Cellular structure and function
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are some common R groups attached to phospholipid heads on the surface of the cell membrane
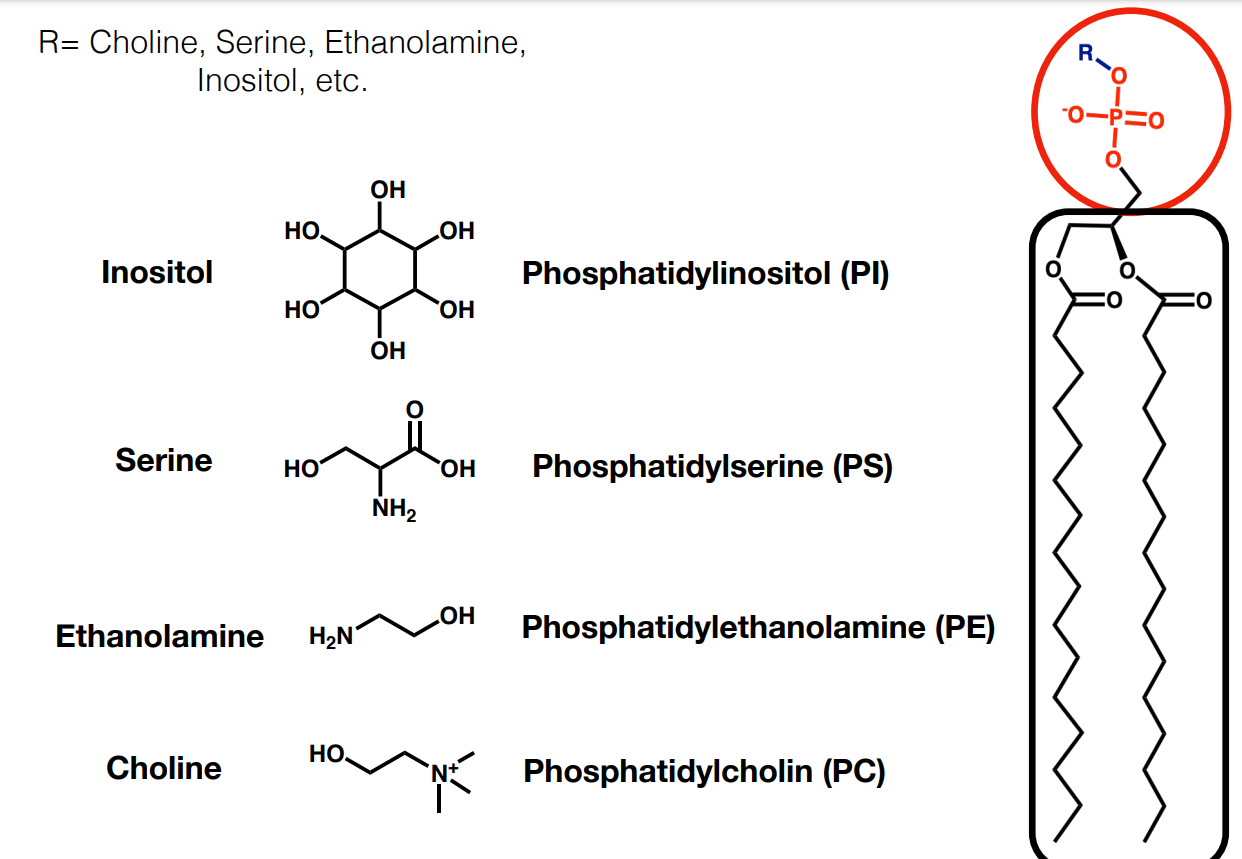
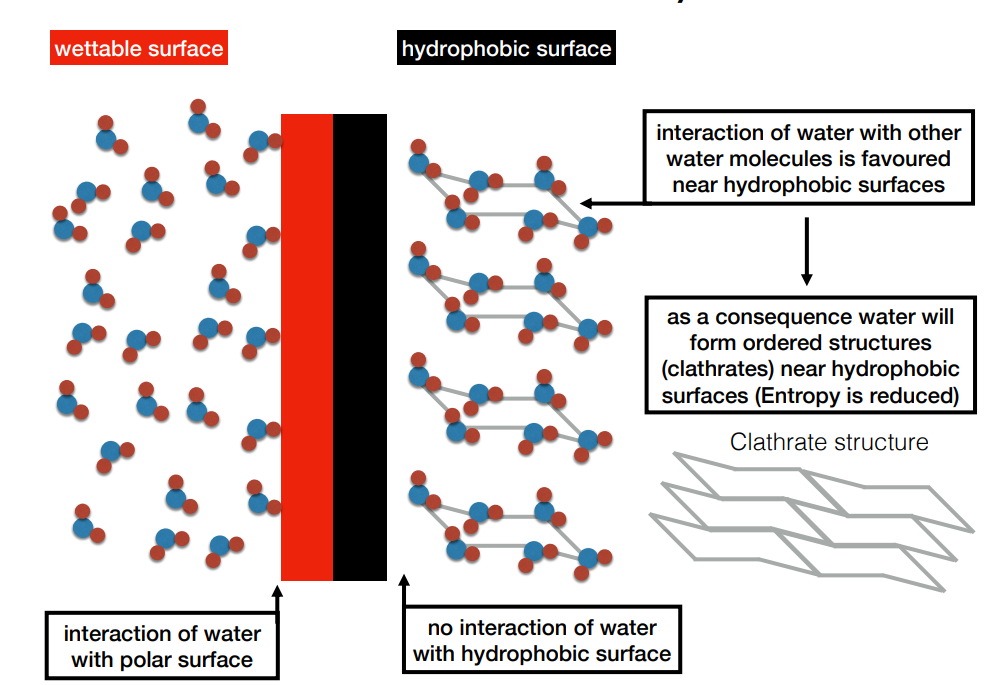
How do the dynamics of interactions between hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces differ
Hydrophilic surfaces form hydrogen bonds with water which are constantly made and broken
Hydrophobic surfaces do not interact well with water so interaction between water molecules is favoured, causing the formation of Clathrate structures in which water molecules bond together in rings. This reduces disorder and hence entropy.
What do you call a protein structure that stretches through the entire bilayer
Transmembrane domain
What is a GPI anchor
Glycerol PI (phosphatidylinositol) which attaches to a carbohydrate on the cell surface membrane
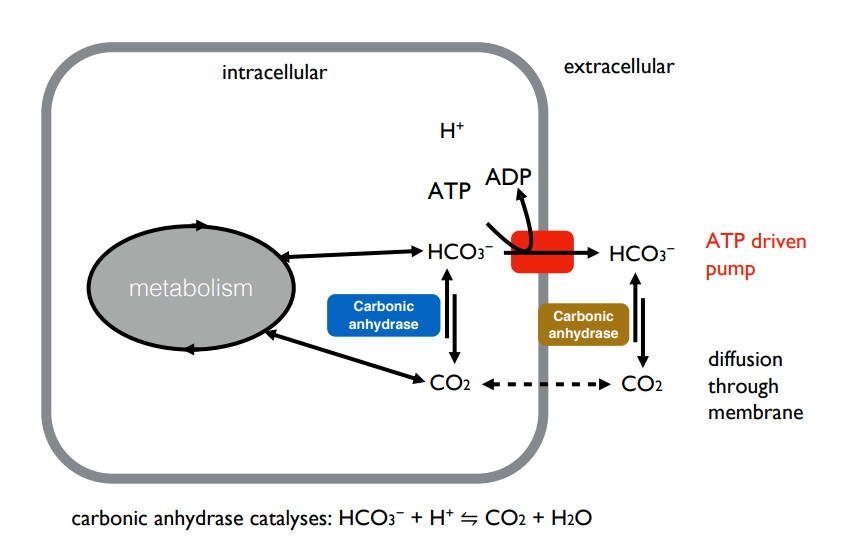
What is the principle behind carbonic anhydrase used to transport CO2
HCO3- is converted into CO2 (catalysed by carbonic anhydrase) which is free to diffuse across the membrane where it is converted back into HCO3- using carbonic anhydrase performing the reverse reaction. HCO3- is charged and cannot travel back across the membrane. Hence this mechanism can be used to transport CO2 in excess out of respiring cells in an energy efficient way.
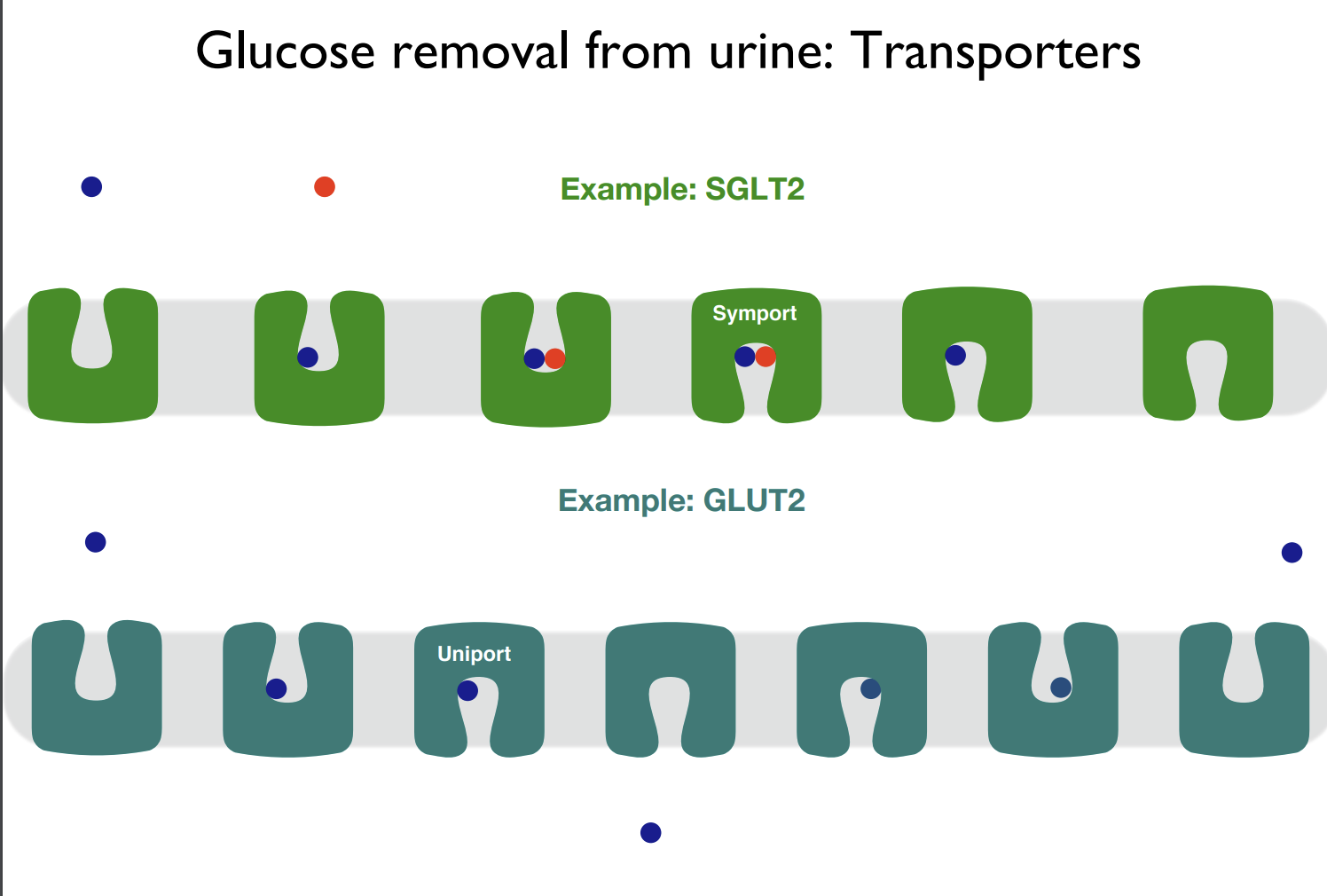
Uniport vs symport channels
Uniport takes 1 molecule through the membrane while symport takes 2.
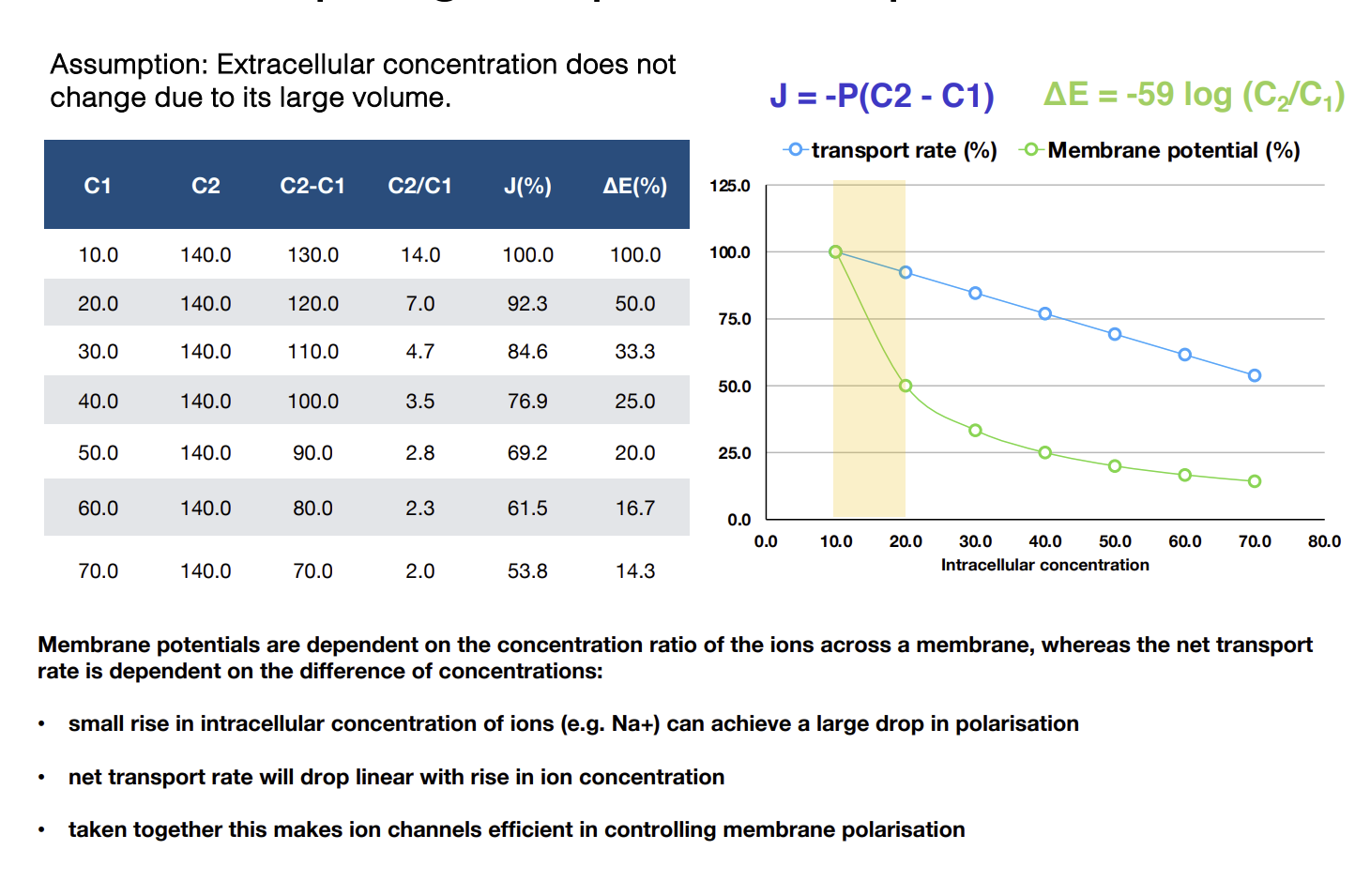
Equation for net rate of transport across membranes
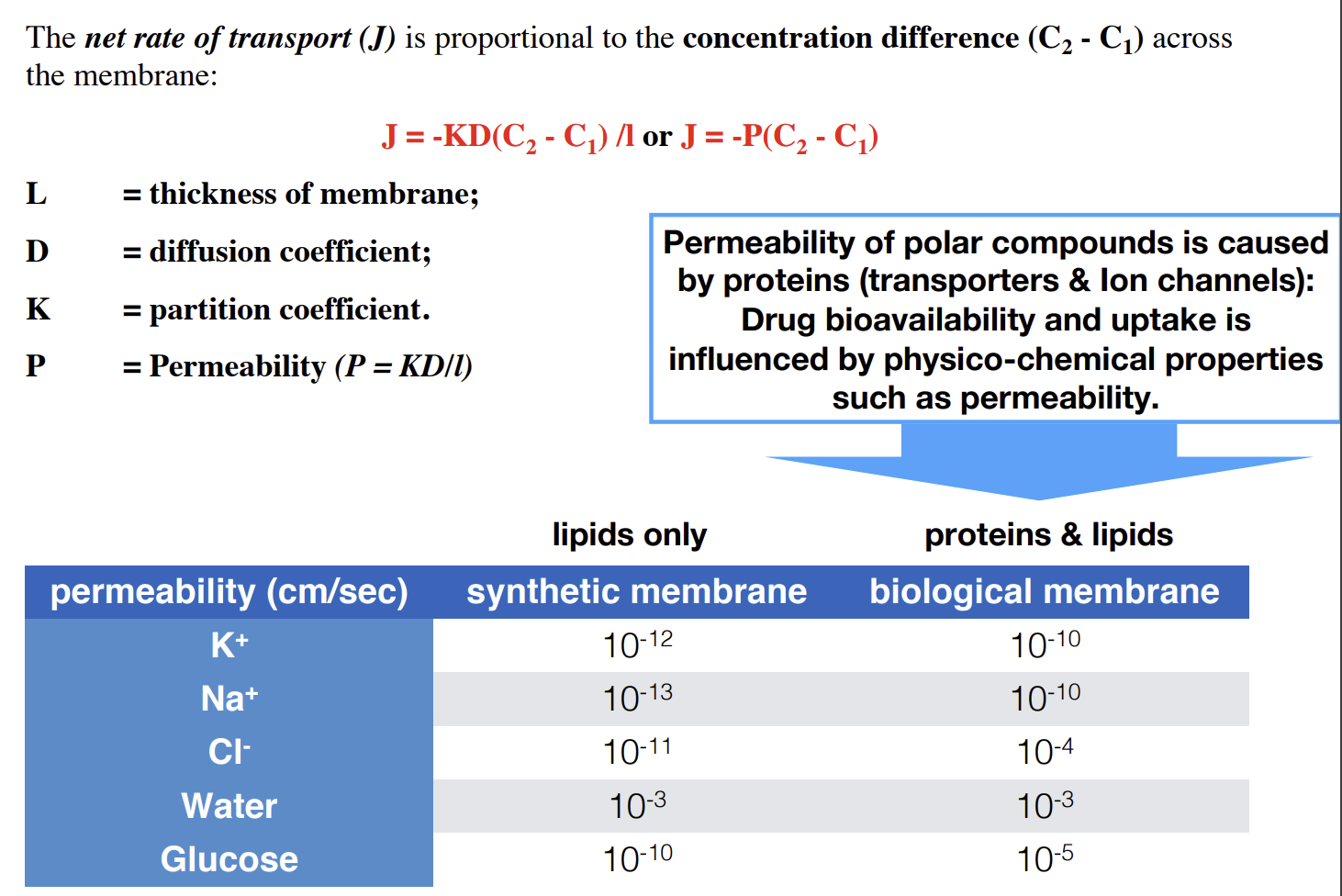
Calculating membrane potential
C1 is conc. inside cell, C2 is conc. outside cell.
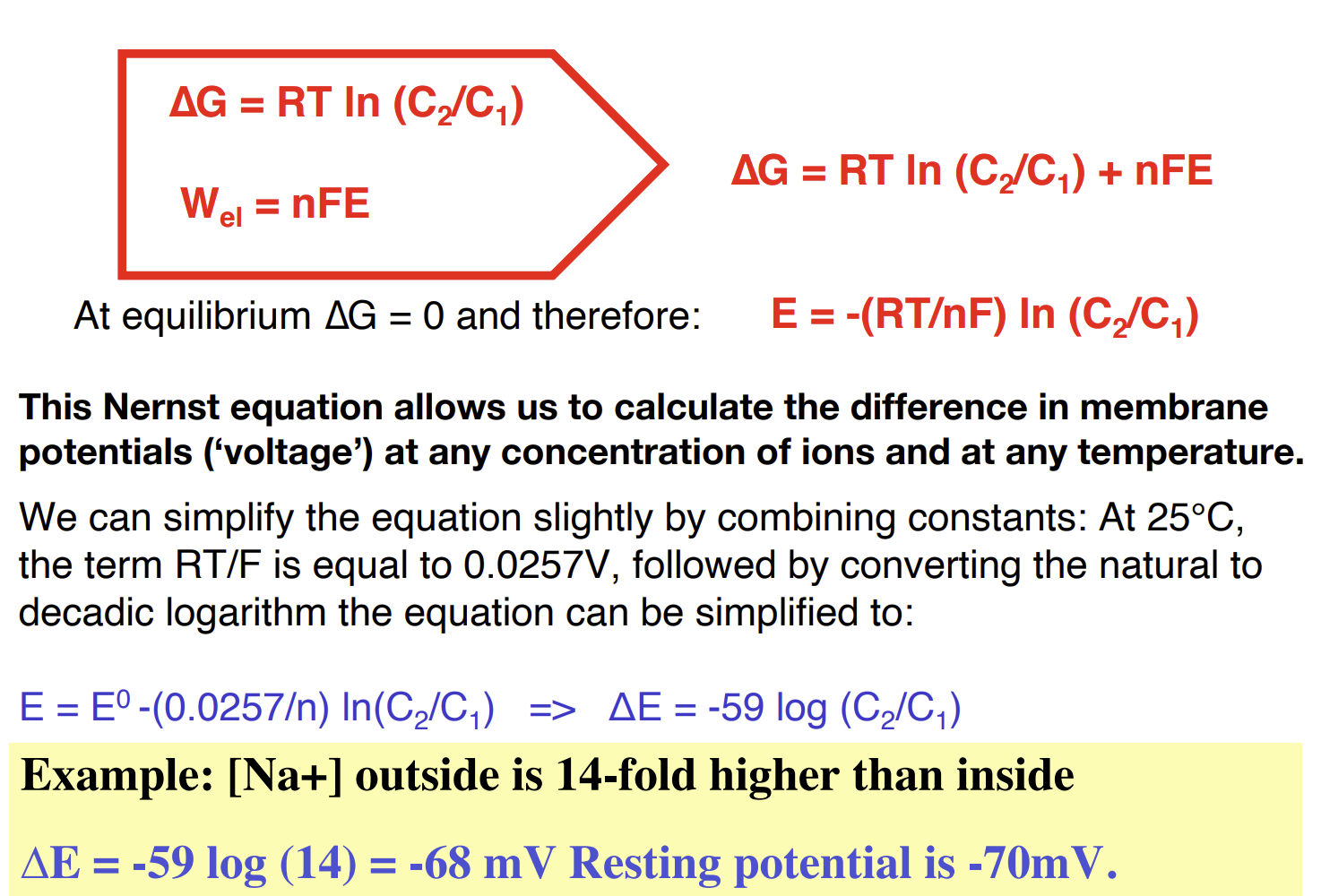
How does polarisation affect transport rate
A small change in polarisation can cause a large increase in the rate of transport across a membrane.
What does EGTA do
It chelates Ca2+ much more than Mg2+.
How do calcium ion channel blockers work
They physically lodge in the ion channel and remain there thanks to their hydrophobic parts.
What does agonist/antagonist imply
They are ligands so bind to a receptor site
what is a G-protein coupled receptor
A receptor coupled to a GTP binding protein (G-protein)
How many parts are there in a G-protein
3 - it is trimeric.
Alpha, beta and gamma. Beta and gamma units do not separate.
The alpha unit carries a nucleotide - GTP or GDP depending on what state the G-protein is in.
All of the units are membrane-bound
G-protein cycle
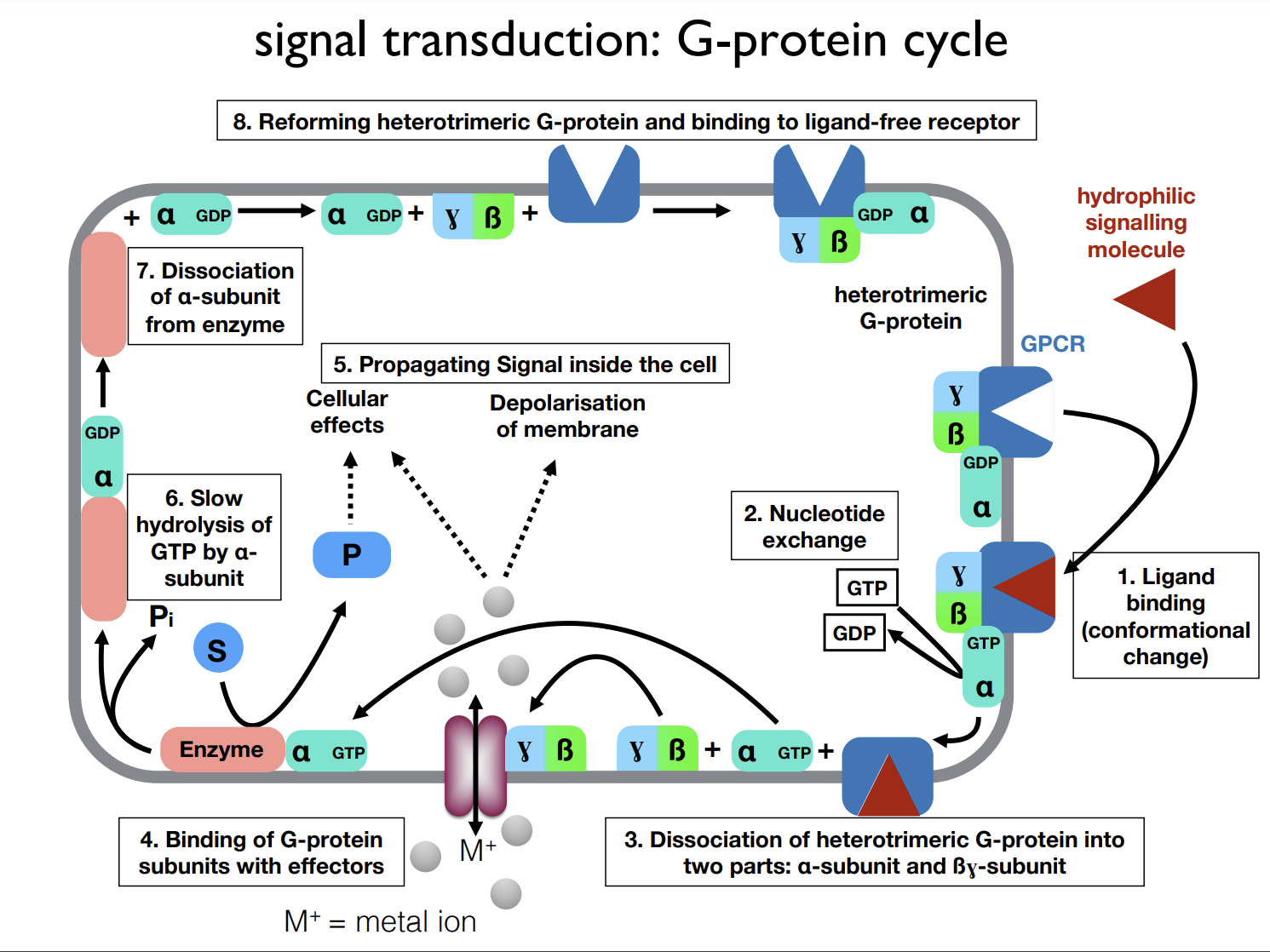
What induces nucleotide exchange
GEP - guanine exchange factor.
In this case it is the receptor.
What is a GAP
GTPase activating protein.