BIO205 Chapter 6: Populations
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Population
all individuals of the same species living in a particular area at the same time
Dispersal
how do individuals move from one area to another?
N =
the whole population
M =
total number of individuals marked and released in the first capture
Death
a mechanism of population decrease whereby individual organisms in a population die within a given time period
Nt+1
population abundance in the next year
t
starting year (time)
What is the Discrete-time population growth model?
Used when species reproduce in distinct time steps (e.g., yearly breeding seasons, growth happens once each time period, not continuously)
When lambda is less than 1
the population decreases
when lambda is greater than 1
the population is growing
Intrinsic rate of increase
A population's maximum per capita growth rate in a particular habitat.
If 1 < rdis < 2
Damped oscillations
Density-independent factor
An event or feature that influences resource levels or influences the mortality and reproduction of individuals in a population in ways that do not depend on the density of the population. (e.g., natural disasters)
Population abundance
the number of individuals in a population; sometimes also called population size
Population density
the number of individuals in a population within a defined spatial area
Geographic range
where can you find these species?
Abundance
how many individuals are in the population?
Density
how crowded the population is
Dispersion
how are the individuals spread?
Mark-recapture model
a model that uses observational data from tagged individuals, who are later recaptured, to estimate population abundance
Mark-recapture equation
N = nM / m
n =
total number of individuals caught in the second capture
m =
previously tagged individuals caught in the second sampling event
Birth
a mechanism of population increase whereby adult organisms in a population produce offspring within a given time period
Immigration
a mechanism of population increase whereby individuals enter a population through dispersal
Emigration
a mechanism of population decrease whereby individuals leave a population through dispersal
Model of Population Growth
Nt+1 = Nt + Bt - Dt
What is the Model of Population Growth?
When you want to track births and deaths directly -- the basic principle of how populations change
Nt
population abundance in a given year
B
total number of births
D
total number of deaths
λ (Lambda)
represents the combined per capita birth and survival rate
Discrete-time population growth model
Nt+1 = Ntλ
When lambda = 1
the population remains the same
Geometric growth equation
Nt = N0λ^t
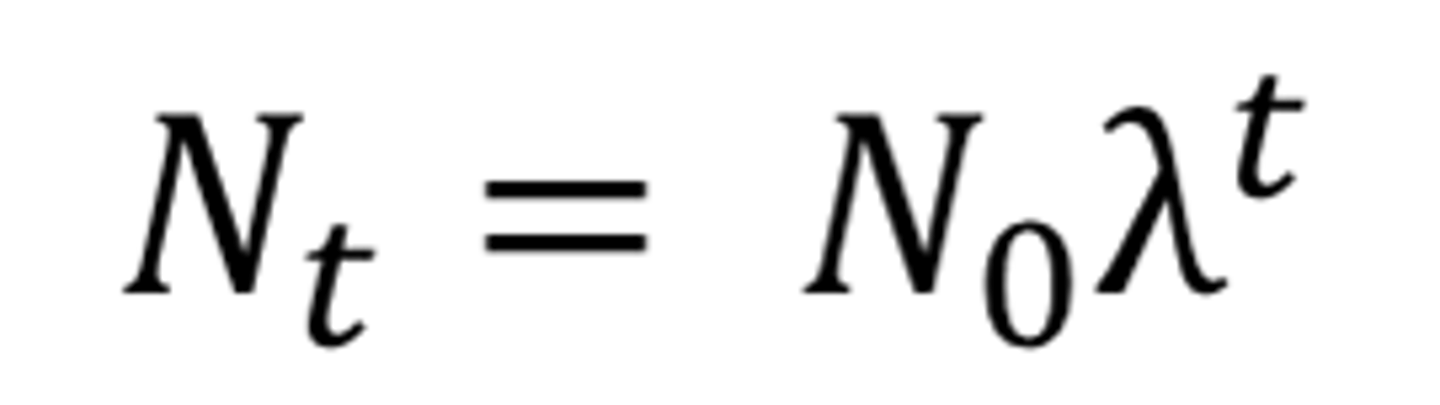
What is the Geometric growth equation and when is it used?
Used when you want to predict population size after several time steps without calculating each year separately (shortcut version of discrete model, assumes constant lambda)
N0
the population abundance in the first year
Continuous-time model/Exponential growth model
Nt = N0eʳᵗ
What is the Continuous-time (exponential) growth model and when is it used?
When reproduction happens all the time -- continuous growth (like microbes, humans)
r
the instantaneous per capita rate of population growth
Density dependence
As a population increases, reproductive rates decline and/or mortality rates increase. The growth rate of population depends on how dense (crowded) it is.
Carrying capacity (K)
The number of individuals in a population that the resources in a habitat can sustain.
Intraspecific competition
Competition between individuals of the SAME species for a limiting resource that is critical for reproduction or survival.
Logistic growth equation
An equation that includes a carrying-capacity term that reflects the effects of limiting resources on population growth rates.
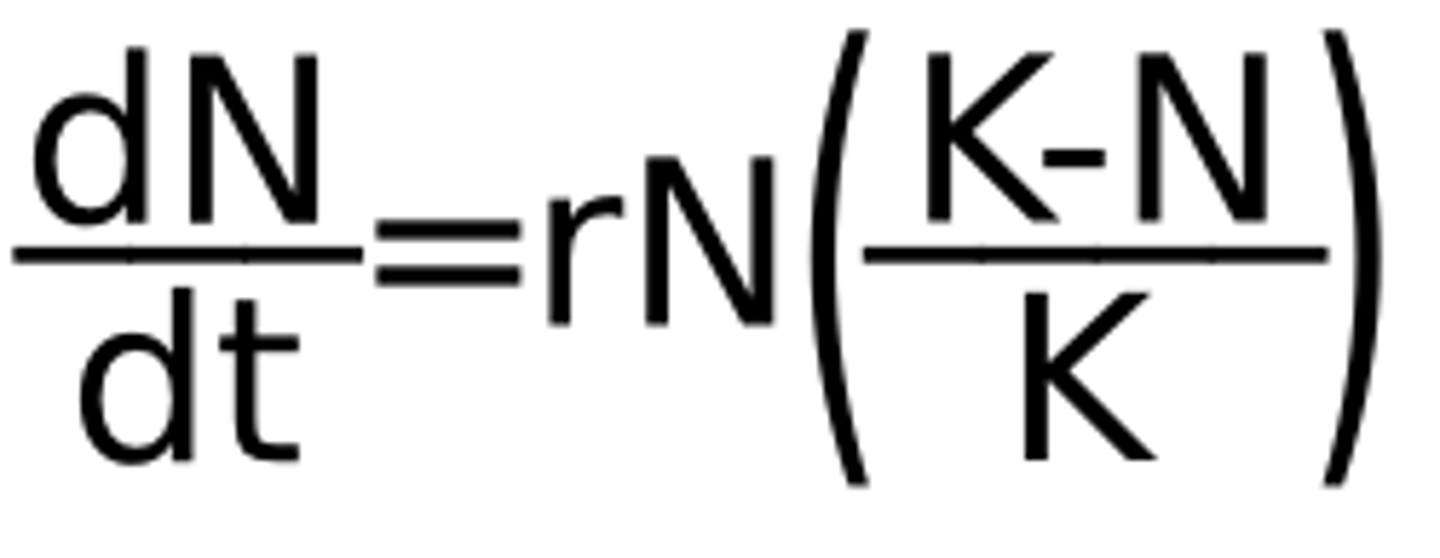
dN / dt
The change in population density over time.
rmax
The intrinsic rate of increase.
Time lag
The time it takes for an effect to become apparent; used to describe the phenomenon in which the effects of density dependence on the rate of population growth are not accounted for until the next time period.
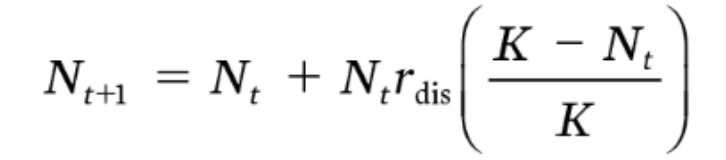
What is the Discrete logistic growth equation and what is it used for?
Used to model populations with limited resources that grow in distinct time steps (discrete-time + logistic equation)
rdis
The maximum per capita rate of population change / Controls how fast the population grows each time step, how "aggressive" reproduction is
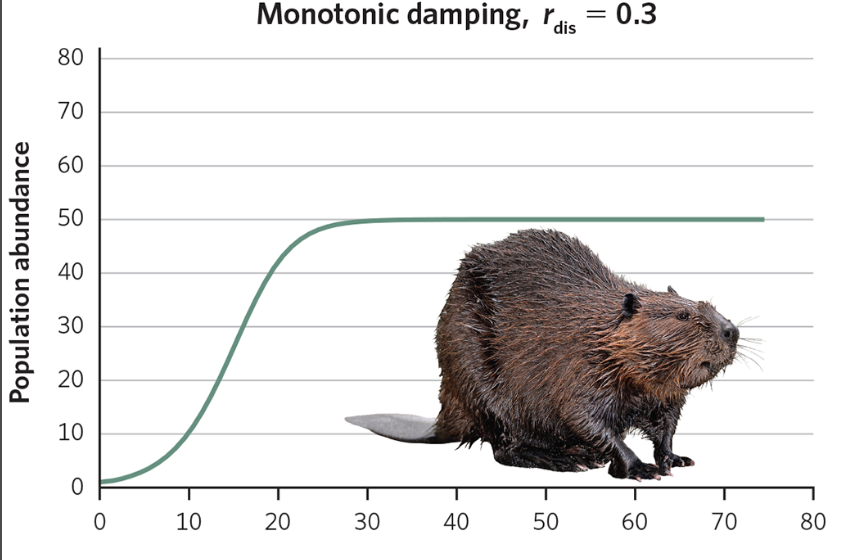
If rdis < 1
Monotonic damping
Monotonic damping
The population smoothy and gradually approaches the carrying capacity (K) with no oscillations
Damped oscillations
The population overshoots K a little, then undershoots, then overshoots again -- each swing gets smaller until it stabilizes at K
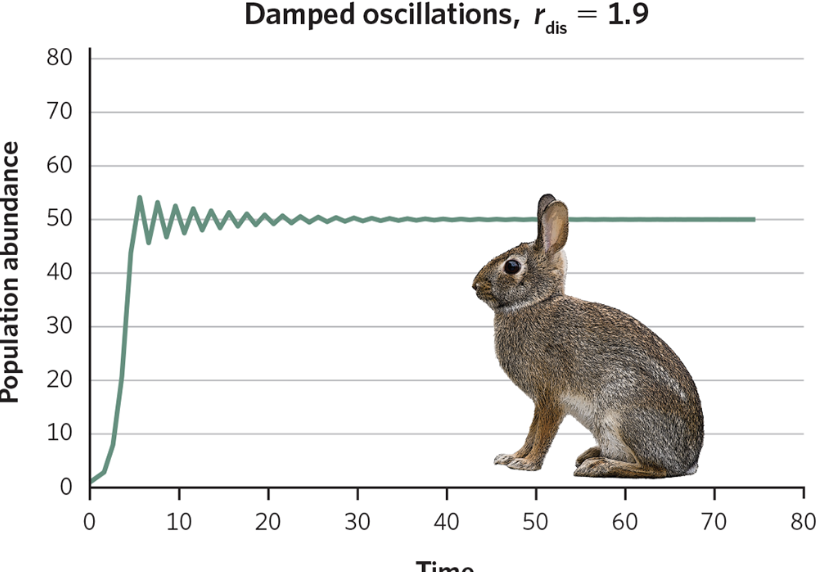
If 2 < rdis < 2.57
Stable limit cycles
Stable limit cycles
The population keeps oscillating around K in a repeating pattern -- it never settles exactly at K
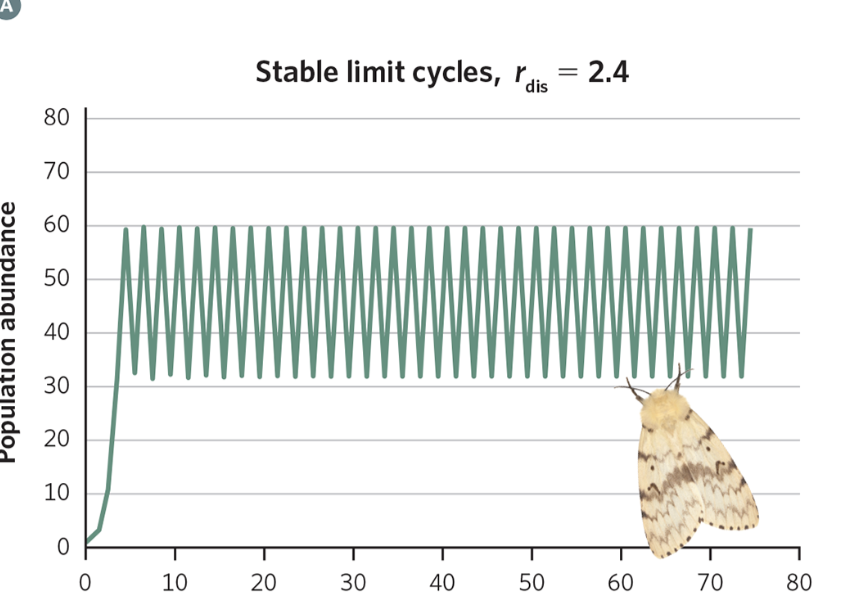
If rdis > 2.57
Chaotic dynamics
Chaotic dynamics
Population becomes unpredictable -- it jumps up and down in irregular, seemingly random ways
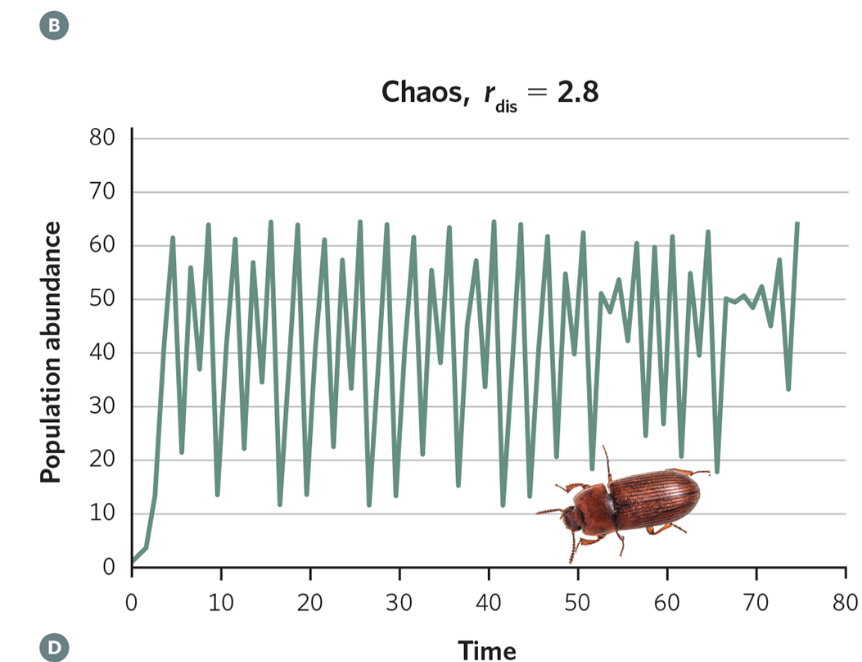
Life history
The temporal sequence of events that determines survival and reproduction from an individual's birth until its death.
Type I survivorship
High early survival until a certain age, and then survival declines rapidly (e.g., humans, elephants, whales).
Type II survivorship
Constant survival throughout its lifetime (e.g., some seabirds and reptiles).
Type III survivorship
Very low initial survival during early stages until a certain age is reached, and then high survival until death (e.g., trees, amphibians, insects, marine invertebrates).