Biology Paper 2 -AQA combined science
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Define homeostasis
Maintenance of internal body conditions to maintain optimum conditions
For cell function and enzyme activity
In response to external or internal changes in environment.
What is a stimulus?
A change in environment.
What are the three main components that an automatic control system is made of?
Receptors, co-ordination centres and effectors.
What is negative feedback?
When the level of something is too high or too low, a response is produced to bring that level back to normal.
What does the CNS consist of?
The brain and the spinal cord.
How are message passed along neurones?
Through electrical impulses.
What may the effectors be in a response?
Glands releasing hormones or muscle contractions
Fill the blanks
____________---> receptor---->_________---> effector ----> response
stimulus --> receptor---->co-ordinator----> effector---> response
what is the synapse? How are signals passed across synapses from neurone to neurone?
The synapse is the gap between two neurones. Chemicals are diffused between neurones which stimulates the electrical impulse in the next neurone.
Why are reflex actions so quick?
They don't involve the conscious part of the brain.
What is a reflex arc?
The passage of information in a reflex (from receptor to effector)
Describe the reflex arc would be if someone touched a hot pan.
Receptors in the skin would detect the stimulus (the hot pan)
Send an electrical impulse to the sensory neurone
The signal is then passed to the relay neurone in the spinal cord via the synapse
Chemicals are diffused across the synapse to stimulate the electrical impulse in the relay neurone
The impulse then travels to the motor neurone, again via the synapse
The impulse then reaches the effector, where a muscle contracts and moves the arm away from the hot pan
Describe how hormones are used in the menstrual cycle
FSH is produced in the pituitary gland
Causes an egg to mature + Stimulates the production of oestrogen
Oestrogen is released from the ovaries
Causes the uterus lining to build up in preparation for an egg + Stimulates the release of LH + Inhibits the release of FSH
LH is produced in the pituitary gland
Stimulates the release of an egg around day 14 of the cycle
Progesterone is released from the ovaries
Iinhibits the release of LH and FSH
Causes the uterus lining to be maintained in preparation of a zygote
If the egg is not fertilised, the uterus lining sheds and the cycle repeats
What hormones does the contraceptive pill contain?
Oestrogen and progesterone
What are the methods of contraception?
hormonal:
-the patch (oestrogen + progesterone)
-the contraceptive injection
-contraceptive implant
-IUD
barrier:
-condom
-femidom
-diaphragm
extreme methods:
-abstinence
-sterilisation
-cycle tracking
What hormone sitmulates the release of thyroxine?
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
What is DNA?
The genetic material of an organism?
What word can be used to describe the shape of the base pairs of DNA>
complimentary
Which base pairs bond together?
A + T (adenine and thymine)
G + C (guanine and cytosine)
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a polymer made of two strands forming a double helix.
Define genome.
The genome is all of the genetic material in an organism.
What is a gene?
A gene is a small section of DNA. Each gene codes for a specific structure of amino acids which make a specific protein.
Why is being able to understand the human genome important scientifically?
-scientists can track human migration patterns
-specific genes can be linked to inherited diseases
-it can allow for treatments to be developed for these inherited diseases
What are the two types of reproduction?
Asexual and sexual
What are the gametes in plants?
egg cells and pollen
What are the gametes in humans?
egg cells and sperm
How many chromosomes does each gamete have?
23 - they fuse to create a cell with 46 chromosomes
What cell division processes are involved in sexual reproduction?
Mitosis and meiosis
Benefits of sexual reproduction
-less chance of contracting inherited disorders
-variation in offspring
Drawbacks of Sexual Reproduction
- Have to find a partner
- Have to wait until sexual maturity
- Not all members of the population reproduce
benefits of asexual reproduction
-quicker than sexual
-don't have to find a partner
drawbacks of asexual reproduction
-no genetic variation
-offspring a more likely to be susceptible to inherited disorders
What term describes a fertilised egg?
zygote
How many daughter cells are produced in meiosis?
4
How many divisons are there in Meiosis?
2 divisions
What does meiosis produce?
gametes
what is an allele?
Different forms of a gene
What is a dominant allele?
A form of a gene that is fully expressed, even when two different alleles are present
What is a recessive allele?
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present, only expressed when two recessive alleles are present
what is a phenotype?
physical characteristics of an organism
What is a genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism, what alleles an organism has
Name a recessive genetic disorder
cystic fibrosis
Name a dominant genetic disorder
polydactyly
What is cystic fibrosis?
Genetic disorder of the cell membranes
Causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in air passages and pancreas
What is polydactyly?
extra fingers or toes
How are embryos screened for inherited disorders?
During IVF, one cell is removed and tested for disorder-causing alleles
If the cell doesn't have any indicator alleles, then the originating embryo is implanted into the uterus
Arguments for and against embryonic screening?
for:
-less money spent on treatment, treatment is expensive
-stops suffering
-laws to stop it getting out of control
against:
-expensive
-ethicality
-Makes those with disorder 'undesirable'
What is variation?
Any difference between individuals of the same species.
What is a mutation?
change in DNA sequence
what is environmental variation?
The environment and the conditions that organisms live and grow in causes differences between members of the same species
What was Charles Darwin's theory?
Natural selection. We all evolved from simple life forms over three billion years ago
What factors can cause a species to go extinct?
-new predators
-new competition
-catastrophic event
-environment changes too quickly
-new disease
What is speciation?
development of a new species
survival of the .......
fittest
What is selective breeding?
choosing organisms with the most desirable characteristics and breeding them to create off spring with these characteristics
What is selective breeding also known as
artificial selection
what are the issues with selective breeding
-it is inbreeding, off spring are more likely to have harmful genetic defects and if a new disease appears, they are more susceptible due to a lack of variation
-the gene pool is far smaller
How does genetic engineering work?
-the gene is cut from a genome using an enzyme
-the gene is then inserted into a vector (usually a virus or a bacterial plasmid)
-the vector is introduced to the target organism and the useful gene is inserted into cells
what are the benefits and drawbacks of GM crops?
+can fortify foods with nutrients people in a community are lacking
+currently being used with no issues
+increased yield
-may reduce biodiversity
-other organisms may get the gene (e.g weeds may become resistant to herbicides
-they may cause health issues, people may develop new allergies
What are fossils?
the preserved remains of organisms that lived millions of years ago
What are the 3 types of fossils that form?
-replacement by minerals
-casts and impressions
-preservation
What are the materials/items that preserve fossils? Why?
-amber : no oxygen or moisture can enter, so decay microorganisms cannot survive
-glaciers: it is too cold for decay microorganisms to survive
-peat bogs: conditions are too acidic for decay microorganisms
Why can't scientists be certain about how life began on Earth?
Early forms were soft bodied and tissue could easily be decayed
So there are gaps in the fossil record
Geological activity has also destroyed many traces of life forms and fossils
What do fossils show?
how life forms have evolved
What can random mutations in the DNA of bacteria lead to?
changes in characteristics and bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics, bacteria reproduce rapidly by binary fission and the gene is passed on very quickly.
Name a common antibiotic resistant bacteria
MRSA
Why is antibiotic resistance a problem?
-overuse or incorrect use of antibiotics
How can people reduce antibiotic resistant bacteria
-use the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms are gone
What does the linnean system class organisms by?
charactersitics
What is the Linnean Classification System? How can you remember it?
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
King Prawn Curry or Fat Greasy Sausages
What does the 3 domain classification system classify organisms by?
Archaea - extremophile bacteria
Bacteria- true bacteria
Eukaryota- organisms like fungi, plants, animals and protists
What is an extremophile?
An organism which can survive in extreme conditions.
How are organisms named?
The binomial system
What does the binomial system name an organism by?
Genus and species
Why is the binomial system useful?
-it avoids confusion between languages as names are the same
What do evolutionary trees show?
Common ancestors and relationships between species
The more recent the common ancestor, the more closely related the two species; therefore, the more characteristics they're likely to share
What is the difference between an abitotic and a biotic factor
abiotic factors are non-living, biotic factors are living
What is a population?
a group of the same species living in the same area at the same time
what is a community?
All the different populations that live together in an area
what is an ecosystem
the interaction of a community of living organisms with the abitoic parts of their environment
What do plants compete for?
light, space, water and mineral ions
What do animals compete for?
Food, mates and territory
What is interdependence?
When species rely on each other for food, shelter, pollination, seed dispersal etc
What is a stable community?
A community is one where all the species and environmental factors are in balance so that the population sizes remain fairly constant.
Name examples of abiotic factors
temperature, soil pH, water levels, light intensity, wind intensity, carbon dioxide levels, oxygen levels
Name examples of biotic factors
new predators, competition, new pathogens, availability of food
Why do organisms need adaptations?
to survive when an environment changes
What are the 3 types of adaptations?
-behavioural : how an organism behaves
-structural: body structure
-functional: processes inside an organism
What is a producer?
The first organism in a food chain, it makes it's own food by photosynthesis
What is biomass?
The mass of living material
what is a population limited by?
the amount of food available
what do quadrats do?
measure the distrubution of an organism
what type of data do you get from the quadrats rp?
quantitative
what is the method for the quadrats rp?
Place a 1m^2 quadrat at a random place within the sample area
Count the number of organisms you are looking for within the quadrat (e.g daisies)
Repeat steps 1-2 for a set amount of random spots eg 20
Calculate the mean number of organisms for all quadrat samples (total organisms/number of quadrats)
Repeat steps 1-4 for another sample area
Compare the means for each area
Estimate = (Total area / area of quadrat) x mean
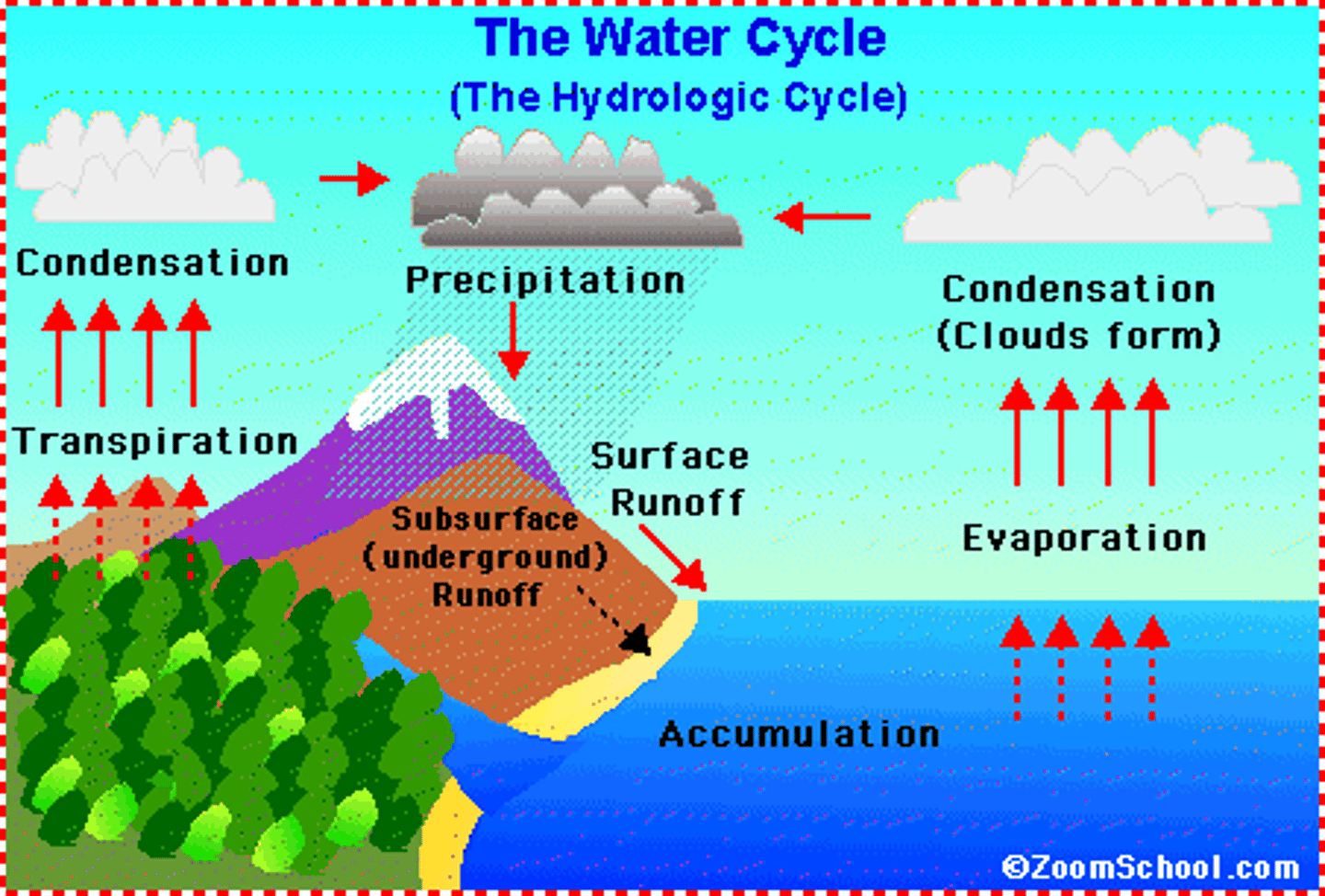
What is transpiration?
evaporation of water from plant leaves
What is precipitation?
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
Describe the water cycle
Evapuration: Energy from the sun evaporates water from the land and sea into water vapour
Condensation: This warm water vapour rises and condenses into clouds
Precipitation: Water falls from the clouds as precipitation and provides fresh water for animals and plants
Plants: soil absorbs water and roots take in water as its needed for photosynthesis, water is passed along through the food chain as plants are eaten
Animals: need water for chemical reactions, return water through excretion
Surface run off: Water not absorbed is runoff and runs into streams and rivers
Water drains back into sea and evaporates
Cycle repeats
Describe the carbon cycle
Photosynthesis: Carbon is removed from the atmosphere through the photosynthesis of green plants and algae
Respiartion: some of the carbon is returned by plant and aniaml respiration
Consumption: Animals absorb carbon from plants when they eat them
Decomposition: When plants and animals die, they are decomposed by decomposers (microorganisms), which releases carbon
Combustion: Burning of wood and fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide
What is biodiversity?
variety of different organisms within an ecosystem
what does high biodiversity ensure?
Stability of ecosystems
Reduces the dependence of one species on another for food, shelter and the maintenance of the physical environment