C2 - Phases of Economic Thought Development in Islam
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Revealed Knowledge
Foundation of Islamic economics from Qur'an and Sunnah.
Qur'an
Word of God revealed to Prophet Muhammad.
Sunnah
Prophet Muhammad's practices and explanations.
Thought
Human interpretations of divine teachings.
Qiyas
Analogical reasoning used in Islamic jurisprudence.
Ijtihad
Original reasoning to address new issues.
Usul al-fiqh
Juristic logic based on Islamic sources.
First Phase
Formation period of Islamic economic thought.
Juristic Logic
Rules derived from Qur'an and Sunnah.
Zayd bin Ali
Leading scholar in Islamic jurisprudence.
Abu Hanifah
Founder of the Hanafi school of thought.
Malik
Founder of the Maliki school of thought.
Shafi'i
Founder of the Shafi'i school of thought.
Ahmad bin Hanbal
Founder of the Hanbali school of thought.
Kitab al-Kharaj
Work by Abu Yusuf on taxation.
Kitab al-Kasb
Work by Muhammad al-Shayban on economic activities.
Zakah
Obligatory almsgiving in Islamic finance.
Inheritance
Distribution of property after death in Islam.
Taxation
Government revenue collection methods in Islam.
Second Phase
Translation period of foreign economic works.
Khalid al-Walid
Advised the establishment of diwan for administration.
Diwan
Office or register for administrative purposes.
Khalid b. Yazid
Initiated systematic translation of classical works.
Bayt al-Hikmah
House of Wisdom established by al-Ma'mun.
Translation Period
Era of translating ancient sciences into Arabic.
Arab-Indian Numerals
Numerical system showcasing East-West intellectual exchange.
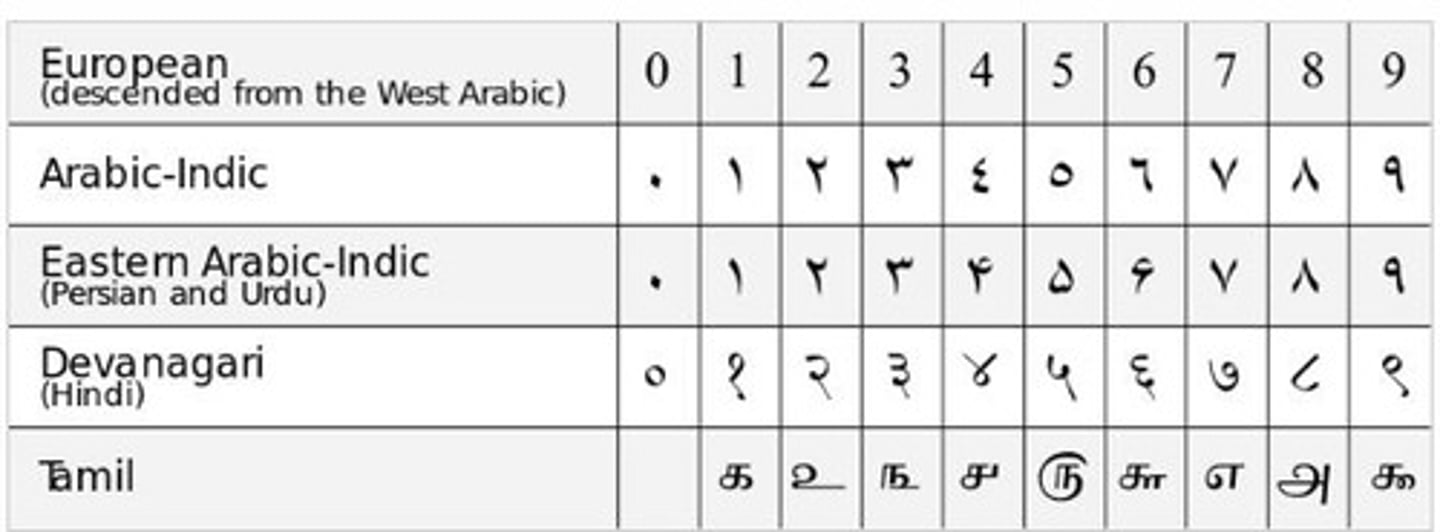
Impact of Translations
Revived ancient works, preventing their oblivion.
Traditionalists
Scholars rejecting Greek ideas, valuing Islamic knowledge.
Mutakallimūn
Scholastics distinguishing beneficial ideas from harmful ones.
Muslim Philosophers
Scholars integrating Greek philosophy with Islamic thought.
Al-Kinani
Representative of traditionalist scholars rejecting Greek influences.
Al-Ghazali
Prominent mutakallimūn synthesizing Islamic and Greek ideas.
Al-Kindi
Muslim philosopher supporting Greek philosophical ideas.
Oikonomia
Translated as 'ilm tadbīr al-manzil', household management science.
Ethics
Known as 'ilm al-akhlāq', branch of Greek philosophy.
Politics
Referred to as 'ilm al-siyāsah', another Greek philosophy branch.
Fifth/Eleventh Century
End of significant translation movement in Islamic scholarship.
Al-Farra
Traditionalist scholar opposing Greek philosophical ideas.
Al-Sarakhsi
Another representative of the traditionalist group.
Al-Mawardi
Mutakallimūn scholar assessing Islamic versus Greek thought.
Fakhr al-Din al-Razi
Influential mutakallimūn synthesizing diverse philosophical ideas.
Ibn Sina
Muslim philosopher deeply influenced by Greek philosophy.
Al-Suhrawardi al-Maqtul
Philosopher associated with later Islamic philosophical thought.
Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Later philosopher contributing to Islamic philosophical discourse.
Sufis
Followers of Sufism emphasizing divine worship and devotion.
Asceticism
Lifestyle rejecting worldly pleasures for spiritual growth.
Zuhd
Ascetic behavior not rejecting worldly affluence.
Translation Period
Era of translating and disseminating economic ideas.
Helmut Ritter
German scholar tracing Islamic economics to Bryson.
Neo-Pythagorean Bryson
Early economic ideas influencing Islamic thought.
Sufism
Mystical Islamic movement focusing on spiritual experience.
Altruism
Selfless concern for the well-being of others.
Hellenistic Influence
Cultural blend affecting early Islamic spiritual movements.
Economic Literature of Islam
Body of work analyzing Islamic economic principles.
Macro-Economic Relations
Large-scale economic interactions emphasized by Keynes.
Prophet's Example
Balanced life approach demonstrated by Prophet Muhammad.
Imbalanced Asceticism
Extreme rejection of worldly life contrary to Islam.
Tasawwuf
Islamic term for Sufism and its practices.
Divine Worship
Religious devotion directed towards Allah.
Material Wealth
Physical possessions often viewed with caution in Islam.
Economic Thought
Intellectual exploration of economic principles and practices.
Sufi Movement
Cult-like development of Sufism in later centuries.
Syrian Monasticism
Early Christian practice influencing Islamic asceticism.
Spiritual Progress
Advancement towards divine connection and understanding.
Sufi Representatives
Notable figures in Sufism's development and teachings.
Sufism's Origins
Theories linking Sufism to various cultural influences.
Economic Altruism
Focus on serving others over accumulating wealth.
Material Values
Focus on non-material virtues for happiness.
Al-Dimashqi
Author of 'The Guide to the Virtues of Trade'.
Translation Period
First phase of Islamic economic thought development.
Retranslation Period
Third phase involving translation to European languages.
Greco-Arab Sciences
Muslim scholars' contributions to Greek philosophy.
Translation Age
Period before the Western Renaissance marked by translations.
Muhaddithūn
Traditionalists whose works were less translated.
Al-Ghazali
Author of 'Ihyā' Ulūm al-Dīn', influential in philosophy.
Hukamā'
Muslim philosophers whose works were widely translated.
Ibn Sina
Prominent Muslim philosopher and physician.
Al-Farabi
Notable Muslim philosopher known for political theory.
Ibn Bajjah
Muslim thinker contributing to philosophy and science.
Ibn Rushd
Commentator on Aristotle, influential in the West.
Christian West
Region that adopted and translated Islamic knowledge.
Vernacular Language
Informal spoken language, often of lower status.
Translation from Arabic
Process of translating Islamic works to Latin.
Transmission of Knowledge
Sharing of ideas through translation and teaching.
European Capitals
Cities where translation of Muslim works occurred.
Sicily and Spain
Regions where Muslim knowledge was appropriated post-conquest.
Aristotle's Economic Views
Found in 'Politics' and 'Nicomachean Ethics'.
Catalan Language
Similar to Spanish but related to French.
Ethical Discourses
Economic ideas intertwined with philosophical discussions.
European Students
Traveled to Muslim lands for advanced learning.
Philosophical Works
Economic ideas translated alongside philosophical texts.