Physiology Lecture 24 - Blood Cells
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are the 3 main functions of blood?
distribution, regulation, protection
what does the blood distribute throughout the body?
deliver oxygen, hormones, transport cellular wastes
what does the blood regulate in the body?
maintain body temperature
how does the blood protect the body?
prevent infection by transporting immune cells
plasma is __ of the whole blood and what color is it?
55%, yellow color
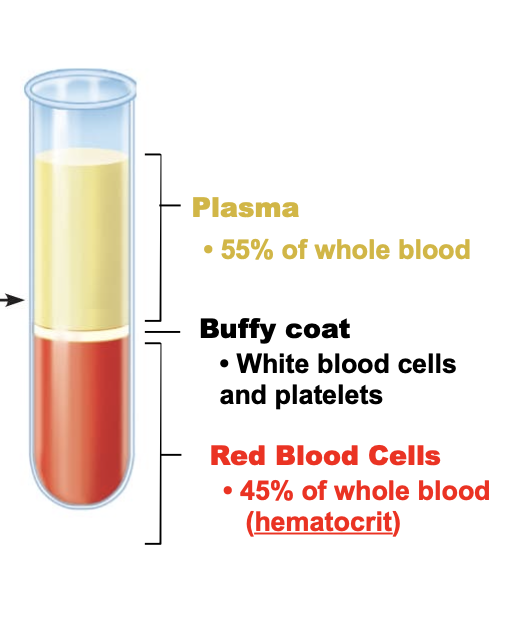
what is the buffy coat in blood?
white blood cells, platelets
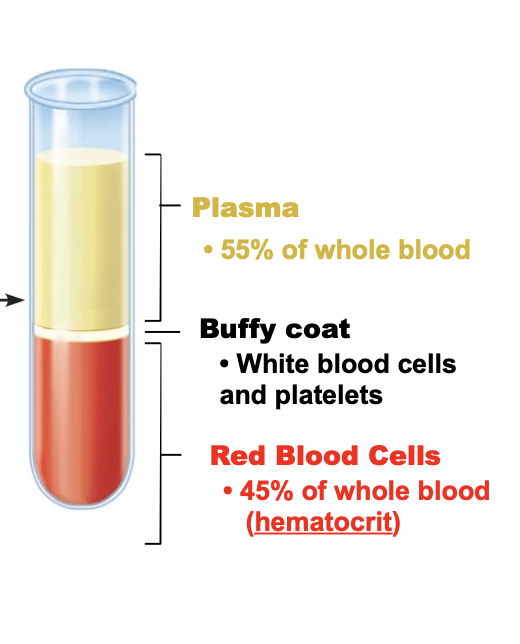
red blood cells make up __ of whole blood
45%
what is blood plasma made of?
mostly water and various proteins
what are some proteins that blood plasma is made up?
fibrinogen (4%), antibodies (36%), albumin (60%)
what is albumin and what does it do?
carrier molecule, maintain plasma osmotic pressure
what are the cellular components of erythrocytes (red blood cells)?
lack of nucleus and organelles, no mitochondria
why do erythrocytes (RBCs) lack a nucleus and organelles?
so that they can change shape in vessels
why do erythrocytes (RBCs) have no mitochondria?
no mitochondria, anaerobic respiration occurs which doesn’t use O2 because hemoglobin transports O2 and CO2
what makes RBCs red and allows for oxygen transport?
hemoglobin
what is the structure of hemoglobin?
4 globin proteins (2 alpha, 2 beta) that each bind a heme group with iron at the center
what does hemoglobin do and what % of RBCs is made up of hemoglobin?
binds reversibly to oxygen and RBCs are 97% hemoglobin
each atom of ___ binds to one molecule of oxygen
iron
____ binds to CO2
globin
what does hemoglobin synthesis require?
iron
A- has what antigens?
A antigen
A+ has what antigens?
A, Rh antigens
B- has what antigens?
B antigen
B+ has what antigens?
B, Rh antigens
what is blood type O considered?
the universal donor, all other blood types can accept O but O can only accept O
what is blood cell formation called?
hematopoiesis
where does hematopoiesis occur?
in the bone marrow and cells arise from hematopoietic stem cells
RBC production takes about days and how many RBCs are made every day?
15 days and 100 billion
what is erythropoietin (EPO)?
hormone produced in the kidneys that causes RBCs to mature quickly to make more RBCs, performance enhancing drug
when would EPO increase naturally?
when donating blood, low oxygen levels (hypoxia)
how long do RBCs last?
about 100 days
why is the life cycle of an RBC only ~100 days?
cells are unable to make new proteins or divide because RBC have no nucleus and hemoglobin begins to degenerate
what destroys old RBCs?
immune cells called macrophages
what are two erythocyte disorders?
anemia and polycythemia
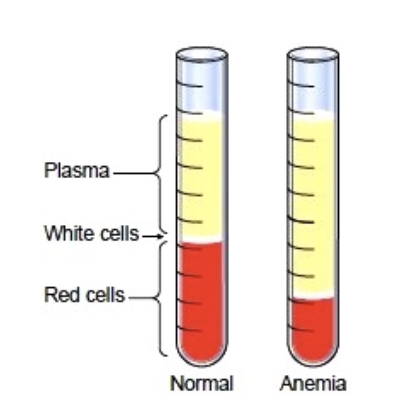
what is anemia?
low RBC count, fatigued, pale, short of breath
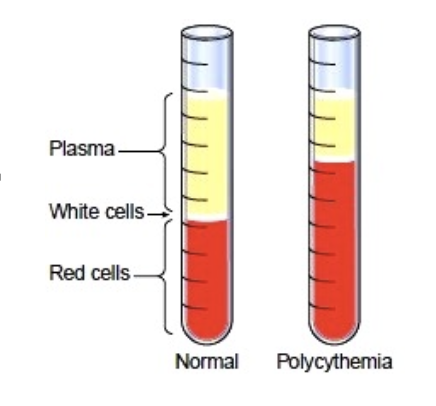
what is polycythemia?
high RBC count, blood becomes thick “sludge”