PAS 604 Intro to Hematology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Plasma, Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets
What are the components of whole blood?
55%; 45%
Blood is made up of ______ plasma and ______ blood cells
- Liquid component of blood, made up of water, sugar, fat, protein, and salts
- Transports blood cells as well as nutrients, waste, antibodies, hormones, proteins
What is plasma?
number of blood elements in relation to volume
What is a Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC)
lavender top tube
What tube is CBC collected in?
EDTA anticoagulant
What is in CBC tube?
inversion of tube several times
What is done after CBC tube is filled to prevent coagulaiton?
ratio of the volume of RBCs to the volume of whole blood expressed as percentage
What is Hematocrit (Hct)?
40
Hct 40% means _____ milliliters of RBCs per 100 milliliters of blood)
plasma
Hbg & Hct are dependent on ________ volume
higher ("hemoconcentrated")
If a patient is dehydrated, the Hgb and Hct will appear:
lower ("hemodiluted")
If a patient is fluid overloaded, the Hgb and Hct will appear:
Hgb
Hct should be equal to 3x:
RBC count
Hgb should be equal to 3x:
average volume of the RBC
What does Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) measure?
Hct and RBC count
What is MCV value derived from?
normocytic
MCV = 80-100 fL
microcytic
MCV < 80 fL
macrocytic
MCV > 80 fL
Average mass of hemoglobin per RBC
What is Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)?
MCV
MCH variation tracks along with:
Measure of the concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of packed RBCs
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
dividing the hemoglobin by the hematocrit
How is MCHC calculated?
- Electronic counter problem
- Spherocytosis
What conditions cause elevated MCHC?
- Iron deficiency anemia
- sideroblastic anemia
- chronic disease anemia
What conditions cause decreased MCHC?
Measure of the variation of RBC volume (size)
What is Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)?
more variation in size
High RDW indicates:
less variation in size
Lower RDW indicates:
Elevated RDW, unequal size
What is anisocytosis?
anisocytosis
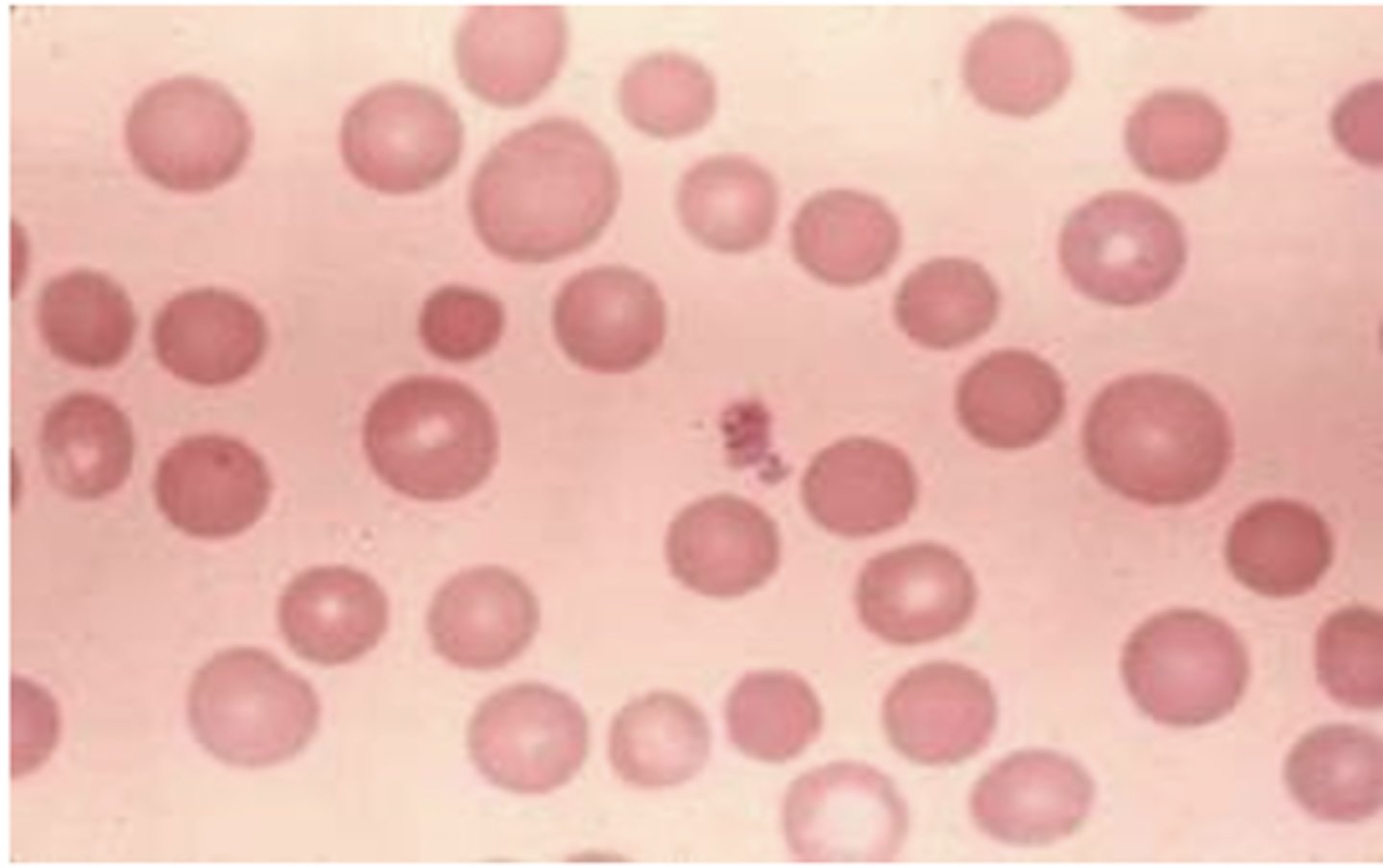
iron deficiency anemia
What condition has high RDW with low MCV?
Folate and vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
What condition has high RDW and high MCV?
Recent Hemorrhage
What condition has high RDW with normal MCV?
Thalassemia
What should be suspected in the setting of anemia with normal RDW?
- Complements RBC indices and RDW
- Size
- Morphology
- Shape and staining characteristics
- Should not see nucleated RBCs
What does peripheral smear show?
unusual shape
What is Poikilocytosis?
less intense staining
What is Hypochromasia?
variation in Hgb content
What is Polychromasia?
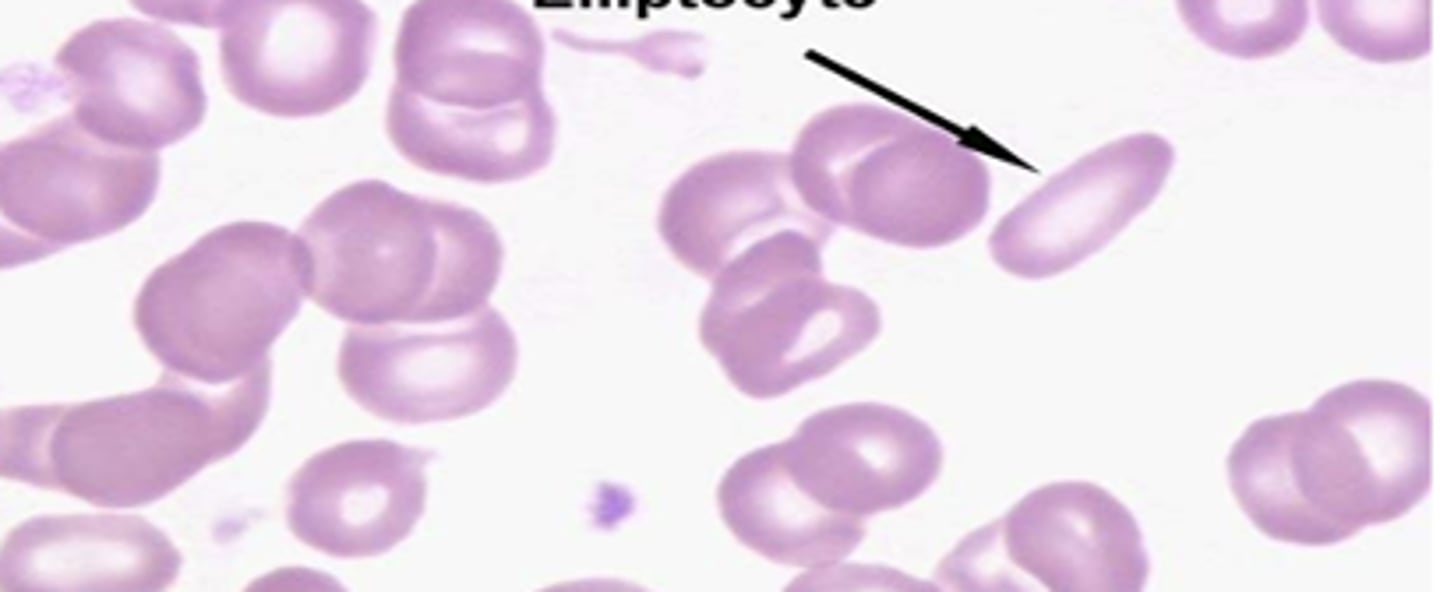
elliptical shaped
What are Elliptocytes?
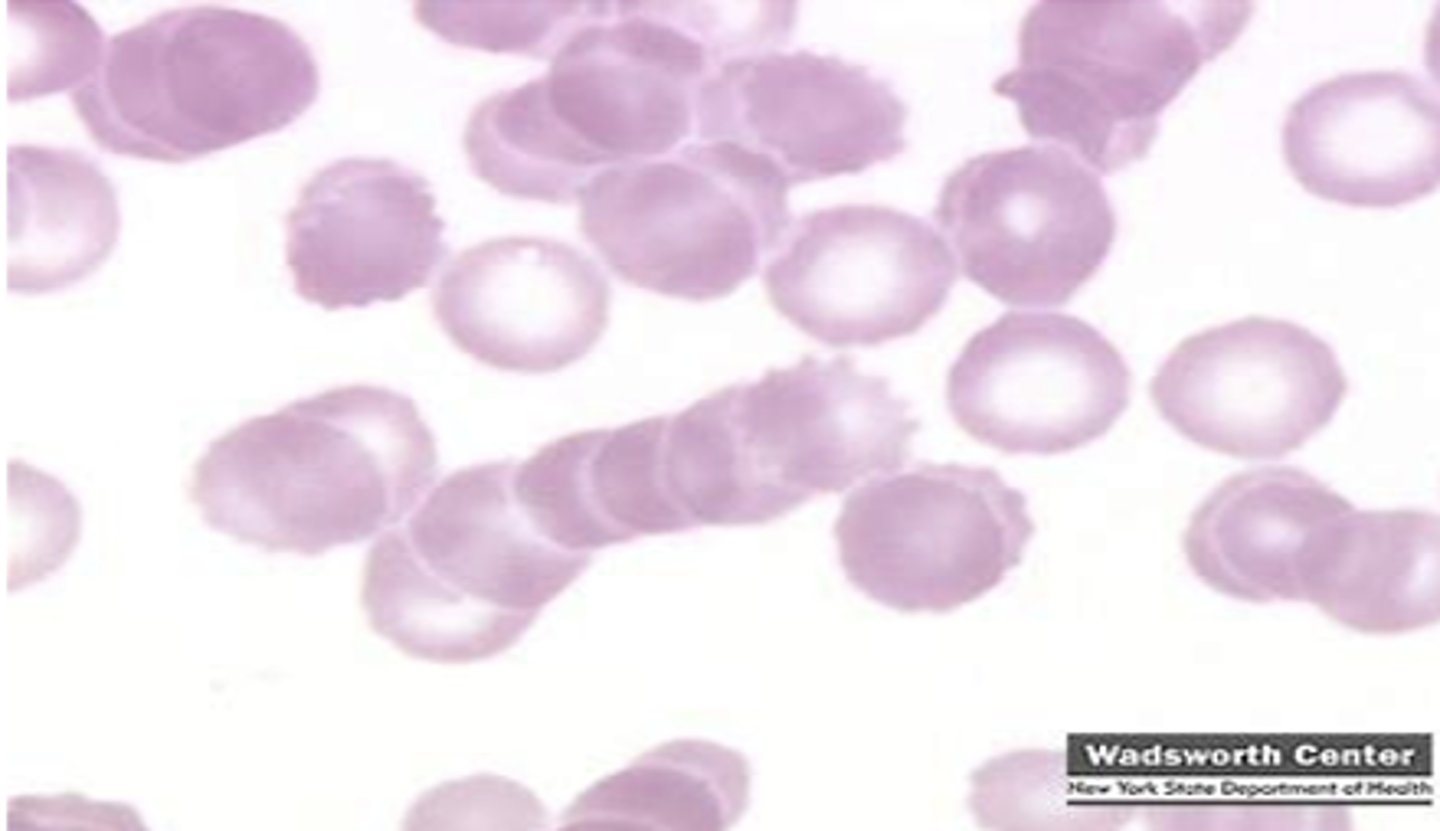
stack of coins
What is Rouleux formation?
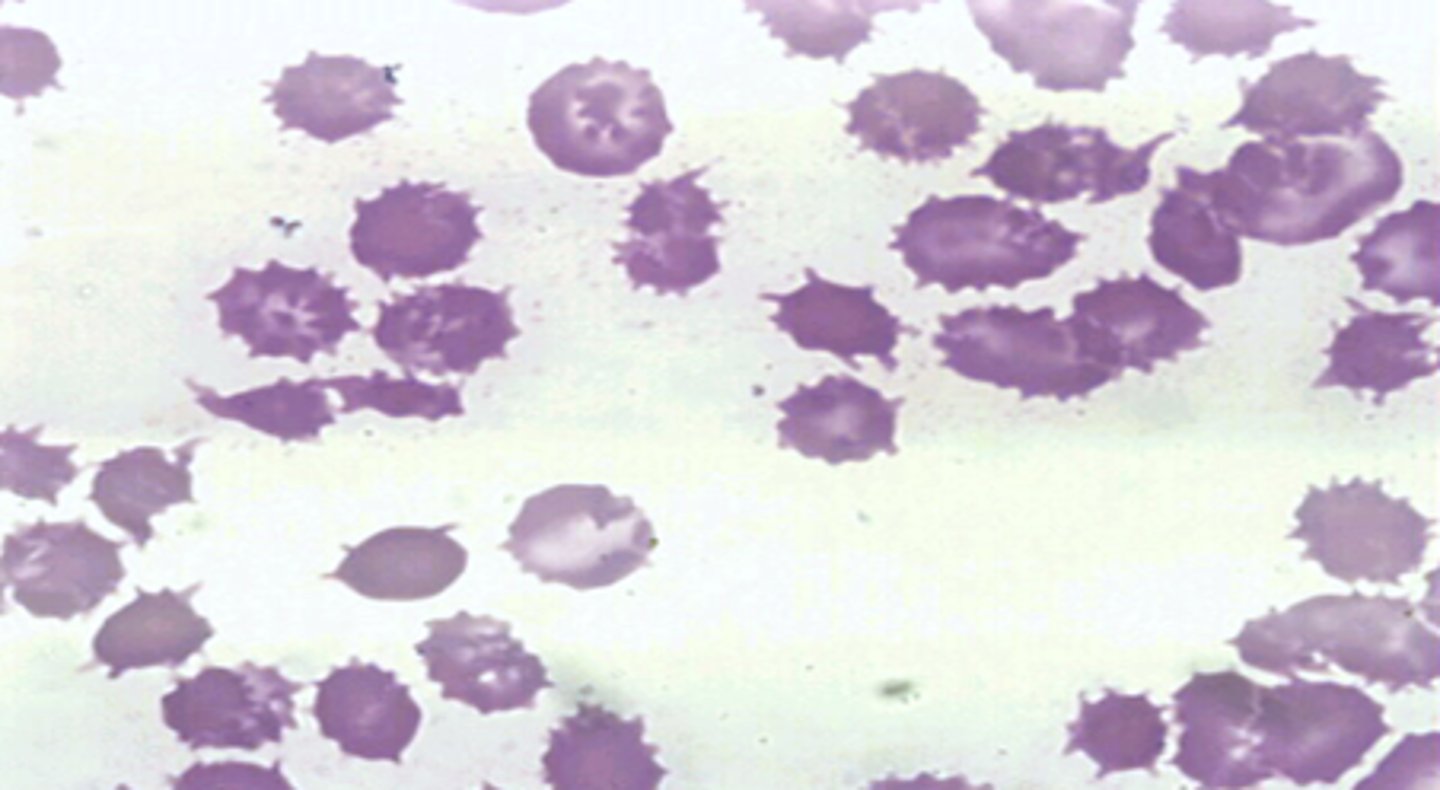
spur, thorn, spiculated cells
What are Acanthocytes?
hypochromasia
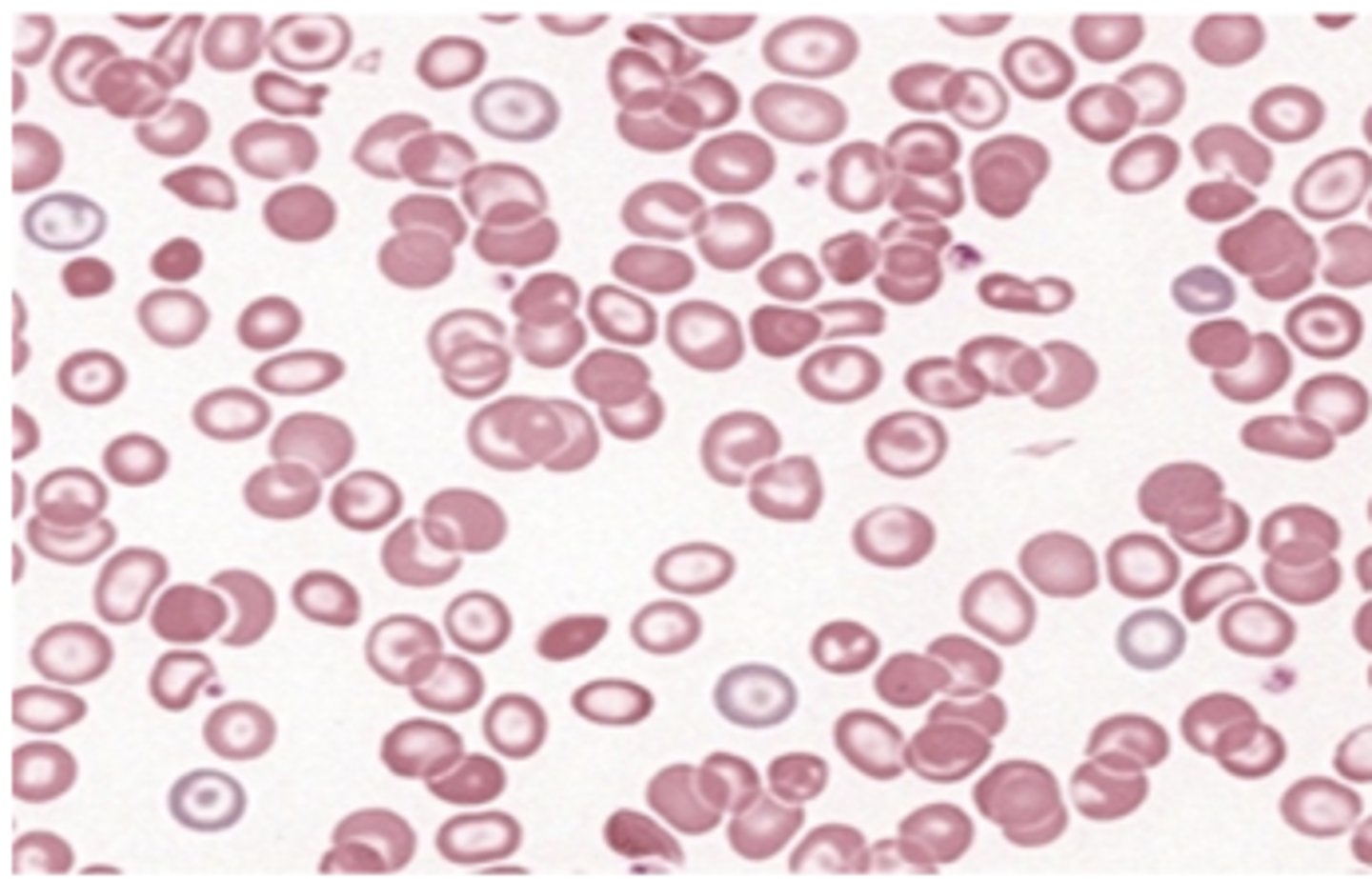
hyperchromasia
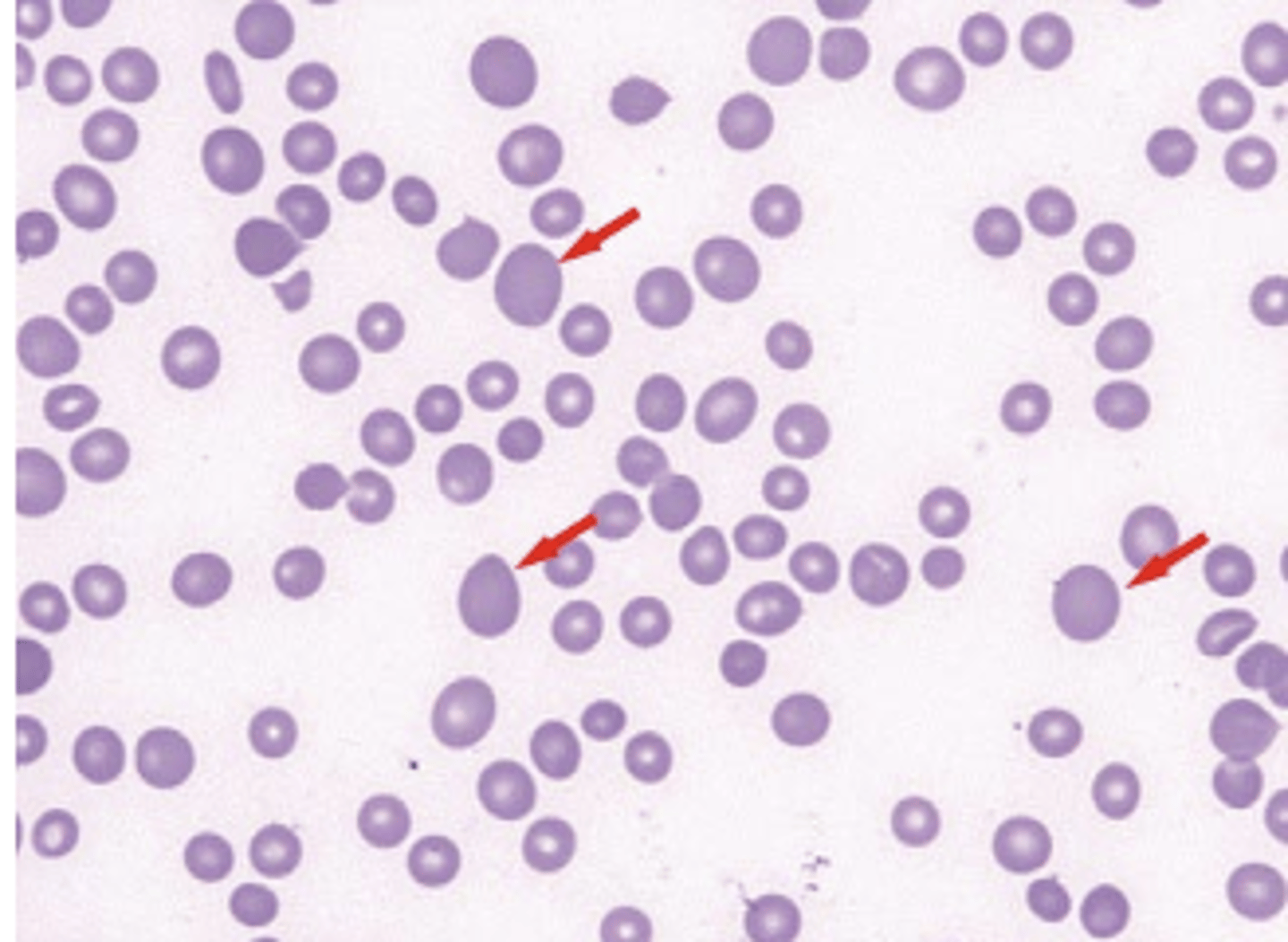
immature and released early from the bone marrow
Polychromasia: blue-staining RBCs indicate they are:
thalassemia and iron deficiency
When is hypochromasia seen?
dehydration or presence of spherocytes
When is Hyperchromasia seen?
sickled cells
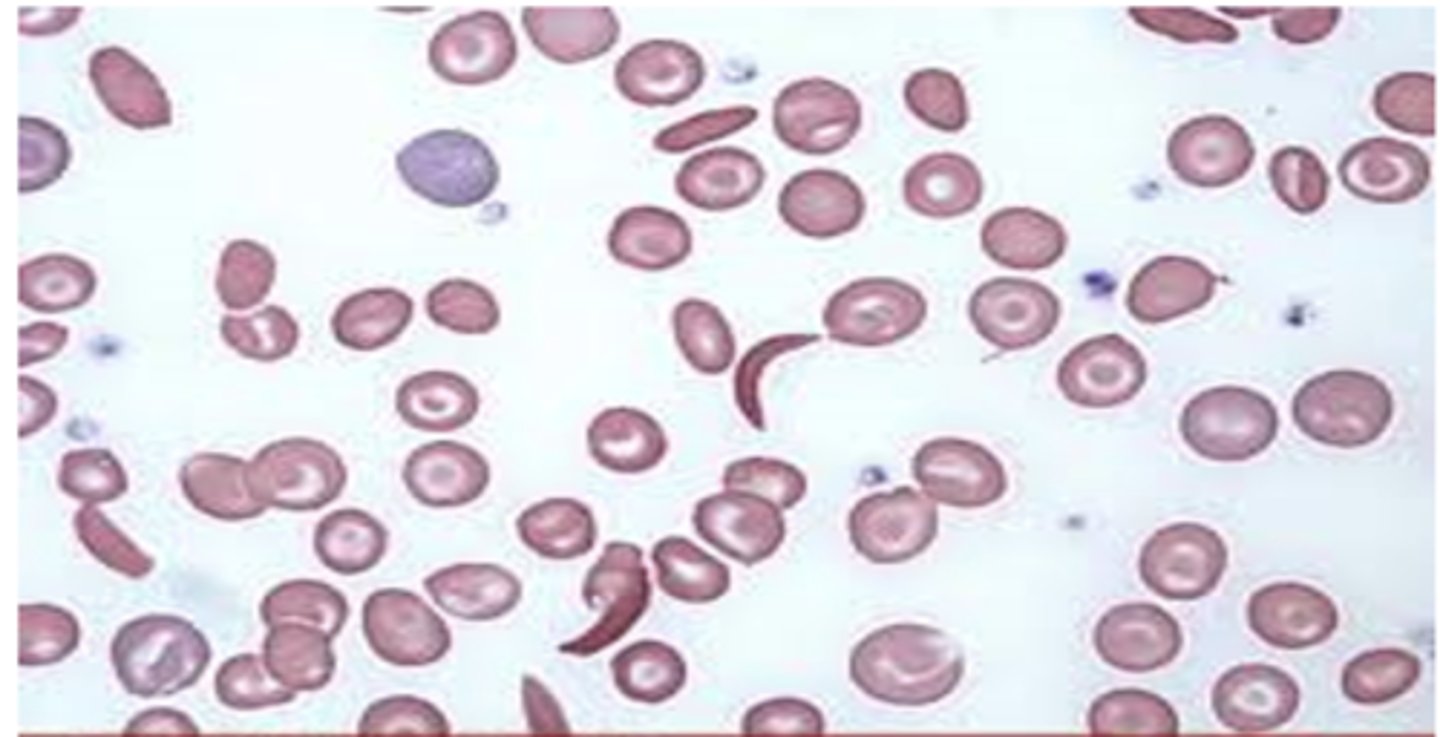
spherocytes
elliptocytes
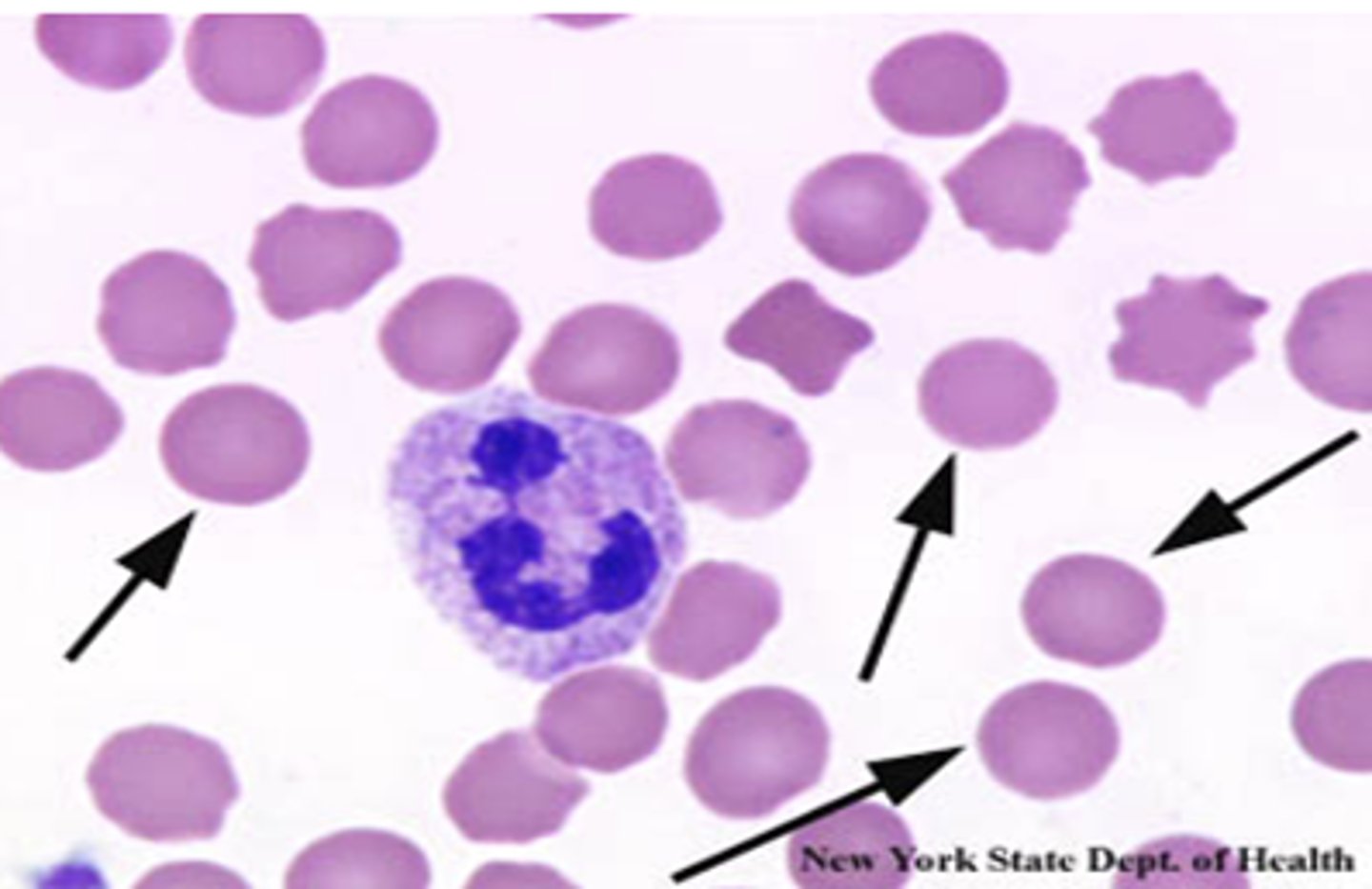
target cells
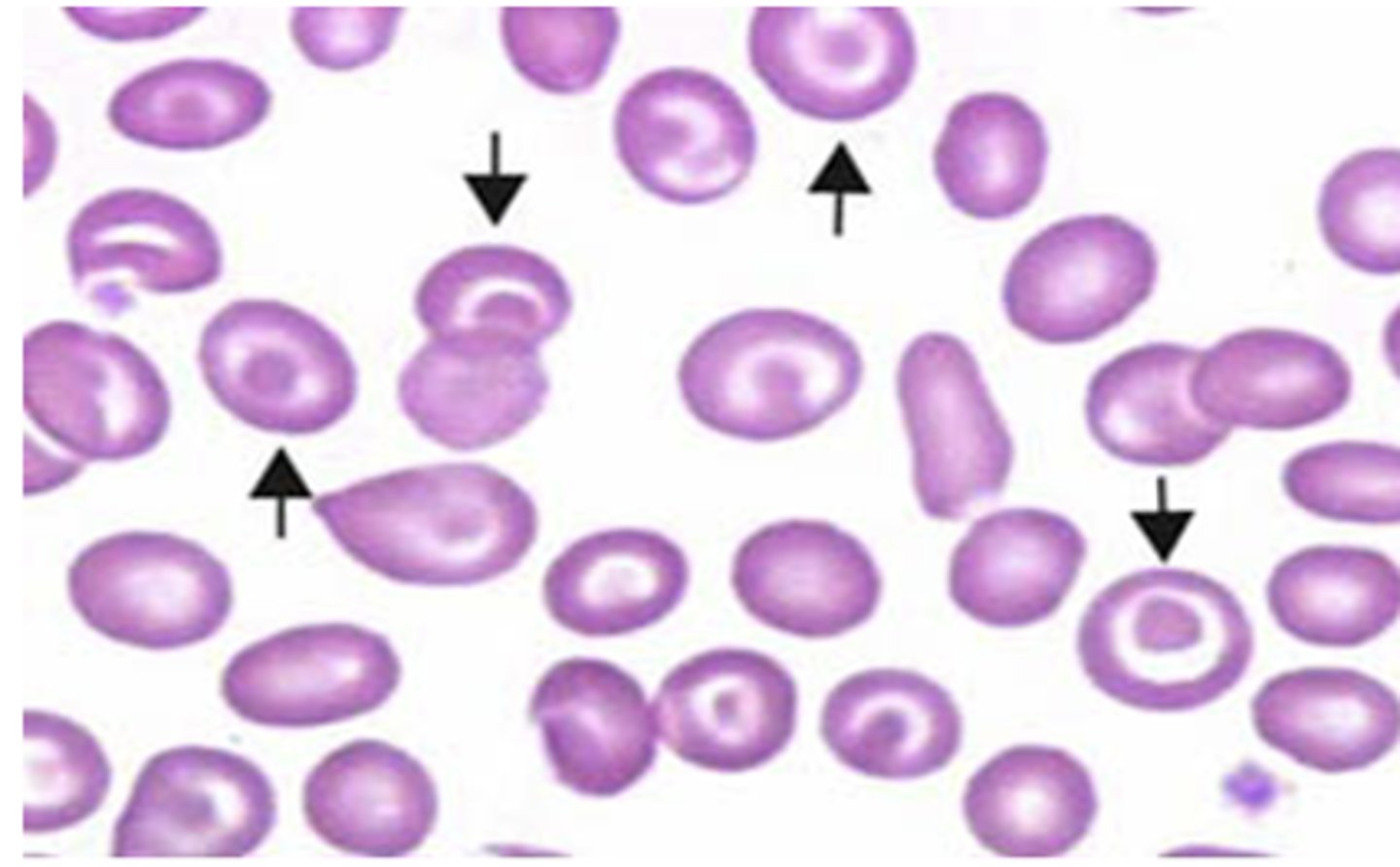
teardrop cells
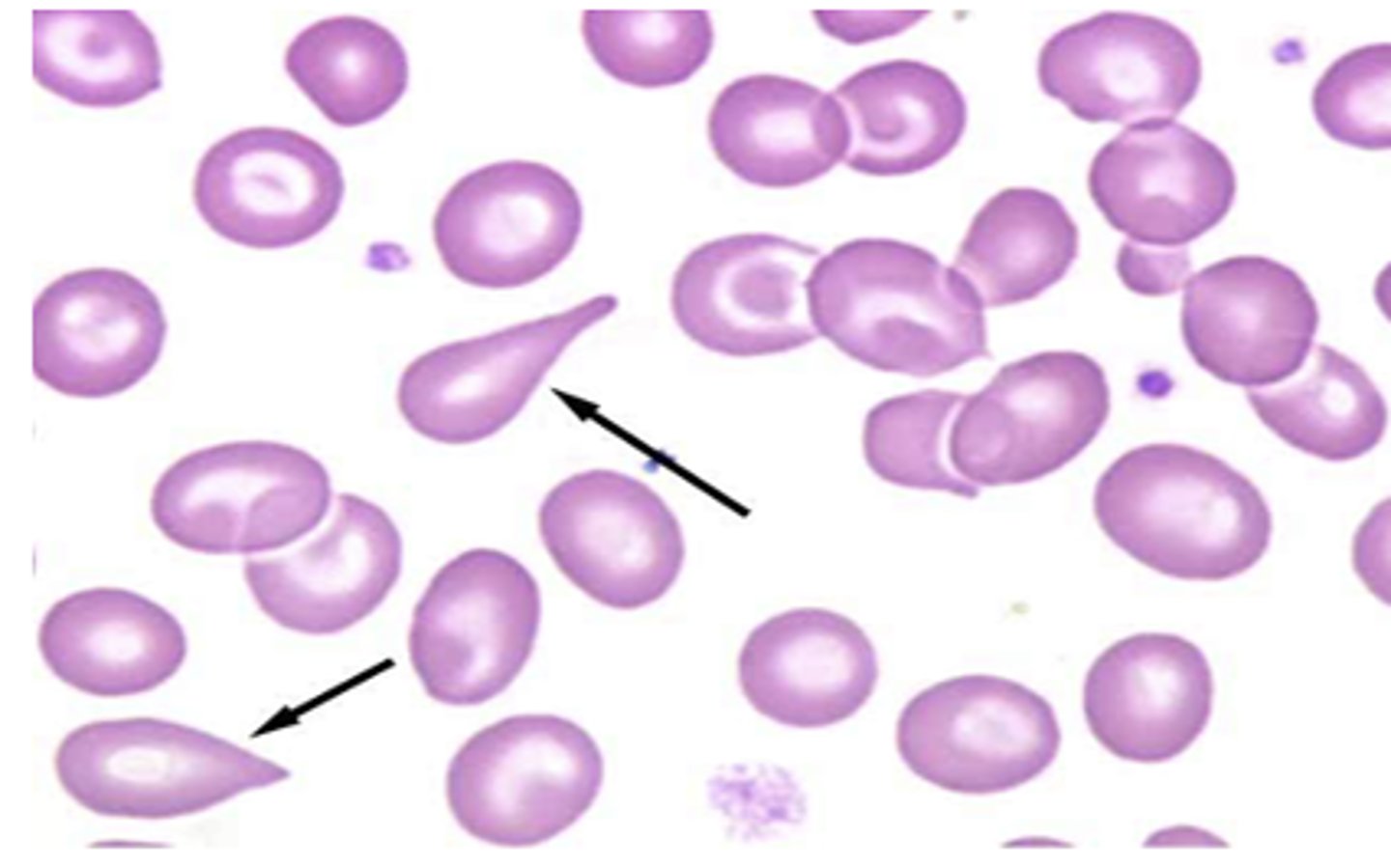
rouleax
acanthocytes
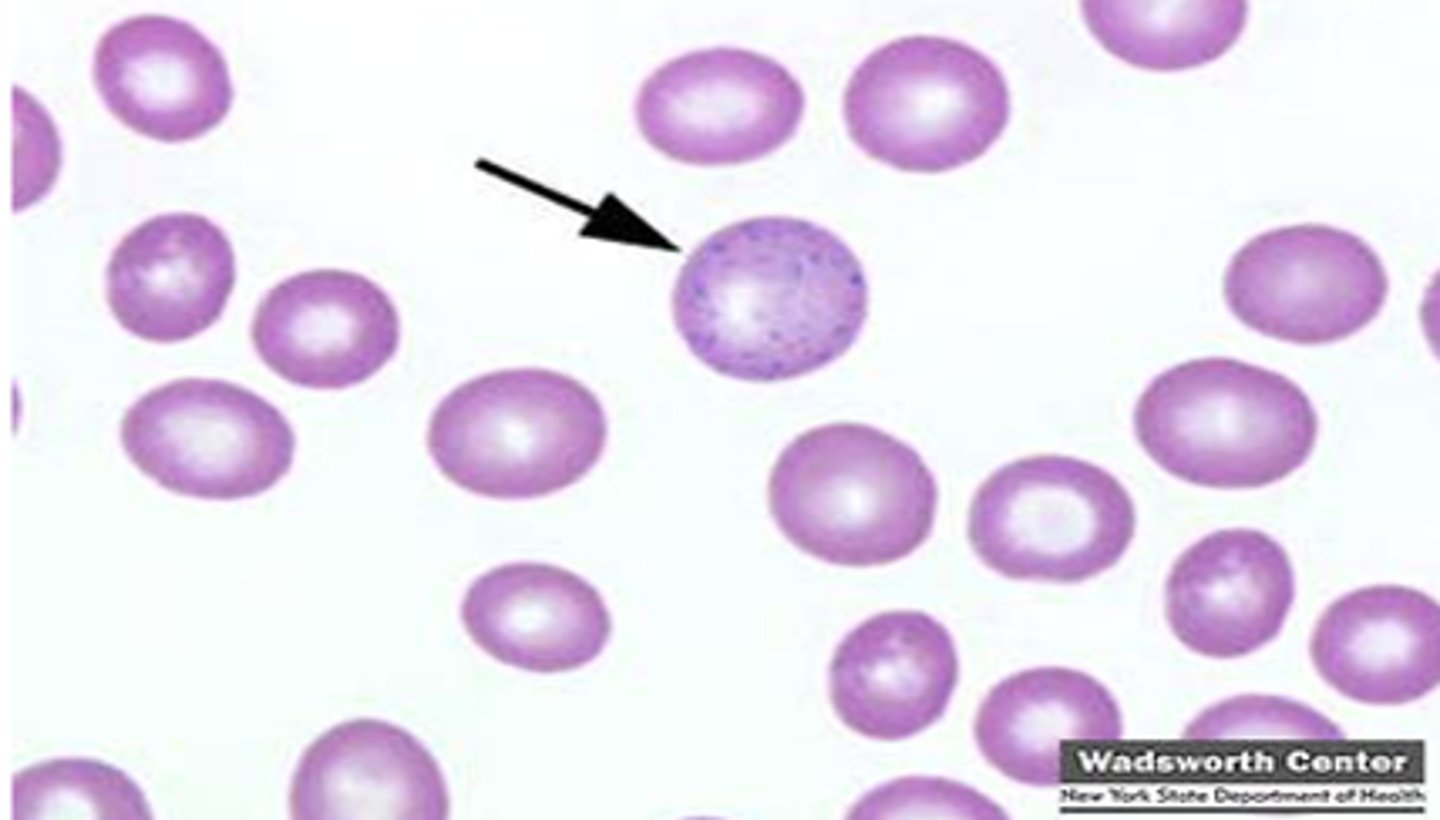
Basophilic stippling
What are -Small, dark blue, dot like structures scattered through cell?
- lead poisoning
- nutritional deficiencies
- myelofibrosis
When is Basophilic stippling seen?
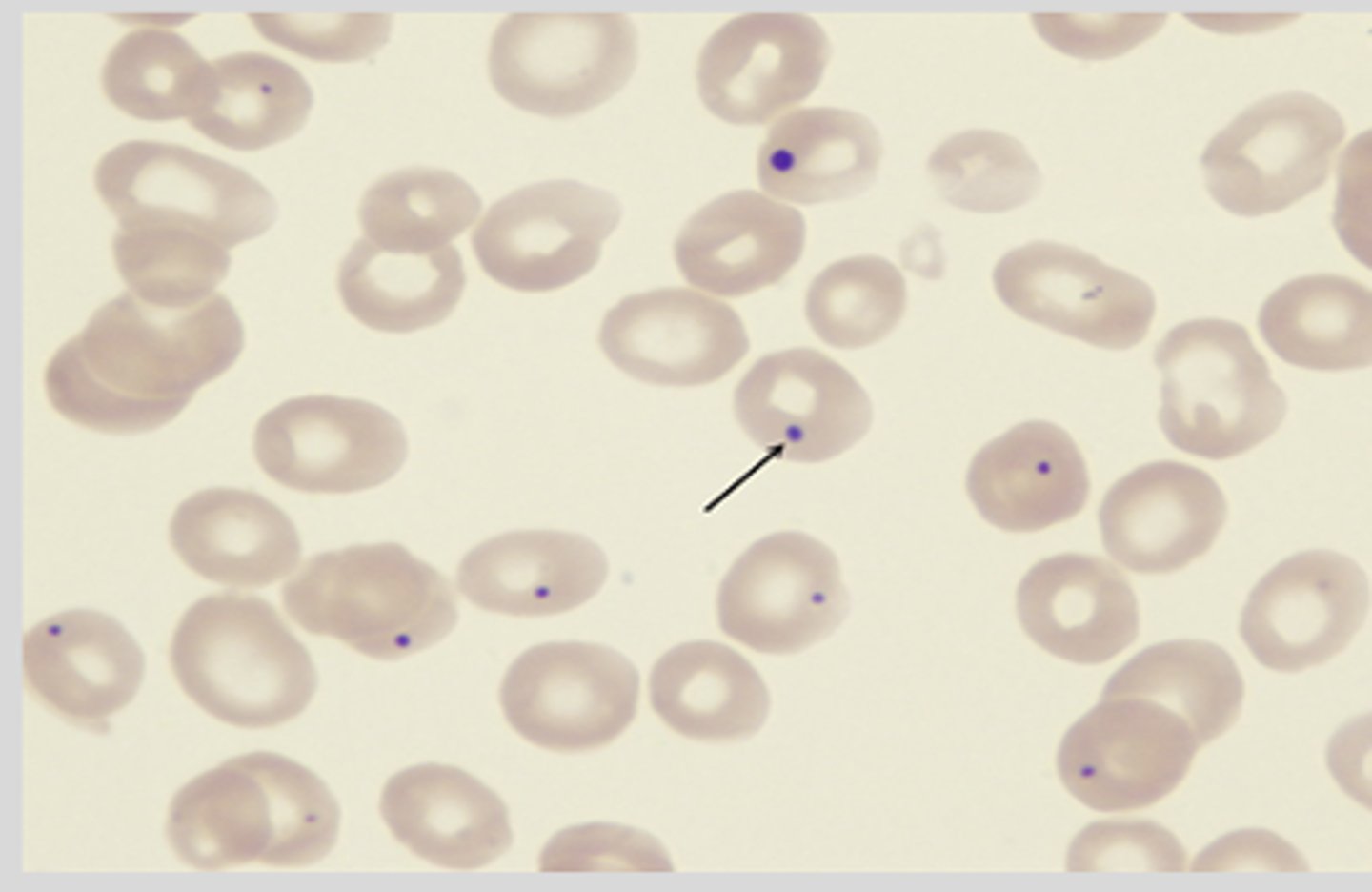
Howell-Jolly bodies
What are blue black inclusions, larger than basophilic stippling and usually one per RBC?
severe anemia, especially hemolytic anemia and after splenectomy
When are Howell-Jolly bodies seen?
Basophilic stippling
Howell-Jolly bodies
CBC + WBC
What is a CBC with differential?
granulocytes and agranulocytes
What are the two major types of leukocytes?
T-cells, B-cells, Natural Killer Cells
What are the lymphocytes?
lymphocyte
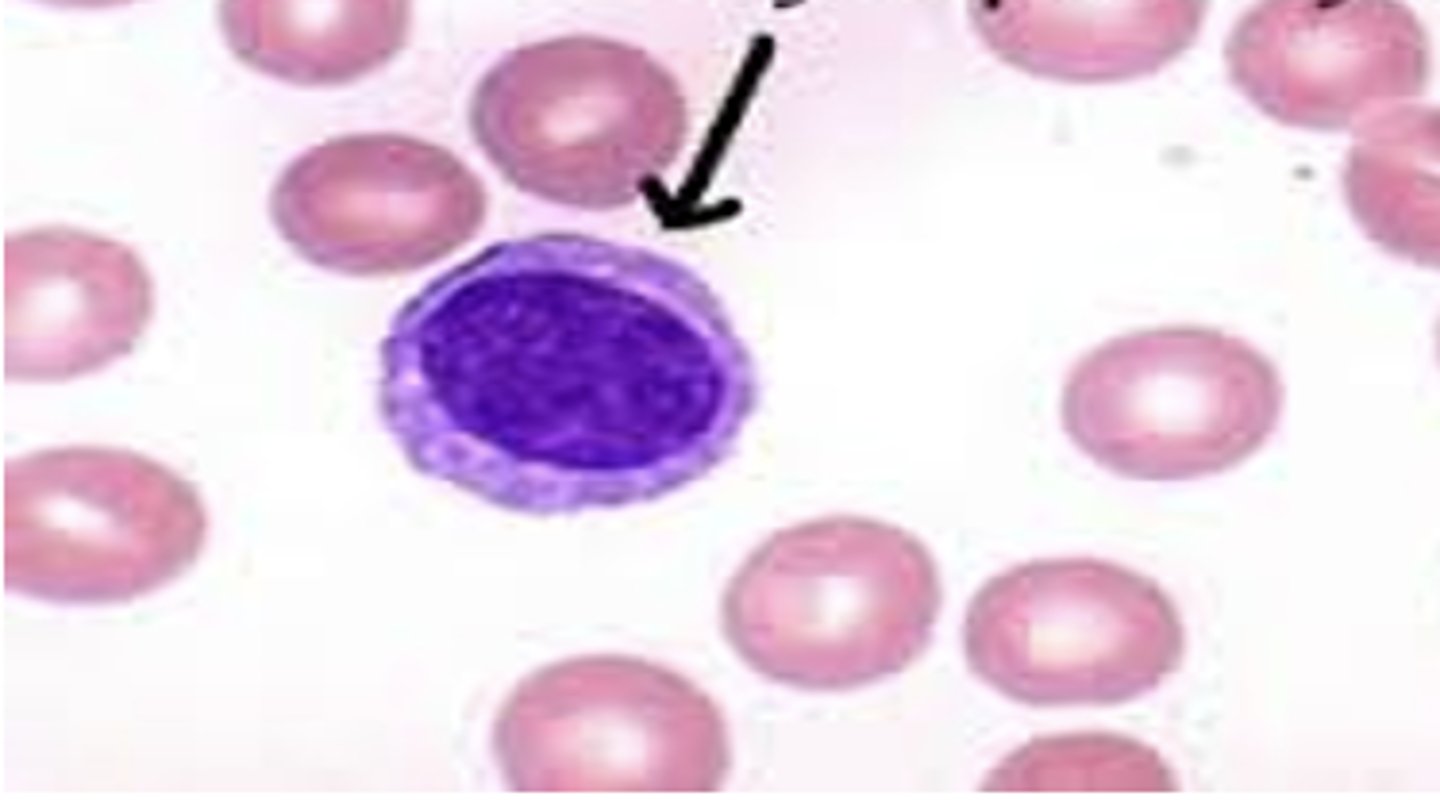
atypical lymphocyte
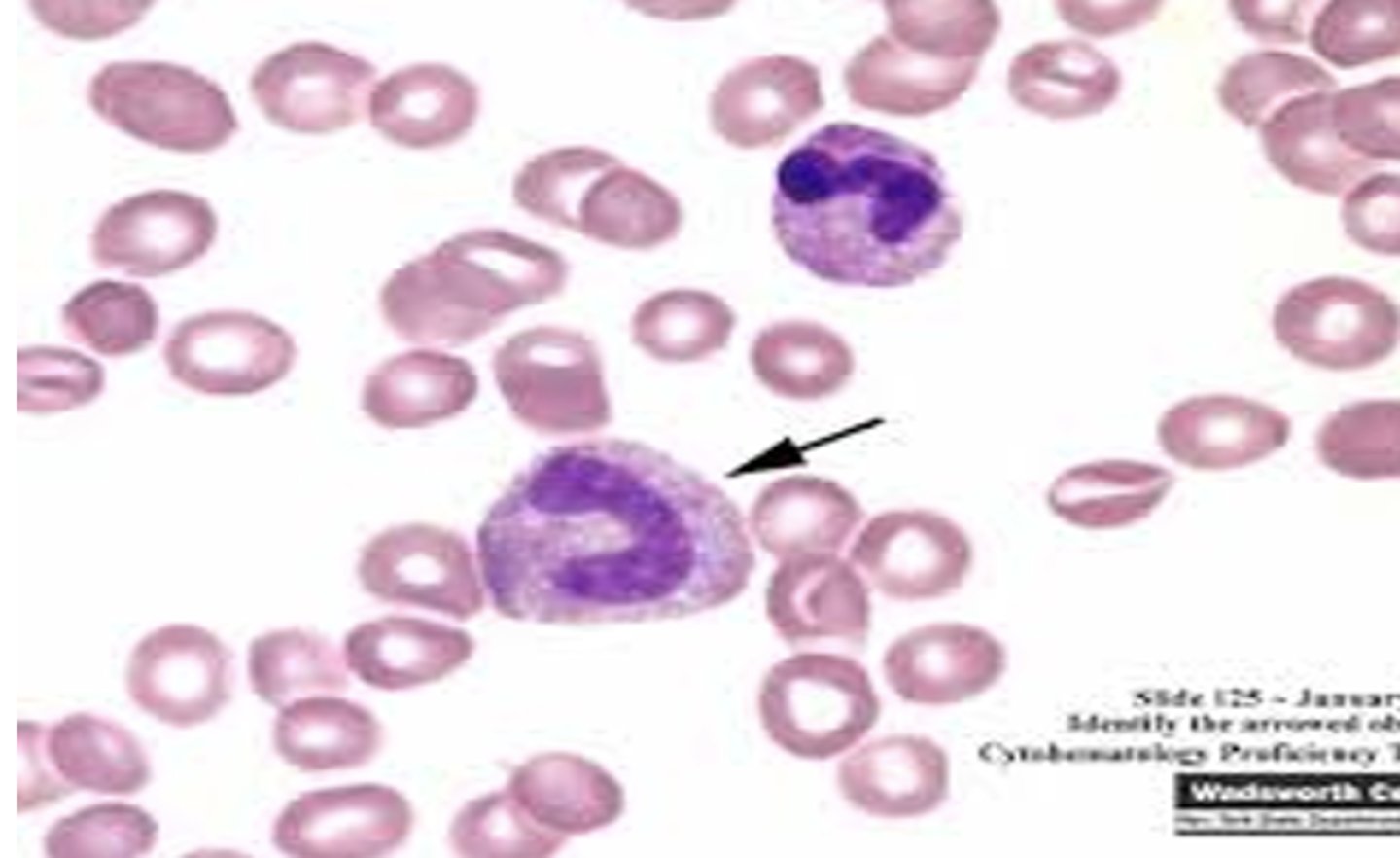
Normal Neutrophils (segmented)
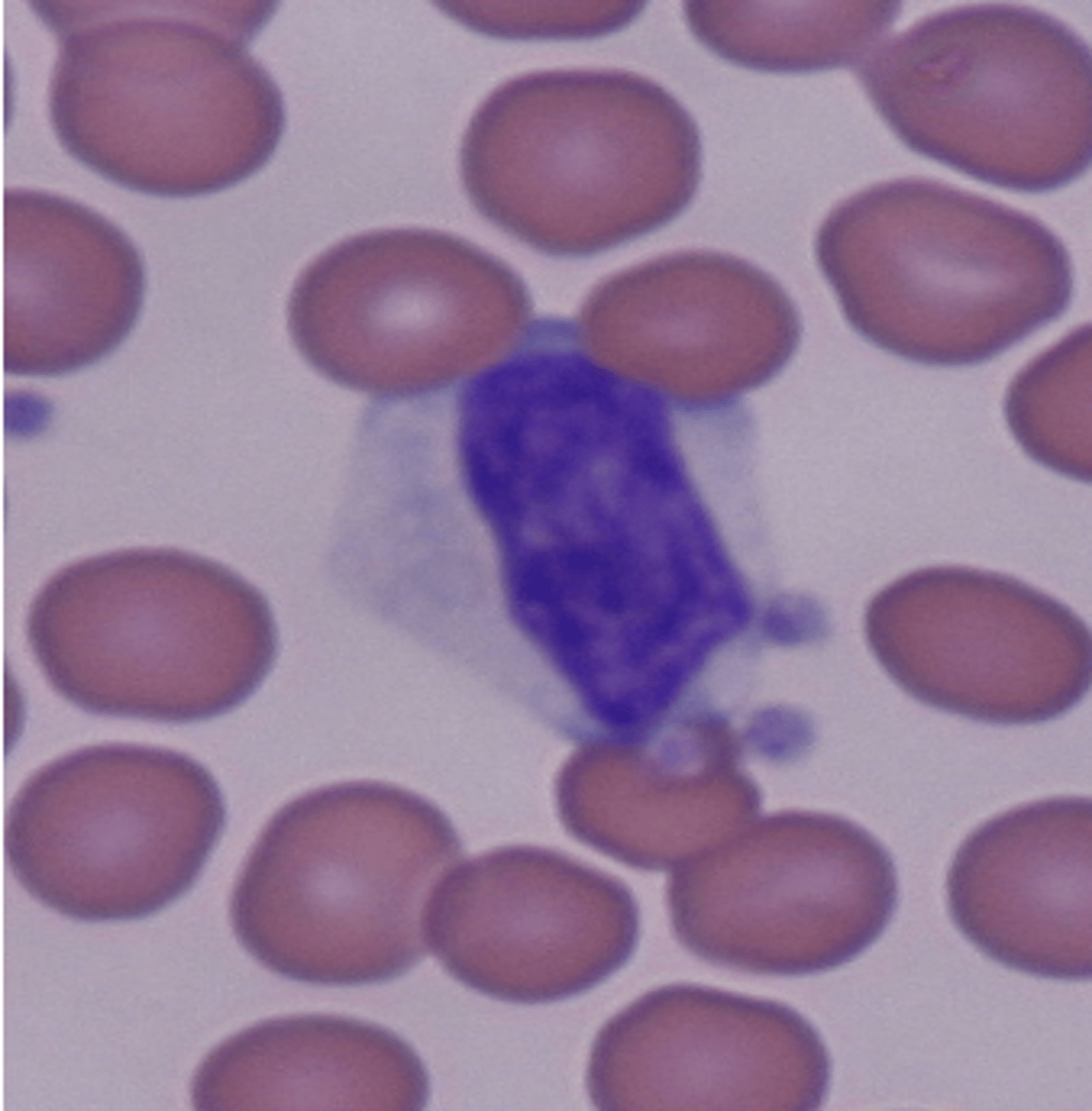
Band Neutrophils
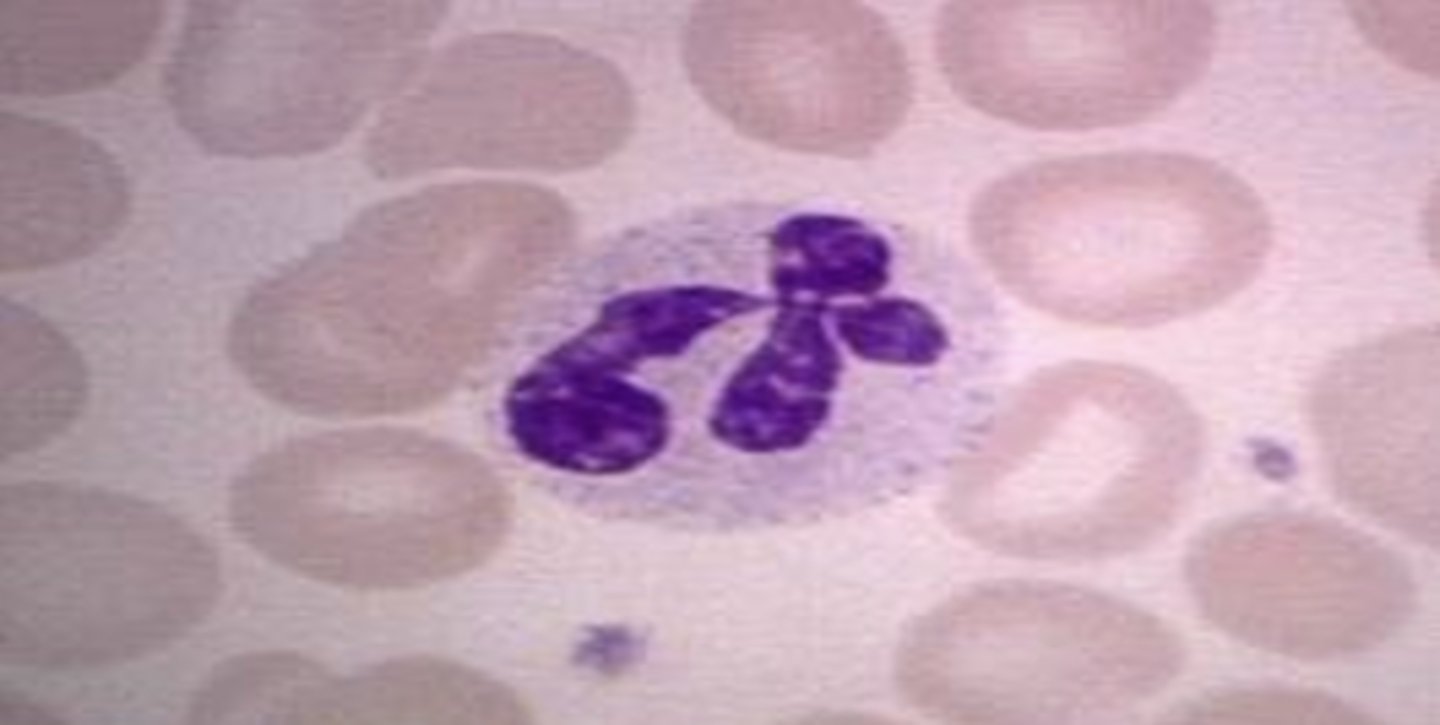
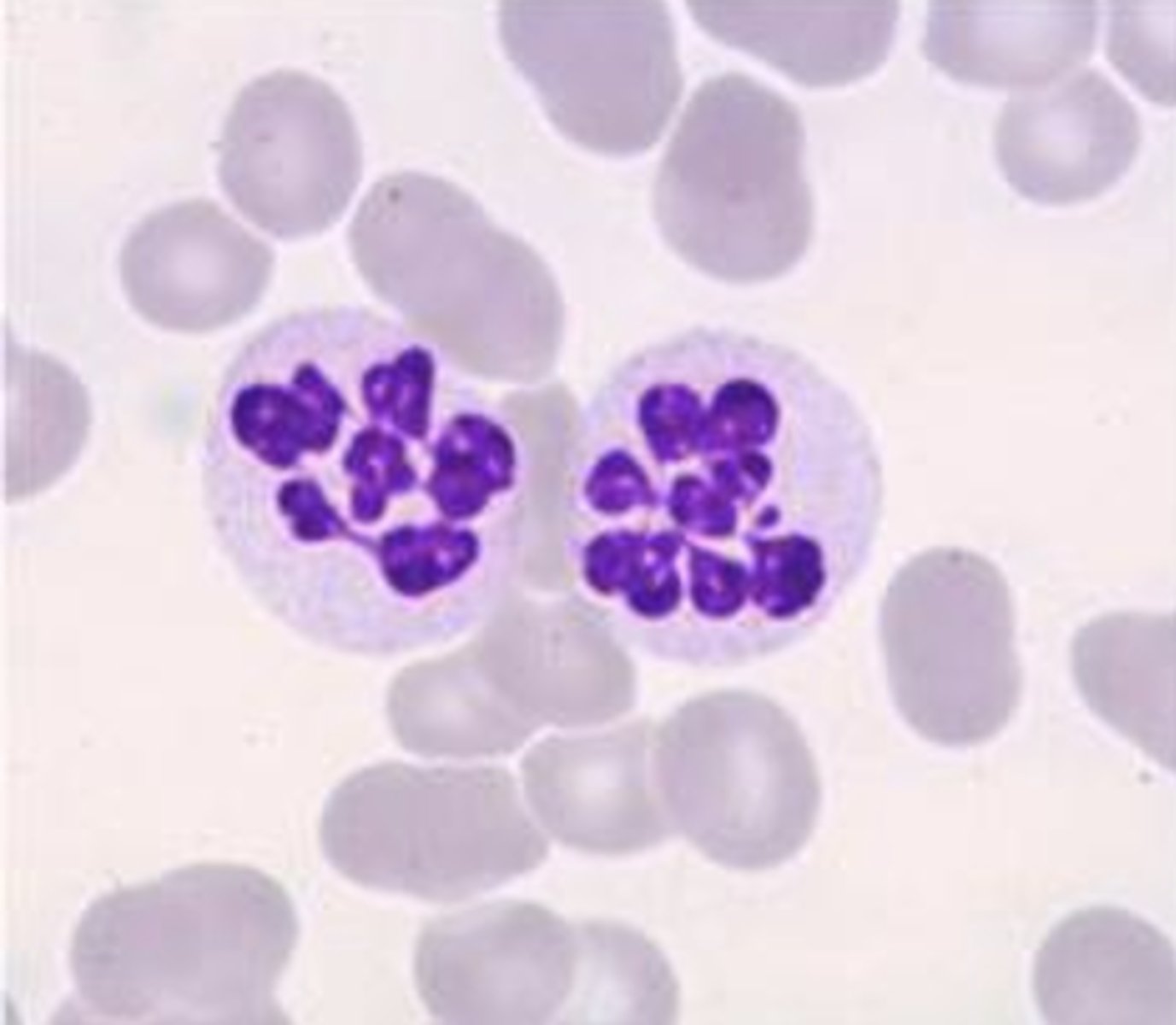
Hypersegmented Neutrophils
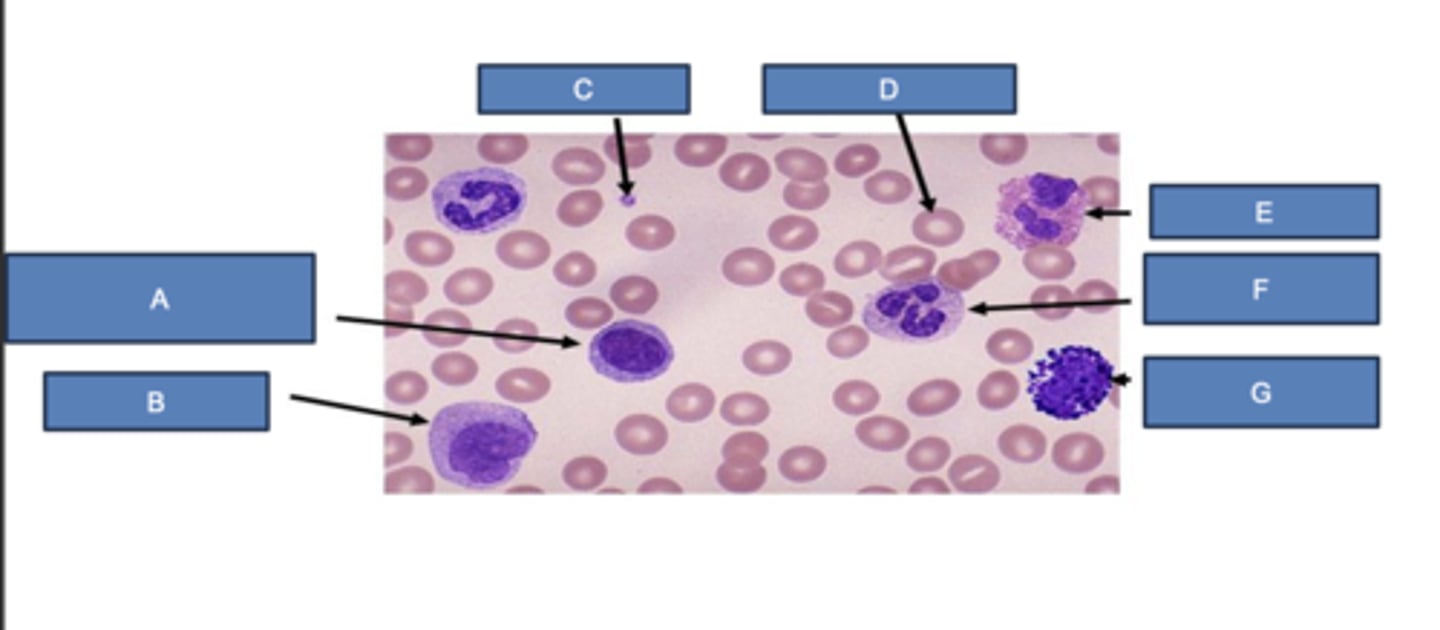
lymphocyte
What is A?
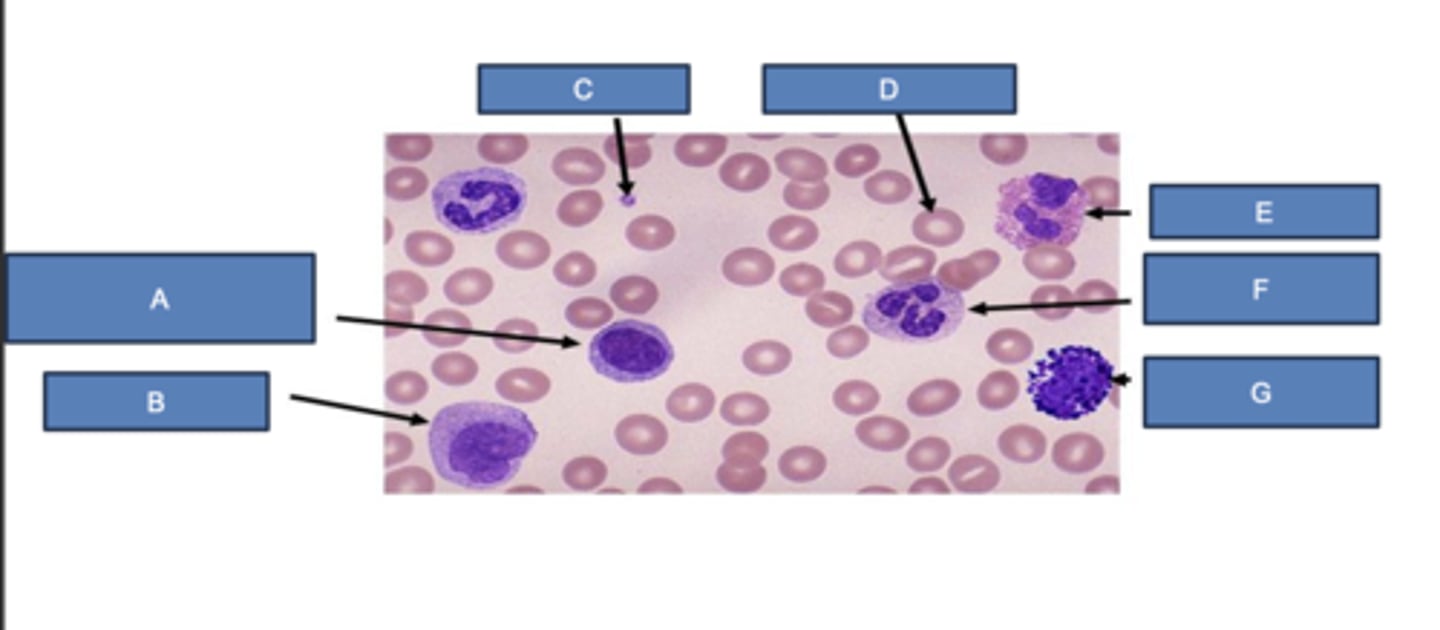
monocyte
What is B?
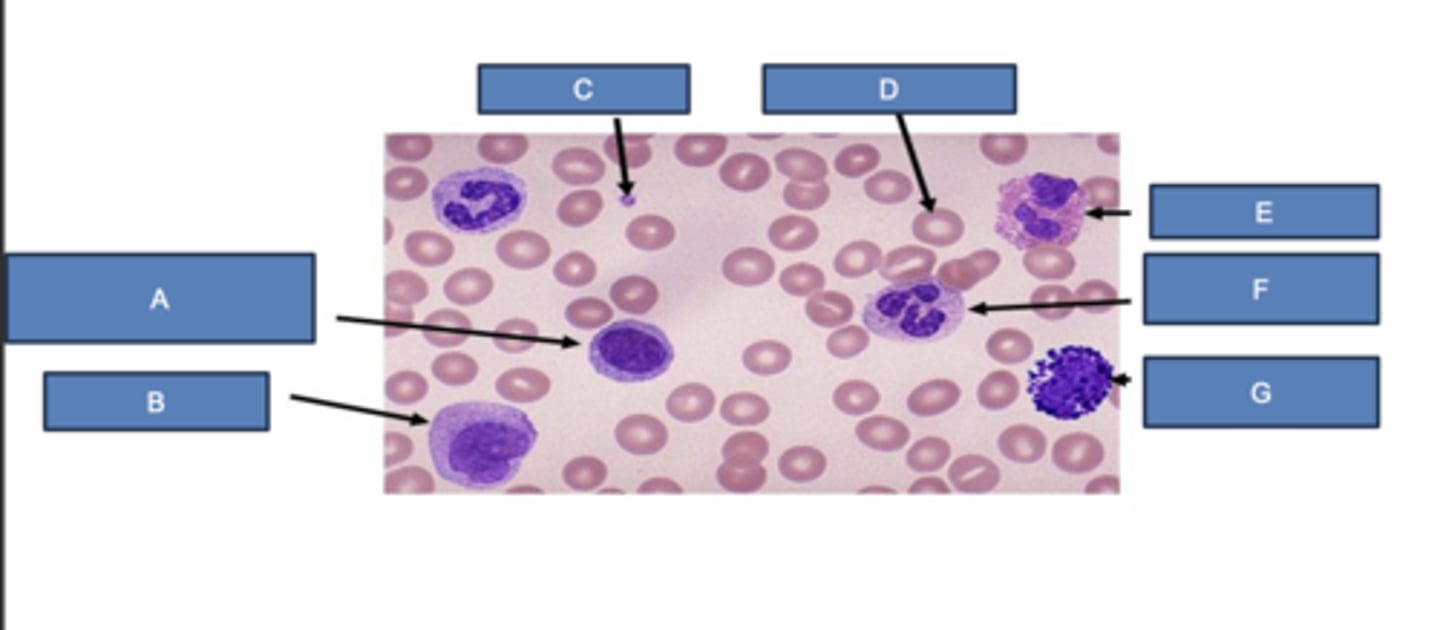
platelet
What is C?
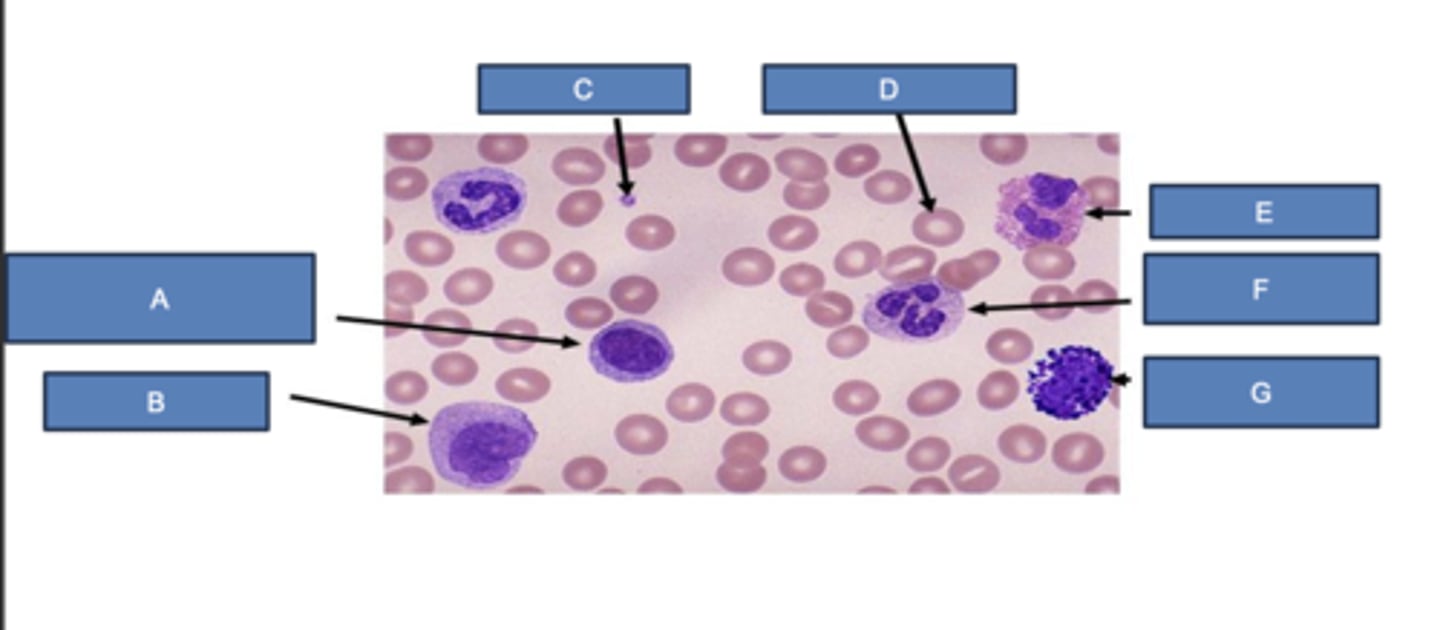
erythrocyte
What is D?
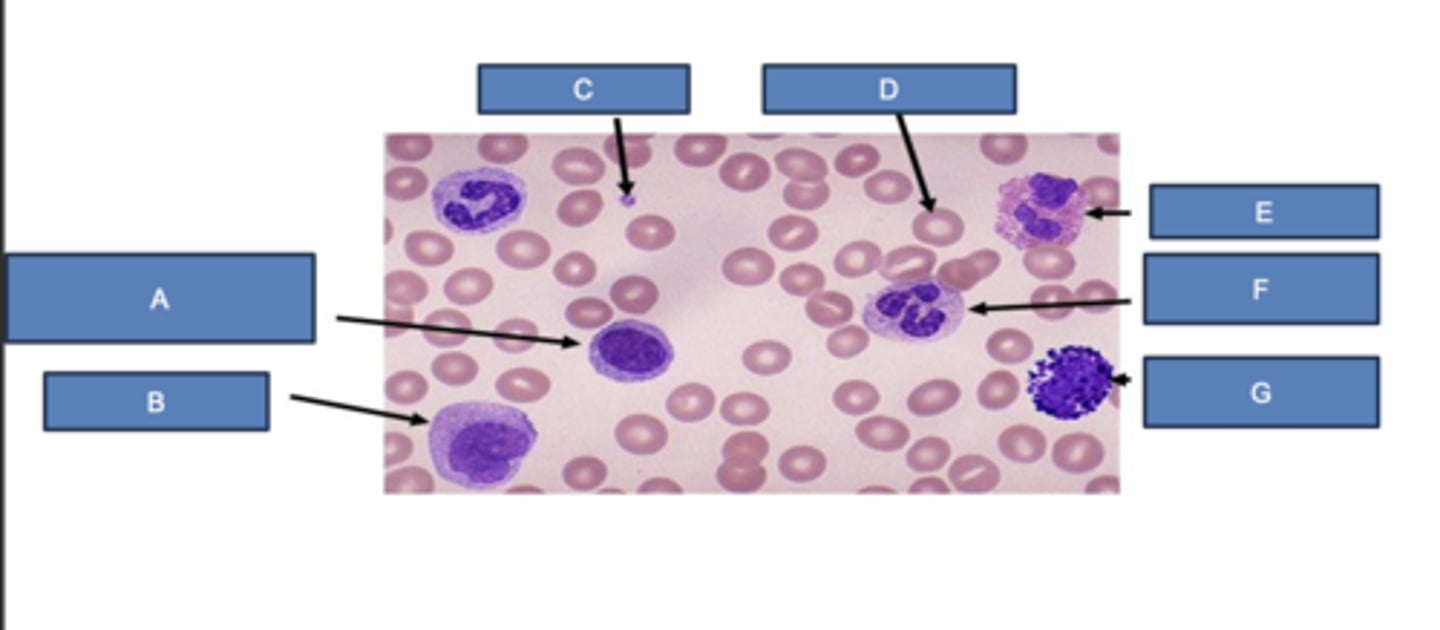
eosinophil
What is E?
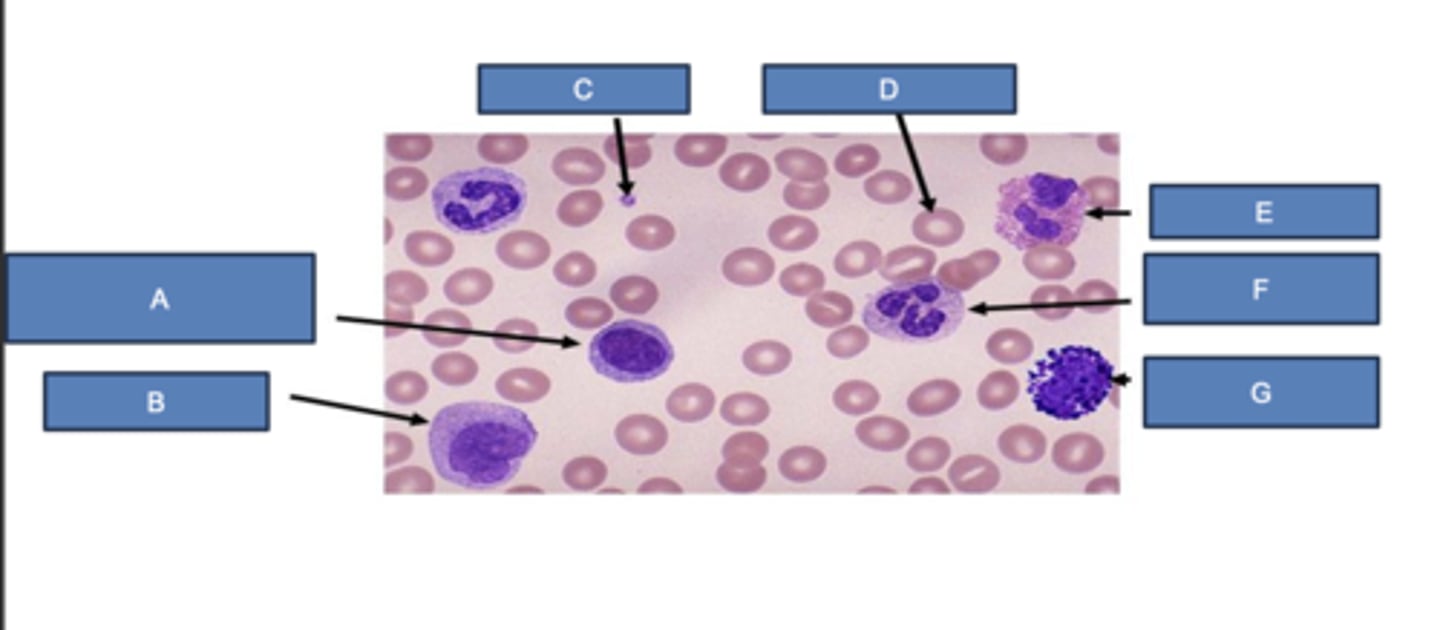
neutrophil
What is F?
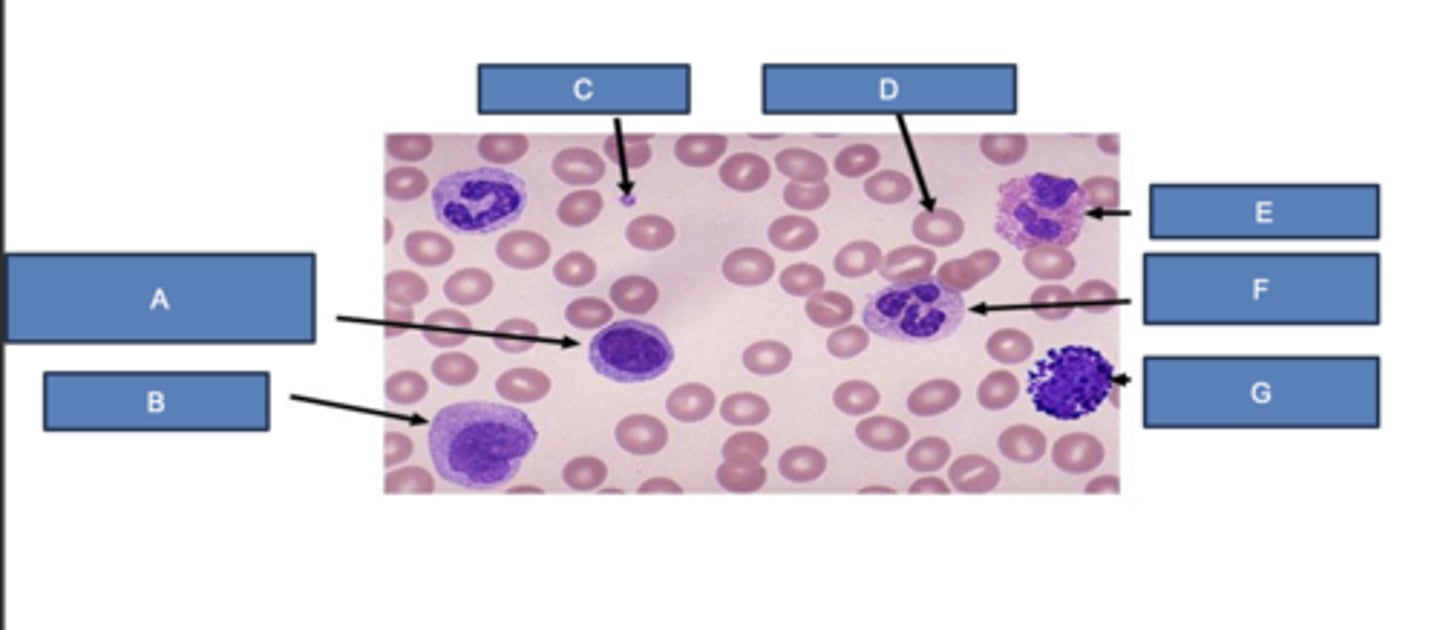
basophil
What is G?
- Disease in the bone marrow (e.g. leukemia)
- Infection
- Immune system disorder
- Reaction to a drug
What can cause leukocytosis?
- Severe infection that use up WBC faster than they are produced
- Drugs, such as antibiotics
- Autoimmune disease that destroy WBC
- Cancer
- Viral infections that disrupt work of the bone marrow
What can cause leukopenia
- increased proportions of younger neutrophils in the blood
- early or premature myeloid cells from the bone marrow
- indicates infection
What is a left shift on WBC?
Non-leukemic WBC count >50,000
What is Leukemoid Reaction?
infections (C. difficile, infectious mononucleosis, tuberculosis, pertussis); certain drugs; organ necrosis; asplenia
What causes Leukemoid Reaction?
(% neutrophils + % bands) x WBC
How is Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) calculated?
Neutropenia
ANC < 1000
Severe Neutropenia
ANC < 500
Profound Neutropenia
ANC < 100
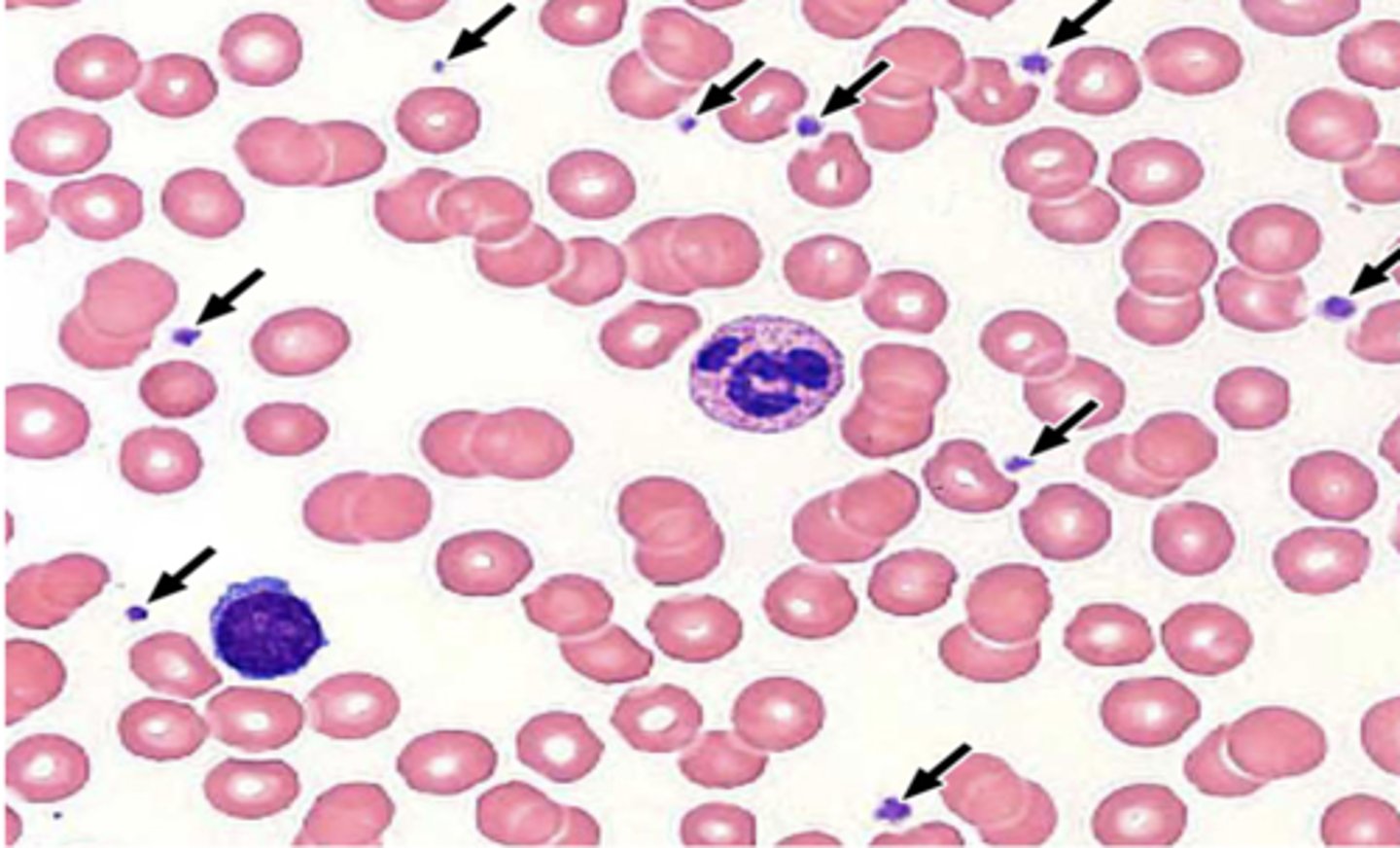
dark purple spots, about 20% the diameter of RBCs
How do platelets appear on smear?
platelets
average volume (size) of platelets
What is Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)?
measure and identify the different types of Hemoglobin
What is hemoglobin electrophoresis?
C, D, E, M, and S
What are abnormal Hgb?
An electrical current is passed through a blood sample and Hgb separates into different bands
How is hemoglobin electrophoresis done?
abnormal
Nucleated Red Blood Cells (NRBC) are __________ in adults
blood loss or RBC destruction (hemolytic anemia)
When is increased reticulocyte count seen?
Rate at which RBCs sediment in a period of one hour
What is Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)?
non-specific
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a ___________ measure of inflammation
temporal arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, lupus, IBD
What is Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) used in dx of?
C-Reactive Protein
What is Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) in conjunction with?
Protein synthesized in the liver found in blood plasma that rises in response to inflammation
What is C-Reactive Protein (CRP)?
non-specific
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) is a ________ measure of inflammation
cylindrical core sample that preserves the marrow's structure
What is collected in a bone marrow biopsy?
sample of the fluid that contains cells
What is collected in a bone marrow aspiration?
iliac crest
Where is Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration collected from?