Immunology exam 3 helminths
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
done slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
reasons for decline in infectious diseases in HICs 1950s-2000 (3)
hygine practices, sanitation, health (vaccine and antibiotics)
what was found to be correlations potentially explaining why inflammatory diseases have been on the rise in HICs?
the higher number of children in a household at age 11 → the lower hay fever incidence at 11 and 23, also lower eczema in the first year of life
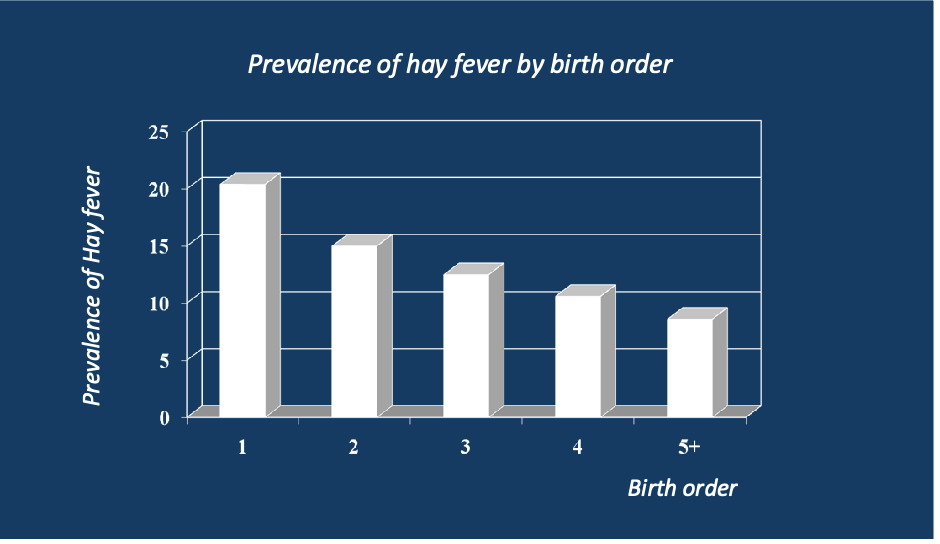
explain
the prevalence of hay fever goes down with birth order- could be because exposed to more germs early on
hygine hypothesis principles
early childhood exposure to microorganisms may protect against allergic diseases by contributing to the development of the immune system, observed rise in inflammatory diseases may be attributed to: improved living standards, increased wealth, reduced exposure to infections
Old friends hypothesis +egs
microorganisms that were once abundant trained our immune system- were tolerated at expense of excessive tissue damage to eliminate them, eg parasitic worms
what microorganisms that we were exposed to during human evolution have been lost in modern urban centers? (5)
lost: helminths (gut & non gut)
mostly lost: ectoparasites (fleas, lice, mites, ticks), carrier states (salmonella, hep A, TB)
diminished diversity: microbiota of other humans
variable loss: microbiota of natural environment
changes in lifestyle rural to urban (3)
outdoor → indoor
physical labor → sitting professions
high fiber food → fast food
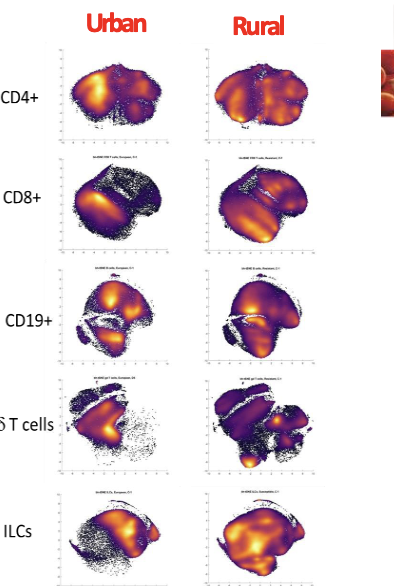
Explain
Vaccines and drugs can act differently, depending on if urban or rural environment, even with the same genetic background!
PARSIFAL study conclusions
Microbial exposure → inversely associated with risk of asthma (38% reduction in risk)
GABRIELA Study conclusions
Microbial exposure → inversely associated with the risk of asthma (14% decrease)
conclusions of the European farming studies
Children growing up and microbial, traditional farming environments → less likely to suffer from asthma and allergies compared to urban counterparts

Explain
No exposure to the farms stables and milk leads increased prevalence of asthma and hayfever
comparing Amish and hutterites
very genetically similar BUT hutterites have much higher asthma- bc Amish have more traditional farming practices with small single family farms and animal barns close to homes
diversity of microbial exposure and risk of asthma
They are inversely associated
How early do microorganism start protecting against diseases?
In utero (0-5yrs most important): maternal farm exposures during pregnancy led to increases in cord blood regulatory T cells that protect against allergies, farm milk exposure associated with a regulatory immune phenotype early in life (protection against allergies)
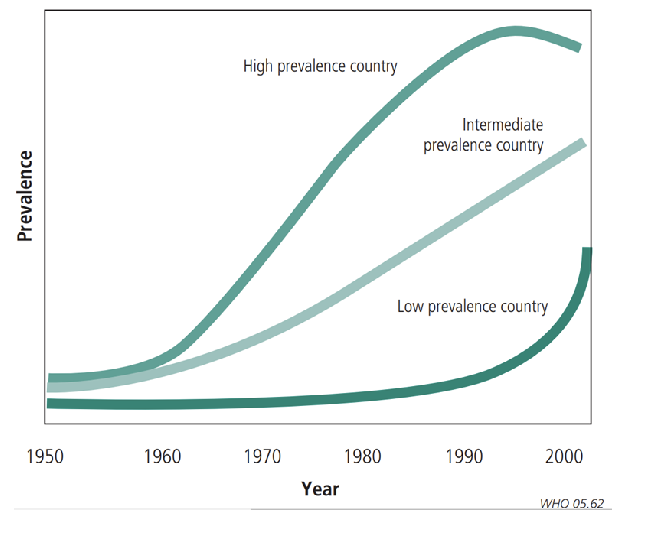
What does a graph show?
Asthma prevalence in various countries over time
urban rural differences with allergy
noticibly different, within-urban differences based on socioeconomic status
2 types of helminths
gut-intestinal, blood-dwelling
what is an endotoxin
Marker of bacteria
helminths (5 points)
Parasitic worms, live in a host organism and need it to survive, 3 billion people have chronic helminth infections, do not kill but infect up to 100% of children in some rural areas, often non-inflammatory infection but can cause immuno pathological reactions
Two types of helminths
Flatworms and roundworms (nematoda)
life cycle of nematoda- hookworm (4)
eggs in feces, larva hatches, development to other larva in environment, it penetrates skin- they exit circulation in the lungs- the coughed up and swallowed, then settle in small intestine before cycle again
nematoda- hookworm basic info
0.8-1.5cm, between 9k &30k eggs a day, eliminated after 1-2 yrs
ascaris lumbricoides life cycle (7)
adults in small intestine, fertilized egg (in feces in soil), embryonated egg with larva, ingestion of embryonated eggs, hatched larva enter circulation and migrate to lungs, larva coughed up and swallowed reentering GI tract- maturation proceeds in smll intestine
ascaris lumbricoides size
up to 35cm
Schistosoma basic info
water based, life span up to 40 yrs
effects of helminths on the immune system
induction of Tregs, Bregs; Th2 activation which leads to mucus production, eosinophilia, bronchochonstriction, etc → airway hyperactivity and inflammation
what did chronic schistosomiasis infection in mice supress?
lung eosinophilia, airway hyperresponsiveness
what did helminth infections do in human studies?
sometimes reduced risk, sometimes non association, sometimes increased risk- inconsistencies
why were there wide variations in observations of human studies w/ helminths (6)
different helminths have different effects (Systemic vs local), mild vs chronic infections, diff populations in diff geographical locations, varying age groups (children vs adults), often cross-sectional studies, varying outcomes and exposure measures (even variations in helminth detection methods)
basic design of anthelminthic treatment trials
intervention group → anthelmic treatment → followup
control group → placebo → followup
outcomes: allergic sensitization, eczema, asthma/wheeze, etc)
helminths and T2D
helminths thought to induce anti-inflammatory immune enviroment which is associated with insulin sensitivity
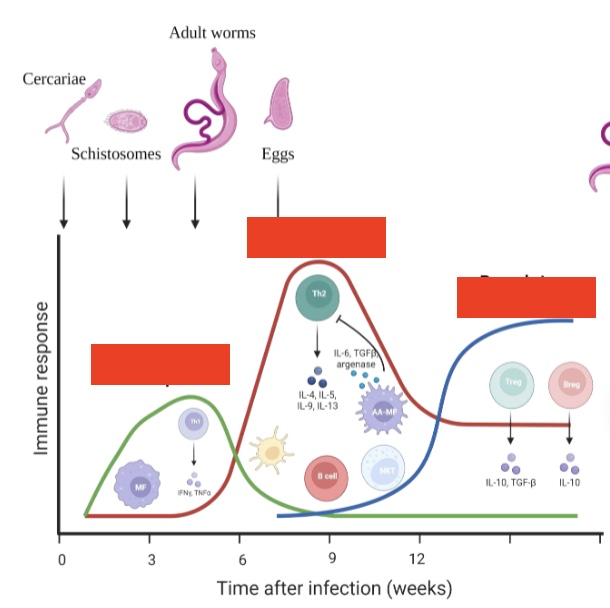
label left to right
Th1 response, Th2 response, regulatory response

what happens after this graph
survival or spill over tolerance (better deal with IBD, T2D, asthma etc)
effects of Treg (5)
inhibition of antigen presentation, B cell modulation, tissue remodeling, inhibition of cells from innate immunity, downregulation of T effector cells (Th1, Th2, Tc)
human worm therapy
trial to treat IBD with nematode- significant improvement by week 6, some other successes but overall mixed results
inconsistency in human studies (6)
clinical outcome/severity, age of infected population, first infectious vs endemic population, type of helminth/intensity, pathology due to worm infection, lack of standardized cultures
dual activity of helminth infection in humans
acute: usually pro-inflammatory, pro-allergenic, Th2 polyclonal IgE induction, IgE potentiation/cross-reactivity
chronic: regulation, anti-allergenic, induction of IL-10, increased Tregs/Bregs, cross-reactive/blocking IgG
acut vs chronic helminth what to do
acute- anthelmintic therapy?
chronic- infection in infancy?
side effects of helminths (6)
+ve: reduced incidence, increased atopy on drug care of allergy/asthma; reduced incidence, suppression of pathology with autoimmunity; reduced incidence, suppression of pathology with IBD
-ve: reduced immune response to pathogens, reduced anti-tumor immunity, reduced immune responses/reduced efficacy to vaccines
immunological equilibrium
healthy microbiota contains a balanced composition of multiple classes of bacteria
symbionts def
organisms with health-promoting functions
pathobionts function
microbiota with potential to induce pathology and inflammation
immunological disequilibrium
dysbiosis: unnatural shift in composition of the microbiota where numbers of symbionts are reduced/pathobionts are increased
what happens with antibiotics
change in microbiota → increases susceptibility to inflammatory disease
SCFA description
produced by the gut microbiota from fermentation of dietary fibers, most common: acetate, butyrate, pro[inate
functions of SCFA
important in immune regulation! Increased immunity, tolerogenic factors, fortified barrier function