Rates of Reaction & Equillibrium
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
reversible vs irreversible reactions
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the products can be converted back to the reactants.
An irreversible reaction is a reaction in which the products cannot be converted back to the reactants.
Reversible reactions can reach a point where the rate of the forward reaction and the rate of the reverse reaction are equal. At this point, a dynamic equilibrium has been achieved.
Rate of reaction
change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time
yield (aka extent of reaction)
AMOUNT of products produced → meaning the MOLES (n), not concentration
go by the DIRECTION BEING FAVOURED, not the actual conc.
For a reaction to occur…
collision must occur so existing bonds within reactants are broken
successful collisions require energy >= activation energy
+ correct orientation
Why is xL of H2 produced?

How can volume of CO2 produced change when mass/volume/conc of a reactant increased?
MUST SAY “IF “X REACTANT” IS LR THEN, “
OR “IF “X REACTANT” IS NOT LR THEN,”

When volume of solution changes in rates reaction but conc doesn’t - effect on ROR?
NONE - bc conc. remains constant even though more particles bc in greater space/vol

How to prove that a temp change is what’s happening
Calculate Kc at equilibrium 1 (before change) and then after change using concs. from graph

When it asks for consequences of increasing temp of equilibrium solution
Describe the changes in conc.
What catalyst being added on equilibrium graph looks like
reaches equilibrium faster - NOTE: wasn’t at equilibrium initially
Transition State
occurs at the maximum potential energy stage (EA)
activation energy
minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to take place
Increasing ROR
increase frequency of successful collisions
increase proportion of particles with energy higher than EA
Increasing ROR Methods
increasing surface area of solid
increasing reactant conc. or pressure
increasing surface area of solid
only surface particles participate in the reaction
the more exposed solid reactant particles there are, the more particles available to react
freq. of collisions increases
freq. of successful collisions increases
increasing reactant conc. or pressure
conc = no of particles in given volume
when sol conc. increases, more reactant particles moving in a given v(solution).
freq. of collisions increases
freq. successful collisions also increases.
ROR increases
MUST SAY: PROPORTION OF REACTANTS WITH ENERGY > EA DOES NOT CHANGE
Increase proportion of particles with energy higher than EA methods
increasing temp (Kinetic E)
catalyst (lowers EA)
increasing temp (Kinetic E)
as temp increases, average kinetic energy of particles increases.
Greater proportion of particles have E >= EA, proportion of successful collisions increases.
Therefore, ROR increases
The increase in kinetic energy also leads to frequency of collisions increasing so freq. of successful collisions also increases
Therefore, ROR increases
catalyst (lowers EA)
lowers the activation energy by providing an alternate pathway with lower energy
because EA is lowered, the proportion of particles with energy >= EA increases
so proportion of successful collisions increases
ROR increases
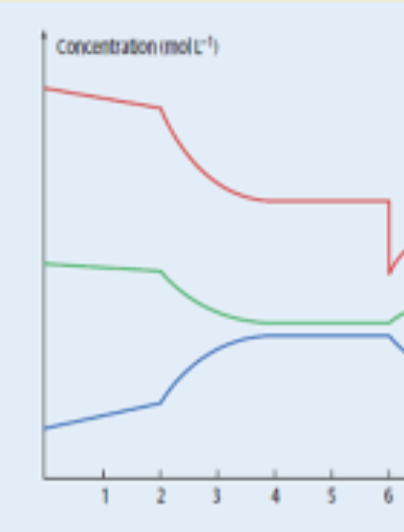
Explaining parts of increase conc. graph
At start, many reactant particles so the frequency of collisions increases, the number of successful collisions increases so the rate of reaction increases
The rate of reaction slows because as the reaction proceeds, the number of reactant particles decreases. The frequency of collisions decreases and the number of successful collisions decreases
The reaction stops because the limiting reactant/ reagent has been used up
When asked to calculate volume of gas
Find moles of reactants
Find limiting reactant (by dividing moles by coeff)
Then solve using pv = rnt or n = v/vm
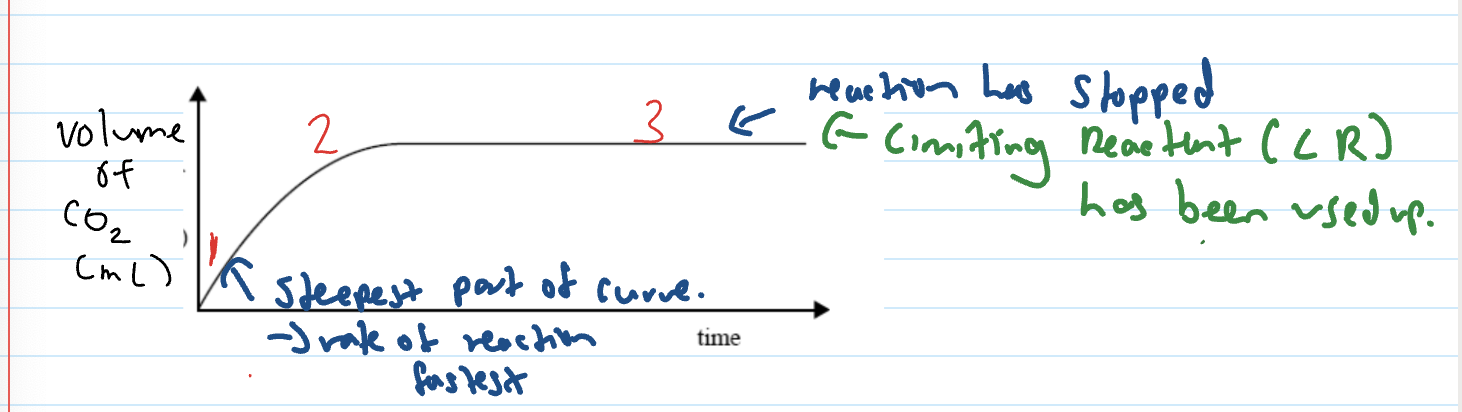
When graph given and temp increased, sketch expected graph
at the start the rate is just faster so reaches maximum faster but the actual volume of gas produced stays same since no change to moles of reaction
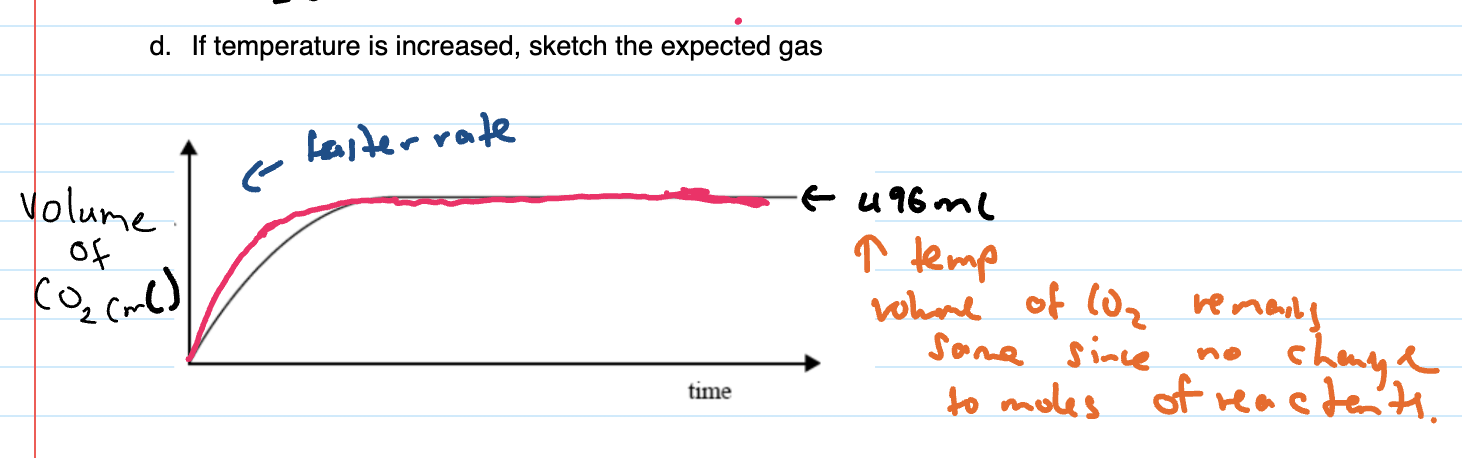
When graph given and conc. increased, sketch expected graph
CHECK IF NEW LIMITING REACTANT based on new conc.
if in excess, does not affect the volume produced, if not in excess does effect the volume produced
re-do calcs to find new LR and new volume
Rate faster so steeper at start

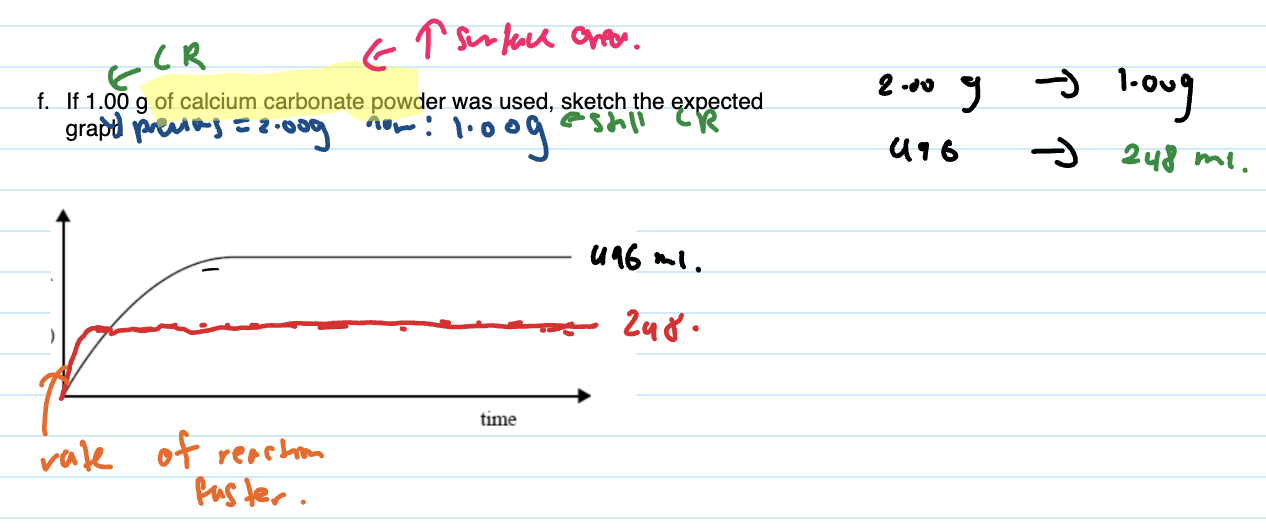
If mass of powder/ some kind of mass change or conc/volume changes the output/volume
Then calculate new final volume and draw the flat line as per that and still steeper at the start.
Finding limiting reactant
Find moles of each
Divide each moles by coeff.
Dynamic Equilibrium
when rate of forward reaction = rate of backwards reaction
Open Systems
matter and energy can be exchanged with the surrounding
Closed systems
only energy is exchanged with the surroundings
dynamic equilibrium conditions
amounts and concs. of chemical substances remain constant
total gas pressure is constant (if gases involved)
temperature remains constant
reaction is incomplete (all substances are present in reaction mixture)
HAS NOT STOPPED REACTING
CONCS. CONSTANT BUT DON’T NEED TO BE SAME
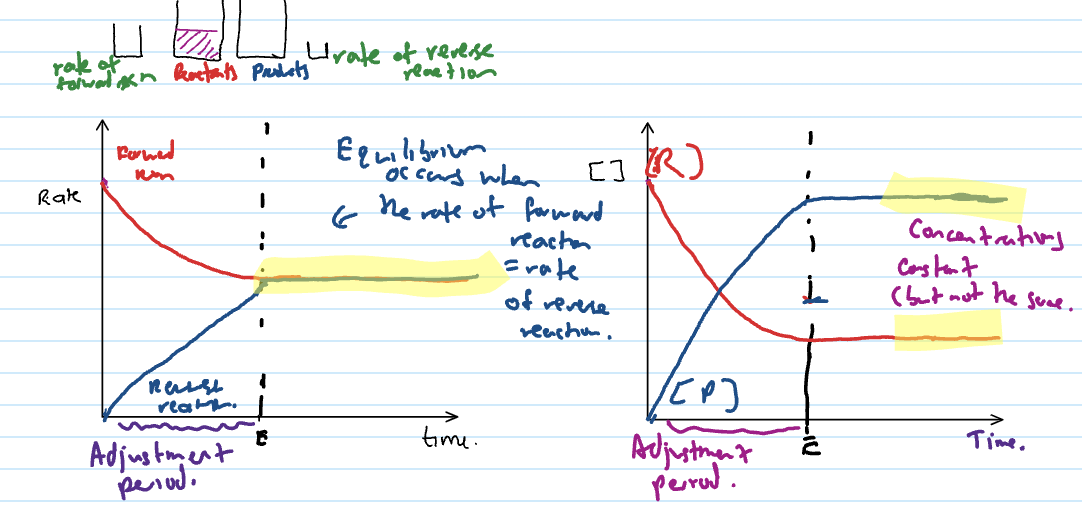
what does dynamic equilibrium mean?
point where the rate of the forward reaction and the rate of the reverse reaction are equal (only closed systems and reversible reactions)
extent of reaction vs rate of reaction
The extent of reaction indicates how much product is formed at equilibrium, whereas the rate of reaction is a measure of the change in concentration of the reactants and products over time.
Adjustment period
the reaction is moving towards equilibrium but not at equilibrium
anything before the lines become flat
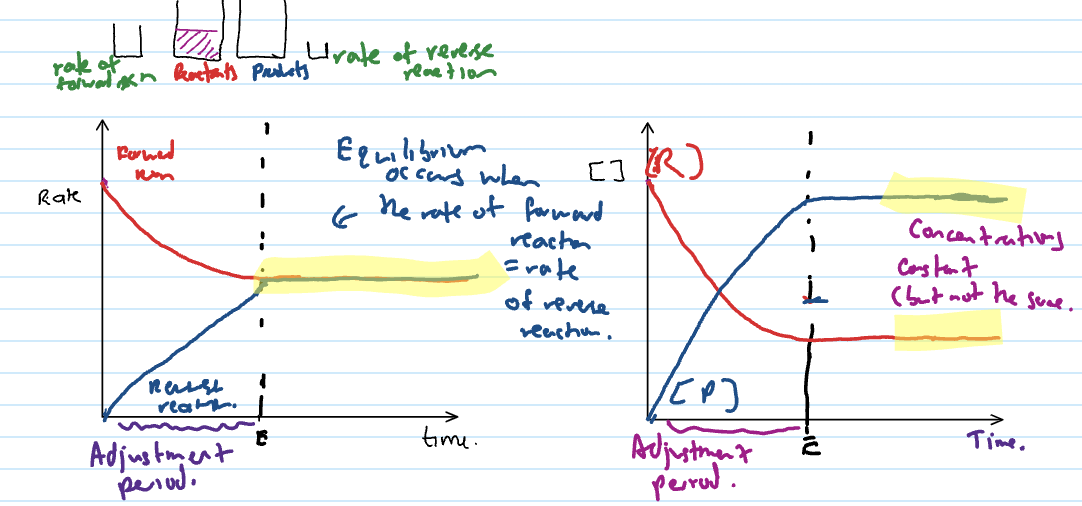
Reaction Quotient (Qc)
reaction quotient is used to compare the concentration of the products and reactants at any point in a reaction
units follow same pattern (M)
Qc Formula
Equilibrium constant (KC)
the equilibrium constant is expression when reaction is at equilibrium
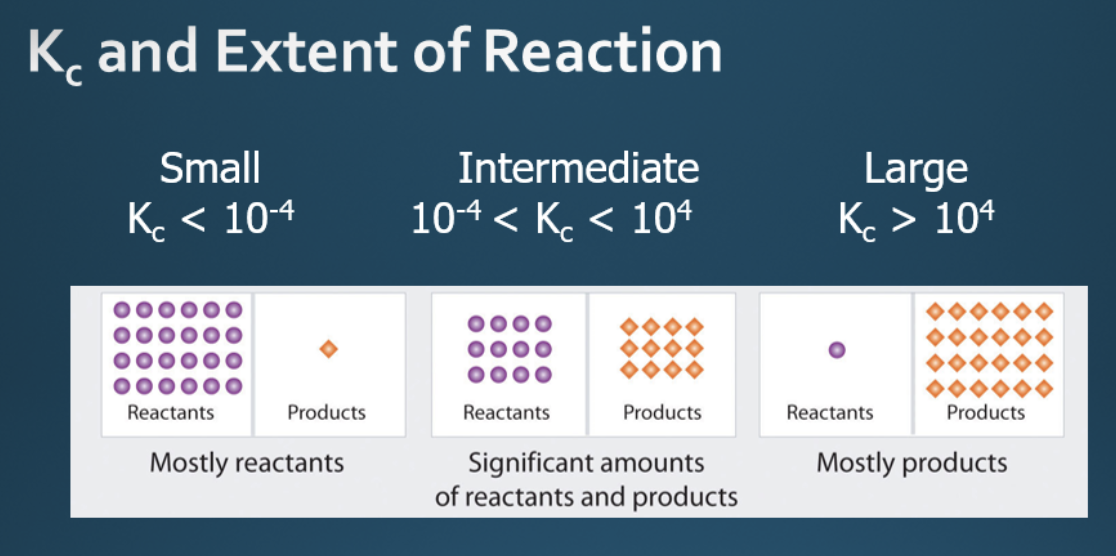
Kc and extent of reaction
Relationship bw Kc and Qc at equilibrium
Qc = Kc
What does equilibrium constant mean?
tells us the extent of the reaction
eg. high Kc = high yield, low Kc = low yield
large KC value means
[products] incr./ [reactants] decr.
means mostly products present
small KC value means
[products] decr./ [reactants] incr.
mostly reactants present
reactant favoured so less proportion of reactant has become product
extent of reaction (proportion of reactant becoming products small) (more reactants at equilibrium compared to products)
Qc < Kc
system needs to form more products to reach equilibrium
forward reaction favoured
Qc > Kc
system needs to form more reactants to reach equilibrium
backward reaction favoured
Important thing about stating Kc value
Must state temp too!
eg. 1.00M at 25 degrees celsius
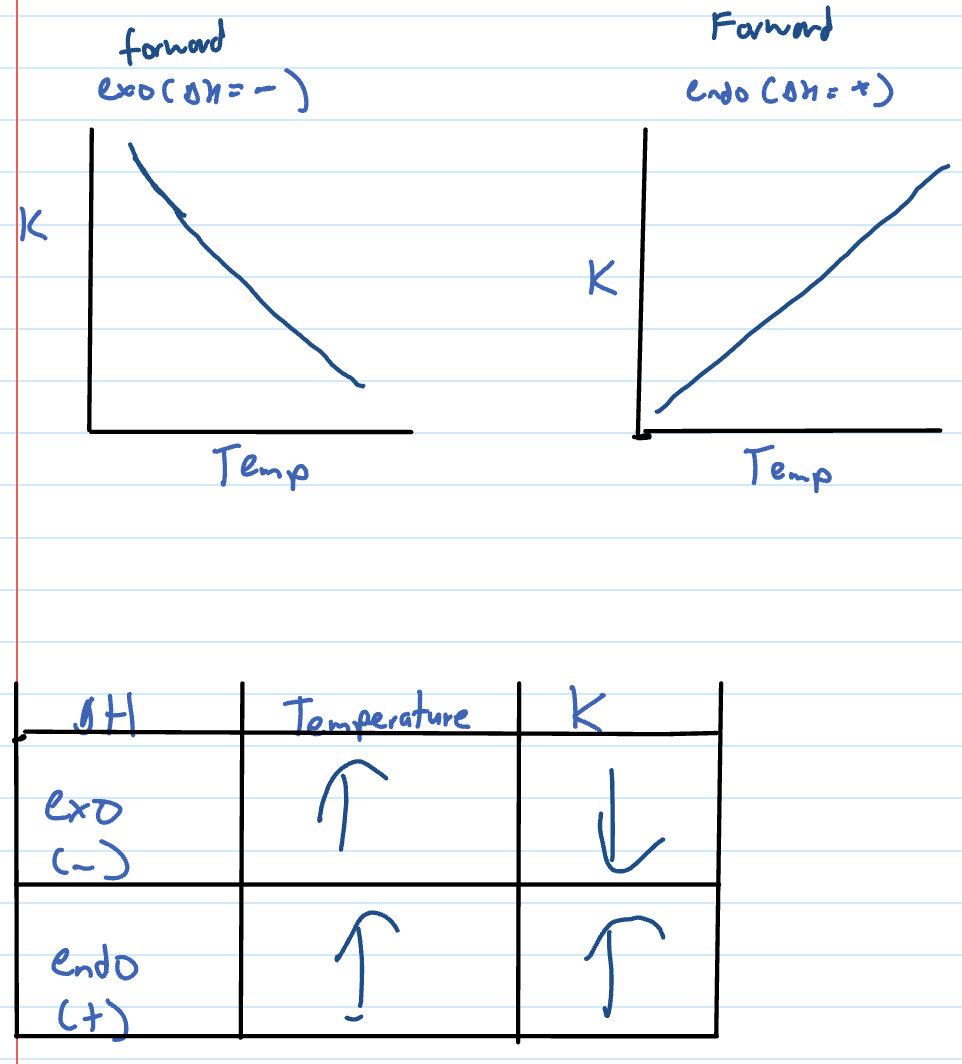
Equilibrium constant changes
ONLY affected by temp
not affected by actions such as adding reactants or products, changes in pressure, use of catalysts
Kc when reaction reversed
Kc becomes reciprocal of original Kc
eg. Kc2 = 1/Kc1
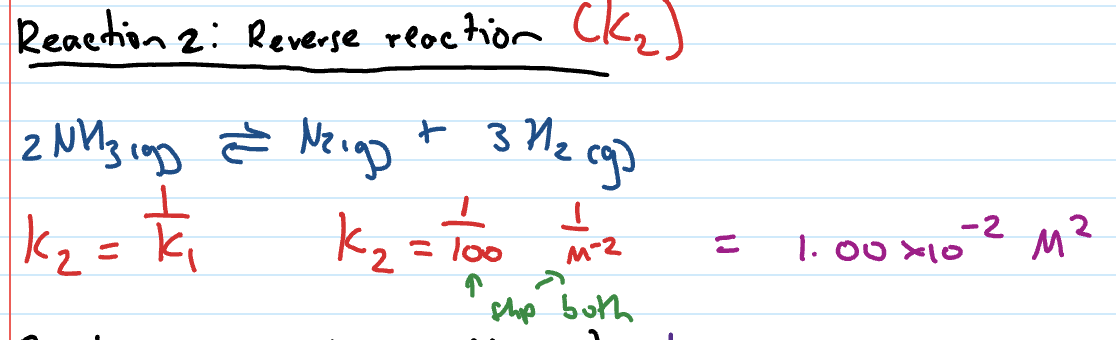
Kc when coefficients doubled
original Kc value squared
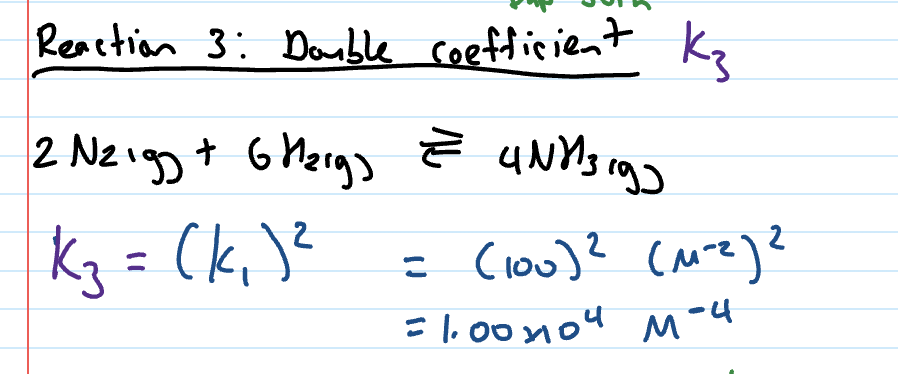
Kc value when coefficient halved
Square root original Kc value
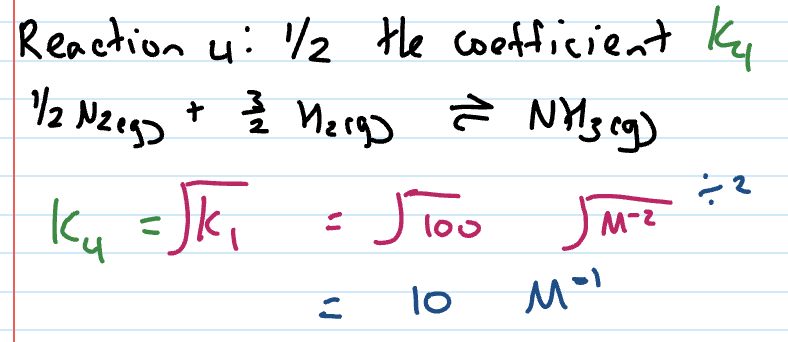
How do you know if ICE table question
The moles of both products and reactants given, if initial moles of something not given, then assume 0
Finding Kc using ICE Tables
Initial moles
Change in moles
Moles at equilibrium
Concentration at equilibrium

Le Chatelier’s principle
If an equilibrium system is subject to change, the system will adjust itself to partially oppose the effect of the change
How equilibrium position can be changed
equilibrium position (relative amounts of reactants + products) of a reaction can be changed by
adding or removing a reactant or product
changing pressure by changing volume (gases)
dilution (for solution)
changing temperature (only thing that effects Kc)
When asked to find Kp
Kp = P(NH3)/ P(H2) * P(N2)
P and round brackets
When describing/ graphing what to consider
C - what is the change you are doing to the system?
O - partially oppose by ______
D - direction favoured (backwards vs forwards)
COLOURS
How to remove reactants/products
Force a precipitate reaction (eg. add Ag+)
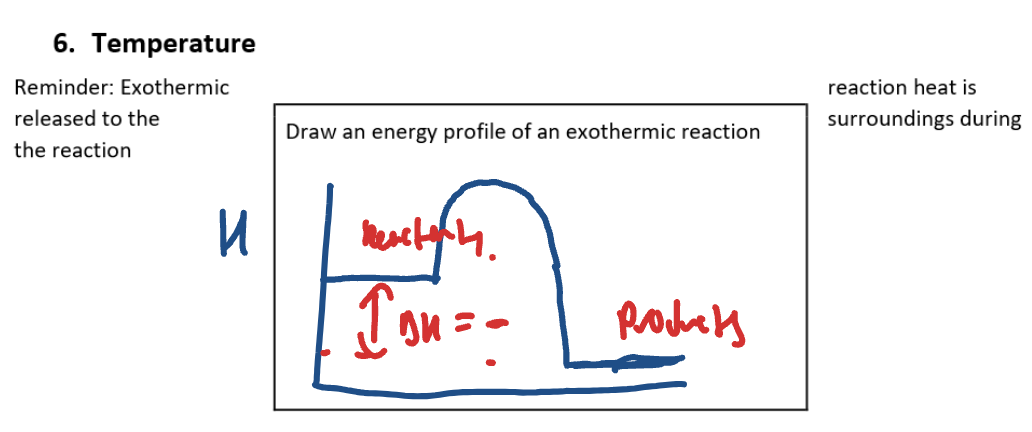
Temperature energy profile diagram
When something added/ removed - special consideration
even though partial opposition, does not go back to original
Therefore, when discussing changes in conc. of each species → make sure you still say that [X] is higher than before (only partially opposed)
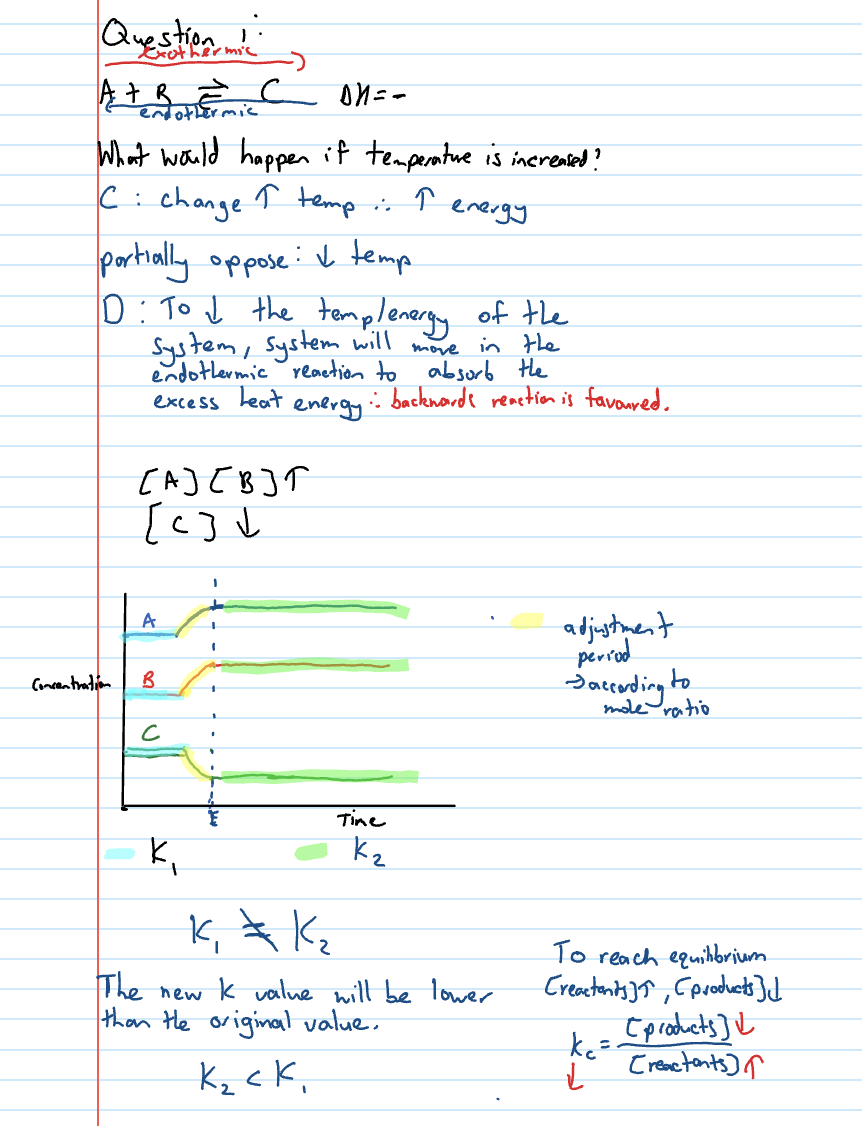
Temp equilibrium graph
Gradual increase/decrease → not as sudden
Kc1 is initial equilibrium → Kc2 is second equilibrium
See if concentration of products increases or decreases and discuss Kc value changes in terms of that
Pressure equilibrium graph
Although system partially opposes change, the overall colour will still be lighter/darker (original change), as will not return to initial concentrations
KC VALUE DOESNT CHANGE
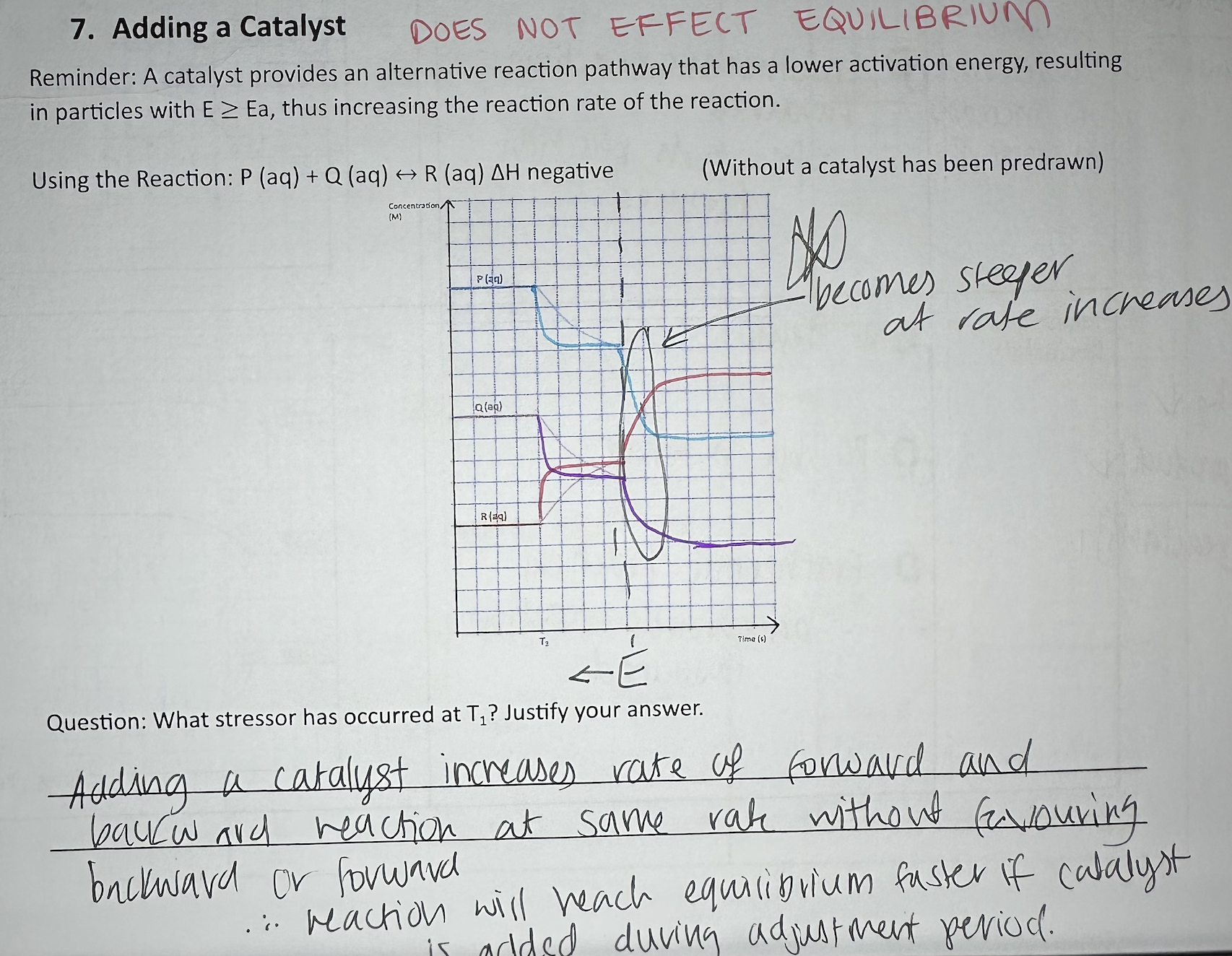
Catalyst equilibrium graph
DOES NOT AFFECT EQUILIBRIUM
Adding catalyst increases rate of both forward and backward reaction at same rate.
reaction will reach equilibrium faster if catalyst added during adjustment period
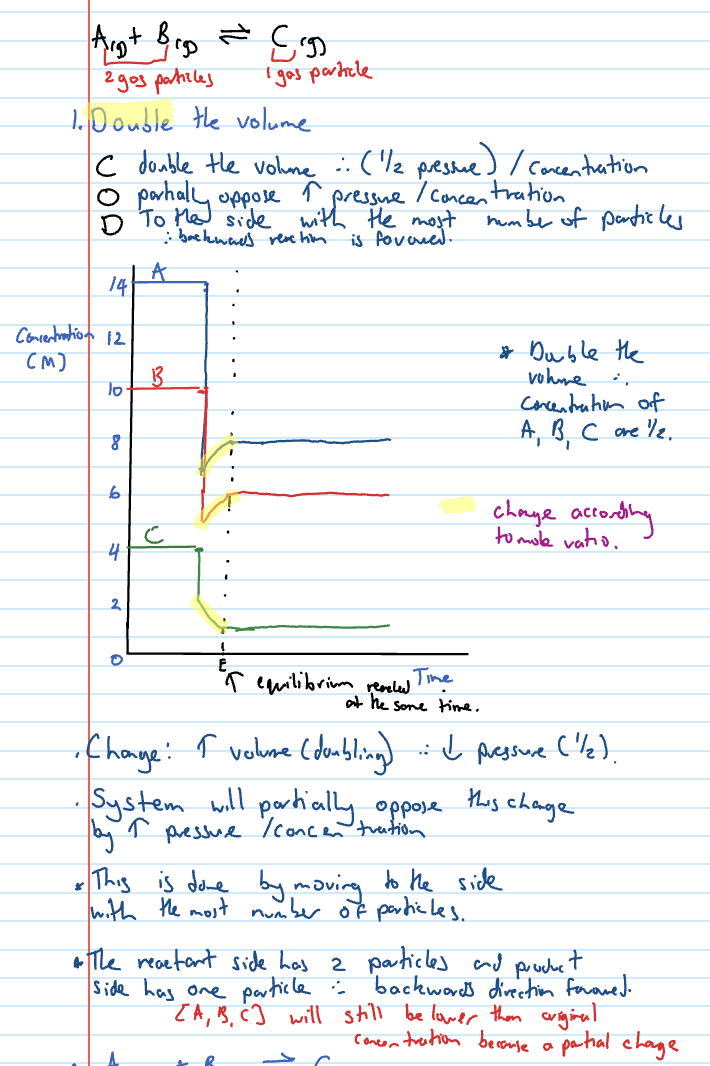
Changing pressure shortcuts
If volume of container increases, then pressure decreases, therefore, conc of reactants and products decreases
If volume of container decreases, then pressure increases, therefore, conc of reactants and products increases
Changing temp shortcut
Temp increase = endo favoured
Temp decrease = exo favoured
Yield
AKA “extent of reaction”
how much product is formed
Conflict (rate vs yield)
High temperatures favour the ROR, low temps favour yield in EXO reactions
Solution: use moderate temperature and add catalyst to increase rate
Conflict 2 (rate vs yield)
High pressure (bc. conc) favours rate of reaction and low pressures favour yield when forward reaction produces more particles
Solution: moderate pressure (Eg. 100kPa SLC) and add catalyst to increase rate
Describe change in conc vs change in moles
Conc: go by graph (is the flat line higher or lower than original flat line?)
Moles: go by direction (which direction is being favoured → more products or reactants?)
ICE Table to calc Kc of gases
Same process and can use c = n/v even if gas (no need for pv = nRT)
SHOW EQUILIBRIUM EXPRESSION BEFORE SUBBING IN VALUES
DON’T FORGET UNITS AND TEMP IF GIVEN
COD - Volume decrease
Decreasing the volume increases the pressure of gas mixture
System partially opposes by decreasing pressure so favours side with least number of particles.
Therefore, F/B reaction is favoured
When drawing pressure incr/decr - how long are the initial vertical lines?
If not given an amount just either double each line or half it
it’s the ratios that matter
eg. if volume doubles, pressure halves, line drops by half the height of the element.
Whenever colour given!
MUST MENTION COLOUR CHANGE AS PART OF COD
Whenever volumes mentioned in questions
check is it doubled/halved? - any special number that conc changes by
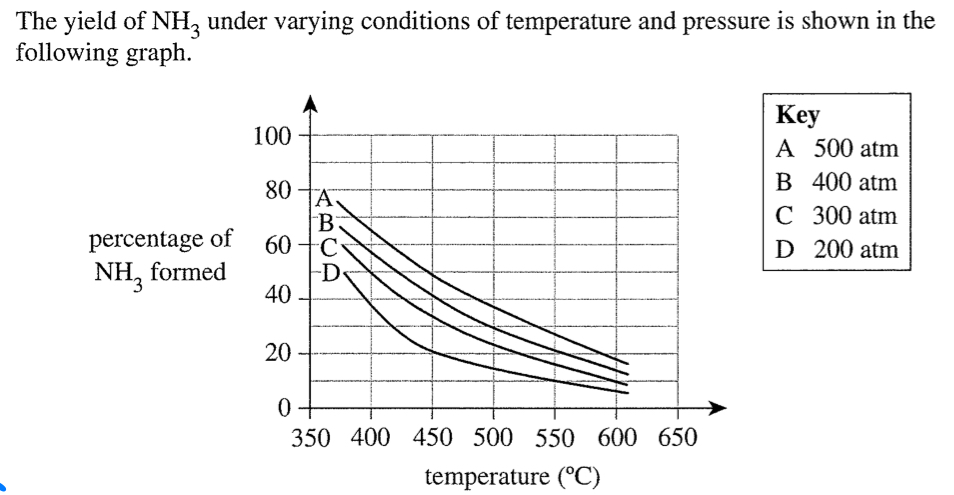
Why no pressure greater than 250atm (even though that's not good for rate or equilibrium)
If smth not good for rate or yield in industrial setting
ALWAYS TALK ABOUT ECONOMICAL ASPECT
1. Although higher pressure means higher yield at faster rate, it’s expensive to maintain high machinery etc.
2. Therefore, more ECONOMICAL to use moderate pressure for moderate yield and rate
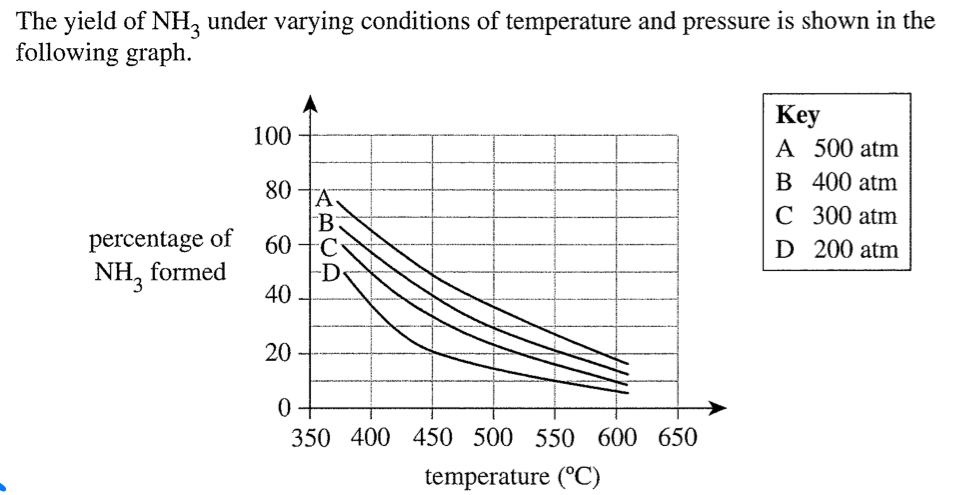
Why temp of only 400 degrees when lower means higher yield
CONFLICT
higher temp = faster rate
lower temp = higher yield
therefore moderate temp = reasonable yield at acceptable rate
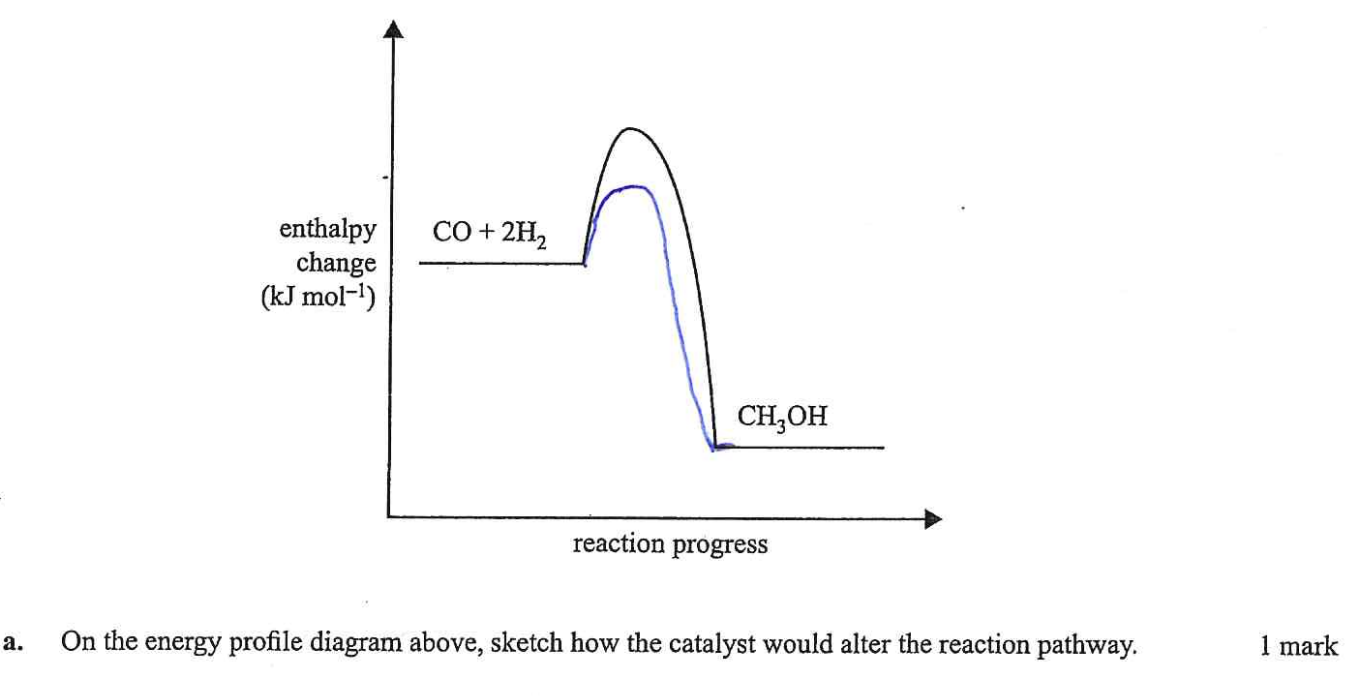
To draw effect of a catalyst on energy profile
Whenever it asks for Kc
UNITS + TEMP
homogeneous chemical systems
all reactants and products same state