The Humanistic Approach
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Describe the main assumptions of the humanistic approach in psychology?
It draws on the work of the field’s founding figures: Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers.
It is focused on discovering what it means to be fully human.
Humanistic psychologists insist that the other approaches in psychology are reductionist, deterministic and so, can’t explain the holistic complexity of human behaviour.
Instead of using generalisable laws, it focuses on subjective experiences.
What does humanistic psychology mean by focusing on the self?
Rogers was primarily interested in two basic human needs:
The need for self worth.
The need for unconditional positive regard from others.
Both emerge from good relationships with supportive parents in childhood, and later on with friends and partners.
An individuals self worth has a direct impact on psychological wellbeing.
Describe what humanistic psychologists mean by free will and its role in the approach?
When the behaviour of a human being expresses choice, and is not determined by biological or external forces.
It suggests that everyone can consciously control and influence their own personal destiny even within the constraints that exist in life from external forces.
It opposes other approaches that see human behaviour as somewhat determined.
Describe Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
1943
Maslow suggests that you usually move up the triangle step by step.
However, some people might skip stages or vice versa.
e.g: someone may need to address their self-esteem before finding love.
Once the deficit needs are met, one can self actualise.
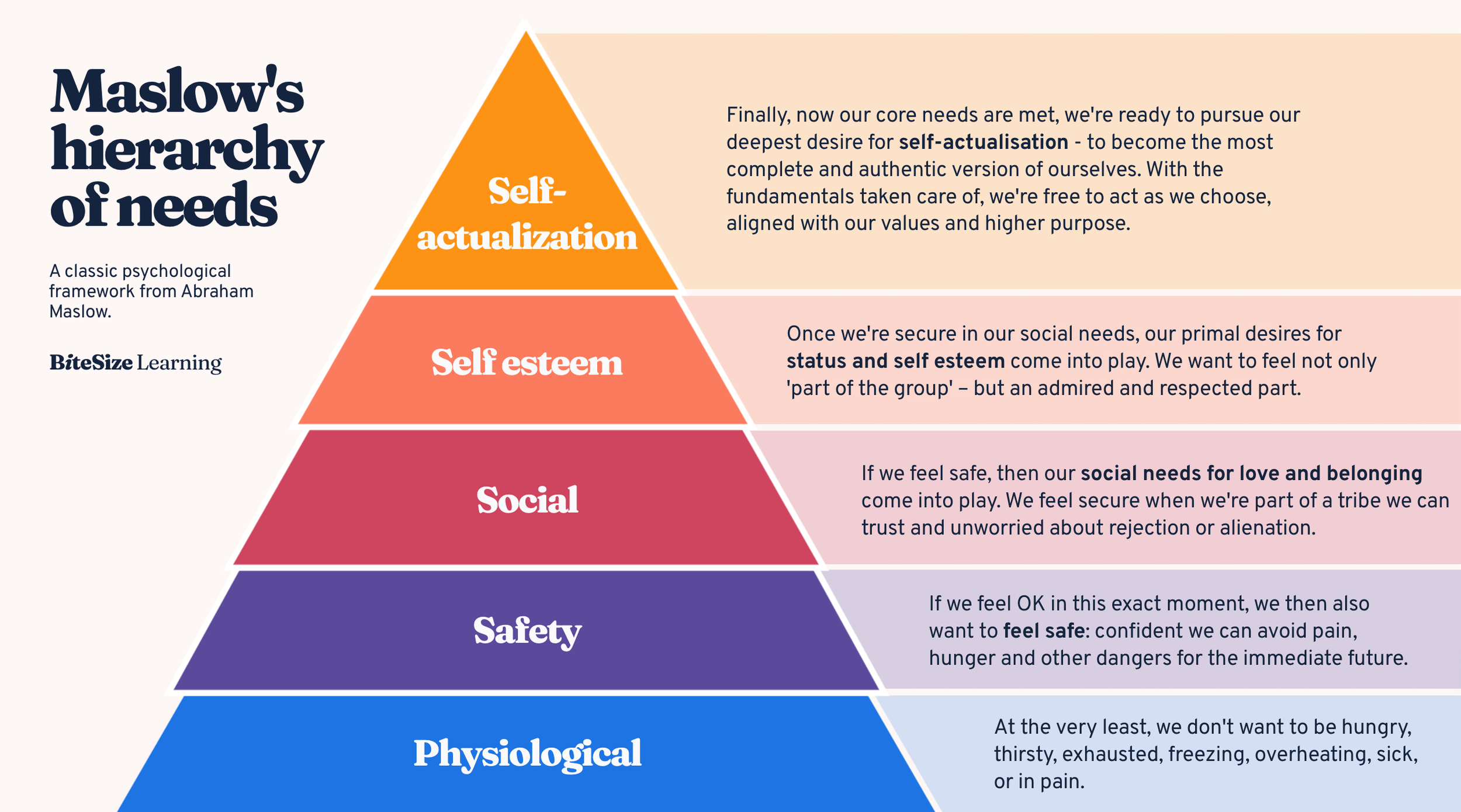
Outline what is meant by self actualisation, and an example of somebody who did?
Self actualisation is rare, but its achievement provides the possibility of true self-awareness and an honest relationship with the realities of an imperfect world.
Maslow believed self actualisation takes the form of peak experiences.
These are characterised by feelings of euphoria, seeing the world with awe and wonder, and without any fear or inhibition.
He cited Einstein as someone who famously self actualised through his creativeness.
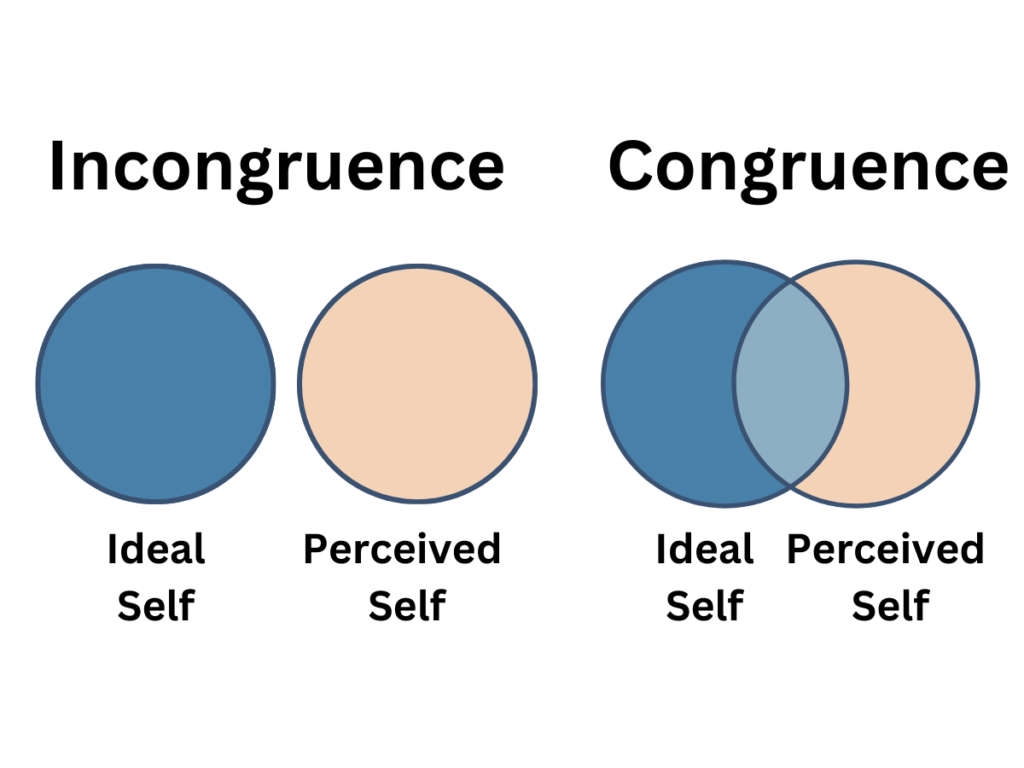
Describe what is meant by congruence?
Rogers argued that in order for personal growth to occur, an individual must experience congruence.
AKA, their concept of self must be broadly equivalent to their idea of self, and their true self.
A barrier to self actualisation is incongruence.
A state of incongruence will exist if the gap between the selves is too big.
Thus, negative feelings of self worth are a barrier to self actualisation.
Describe the role of conditions of worth in humanistic psychology?
Incongruence stems from a lack of unconditional positive regard from our parents during childhood.
Results in low self esteem and feelings of worthlessness as an adult.
Unconditional positive regard is when parents set conditions of worth on their children.
“I’ll love you when you…”
So, people in later life do things to please others and gain approval rather than to please themselves.
Therefore, self actualisation cannot be achieved.
Describe the influence of humanistic psychology on counselling?
The purpose of Rogerian therapy is to close the gap of incongruence.
Thus, allowing an individual to recognise their psychological limits and their strengths, to create a realistic balance.
He believed that taking a client-centred approach to counselling would allow an individual to take positive steps towards resolving their issues, to understand themselves and to achieve self actualisation.
The role of the therapist is to provide unconditional positive regard by expressing acceptance, empathy, and understanding no matter what.
This dissolves the client’s conditions of worth and allows them to become more authentic and true to self.
Evaluate the strengths of the humanistic approach?
STRENGTH: NOT REDUCTIONIST
It rejects the attempt to break behaviour and experience into smaller bits.
The cognitive approach sees humans as little more than information processing machines, while biological psychologists reduce behaviour to its basic physiological processes.
Finally, Freud described the whole psyche as a conflict between id, ego and super-ego.
In contrast, humanists advocate holism- the idea that subjective experiences can only be understood by considering the whole person.
STRENGTH: A POSITIVE APPROACH
The approach is often praised for bringing the person back into psychology, and promoting a positive image of the human condition.
While Freud said that human beings are slaves to their past, and “always existed somewhere between unhappiness and absolute despair”.
In contrast, humanists see all people as good and free to work towards their best self.
Thus, it is an optimistic and refreshing approach.
Evaluate the limitations of the humanistic approach?
LIMITATION: NON SCIENTIFIC
In order to conduct scientific research, variables must be operationalised, and behaviour broken down into its constituent parts.
However, there are relatively few humanistic concepts that can be broken down.
It lacks falsifiability due to its abstract concepts, and the approach lacks empirical evidence to support its claims.
LIMITATION: WESTERN CULTURE BIAS
Many central ideas such as individual freedoms, autonomy and personal growth would be more readily associated with the west.
Whereas, collectivist cultures such as India, emphasise the need for groups, community and interdependence.
Such cultures might not identify with the values of the humanistic approach.
Thus, it does not apply universally.