RM1 Step 5: Select a research design (pt 2)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Non-experimental and Quasi-experimental strategies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
When do you use Non-experimental (NE) and Quasi-experimental (QE) strategies?
When manipulation and random assignment is not possible or unethical
How to distinguish between NE & QE?
NE: little or no attempt to minimise threats/confounds
QE: some attempt to minimise threats
Similarity between NE & QE
Both are NOT true experiments since cannot establish cause-and-effect r/s
Degree of accuracy among the 3 experimental strategies
Experimental > QE > NE
4 types of NE research designs
Differential research design (DRD)
Developmental research design (DRD) - cross-sectional & longitudinal
Posttest-only non-equivalent control group design (PoNCGD)
Pretest-posttest design (PPD)
Differential research design
A research study that simply compares pre-existing groups
Process of participant grouping
Does not randomly assign participants to groups, but automatically separates participants based on pre-exisiting characteristics (eg. gender, race or personality)
Eg. attachment styles studies - separated based on pre-existing attachment styles (secure vs insecure)
Differential research design is ALWAYS a
BSD
(recap: individual differences as a confound)
Developmental research design
A research study used to study behavioural changes related to age
2 types of developmental research designs:
Cross-sectional design
Longitudinal design
Cross-sectional design (CSD)
A BSD that measures separate groups of individuals of different ages
Cross-sectional design has the same concept as differential research design, but what makes it distinct?
When age is the main variable of interest
Advantage & Limitation of CSD
(+)
Convenient and less costly (don’t have to wait for a group of participants to grow older)
(-)
Susceptible to cohort effect
Cohort effect
When differences between age groups (or cohorts) are caused by unique characteristics other than age
Eg. increasingly lower computer literacy rate from 40yo - 60yo - 80 yo may be due to lack of exposure to computers in their lives rather than age
What do we do to address cohort effect as a potential confound?
Use longitudinal design
Longitudinal design
A WSD that measures the same group of individuals over a period time as they age (typically every few months or years)

Advantage & Limitations of LD
(+)
Rules our cohort effect as a potential confound as the same group of people is being measured
(-)
Extremely costly and time consuming
Susceptible to high dropout rate; participant attrition
Can be affected by all time-related confounds that affect WSD (eg. order effect)
What are the consequences of participant attrition?
IV is weakened if participants who drop out are systematically different from those remaining, as the final group characteristic used to explain changes observed over time might differ
Posttest-only non-equivalent control group design (PoNCGD)
A research study that separates pre-existing groups, one as treatment and the other as control
When are non-equivalent groups commonly used?
When the goal is to evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment (one group receives the treatment, the other doesn’t) → non-equivalent
*Note: no random assignment (pre-existing)
What does posttest mean?
Both groups are measured AFTER the test
Example of when to use PoNCGD
Testing the effectiveness of Covid vaccine
Use pre-existing groups based on preferences (want to take vaccine - treatment & don’t want to take the vaccine - control)
OR effectiveness of different math classes

PoNCGD is ALWAYS a
BSD
Pretest-Posttest Design (PPD)
A research study that measures each participant ONCE before the treatment and ONCE after
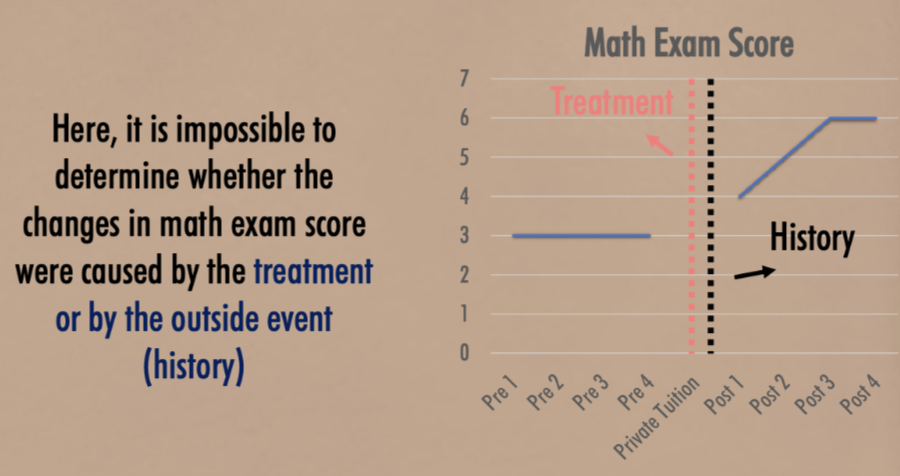
Eg. the effectiveness of math tuition

When is the difference between PPD and WSD
WSD: counterbalancing can be done to make it experimental
PPD: counterbalancing is not feasible or impossible
What is the similarity between PPD and WSD?
Both can be confounded by any time-related threats, affecting IV
Temporal precedence of PPD
The before-treatment observations (pre-test) must always precede the after-treatment observations (post-test)
What to do to improve the IV of PoNCGD and PPD?
Use QE research designs
2 types of QE research designs
Pretest-posttest non-equivalent control group design (PPNCGD)
Time-series design (TSD)
What does a PPNCGD design consist of?
A research study that consists of a pretest and a post-test for two non-equivalent groups
Eg. effectiveness of math tuition
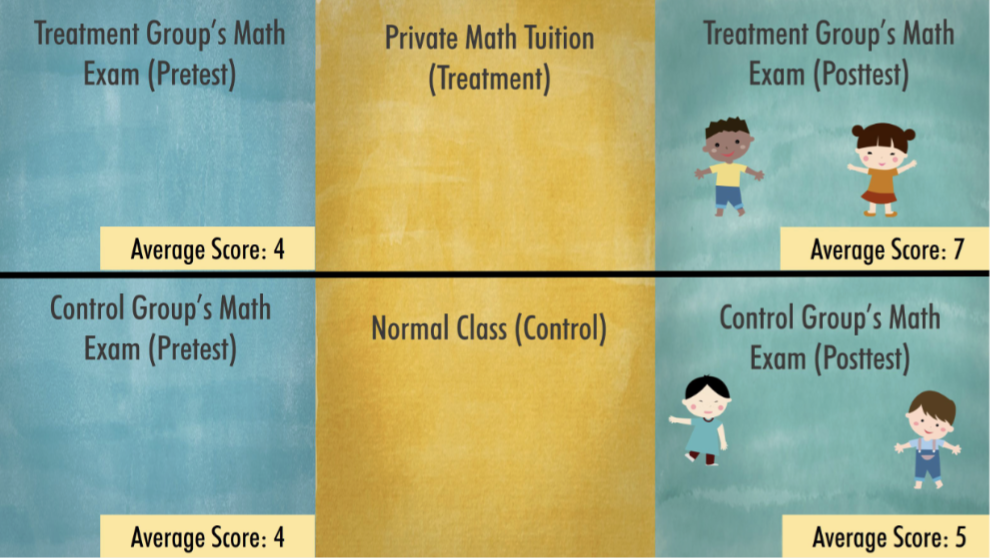
2 advantages of PPNCGD (related to IV)
Addition of the pretest measurement reduces the threat of individual differences as a confound
Reduces time-related threats
Reducing threat of individual differences (due to selection bias)
If both groups are similar in the pretest, differences in posttest will be more likely due to the treatment, and less likely due to pre-existing differences
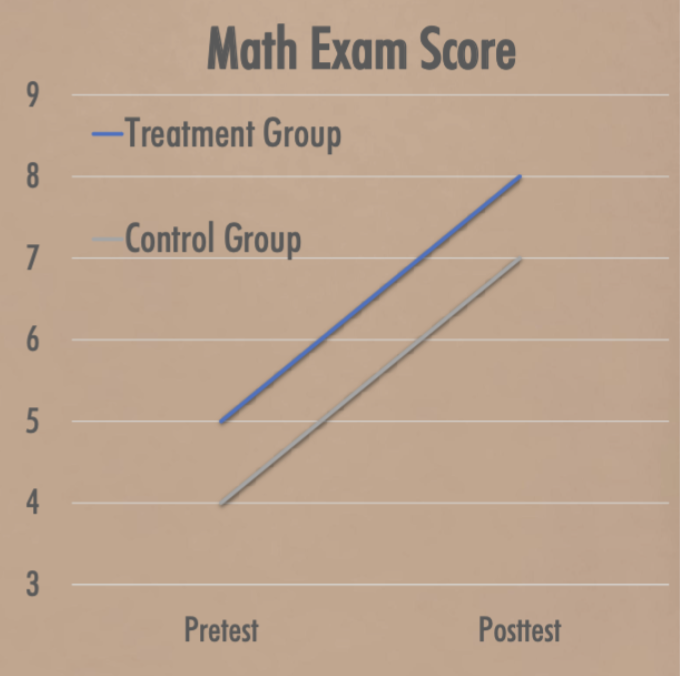
Graphical interpretation
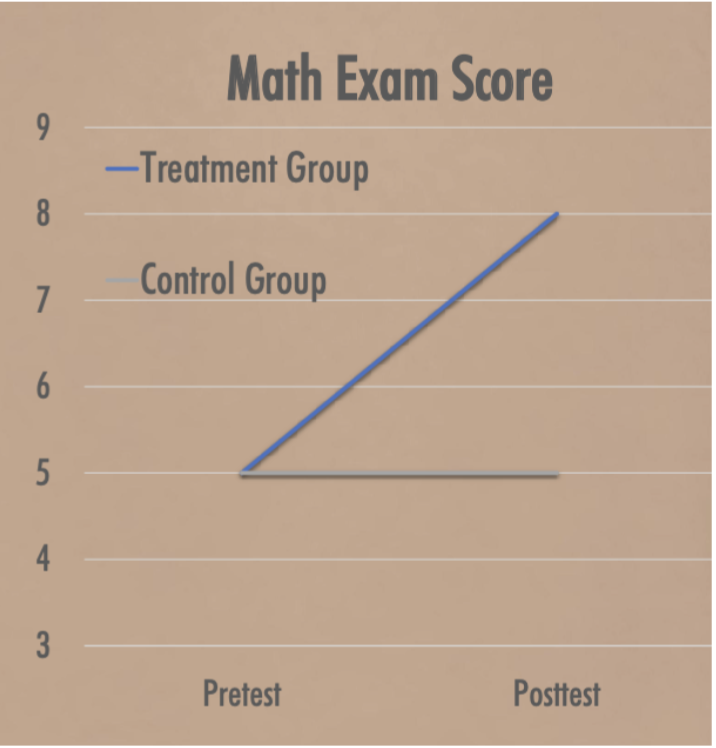
Why is time-related threats limited?
Since both t&c groups are observed over the same period, they should experience the same time-related factors
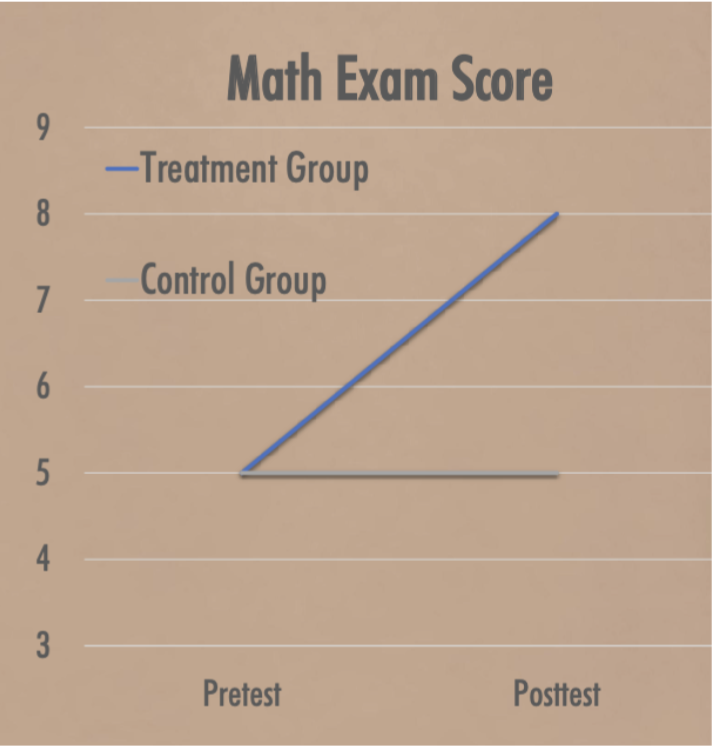
What is a possible explanation for this result?
Since there is a posttest difference, it’s more likely due to the treatment effect and less of time-related threats

What is a possible explanation for this result?
Since both groups show the same degree of change, some other factor must be responsible eg. maturation
What is a limitation of PPNCGD?
Even though the time-related threats and individual differences are reduced, they are not completely eliminated
Why can’t they be completely eliminated?
There is no random assignment (individual diff) and counterbalancing (time-related threats)
Differential effects in time-related threats
(ALL) Time-related threats affecting groups differently (since non-equivalent groups come from different settings)
Eg. differential history effect (refer to docs)
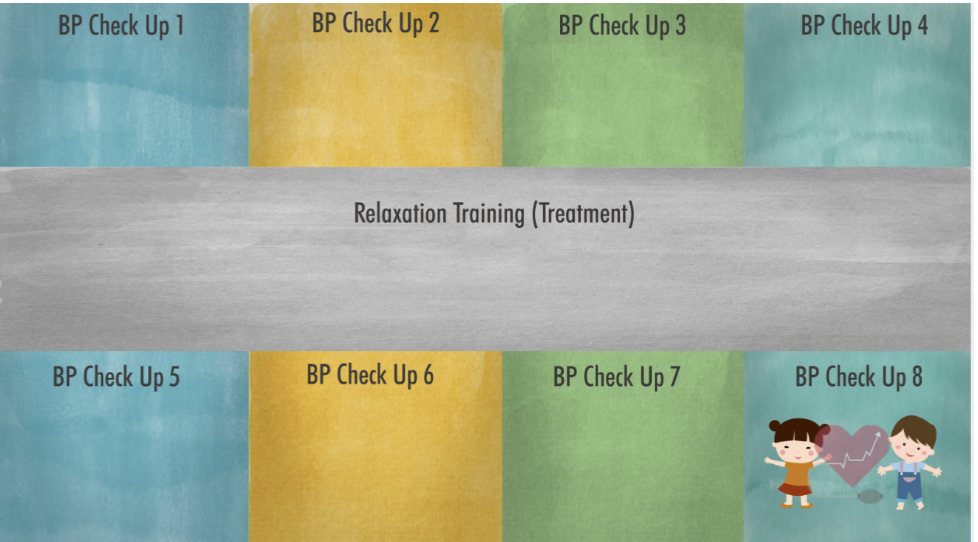
Time series design (TSD)
A research study that measures each participant MULTIPLE times (series of observations) before the treatment and MULTIPLE times after the treatment
Eg. Recording a series of blood pressures before and after relaxation training
Interrupted time-series design
A study measuring an intervening event that is not manipulated by the researcher eg. earthquake event
Advantage of TSD
Able to minimise some threats to IV as pretest observations can show pre-existing trends that can indicate the influence of other unrelated factors
(refer to docs for examples)
Limitation of TSD
Unable to rule out the possibility of a simultaneous occurrence of any time-related threats and the treatment