Ch 9 - social networking, e-commerce, and the web
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Social Media (SM)
The use of IT to share content among networks of users.
Enables communities of practice or communities (groups of people related by a common interest)
Example: Posting on Instagram or tweeting news.
Social Media Information System (SMIS)
An information system that supports sharing of content among networks of users.
3 SMIS roles
Social media providers
Users
Communities
Social Media Provider
Companies that provide platforms for social networking.
Examples: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.
Attract and target demographic groups
User (in SMIS)
Individuals or organizations who use social media platforms to build social relationships.
Example: A person posting pictures on Instagram.
Many users are a particular demographic. Ex: Pinterest is 70% female, Linkedin is 80% of 35 yrs+, etc.
Communities (in SMIS)
Groups formed around common interests that go beyond familial, geographic, and organizational boundaries
Example: A Facebook group for dog lovers or LinkedIn group for accountants.
5 Components of SMIS
The same as all information systems:
Hardware (devices used)
Software (apps and browsers)
Data (includes content data, like user-generated content, and connection data, which is data on relationships between users)
Procedures (how it's used)
People (users and employees).
Procedures (in SMIS)
Instructions for using and managing SMIS.
Informal for users (copying friends)
Formal for organizations (content management policies).
People (in SMIS)
Users and employees managing social media.
Users may behave emotionally, while companies need trained personnel and policies.
NoSQL
A type of database used by social media sites to handle large volumes of unstructured data.
Example: Facebook initially used Cassandra.
Exponential Community Growth
Communities expand rapidly across tiers of users.
Example: If each user connects to 100 more, you get 10,000 second-tier connections.
How does social media affect organizational strategy?
A company’s organizational strategy determines its value chain, the value chain determine its business processes, and those processes determine SMIS requirements.
SMIS are dynamic, meaning processes constantly change and adapt to user input and activity, dynamic process flows cannot be designed or diagrammed
Social media in value chain activities
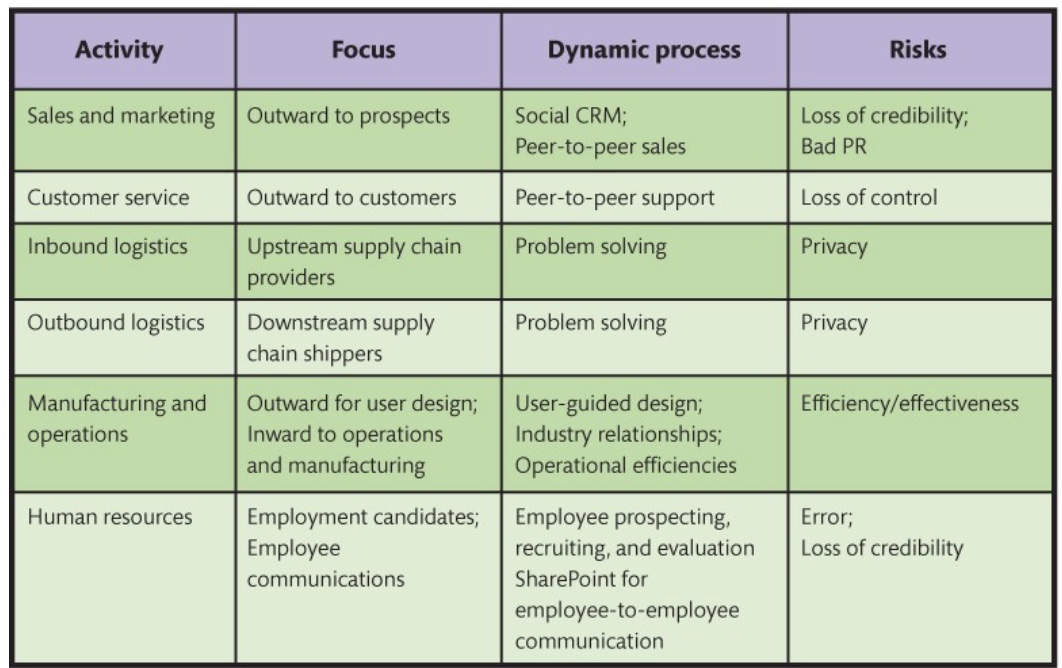
Social consumer relationship management (CRM)
A dynamic, social media based CRM process
Each customer crafts relationship through blogs, discussion lists, FAQs, etc (all dynamic content)
Not centered on customer lifetime value
Customers have as much control as companies (which can be challenging for some managers)
Product users freely help each other solve problems
Peer-to-peer support on social media risks a loss of control by the company
SMIS and inbound/outbound logistics
Benefits:
Numerous Solution Ideas + Fast Evaluation: Social platforms allow quick sharing and testing of logistics ideas (e.g., alternate shipping routes, warehouse strategies).
Better Solutions to Complex Supply Chain Problems: Teams from different companies, locations, or departments can collaborate in real time, increasing innovation.
User-Created Content + Feedback: Stakeholders (e.g., suppliers, employees, customers) can share input, helping identify problems and improve logistics solutions.
Risks:
Loss of Privacy: When logistics problems are discussed openly on social media or collaborative networks, sensitive information might be exposed.
Competitors May See Your Problems: Since problem-solving is public, competitors can observe your weaknesses, constraints, and strategies, giving them an advantage.
SMIS and manufacuring/operations
Social media improves communication channels within the organization and externally with consumers, allowing them to help design products, develop supplier relationships, and improve operations
SMIS and HR
People in HR can find employee prospects, recruit candidates, and complete candidate evaluations through social media
Social media is a place for employees to post their expertise
Risks: easy to form wrong conclusions about employees, can push unpopular message for company you are working for
Crowdsourcing
Asking the public for help designing or improving products.
Social media speeds up this process
Capital
Investment of resources for future profit
Types of business capital
Physical capital: Produces goods and services (factories, machines, manufacturing equipment)
Human capital: human knowledge and skills
Social capital: social relations with expectation of marketplace returns
Value of social capital
Determined by the number of relationships, strength of relationships, and resources controlled by those related
SMIS increases social capital
Benefits of social capital
Information: opportunities, alternatives, problems, and other factors important professionally and personally
Influence: decision making and peers
Social credentials: being linked to a network of highly regarded contracts
Personal reinforcement: professional identity, image, and position in an organization or industry
How professionals gain social capital
By adding more friends and strengthening relationships with:
Existing friends
People who control resources important to you
Linkedin is also a good way
Benefits of social networks
Can increase the number of relationships
Can increase the strength of relationships (likelihood that another entity will do something that benefits your organization)
Can connect to those with more resources
How do some companies earn revenue from social media?
Monetization
Social media companies often offer free services to establish large networks, so they montetize through:
Being a hyper-social organization: using SM to transform interactions with customers, employees, and partners into mutually satisfying relationships with them and their communities
“You are the product” mindset
If people are not paying, they are the product
They rent your eyes to advertisements
They generate data
Revenue models for social media
Advertising: paid search results, display ads, pay-per-click revenue models (use of these increases their value)
Freemium revenue model: offering users a basic service for free, then charging a premium for upgrades or advanced features.
Sales: of apps and virtual goods (ex: avatars), affiliate commissions through referrals, donations (ex: wikepedia), and other referrals
Mobility and online ad revenue
Increased mobility (such as on an iphone) reduces online ad revenue in comparison to other hardware such as PCs
The average “click-through” rate on smartphones is lower than on PC
There is less advertising space on a phone compared to PC
Conversion rates: the frequency someone takes an action desired by the advertiser (this is higher on PC than on mobile devices)
Companies need to redesign the mobile experience to ensure advertising revenue model is profitable
How can organizations address SMIS security concerns?
They can manage the risk of employee communication by developing a social media policy.
Should clearly outline employee rights and responsibilities
Intel’s rules of social media engagement
Disclose
Protect
Use common sense
Disclosing in social media engagement
Be transparent: use your real name and employer
Be truthful: point out if you have a vested interest
Be yourself: stick to your expertise and write what you know
Protecting in social media engagement
Dont tell secrets
Dont slam the competition
Dont overshare
Using common sense in social media engagement
Add value: make your contributions worthwhile
Keep it cool: dont inflame or respond to every criticism
Admit mistakes: be upfront and quick with corrections
How to manage the risk of inappropriate content on social media
Centralize (use 1 individual) on official organizational social media interactions and create process to monitor and manage content
User-generated content is the essence of social media relationships, so this must be monitored
Avoid problems from external sources, such as junk and eccentric contributions, inappropriate content, unfavourable reviews, and rebellious movements
Responding to social networking problems
Leave it, respond to it, or delete it
A general rule is to never set up a site that will generate content for which you have no effective response
Internal risks from social media
Threats to information security (Ex: bad idea to tell everyone its your birthday because your DOB can be used to steal your identity/password)
Employees increase organizational liability when they use social media (they can spring sexual harassment liabilities and leak confidential information)
Decreased employee productivity can result (64% of employees visit non-work-related websites every day)
Ecommerce
Buying and selling of goods and services over computer networks
Implications of ecommerce
From a technology perspective: it defines the need for additional infrastructure
From a management and government perspective: There must be high coordination for smooth business operations, and there are high security requirements
Types of ecommerce organizations
Merchant companies
Nonmerchant companies
Merchant companies
Own/buy goods and resell them
Sell services that they provide
Includes:
Business to consumer (B2C)
Business to business (B2B)
Business to government (B2G)
Nonmerchant companies
Arrange for the purchase and sale of goods without ever owning or taking title to those goods
Sell services provided by others
They sell services through the following methods:
E-commerce auctions
Clearinghouses
Electronic exchanges
Disintermediation
E-commerce auctions
Match buyers and sellers by using an ecommerce version of an auction
Ex: eBay, Poshmark, etc
Clearinghouses
Provide goods and services at a stated price and arrange for the delivery of the goods, but they never take the title
Ex: Amazon
Electronic exchanges
Match buyers and sellers, the business process is similar to that of a stock exchange
Ex: Facebook Marketplace
Leads to greater market efficiencies
Disintermediation
Removing intermediaries between parties (Manufacturer directly to consumer)
Benefits of Ecommerce
Improves flow of price information (sites provide price comparisons)
Sellers have access to better information about what customers will pay
Price elasticity: how much demand rises/falls with changes in price (auction sites are helpful to conduct price experiments with customers)
The challenges of Ecommerce
Channel conflict: if a company sells to a retailer, then adds a channel directly to consumers, will the retailer drop them?
Price conflict: if a manufacturer sells directly to consumer at a lower price than a retailer, this will disrupt the retailer
Logistics expense: manufacturers need to factor in the costs of the logistics that the distributors and retailers would do, this could result in higher costs
Customer service expense: manufacturers will need to support customers that arent as knowledgable as retailers
Showrooming: merchants lose money if a customer tries a product out in store, then later purchases it online at a lower cost
Taxation: problem for shipments crossing boarders, must collect the correct taxes