Comparative female reproductive anatomy
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
How is mammary tissue attached
Via lateral and median suspensory ligaments
What is the milk vein
Subcutaneous abdominal vein
Blood combined from cranial and caudal superficial epigastric veins
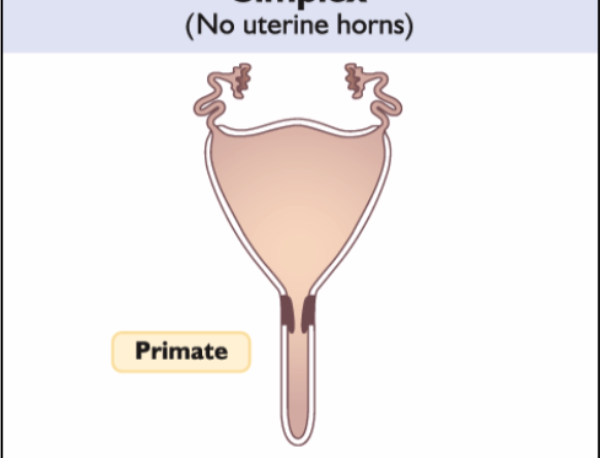
What is a simplex uterus
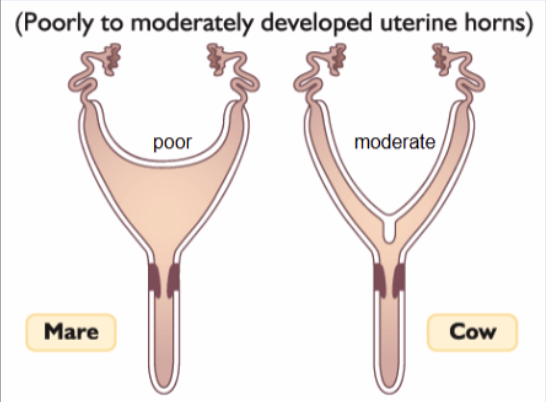
What is a bicornuate uterus
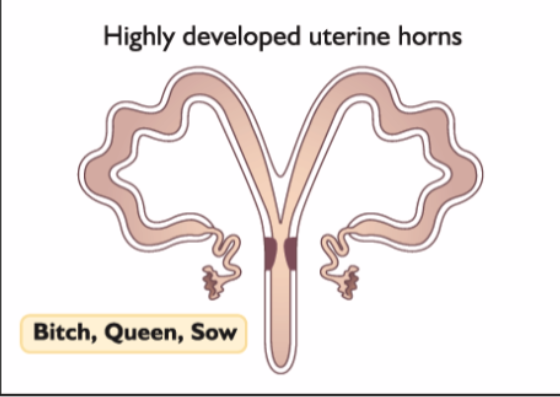
What is a highly developed bicornuate uterus
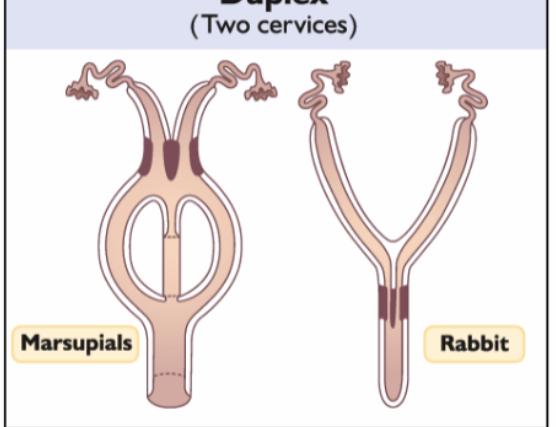
What is a duplex uterus
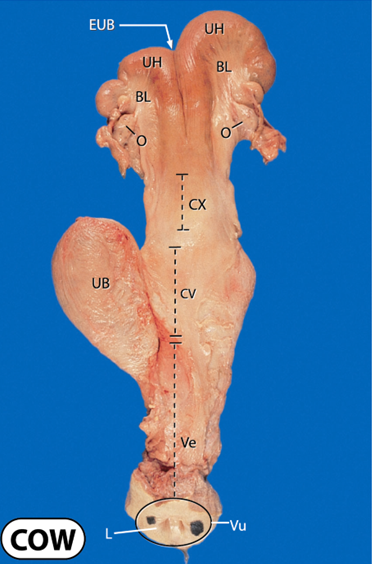
What does the uterus of a non pregnant cow look like
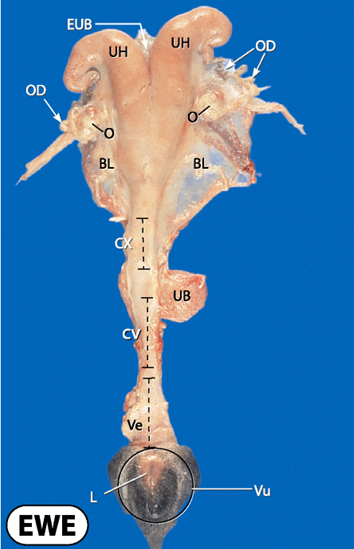
What does the uterus of a non pregnant ewe look like
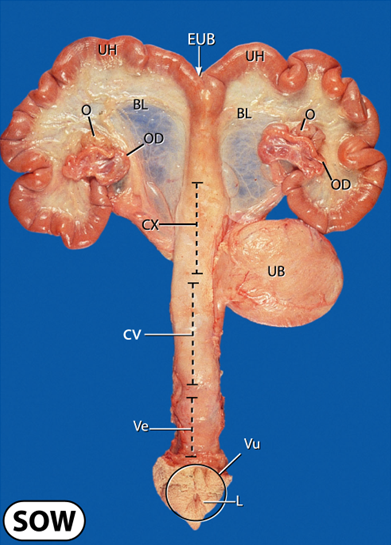
What does the uterus of a non pregnant sow look like
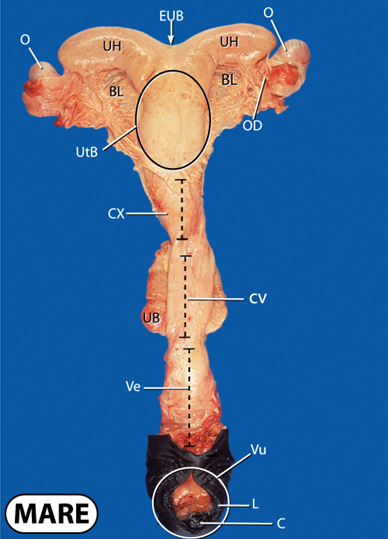
What does the uterus of a non pregnant mare look like
What does the uterus of a non pregnant bitch look like
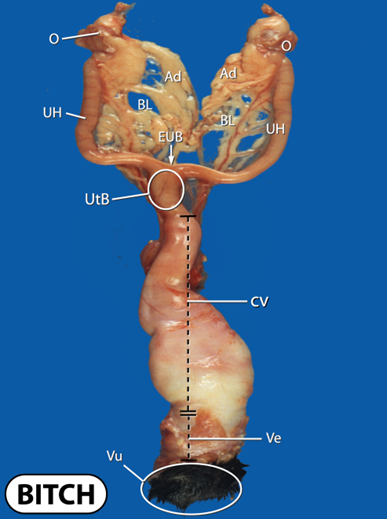
What does the uterus of a non pregnant queen look like

Why can’t you pick up the cervix in a mare
Due to tight dorsal attachment of mesometrium
Is the corpus luteum palpable
It protrudes in most species so is palpable except in the mare
What are follicles
Thin walled and fluid filled
Granulosa cells synthesise oestrogen
What is the corpora lutea
Filled with luteal cells
Sometimes central cavity
Grey yellow with yellow cut surface
How do cows and mares ovaries compare
Cows smaller then mare
Mares bean shaped
Mares ovulatory follicle bigger
Mares have distinct ovulatory fossa
Cows ovulates from different places
What do follicles and CLs look on ultrasound examinations
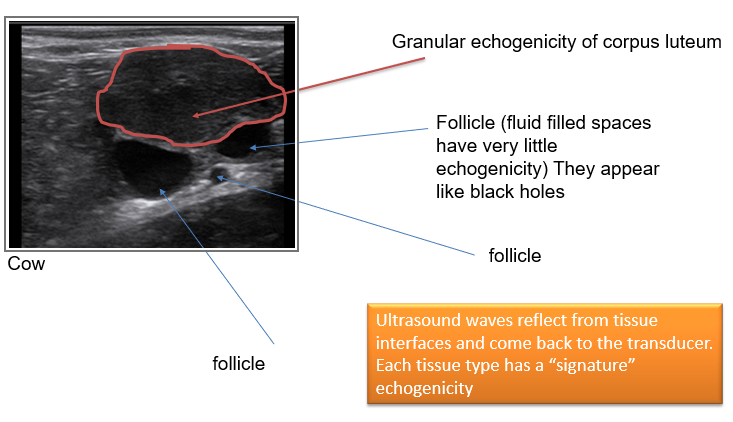
What do mares ovaries look like on ultrasound

What is the infundibulum
Funnel shaped opening at ovarian end which captures oocyte
What is the ampulla
Relatively large diameter ciliated and site of fertilisation
What is the isthmus
Small diameter with thicked muscular walls connected to the uterus at uterotubual junction used for sperm storage
Why is the mares infundibulum less extensive
The mare ovulates from a single ovulation fossa
What are the different uterine tissues
Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
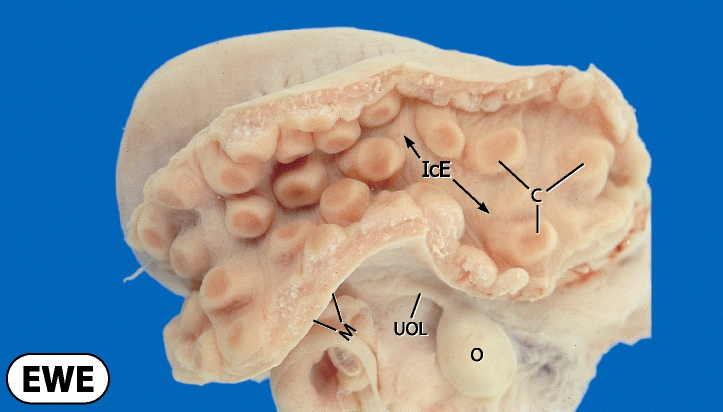
What do ewes distinct maternal caruncles look like
What is the cervix
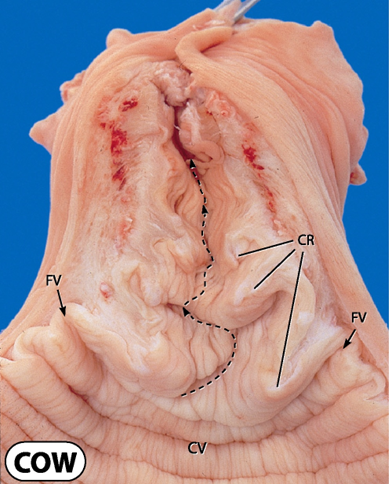
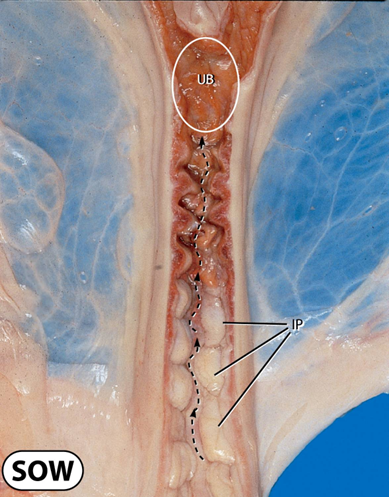
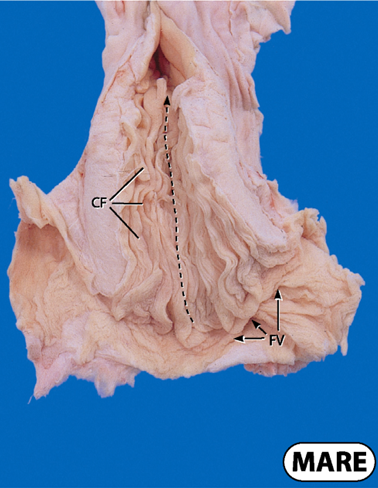
Thick walled and non complaint
Cervical canal surrounded by folds or rings
Barrier to sperm transport in ewe, cow, bitch and queen
What does the cervix do during pregnancy
It isolates coceptus from external environment
What does the queen and bitch cervix look like
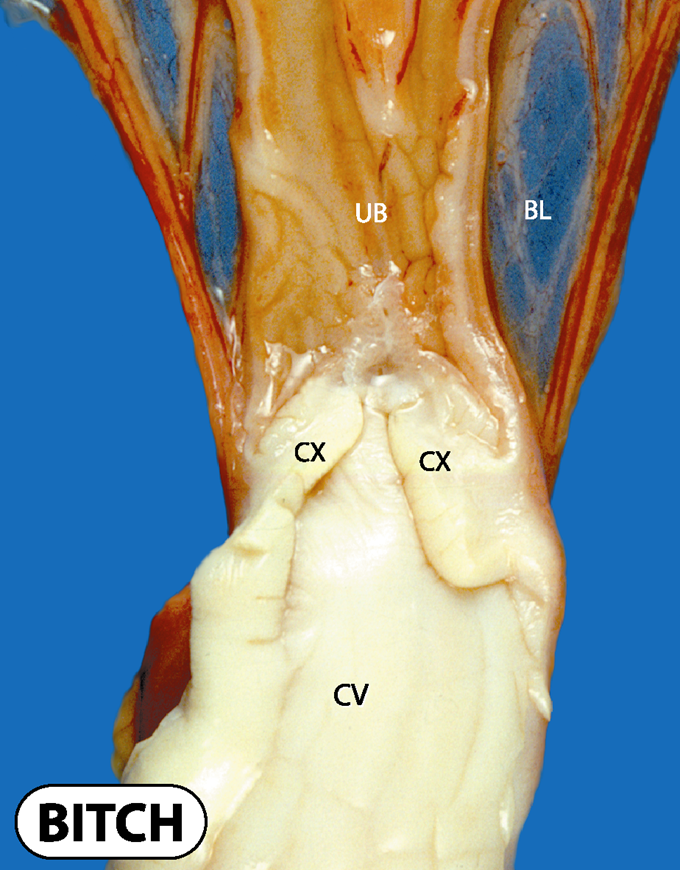
What does the cow cervix look like
What does the ewe cervix look like

What does the sow cervix look like
What does the mare cervix look like
Why might you introduce a catheter through the cervix
AI
Embryo transfer
Treating uterine infections
Where does the caudal vagina develop from
The ectoderm
Where does the cranial vagina and uterus develop from
Mesoderm which is sensitive to the effect of AMH
What is the foetal origin of the inner sac
Amnion
What is the foetal origin of the outer sac
Chorioallantois formed by fusion of inner allantois and outer chorion
What is the allantoic cavity continuous with
The baldder of developing foetus
What provides interface with the foetus and the dam
Chorionic villi
What type of placenta do cattle and sheep have
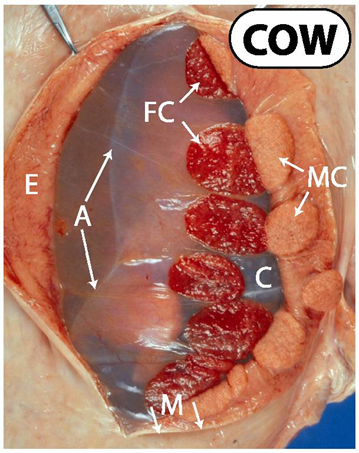
Cotyledonary - discrete button like regions of chorionic villi
What do cotyledonary placantae look like
What type of placenta do sows and mares have
Diffuse placenta with uniform distribution of chorionic villi
How many layers does the cattle, sheep pig and mare horse placentas have
6 layers
How many layers do dog and cat placentas have
5 layers
How many layers do primate placentas have
3 layers
How are primate placentas different
They implant
Relatively high risk of ectopic pregnancies
High risk of excessive blood loss at parturition
What are the features of pig placentas
Diffuse
Epitheliochorial
What are the features of sheep placentas
Cotyledonary
Epitheliochorial
Concave maternal caruncles
What are the features of cattle placentas
Cotyleconary
Epitheliochorial
Convex maternal caruncles
What are the features of dog and cat placentas
Zonary
Endotheliochorial
Pigment zone
What are the features of horse placentas
Diffuse
Epitheliochorial
Conceptus remains spherical in early pregnancy and migrates
Endometrial cups are transient placental endocrine gland producing eCG
What are the umbilical vessels
Umbilical arteries
Umbilical vein
Urachus
What do the umbilical arteries connect
Left and right internal iliac arteries to foetal maternal blood exchange at the chorionic villi
What does the umbilical vein connect
Foetal maternal blood exchange at the chorionic villi to the ductus venosus and vena cava
What does the urachus connect
The bladder to the allantoic cavity
What happens at birth
Amniotic membrane of cord is broken
Umbilical arteries retract back
Umbilical vein and urachus close and temporarily remain outside the body
What does the umbilical artery become
Round and lateral ligaments of the liver
What does the umbilical vein become
The round ligament of the liver
What does the urachus become
The median ligament of the bladder