Human Geography - Urban Futures
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Why did cities first develop?
agricultural knowledge increased
food surplus
not all had to work in agriculture
migration to cities
increase urbanisation
industrial revolutions
new jobs and opportunities open
further migration
full urbanisation
Why are the rates of urban growth faster in EDCS+LIDCS than ACS
urban growth has already taken place in ACS so do not grow as much now as large amounts of urbanisation have alr occured
70% are alr urbanised
Why is urban growth taking place in EDCS and LIDCS
typically youthful pops
encourage rural urban migrations
young people move to urban for jobs
`child bearing age so natural rapid pop growth
World City Definition
important hub in global economic system with iconic status and buildings
London as world city
tnc hq - shell
centre for business innovation - canary wharf
25% of uk economy
Megacity Definition
city that has a pop of 10mill+ people
megacities advantages
social opportunities eg schools +cinemas etc
variety of employment
marginal groups
megacities disadvantages
congestion
air pollution
inadequate housing
social unrest
marginal groups
Why are megacities important
provide greater financial security for families
better public services
civic identity
lower avg cost as production is higher
Ulaanbaatar rapid growth LIDC CITY - RAPID URBANISATION CAUSE
capital of Mongolia
rapid urbanisation due to urban migration due to push and pull factors (dzud makes people want to move to city as weather is less extreme BUT great job opportunities)
internal growth due to youthful pop to rapid urbanisation
dzud - cold weather that freezes animals which doesn’t happen in city
many Mongolians live in Gers (portable round tent) allows farmers in rural areas to move around countries with animals
farmers now moved to ulaanbaatar now there is a ger district in urban area
internal growth
natural increase (birth rate higher than death rate) within an urban area
Push + pull factors result in
rural urban migration
push factors
drive people away from a place
eg:
poverty
conflict
natural disasters
crop failure
pull factors
attracting people to a place
eg:
jobs
education
safety
housing
infrastructure
basic physical and organisational structures and facilities (eg buildings, roads, power supplies, sanitation) needed for modern society to function
informal housing/ squatter settlements
residential area which has developed without legal claims to the land/permission
informal sector
part of economy that isn’t taxed or monitored by any form of government
rural urban migration
movement of people from countryside to city areas
quality of life
extent to which an individual is healthy, has a suitable social, economic and environmental situation and is able to enjoy life
urban structure in LIDCS- how does this differ from ACS?
in AC, high quality housing is at the edge of the city
there are less/no squatter settlements in ACS
because in ACS land is cheaper as you move away from city and transport is better so people can have larger land and housing
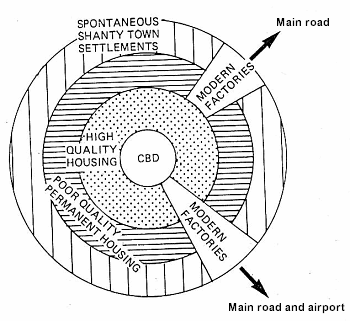
why are squatter settlements often at edges of urban areas in LIDCS
furthest from centre
poor quality transport to centre
poor quality land
land could be more polluted
undesirable land unwanted by others
people there cannot afford to live closer to centre (CBD)
rapid urbanisation
the movement of populations from rural areas to towns and cities at a fast rate
negative consequences of rapid urbanisation
not enough jobs to go around
-unemployment
-crime
not enough houses
-squatter settlements develop
no rubbish collection
-toxic rubbish heaps
jobs in informal sector
-unregulated + long hrs
-low pay
-poor conditions
infrastructure can’t keep up
-no basic services eg sewers + water
road systems can’t cope
-congestion
-air pollution
lack of access to education
-can’t get skills to get a better job
sewage + chemicals dumped in rivers
-wildlife and humans harmed
inequalities develop
urban structure ac
centre
cbd → shops, restaurants, offices, banks, few houses, land values high, tall buildings, first area in city to be built
inner city → lower quality housing, crowding, smaller, older houses, closed factories, run down, development taking place?
suburbs → safer, more expensive housing, luxury, larger houses, some parks/shops, mainly residential, new developments (eg housing)
rural urban fringe → villages in the countryside, some land protected eg green belt, least densely populated area
outer
suburbanisation
process by which suburbs (residential areas at edge of city) grow as city expands outwards
why do people want to move to the edge of the city?
ppl want better quality of life (for kids?), safer, less pollution (noise/cars), bigger garden, less congestion, better value for money
consequences of suburbanisation
commuting time increase as further away from work in CBD
→ air pollution/congestion as more commuting
larger demand on water supply
→ water stress?
empty housing in inner city
counter urbanisation
movement of ppl out of cities into countryside or smaller towns
causes of counter urbanisation SIMILAR TO CAUSES OF SUBURBANISATION
ppl want:
PERCIEVE IT IS SAFER
more peaceful place to live and raise family
lower crime rates
lower cost of living
can travel into CBD → good trainlines
consequences of counter urbanisation
increased house prices
gentrification
less decentralisation
Re-urbanisation
process of ppl moving back into city centres
causes of re urbanisation
re development of inner urban areas eg new homes/jobs created → gov targets deprived areas to make more desirable
consequences of re urbanisation
lack of affordable housing → empty and expensive apartments
congestion due to more residents → more air/noise pollution → decreased quality of life
movement of ppl over time through diff sections of cities
younger ppl move to inner city for work/services
have kids so move to outer suburbs to raise family SUBURBANISATION
when retire, may move to countryside COUNTERURBANISATION
any point may chose to to go back to inner city for work or services RE URBANISATION
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
location + motorways
se of england , surrounded by m25 motorway. lots of motorways start in london eg: m1 and m4. london is s of cambridge
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how did londons location help its development?
located on e coast of england so trade w europe easier
on river thames allowing shipping + transporting
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how has london developed over time?
roman settlement with 30,000 ppl
saxon city
medieval villages
tudors → pop/trade/wealth growth
great fir of london 1666 destroyed ¾ of london
5 mill houses built by victorians
LODNON HAS EXPANDED BY 60% IN LAST 100YRS
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how important is london REGIONALLY
influences surrounding areas:
companies attracted to region → increasing jobs and wealth
se and e of england are 2 biggest economies in uk
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how important is london within COUNTRY
uk’s capital
essential for uk’s economy
over 20% of uk’s capital comes from london
centre of uk’s transport system → road, rail, air and shipping links
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how important is london within WORLD
world city
one of 2 most important financial centres of world (w new york)
more foreign banks in london than anywhere else
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
pop?
9mill ppl
growing by 100,000+ ppl/year
more ppl living in lodnon than scotland wales put together
bigger pop than most other uk cities
birth rate
number babies born/thousand/year
migration
movement of ppl from 1 place to another, usually to live
immigrant
person who comes into a country to live permanently
death rate
number of ppl who die/thousand/year
domestic migrant
person moving to live somewhere else in their own country
international migrant
person moving to live in another country
emigration
process of leaving a place in order to start a new life in a new country
net migration
difference between number of immigrants and emigrants.
if more emigrants than immigrants = neg net migration
if more immigrants than emigrants = pos net migration
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
pop over time
grown overall but also decreased
net migration has been stable since 1998
number of ppl moving out = number moving in
growth is due to higher birth rate than death rate
birth rate rising mostly amongst young immigrants
8.5mill ppl
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
immigrants in london
pre 1950s = irish + sailors
1950s = windrush gen + commonwealth migrants eg india, pakistan
2004 = eu lead to polish and lithuanian
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
ppl of same ethnicity group in an area eg:
want to be somewhere where ppl speak same lang and familiar food
eg: southall = punjabi
chinatown = china
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
chinatown
where? soho
history? 200yrs old og small settlement and moved places in 1950
egs? bubblewrap waffle + golden dragon restaurants, see woo shops, stone lions
events? new year with stalls and parades, vitnamese parade, zongzi making = stuffed rice
shops? chinatown bakery = fish shaped pastries, see woo = spices, fresh fruit and veg
restaurants? golden dragon = dim sum = cantonese food form s china, four seasons = roast duck
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
how wld youthful pop affect character of london?
leisure activities more gyms/cinemas/night clubs
housing cheaper + smaller
shops fast fashion = cheap
tensions w/ og residents young ppl changing their towns
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
what is life like in london?
housing luxury waterfront apartments eg battersea power station redevelopment VS tower blocks eg grenfell
leisure west end theatres eg collesium, tate modern art gallery, 02 concert
consumption westfield shopping centre, oxford st shops
culture notting hill carnaval, chinese new year in chinatown
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
housing availability
icnreasing pop but not housing
not enough housing for demand so incrs prices eg avg london rent x2 elsewhere + some of least affordable in world
workers on low incomes cant affrod to live near work = house sharing incr
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
transport provision
best access to transport in centre however most areas have access to bus/rail
roads congested - 7am-7pm avg traffic speed only 8mph
1mill trains passages/day = overcrowded
underground overcrowding doubvled delays between 2013-15
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
access to services
quality eductaion - higher gcse aps in ne london
healthcare - free on nhs but overwhelmed incr waiting times - dermatology wait 54 wks
school availability - best state schools eg Holland park are over subscribed and wealthy to private so poor state
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
inequality + deprivation
more deprivation inner london eg hackney
uneven spreads of deprivation
home to richest and poorest ppl in uk eg avg income in kensignton = £130000 vs newham £35000
unhealthy lifestyles eg drinking/smoking/ drugs in deprived areas making life expectancy 5yrs lower
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in AC (London, UK)
one initiative to make london more sustainable
BedZED
beddington zero energy development near croydon is largest carbon neutral eco community in uk
100 homes completed in 2002
eco - town built on brownfield site so did not damage any ecosystems when built
homes use 80% less energy and recycle 15% more waste than rest of uk
social
clothes and furniture swaps
ppl eat tgther reducing costs + energy used and also talk
economic
insulation (double-glazing) = no heating
wind cowls keep rooms supplied w fresh air so no ac needed
clothes and furniture swaps
solar panels cut energy bills
environmental
community composting scheme = food waste made into compost used on site
homes face south so natural heating
segregated under sink recycling bins: green = compostable, grey = recyclable, brown = non recyclables
clothes and furniture shops was swap shop now residents email group
low energy lighting + energy efficient appliances used
solar panels
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
location
ne argentina
on parana river
200km from capital = buenos aires
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
history
started as small settlement, became argentina’s first port with a large Italian settlement.
lots of heavy industry, encouraging workers to move there.
this industry now closed so they focus on tourism, corned beef, food/veg processing
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
importance regionally
largest city in santa fe region = 1mill ppl
regional transport hub w/ major roads eg national route 9 + international airport (islas malvinas) and lies on parana river so boats
important industrial centre in region
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
importance nationally
3rd largest city in argentine after buenos aires and cordoba
first port in 1800s to export goods abroad
city declined when chemical + steel plants closed
new investments made city more important within country eg tourism
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
importance internationally
developed due to agricultural trade
location on parana river connecting to atlantic so allowed export of corned beef + cereals across world
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
international migration
1800s european migrants especially italians
62.5% of argentine pop is of italian descent
recently s american immigrants and se asians eg koreans
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
how italian migrants have changed rosario
food
architecture
mafia
messi is from roasario, from italian descent
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
what is rosario like
culture + ethnicity
national flag monument = monumento nacional a la bandera
museum of contemporary art
french renaissance architecture
consumption
restaurants where beef is cooked on asado (grill) eg la huella
cafe chico
el centro = shopping ppl for youth and families
leisure
river parana has sandy beaches
parque de espana due to warmer summer temps
salsa and tango clubs
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
whats life like in roasrio - social inequality
100,000+ rosarians (10% pop) live in slums = villas miserias
slums created due to cities infrastructure not meeting growth + arrival of migrants
slums next to main roads eg national route 9 + railways
pop density v high there = poor sanitation and lack of healthcare facilities
ppl do not own land on which they hve built housing
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
whats life like in roasrio - unemployment
high rates of unemployment = riots and looting in supermarkets in 2001
since 2001, initiatives have reduced unemployment
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
whats life like in roasrio - crime
villas miserias hve high poverty, crime, drug use levels eg drug war resulting to deaths of 570+ ppl 2011-14 HOMOCIDE RATE 5X REST OF ARGENTINA
2 football teams in rosaria are associated with villas miserias and crime
main routed eg national route 9 link cocaine producing bolivia and marijuana producing paraguay to rosario and buenos aires
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
initiative to make rosario more sustainable = pro huerta programme
aims to get ppl to produce their own food as in 2000 1/3 of workforce was unemployed due tio ckosed industry = hyperinflstion meant proce of food incrs 400% = looting. pro huerta introduced to reduce this.
= pro garden aiming to produce food locally and small scale alonmg roads andd railways
environmental
veggies + aromatic plants eg sage, are 100% organic and chemical free
crops planted in rotation to prevent pest attacks and diseases
social
low income families involved as majority
800 community gardens supporting 40000+ ppl
2/3 gardeners are women
economic
low income families involved earning $150/month from sales = well above poverty line
plots assigned annually, free of charge as long as crops grown year round
challenges and opportunities for cities today CASE STUDY of city in EDC = rosario (argentina)
initiative to make rosario more sustainable = habitat programme
set up to reduce inequalities. staerted in 2000 + has helped 5000 ppl upgrade their houses by:
social
new urban planning with new roads and infrastructure eg storm drains and sewage management
toilet facilities in houses
education programme for youth regarding dangerous behaviours
targeted support for women
economic
legal ownership of land they live on
employment + income for younger residents thru training and work experience for 16-25 yr olds
environmental
toilets in houses
improved sewage systems