animal reproduction exam 1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Which structure of the female’s repro tract is most dynamic and physically and functionally changes throughout her changing cycle?
a. Vagina
b. Ovary
c. Oviduct
d. External genitalia
b. Ovary
What are the benefits of rectal palpation while examining the female?
a. Appreciation of tract anatomy
b. Early pregnancy diagnosis
c. Monitoring of follicular growth
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
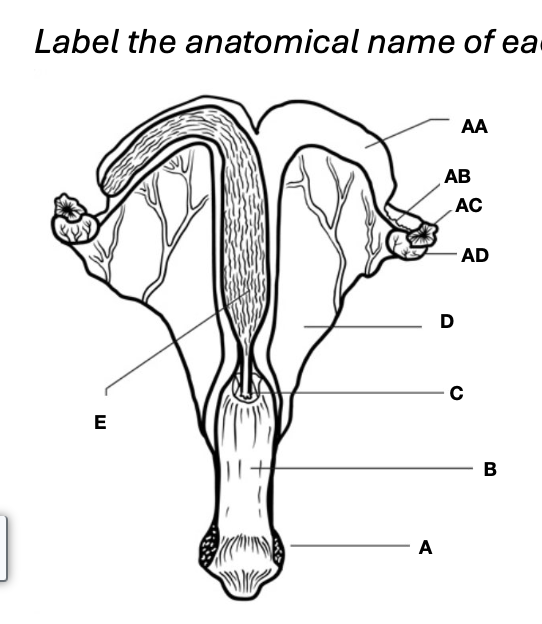
Oviduct
AB
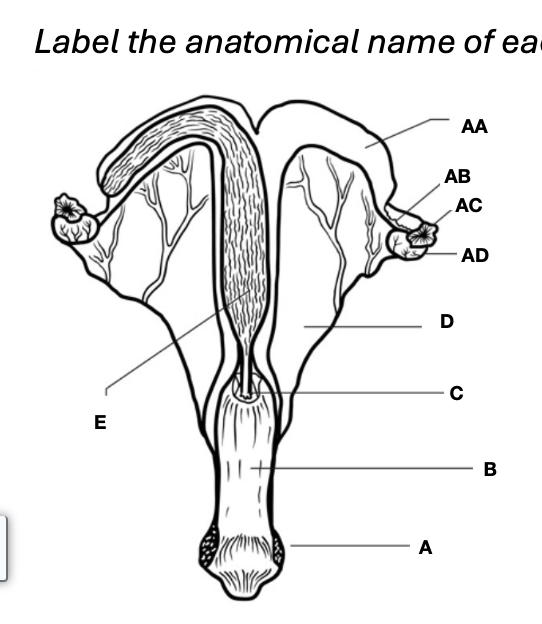
Vagina
B
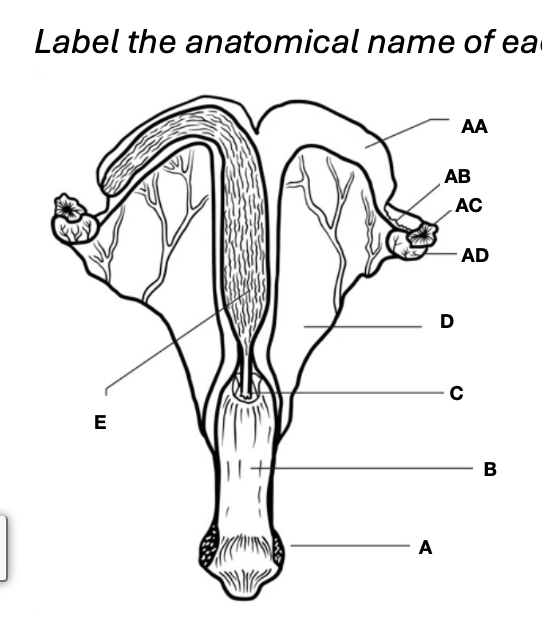
Uterine horns
AA
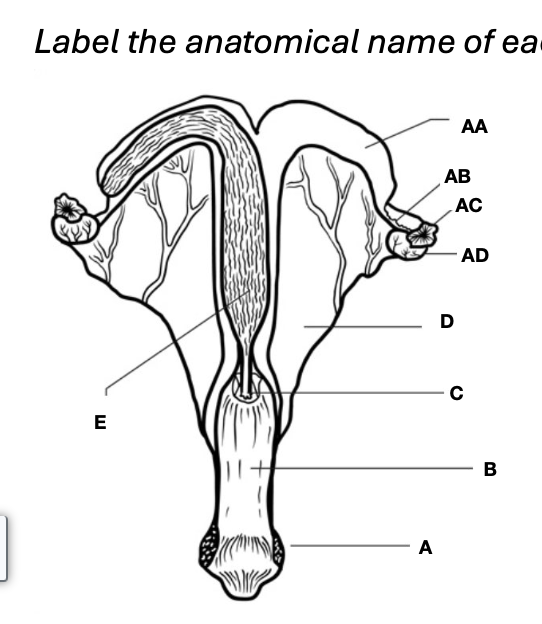
Cervix
C
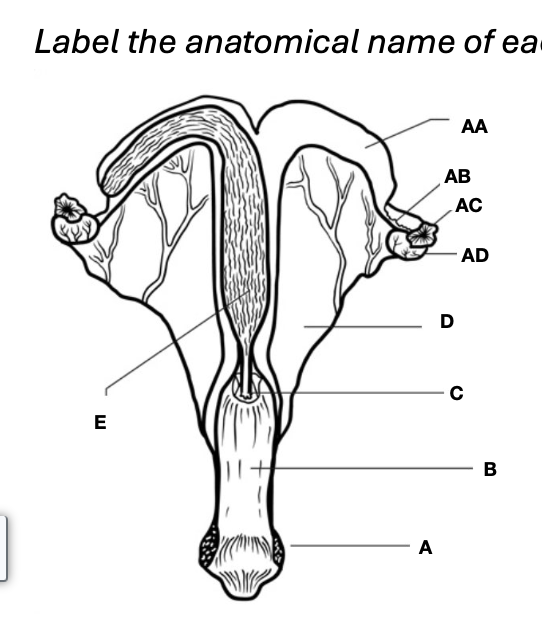
Uterine body
E
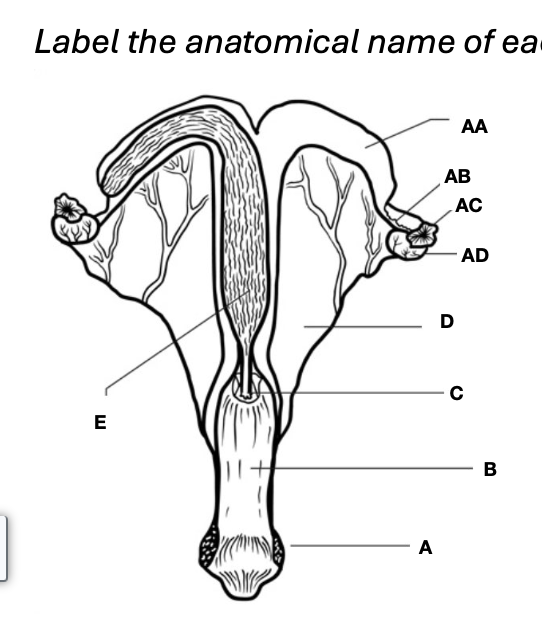
Ovary
AD
Which of the following is the female copulatory organ?
a. Cervix
b. Ovary
c. Uterus
d. Vagina
d. Vagina
How do accessory sex glands assist in the male repro tract?
a. Aids in sperm production through steroidogenesis
b. Secretes fluids and proteins to aid in sperm transport and protection
c. Provides contractions for movement of semen trough tract
d. Supports the male reproductive system
b. Secretes fluids and proteins to aid in sperm transport and protection
Uterus with 2 horns and a small uterine body
A: Simplex
B: bicornate
C: Duplex
B: bicornate
Uterus with 2 Cervices
A: Simplex
B: bicornate
C: Duplex
C: Duplex
Uterus that lacks true uterine horns
A: Simplex
B: bicornate
C: Duplex
A: Simplex
Support of entire reproductive tract
A: Mesometrium
B: Mesosalpinx
C: Broad ligament
D: Mesovarium
C: Broad ligament
Support of ovary
A: Mesometrium
B: Mesosalpinx
C: Broad ligament
D: Mesovarium
D: Mesovarium
Support of uterine horns (largest)
A: Mesometrium
B: Mesosalpinx
C: Broad ligament
D: Mesovarium
A: Mesometrium
Support of oviduct
A: Mesometrium
B: Mesosalpinx
C: Broad ligament
D: Mesovarium
B: Mesosalpinx
LH & FSH act on the gonads, but they aren’t secreted from there; where are these
gonadotropins synthesized and secreted?
a. Hypothalamus
b. Anterior pituitary
c. Posterior pituitary
d. Pineal gland
b. Anterior pituitary
Which species does NOT have a fibroelastic penis, one with limited
erectile/muscular tissue?
a. Stallion
b. Bull
c. Boar
d. Ram
a. Stallion
ANK IN ORDER the stages of chronological estradiol production from 1st to 5th (with the first step to be A and the 5th step to be E), 2:B, 3:C, 4:D
FSH binds to receptors at the level of the granulosa cells 3:C _
E2 enters circulation 5:E
Cholesterol is converted to testosterone & dicuses into granulosa cells 2:B
LH release & binding to theca interna 1:A _
Testosterone is converted to E2 4:D _
In which species can placental caruncles be found?
a. Mare & sow
b. Sow & ewe
c. Cow & ewe
d. Cow & mare
c. . Cow & ewe
The serosal layer of the uterus is also referred to as the
a. Perimetrium
b. Myometrium
c. Endometrium
a. Perimetrium
Where do sperm go after leaving the rete teste?
a. Seminiferous tubules
b. Penis
c. EIerent ducts
d. Tunica dartos
c. EIerent ducts
Which cells produce testosterone through second-messenger activation?
a. Sertoli
b. Leydig
c. Granulosa
d. Theca
b. Leydig
A unilateral cryptorchid can produce some sperm. T/F
True
A lack of the SRY gene presence during embryogenesis leads to what?
a. Testicular retention
b. Development of paramesonephric duct
c. Dicerentiation of Leydig cells
d. Testicular development
b. Development of paramesonephric duct
Which of the following is the primary hormone being produced by the antral follicle:
a. Estrogen
b. Oxytocin
c. Prostaglandins
d. Progesterone
a. Estrogen
Which of the following is NOT an ASSISTED method (ART) of depositing sperm into
the female reproductive tract:
a. Embryo transfer
b. Natural cover
c. Artificial insemination (AI)
d. In vitro fertilization (IVF)
b. Natural cover
The male reproductive tract functions primarily for...
a. Testosterone production
b. Temperature regulation
c. Sperm production
d. Seminal plasma production
c. Sperm production
hich structure is not part of the spermatic cord?
a. Ductus deferens
b. Seminiferous tubules
c. Cremaster muscle
d. Pampiniform plexus
b. Seminiferous tubules
Which cell type within the antral follicle has LH receptors?
a. Theca interna
b. Granulosa
c. FSH
d. LH
a. Theca interna
Which component of the male repro tract is capable of providing the testes with a
cooler environment by somewhat “sweating” .
a. Epididymis
b. Prostate
c. Scrotum
d. Accessory sex glands
c. Scrotum
Select the term that refers to only one testes descending compared to two.
a. Freemartinism
b. Uni-lateral Cryptorchidism
c. Bilateral Cryptorchidism
b. Uni-lateral Cryptorchidism
Which accessory gland produces the littlest overall seminal volume?
a. Vesicular gland
b. Prostate
c. Ampulla
d. Bulbourethral gland
d. Bulbourethral gland
What is the primary impact of increased E2 in the female?
a. Mammary gland development
b. Lysis of corpus luteum
c. Increase in progesterone
d. Expression of estrus-like behaviors
d. Expression of estrus-like behaviors
Which layers make up the endometrium?
a. Submucosa & mucosa
b. Longitudinal & circular
a. Submucosa & mucosa
Infundibulum
A.allows only fertilized oocyte to pass
through in most species
B. connects to horn, narrow
C. finger-like projections, connects to ovary
D. largest portion of the oviduct
C. finger-like projections, connects to ovary
Ampulla
A.allows only fertilized oocyte to pass
through in most species
B. connects to horn, narrow
C. finger-like projections, connects to ovary
D. largest portion of the oviduct
Isthmus
A.allows only fertilized oocyte to pass
through in most species
B. connects to horn, narrow
C. finger-like projections, connects to ovary
D. largest portion of the oviduct
B. connects to horn, narrow
Ampullary-isthmic-junction
A.allows only fertilized oocyte to pass through in most species
B. connects to horn, narrow
C. finger-like projections, connects to ovary
D. largest portion of the oviduct
A.allows only fertilized oocyte to pass through in most species
Which of the following species is an example that has a duplex uterus?
a. Primate
b. Cat
c. Rabbit
d. Human
c. Rabbit
How many sperm are produced on a daily basis?
a. 1 million
b. 500 million
c. 25 billion
d. 500 billion
d. 500 billion
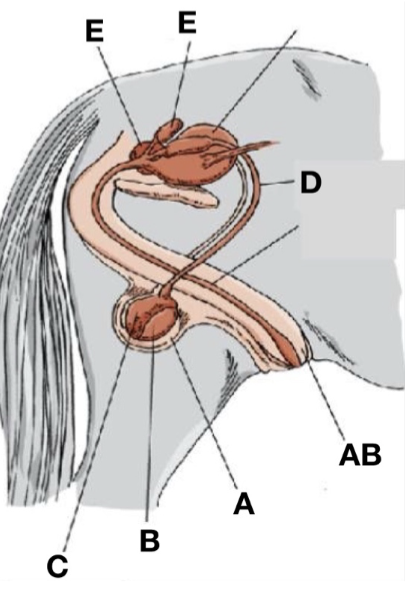
Accessory sex glands
E
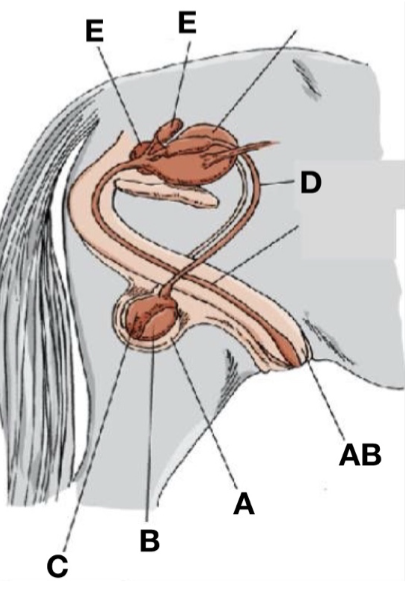
Scrotum
A
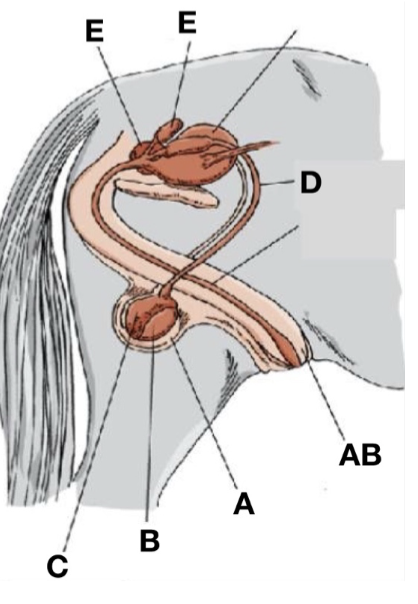
Ductus deferens
D
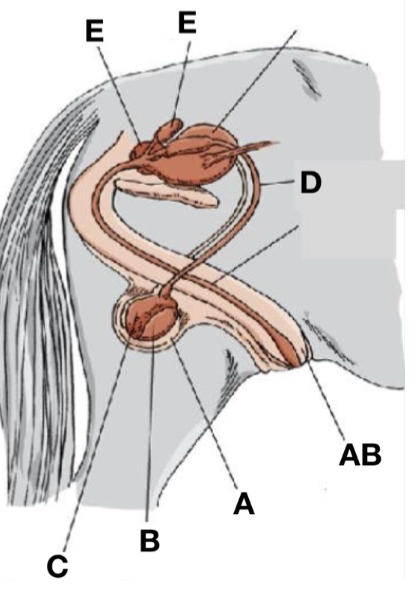
Testes
B
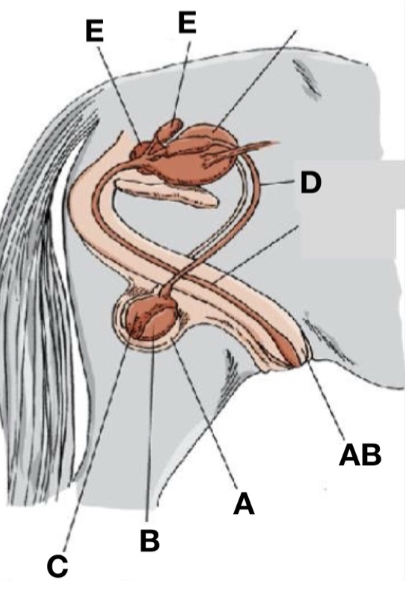
Penis
AB
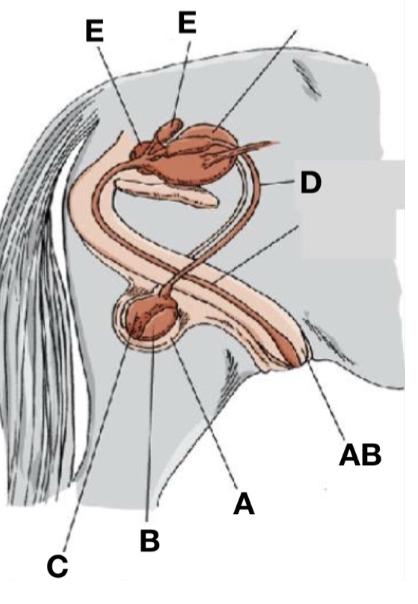
Epididymis
C
After fertilization, the now embryo resides here for
several days?
a. Oviduct
b. Uterus
c. Cervix
d. Vagina
a. Oviduct
Which statement about embryogenesis is FALSE?
a. Organs dicerentiate from germ cell layers in early embryo
b. Development of male tract relies on SRY gene on Y chromosome
c. The ectoderm diIerentiates into the reproductive tract
d. The endoderm dicerentiates into the digestive system
c. The ectoderm diIerentiates into the reproductive tract
Origin of LH
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
C: Anterior pituitary
Origin of FSH
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
C: Anterior pituitary
Location of conversion of cholesterol to testosterone (female)
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
B: Theca interna cells
Location of conversion of testosterone to estrodiol (female)
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
A: Granulosa cells
Which cell type does FSH act on?
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
A: Granulosa cells
Where is the site of secretion of oxytocin.?
A: Granulosa cells
B: Theca interna cells
C: Anterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary
D: Posterior pituitary