Chapter 17: Projects
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Projects
Unique, one-time operations designed to accomplish a specific set of objectives in a limited time frame
Project Life Cycle
It’s the full journey of a project—from the idea stage all the way to the final result.
The 5 Phases of the Project Life Cycle
initiating
planning
executing
monitoring and controlling
close
1st Phase of Project Life Cycle
Initialing
2nd Phase of Project Life Cycle
Planning
3rd Phase of the Project Life Cycle
Executing
4th Phase of the Project Life Cycle
Monitoring and Controlling
5th Phase of the Project Life Cycle
Closing
Initiating Phase
outlines expected costs, benefits, and risks
goals
specifications
feasibility
tasks
responsibilities
Planning Phase
provides details on deliverables, the scope of project, the budget schedule and milestones, performance objectives, resources needed, and quality plan
schedules
budgets
resources
risks
staffing
Executing
the actual work of the project is carried out
status reports
changes
quality
manage
monitor and control
Monitoring and Controlling
Compares actual progress with planned and undertakes corrective actions if needed
status reports
changes
quality
manage
monitor and control
Execution and Monitoring and Controlling
What phases of the Project Life Cycle require the most level of effort?
train customer
transfer documents
release resources
reassign staff
lessons learned
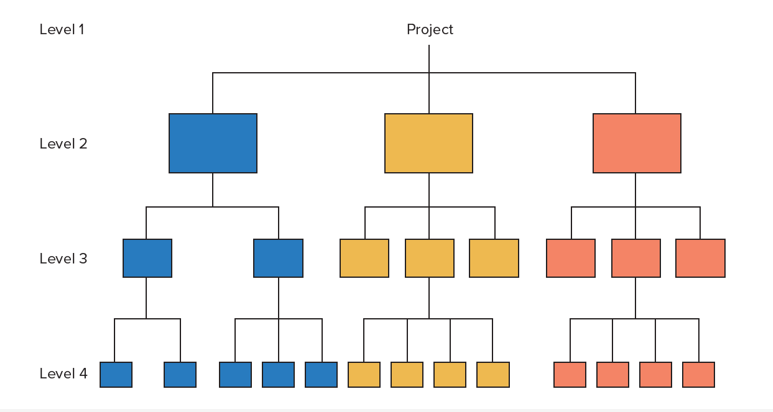
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A hierarchical listing of what must be done during the project that establishes a logical framework for identifying the required activities for the project
1.Identify the major elements of the project.
2.Identify the major supporting activities for each of the major elements.
3.Break down each major supporting activity into a list of the activities that will be needed to accomplish it.
Work Breakdown Structure Diagram
Critical Path
is the longest path through the network and is the shortest time in which the project can be completed. Any delay delays the whole project
Crashing
means speeding up a project by making some tasks go faster. This usually means spending more money—like hiring extra people, using faster equipment, or making the work easier.
critical path
You only crash tasks that are on the ———— because speeding up tasks not on the critical path won’t shorten the total project time.
Crashing Example
You’re building a deck and it will take 10 days. The most important task (on the critical path) is laying the boards, which takes 4 days. If you need the project done faster, you hire more workers to finish that part in 2 days instead.
Good risk management
•Identifying as many potential risks as possible.
•Analyzing and assessing those risks.
•Working to minimize the probability of their occurrence.
•Establishing contingency plans (and funds) for dealing with any that do occur.