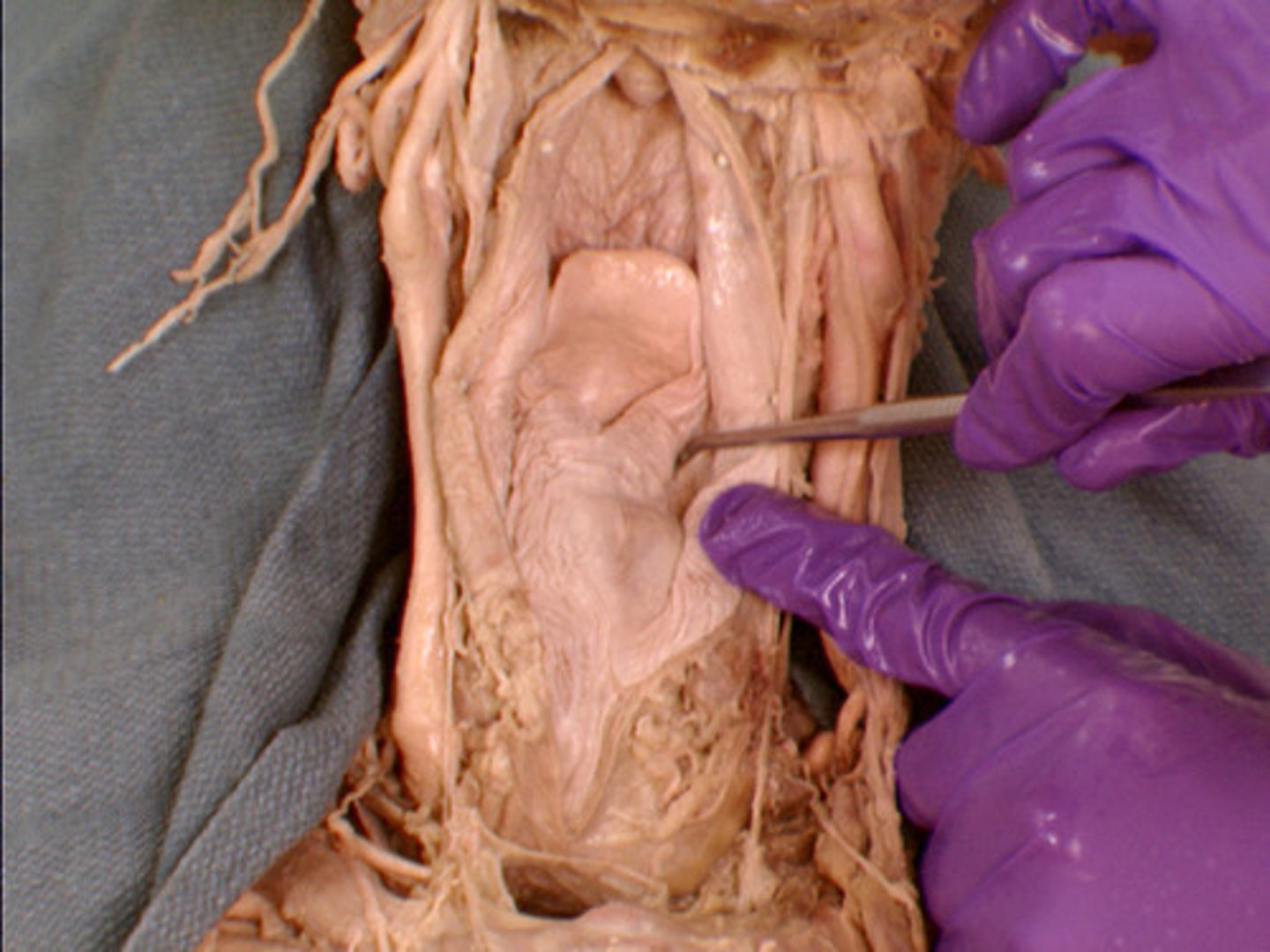
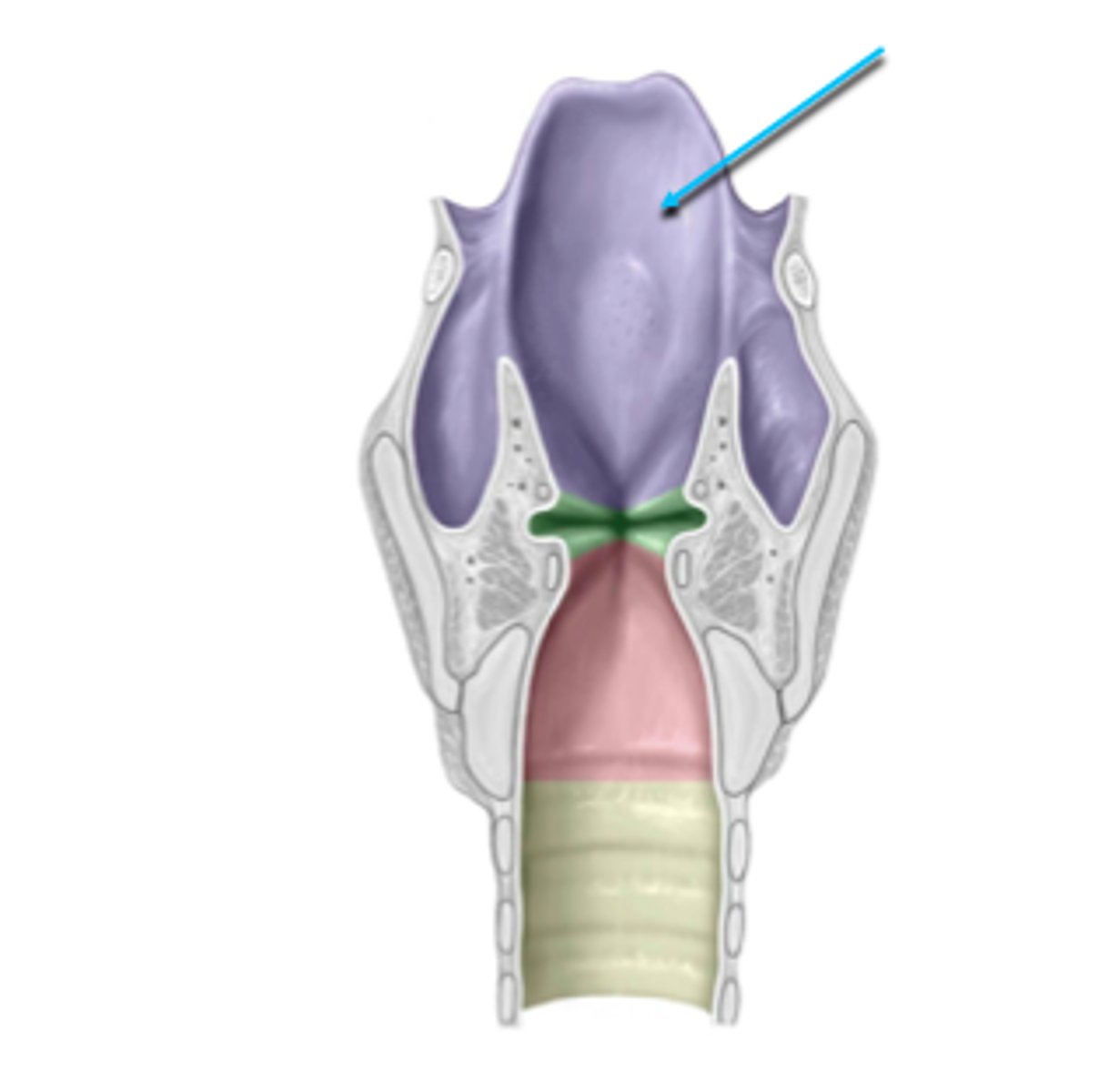
laryngeal vestibule/ supraglottic space
laryngeal ventricle
space between true and false vocal folds
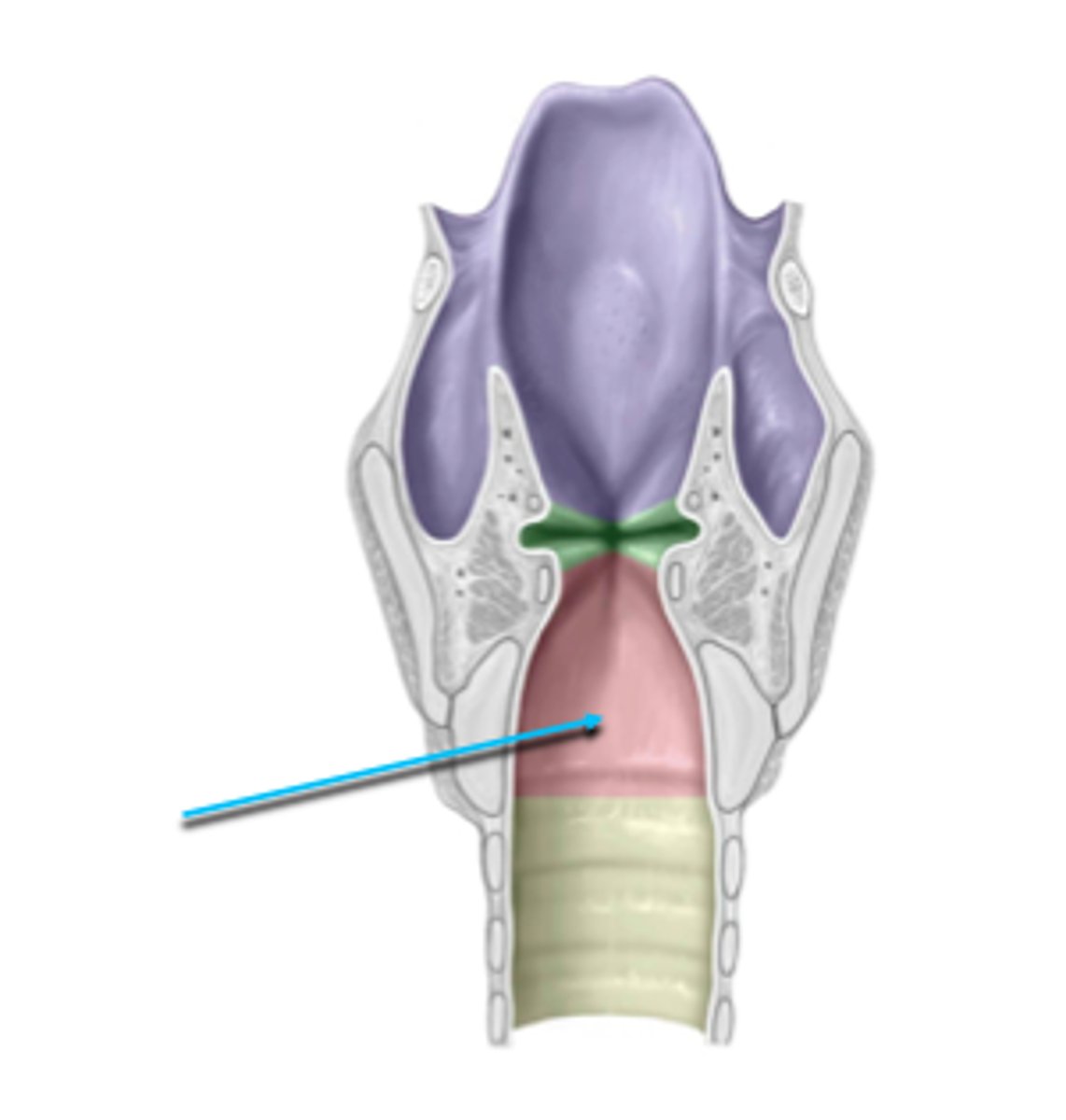
infraglottic space
area inferior to the vocal folds
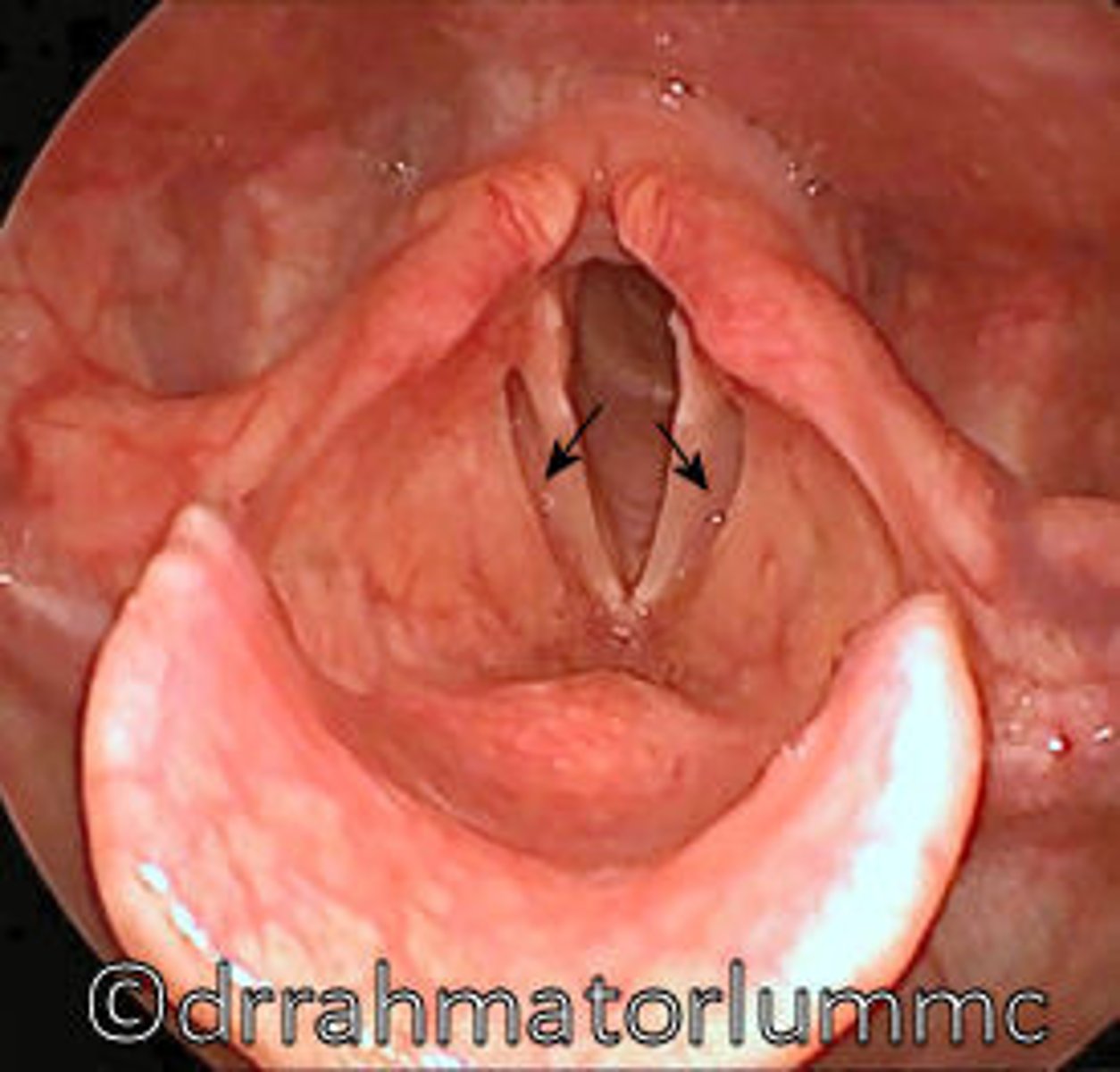
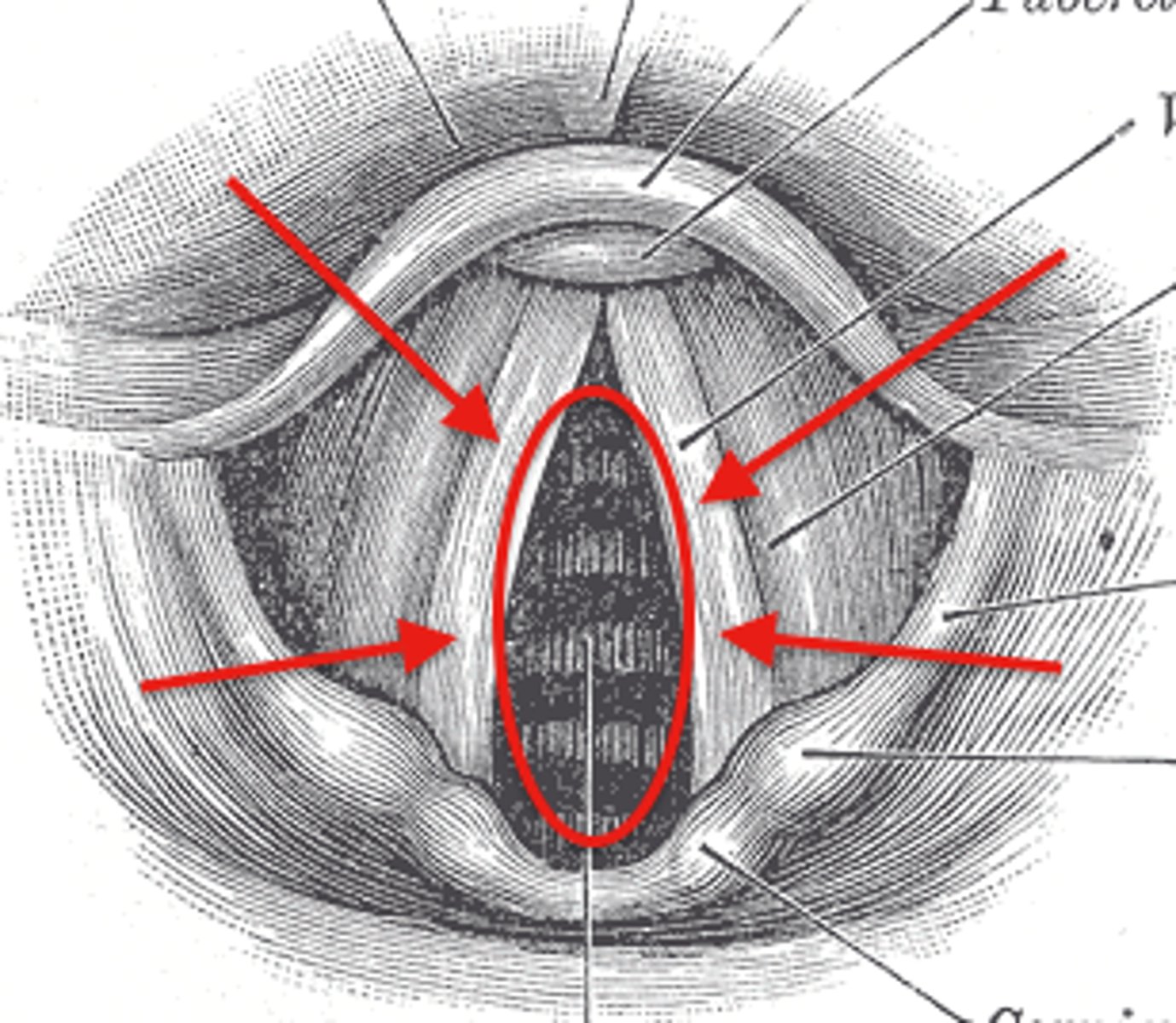
rima glottidis
opening between vocal folds
cricothyroid muscle, lengthen vocal cords, high pitch
structure, function, action
aryepiglottic muscle
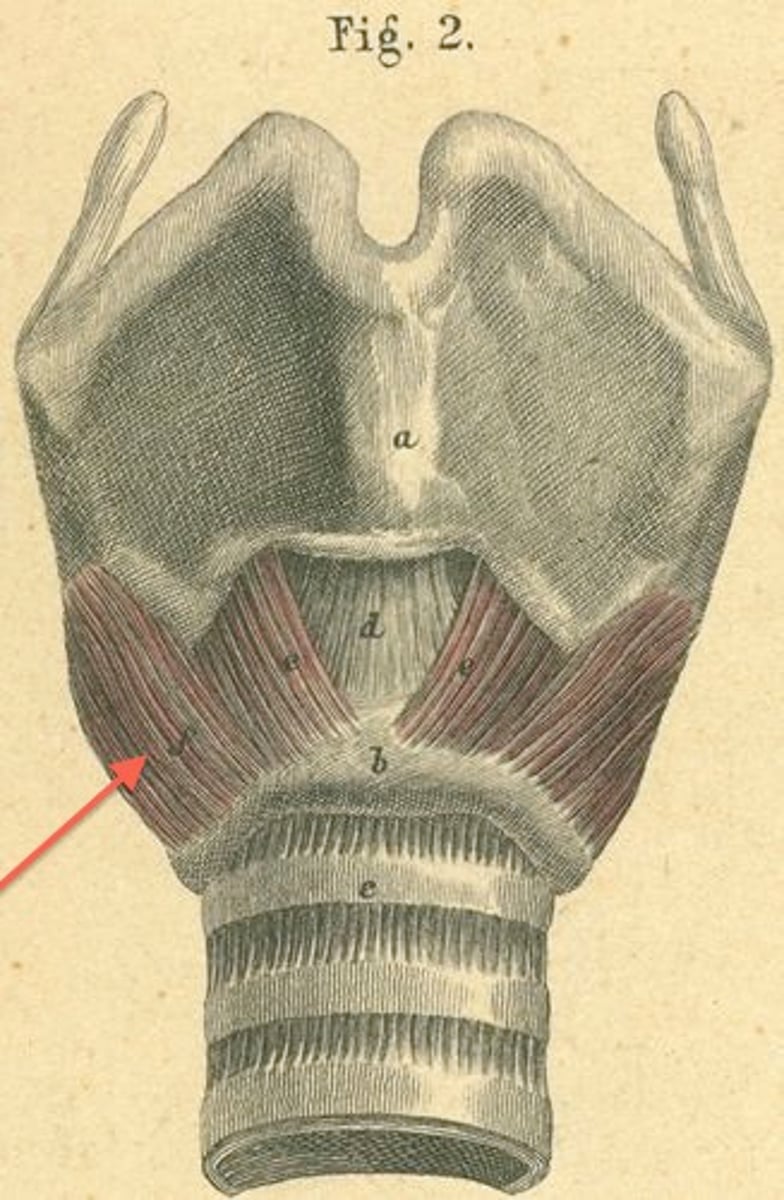
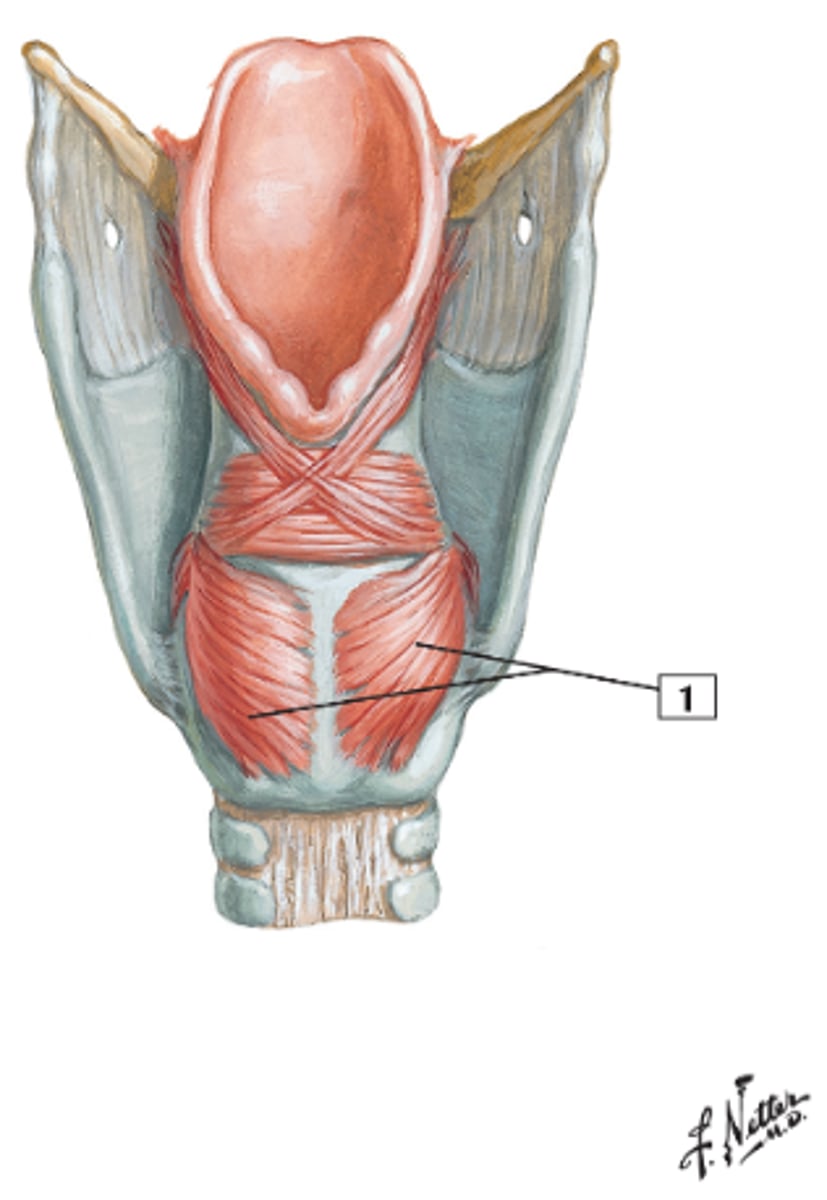
posterior cricoarytenoid, abducts vocal folds, forced respiration
name, function, action?
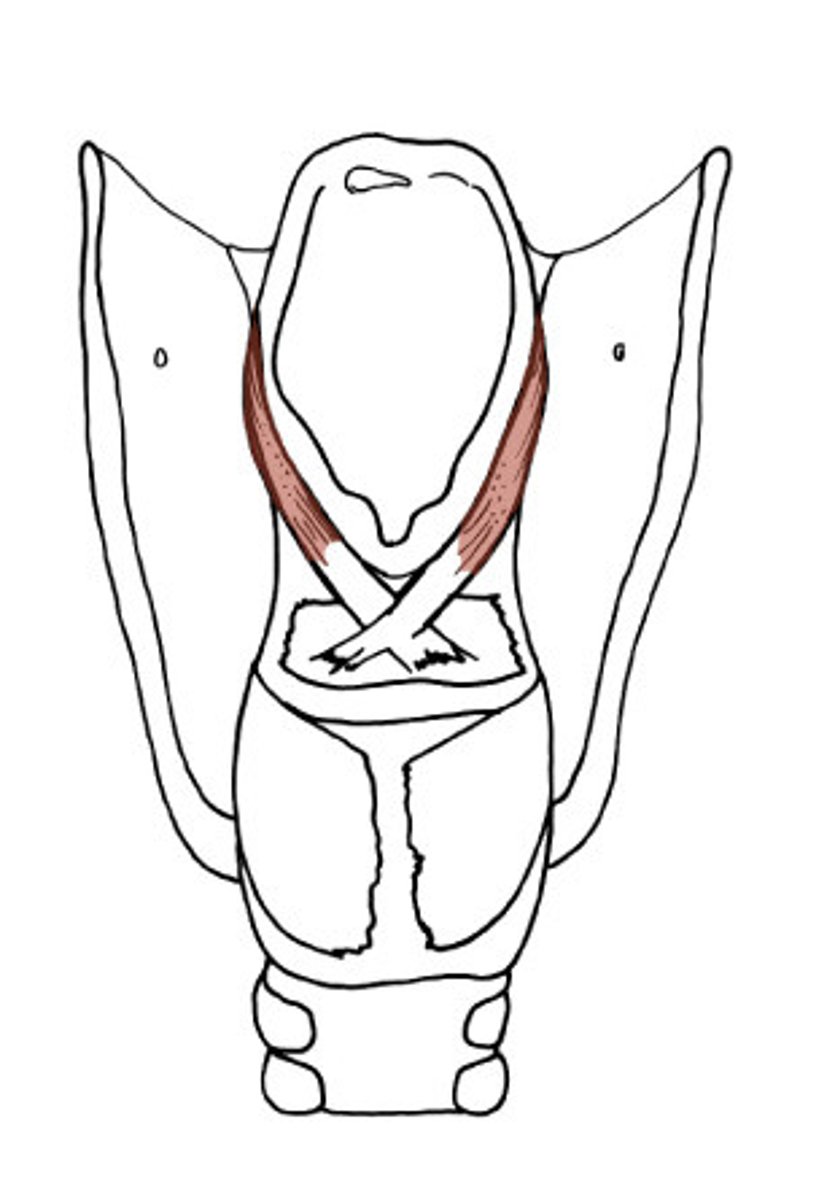
arytenoid muscle (transverse and oblique) , adducts vocal folds, bear down
name,function, action?
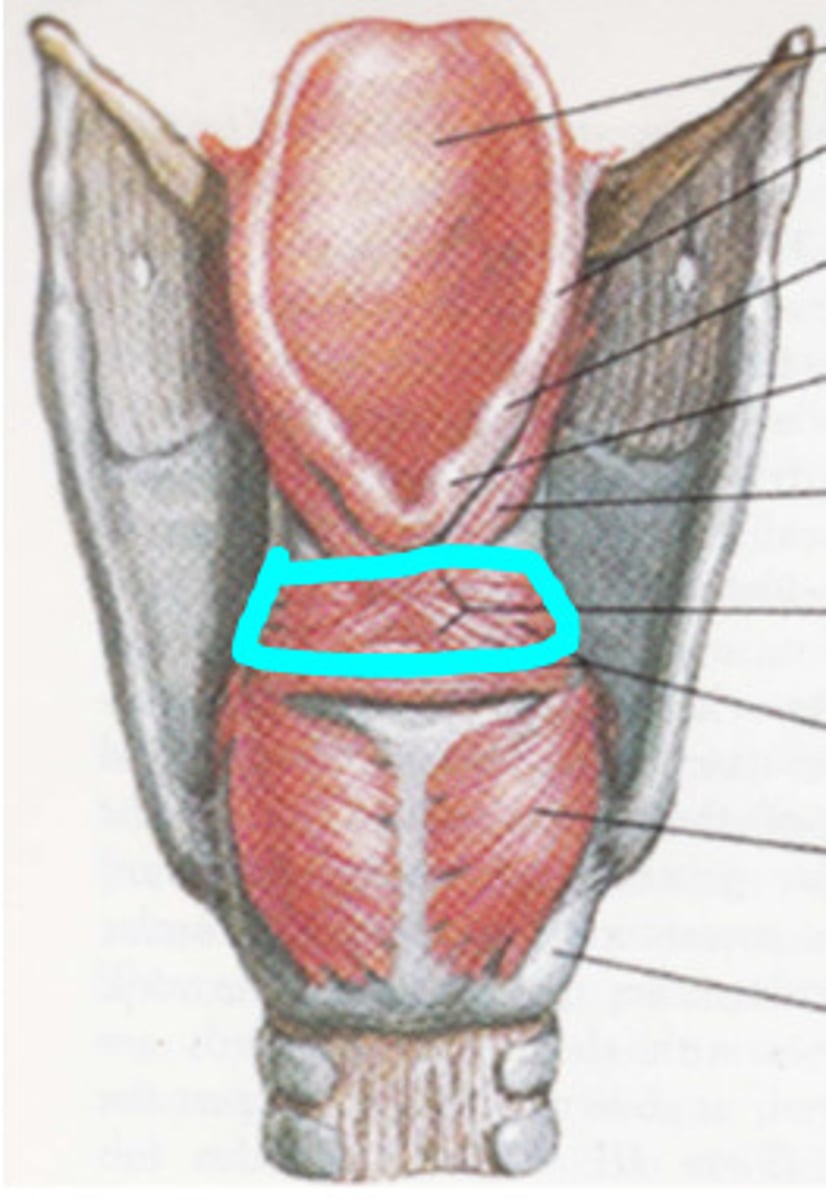
lateral cricoarytenoid, adducts vocal cords, bear down
name,function, action?
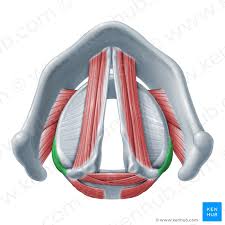
thyroarytenoid muscle, shorten vocal cords, low pitch
name, function, action
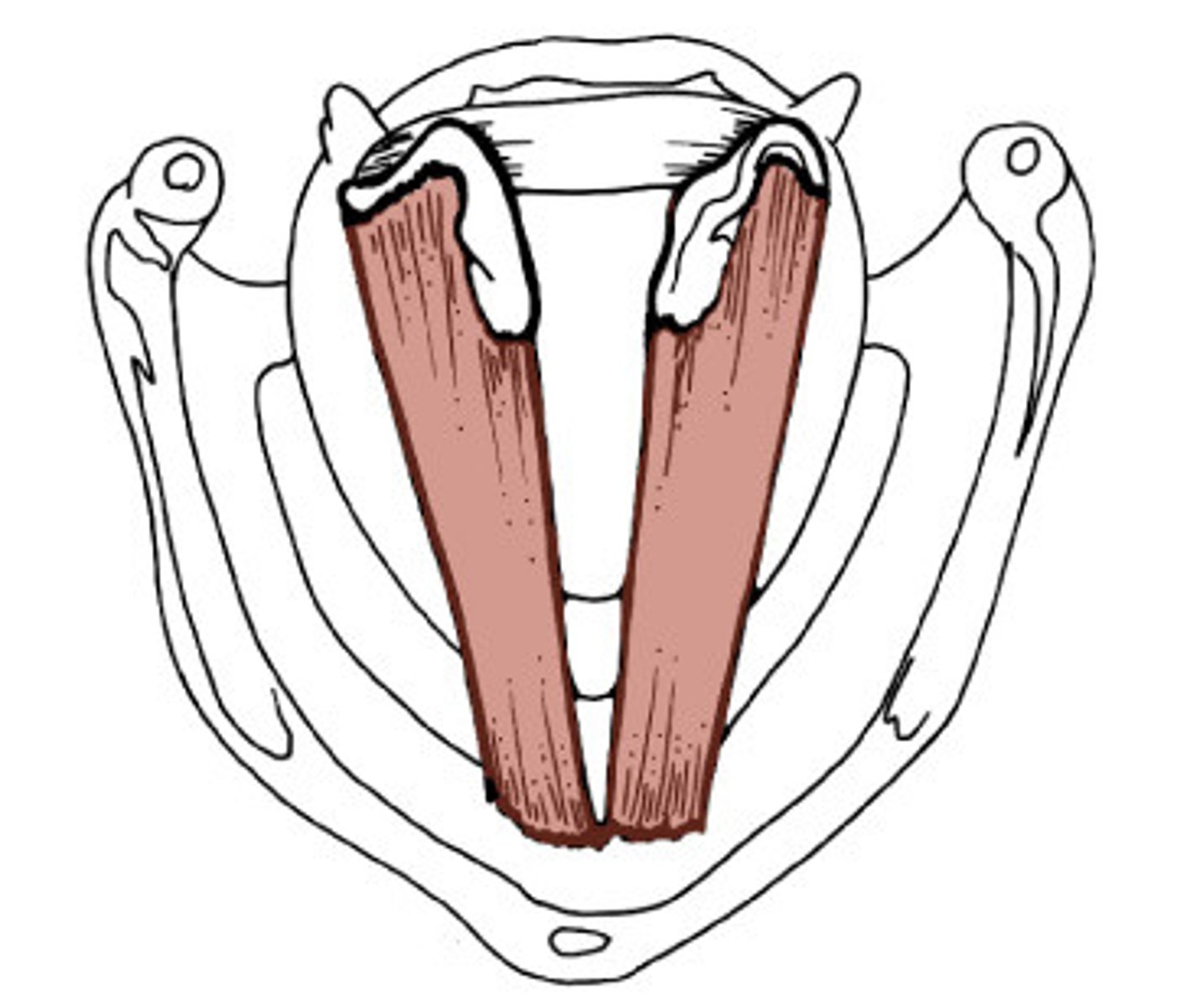
vocalis, fine tune pitch
structure and function
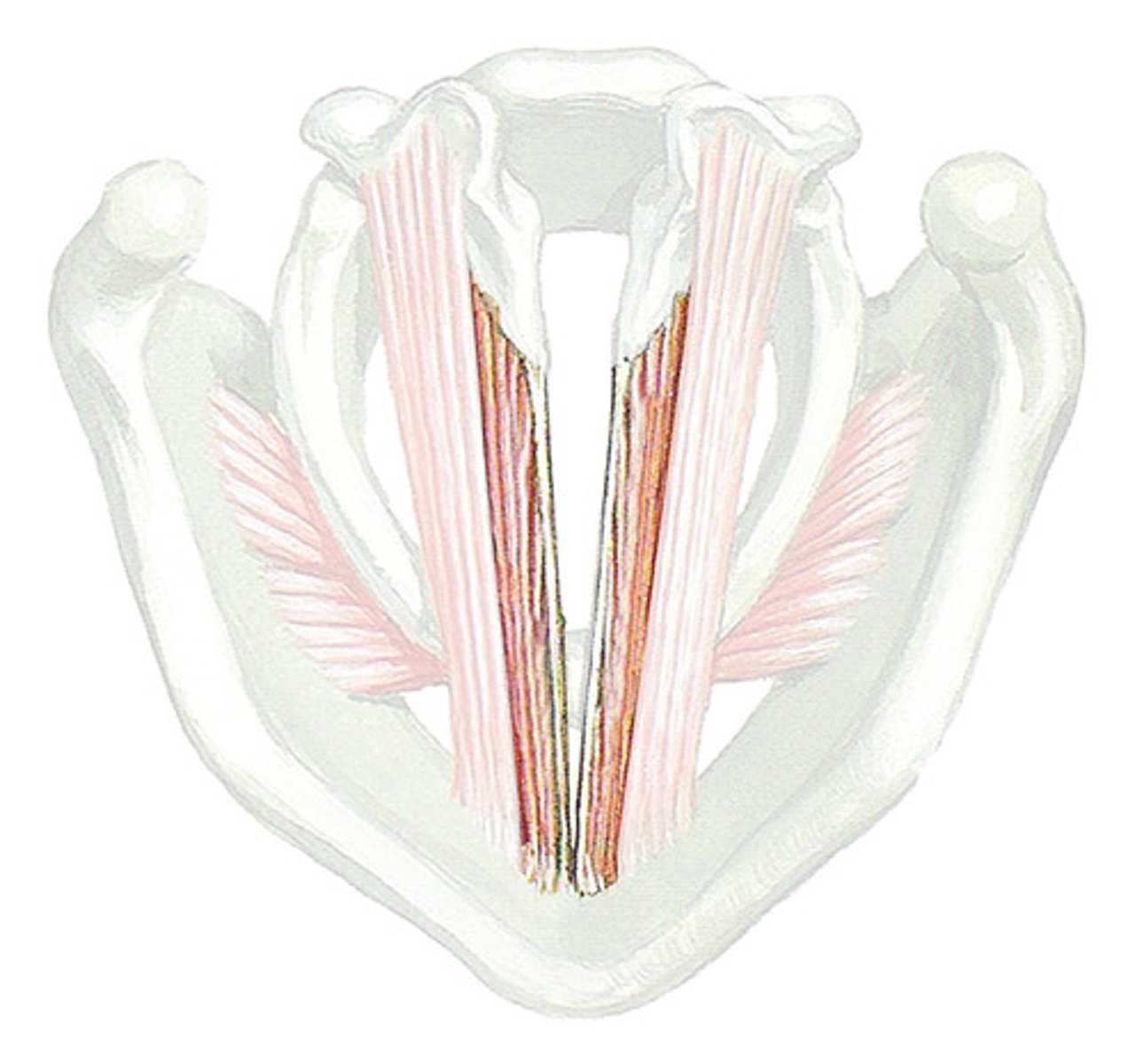
sensation of mucosa below vocal folds, larnygeal muscles (except cricothyroid)
what does the recurrent laryngeal innervate
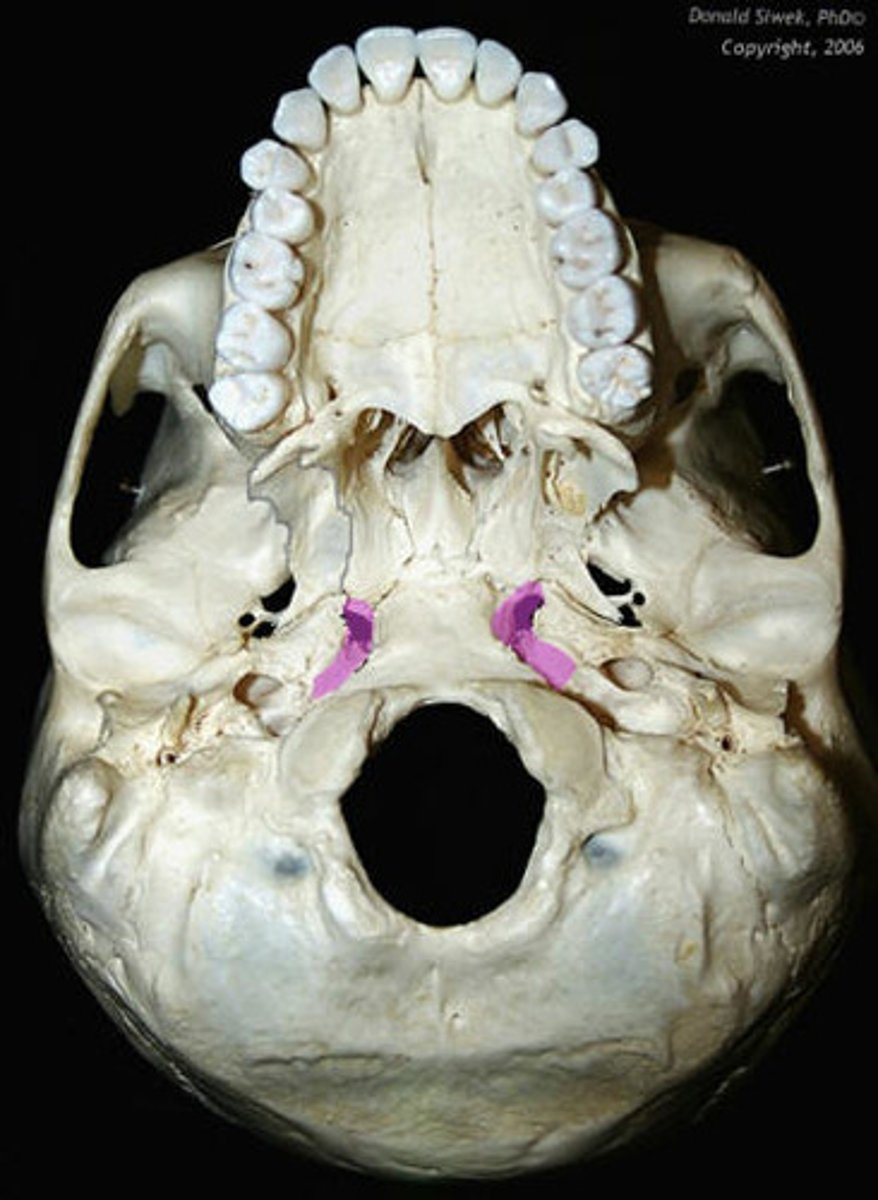
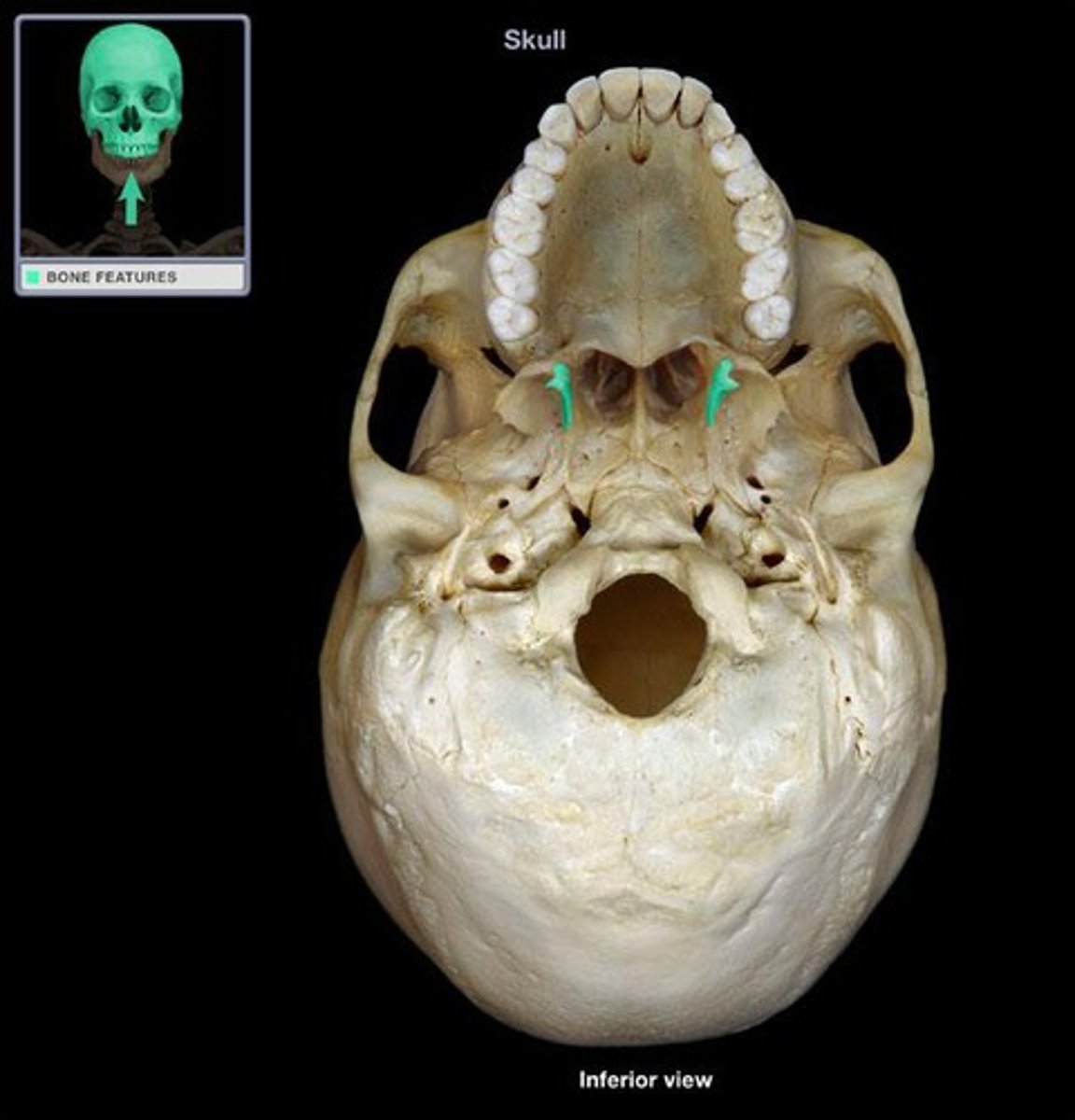
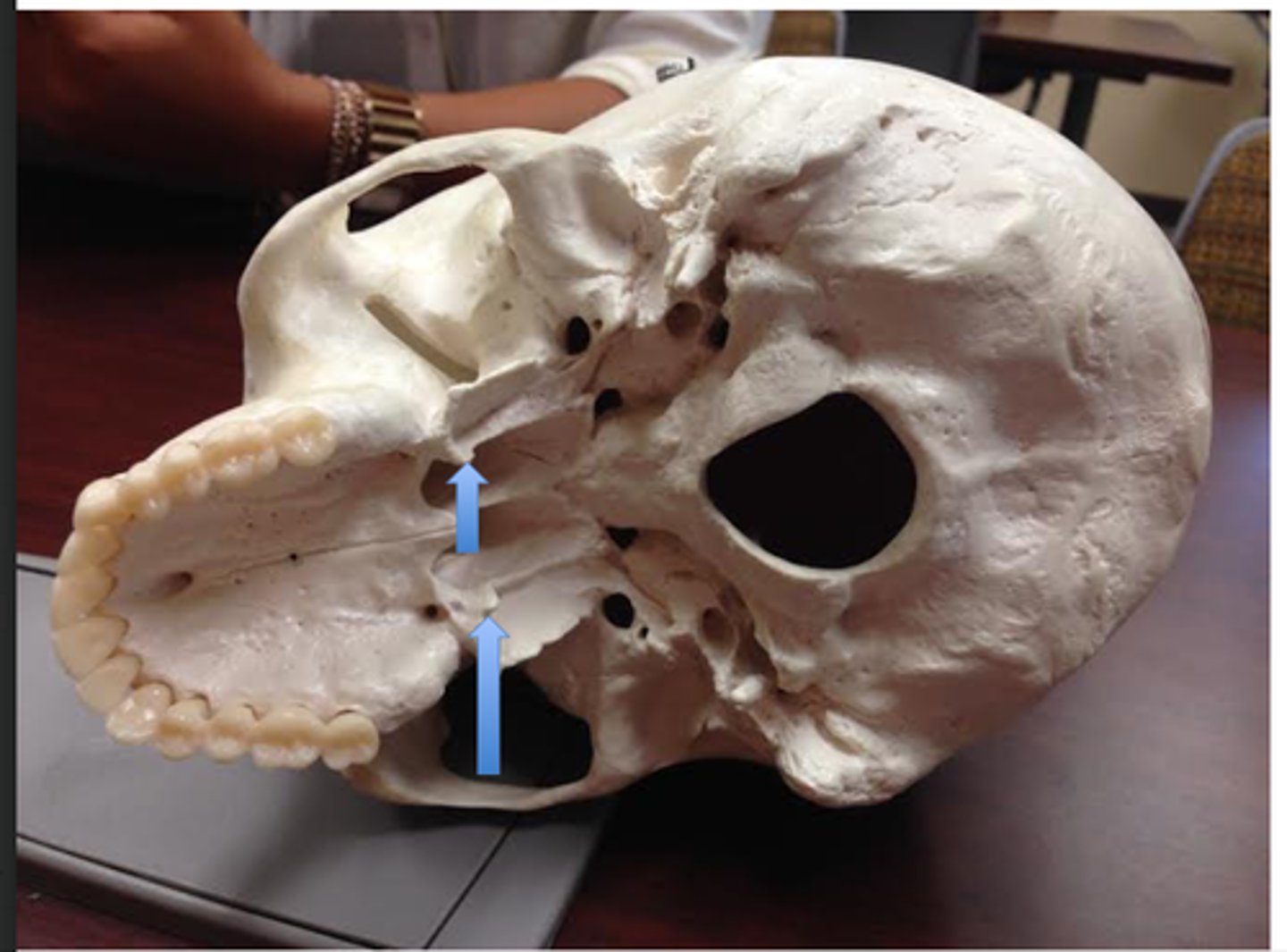
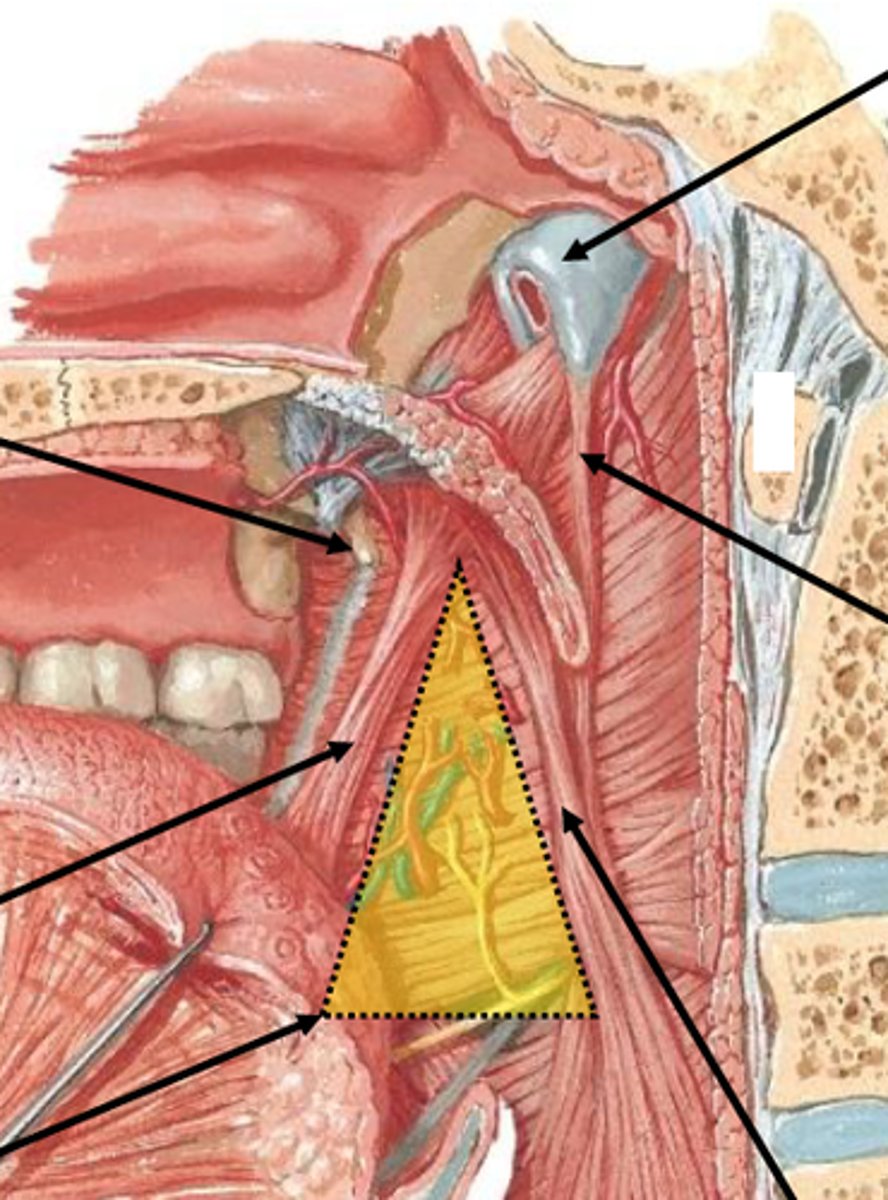
sphenopetrosal fissure
leads to bony potrion of pharyngotympanic tube
petrous part of temporal bone
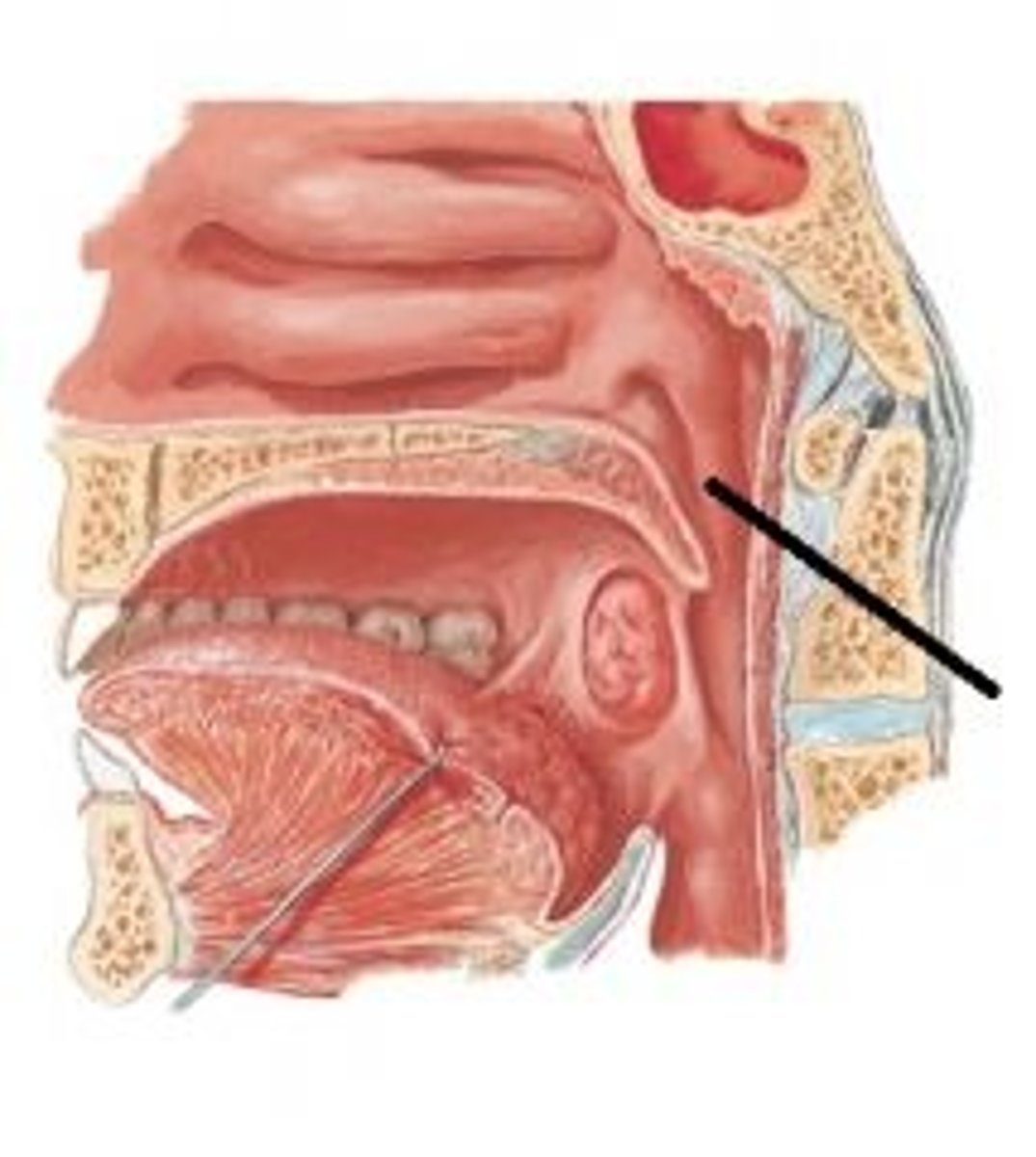
scaphoid fossa, tensor veli palatini
structure, what attaches here
medial pterygoid plate
hamulus
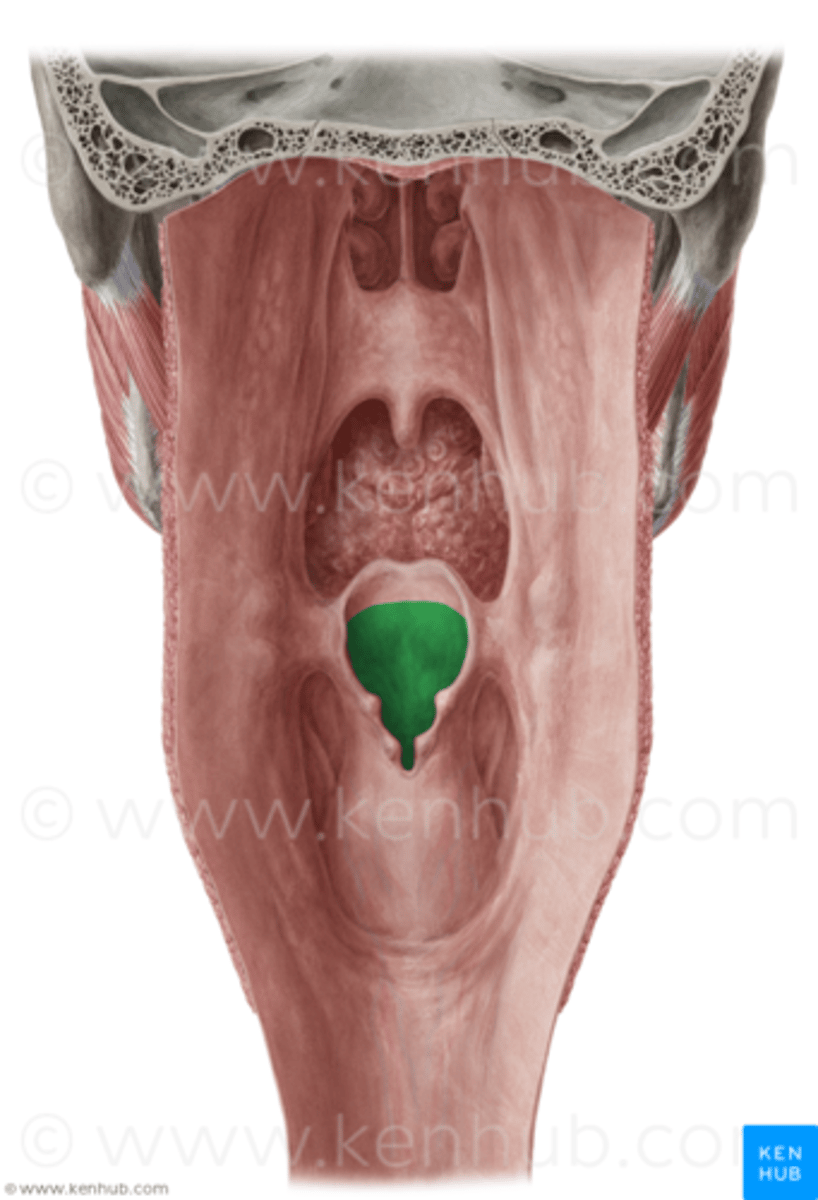
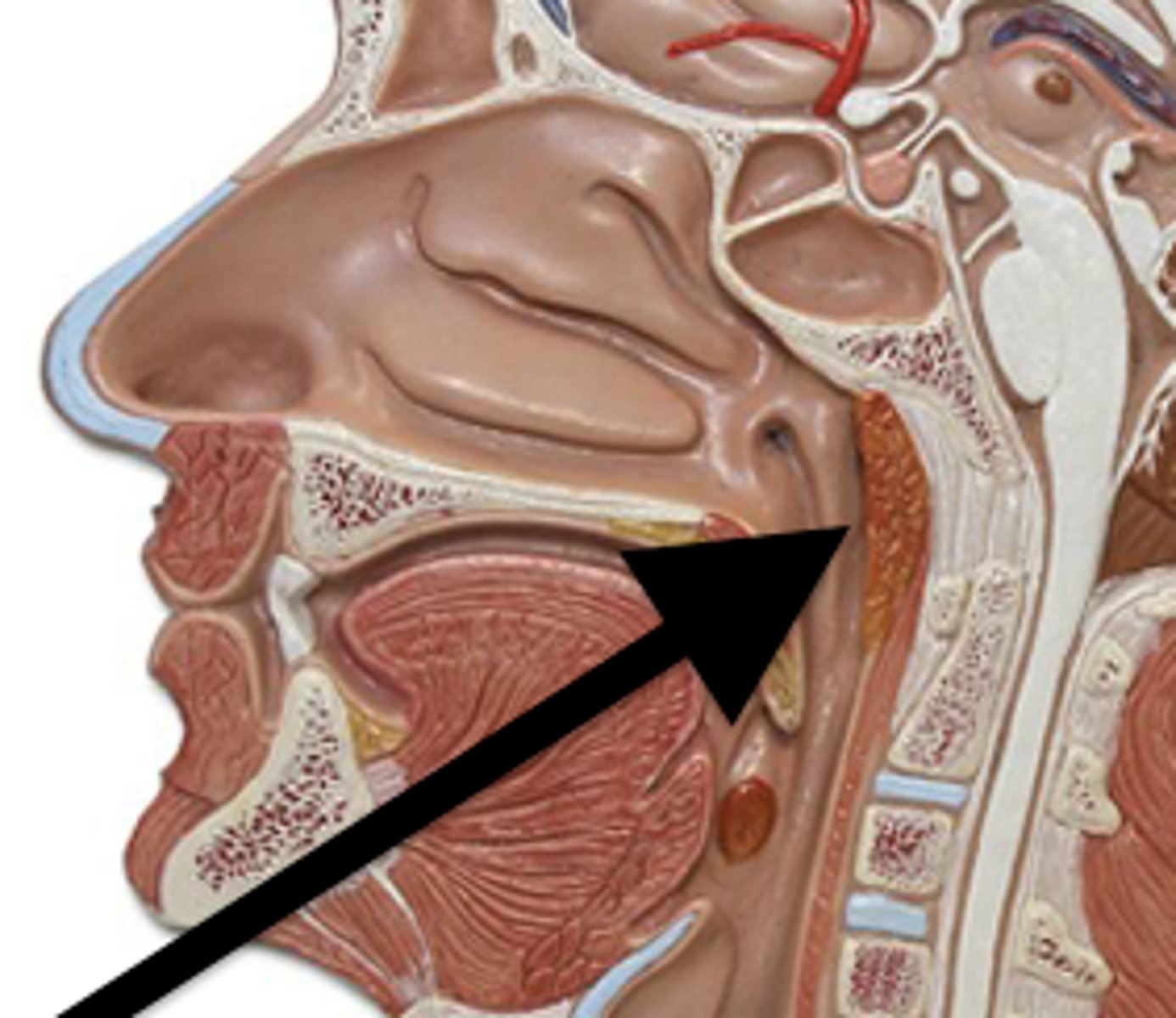
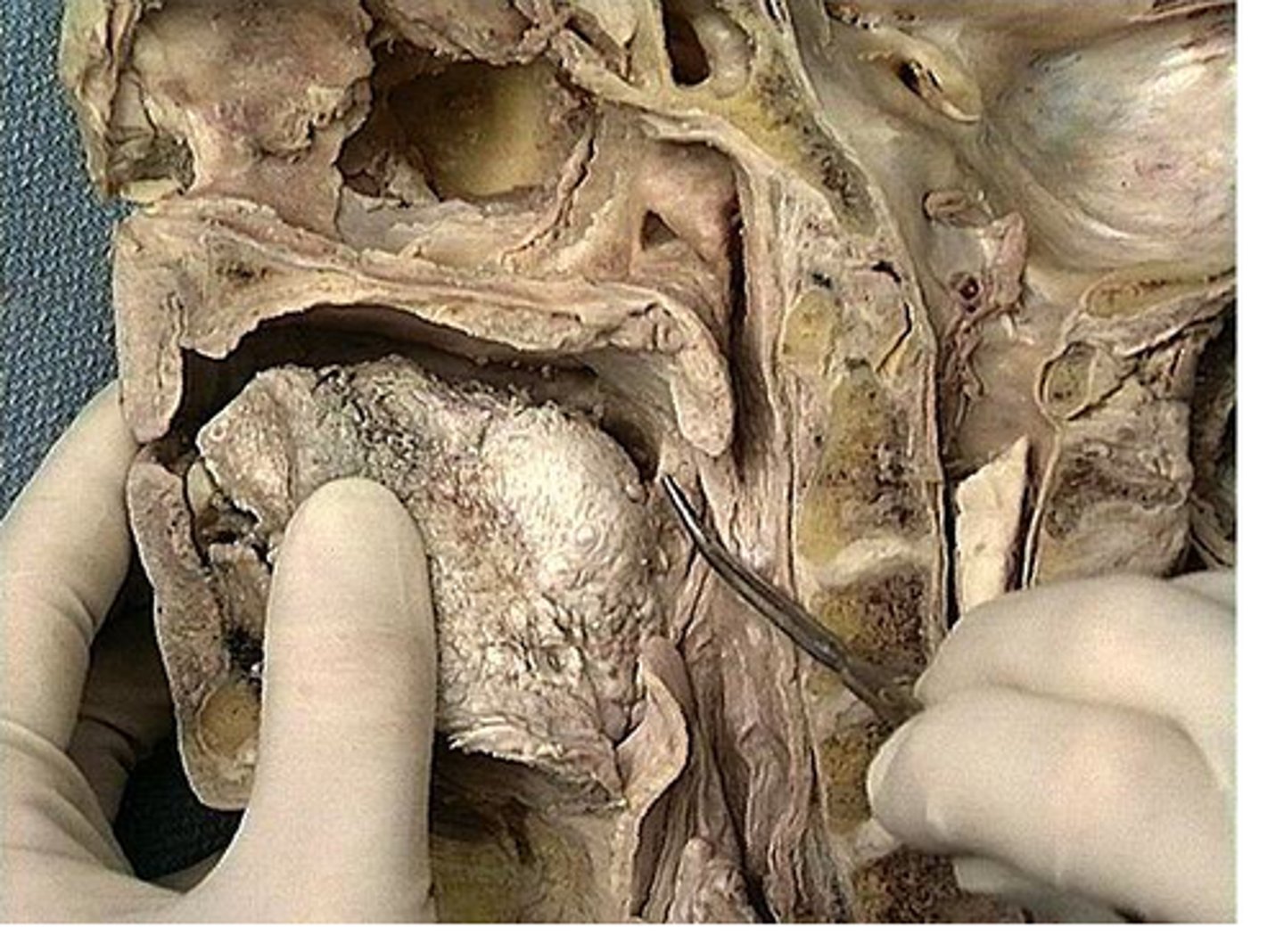
pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
what tonsilar tissue is found here
tubal tonsils
what tosilar tissue is found here
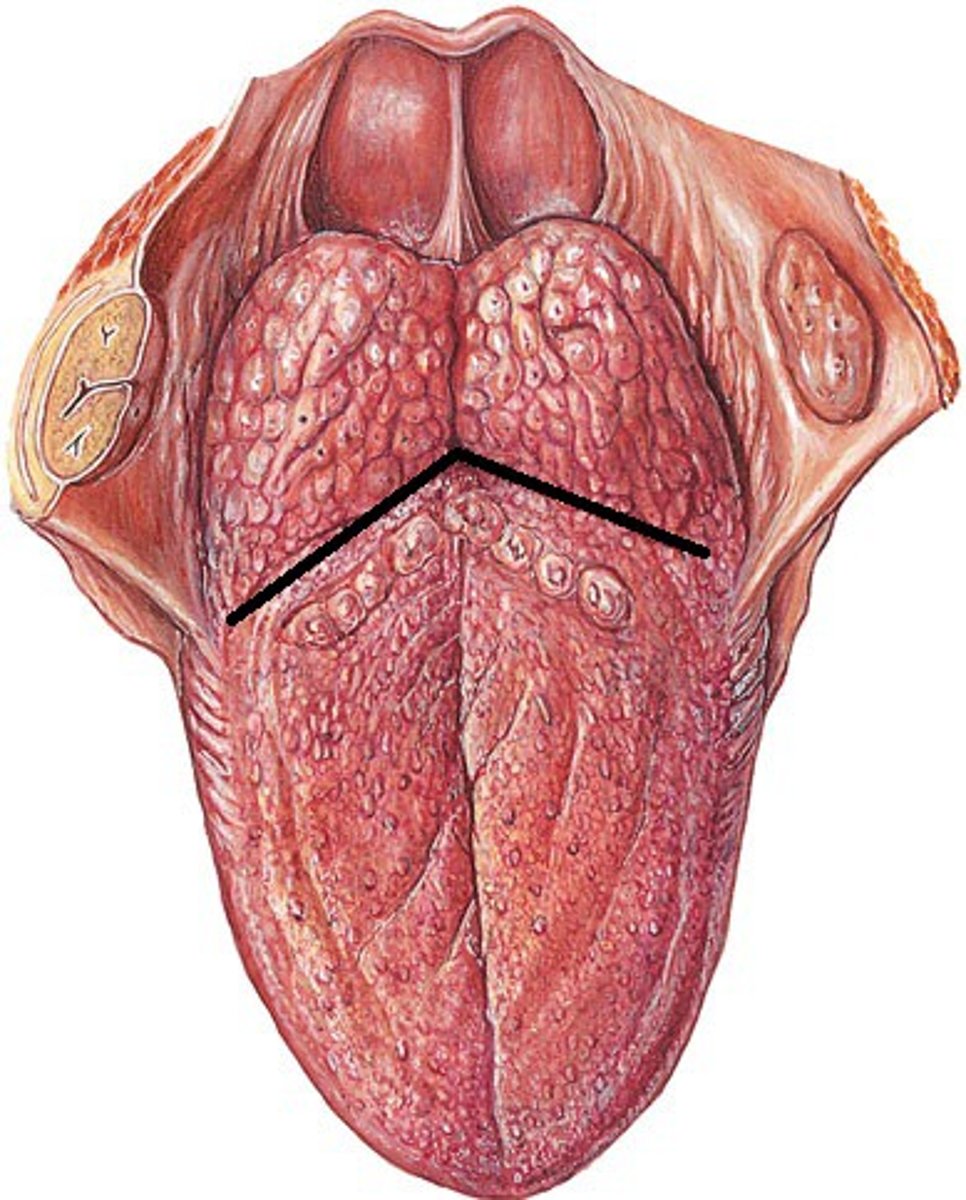
palatine tonsils
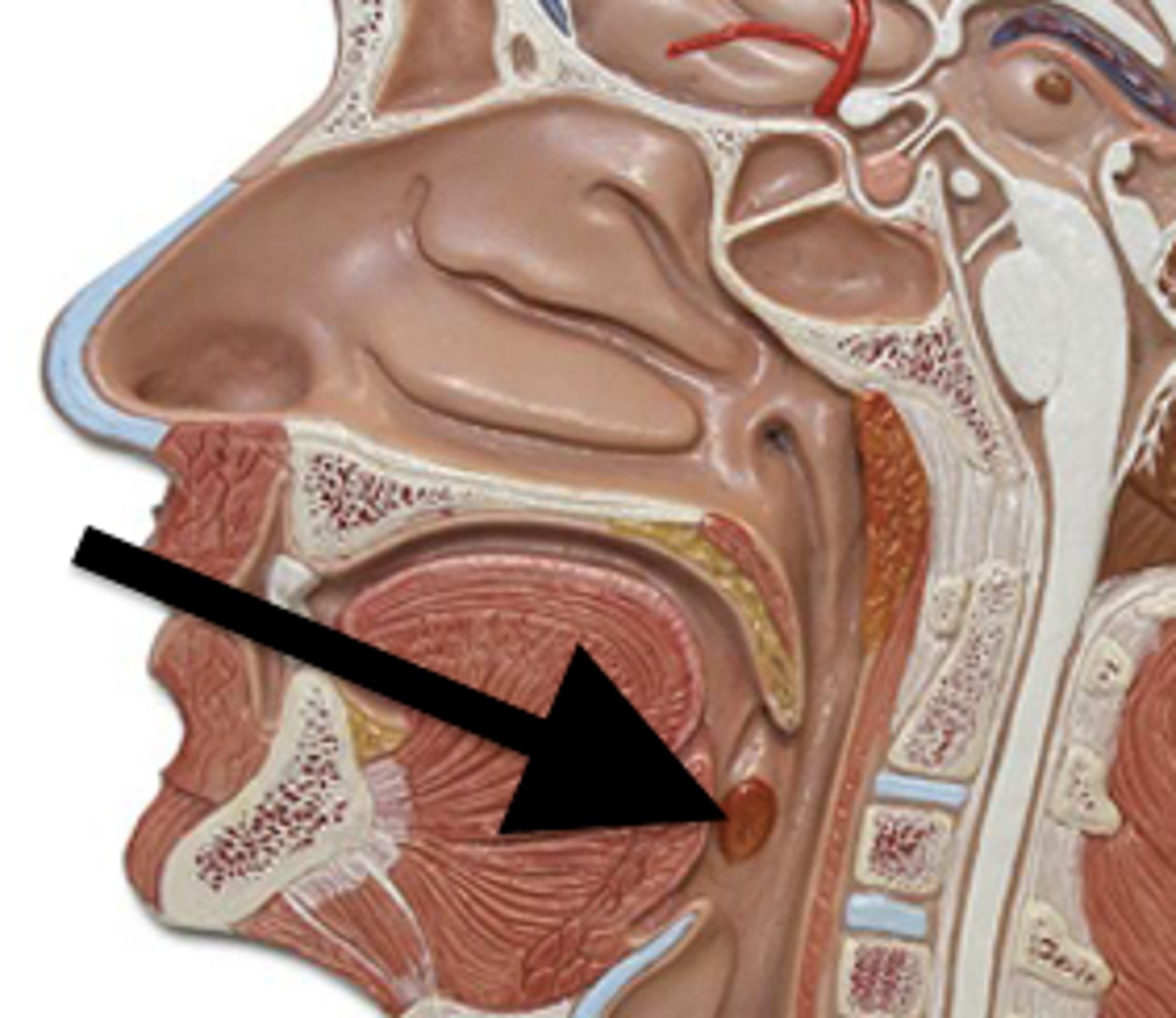
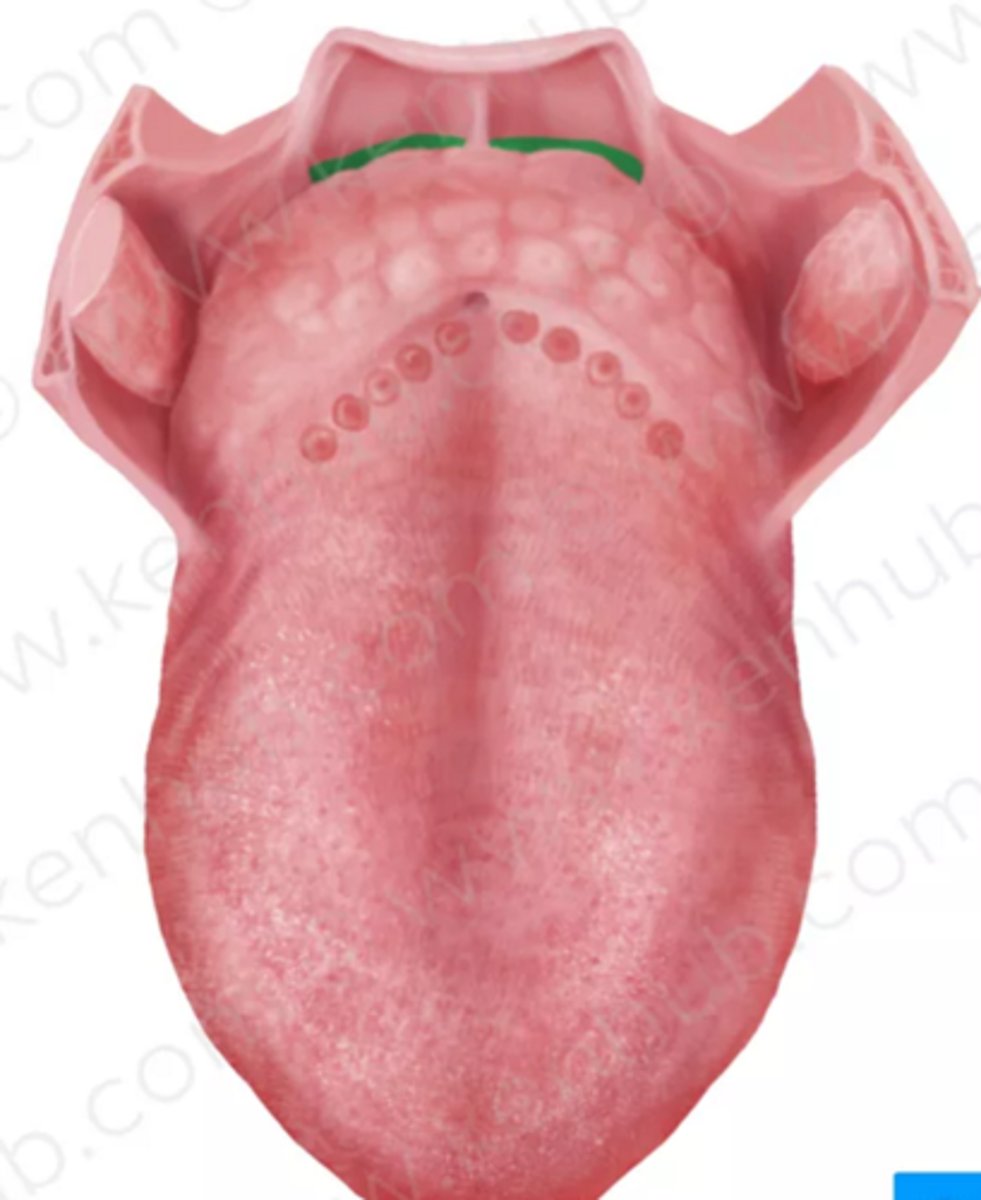
lingual tonsils
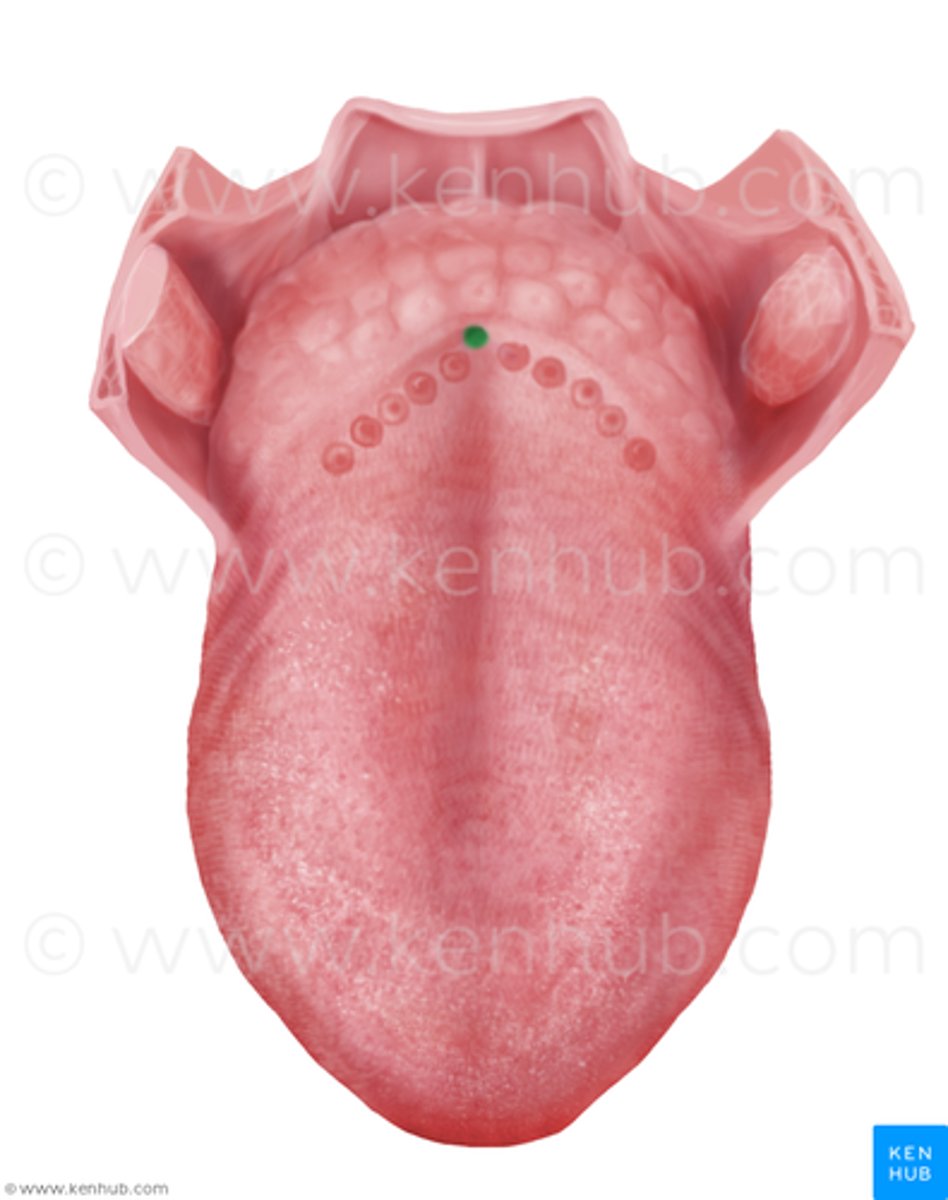
sulcus terminalis
foramen cecum
vallate papillae
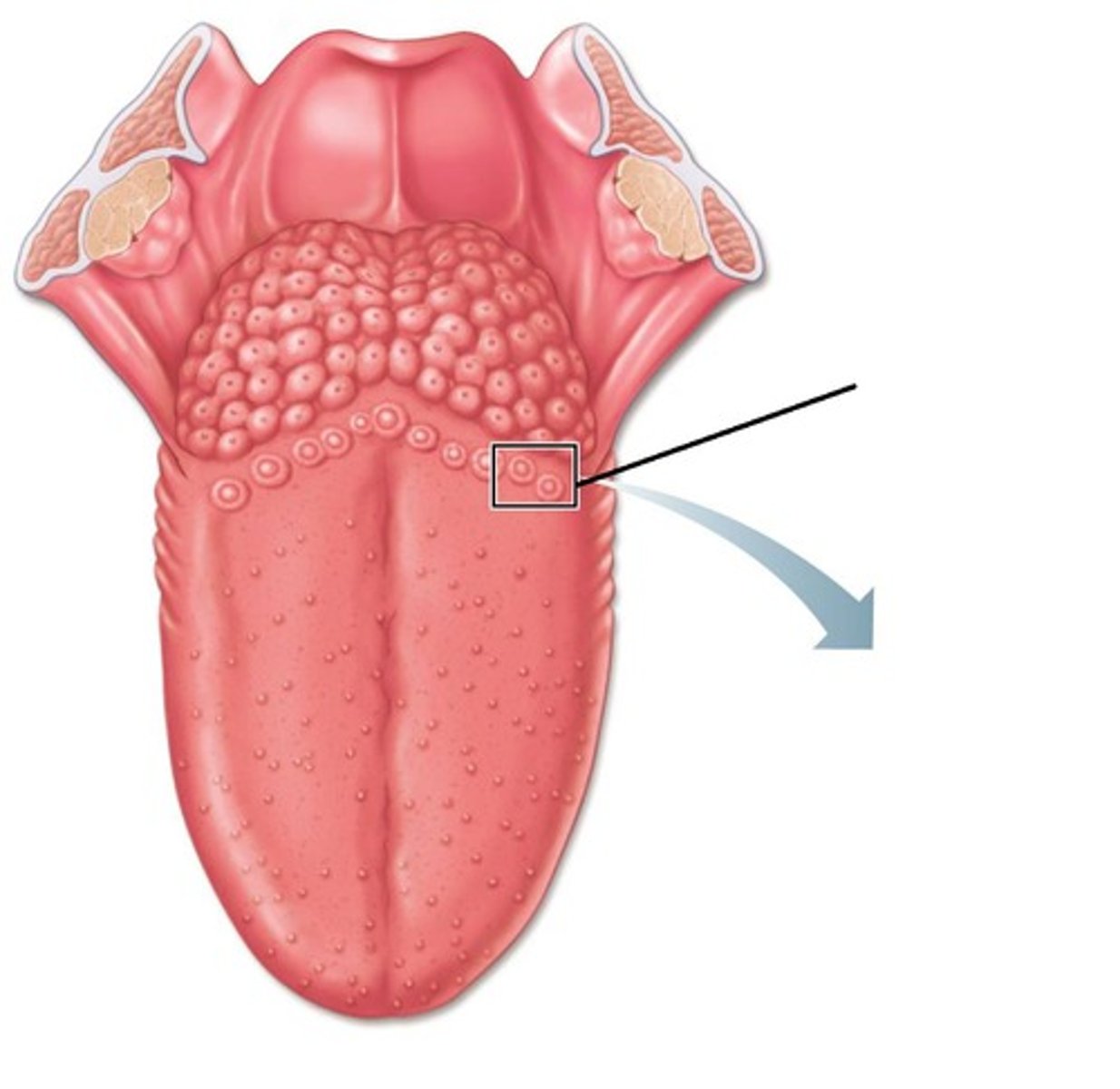
valleculae
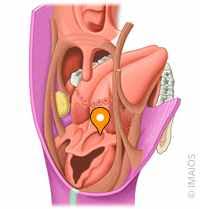
torus tubarius
elevation of cartilage caused by the auditory tube
salpingopharyngeal fold and muscle (CN X)
pharyngeal recess
a groove between salpingopharyngeal fold and
posterior wall of nasopharynx
tonsillar fossa
the space between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch
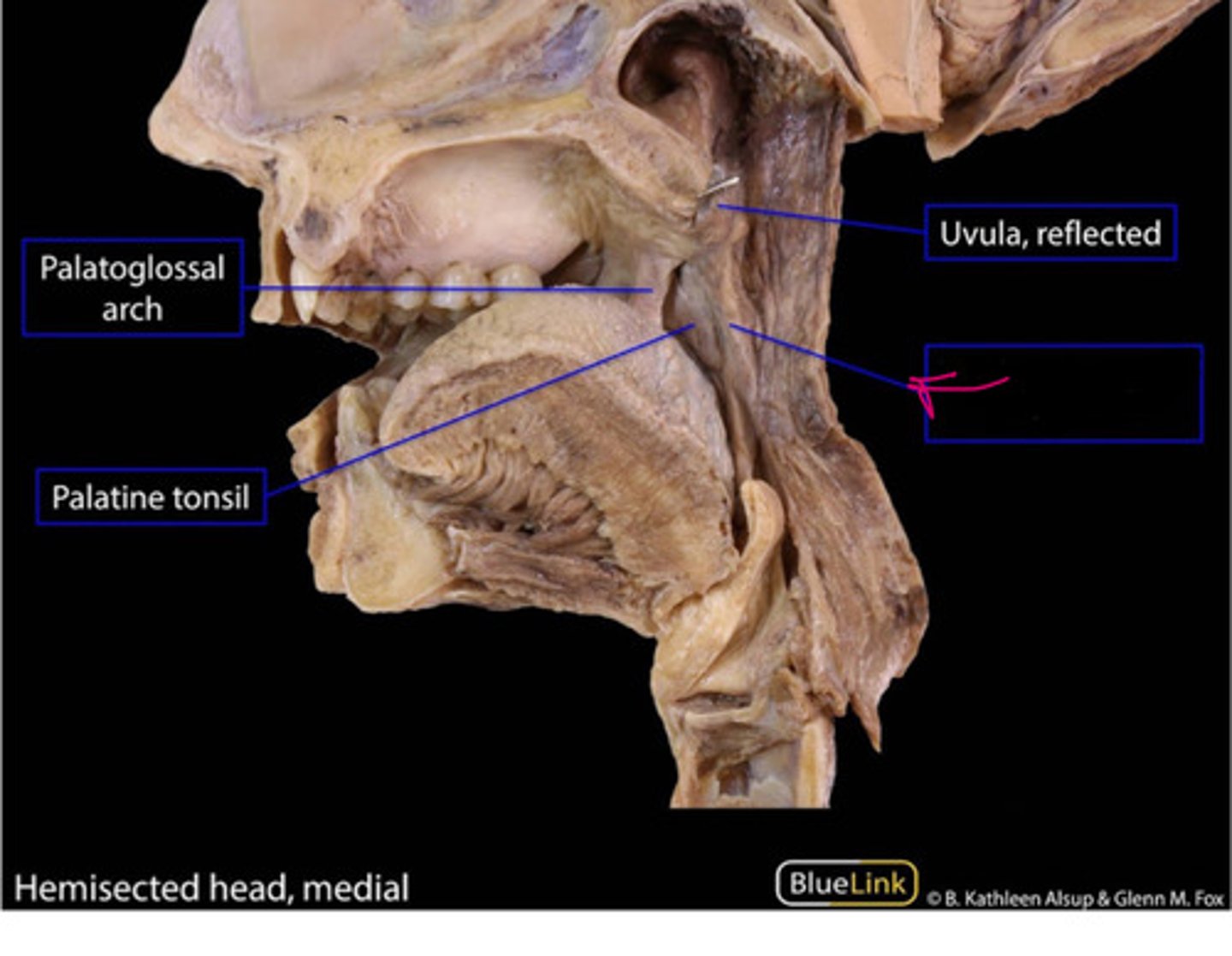
uvula
small projection hanging from the back middle edge of the soft palate
musculus uvulae (CN X)
what muscle controls this structure
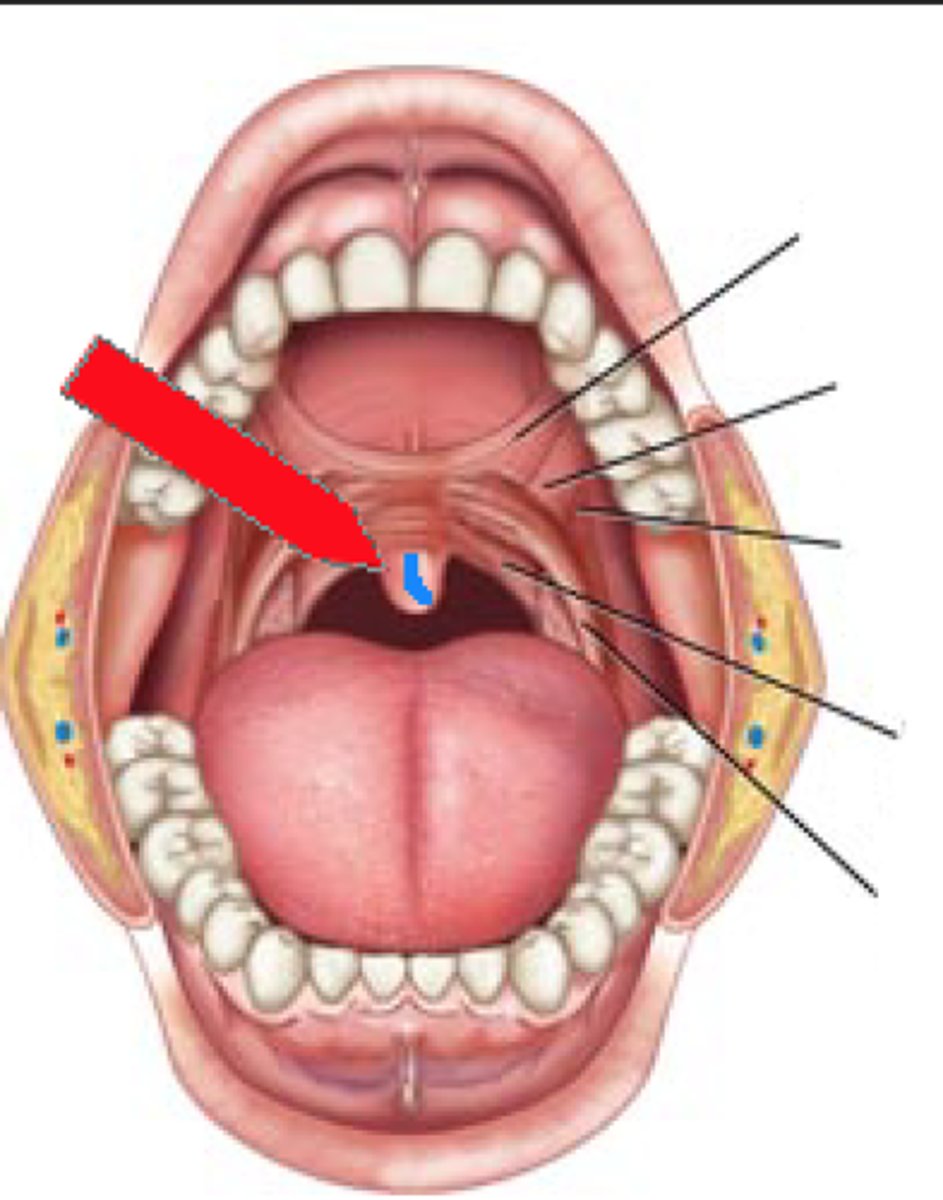
palatoglossal arch/muscle (Cn X)
palatopharyngeal arch/muscle (CN X)
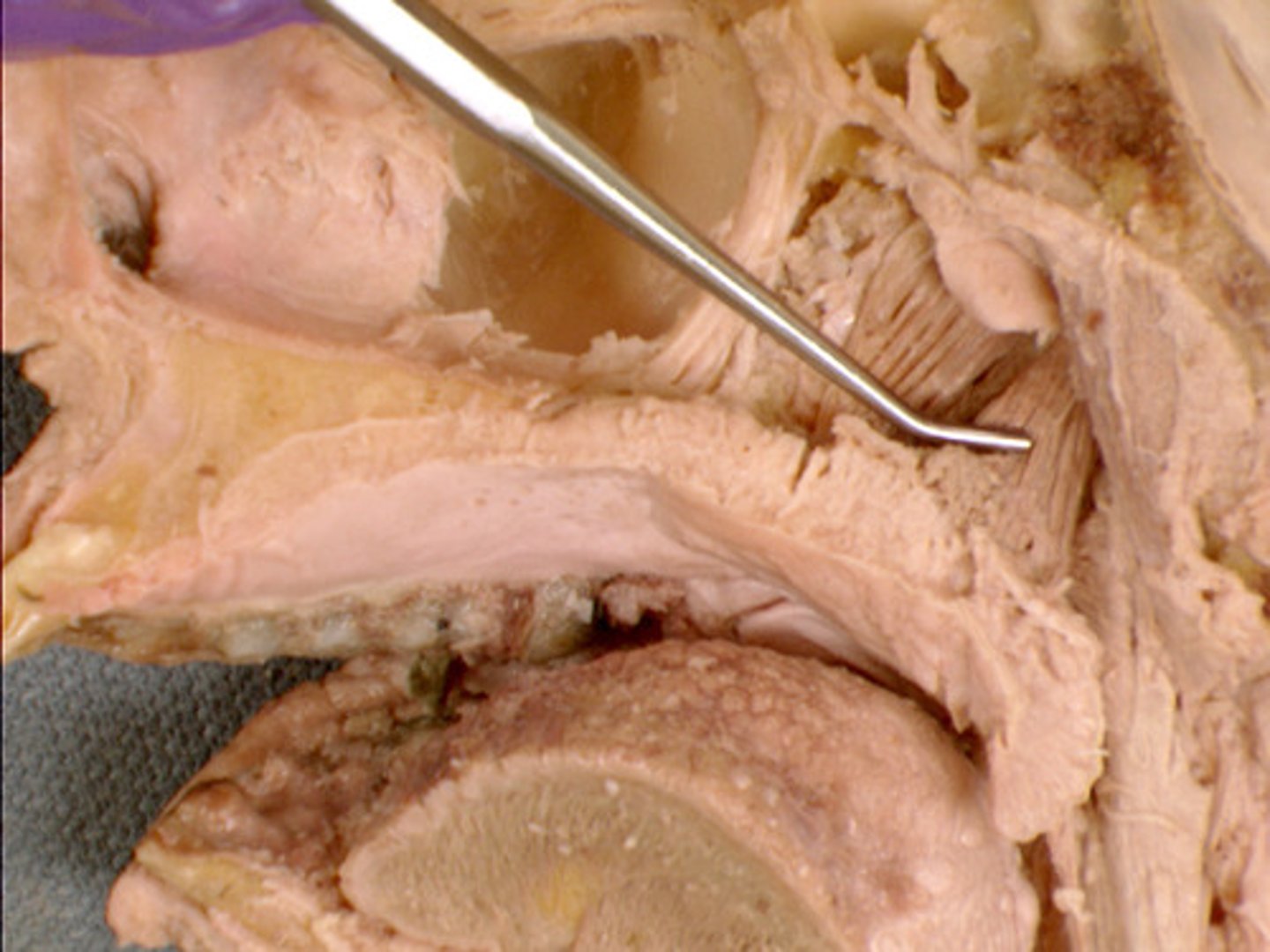
levator veli palatini muscle, elevate soft palate (CN X)
name and function
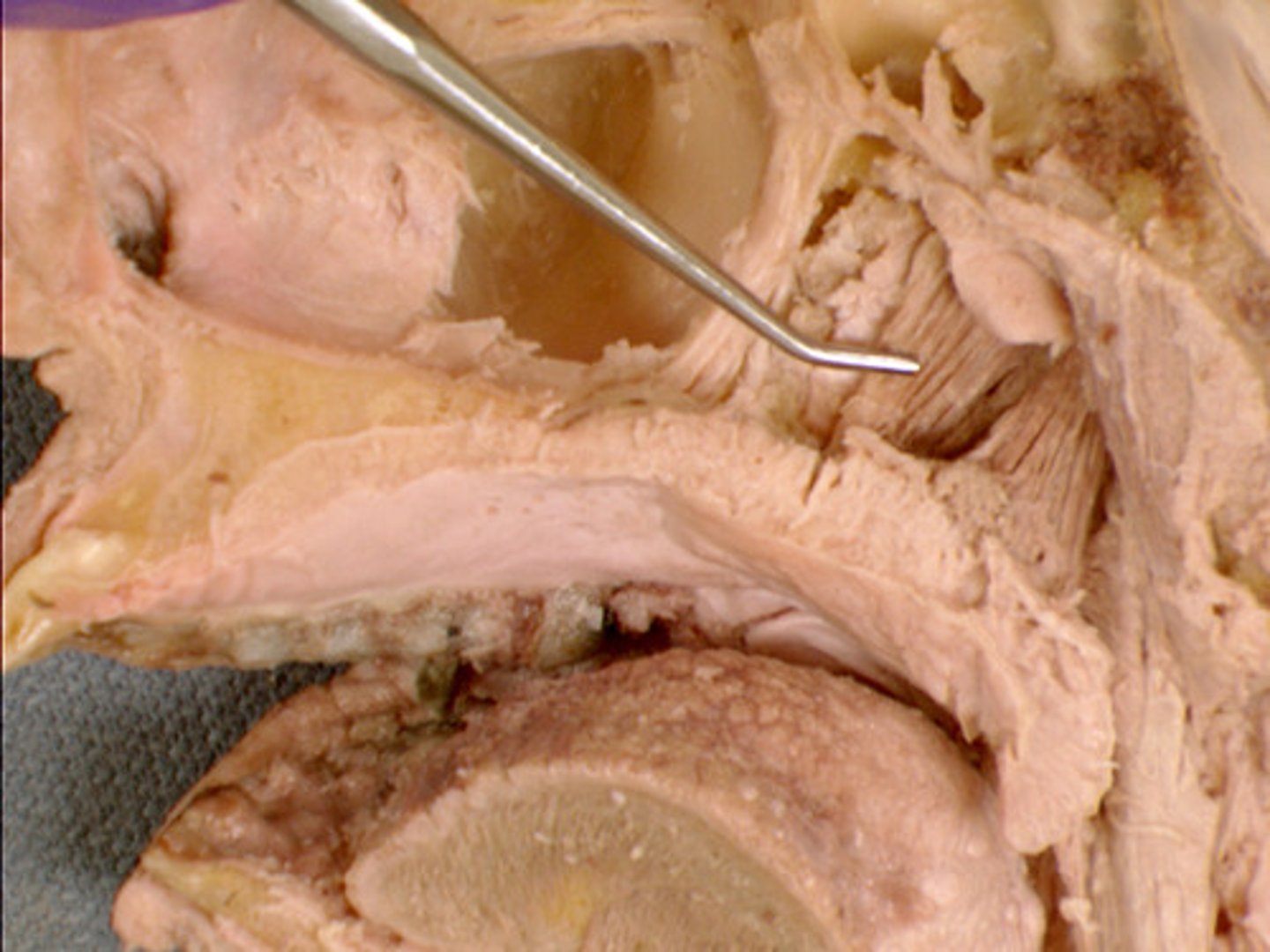
tensor veli palatini muscle, tenses soft palate (CN V3)
name and function
CN V3
what innervates this muscle?
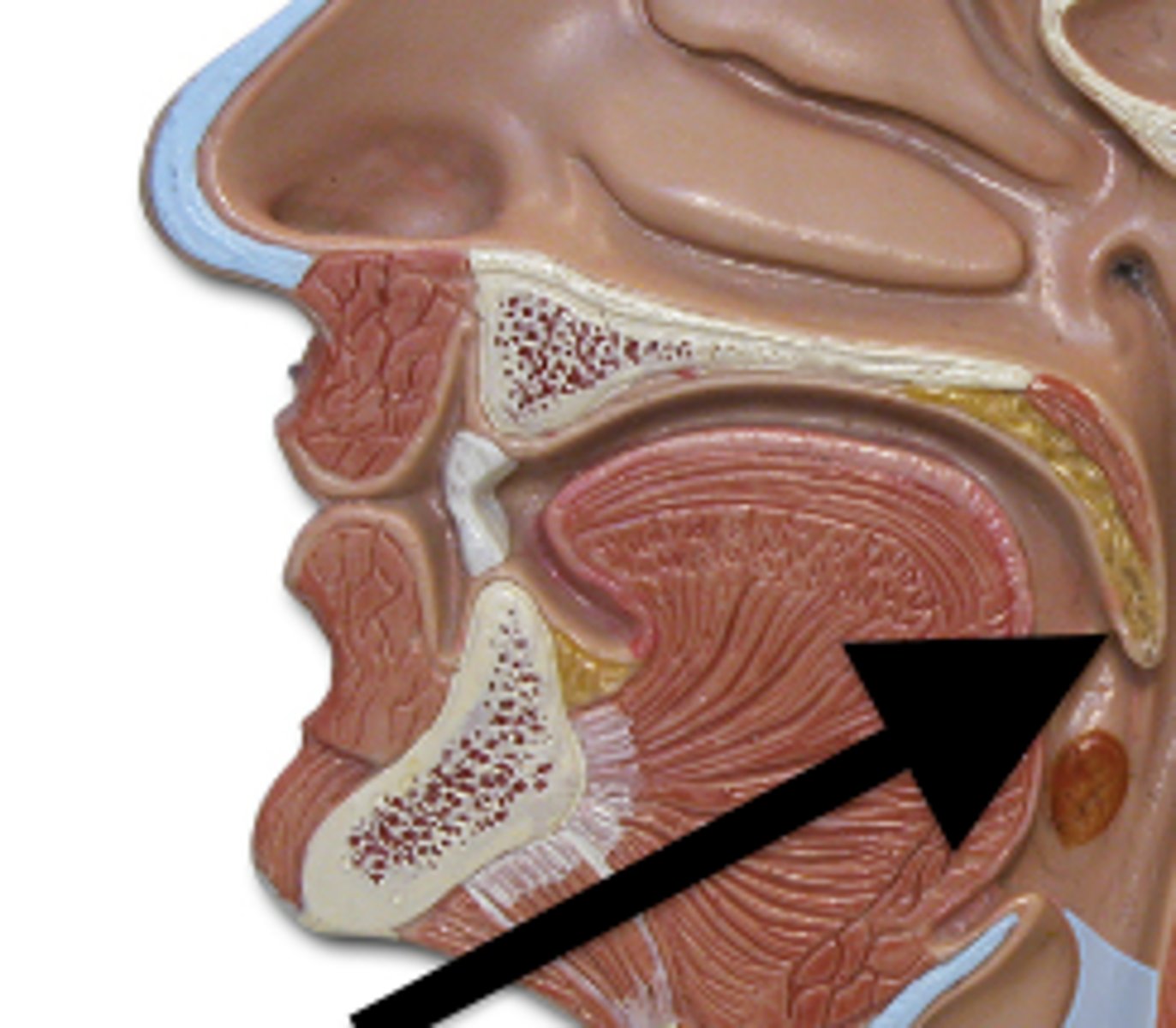
lacrimal fossa
depression where lacrimal sac sits
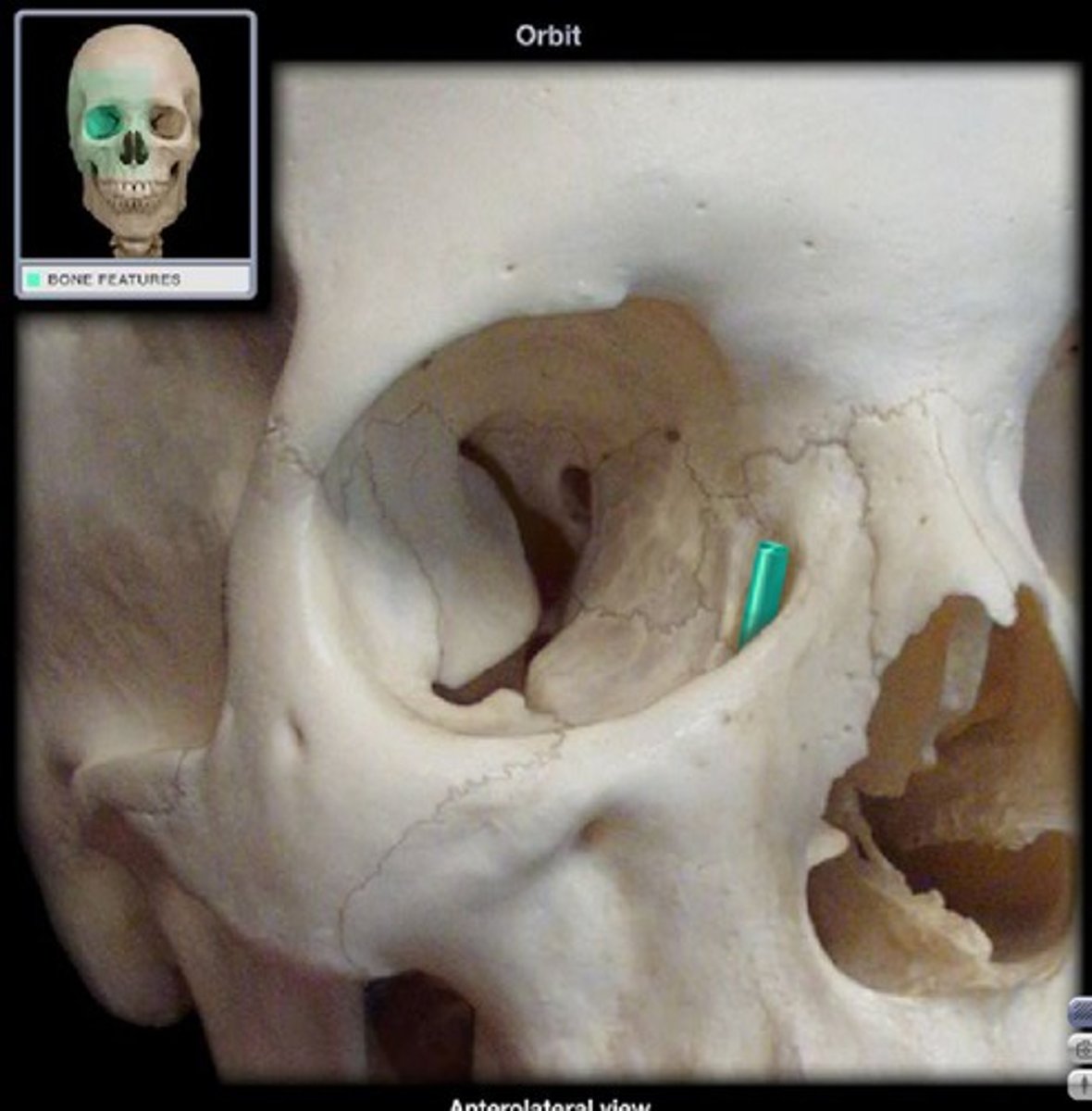
nasolacrimal canal/duct
empties lacrimal fluid into the nasal cavity
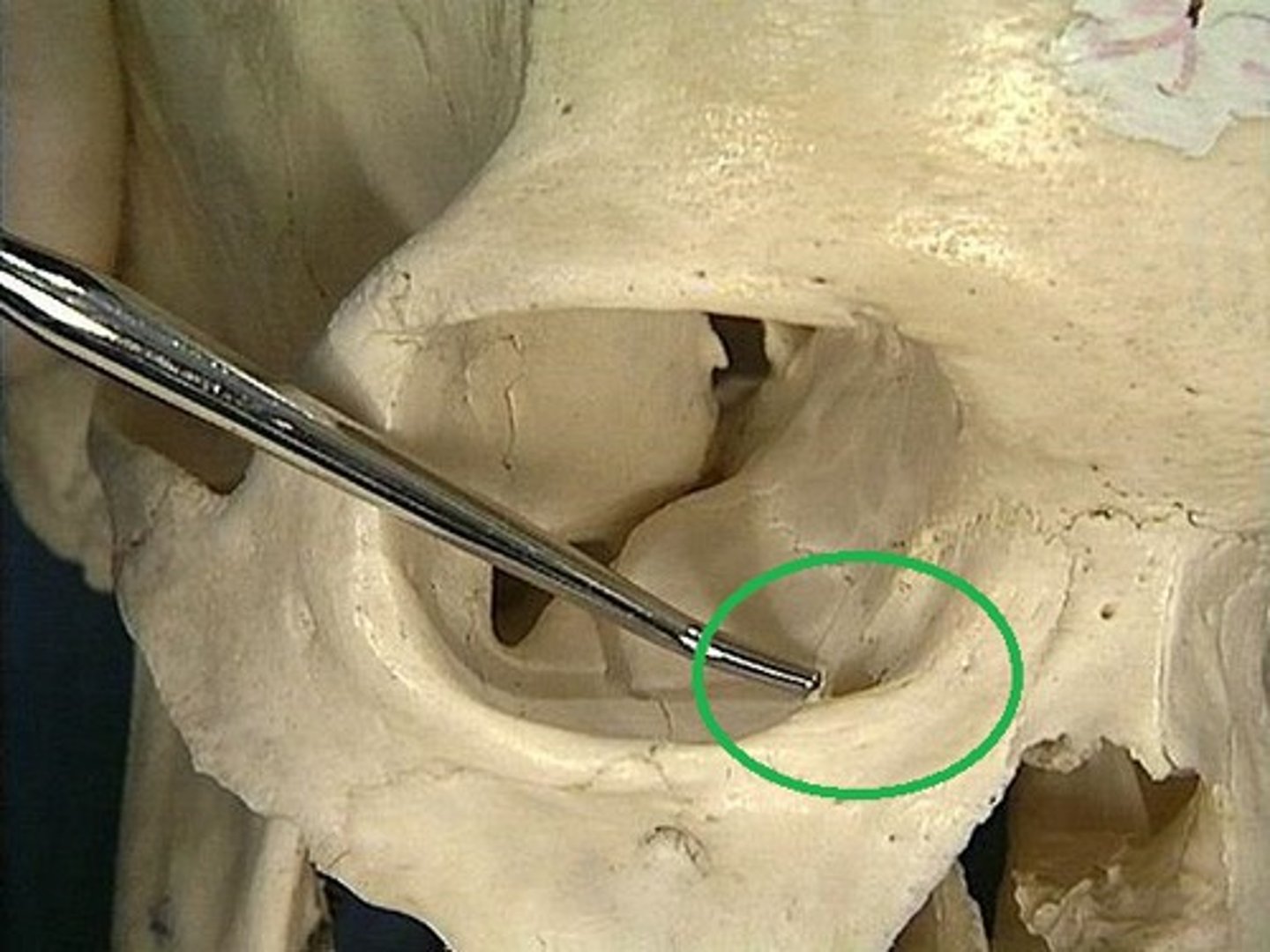
inferior meatus
where does the nasolacrimal duct drain into
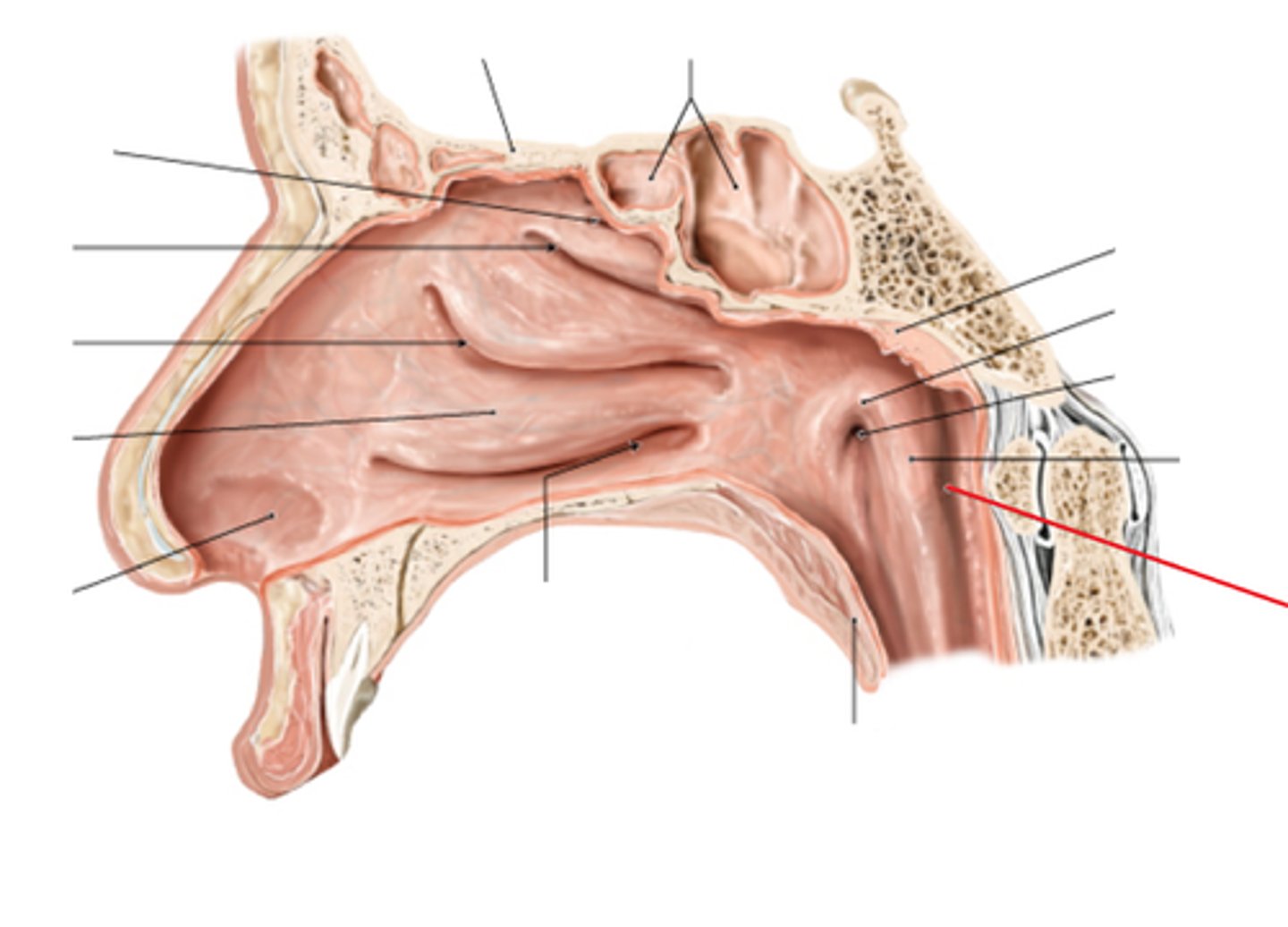
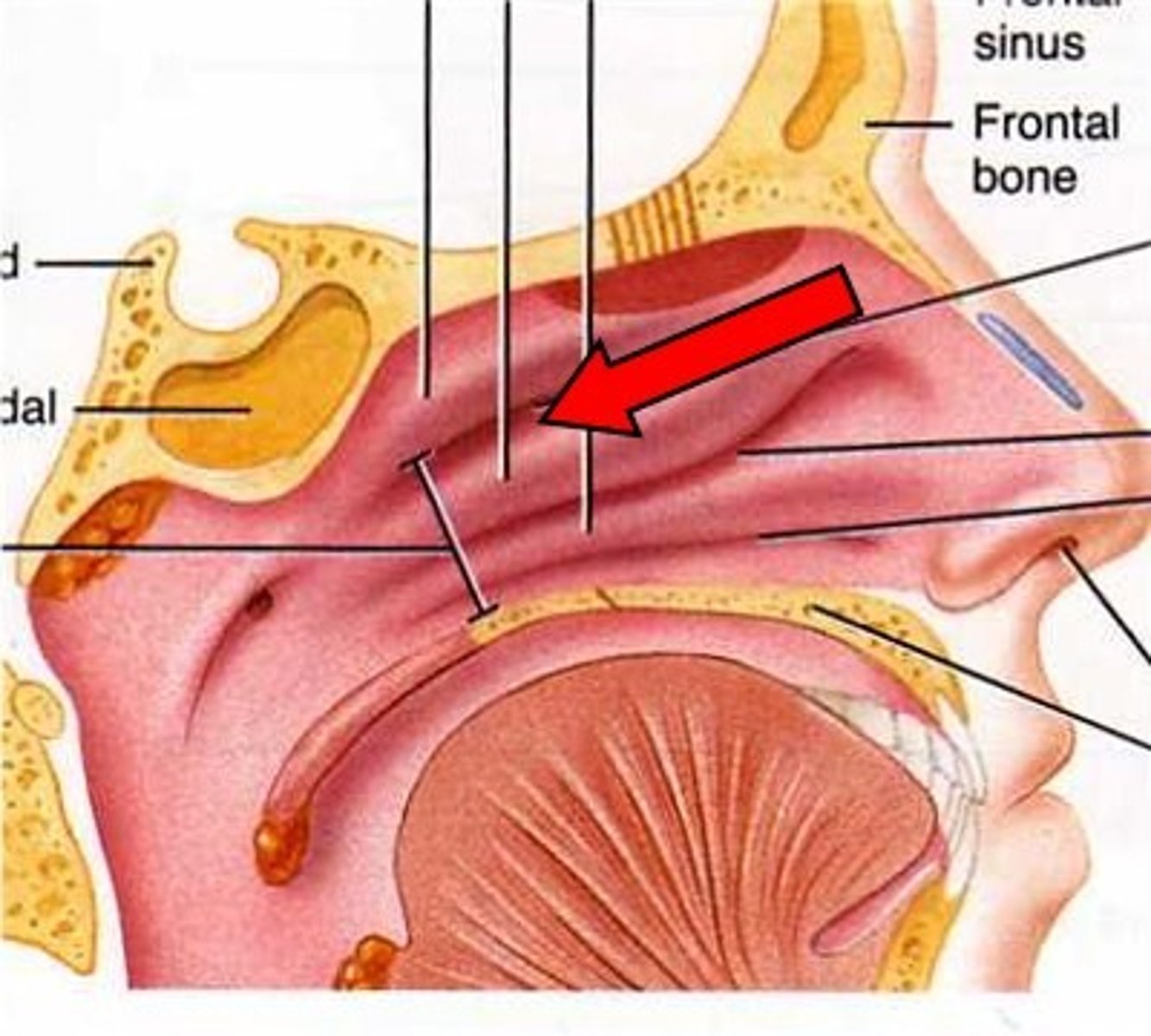
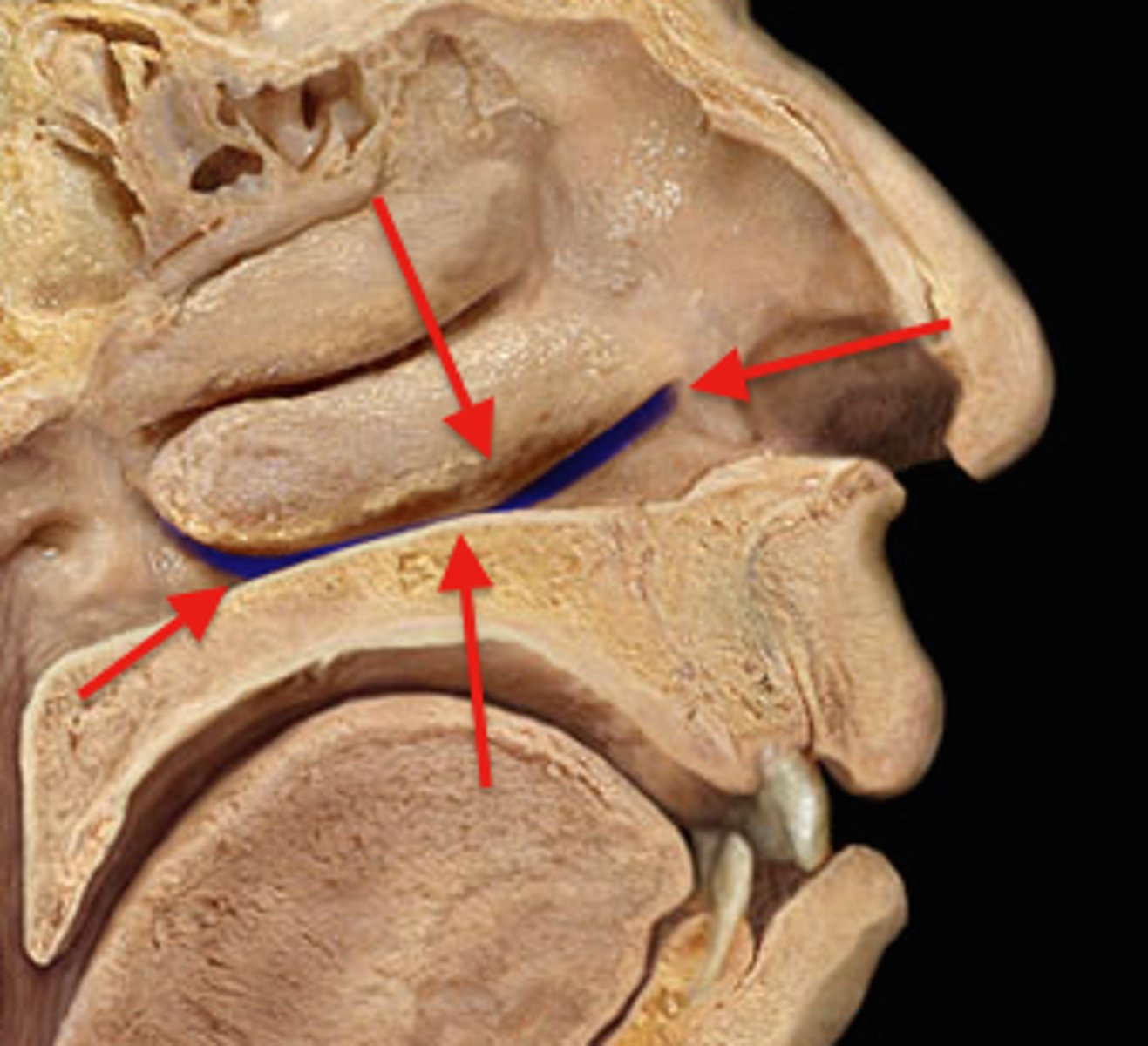
superior concha
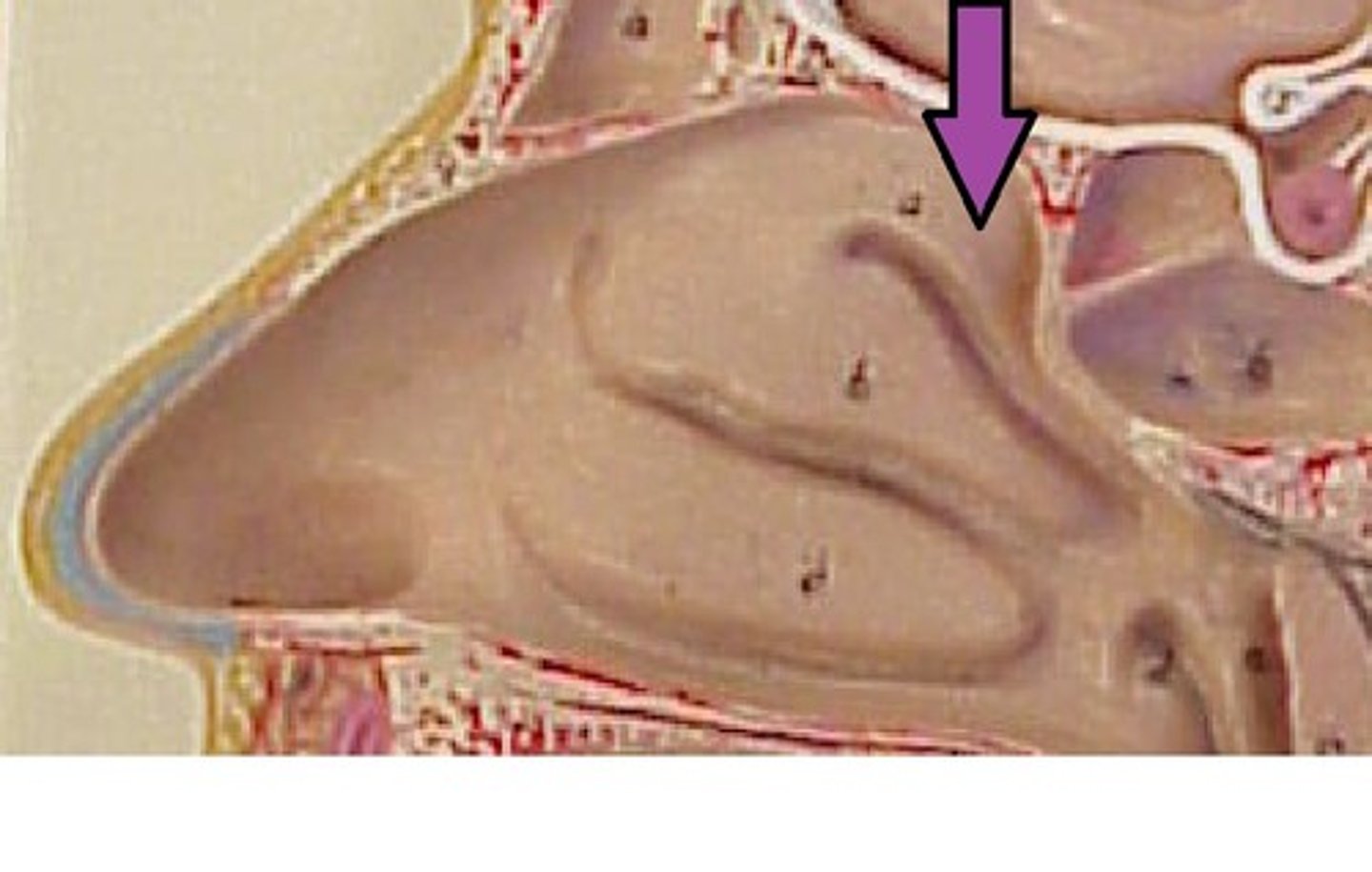
middle concha
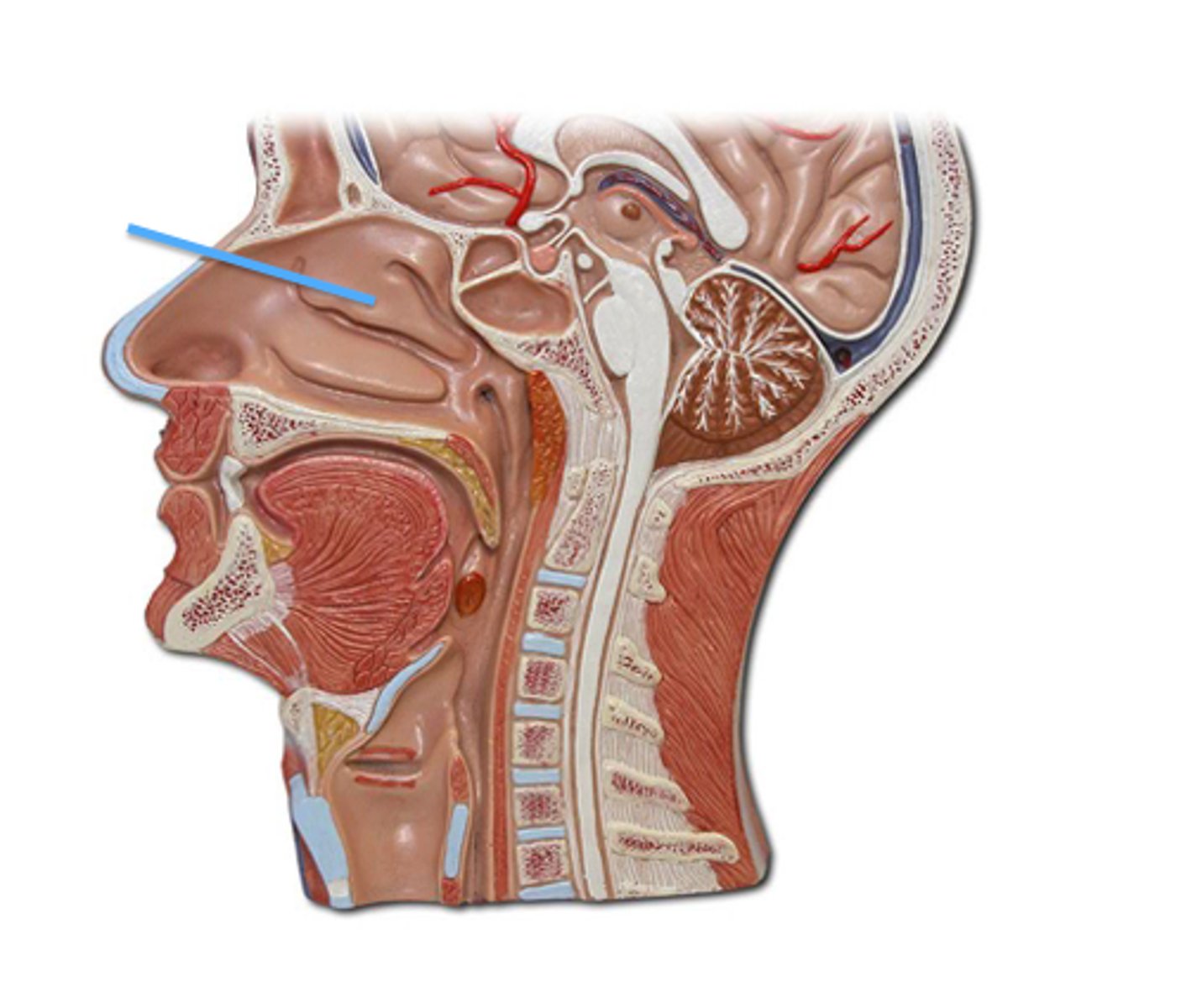
inferior concha
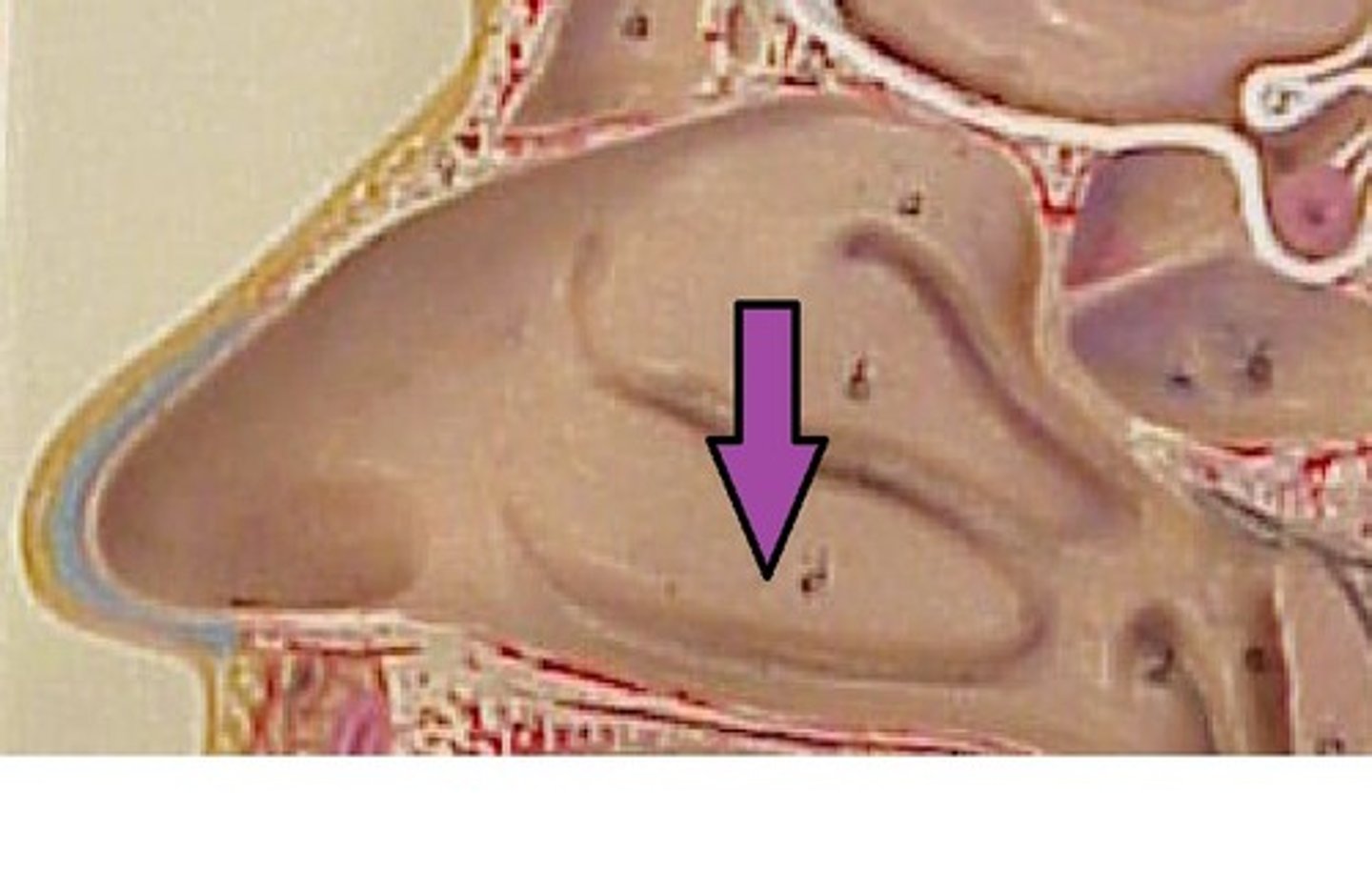
superior nasal meatus
middle nasal meatus
where frontal, maxillary, sinuses and ethmoid air cells drain
inferior nasal meatus
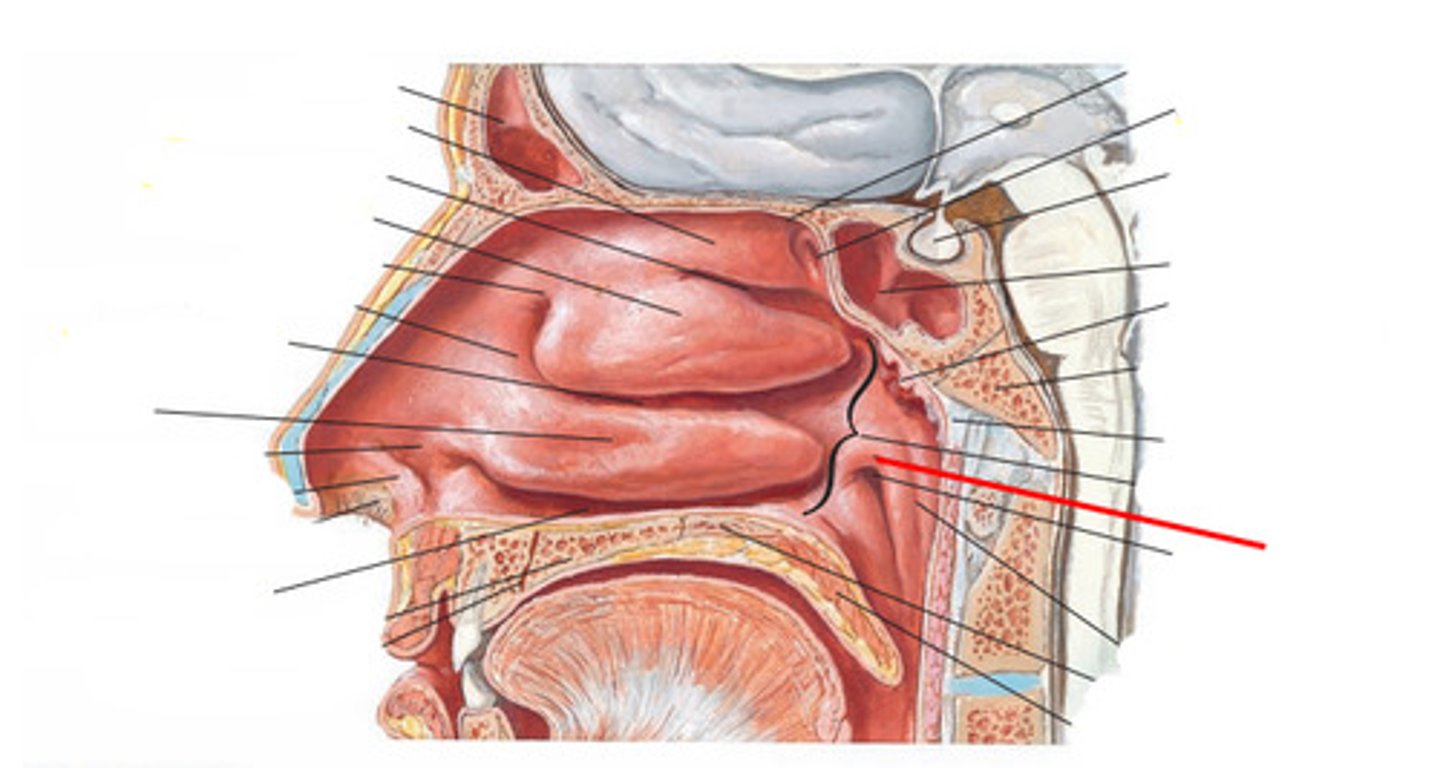
sphenoethmoidal recess
sphenoid sinus drains into
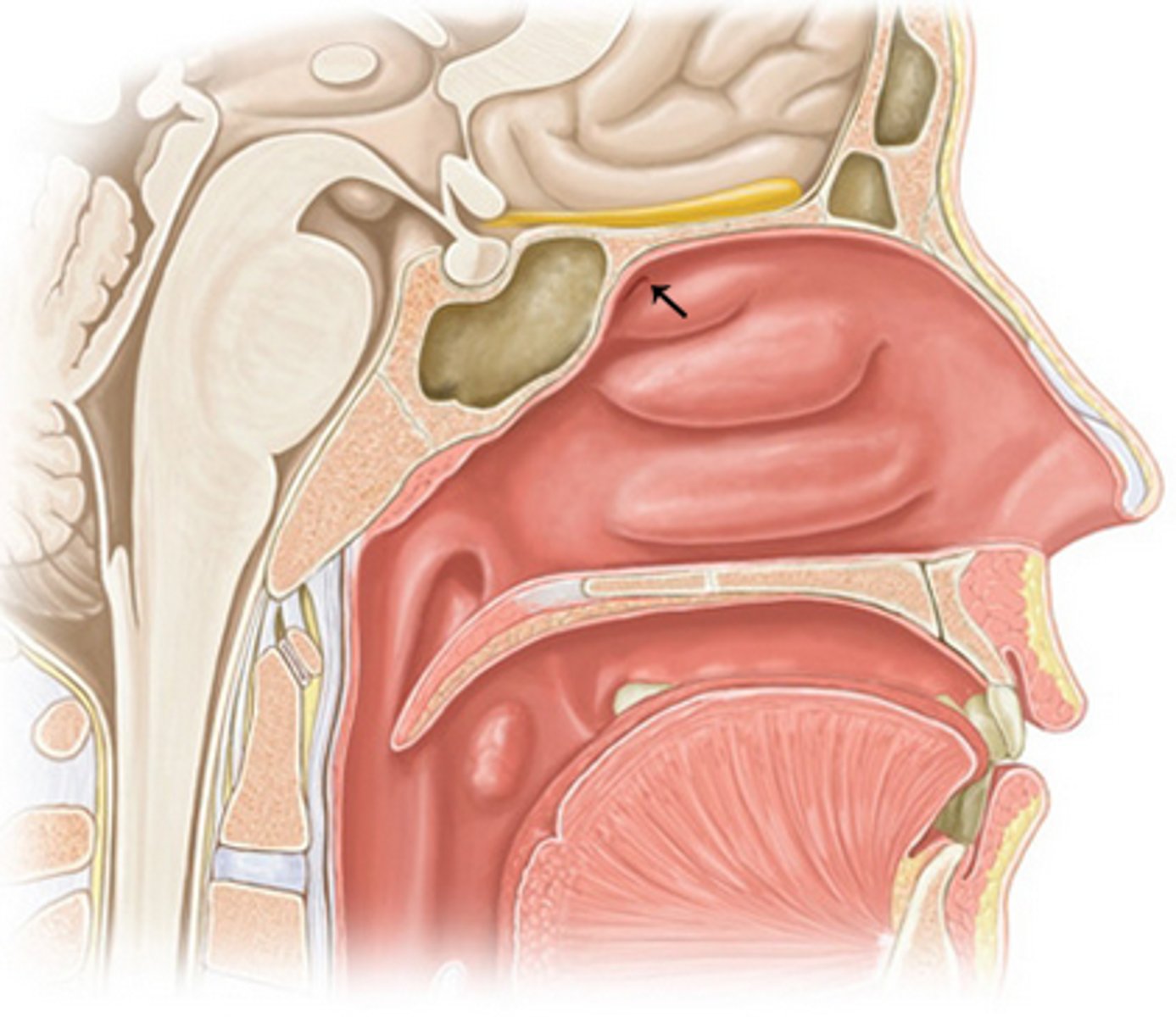
ethmoid bulla
locateed in middle meatus, where middle ethmoidal air cells drain
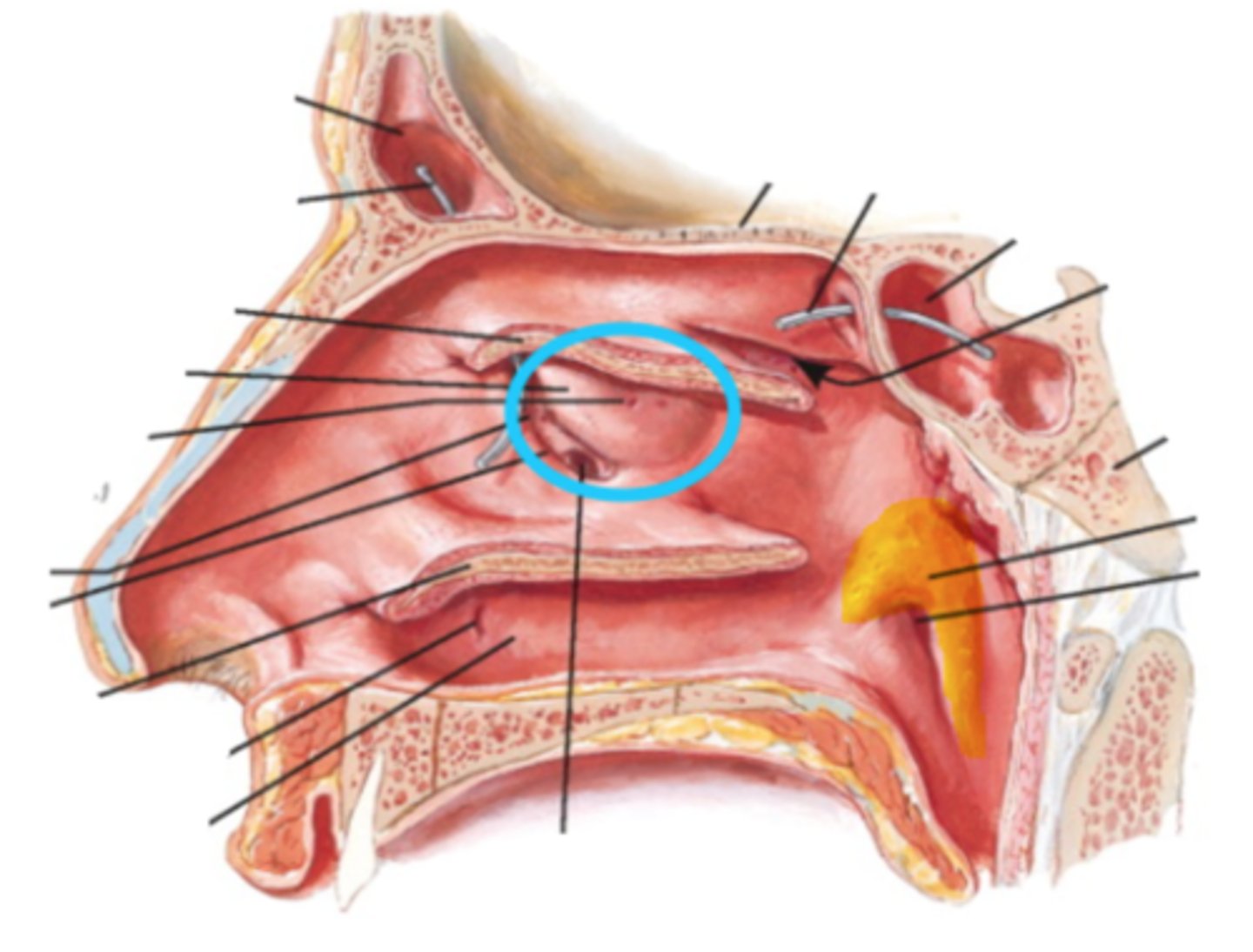
hiatus semilunaris
opening separating middle meatus and infundibulum
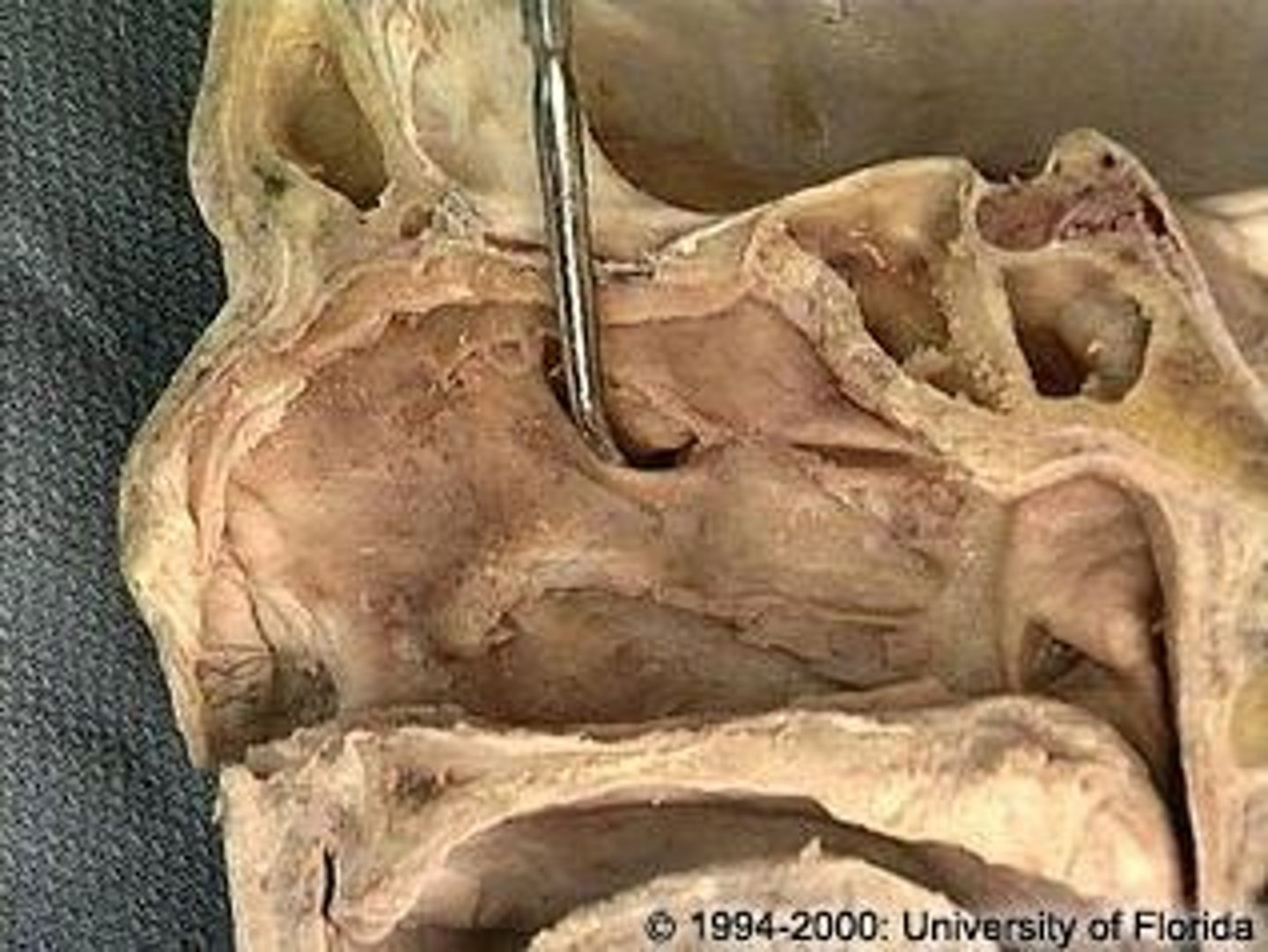
sphenoid sinus, sphenoethmoidal recess
structure and where it drains
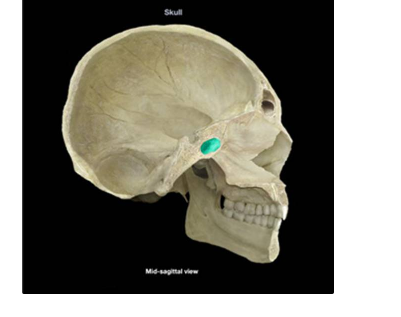
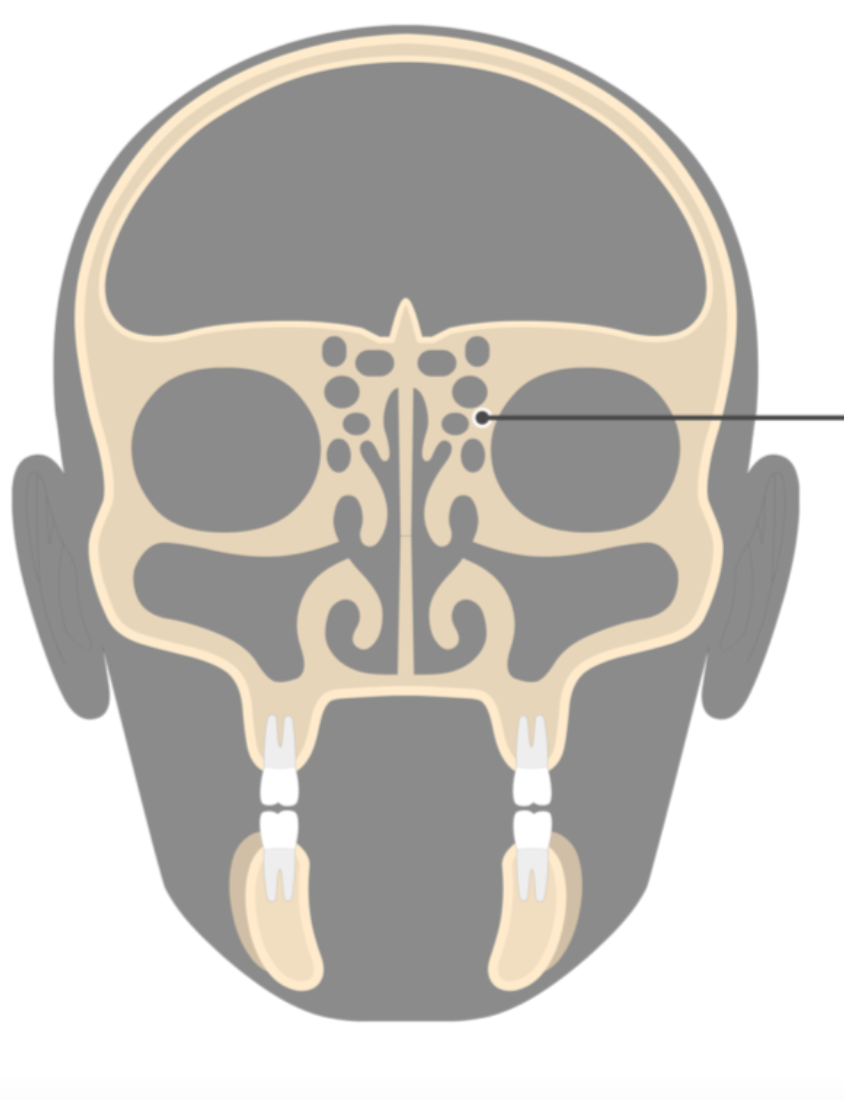
frontal sinus, middle meatus
structure and where it drains
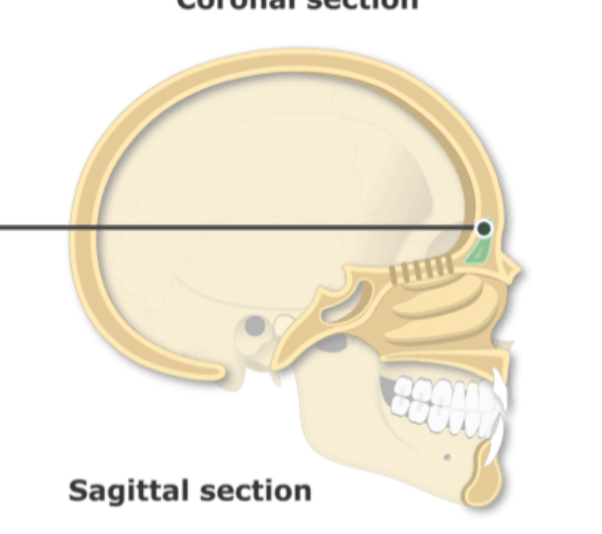
maxillary sinus, middle meatus
structure and where it drains
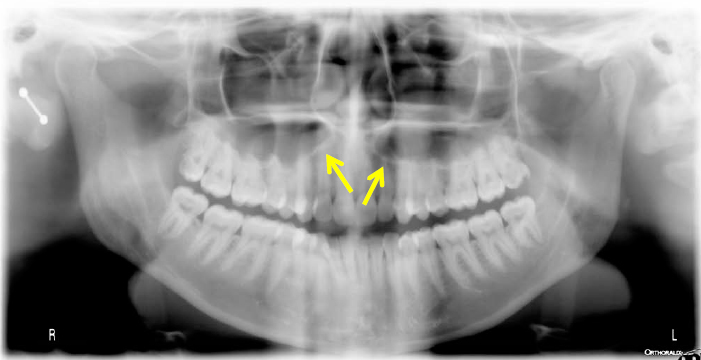
ethmoid air cells, middle meatus (ethmoid bulla)
structure and where it drains
incisive fossa/foramen
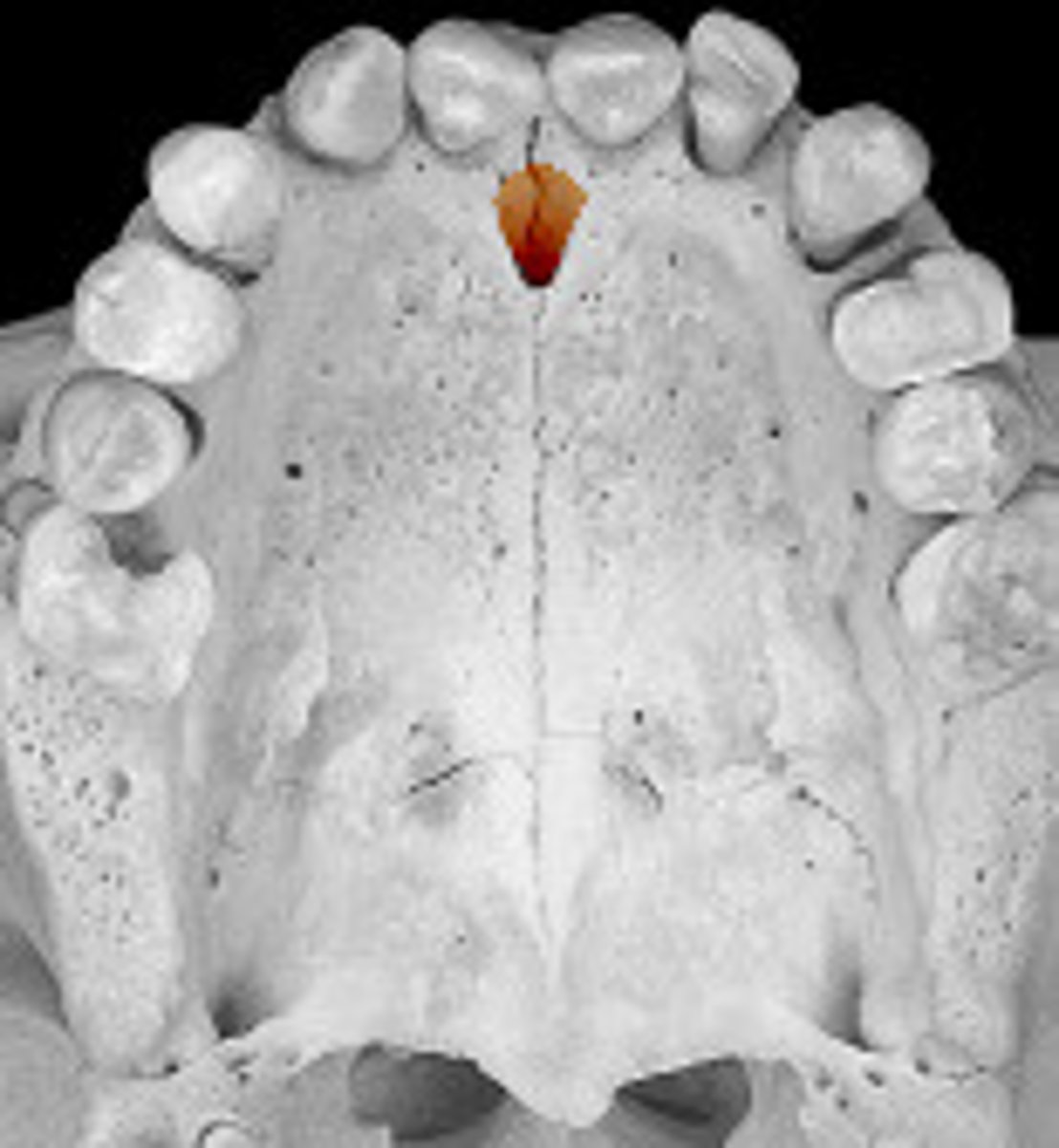
nasopalatine (CN V2)
what nerve travels through this opening
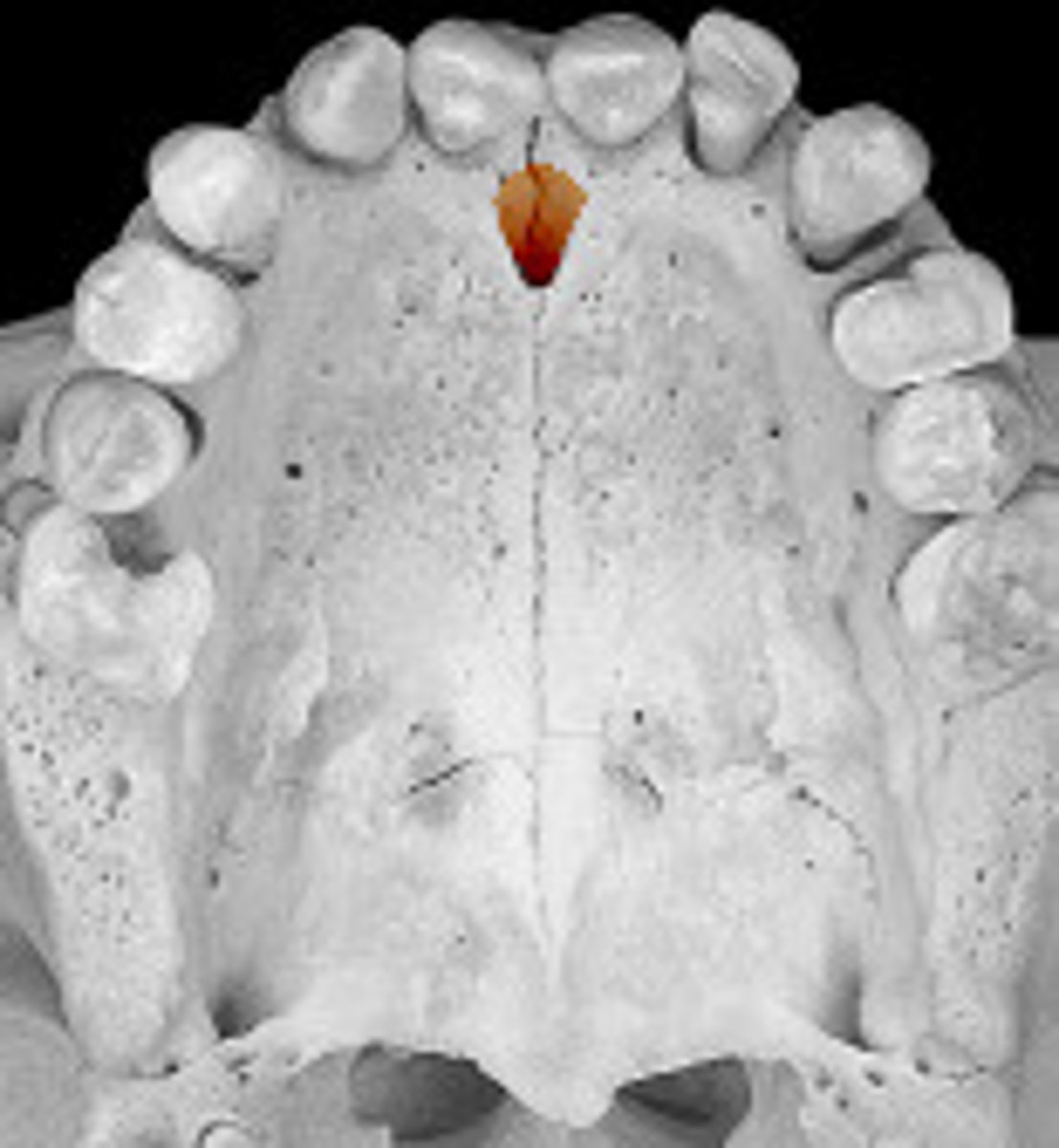
Sphenopalantine artery
what artery travels through this opening
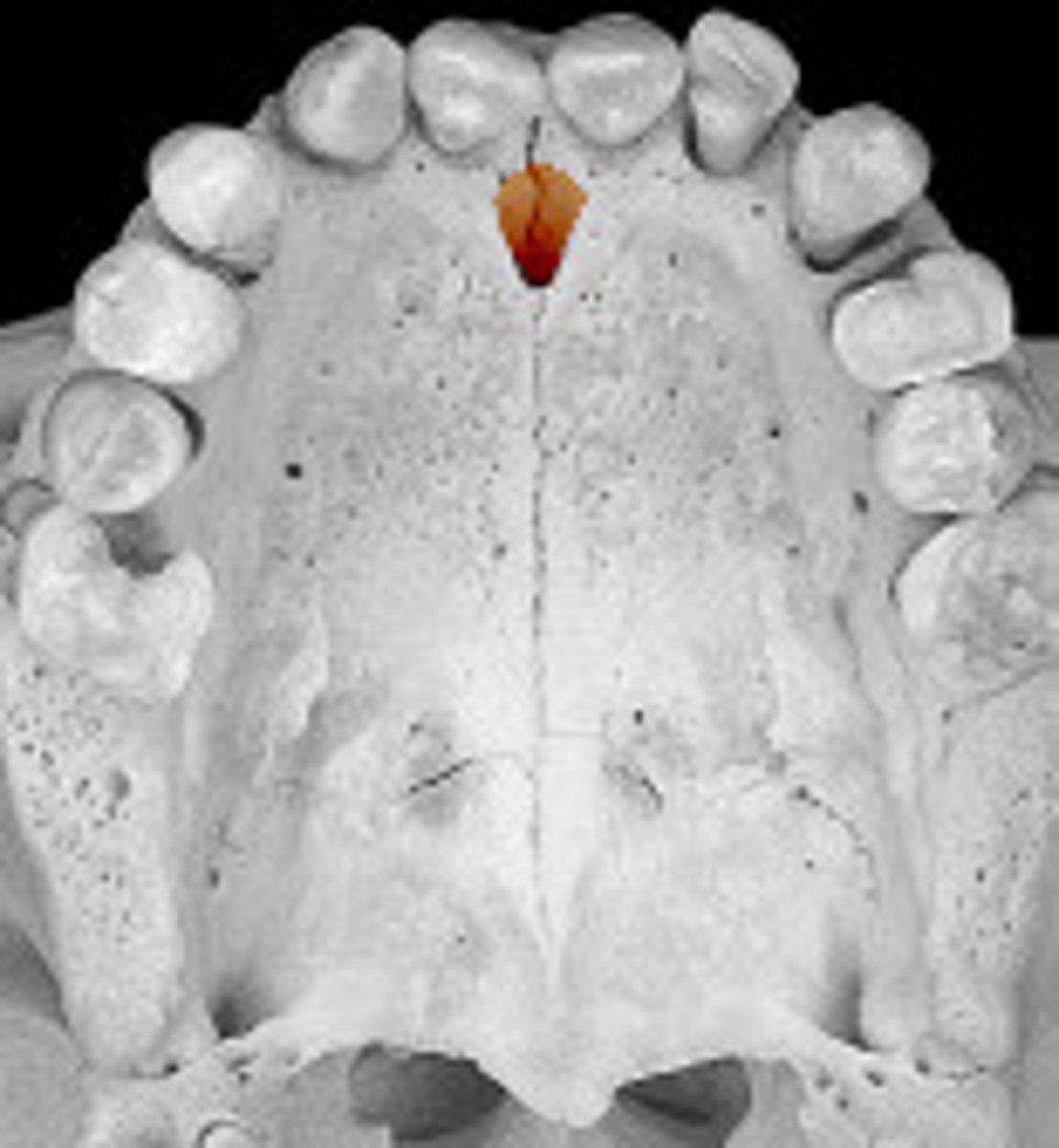
nasopalatine
what nerve innervates this portion of the palate
naris
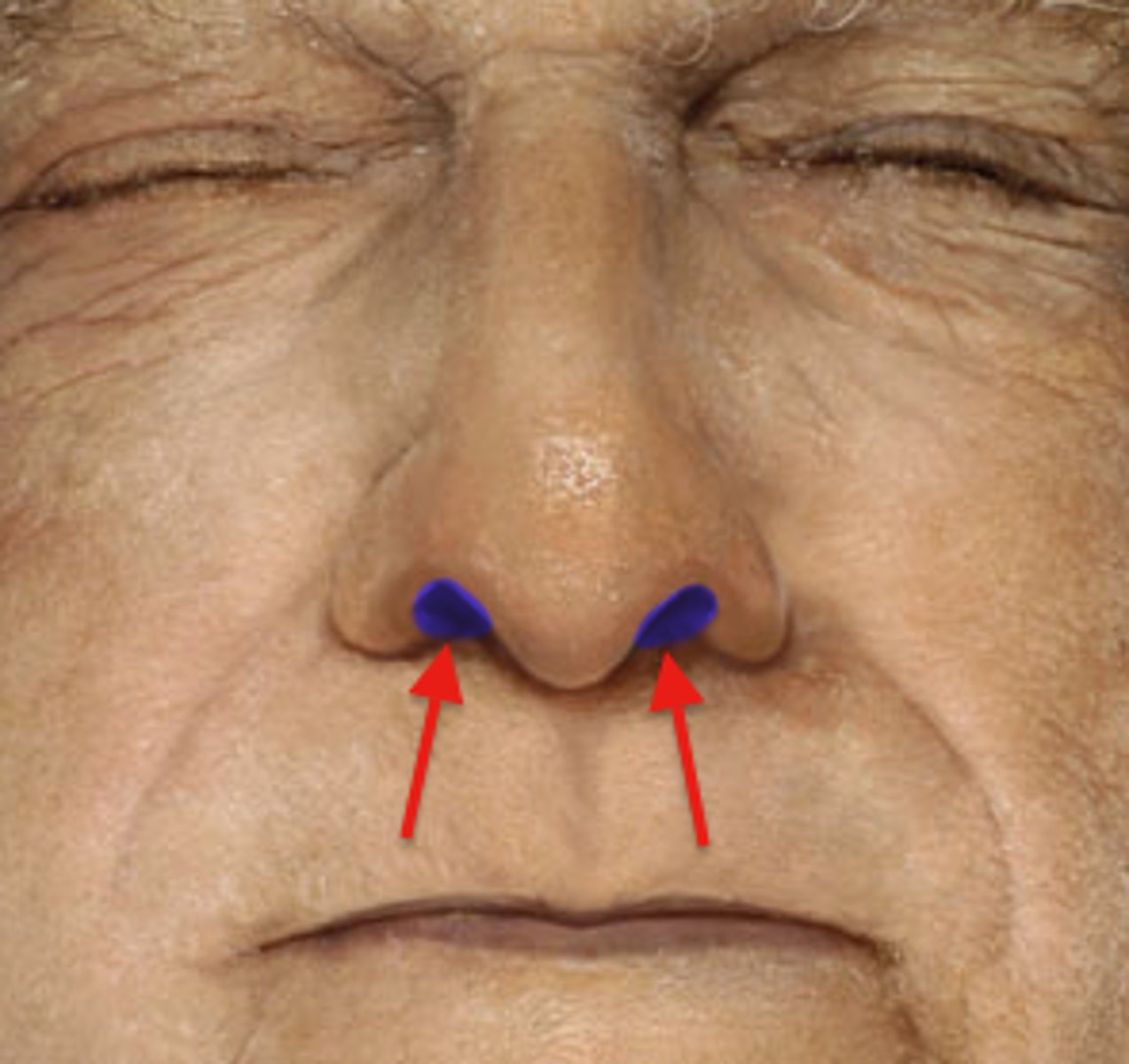
nasal vestibule
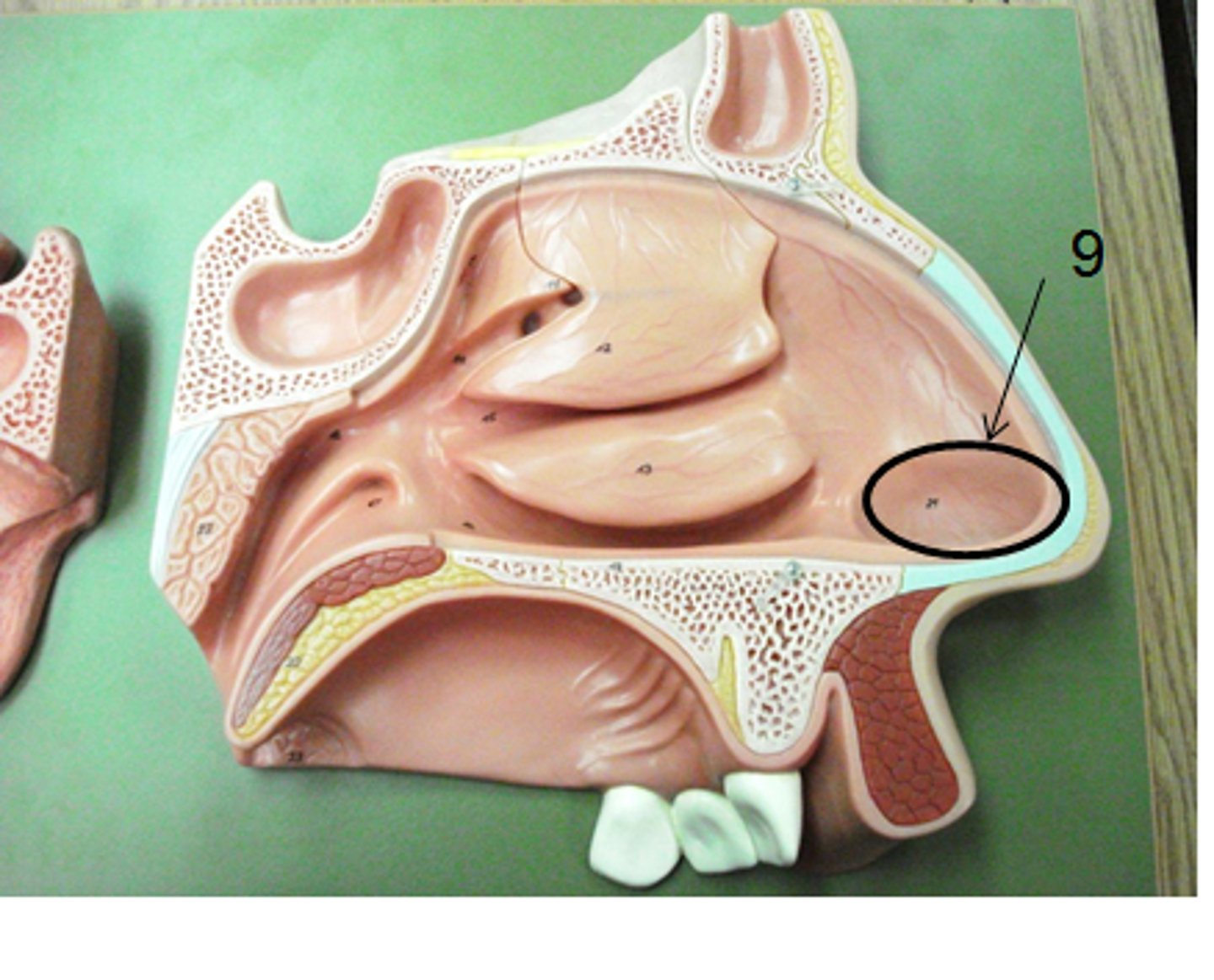
nasal atrium
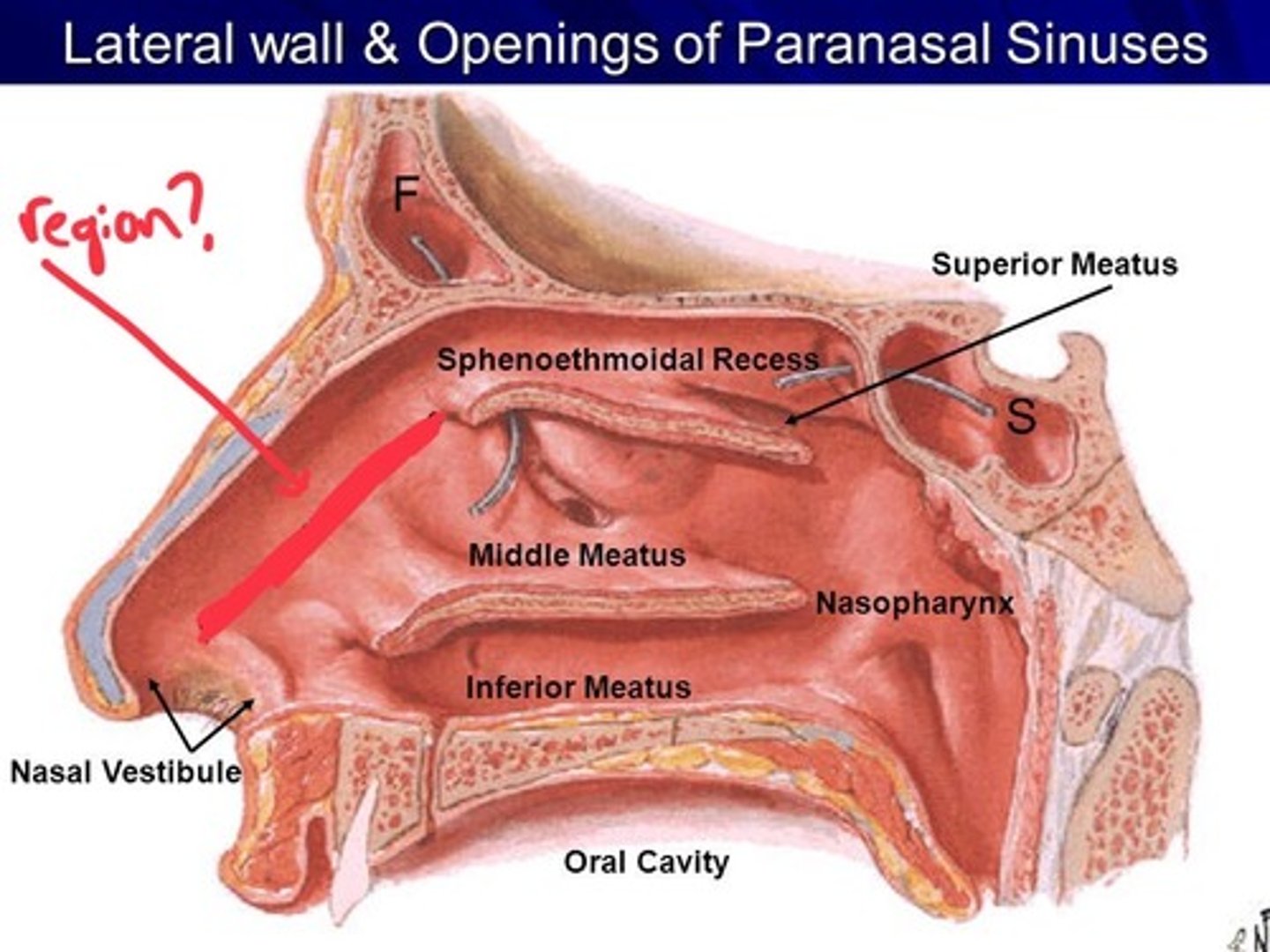
choanae
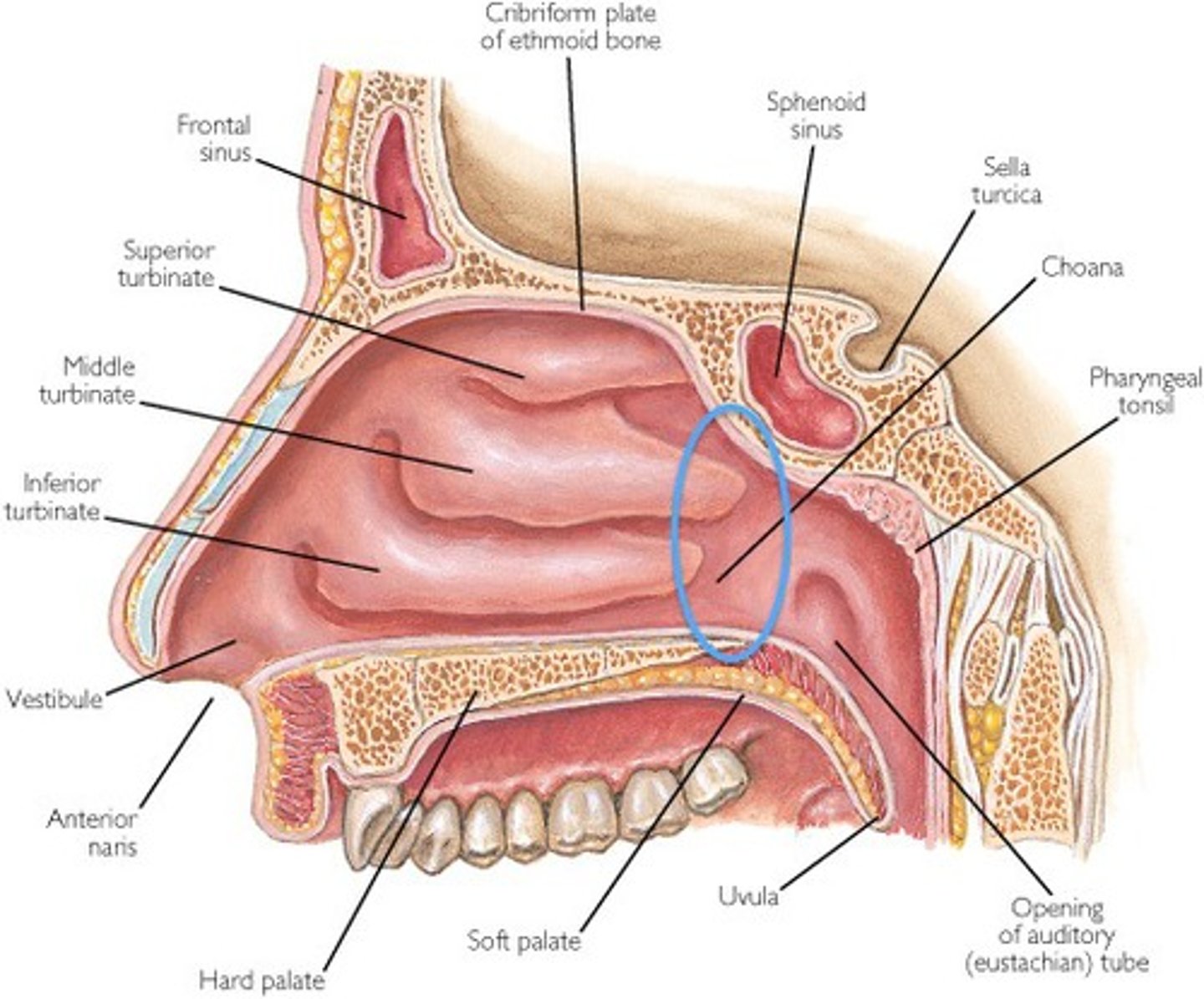
alar cartilage
cartilage that supports the apex of the nose and helps shape the nares; it is connected to the septal cartilage and connective tissue of the alae