GI USMLE
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
G cells
produce gastrin
antrum of stomach/ duodenum
promote gastric acidity and motility
ghrelin
hunger hormone
produced by stomach
D cells
somatostatin
produced in pancreatic islets/ GI mucosa
decrease insulin and glucagon release/ and gastric acidity
I cells
cholecystokinin
duodenum/ jejunum
promote pancreatic secretions and sphincter of oddi relaxation
S cells
secretin
duodenum
neutralize stomach acidity/ promote bile secretion
K cells
glucose dependant insulinotropic peptide
duodenum, jejunum
promote bile secretion and gastric neutrality
motilin
SI
raised in fasting state
vasoactive intestinal peptide
parasympathetic ganglia in sphincters/ gallbladder/ SI
promotes intestinal water and electrolyte secretion/ smooth muscle relaxation
decrease gastric secretion
nitric oxide
promotes smooth muscle relaxation
induces lower esophageal sphincter
gastric acid
parietal cells
intrinsinc factor
parietal cells
vitamin B12 binding protein
chief cells
pepsin
protein digestion
bicarbonate
produced by mucosal cells of stomach/ duodenum/ salivary glands/ pancreas AND BRUNNER GLANDS (duodenum)
neutralizes acid
cleft lip and palate
failure of facial prominence to fuse
seen in digeorge
aphtous ulcer
A. Painful, superficial ulceration ofthe oral mucosa
B. Arises in relation to stress and resolves spontaneously, but often recurs
C. Characterized by a grayish base surrounded by erythema
behcet syndrome
reccurent aphtous ulcers/ genital ulcers and uvitis
due to immune complex small vessel vasculitis
etiology unknown, usually seen after viral infection
oral herpes
rupture of oral mucosa vesicles → shallow painful ulcers
HSV1
often primary infection in childhood that remains dormant
can be reactivated by stress/ sun exposure
SCC mouth
risk factors; tobacco, alcohol
often floor of mouth
leukoplakia/ erythroplakia are precursor lesions
mumps
bilateral inflammed parotid gland
orchitis, pancreatitis and aseptic meningitis can also present
serum amylase increase
orchitis carries sterility risk in teens
sialadenitis
salivary gland inflammation
most commonly due to obstructing stone → staph infection
usually unilateral
pleomorphic adenoma salivary gland
made of cartilage and epithelial tissue
most common salivary gland tumor
usually in parotid
mobile/ painless/ circumsised mass at jaw angle
high rate of reccurence
can become carcinoma → presenst w/ facial nerve damage
warthin tumor salivary gland
benign cystic tumor
abundant lymphocytes/ germinal centers
almost always parotid gland\
second most common tumor
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
maligannt tumor salivary gland made of mucinous and squamous cells
most common malignant tumor salivary gland
usually arise in parotid
commonly affects facial nerve
tracheoesophageal fistula
congenital defect→ connection between esophagus and trachea
most common→ proximal esophageal atresia (distal esophagus arising from trachea)
presents w/ vomiting/ abdominal distention/ aspiration/ polyhydramnios
esophageal web
thin protusion esophageal mucosa
upper esophagus most common
presents w/ dysphagia for poorly chewed food
increased risk of esophageal SCC
plummer vinson syndrome
can occur as result of esophageal web
severe iron def anemia and beefy red tongue due to atrophic glossitis
zenker diverticulum
outpouching of pharyngeal mucosa through acquired defect in muscular wall (false diverticulum)
arises above upper esophageal sphincter at junction of esophagus and pharynx
presents w/ bad breath, dysphasia and obstruction
mallory weiss syndrome
longitudinal laceration of mucosa at gastroesophageal junction
caused by severe vomiting (common causes include bulimia and alcohol)
painful hematemesis
boerhaave syndrome
complication of amllory weiss syndrome
esophageal rupture → air in mediastinum and subq emphysema
esophageal varices
dilated submucosal veins in lower esophagus
secondary to portal hypertension
if rupture
painless hematemesis
most common cause of death in cirrhosis
achalasia
disordered esophageal motility
cant relax lower esophageal sphincter due to damaged ganglion in myenteric plexus
can be secondary to changa disease
clinical features
dysphasia
high LES pressure on manometry
bad breath
bird beak sign on barium swallow study
increased risk esophageal SCC
GERD
acid reflux from stomach due to lower LES tone
risk factor; alcohol, tobacco, fat rich diet, caffeine, hiatal hernia
clinical features
heartburn
asthma
damage to teeth enamel
ulceration with stricture and barrett esophagus are late complications
barrett esophagus
metaplasia of lower esophageal mucosa from stratified squamous epithelium to noncilliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
10% of patients with GERD have it
may progress to dysplasia and adenocarcinoma
esophageal carcinoma
adenocarcinoma- western world, barrett esophagus, lower 1/3 esophagus
SCC- most common worldwide, risk factors include hot foods, alcohol, tobacco, achalsia, esophageal web/ injury
often upper/ middle third esophagus
gastrochisis
congenital malformation of anterior abdominal wall
exposure abdominal content
omphalocele
persistant herniation of bowel into umbilical cord
due to failure of herniated intestines to return to body cavity during development
content covered by peritoneum and amnion of umbilical cord
pyloric stenosis
congenital hypertrophy of pyloric smooth muscles
classically presents 2 weeks after birth
projectile non billious vomiting
visible peristalsis
olive like mass in abdomen
tx is myotomy
acute gastritis
acidic damage to stomach mucosa due to imbalance between mucosal defense and acidic environment
risk factors
ulcers
NSAIDs
heavy alcohol consumption
chemo
shock
chronic gastritis
chronic inflammation stomach mucosa
H pylori
90%
autrum most commonly affected
epigastric abdominal pain
risk of ulcers/ adenocarcinoma/ malt lymphoma
tx; triple therapy
diagnosis; breath test/ stool antigen
chronic autoimmune
10%
type IV T cell hypersensitivity
atrophy of mucosa w/ intestinal metaplasia
achlorhydria w/ increased gastrin levels and antral G cells hyperplasia
megaloblastic anemia
raised risk adenocarcinoma
PUD
solitary ulcer
often duodenal > stomach
almost always caused by H pylori
id duodenal- and gets better w/ food
on endoscopy; ulocer w/ brunner gland hypertrophy
if gastric- pain worsens with meals
lesser curvature of antrum
can be caused by gastric carcinoma
gastric carcinoma
adenocarcinoma
presents late
2 types
intestinal; most common type, large irregular ulcers w/ heaped up marginssome risk factors include nitrosamines in smoked food and type A blood
diffuse; signet ring cells diffusely infiltrating gastric wall/ stomach wall thickening
bilateral ovaries can occur with this type
duodenal atresia
congenital failure of duodenum to canalize
double distention/ double bubble sign
billious vomiting
associated w/ down syndrome
meckel diverticulum
outpouching of all 3 layers of bowel wall due to failure of vitteline duct to involute
most common congenital anomaly of GI tract
presents within first 2 years of life w/ bleeding, volvulus, intussuspection or obstruction
volvulus
twisting of bowel along mesentery → obstruction and blood supply restriction
sigmoid colon- elders
cecum- young adults
intussuspection
telescoping of proximal segment of bowel forward into distal segment
telescoped segment pulled forward by peristalsis → obstruction and blood flow restriction/ infarct
in children- often caused by lymphoid hyperplasia secondary to rotavirus
in adults- usually caused by tumors
small bowel infarct
risk of ischemia
transmural; w/ thrombosis/ embolism of superior mesenteric artery/ vein
mucosal infarct occurs with marked hypotension
comes w/ abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and decreased bowel sound
lactose intolerance
decreased function of lactase enzyme found in brush border of enterocytes
presents w/ abdominal distension and diarrhea after milk consumption
temporary deficiency is seen after small bowel infection
celiac disease
immune mediated damage of small bowel villi due to gluten exposure associated w/ HLA DQ2 and DQ8
pathogenic component of gluten is gliadin
deaminated by TTG
THC II → T cells mediated tissue damage
small herpes like vesicles may arise on skin due to IgA deposits at tips of dermal papillae
usually pts are IgA def
flattening of villi, hyperplasia of crypts and increased lymphocytes in duodenum
complications include small bowel carcinoma and T cell lymphoma
tropical sprue
damage to small bowel villi due to unknown organism resulting in malabsorption
similar to celiac but occurs in tropical regions, responds to antibiotics and damage more so in ileum/ jejunum
whipple disease
systemic tissue damage characterized by macrophages loaded with tropheryma whippelii organisms within macrophages
usually affect lamina propria of small bowel
leads to malabsorption of fat and steatorrhoea
other common involvements include arthritis, cardiac valves, lymph nodes and CNS
abetalipoproteinemia
autosomal recessve deficiency of apoliprotein B48 and B100
leads to malabsorption due to absent VLDL/ LDL
carcinoid tumor
malignant proliferation of neuroendocrine cells
low grade malignancy
can occur anywhere along gut but small bowel is most common site
polyp like nodule
seretonin secreting, metabolized by liver MAO into 5HIAA
mets to liver
carcinoid syndrome; flushing, bronchospasms, diarrhea
carcinoid heart disease; right sided valvular fibrosis (increased collagen) → tricuspid regurg and pulmonary valve stenosis
acute appendicitis
most common cause of acute abdomen
related to obstruction of appendix by lymphoid hyperplasia in children or fecalith in adults
mcburney point
rupture; peritonitis w/ guarding/ rebound tenderness
IBD
chronic relapsing
potentially due to abnormal immune response to enteric flora
young women
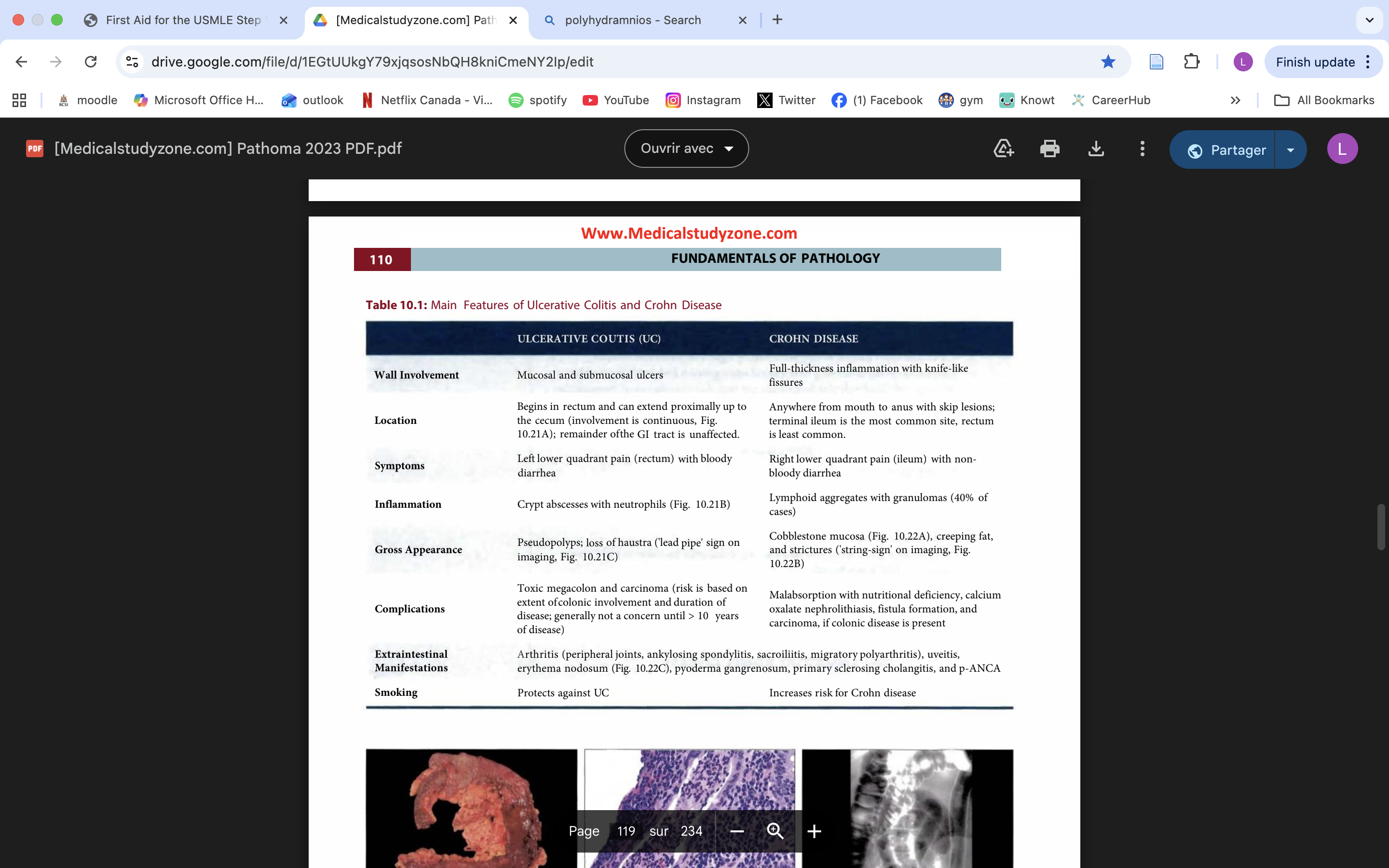
UC vs CD
hirschsprung disease
defective relaxation and peristalsis of rectum and distal sigmoid colon
down syndrome association
due to congenital failure of ganglion cells to descend in myenteric and submucosal plexus
clinical failures include failure to pass meconium, empty rectal vault on DRE and megacolon
rectal colon biospy shows lack of ganglion cells
Tx; colon resection
colonic diverticula
outpouching of mucosa/ submucosa through muscularis propria
related to wall stress
usually asymptomatic, symptoms include constipation, straining…
usually older adults with low fiber diet
complications include rectal bleeding, fistula and diverticulitis
angiodysplasia
acquired malformation of mucosal and submucosal capillary beds
usually arise from cecum and right coloin due to high wall tension
rupture presents as hematochezia in older adults
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
autosomal dominant disorder
thin walled blood vessels in mouth and GI
rupture → bleeding
ischemic colitis
ischemic damage to colon at spenic flexure
artherosclerosis of SMA is most common cause
presents with postprandial pain and weight loss
infarcts lead to pain and bloody diarrhea
IBS
relapsing abdominal pain with bloating, flatulance and change in bowel habits improving w/ defecation
classically affects middle aged females
related to disturbed intestinal mobility
can be solved by increasing fiber intake
hyperplastic colonic polyps
hyperplasia of glands
serrated appearnce on micro
most common
benign
usually left colon
adenomatous colonic polyps
neoplastic proliferation of glands
second most common polyp type
benign but may progress to adenoma-carcinoma → adenocarcinoma
APC
Kras
p53
greatest risk of becoming carcinoma is polyp >2cm, sessile growth and villous histology
familial adenomatous polyp
autosomal dominant disorder
100s-1000s of polyps
due to APC mutation on chromosme 5
colon and rectum remove prophuylactically- otherwise carcinoma by 40s
gardner syndrome
FAP w/ fibromastosis (fibroblasts in retroperitoneum) and osteomas (skull)
turcot syndrome
FAP w/ CNS tumors (medulloblastoma and glial )
juvenile polyp
sporadic hamartomatous polyp in children
usually solitary polyp that prolapses and bleeds
juvenile polyposis; many polyps in stomach and colon, incraeses carcinoma progression risk
peutz jeghers
benign polyp through GI and mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation on lips, oral mucosa and genitalia
autosomal dominant
increases risk of colorectal, breast and gyno cancer
colorectal carcinoma
carcinoma arising from colonic/ rectal mucosa
3rd most common cancer/ 3rd most deadly
peak incidence 60s-70s
mostly arise from adenoma-carcinoma sequence
or microsatellite instability
or hereditary (HNPCC)- early age, right sided
screening starts at 50 w/ fecal ocult blood and colonoscopy
left lesion; napkin ring lesion, blood streak stool
right lesion; raised, occult bleeding and iron def anemia
colon carcinoma is risk factor for strep bovis endocarditis
CEA serum marker used to assess treatment response amd reccurence but not screening
annular pancreas
developmental malformation in which pancreas forms ring around duodenum
risk of duodenal obstruction
acute pancreatitis
inflammation and hemorrhage of pancreas
due to autodigestion of parenchyma by pancreatic enzymes
premature activation of trypsin → cascade activation of other enzymes
results in liquefctive hemorrhagic necrosis of pancreas and fat necrosis or peripancreatic fat
most common causes are alcohol and gallstones
clinical features include epigastric abdominal pain radiating to back, nausea and vomiting, cullens and gray hemorrhage, elevated serum amylase and lipase and hypocalcemia
complications include shock, pseudocyst, DIC, ARDS and abscess (e coli related)
chronic pancreatitis
fibrosis of pancreatic parenchyma → most often follows reccurent acute pancreatitis
common causes include CF and alcohol
clinical features include epigastric abdominal pain radiating to back, pancreatic insufficiency → malabsorption/ vitamin def, dystrophic calcifications with chain of lakes patterns on contrast studies, secondary DM
risk of pancreatic carcinoma
amylase/ lipase not useful markers here
pancreatic carcinoma
adenocarcinoma of pancreatic ducts
older adults
risks include smoking and chronic pancreatitis
late diagnosis
symptoms include epigastric pain, weight loss, obstructive jaundice, pale stool, palpable gallbladder, secondary DM, pancreatitis, migratory thrombophlebitis (trousseau syndrome)
serum tumor marker is CA 19-99
surg- whipple
poor prognosis
biliary atresia
failure to form/ early destruction of extrahepatic biliary tree
biliary obstruction within forst 2 months of life
jaundice → cirrhosis
cholelithiasis
aka gallstones
solid, round stones of gallbladder
due to cholesterol (most common)/ bilirubin precipitation
supersaturation of either substances
decreased phospholipids/ bile acids
stasis
cholesterol stones are usually radiolucent and more common in middle aged women w/ chrons disease/ cirrhosis
bilirubin stones are usually opaque and associated w/ extravascular hemolysis and biliary tract infections
by themselves gallstones are typically asymptomatic
biliary colic
waxing and waning RUQ pain
due to gallbaldder contracting against stone in cystic duct
symptoms relieved if stone passed
common bile duct obstruction can lead t acute pancreatitis / obstructive jaundice
acute cholecystitis
acute inflammation gallbladder wall
impacted stone in cystic duct → dilation w/ pressure ischemia, bacterial overgrowth (e coli) and inflammation
presents w/ RUQ pain radiating to right scapula, fever w/ raised WBC, nausea, vomiting and raised serum alkaline phosphate from duct damage
risk of rupture if left untreated
chronic cholecystitis
chronic gallbladder inflammation
due to chemical irritation from longstanding cholelithiasis
can present with or without bouts of acute cholecystitis
charcaterized by herniation of gallbladder mucosa into muscular wall
vague RUQ pain after eating
tx is cholecystomy
porcelain gallbladder
late complication of chronic cholecystitis
shrunken, hard gallbladder due to chronic inflammation w/ fibrosis and dystrophic calcification
incraesed carcinoma risk
tx is cholecystomy
ascending cholangitis
bacterial infection of bile duct
gram neg bacteria
presents as sepsis, jaundice, and abdominal pain
increased incidence w/ choledocholithioasis
gallstone ileus
obstruction of small bowel w/ gallstone
due to cholecystitis w/ fistual formation between gallbladder and small bowel
gallbladder carcinoma
adenocarcinoma of glandular epithelium lining gallbladder wall
gallstones are a major risk factor, esp w/ porcelain gallbladder
classically presents as cholecystitis in older women
poor prognosis
jaundice
yellow discouloration of skin
earliest sign is scleral icterus
serum bilirubin > 2.5 mg/dL
arises w/ disturbances in bilirubin metabolism
causes include
extravascular hemolysis / ineffective erythropoiesis
gilbert syndrome
dubin johnson
viral hepatitis
biliary tract obstruction
normal bilirubin metabolism
rbc consumed by macrophages of reticuloendothelial system
protoporphyrin form heme converted to unconjugated bilirubin
albumin carries UCB to liver
UGT in hepatocytes conjugates bilirubin
conjugated bilirubin transferred to bile canaliculi to form bile, which is stored in gallbladder
bile released in small bowel to aid digestion
excreted via poop and pee → make them colour that they are
extravacsular hemolysis/ ineffective erythropoiesis
causes jaundice
elevated UCB is too much for liver to process
dark urine
increased risk of pigmented bilirubin gallstones
physiologic jaundice of newborn
causes jaundice
elevated UCB
treatment is phototherapy
untreated→ neuro deficits and death
gilbert syndrome
causes jaundice
elevated UCB
autosomal recessive
jaundice during stress (severe infection)
crigler najar syndrome
causes jaundice
elevated UCB
abscence of UGT
kernicterus, usually fatal
dubin johnson syndrome
def of bilirubin canalicular transport protein
autosomal recessive
causes jaundice
elevated CB and alkaline phosphatase
low urine urobilinogen
dark urine and pale stool
pruritus
hypercholesterolemia
steatorrhea
viral hepatitis
inflammation of liver parenchyma, other causes tha hepatitis include EBV and CMV
raised UCB and CB
jaundice
inflammation disrupts hepatocytes and small bile ductules
dark urine
raised liver enzymes
nausea/ vomiting
acute hepatitis
symptoms last under 6 months
inflammation of liver lobules/ portal tracts → apoptosis of hepatocytes
chronic hepatitis
symptoms last over 6 months
inf of portal tract
can progress to cirrhosis
hep A
fecal oral
travellers
acute
anti IgM- active inf
anti IgG- protective
hep E
fecal oral
contaminated water/ undercooked seafood
acute
anti IgM- active inf
anti IgG- protective
in pregnancy- liver failure/ necrosis
hep B
parental transmission/ needles
chronic disease in 20% cases
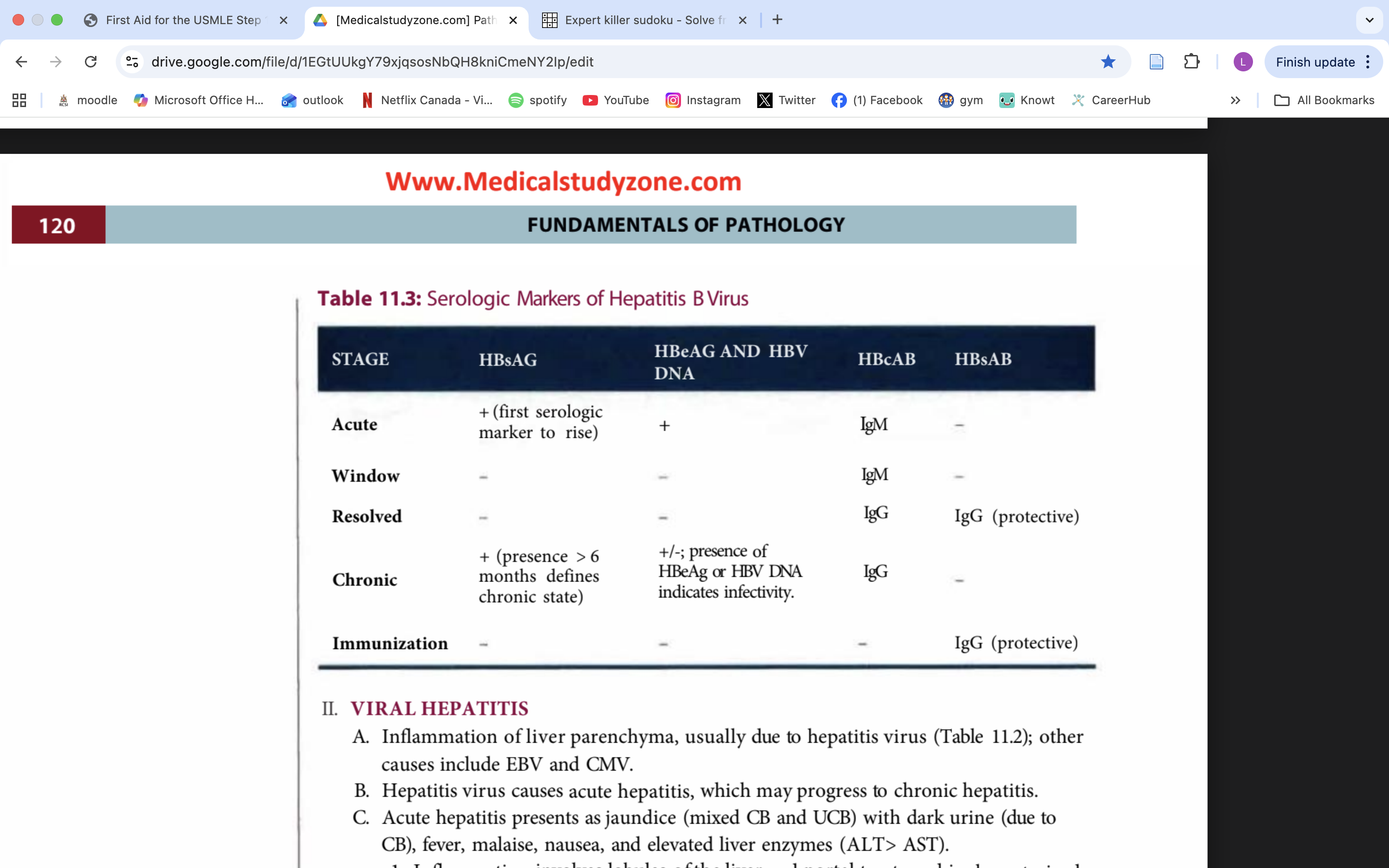
hep C
parental transmission
risk from transfusion almost inexistant due to screening of blood supply
chronic disease common
HCV RNA confirms infection
low RNA indicates recovery
persistance of RNA → chronic disease
hep D
dependant on Hep B for infection
superinfection upon existing hep B more severe > coinfection
cirrhosis
end stage liver damage charcaterized by disruption of normal hepatic parenchyma by bands of fibrosis and regenerative nodules of hepatocytes
fibrosis mediated by TGF-B from stellate cells
portal HPT leads to
ascites
congestive splenomegaly/ hypersplanism
portosystemic shunts/ esophageal varices/ hemmorhoids
hepatorenal syndrome
decreased detox leads to
mental status change/ asterixis
gynecomastia/ spider nevi
jaundice
decreased protein synthesis leads to
hypoalbumineria
coagulopathy
alcohol related liver disease
damage to hepatic parenchyma due to consumption of alcohol
fatty liver- accumulation of fats in hepatocytes
alcoholic hepatitis; chemical injury
acetaldehyde mediates damage
characterized by swelling of hepatocytes and formation of mallory bodies, necrosis and acute inf
presents w/ painful hepatomegaly and elevated liver enzymes
cirrhosis is a long term complication
non alcoholic fatty liver disease
fatty changes, hepatitis and/or cirrhosis developping without alcohol exposure OR OTHER KNOWN INSULTS
associated w/ obesity
diagnosis of exclusion
ALT> AST
hemochromatosis
excess body iron → deposition in tissue (hemosiderosis)
hemochromatosis is the organ damage
due to autosomal recessive defect in iron absorption (primary) in HFE/ C282Y gene or chronic transfusion (secondary)
presents in late adulthood
traid; cirrhosis, secondary DM and bronze skin
other findings include dilated cardiomyopathy, arrhytmia and testicule atrophy
high serum ferritin/ iron/ % sat
low serum TIBC
on biopsy; brown deposits liver
prussian blue stain distinguishes iron from lipofuscin (by product from turnover/ wear and tear) of peroxidized lipids
increasec risk of carcinoma
tx; phlebotomy
wilson disease
autosomal recessive defect of ATP7B in atp mediated hepatocyte copper transport
lack of copper transport into bile and lack of copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin
copper builds up in hepatocytes, leaks in serum and deposits in tissues
tissue damage due to free radicals
presents w/ cirrhosis, neuro damage and kayser fleisher rings in childhood
increased urinary copper/ serum copper
low serum ceruloplasmin
risk of carcinoma of liver
tx; D penicillamine
primary biliary cirrhosis
autoimmune granulomatous destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts
women w/ other autoimmune diseases
w/ antimitochoindrial atb
presents w/ features of obstructive jaundice
cirrhosis a late complication