AP Psych Unit 1: Biological Basis of Behavior
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
nature vs. nurture
false dichotomy
The Jim Twins Minnesota 1979
Three Identical Strangers
genetic determision
genetically determined (ex: eye color, ear shape)
genetic predisposition
genetic “push” or inclination in a certain direction (no certainity)
(Psych are genetically predisposed,
but not genetically determined)
epigenetics
genes can get “turned on/off” as a result of interacting with environment, “experiences after the activity of genes” (epi= above or in addition)
How do we know stuff about the brain
open skull (people who die)
case studies → injury to brain regions
brain scans
Phineas Gage Case Study 1848
Brain specificity/Brain localization
certain brain parts have specific functions
Brain plasticity/neroplasicity
the brain wires and re-wires itself in response to new experiences (the brain adapts and motifs itself)
Type 1: Structural- experiences or memories change a brains physical structure
Type 2: Functional- brain functions move from damaged area to undamaged area
neurogenesis→ nuero-regrowth
Hemispherectomy
lose whole half of brain
Long Term Potentiation (LTP)
persistent strengthening of neural synapses based on frequent activity
(intertwined with brain plasticity)
Brain Scans
Function:
EGG- measure electrical activity in the brain
FMRI- structure and function in high resolution using magnetics
PET- function radioactive glucose injected, tracks as flows to active brain area, and structure
Structure:
CAT: read soft tissue (cross-section view) → only structure computerized x-ray
MRI: reads with magnets- images of structure and potential damage
Jody Case Study
The Nervous System
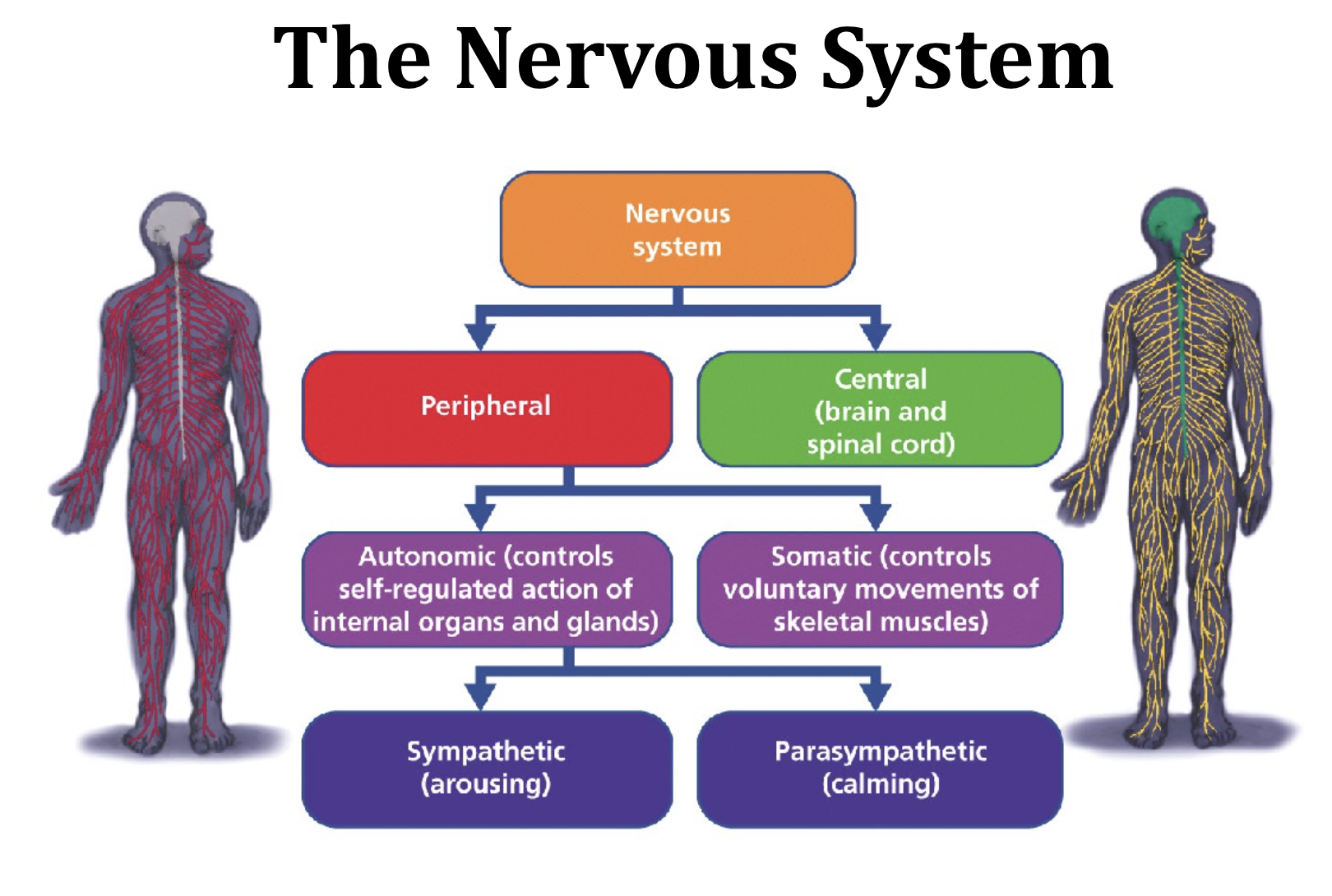
Fight or Flight Response
Heart rate: Increase
Respiration: Decrease
Adrenaline: Increase
Endorphin: Increase
Pupils: Increase
Salvation: Decrease
Digestion: Decrease
Bladder: Release
Limbic System
emotion and drive
Amygdala: Aggression and Fear
Hippocampus: new memories
Hypothalamus: Fighting, Fleeing, Feeding, Fornication
Pituitary gland: “master gland”
Case Study HM 1953
Aphasis
loss of ability to understand or speak language
Brain Stem
Thatamus: Relay Station/Sensory Switchboard
Reticular Formation: Alertness and Attention
Pons: (no need to know)- sleep
Medulla: Heart beat, breathing, blood circulation, digestion (MIKE THE CHICKEN)
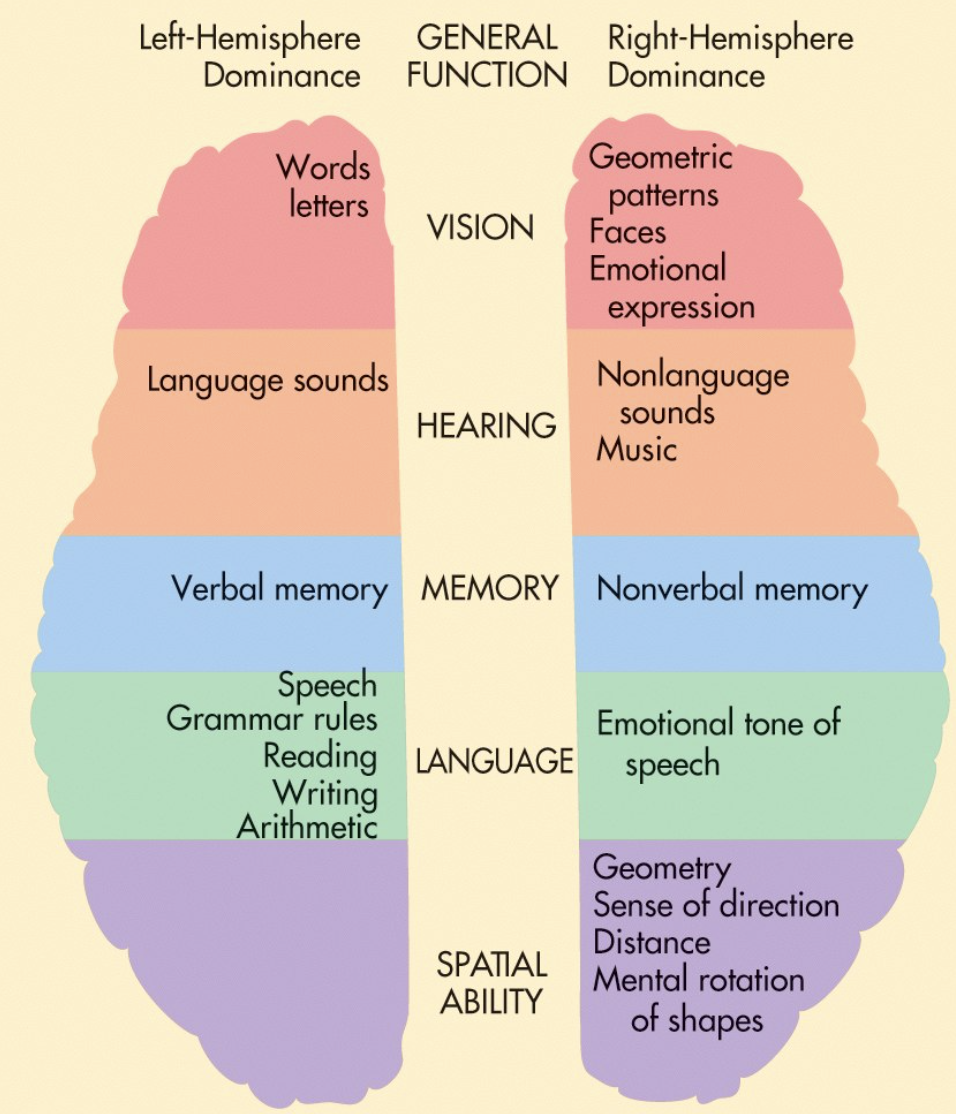
Left vs. Right Brain
Left: math and logic, language centers
Right: visual/spatial, non-verbal, facial recognition, artistic/creative
(not processed through words) → can draw, “I saw nothing”
Corpus Callosum
think bundle of nerve fibers that link the two hemispheres
Sperry and Gazzaniga: split brain procedure
Endocrine system: glands and hormones, travel through bloodstream and secreted by glands
“The Neural Chain”
How neurons in the human brain communicate
about 86 billion nuerons in the brain
Glial Cells
“Glue” neurons in place
Support and provide nutrients
Form myelin around axons
There are two categories of “message sending neurons”
Sensory: Afferent neurons carry messages in to the CNS →
Afferent = Approach
The CNS
Motor: Efferent neurons carry messages out from the CNS to the muscles and glands →
Efferent = Exit
Reflex Arc
neural pathway that controls the bodies automatic response (does not need to be processed in the brain)
Neural Specificity
Some neurons have specific functions
Nuerons (in breif)
Cells fire in patterns
Binary… “The all or none law”
Specificity
Feature detectors, motion detectors, mirror neurons
A Typical Neuron
Nucleus:
Cell Body (Soma): the cells life-support center
Dendrites: receiving messages form other cells
Axon: passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Myelin Sheath: covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
Axon Terminal Branch: form junctions with other cells
Neural Impulse: action potential, electrical signal traveling down the axon

Multiple Sclerosis
autoimmune disease, body attacks the myelin and disrupts the neural firing
Presynaptic Neuron
sending message
Postsynaptic Neuron
receiving message
Resting State
neuron is negatively charged, the neuron could “fire” but it’s not (aka resting potential)
Firing State
when then neuron receives enough of an electrical charge, it “fires” in an all-or-none manner
All-Or-None Law
the neuron fires fully or not at all
“Toilet”
Action Potential
the electrical charge that skips down the axon of the neuron
polarized → depolarized → polarized state
Re-Uptake
recollecting/recycling excess neurotransmitter left out in the synapse
Refractory Period
a brief period in which the neuron cannot fire while it “reloads”
Polarized Neuron
a neuron that has a distinct structural and functional asymmetry between its two main processes: the axon (output) and the dendrites (input)
Depolarized Neuron
a process in which the membrane potential of a neuron becomes less negative, or more positive
How neurons communicate
synaptic transmission
Agonists
Drugs that mimic or encourage the activity of a specific neurotransmitter
Antagonists
Drugs that block the effect of a particular neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters (in brief)
Chemical messengers
Excite or inhibit?
Neurotransmitters vs. hormones?
There are 2 basic categories of neurotransmitter activity
Excitatory: Neurotransmitters that stimulate neural activity, Think of the accelerator in a car
Inhibitory: Neurotransmitters that slow neural activity; Think of the brakes in a car
Opiates
artificial endorphins, body stops producing natural endorphins
Myasthenia Gravis
Autoimmune neuromuscular disorder of any voluntary muscle movement. Body attacks acetylcholine receptors making muscle contraction difficult.
→ causes paralysis
Rem Sleep
sleep with eyes open
What is the neurotransmitter involved with sleep
Serotonin
Adenosine (inhibitory neurotransmitter)
What brain structures are involved with sleep and alertness
Medulla
RAS
Hormone that secretes sleep
Melatonin
The Pineal Gland
secretes melatonin, the “sleep hormone” which helps regulate internal bodily rythms
Hypothalamus
sleep control center monitoring day/night changes, especially in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
Circadian Rythms
24hr sleep/wake cycle, governed by the SCN and Pineal gland
Why do humans sleep?
Restorative Theory: Humans sleep to replenish physical energy
Memory Consolidation Theory: Human sleep helps in sorting and filing info, and in strengthening some neural connections, while pruning others away
Adaptive Theory/Evolution Theory: Humans sleep at night because it’s historically been best for their survival to do so
D.J. Peter Tripp (1959)
REM (“Paradoxical Sleep”)
While your major muscle groups are essentially shut down, your brain is nearly as active as when awake
The dream stage?
Paralysis
Tetris Study (link to info processing)
REM deprivation
REM rebound
Babies and REM: (bodies natural response to sleep deprivation leading to an increase in REM sleep)
Insomnia
a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, despite having adequate opportunity to do so
Hypersomnia
sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) that cannot be relieved by adequate sleep
Sleep Disorders
Sleep Apnea- frequent stoppages of breathing during sleep
Narcolepsy- a sudden, involuntary drop into REM sleep
Night Terrors- screaming, sweating, can’t link to dream, no recall in AM
Somnambulism and Somniloquy- sleepwalking and talking
Rem sleep disorder- the muscles don’t shut down as they should, potentially dangerous