AHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
The Dorsal horns are interneurons that receive somatic and receive what type of visceral input:
Sensory neurons
Destruction of ventral horn motor neurons and fibers of pyramidal tract. Symptoms include loss of ability to speak, swallow, and breathe:
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Somatosensory signals travel along three main pathways on each side of spinal cord, and two pathways transmit somatosensory information to sensory cortex via One Conveys sensation of fine touch, vibration, pressure, two-point discrimination and proprioception from the skin and joints. Which of the following is this describing:
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathways
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there:
31
The spinal cord terminates at a structure called:
conus medullaris
Regarding the spinal nerve divisions, the dorsal ramus is responsible for the following:
Innervates muscles, joints, and skin of the back
The spinal cord ends at what level:
L1-L2
The following is caused by damage to dorsal roots or sensory tracts and leads to sensory function loss:
Paresthesias
This pathway originate from superior colliculi and mediate head movements in response to visual stimuli
Tectospinal tracts
Gray matter divided into four groups based on of somatic or visceral innervation. The following is not one of that is part of the group:
Interneurons receiving input from proprioceptors and baroreceptors
The following is not a nerve that divides off of the brachial plexus:
Thoracic
The cervical dermatomes are divided into what numbers
C1-C8
The myotome C6 and C7 allow for what action:
Elbow flexion
The brachial plexus are divided into 5 groups, the following is not one of them:
Peripheral nerves
What is the largest nerve of the human body:
Sciatic
Reflexes that control or adjust activities of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, and adipose tissue.
Visceral
The following is not a nerve plexus:
Thoracic
Result from connections formed during development. Genetically or developmentally programmed. Some are simple (withdrawal from pain) to more complex (chewing, tracking objects with the eyes).
Innate
A long branch of what plexus innervates muscles of the diaphragm
Cervical
The origins of the lumbar plexus lie within what muscle:
Psoas major
The following is an example of a special sense receptor?
taste
One way to assist in the diagnosis of compartment syndrome is to conduct a two-point discrimination test.
True
translation of stimulus into an action potential (nerve impulse) is known as:
Transduction
Which of the following is true when comparing types of pain sensations?
C fibers, unmyelinated, chronic pain
These receptors are always active produce constant rate of firing long as stimulus is applied (pain):
tonic receptors
Which of the following would not be considered to be a sensory modality?
Thought
The awareness of differences in the external or internal environment is defined as:
sensation
The Sensory unit is a multi-sensory axon and all its peripheral branches.?
False
Which somatic sensory receptor is rapidly adapting and responsible for fine touch?
corpuscle of touch
The anatomical structure responsible for monitoring the change in length of a muscle is called:
muscle spindle
Gustation uses what type of receptors to perceive taste:
Chemoreceptors
What allows us to determine appreciation of taste
hypothalamus
What two ions are involved in the physiology of smell:
Sodium, calcium
In detection of smell, odorants themselves:
bind to receptors and stimulate opening of ion channels.
The receptive structures for smell are the:
olfactory receptor cells and cilia
On what lobe is the gustatory cortex located on:
insula
What receptors for taste ate the most sensitive:
Bitter
What type of receptor allows to taste alkaloids such as quinine and nicotine, caffeine, and nonalkaloids such as aspirin
Bitter
what two cranial nerves relay taste sensory information to the brain
facial, glossopharyngeal
Taste is 80% smell. The relationship between smell and taste is evidenced by the fact that both sensations are a type of __________.
chemoreception
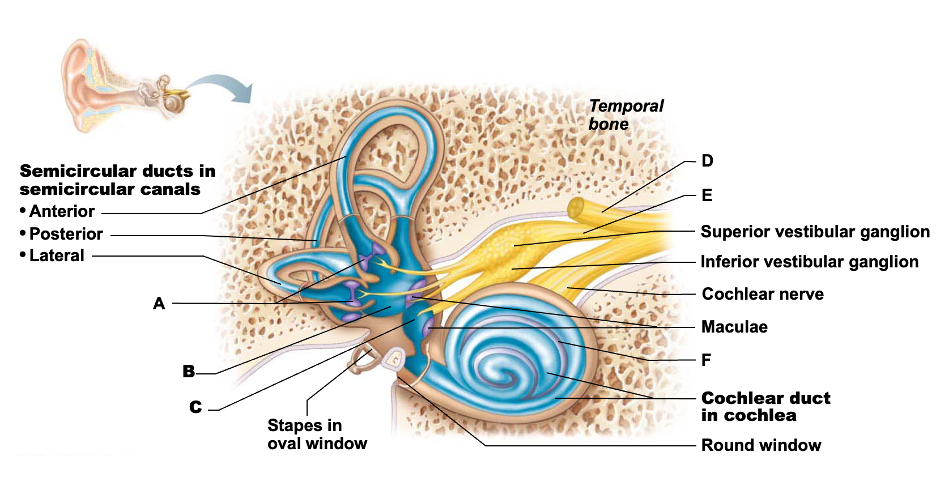
Identify letter "B"
Utricle in vestibule
The pharyngotympanic tube connects the throat with which part of the ear?
middle ear
The hearing receptors are located in the __________.
internal ear
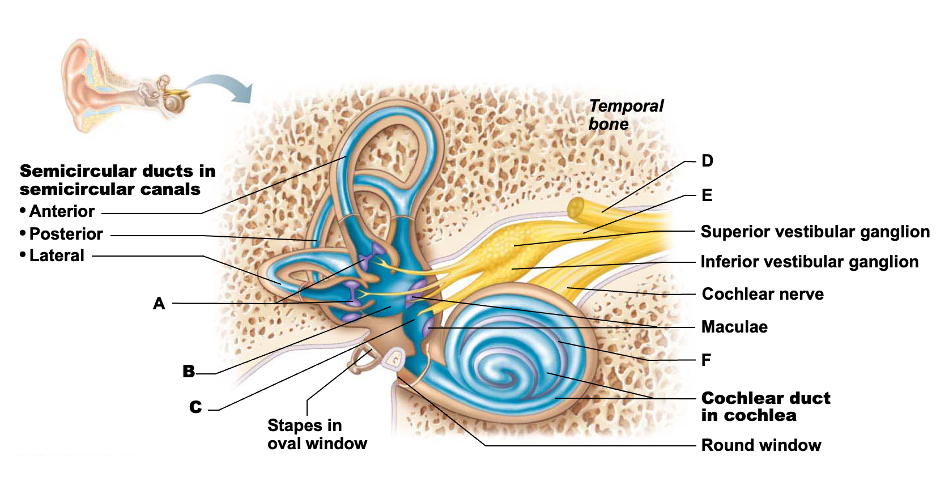
What structure represents the spiral organ
F
The scala tympani extends from the apex of the cochlea to the _______.
round window
The bony labyrinth forms the boundary wall for _______.
endolymph
The stapes connects with the internal ear via the _______
oval window
Otitis media is an infection of what compartment:
middle ear
The spiral organ is found in the _______.
cochlea
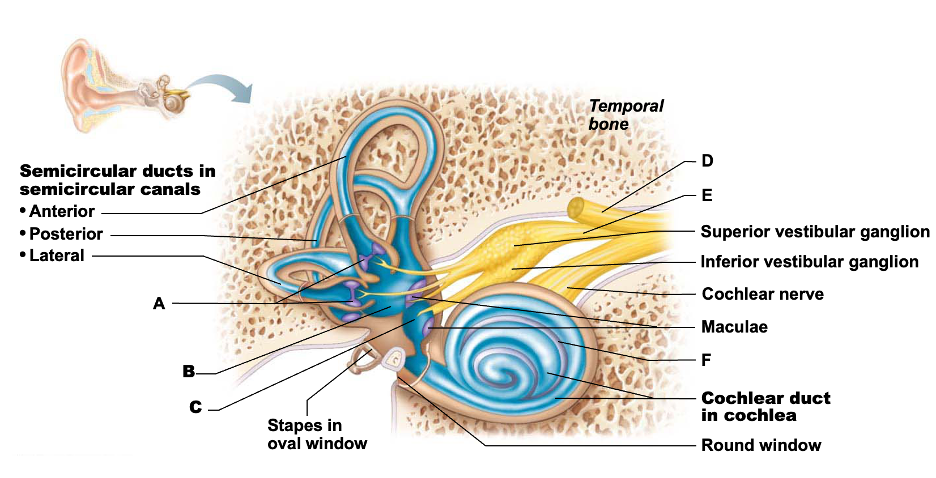
Sacs house equilibrium receptor regions (maculae) that respond to gravity and changes in position of head.
B,C
The cornea is actually part of the __________ layer of the eye.
fibrous
Glaucoma is a disorder in which:
all of the above occur
Of the following senses, which accounts for the majority of sensory receptors in the body? Of the following senses, which accounts for the majority of sensory receptors in the body?
Vision
Sympathetic fibers innervating the iris of the eye cause which response?
Dialation
Which of the following terms is a synonym for eyelids?
Palpebrae
Focusing an object on the __________ provides the highest visual acuity.
fovea centralis
In order to turn the eye to move in different directions, the actions of the following cranial nerves are needed:
III,IV,VI
Sympathetic innervation is more predominant during __________.
distant vision
Pinkeye is an infection of the __________ of the eye.
conjunctiva
The formation of rainbows reflects the fact that:
visible light consists of multiple wavelengths of light